-
Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet 1300 Series Outdoor Access Point/Bridge 12.3(7)JA
-
Preface
-
Overview
-
Configuring the Access Point/Bridge for the
-
Using the Web-Browser Interface
-
Using the Command-Line Interface
-
Administering the Access Point/Bridge
-
Configuring Radio Settings
-
Configuring Multiple SSIDs
-
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
-
Configuring Cipher Suites and WEP
-
Configuring Authentication Types
-
Configuring WDS, Fast Secure Roaming, Radio Management, and Wireless Intrusion Detection Services
-
Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+ Servers
-
Configuring VLANs
-
Configuring QoS
-
Configuring Filters
-
Configuring CDP
-
Configuring SNMP
-
Managing Firmware and Configurations
-
Configuring System Message Logging
-
Configuring Repeater and Standby Access Points and Workgroup Bridge Mode
-
Troubleshooting
-
Protocol Filters
-
Supported MIBs
-
Error and Event Messages
-
Glossary
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring Filters Using the CLI
Configuring Filters Using the Web-Browser Interface
Configuring and Enabling MAC Address Filters
Using MAC Address ACLs to Block or Allow Client Association to the Access Point
Configuring and Enabling IP Filters
Configuring and Enabling Ethertype Filters
Configuring Filters
This chapter describes how to configure and manage MAC address, IP, and Ethertype filters on the access point/bridge using the web-browser interface. This chapter contains these sections:
•
Configuring Filters Using the CLI
•
Configuring Filters Using the Web-Browser Interface
Understanding Filters
Protocol filters (IP protocol, IP port, and Ethertype) prevent or allow the use of specific protocols through the access point/bridge's Ethernet and radio ports. You can set up individual protocol filters or sets of filters. You can filter protocols for wireless client devices, users on the wired LAN, or both. For example, an SNMP filter on the access point/bridge's radio port prevents wireless clients from using SNMP with the access point/bridge but does not block SNMP access from the wired LAN.
IP address and MAC address filters allow or disallow the forwarding of unicast and multicast packets either sent from or addressed to specific IP or MAC addresses. You can create a filter that passes traffic to all addresses except those you specify, or you can create a filter that blocks traffic to all addresses except those you specify.
You can configure filters using the web-browser interface or by entering commands in the CLI.
Tip
You can include filters in the access point/bridge's QoS policies. Refer to "Configuring QoS," for detailed instructions on setting up QoS policies.
Configuring Filters Using the CLI
To configure filters using IOS commands, you use access control lists (ACLs) and access point/bridge groups. You can find explanations of these concepts and instructions for implementing them in these documents:
•
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide, Release 12.2. Click this link to browse to the "Configuring Transparent Bridging" chapter: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fibm_c/bcfpart1/bcftb.htm
•
Catalyst 4908G-L3 Cisco IOS Release 12.0(10)W5(18e) Software Feature and Configuration Guide. Click this link to browse to the "Command Reference" chapter: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/l3sw/4908g_l3/ios_12/10w518e/config/cmd_ref.htm
Configuring Filters Using the Web-Browser Interface
This section describes how to configure and enable filters using the web-browser interface. You complete two steps to configure and enable a filter:
1.
Name and configure the filter using the filter setup pages.
2.
Enable the filter using the Apply Filters page.
These sections describe setting up and enabling three filter types:
•
Configuring and Enabling MAC Address Filters
•
Configuring and Enabling IP Filters
•
Configuring and Enabling Ethertype Filters
Configuring and Enabling MAC Address Filters
MAC address filters allow or disallow the forwarding of unicast and multicast packets either sent from or addressed to specific MAC addresses. You can create a filter that passes traffic to all MAC addresses except those you specify, or you can create a filter that blocks traffic to all MAC addresses except those you specify. You can apply the filters you create to either or both the Ethernet and radio ports and to either or both incoming and outgoing packets.
Note
Using the CLI, you can configure up to 2,048 MAC addresses for filtering. Using the web browser interface, you can configure only up to 43 MAC address for filtering.
Note
MAC address filters are powerful, and you can lock yourself out of the access point/bridge if you make a mistake setting up the filters. If you accidentally lock yourself out of your access point/bridge, use the CLI to disable the filters, or use the Mode button on the access point/bridge power injector to reset the access point/bridge to factory defaults.
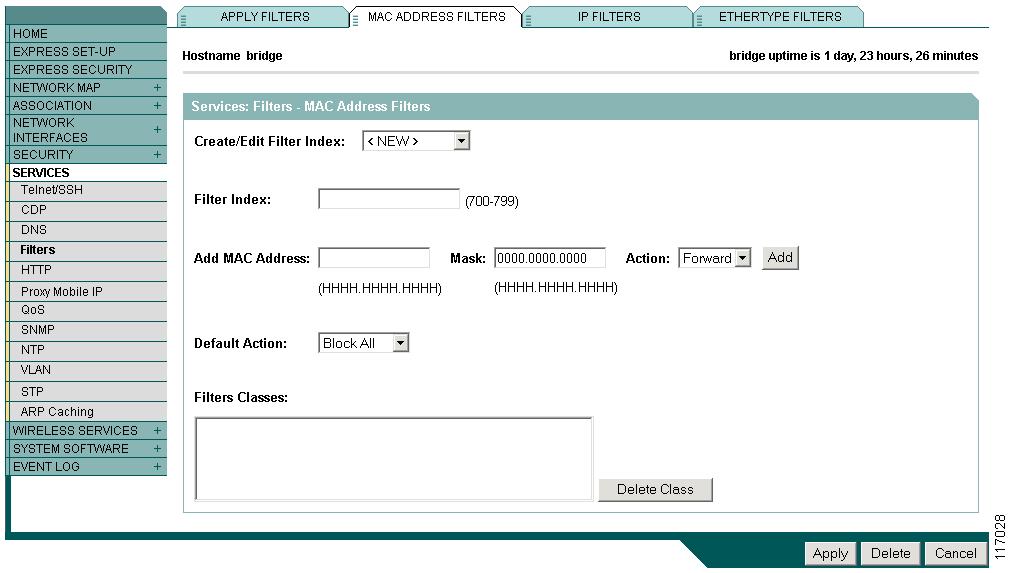
Use the MAC Address Filters page to create MAC address filters for the access point/bridge. Figure 15-1 shows the MAC Address Filters page.
Figure 15-1 MAC Address Filters Page
Follow this link path to reach the Address Filters page:
1.
Click Services in the page navigation bar.
2.
In the Services page list, click Filters.
3.
On the Apply Filters page, click the MAC Address Filters tab at the top of the page.
Creating a MAC Address Filter
Follow these steps to create a MAC address filter:
Step 1
Follow the link path to the MAC Address Filters page.
Step 2
If you are creating a new MAC address filter, make sure <NEW> (the default) is selected in the Create/Edit Filter Index menu. To edit a filter, select the filter number from the Create/Edit Filter Index menu.
Step 3
In the Filter Index field, name the filter with a number from 700 to 799. The number you assign creates an access control list (ACL) for the filter.
Step 4
Enter a MAC address in the Add MAC Address field. Enter the address with periods separating the three groups of four characters (0005.9a39.3456, for example).
Note
To make sure the filter operates properly, use lower case for all the letters in the MAC address that you enter.
Step 5
Use the Mask entry field to indicate how many bits, from left to right, the filter checks against the MAC address. For example, to require an exact match with the MAC address (to check all bits) enter 0000.0000.0000. To check only the first 4 bytes, enter 0.0.FFFF.
Step 6
Select Forward or Block from the Action menu.
Step 7
Click Add. The MAC address appears in the Filters Classes field. To remove the MAC address from the Filters Classes list, select it and click Delete Class.
Step 8
Repeat Step 4 through Step 7 to add addresses to the filter.
Step 9
Select Forward All or Block All from the Default Action menu. The filter's default action must be the opposite of the action for at least one of the addresses in the filter. For example, if you enter several addresses and you select Block as the action for all of them, you must choose Forward All as the filter's default action.
Tip
You can create a list of allowed MAC addresses on an authentication server on our network. Consult the "Configuring Authentication Types" for instructions on using MAC based authentication.
Step 10
Click Apply. The filter is saved on the access point/bridge, but it is not enabled until you apply it on the Apply Filters page.
Step 11
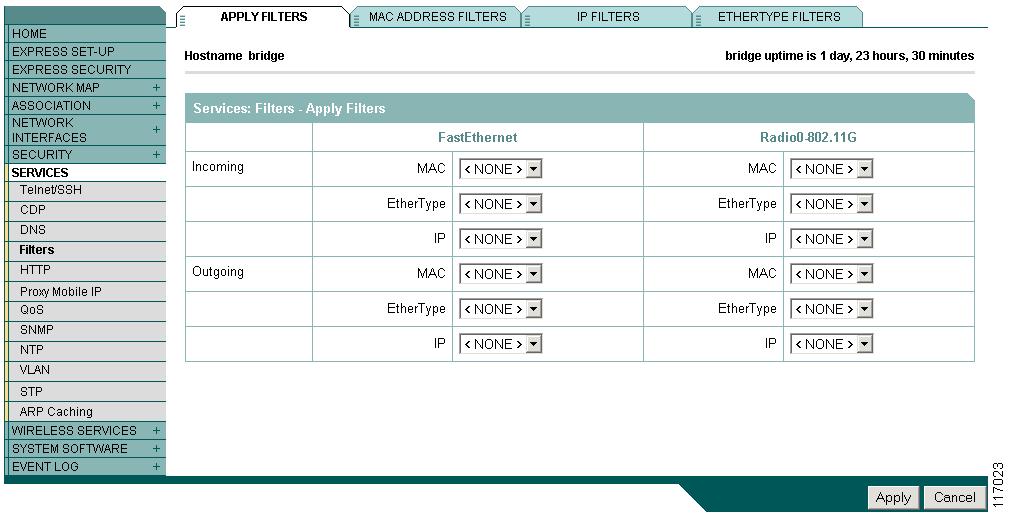
Click the Apply Filters tab to return to the Apply Filters page. Figure 15-2 shows the Apply Filters page.
Figure 15-2 Apply Filters Page
Step 12
Select the filter number from one of the MAC drop-down menus. You can apply the filter to either or both the Ethernet and radio ports, and to either or both incoming and outgoing packets.
Step 13
Click Apply. The filter is enabled on the selected ports.
If clients are not filtered immediately, click Reload on the System Configuration page to restart the access point/bridge. To reach the System Configuration page, click System Software on the task menu and then click System Configuration.
Using MAC Address ACLs to Block or Allow Client Association to the Access Point
You can use MAC address ACLs to block or allow association to the access point. Instead of filtering traffic across an interface, you use the ACL to filter associations to the access point radio.
Follow these steps to use an ACL to filter associations to the access point radio:
Step 1
Follow Steps 1 through 10 in the "Creating a MAC Address Filter" section to create an ACL. For MAC addresses that you want to allow to associate, select Forward from the Action menu. Select Block for addresses that you want to prevent from associating. Select Block All from the Default Action menu.
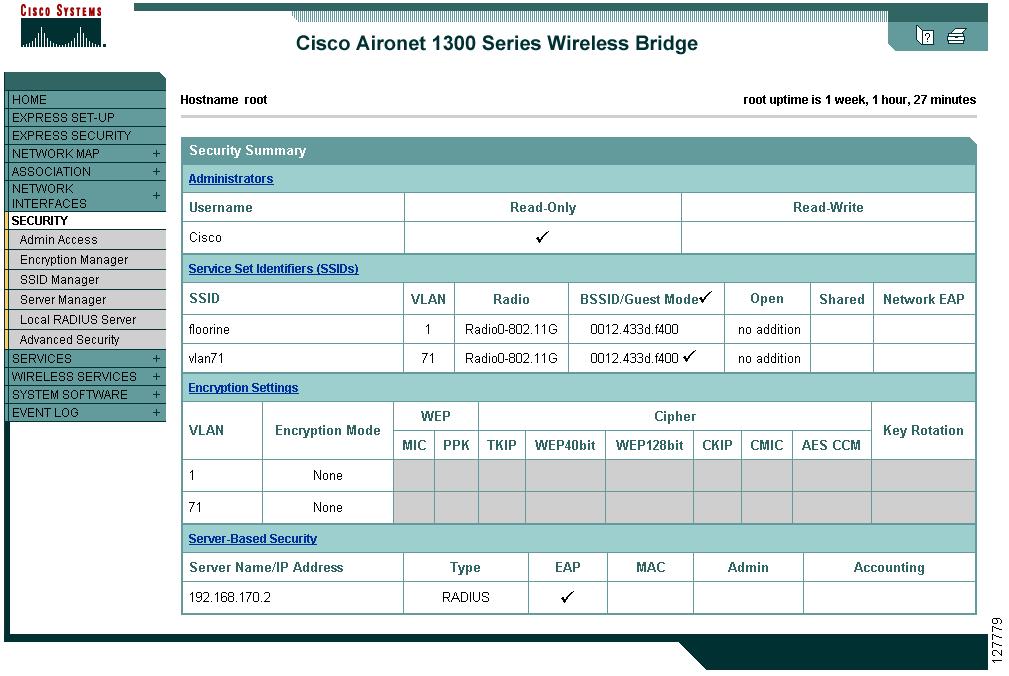
Step 2
Click Security to browse to the Security Summary page. Figure 15-3 shows the Security Summary page.
Figure 15-3 Security Summary Page
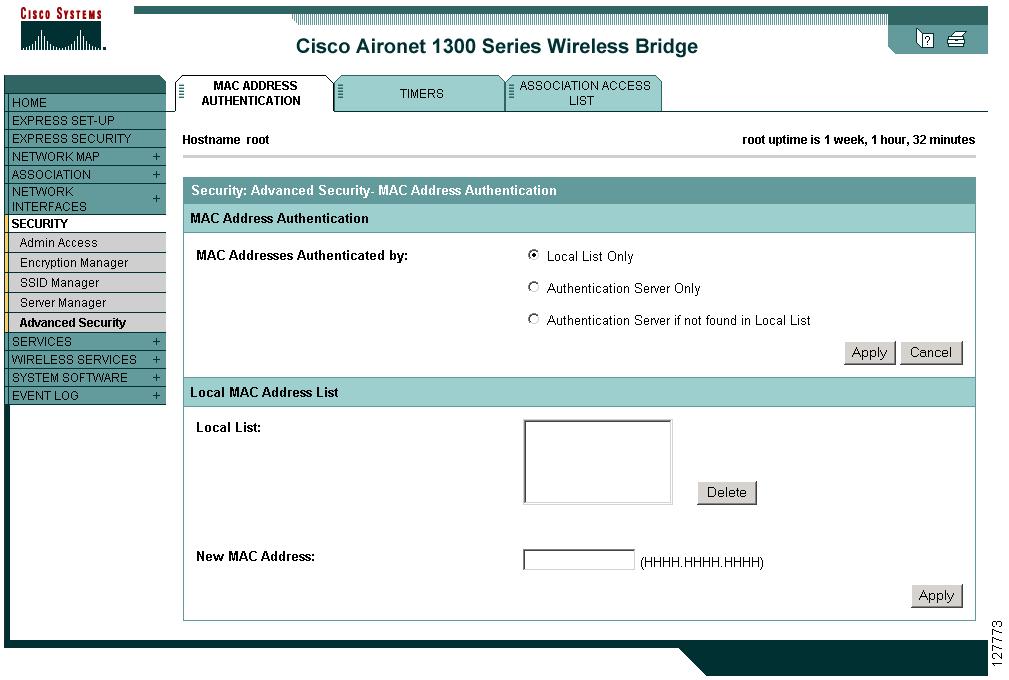
Step 3
Click Advanced Security to browse to the Advanced Security: MAC Address Authentication page. Figure 15-4 shows the MAC Address Authentication page.
Figure 15-4 Advanced Security: MAC Address Authentication Page
Step 4
Click the Association Access List to tab to browse to the Association Access List page. Figure 15-5 shows the Association Access List page.
Figure 15-5 Association List Page
Step 5
Select your MAC address ACL from the drop down menu.
Step 6
Click Apply.
This example shows the CLI commands that are equivalent to the steps listed in the "Using MAC Address ACLs to Block or Allow Client Association to the Access Point" section:
ap# configure terminalap(config)# dot11 association access-list 777ap(config)# endIn this example, only client devices with MAC addresses listed in access list 777 are allowed to associate to the access point. The access point blocks associations from all other MAC addresses.
For complete descriptions of the commands used in this example, consult the Cisco IOS Command Reference for Cisco Aironet Access Points and Bridges.
Configuring and Enabling IP Filters
IP filters (IP address, IP protocol, and IP port) prevent or allow the use of specific protocols through the access point/bridge's Ethernet and radio ports, and IP address filters allow or prevent the forwarding of unicast and multicast packets either sent from or addressed to specific IP addresses. You can create a filter that passes traffic to all addresses except those you specify, or you can create a filter that blocks traffic to all addresses except those you specify. You can create filters that contain elements of one, two, or all three IP filtering methods. You can apply the filters you create to either or both the Ethernet and radio ports and to either or both incoming and outgoing packets.
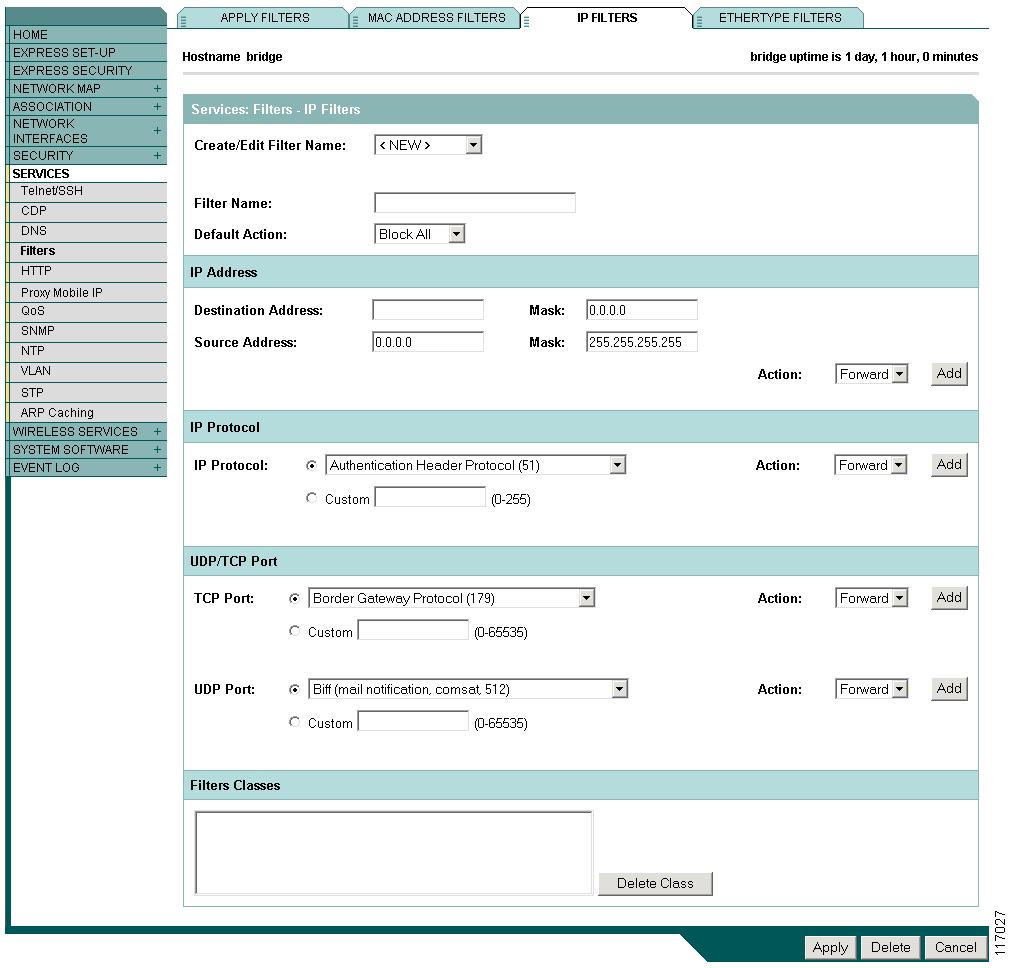
Use the IP Filters page to create IP filters for the access point/bridge. Figure 15-6 shows the IP Filters page.
Figure 15-6 IP Filters Page
Follow this link path to reach the IP Filters page:
1.
Click Services in the page navigation bar.
2.
In the Services page list, click Filters.
3.
On the Apply Filters page, click the IP Filters tab at the top of the page.
Creating an IP Filter
Follow these steps to create an IP filter:
Step 1
Follow the link path to the IP Filters page.
Step 2
If you are creating a new filter, make sure <NEW> (the default) is selected in the Create/Edit Filter Index menu. To edit an existing filter, select the filter name from the Create/Edit Filter Index menu.
Step 3
Enter a descriptive name for the new filter in the Filter Name field.
Step 4
Select Forward all or Block all as the filter's default action from the Default Action menu. The filter's default action must be the opposite of the action for at least one of the addresses in the filter. For example, if you create a filter containing an IP address, an IP protocol, and an IP port and you select Block as the action for all of them, you must choose Forward All as the filter's default action.
Step 5
To filter an IP address, enter an address in the IP Address field.
Note
If you plan to block traffic to all IP addresses except those you specify as allowed, put the address of your own PC in the list of allowed addresses to avoid losing connectivity to the access point/bridge.
Step 6
Type the mask for the IP address in the Mask field. Enter the mask with periods separating the groups of characters (112.334.556.778, for example). If you enter 255.255.255.255 as the mask, the access point/bridge accepts any IP address. If you enter 0.0.0.0, the access point/bridge looks for an exact match with the IP address you entered in the IP Address field. The mask you enter in this field behaves the same way that a mask behaves when you enter it in the CLI.
Step 7
Select Forward or Block from the Action menu.
Step 8
Click Add. The address appears in the Filters Classes field. To remove the address from the Filters Classes list, select it and click Delete Class. Repeat Step 5 through Step 8 to add addresses to the filter.
If you do not need to add IP protocol or IP port elements to the filter, skip to Step 15 to save the filter on the access point/bridge.
Step 9
To filter an IP protocol, select one of the common protocols from the IP Protocol drop-down menu, or select the Custom radio button and enter the number of an existing ACL in the Custom field. Enter an ACL number from 0 to 255. See "Protocol Filters," for a list of IP protocols and their numeric designators.
Step 10
Select Forward or Block from the Action menu.
Step 11
Click Add. The protocol appears in the Filters Classes field. To remove the protocol from the Filters Classes list, select it and click Delete Class. Repeat Step 9 to Step 11 to add protocols to the filter.
If you do not need to add IP port elements to the filter, skip to Step 15 to save the filter on the access point/bridge.
Step 12
To filter a TCP or UDP port protocol, select one of the common port protocols from the TCP Port or UDP Port drop-down menus, or select the Custom radio button and enter the number of an existing protocol in one of the Custom fields. Enter a protocol number from 0 to 65535. See "Protocol Filters," for a list of IP port protocols and their numeric designators.
Step 13
Select Forward or Block from the Action menu.
Step 14
Click Add. The protocol appears in the Filters Classes field. To remove the protocol from the Filters Classes list, select it and click Delete Class. Repeat Step 12 to Step 14 to add protocols to the filter.
Step 15
When the filter is complete, click Apply. The filter is saved on the access point/bridge, but it is not enabled until you apply it on the Apply Filters page.
Step 16
Click the Apply Filters tab to return to the Apply Filters page. Figure 15-7 shows the Apply Filters page.
Figure 15-7 Apply Filters Page
Step 17
Select the filter name from one of the IP drop-down menus. You can apply the filter to either or both the Ethernet and radio ports, and to either or both incoming and outgoing packets.
Step 18
Click Apply. The filter is enabled on the selected ports.
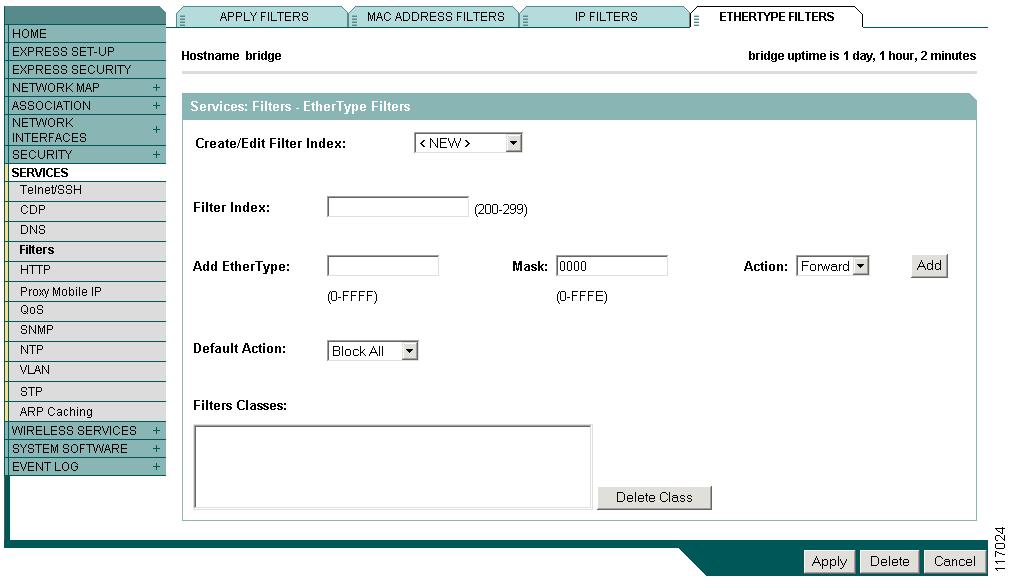
Configuring and Enabling Ethertype Filters
Ethertype filters prevent or allow the use of specific protocols through the access point/bridge's Ethernet and radio ports. You can apply the filters you create to either or both the Ethernet and radio ports and to either or both incoming and outgoing packets.
Use the Ethertype Filters page to create Ethertype filters for the access point/bridge. Figure 15-8 shows the Ethertype Filters page.
Figure 15-8 Ethertype Filters Page
Follow this link path to reach the Ethertype Filters page:
1.
Click Services in the page navigation bar.
2.
In the Services page list, click Filters.
3.
On the Apply Filters page, click the Ethertype Filters tab at the top of the page.
Creating an Ethertype Filter
Follow these steps to create an Ethertype filter:
Step 1
Follow the link path to the Ethertype Filters page.
Step 2
If you are creating a new filter, make sure <NEW> (the default) is selected in the Create/Edit Filter Index menu. To edit an existing filter, select the filter number from the Create/Edit Filter Index menu.
Step 3
In the Filter Index field, name the filter with a number from 200 to 299. The number you assign creates an access control list (ACL) for the filter.
Step 4
Enter an Ethertype number in the Add Ethertype field. See "Protocol Filters," for a list of protocols and their numeric designators.
Step 5
Enter the mask for the Ethertype in the Mask field.
Step 6
Select Forward or Block from the Action menu.
Step 7
Click Add. The Ethertype appears in the Filters Classes field. To remove the Ethertype from the Filters Classes list, select it and click Delete Class. Repeat Step 4 through Step 7 to add Ethertypes to the filter.
Step 8
Select Forward All or Block All from the Default Action menu. The filter's default action must be the opposite of the action for at least one of the Ethertypes in the filter. For example, if you enter several Ethertypes and you select Block as the action for all of them, you must choose Forward All as the filter's default action.
Step 9
Click Apply. The filter is saved on the access point/bridge, but it is not enabled until you apply it on the Apply Filters page.
Step 10
Click the Apply Filters tab to return to the Apply Filters page. Figure 15-9 shows the Apply Filters page.
Figure 15-9 Apply Filters Page
Step 11
Select the filter number from one of the Ethertype drop-down menus. You can apply the filter to either or both the Ethernet and radio ports, and to either or both incoming and outgoing packets.
Step 12
Click Apply. The filter is enabled on the selected ports.

 Feedback
Feedback