-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
-
Feature Map
-
Feature History
-
Cisco Unified CME Overview
-
Before You Begin
-
Installing and Upgrading Cisco Unified CME Software
- Setting Up Basic Configuration
-
Configuring Dialing Plans
-
Configuring Localization Support
-
Configuring Transcoding Resources
-
Configuring Video Transcoding
-
Configuring Toll Fraud Prevention
-
Enabling the GUI
-
Integrating Voice Mail
-
Configuring Security
-
Adding Features
-
Configuring Automatic Line Selection
-
Configuring Barge and Privacy
-
Configuring Call Blocking
-
Configuring Call Park
-
Call Restriction Regulations
-
Configuring Call Transfer and Forwarding
-
Configuring Call-Coverage Features
-
Configuring Caller ID Blocking
-
Configuring Conferencing
-
Configuring Video Conferences
-
Configuring Voice and Video Hardware Conferencing
-
Configuring Directory Services
-
Configuring Do Not Disturb
-
Configuring Enhanced 911 Services
-
Configuring Extension Mobility
-
Configuring Fax Relay
-
Configuring Feature Access Codes
-
Configuring Forced Authorization
-
Configuring Headset Auto-Answer
-
Configuring Intercom Lines
-
Configuring Loopback Call Routing
-
Configuring MLPP
-
Configuring Music on Hold
-
Configuring Paging
-
Configuring Presence Service
-
Configuring Ring Tones
-
Configuring Single Number Reach
-
Customizing Soft Keys
-
Configuring Speed Dial
-
Configuring Video Support
-
Configuring SSL VPN Client for SCCP IP Phones
-
-
Creating Templates
-
Modifying Cisco Unified IP Phone Options
-
Configuring Interoperability with Cisco Unified CCX
-
Configuring the CTI CSTA Protocol Suite
-
Configuring SRST Fallback Mode
-
Configuring VRF Support on Cisco Unified CME
-
Configuring the XML API
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Information About Conferencing
Secure Conferencing Limitation
Multi-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing for More Than Three Parties
Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and Later versions
Soft Keys for Conference Functions
Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0
Modifying the Default Configuration for Three-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing
SCCP: Configuring Conferencing Options on a Phone
SIP: Configuring Conferencing Options on a Phone
Verifying Three-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing
Troubleshooting Three-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing
SCCP: Enabling DSP Farm Services for a Voice Card
SCCP: Configuring Join and Leave Tones
SCCP: Configuring SCCP for Cisco Unified CME
SCCP: Configuring the DSP Farm
SCCP: Associating Cisco Unified CME with a DSP Farm Profile
SCCP: Enabling Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing
SCCP: Configuring Multi-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing and Meet-Me Numbers
SCCP: Configuring Conferencing Options for a Phone
SCCP: Verifying Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing
show ephone-dn conference: Example
show telephony-service conference hardware detail: Example
SCCP: Configuring Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0
Configuration Examples for Conferencing
End of Conference Options: Example
DSP Farm and Cisco Unified CME on the Same Router: Example
DSP Farm and Cisco Unified CME on Different Routers: Example
Cisco Unified CME Router Configuration: Example
DSP Farm Router Configuration: Example
Feature Information for Conferencing
Configuring Conferencing
Last Updated: May 16, 2011This chapter describes the conferencing support in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (Cisco Unified CME).
Finding Feature Information in This Module
Your Cisco Unified CME version may not support all of the features documented in this module. For a list of the versions in which each feature is supported, see the "Feature Information for Conferencing" section.
Contents
•
Restrictions for Conferencing
•
Information About Conferencing
•
How to Configure Conferencing
•
Configuration Examples for Conferencing
•
Feature Information for Conferencing
Restrictions for Conferencing
When you are configuring dial peers or ephone-dns, including park slots and conferencing extensions, on Cisco Integrated Services Router Voice Bundles, the following message may appear to warn you that free memory is not available:
%DIALPEER_DB-3-ADDPEER_MEM_THRESHOLD: Addition of dial-peers limited by available memory
To configure more dial peers or ephone-dns, increase the DRAM in the system. A moderately complex configuration may exceed the default 256 MB DRAM and require 512 MB DRAM. Note that many factors contribute to memory usage, in addition to the number of dial peers and ephone-dns configured.
Information About Conferencing
To enable conferencing, you should understand the following concepts:
•
Secure Conferencing Limitation
•
Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and Later versions
•
Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0
Conferencing Overview
Conferencing allows you to join three or more parties in a telephone conversation. Two types of conferencing are available in Cisco Unified CME: ad hoc and meet-me.
Ad hoc conferences can be hardware-based or software-based. Software-based conferences use the router CPU to provide audio mixing (G.711) and are limited to 3 parties. Hardware-based multi-party ad hoc conferencing uses digital signal processors (DSPs) to allow more parties than software-based ad hoc conferencing and also provides additional features such as Join and Conference Participant List (ConfList).
Meet-me conferences are created by parties calling a designated conference number. Meet-me conferencing is hardware-based only. If you configure software-based conferencing, you cannot have meet-me conferences.
Conferencing with Octo-Lines
In Cisco Unified CME 4.3 and later versions, when a conference initiator is an octo-line directory number, Cisco Unified CME selects an idle channel from that directory number and the user must establish a new call to complete the conference. If an idle channel is not available on the same octo-line directory number, the conference aborts and a "No Line Available" message displays. Cisco Unified CME does not select an idle channel from another directory number and the user cannot select "hold" calls on the other channels of the directory number or other directory numbers, which is the behavior for single-line and dual-line directory numbers.
With octo-line directory numbers, only one directory number is required for an 8-party meet-me or ad hoc conference. Up to eight select and join instances are supported.
Secure Conferencing Limitation
Cisco Unified CME cannot use the secure conference DSP farm capability. If Cisco Unified CME needs a conference DSP farm resource for multiparty ad hoc or meet-me conferencing, it will use a secure or nonsecure DSP farm resource depending on what resources have been registered with Cisco Unified CME. If Cisco Unified CME happens to pick a secure DSP farm resource, the conference itself will not be secure, which is a waste, in terms of sessions capacity, of the more expensive secure DSP farm resource.
To avoid using valuable secure DSP farm resources, we recommend that you do not register a secure conference DSP Farm profile to a Cisco Unified CME because Cisco Unified CME cannot use the DSP farm's secure capabilities.
Ad Hoc Conferencing
Before Cisco Unified CME 4.1, support for conferencing is limited to three-party ad hoc conference calls using a G.711 codec. To have an ad hoc conference with a party that is not using a G.711 codec, transcoding is necessary. For more information, see the "Transcoding When a Remote Phone Uses G.729r8" section.
The maximum number of simultaneous conferences is platform-specific to the type of Cisco Unified CME router, and each individual Cisco Unified IP phone can host a maximum of one conference at a time. You cannot create a second conference on a phone if you already have an existing conference on hold.
Conference Gain Levels
In Cisco Unified CME 3.3 and later versions, you can adjust the gain level of an external call to provide more adequate volume. This functionality is applied to inbound audio packets so that conference participants can more clearly hear a remote PSTN or VoIP caller joining their call. Note that this functionality cannot discriminate between a remote VoIP/foreign exchange office (FXO) source, which requires a volume gain, and a remote VoIP/IP phone, which does not require a volume gain and may therefore incur some sound distortions.
End-of-Conference Options
For Cisco CME 3.2 and later versions, a person who initiates a conference call and hangs up can either keep the remaining parties connected or disconnect them.
Cisco Unified IP phones can be configured to keep the remaining conference parties connected when the conference initiator hangs up (places the handset back in the on-hook position). Conference originators can disconnect from their conference calls by pressing the Confrn (conference) soft key. When an initiator uses the Confrn key to disconnect from the conference call, the oldest call leg will be put on hold, leaving the initiator connected to the most recent call leg. The conference initiator can then navigate between the two parties by pressing either the Hold soft key or the line buttons to select the desired call.
In Cisco Unified CME 4.0 and later versions, behavior for the end of three-way conferences can be configured at a phone level. The options specify whether the last party that joined a conference can be dropped from the conference and whether the remaining two parties should be allowed to continue their connection after the conference initiator has left the conference.
Multi-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing for More Than Three Parties
In Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and later versions, hardware-based multi-party ad hoc conferences allow more than three parties. Ad hoc conferences are created when one party calls another, then either party decides to add another party to the call. Ad hoc conferences can be created in several ways.
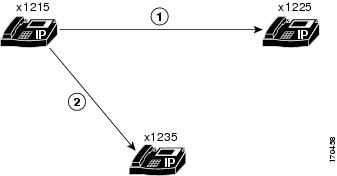
The conference shown in Figure 30 is created when extension 1215 dials extension 1225. The two parties decide to add a third party, extension 1235. Extensions 1215, 1225, and 1235 are now parties in an ad hoc conference. Extension 1215 is the creator.
Figure 30 Simple Ad Hoc Conference Using the Conf Soft Key
You can configure ad hoc conferencing so that only the creator can add parties to the conference. The default is that any party can add other parties to the conference.
You can configure conferencing so that the conference drops when the creator hangs up, and you can configure it so that the conference drops when the last local party hangs up. The default is that the conference is not dropped, regardless of whether the creator hangs up, provided three parties remain in the conference.
For configuration information, see the "SCCP: Configuring Conferencing Options for a Phone" section for more information.
Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and Later versions
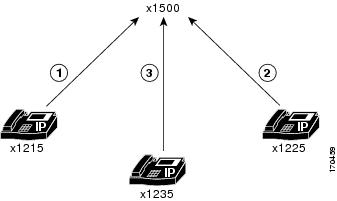
In Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and later versions, meet-me conferences consist of at least three parties dialing a meet-me conference number predetermined by a system administrator. For example, the conference shown in Figure 31 is created when the conference creator at extension 1215 presses the MeetMe soft key and hears a confirmation tone, then dials the meet-me conference number 1500. Extension 1225 and extension 1235 join the meet-me conference by dialing 1500. Extensions 1215, 1225, and 1235 are now parties in a meet-me conference on extension 1500.
Figure 31 Simple Meet-Me Conference Scenario
Configuring Maximum Parties
You can configure the maximum number of conference parties to be lower than the actual maximum of 32 for meet-me conferences. See the "SCCP: Configuring the DSP Farm" section for more information.
Freeing Conference Resources
If only one party remains in the meet-me conference, for example, if one party has forgotten to hang up, the conference call is disconnected after five minutes to free system resources.
If the creator is waiting for parties to join the conference and is the only party on the conference, the conference is not disconnected because significant resources are not being used.
Soft Keys for Conference Functions
In Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and later versions, the following soft keys provide conferencing functions for hard-ware based multi-party conferencing enhancements on your phone and require the appropriate DSP farm configuration. For configuration information, see the "SCCP: Configuring Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and Later Versions" section.
•
ConfList—Conference list. Lists all parties in a conference. For multi-party ad hoc conferences, this soft key is available for all parties in a conference. For meet-me conferences, this soft key is available for the creator only. Press Update to update the list of parties in the conference, for instance, to verify that a party has been removed from the conference.
•
Join—Joins an established call to an adhoc conference. You must first press Select to choose each connected call that you want to join in a conference, then press Join to join the selected calls to the conference.
•
RmLstC—Remove last caller. Removes the last party added to the conference. This soft key works for the creator only.
•
Select—Selects a call or conference to join to a conference and selects a call to remove from a conference. The creator can remove other parties by pressing the ConfList soft key, then use the Select and Remove soft keys to remove the appropriate parties.
•
MeetMe—Initiates a meet-me conference. The creator presses this soft key before dialing the conference number. Other meet-me conference parties only dial the conference number to join the conference. This soft key must be configured before you can initiate meet-me conferences.
Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0
Unlike the built-in Cisco Unified CME conference feature, a meet-me conference does not have a three-party limit. Meet-me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0 requires Cisco Unity Express auto-attendant to transfer callers to the correct Meet-Me bridge and a dual T-1/E-1 VWIC card for providing DSP resources. By default three Meet-Me bridge's with 8 callers each are defined with the maximum number of callers restricted by the number of DSP resources available in the Cisco router. A maximum of 96 callers in conference is supported. Multicast conferences can be accessed from IP phones, public switched telephone network (PSTN) callers, and Cisco Land Mobile Radio (LMR) devices connected to ear and mouth (E&M) voice ports on the Cisco Unified CME router.
The only limiting factor for this solution is the number of T1 or E1 loopback ports and digital-signal-processor (DSP) resources available.
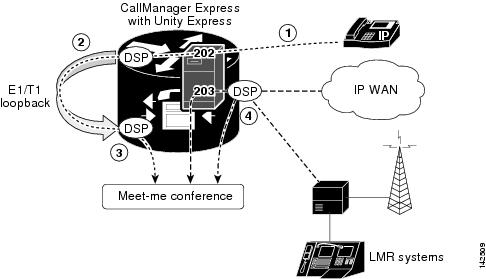
Figure 32 illustrates the callflow for Meet-Me Conferencing on a Cisco router with Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0 and Cisco Unity Express. IP phones and PSTN callers dial into Cisco Unity Express Auto Attendant using separate access numbers. Cisco Unity Express Auto Attendant routes calls to a multicast conference based on which access number is called. In this example, local IP phones call 202 and PSTN users call 203 to dial into Cisco Unity Express.
Figure 32 Meet-Me Conference in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0
1.
In order to send or receive audio from a multicast conference, calls must pass through a DSP for audio mixing. By default, IP phone calls are not passed through a DSP. IP phone calls can be routed to T1 or E1 loopback, forcing the call to pass through a DSP. In this example, Cisco Unity Express routes callers who dialed 202, through the E1/T1 loopback.
2.
The T1/E1 loopback ports are permanently trunked to the multicast conference. Incoming calls to T1 loopback are routed back to the multicast conference on Cisco CME.
3.
All PSTN calls must pass through a DSP, so incoming PSTN calls do not have to be routed to T1 loopback. The Auto Attendant routes PSTN calls directly to the multicast conference. In this example, Cisco Unity Express routes callers who dialed 203 directly into the multicast conference.
4.
Cisco LMR ports are permanently trunked into the multicast conference, so radio parties can listen to audio from both the IP phone and the PSTN. Pushing the "talk" button on a radio handset keys the M lead on the Cisco CME E&M port and the radio handset can transmit audio.
Note
Cisco LMR devices typically cannot transmit and receive audio at the same time. If a Cisco LMR device receives audio from a multicast conference, it cannot transmit audio. In order for a Cisco LMR device to transmit audio to the conference, all IP phone and PSTN parties must be on mute so the LMR device does not receive any audio. If a single IP phone or PSTN device in the conference is transmitting audio, the individual using the Cisco LMR device cannot talk.
Dial Plan
Before configuring Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Unity Express, you should plan your dial plan for Meet-Me Conferencing. Table 28 lists the dial-plan parameters that must be defined before you can configure Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0.
To prevent IP phones from dialing into the multicast bridge directly, the multicast bridge numbers should be set to nondialable numbers starting with an alphabetical character.
IP phones that dial into the multicast bridge cannot send or receive audio, so IP phone calls must be routed to the loopback number. These numbers are required to configure Cisco Unity Express Auto Attendant, which controls all access to the multicast bridge.
How to Configure Conferencing
This section contains the following tasks:
(Software-based) Three-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing
•
Modifying the Default Configuration for Three-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing (optional)
•
SCCP: Configuring Conferencing Options on a Phone (optional)
•
SIP: Configuring Conferencing Options on a Phone (optional)
(Hardware-based) Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and Later Versions
•
SCCP: Configuring Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and Later Versions (required)
•
SCCP: Verifying Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing (optional)
Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0
•
SCCP: Configuring Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0 (required)
Modifying the Default Configuration for Three-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing
To globally modify the default configuration and change any of the following parameters for three-party ad hoc conferencing, perform the following steps.
•
Maximum number of three-party conferences that are supported simultaneously by the Cisco Unified CME router. Maximum number of simultaneous three-party conferences supported by a router is platform-dependent. The default value is half of the maximum number.
•
Increase the sound volume of VoIP and public switched telephony network (PSTN) parties joining a conference call
Restrictions
•
When a three-way conference is established, a participant cannot use call transfer to join the remaining conference participants to a different number.
•
Three-party ad hoc conferencing does not support meet-me conferences.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
telephony-service
4.
max-conferences max-conference-number [gain -6 | 0 | 3 | 6]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SCCP: Configuring Conferencing Options on a Phone
To configure optional end-of-conference options for three-party ad hoc conferencing on a Cisco Unified IP phone running Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP), perform the following steps for each phone to be configured.
Prerequisites
•
Conferencing uses call transfer to connect the two remaining parties of a conference when a conference initiator leaves the conference. To use this feature, you must configure the transfer-system command. For configuration information, see "Configuring Call Transfer and Forwarding".
•
Drop-last feature of Keep Conference on analog phones connected to the Cisco Unified CME system through a Cisco VG 224 requires Cisco IOS Release 12.4(9)T or later release.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ephone phone-tag
4.
keep-conference [drop-last] [endcall] [local-only]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
What to Do Next
If you are finished modifying the configuration, you are ready to generate configuration files for the phones to be connected. See "SCCP: Generating Configuration Files for SCCP Phones".
SIP: Configuring Conferencing Options on a Phone
To configure optional end-of-conference options for three-party ad hoc conferencing on a Cisco Unified IP phone running SIP, perform the following steps for each phone to be configured.
Prerequisites
•
To facilitate call transfer by using the Confrn soft key, conference and transfer attended or transfer blind must be enabled. For configuration information, see "Configuring Call Transfer and Forwarding".
Restrictions
Music on hold (MOH) is not supported for call hold invoked from a SIP phone. A caller hears only silence when placed on hold by a SIP phone.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice register pool pool-tag
4.
keep-conference
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
What to Do Next
•
If you are finished modifying the configuration, you are ready to generate configuration files for the phones to be connected. See "SIP: Generating Configuration Profiles for SIP Phones".
Verifying Three-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing
Step 1
Use the show running-config command to verify your configuration. Any non-default conferencing parameters are listed in the telephony-service portion of the output, and end-of-conference options are listed in the ephone portion.
Router# show running-config
!
ephone-dn 1 dual-line
ring feature secondary
number 126 secondary 1261
description Sales
name Smith
call-forward busy 500 secondary
call-forward noan 500 timeout 10
huntstop channel
no huntstop
no forward local-calls
!
ephone 1
mac-address 011F.92A0.C10B
type 7960 addon 1 7914
no dnd feature-ring
keep-conference
Troubleshooting Three-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing
Step 1
Use the debug ephone commands to observe messages and states associated with an ephone. For more information, see the Cisco Unified CME Command Reference.
SCCP: Configuring Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and Later Versions
To configure multi-party ad hoc conference support for 3-8 parties plus Meet-Me conferencing for up to 32 parties, perform the following tasks:
•
SCCP: Enabling DSP Farm Services for a Voice Card (required)
•
SCCP: Configuring Join and Leave Tones (optional)
•
SCCP: Configuring SCCP for Cisco Unified CME (required)
•
SCCP: Configuring the DSP Farm (required)
•
SCCP: Associating Cisco Unified CME with a DSP Farm Profile (required)
•
SCCP: Enabling Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing (required)
•
SCCP: Configuring Multi-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing and Meet-Me Numbers (required)
•
SCCP: Configuring Conferencing Options for a Phone (required)
•
SCCP: Verifying Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing (optional)
Prerequisites
•
Cisco Unified CME 4.1 or a later version
•
You must have a PVDM2-8, PVDM2-16, PVDM2-32, or PVDM2-64 high-density packet voice digital signal processor module hosted on the motherboard or on a module such as the NM-HDV2 or NM-HD-2VE.
•
For Cisco Unified IP Phone 7985, firmware version 4-1-2-0 or a later version
Restrictions
•
The maximum number of meet-me conference parties is 32 for one DSP using the G.711 codec and 16 for the G.729 codec.
•
A participant cannot join more than one conference at the same time.
•
Hardware-based multi-party ad hoc conferencing for more than three parties is not supported on phones that do not support soft keys.
•
Hardware-based multi-party ad hoc conferencing for more than three parties is not supported on Cisco Unified IP phones running SIP.
•
Hardware-based multi-party ad hoc conferencing does not support the local-consult transfer method (transfer-system local-consult command).
SCCP: Enabling DSP Farm Services for a Voice Card
To enable DSP farm services for a voice card to support multi-party ad hoc and meet-me conferences, perform the following steps.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice-card slot
4.
dsp services dspfarm
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
SCCP: Configuring Join and Leave Tones
To configure tones to be played when parties join and leave multi-party ad hoc conferences and meet-me conferences, perform the following steps for each tone to be configured.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice class custom-cptone cptone-name
4.
dualtone conference
5.
frequency frequency-1 [frequency-2]
6.
cadence {cycle-1-on-time cycle-1-off-time [cycle-2-on-time cycle-2-off-time] [cycle-3-on-time cycle-3-off-time] [cycle-4-on-time cycle-4-off-time] | continuous}
7.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SCCP: Configuring SCCP for Cisco Unified CME
To enable SCCP on Cisco Unified CME to support multi-party ad hoc and meet-me conferences, perform the following steps:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
sccp local interface-type interface-number [port port-number]
4.
sccp ccm {ip-address | dns} identifier identifier-number [port port-number] [version version-number]
5.
sccp ccm group group-number
6.
bind interface interface-type interface-number
7.
exit
8.
sccp
9.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
SCCP: Configuring the DSP Farm
To configure the DSP farm profile for multi-party ad hoc and meet-me conferencing, perform the following steps.
Note
The DSP farm can be on the same router as the Cisco Unified CME or on a different router.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
dspfarm profile profile-identifier conference
4.
codec {codec-type | pass-through}
5.
conference-join custom-cptone cptone-name
6.
conference-leave custom-cptone cptone-name
7.
maximum conference-participants max-participants
8.
maximum sessions number
9.
associate application sccp
10.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
enable
Example:Router> enable
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
•
Enter your password if prompted.
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:Router# configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Step 3
dspfarm profile profile-identifier conference
Example:Router(config)# dspfarm profile 1 conference
Enters DSP farm profile configuration mode and defines a profile for DSP farm services.
Step 4
codec {codec-type | pass-through}
Example:Router(config-dspfarm-profile)# codec g711ulaw
Specifies the codecs supported by a DSP farm profile.
Note
Repeat this step as necessary to specify all the supported codecs.
Step 5
conference-join custom-cptone cptone-name
Example:Router(config-dspfarm-profile)# conference-join custom-cptone jointone
Associates a custom call-progress tone to indicate joining a conference with a DSP farm profile.
Note
The cptone-name argument in this step must be the same as the cptone-argument in the voice class custom-cptone command configured in the "SCCP: Enabling DSP Farm Services for a Voice Card" section.
Step 6
conference-leave custom-cptone cptone-name
Example:Router(config-dspfarm-profile)# conference-leave custom-cptone leavetone
Associates a custom call-progress tone to indicate leaving a conference with a DSP farm profile.
Note
The cptone-name argument in this step must be the same as the cptone-argument in the voice class custom-cptone command configured in the "SCCP: Enabling DSP Farm Services for a Voice Card" section.
Step 7
maximum conference-participants max-participants
Example:Router(config-dspfarm-profile)# maximum conference-participants 32
(Optional) Configures the maximum number of conference parties allowed in each meet-me conference. The maximum is codec-dependent.
Step 8
maximum sessions number
Example:Router(config-dspfarm-profile)# maximum sessions 8
Specifies the maximum number of sessions that are supported by the profile.
Step 9
associate application sccp
Example:Router(config-dspfarm-profile)# associate application sccp
Associates SCCP with the DSP farm profile.
Step 10
end
Example:Router(config-dspfarm-profile)# end
Exits to privileged EXEC mode.
SCCP: Associating Cisco Unified CME with a DSP Farm Profile
To associate a DSP farm profile with a group of Cisco Unified CME routers that control DSP services, perform the following steps.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
sccp ccm group group-number
4.
associate ccm identifier-number priority priority-number
5.
associate profile profile-identifier register device-name
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SCCP: Enabling Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing
To allow hardware-based multi-party ad hoc conferences with more than three parties and meet-me conferences, perform the following steps.
Note
Configuring multi-party ad hoc conferencing in Cisco Unified CME disables three-party (software-based) ad hoc conferencing.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
telephony-service
4.
conference hardware
5.
transfer-system full-consult
6.
sdspfarm units number
7.
sdspfarm tag number device-name
8.
sdspfarm conference mute-on mute-on-digits mute-off mute-off-digits
9.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
enable
Example:Router> enable
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
•
Enter your password if prompted.
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:Router# configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Step 3
telephony-service
Example:Router(config)# telephony-service
Enters telephony-service configuration mode.
Step 4
conference hardware
Example:Router(config-telephony)# conference hardware
Configures a Cisco Unified CME system for multi-party conferencing only.
Step 5
transfer-system full-consult
Example:Router(config-telephony)# transfer-system full-consult
Transfers calls using H.450.2 with consultation using a second phone line, if available.
•
The calls fall back to full-blind if a second line is not available.
•
This is the default transfer method in Cisco Unified CME 4.0 and later versions.
Step 6
sdspfarm units number
Example:Router(config-telephony)# sdspfarm units 3
Specifies the maximum number of DSP farms that are allowed to be registered to the SCCP server.
Step 7
sdspfarm tag number device-name
Example:Router(config-telephony)# sdspfarm tag 2 confdsp1
Permits a DSP farm to register to Cisco Unified CME and associates it with a SCCP client interface's MAC address.
Note
The device-name in this step must be the same as the device-name in the associate profile command in Step 5 of the "SCCP: Associating Cisco Unified CME with a DSP Farm Profile" section.
Step 8
sdspfarm conference mute-on mute-on-digits mute-off mute-off-digits
Example:Router(config-telephony)# sdspfarm conference mute-on 111 mute-off 222
Defines mute-on and mute-off digits for conferencing.
•
Maximum: 3 digits. Valid values are the numbers and symbols that appear on your telephone keypad: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, *, and #.
•
Mute-on and mute-off digits can be the same.
Step 9
end
Example:Router(config-telephony)# end
Exits to privileged EXEC mode.
SCCP: Configuring Multi-Party Ad Hoc Conferencing and Meet-Me Numbers
To configure extension numbers for hardware-based multi-party ad hoc and meet-me ad hoc conferencing, based on the maximum number of conference participants you configure, perform the following steps. Ad hoc conferences require four extensions per conference, regardless of how many extensions are actually used by the conference parties.
Note
Ensure that you configure enough directory numbers to accommodate the anticipated number of conferences. The maximum number of parties in a multi-party ad hoc conference on an IP phone is eight; the maximum on an analog phone is three.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ephone-dn dn-tag [dual-line]
4.
number number [secondary number] [no-reg [both | primary]]
5.
conference {ad-hoc | meetme}
6.
preference preference-order [secondary secondary-order]
7.
no huntstop [channel]
8.
end
DETAILED STEPS
SCCP: Configuring Conferencing Options for a Phone
To configure a template of conferencing features such as the add party mode, drop party mode, and soft keys for hardware-based multi-party ad hoc and meet-me conferences and apply the template to a phone, perform the following steps.
Note
The following commands can also be configured in ephone configuration mode. Commands configured in ephone configuration mode have priority over commands in ephone-template configuration mode.
Prerequisites
•
The RmLstC, ConfList, Join, and Select functions and soft keys are supported for hardware-based conferencing only and require the appropriate DSP farm configuration. For configuration information, see these tasks in this module:
–
"SCCP: Enabling DSP Farm Services for a Voice Card" section
–
"SCCP: Configuring the DSP Farm" section
–
"SCCP: Associating Cisco Unified CME with a DSP Farm Profile" section
Restrictions
•
The ConfList (including the Remove, Update, and Exit soft keys within the ConfList function) and RmLstC soft keys do not work on a Cisco Unified IP Phone 7902, 7935, and 7936.
•
The RmLstC, ConfList, Join, and Select functions and soft keys are not supported for software-based conferencing.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ephone-template template-tag
4.
conference add-mode [creator]
5.
conference drop-mode [creator | local]
6.
conference admin
7.
softkeys connected {[Acct] [ConfList] [Confrn] [Endcall] [Flash] [HLog] [Hold] [Join] [LiveRcd] [Park] [RmLstC] [Select] [TrnsfVM] [Trnsfer]}
8.
softkeys hold {[Join] [Newcall] [Resume] [Select]}
9.
softkeys idle {[Cfwdall] [ConfList] [Dnd] [Gpickup] [HLog] [Join] [Login] [Newcall] [Pickup] [Redial] [RmLstC]}
10.
softkeys seized {[CallBack] [Cfwdall] [Endcall] [Gpickup] [HLog] [MeetMe] [Pickup] [Redial]}
11.
exit
12.
ephone phone-tag
13.
ephone-template template-tag
14.
end
DETAILED STEPS
What to Do Next
If you are finished modifying the configuration, you are ready to generate configuration files for the phones to be connected. See "SCCP: Generating Configuration Files for SCCP Phones".
SCCP: Verifying Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing
Use the following show commands to verify multi-party ad hoc and meet-me conferencing:
•
show ephone-dn conference—Displays information about ad hoc and meet-me conferences.
•
show telephony-service conference hardware—Displays information about hardware-based conferences.
show ephone-dn conference: Example
type active inactive numbers
=======================================
Meetme 0 8 2345
DN tags: 9, 10, 11, 12
Ad-hoc 0 8 A001
DN tags: 13, 14, 15, 16
Meetme 0 8 1234
DN tags: 20, 21, 22, 23
show telephony-service conference hardware detail: Example
Conference Type Active Max Peak Master MasterPhone Last
cur(initial)
==================================================================
8889 Ad-hoc 3 8 3 8044 29 ( 29) 8012
Conference parties:
8012
8006
8044
SCCP: Configuring Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0
Refer to the "Examples" section to configure Meet-Me Conferencing on a Cisco router with Cisco CME 3.2 or a later version and Cisco Unity Express.
Note
To configure Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 or a later version, see the "SCCP: Configuring Multi-Party Ad Hoc and Meet-Me Conferencing in Cisco Unified CME 4.1 and Later Versions" section
Prerequisites
•
Cisco CME 3.2 to Cisco Unified CME 4.0.
•
A dual VWIC-2MFT-T1 or E-1 loopback for internal callers. The number of VWIC-2MFT-T1 cards required depends on the number of local IP phones parties that need to dial into the meet-me conference. Each VWIC-2MFT-T1 card can support 24 local IP phone parties.
•
Packet Voice DSP Modules (PVDM DSPs) to handle the number of callers in conference. A maximum of 96 conference parties is supported using an approved platform, such as a Cisco 3800 router, with at least two PVDM2-64DSPs installed.
•
Your IP network is operational and you can access Cisco web.
•
You have a valid Cisco.com account.
•
The recommended Cisco IOS release and Cisco Unified CME phone firmware and GUI files to support Cisco Unity Express are installed on the Cisco Unified CME router.
To determine whether the Cisco IOS software release and Cisco Unified CME software version are compatible with the Cisco Unity Express version, Cisco router model, and Cisco Unity Express hardware that you are using, see the Cisco Unity Express Compatibility Matrix.
To verify installed Cisco Unity Express software version, enter the Cisco Unity Express command environment and use the show software version user EXEC command. For information about the command environment, see the appropriate Cisco Unity Express CLI Administrator Guide at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/unity_exp/roadmap/cuedocs.html.
•
The proper Cisco Unity Express license for Cisco Unified CME, not Cisco Unified Communications Manager, is installed. To verify installed license, enter the Cisco Unity Express command environment and use the show software license user EXEC command. For information about the command environment, see the appropriate Cisco Unity Express CLI Administrator Guide at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/unity_exp/roadmap/cuedocs.html.
This is an example of the Cisco Unified CME license:
se-10-0-0-0> show software licensesCore:- application mode: CCME- total usable system ports: 8Voicemail/Auto Attendant:- max system mailbox capacity time: 6000- max general delivery mailboxes: 15- max personal mailboxes: 50Languages:- max installed languages: 1- max enabled languages: 1•
Calls can be successfully completed between phones on the same Cisco Unified CME router.
•
Dial plan for Meet-Me Conferencing is defined. For information, see "Dial Plan" section.
Restrictions
•
The number of meet-me conferences and parties per conference is limited by the number of DSP resources and number of voice ports available to handle callers.
•
There is no set maximum for the number of parties per conference. However, since only the three loudest parties on a multicast conference can be heard, we recommend that the maximum number of parties per conference be limited to eight.
•
Only a minimal set of features are provided. Conference bridges can be accessed by any user knowing the correct number to dial (internal or external) with no option to set a password. Callers entering a Meet-Me conference though Cisco Unity Express auto-attendant application are prompted to record their name for playback to all callers on the bridge. No exit tone is played when users leave a conference, nor can a Meet-Me bridge be reserved for use at a future time or date.
Examples
The following partial output from the show running-config command shows the configuration on a Cisco 2821 router with Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Unity Express, with comments describing the configuration for setting up Meet-Me Conferencing.
Router# show running-config
building configuration...
.
.
.
.
.
!
!---Two T1 ports connected back-to-back to bridge VOIP to Multicast
controller T1 0/3/0
framing esf
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 2 timeslots 2 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 3 timeslots 3 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 4 timeslots 4 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 5 timeslots 5 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 6 timeslots 6 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 7 timeslots 7 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 8 timeslots 8 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 9 timeslots 9 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 10 timeslots 10 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 11 timeslots 11 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 12 timeslots 12 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 13 timeslots 13 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 14 timeslots 14 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 15 timeslots 15 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 16 timeslots 16 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 17 timeslots 17 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 18 timeslots 18 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 19 timeslots 19 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 20 timeslots 20 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 21 timeslots 21 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 22 timeslots 22 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 23 timeslots 23 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 24 timeslots 24 type e&m-immediate-start!
controller T1 0/3/1
framing esf
clock source internal
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 2 timeslots 2 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 3 timeslots 3 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 4 timeslots 4 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 5 timeslots 5 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 6 timeslots 6 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 7 timeslots 7 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 8 timeslots 8 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 9 timeslots 9 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 10 timeslots 10 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 11 timeslots 11 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 12 timeslots 12 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 13 timeslots 13 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 14 timeslots 14 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 15 timeslots 15 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 16 timeslots 16 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 17 timeslots 17 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 18 timeslots 18 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 19 timeslots 19 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 20 timeslots 20 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 21 timeslots 21 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 22 timeslots 22 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 23 timeslots 23 type e&m-immediate-startds0-group 24 timeslots 24 type e&m-immediate-start!
!
!
!--- Disable keepalive packet to multicast network on voice class and apply to LMR port
!
voice class permanent 1
signal timing oos restart 50000
signal timing oos timeout disabled
signal keepalive disabled
signal sequence oos no-action
!---Loopback0 used as source for all H323 and SCCP packets generated by CME
interface Loopback0
ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
h323-gateway voip interface
h323-gateway voip bind srcaddr 11.1.1.1
!
!---Vif1 (virtual host interface) used as source for all multicast packets generated by CME
!
interface Vif1
ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.252
ip pim dense-mode
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
!---Service-engine interface used to access Cisco Unity Express
!
interface Service-Engine0/0
ip unnumbered Vlan10
service-module ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
service-module ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/0/0
switchport access vlan 10
no ip address
!
interface FastEthernet0/0/1
switchport access vlan 10
no ip address
!
interface FastEthernet0/0/2
switchport access vlan 10
no ip address
!
interface FastEthernet0/0/3
switchport access vlan 10
no ip address
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
!
!---All IP phones reside on VLAN 10
interface Vlan10
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip pim dense-mode
!
ip classless
!--- Static route to reach other devices on network
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2
!--- Static route to reach Cisco Unity Express
ip route 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.255 Service-Engine0/0
!
ip http server
ip http path flash:
!
!
tftp-server flash:P00305000301.sbn
!
control-plane
!
!
!
!---VOIP side of the Back-to-Back T1 used for bridging VOIP to
!---Multicast (Hoot n' Holler)
!---Port 0/3/0:x connects to Port 0/3/1:x
voice-port 0/3/0:1
auto-cut-through
!
voice-port 0/3/0:2
auto-cut-through
!
.
.
.
!
voice-port 0/3/0:24
auto-cut-through
!
!---Multicast side of the Back-to-Back T1 used for bridging VOIP to
!---Multicast (Hoot n' Holler)
!--- Port 0/3/1:1 - 8 is permanently trunked to multicast bridge A212
!--- Port 0/3/1:9 - 16 is permanently trunked to multicast bridge A213
!--- Port 0/3/1:17 - 24 is permanently trunked to multicast bridge A214
voice-port 0/3/1:1
auto-cut-through
timeouts call-disconnect 3
connection trunk A212
!
.
.
.
!
voice-port 0/3/1:9
auto-cut-through
timeouts call-disconnect 3
connection trunk A213
!
.
.
.
!
voice-port 0/3/1:17
auto-cut-through
timeouts call-disconnect 3
connection trunk A214
.
.
.
!
!--- Analog FXO lines on port 0/2/x route incoming calls to CUE AA external extension 203
voice-port 0/2/0
connection plar opx 203
!
voice-port 0/2/1
connection plar opx 203
!
voice-port 0/2/2
connection plar opx 203
!
voice-port 0/2/3
connection plar opx 203
!
!--- LMR devices are connected to E&M ports 0/1/x. The E&M ports are permanently trunked to multicast conference bridges. Port 0/1/0 will send and receive audio from conference A212 and port 0/1/1 will send and receive audio from conference A213.
voice-port 0/1/0
voice-class permanent 1
lmr m-lead audio-gate-in
lmr e-lead voice
auto-cut-through
operation 4-wire
type 3
signal lmr
timeouts call-disconnect 3
connection trunk A212
!
voice-port 0/1/1
voice-class permanent 1
lmr m-lead audio-gate-in
lmr e-lead voice
auto-cut-through
operation 4-wire
type 3
signal lmr
timeouts call-disconnect 3
connection trunk A213
!
!--- Dial-peers to route extension 212 to T1 loopback, which is trunked to bridge A212
dial-peer voice 1 pots
preference 1
destination-pattern 212
port 0/3/0:1
!
.
.
.
!
dial-peer voice 8 pots
preference 8
destination-pattern 212
port 0/3/0:8
!
!--- Dial-peers to route extension 213 to T1 loopback, which is trunked to bridge A213
dial-peer voice 9 pots
preference 1
destination-pattern 213
port 0/3/0:9
!
.
.
.
!
dial-peer voice 16 pots
preference 8
destination-pattern 213
port 0/3/0:16
!
!--- Dial-peers to route extension 214 to T1 loopback, which is trunked to bridge A214
dial-peer voice 17 pots
preference 1
destination-pattern 214
port 0/3/0:17
!
.
.
.
!
dial-peer voice 24 pots
preference 8
destination-pattern 214
port 0/3/0:24
!--- Dial-peer to route calls to CUE AA for internal ext. 202 and external ext. 203
dial-peer voice 200 voip
destination-pattern 20.
session protocol sipv2
session target ipv4:192.168.1.2
dtmf-relay sip-notify
codec g711ulaw
no vad
!
!--- Dial-peers for multicast bridges
dial-peer voice 212 voip
destination-pattern A212
voice-class permanent 1
session protocol multicast
session target ipv4:237.111.0.0:22222
dtmf-relay cisco-rtp
codec g711ulaw
vad aggressive
!
dial-peer voice 213 voip
destination-pattern A213
voice-class permanent 1
session protocol multicast
session target ipv4:237.111.0.1:22222
dtmf-relay cisco-rtp
codec g711ulaw
vad aggressive
!
dial-peer voice 214 voip
destination-pattern A214
voice-class permanent 1
session protocol multicast
session target ipv4:237.111.0.2:22222
dtmf-relay cisco-rtp
codec g711ulaw
vad aggressive
!
telephony-service
load 7960-7940 P00305000301
max-ephones 24
max-dn 144
ip source-address 11.1.1.1 port 2000
create cnf-files version-stamp Jan 01 2002 00:00:00
voicemail 200
web admin system name cisco password cisco
max-conferences 8 gain -6
transfer-system full-consult
!
!
ephone-dn 1 dual-line
number 150
!
.
.
.
What to Do Next
Load and configure the auto-attendant script file for Meet-me Conferencing. For information about logging into and GUI windows and menus, see the appropriate Cisco Unity Express GUI Administrator Guide at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/unity_exp/roadmap/cuedocs.html.
Step 1
Go to the Download Software site. Download the Conference Express TCL and AA voice files (conf-express.zip). Unzip the archive to a folder on your PC.
Step 2
Log into Cisco Unity Express as administrator.
Step 3
Navigate to the Voice mail> Auto Attendant menu and click Add. The Add a New Automated Attendant window appears.
Step 4
In the Select Automated Attendant area, configure the parameters listed in the following table. Enter the required information in the corresponding field.
.
Select Automated Attendant Script
mp-exp.aef
Application Name (lower case)
conference-express
Destination file name
mp-exp.aef
Step 5
Click Next. The Upload window appears.
Step 6
Upload the script (mp-exp.aef) from your PC to the auto-attendant application. For information, see online help.
Step 7
On the Add a New Automated Attendant window, configure parameters with numbers as defined in your dial plan and with the values listed in following table. Enter the required information in the corresponding field. For dial plan information, see the "Dial Plan" section.
Step 8
Click Finish.
Step 9
Navigate to the Administration>Call-In Numbers menu and click Add.
Step 10
On the Add a Call-In Number window, configure the parameters listed in the following table. Enter the required information in the corresponding field.
Application
conference-express
Call-in Number
ExternalNumber as defined in dial plan
Maximum Sessions
4
Step 11
Click Add.
Step 12
Confirm that two call-in numbers for the conference-express application are enabled on the Administration>Call-In Numbers window.
Configuration Examples for Conferencing
This section provides the following configuration examples:
•
End of Conference Options: Example
•
DSP Farm and Cisco Unified CME on the Same Router: Example
•
DSP Farm and Cisco Unified CME on Different Routers: Example
Basic Conferencing: Example
The following example sets the maximum number of conferences for a Cisco Unified IP phone to 4 and configures a gain of 6 db for inbound audio packets from remote PSTN or VoIP calls joining a conference:
telephony-service
max-conferences 4 gain 6
End of Conference Options: Example
In the following example, extension 3555 initiates a three-way conference. After the conference is established, extension 3555 can press the Confrn soft key to disconnect the last party that was connected and remain connected to the first party that was connected. If extension 3555 hangs up from the conference, the other two parties remain connected if one of them is local to the Cisco Unified CME system.
ephone-dn 35
number 3555
ephone 24
button 1:35
keep-conference drop-last local-only
In the following example, extension 3666 initiates a three-way conference. After the conference is established, extension 3666 can press the Confrn soft key to disconnect the last party that was connected and remain connected to the first party that was connected. Also, extension 3666 can hang up or press the EndCall soft key to leave the conference and keep the other two parties connected.
ephone-dn 36
number 3666
ephone 25
button 1:36
keep-conference drop-last endcall
In the following example, extension 3777 initiates a three-way conference. After the conference is established, extension 3777 can press the Confrn soft key to disconnect the last party that was connected and remain connected to the first party that was connected. Also, extension 3777 can hang up or press the EndCall soft key to leave the conference and keep the other two parties connected only if one of the two parties is local to the Cisco Unified CME system.
ephone-dn 38
number 3777
ephone 27
button 1:38
keep-conference drop-last endcall local-only
In the following example, extension 3999 initiates a three-way conference. After the conference is established, extension 3999 can hang up or press the EndCall soft key to leave the conference and keep the other two parties connected only if one of the two parties is local to the Cisco Unified CME system. Extension 3999 can also use the Confrn soft key to break up the conference but stay connected to both parties.
ephone-dn 39
number 3999
ephone 29
button 1:39
keep-conference endcall local-only
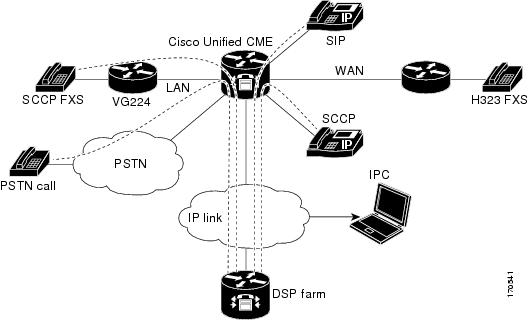
DSP Farm and Cisco Unified CME on the Same Router: Example
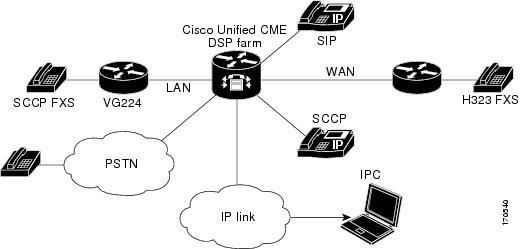
In this example, the DSP farm and Cisco Unified CME are on the same router as shown in Figure 33.
Figure 33 CME and the DSP Farm on the Same Router
Current configuration : 16345 bytes
!
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
service internal
!
hostname cmedsprtr
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
logging buffered 90000 debugging
!
no aaa new-model
!
resource policy
!
no network-clock-participate slot 1
no network-clock-participate wic 0
ip cef
!
!
ip dhcp pool phone1
host 10.4.188.66 255.255.0.0
client-identifier 0100.0ab7.b144.4a
default-router 10.4.188.65
option 150 ip 10.4.188.65
!
ip dhcp pool phone2
host 1.4.188.67 255.255.0.0
client-identifier 0100.3094.c269.35
default-router 10.4.188.65
option 150 ip 10.4.188.65
!
!
voice-card 1
dsp services dspfarm
!
!
voice call send-alert
voice call carrier capacity active
!
voice service voip
allow-connections h323 to h323
supplementary-service h450.12
h323
!
!
!
!
controller E1 1/0
framing NO-CRC4
!
controller E1 1/1
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.4.188.65 255.255.0.0
duplex auto
speed auto
no keepalive
no cdp enable
no clns route-cache
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
no clns route-cache
!
ip route 10.4.0.0 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet0/0
ip route 192.168.254.254 255.255.255.255 10.4.0.1
!
ip http server
!
!
control-plane
!
!
sccp local FastEthernet0/0
sccp ccm 10.4.188.65 identifier 1 version 4.0
sccp
!
sccp ccm group 123
associate ccm 1 priority 1
associate profile 1 register mtp00097c5e9ce0
keepalive retries 5
!
!
dspfarm profile 1 conference
codec g711ulaw
codec g711alaw
codec g729ar8
codec g729abr8
codec g729r8
codec g729br8
maximum sessions 6
associate application SCCP
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
!
!
dial-peer voice 6 voip
destination-pattern 6...
session target ipv4:10.4.188.90
!
telephony-service
conference hardware
load 7960-7940 P00307020400
load 7905 CP7905060100SCCP050309A.sbin
max-ephones 48
max-dn 180
ip source-address 10.4.188.65 port 2000
timeouts ringing 500
system message MY MELODY (2611)
sdspfarm units 4
sdspfarm tag 1 mtp00097c5e9ce0
max-conferences 4 gain -6
call-forward pattern ....
transfer-system full-consult
transfer-pattern 7...
transfer-pattern ....
create cnf-files version-stamp Jan 01 2002 00:00:00
!
!
ephone-template 1
softkeys hold Newcall Resume Select Join
softkeys idle Cfwdall ConfList Dnd Gpickup HLog Join Login Newcall Pickup Redial RmLstC
softkeys seized Redial Pickup Gpickup HLog Meetme Endcall
softkeys connected Acct ConfList Confrn Endcall Flash HLog Hold Join Park RmLstC Select
Trnsfer!
!
ephone-dn 1 dual-line
number 8001
name melody-8001
!
!
ephone-dn 2 dual-line
number 8002
!
!
ephone-dn 3 dual-line
number 8003
!
!
ephone-dn 4 dual-line
number 8004
!
!
ephone-dn 5 dual-line
number 8005
!
!
ephone-dn 6 dual-line
number 8006
!
!
ephone-dn 7 dual-line
number 8007
!
!
ephone-dn 8 dual-line
number 8008
!
!
ephone-dn 60 dual-line
number 8887
conference meetme
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 61 dual-line
number 8887
conference meetme
preference 1
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 62 dual-line
number 8887
conference meetme
preference 2
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 63 dual-line
number 8887
conference meetme
preference 3
!
!
ephone-dn 64 dual-line
number 8889
name Conference
conference ad-hoc
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 65 dual-line
number 8889
name Conference
conference ad-hoc
preference 1
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 66 dual-line
number 8889
name Conference
conference ad-hoc
preference 2
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 67 dual-line
number 8889
name Conference
conference ad-hoc
preference 3
!
!
ephone 1
ephone-template 1
mac-address 0030.94C2.6935
type 7960
button 1:1 2:2
!
!
ephone 2
ephone-template 1
mac-address 000A.B7B1.444A
type 7940
button 1:4 2:8
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
line aux 0
exec-timeout 0 0
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
login
line vty 5 15
login
!
!
end
DSP Farm and Cisco Unified CME on Different Routers: Example
In this example, the DSP farm and Cisco Unified CME are on different routers as shown in Figure 34.
Figure 34 Cisco Unified CME and the DSP Farm on Different Routers
This section contains configuration examples for the following routers:
•
Cisco Unified CME Router Configuration: Example
•
DSP Farm Router Configuration: Example
Cisco Unified CME Router Configuration: Example
Current configuration : 5659 bytes
!
version 12.4
no service timestamps debug uptime
no service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
card type command needed for slot 1
logging buffered 3000000 debugging
!
no aaa new-model
!
resource policy
!
no network-clock-participate slot 1
no network-clock-participate aim 0
!
voice-card 1
no dspfarm
!
voice-card 3
dspfarm
!
ip cef
!
!
no ip dhcp use vrf connected
!
ip dhcp pool IPPhones
network 10.15.15.0 255.255.255.0
option 150 ip 10.15.15.1
default-router 10.15.15.1
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.3.111.102 255.255.0.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1.1
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ip address 10.15.14.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/1.2
encapsulation dot1Q 20
ip address 10.15.15.1 255.255.255.0
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.5.51.1
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.3.0.1
!
ip http server
!
!
!
!
control-plane!
!
!
!
dial-peer voice 1 voip
destination-pattern 3...
session target ipv4:10.3.111.101
!
!
telephony-service
conference hardware
load 7910 P00403020214
load 7960-7940 P003-07-5-00
max-ephones 50
max-dn 200
ip source-address 10.15.15.1 port 2000
sdspfarm units 4
sdspfarm transcode sessions 12
sdspfarm tag 1 confer1
sdspfarm tag 4 xcode1
max-conferences 8 gain -6
moh flash:music-on-hold.au
multicast moh 239.0.0.0 port 2000
transfer-system full-consult
create cnf-files version-stamp Jan 01 2002 00:00:00
!
!
ephone-template 1
softkeys hold Resume Newcall Select Join
softkeys idle Redial Newcall ConfList RmLstC Cfwdall Join Pickup Login HLog Dnd Gpickup
softkeys seized Endcall Redial Cfwdall Meetme Pickup Callback
softkeys alerting Endcall Callback
softkeys connected Hold Endcall Confrn Trnsfer Select Join ConfList RmLstC Park Flash
!ephone-dn 1 dual-line
number 6000
!
!
ephone-dn 2 dual-line
number 6001
!
!
ephone-dn 3 dual-line
number 6002
!
!
ephone-dn 4 dual-line
number 6003
!
!
ephone-dn 5 dual-line
number 6004
!
!
ephone-dn 6 dual-line
number 6005
!
!
ephone-dn 7 dual-line
number 6006
!
!
ephone-dn 8 dual-line
number 6007
!
!
ephone-dn 9 dual-line
number 6008
!
!
ephone-dn 10 dual-line
number 6009
!
!
ephone-dn 11
number 6011
!
!
ephone-dn 12
number 6012
!
!
ephone-dn 13
number 6013
!
!
ephone-dn 14
number 6014
!
!
ephone-dn 15
number 6015
!
!
ephone-dn 16
number 6016
!
!
ephone-dn 17
number 6017
!
!
ephone-dn 18
number 6018
!
!
ephone-dn 19
number 6019
!
!
ephone-dn 20
number 6020
!
!
ephone-dn 21
number 6021
!
!
ephone-dn 22
number 6022
!
!
ephone-dn 23
number 6023
!
!
ephone-dn 24
number 6024
!
!
ephone-dn 25 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 1
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 26 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 2
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 27 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 3
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 28 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 4
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 29 dual-line
number 8888
conference meetme
preference 1
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 30 dual-line
number 8888
conference meetme
preference 2
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 31 dual-line
number 8888
conference meetme
preference 3
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 32 dual-line
number 8888
conference meetme
preference 4
!
!
ephone-dn 33
number 6033
!
!
ephone-dn 34
number 6034
!
!
ephone-dn 35
number 6035
!
!
ephone-dn 36
number 6036
!
!
ephone-dn 37
number 6037
!
!
ephone-dn 38
number 6038
!
!
ephone-dn 39
number 6039
!
!
ephone-dn 40
number 6040
!
!
ephone-dn 41 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 5
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 42 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 6
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 43 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 7
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 44 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 8
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 45 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 9
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 46 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 10
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 47 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 10
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 48 dual-line
number 6666
conference meetme
preference 10
!
!
ephone-dn 51 dual-line
number A0001
name conference
conference ad-hoc
preference 1
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 52 dual-line
number A0001
name conference
conference ad-hoc
preference 2
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 53 dual-line
number A0001
name conference
conference ad-hoc
preference 3
no huntstop
!
!
ephone-dn 54 dual-line
number A0001
name conference
conference ad-hoc
preference 4
!
!
ephone 1
ephone-template 1
mac-address C863.B965.2401
type anl
button 1:1
!
!
!
ephone 2
ephone-template 1
mac-address 0016.C8BE.A04A
type 7920
!
!
!
ephone 3
ephone-template 1
mac-address C863.B965.2400
type anl
button 1:2
!
!
!
ephone 4
no multicast-moh
ephone-template 1
mac-address 0017.952B.7F5C
type 7912
button 1:4
!
!
!
ephone 5
ephone-template 1
ephone 6
no multicast-moh
ephone-template 1
mac-address 0017.594F.1468
type 7961GE
button 1:6
!
!
!
ephone 11
ephone-template 1
mac-address 0016.C8AA.C48C
button 1:10 2:15 3:16 4:17
button 5:18 6:19 7:20 8:21
button 9:22 10:23 11:24 12:33
button 13:34 14:35 15:36 16:37
button 17:38 18:39 19:40
!
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
!
end
DSP Farm Router Configuration: Example
Current configuration : 2179 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 05:47:23 UTC Wed Jul 12 2006
!
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime
no service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
hostname dspfarmrouter
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
card type command needed for slot 1
logging buffered 4096 debugging
enable password lab!
no aaa new-model
!
resource policy
!
no network-clock-participate slot 1
!
!
ip cef
!
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
voice-card 0
no dspfarm
!
voice-card 1
no dspfarm
dsp services dspfarm
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 10.3.111.100 255.255.0.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1.1
encapsulation dot1Q 100
ip address 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1.2
encapsulation dot1Q 200
ip address 192.168.2.10 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1.3
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ip address 10.15.14.10 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1.4
encapsulation dot1Q 20
ip address 10.15.15.10 255.255.255.0
!ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.3.0.1
ip route 192.168.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.3.0.1
!
!
ip http server
!
!
!
!
control-plane
!
sccp local GigabitEthernet0/0
sccp ccm 10.15.15.1 identifier 1 version 4.1
!
!
sccp ccm group 1
associate ccm 1 priority 1
associate profile 101 register confer1
associate profile 103 register xcode1
!
!
dspfarm profile 103 transcode
codec g711ulaw
codec g711alaw
codec g729r8
maximum sessions 6
associate application SCCP
!
dspfarm profile 101 conference
codec g711ulaw
codec g711alaw
codec g729r8
maximum sessions 5
associate application SCCP
!
!
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
session-timeout 300
exec-timeout 0 0
password
no login
!
scheduler allocate 20000 1000
!
end
Where to Go Next
Controlling Use of the Conference Soft Key
To block the functioning of the conference (Confrn) soft key without removing the key display, create and apply an ephone template that contains the features blocked command. For more information, see "Creating Templates".
To remove the conference (Confrn) soft key from one or more phones, create and apply an ephone template that contains the appropriate softkeys command. For more information, see "Customizing Soft Keys".
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to conferencing.
Related Documents
Cisco Unified CME configuration
•
Cisco Unified CME Command Reference
Cisco IOS commands
•
Cisco IOS Voice Command Reference
Cisco IOS configuration
•
Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library
Phone documentation for Cisco Unified CME
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for Conferencing
Table 29 lists the features in this module and enhancements to the features by version.
To determine the correct Cisco IOS release to support a specific Cisco Unified CME version, see the Cisco Unified CME and Cisco IOS Software Version Compatibility Matrix at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cucme/requirements/guide/33matrix.htm.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which Cisco IOS software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Note
Table 29 lists the Cisco Unified CME version that introduced support for a given feature. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent versions of Cisco Unified CME software also support that feature.

 Feedback
Feedback