-
Administration Guide for Cisco Virtualization Experience Client Manager 4.9
-
Preface
-
Getting Started
-
Device Manager
-
Package Manager
-
Cisco VXC Firmware and Configuration Upgrade Procedures
-
Update Manager
-
Report Manager
-
Configuration Manager
-
Appendix A: Working with Groups and Views
-
Appendix B: About Cisco VXC Manager Security
-
Appendix C: Upgrading Cisco VXC Manager Agents
-
Appendix D: Device Discovery, Device Imaging, and Mass Imaging Tool
-
Appendix E: Troubleshooting
-
Appendix F: Licensing and Sales Keys
-
Appendix G: Additional Package Manager Procedures
-
Appendix H: Cisco VXC Manager ScriptBuilder Tool and Scripting Language
-
Appendix I: Autogenic Imaging
-
Table Of Contents
About Cisco VXC Manager Security
Importing Certificates on Devices
Using Secure Communication (HTTPS)
HTTPS Communication Initiated by Cisco VXC Manager Agent
HTTPS Communication Initiated by the Cisco VXC Manager Administrator Console
Enabling Cisco VXC Manager Device Security
Changing the Cisco VXC Manager Security Certificate
About Cisco VXC Manager Security
This appendix contains advanced information about Cisco VXC Manager security.
Note
For detailed information about setting up Cisco VXC Manager for HTTPS communications, see Installation Guide for Cisco Virtualization Experience Client Manager.
Cisco VXC Manager allows you to set a Device Manager preference that prevents unauthorized Cisco VXC Manager installations from managing your devices. When the Enable Device Security option is set, the Cisco VXC Manager Agent (HAgent) and the Cisco VXC Manager Web Service enter into a one-to-one relationship. In this relationship, both the device and the Web Service share a unique security certificate in common. Before processing any Cisco VXC Manager requests, the Cisco VXC Manager Agent on the device verifies the certificate. If the Web Service certificate matches its own, the Cisco VXC Manager Agent allows the device to perform the requested functions or instructions. If the certificates do not match, the Cisco VXC Manager Agent prevents the device from complying with any of the requests.
Note
Cisco ThreadX devices do not support device security.
CautionWhen Enabling Device Security: If you decide to enable device security, be sure to write down your certificate number and keep it in a safe place. If your Cisco VXC Manager installation becomes corrupt for any reason, and you must reinstall Cisco VXC Manager, you will get a new certificate number. Without the original certificate number, however, you will not be able to manage your devices. Cisco VXC Manager gives you the option of either changing a security certificate to a new one, or restoring an older certificate.
When Disabling Device Security: If you decide to disable device security, existing devices will not release their security certificate until their next check-in. They cannot be refreshed or rediscovered because the server no longer presents a certificate. They must check-in on their interval (that is, pull not push).
To enable Cisco VXC Manager Security, perform the following procedures:
•
Importing Certificates on Devices
•
Using Secure Communication (HTTPS)
•
Enabling Cisco VXC Manager Device Security
•
Changing the Cisco VXC Manager Security Certificate
Importing Certificates on Devices
Before starting secure communication between the components of Cisco VXC Manager, import the certificate to the devices. There are two ways to import certificates. One is to create and deploy a package containing the certificate. The other is to create a DDC containing the certificate, and allow the DDC to automatically deploy the certificate to all devices. The import procedure depends upon the device OS.
Tip
Certificate Authentication: After deploying the certificate package to the devices, you need to authenticate the certificate with the server. The criteria for authentication of the certificate between the server and clients are based on the Certificate Issuing Authority, certificate creation date and name of the certificate. Upon successful certificate authentication, the server and the clients begin secure communication with one another.
WTOS
To import the certificate on devices running WTOS, you need to register two packages (like any other package you register in Cisco VXC Manager). One package is for adding the certificate and the other package is for removing the certificate from the devices. When you want to add or delete a certificate, you need to change the wnos.ini file and register two separate packages.
The folder structure for the certificate package is VXC-M Package\CADeployment and the folder named CADeployment contains one folder named wnos. The folder named wnos contains a folder named cacerts and a file named wnos.ini. The folder named cacerts contains the actual certificate file.
A sample wnos.ini for adding the certificate is shown below:
# Bypass the user log in to the local device
signon=0
# Set the Privilege to high
Privilege=high
# Command to Import the certificate to WTOS devices
AddCertificate= CA certificate file nameA sample wnos.ini to delete a certificate is shown below:
# Bypass the user log in to the local device
signon=0
# Set the Privilege to high
Privilege=high
# Command to delete the certificate in WTOS devices
DelCertificate= CA certificate file nameA sample rsp file for adding the certificate to WTOS devices is shown below:
[Version]
Number=CADeployment
Description=CA Certificate Deployment
OS=BL
Category=Images
ImageSize=
[Script]SUSE Linux
A sample wlx.ini configuration for adding a SUSE Linux certificate is shown below:
ImportCerts=yes
Certs=rootca_new.cer;vxcm_new.cerA sample rsp file for adding the certificate to SUSE Linux devices is shown below:
[Version]
Number=Certs_Package
OS=SLX
Category=Other Packages
[Script]
RP= "<regroot>"Using Secure Communication (HTTPS)
Cisco VXC Manager supports secure HTTPS communication between components of Cisco VXC Manager.
The secure communication can be initiated in two ways:
•
HTTPS Communication Initiated by Cisco VXC Manager Agent
•
HTTPS Communication Initiated by the Cisco VXC Manager Administrator Console
HTTPS Communication Initiated by Cisco VXC Manager Agent
The Cisco VXC Manager Agent can initiate communication with the HServer during client device startup. When the Cisco VXC Manager Agent on a client boots up, it requests the following information from the DHCP server or proxy server:
•
Server IP address
•
HTTPS port number used for communication
If the Cisco VXC Manager Agent can retrieve the HTTPS port number from the DHCP option tags, it uses the IP address and port number to communicate with the HServer via HTTPS.
If the Cisco VXC Manager Agent cannot retrieve the HTTPS Port number from the DHCP option tags, it follows the sequence below:
1.
The Cisco VXC Manager Agent tries to communicate via HTTPS using ports 443 and 8443.
2.
If the Cisco VXC Manager Agent cannot communicate via HTTPS, it tries to connect via HTTP using ports 80 and 280.
3.
If the Cisco VXC Manager Agent successfully initiates communication with the HServer, it caches the communication mechanism, IP address, and port number used and uses that information for any subsequent requests.
4.
If HTTPS communication fails during startup, the Cisco VXC Manager Agent will not try the HTTPS protocol again.
HTTPS Communication Initiated by the Cisco VXC Manager Administrator Console
You can configure your network to allow the Administrator Console to determine the port number and protocol to use for communication with the HServer.
Determining the Port Number
To allow the Administrator Console to determine the port number for communication:
Procedure
Step 1
Configure the IIS that hosts the HServer with the desired port number.
Step 2
Stop the IIS and WWW service.
Step 3
Start the HServerInit service.
When the Administrator Console starts, it queries the database to retrieve the port number and IP address to use for communication with the HServer.
Determining the Protocol
To allow the Administrator Console to determine the protocol for communication:
Procedure
Step 1
Bind the IIS that hosts the HServer with a TCP, SSL, or TCP and SSL port.
Tip
For an SSL port, you must install a certificate.
Step 2
Stop the IIS and WWW service.
Step 3
Start the HServerInit Service.
The port number and IP address are stored in the Cisco VXC Manager Database.
If the request came via SSL, the entire Cisco VXC Manager configuration is set to secure.
No configuration is required in the Administrator Console, but the Secure Communications check box will appear in the Serv/Port Settings Preferences dialog box for information purposes.
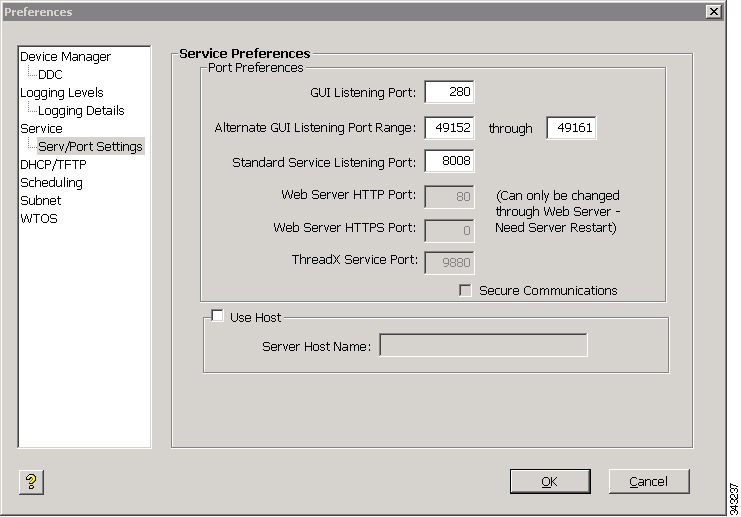
Figure B-1 Serv/Port Settings Preferences
If an SSL port is configured on IIS, the Secure Communications check box is checked; otherwise it is unchecked.
Before starting secure communication, make sure all the following settings are configured:
•
GUI Listening Port is 280.
•
Alternate GUI Listening Port Range is 49152 through 49161.
•
Standard Service Listening Port is 8008.
•
Web Server HTTP Port is 80.
•
Web Server HTTPS Port is 443.
•
Secure Communications is checked.
•
Check the Use Host check box to have the Cisco VXC Manager Agent use the Server Host Name you enter to connect to the server. Note that the Server Host Name will have a default value of the host machine and an administrator can change this value to a different host name (useful in cases of request forwarding through an HTTP Proxy).
Tip
The secure communications flag applies to both remote and master repositories.
Enabling Cisco VXC Manager Device Security
Cisco VXC Manager allows you to set a Device Manager preference that prevents unauthorized Cisco VXC Manager installations from managing your devices.
To enable device security:
Procedure
Step 1
In the tree pane of the Administrator Console, expand the Configuration Manager and choose Preferences to view the details pane displaying the categories for the Cisco VXC Manager Preferences.
Step 2
Double-click Device Manager Preferences to open the Device Manager Preferences dialog box.
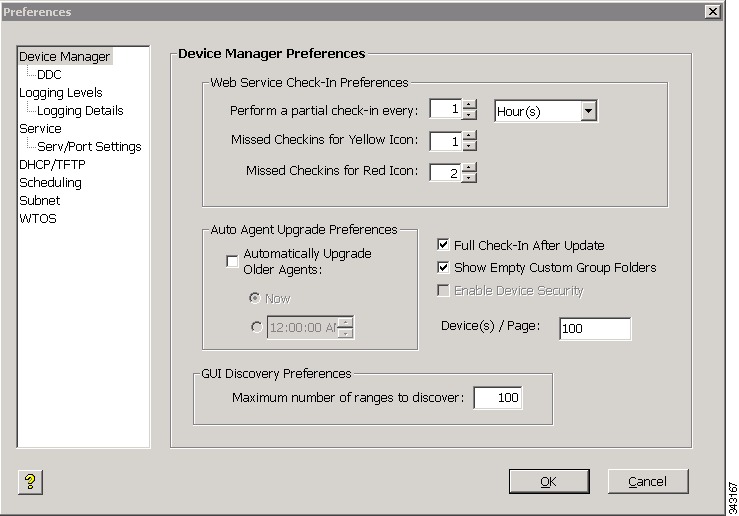
Figure B-2 Device Manager Preferences
Step 3
Check the Enable Device Security check box, click OK, and then click Yes to confirm.
From this point forward, if a device does not already possess a security certificate, then the next time the device is discovered or checks-in, Cisco VXC Manager will establish the one-to-one relationship between the Cisco VXC Manager Agent of the device and the Cisco VXC Manager installation. This relationship prevents unauthorized Cisco VXC Manager installations from managing the devices.
Tip
When you enforce device security, Cisco VXC Manager automatically encrypts all communications between the Web Service and the Cisco VXC Manager Agents. However, encryption can be turned on independently of device security (see Service Preferences).
Changing the Cisco VXC Manager Security Certificate
Before you change the Cisco VXC Manager security certificate, ensure that you have disabled device security. After changing the certificate number, you can re-enable device security (see Enabling Cisco VXC Manager Device Security).
Use this procedure to change the Cisco VXC Manager certificate number (you can change the certificate to a new number or restore an older certificate).
To change the Cisco VXC Manager Security Certificate:
Procedure
Step 1
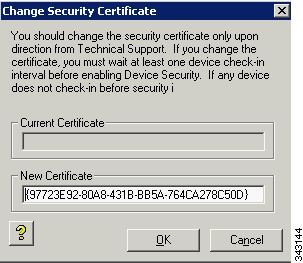
Expand the Configuration Manager, right-click the Licensing node, and choose New > Certificate to open the Change Security Certificate dialog box (note that Cisco VXC Manager creates a new certificate number in the New Certificate box).
Figure B-3 Change Security Certificate
Tip
If you have not disabled device security, you will see a warning message.
Step 2
Depending on whether or not you want to accept the new certificate, complete one of the following:
•
If yes, click OK. You are done with this procedure.
•
If no, enter the security certificate to restore (presumably, your devices share this certificate from a previous Cisco VXC Manager installation; by restoring the security certificate, you will regain control of the devices), and then click OK.
CautionBefore changing the security certificate, wait for a period of one check-in interval to allow all devices to check-in and release the current certificate. If a device that uses the current certificate does not check-in within this time, and you enable security for the new certificate, the device that did not check-in will be unmanageable (as it still has the old certificate).

 Feedback
Feedback