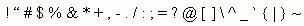-
Cisco Content Security and Control SSM Administrator Guide, 6.1
-
Preface
-
Introducing the Content Security and Control SSM
-
Verifying Initial Setup
-
Configuring Mail Traffic (SMTP and POP3)
-
Configuring Web (HTTP) and File Transfer (FTP) Traffic
-
Managing Updates and Log Queries
-
Administering Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM
-
Monitoring Content Security
-
Troubleshooting Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM
-
Reimaging and Configuring the CSC SSM Using the Command Line
-
Using CSC SSM with Trend Micro Control Manager
-
Glossary
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Troubleshooting Trend Micro InterScan
for Cisco CSC SSMWhat To Do If Installation Fails
Troubleshooting Basic Functions
Summary Status and Log Entries Out of Synch
Access to Some Websites Is Slow or Inaccessible
Reimaging or Recovery of CSC Module
Troubleshooting Scanning Functions
Cannot Update the Pattern File
Cannot Create a Spam Stamp Identifier
Unacceptable Number of Spam False Positives
Cannot Accept Any Spam False Positives
Virus Is Detected but Cannot Be Cleaned
Scanning Not Working Because of Incorrect ASA Firewall Policy Configuration
Scanning Not Working Because the CSC SSM Is in a Failed State
Status LED Flashing for Over a Minute
SSM Cannot Communicate with ASDM
Logging in Without Going Through ASDM
CSC SSM Throughput is Significantly Less Than ASA
Using the Security Information Center
Understanding the CSC SSM Syslogs
SSM Application Mismatch [1-105048]
Traffic Dropped Because of CSC Card Failure [3-421001]
Skip Non-applicable Traffic [6-421002]
Drop ASDP Packet with Invalid Encapsulation[3-421003]
Failed to Inject Packet [7-421004]
Account Host Toward License Limit [6-421005]
Traffic Dropped Because of CSC Card Failure [6-421007]
New Application Detected [5-505011]
Application Stopped [5-505012]
Application Version Changes [5-505013]
Data Channel Communication Failure [3-323006]
Data Channel Communication OK [5-505010]
Spyware/Grayware detection event
Resource availability of the CSC SSM falls below the desired level
Resource availability of the CSC SSM has been restored
CSC has actively disconnected a connection
Connection capacity has been reached
Connection capacity has been restored
Failover service encountered an internal error
Failover service communication failed
Failover service email could not be sent
Service module informational report
Service module show module 1 details
Time synchronization with the ASA chassis failed
Service module cannot create FIFO
Service module internal communication error
Service module encountered a problem when communicating with the ASA chassis
Troubleshooting Trend Micro InterScan
for Cisco CSC SSM
This chapter is provided to help you troubleshoot potential issues before contacting Cisco TAC for assistance, and includes the following sections:
•
What To Do If Installation Fails
•
Troubleshooting Basic Functions
–
Summary Status and Log Entries Out of Synch
–
Access to Some Websites Is Slow or Inaccessible
•
Reimaging or Recovery of CSC Module
–
Cannot Update the Pattern File
–
Cannot Create a Spam Stamp Identifier
–
Unacceptable Number of Spam False Positives
–
Cannot Accept Any Spam False Positives
–
Virus Is Detected but Cannot Be Cleaned
–
Status LED Flashing for Over a Minute
–
SSM Cannot Communicate with ASDM
–
Logging in Without Going Through ASDM
–
CSC SSM Throughput is Significantly Less Than ASA
•
Understanding the CSC SSM Syslogs
–
SSM Application Mismatch [1-105048]
–
Traffic Dropped Because of CSC Card Failure [3-421001]
–
Skip Non-applicable Traffic [6-421002]
–
Drop ASDP Packet with Invalid Encapsulation[3-421003]
–
Failed to Inject Packet [7-421004]
–
Account Host Toward License Limit [6-421005]
–
Traffic Dropped Because of CSC Card Failure [6-421007]
–
New Application Detected [5-505011]
–
Application Stopped [5-505012]
–
Application Version Changes [5-505013]
–
Data Channel Communication Failure [3-323006]
–
Data Channel Communication OK [5-505010]
•
Using the Security Information Center
•
Understanding the CSC SSM Syslogs
Troubleshooting Installation
The following describes a successful command-line version of the installation. If trouble arises during the installation, see the "What To Do If Installation Fails" section.
To install the CSC SSM via the command-line interface, perform the following steps.
Step 1
From the command-line prompt, type the following to begin the installation:
hostname# hw-module module 1 recover configureThe output appears similar to the following:
Image URL [tftp://171.69.1.129/dqu/sg-6.0-1345-tftp.img]:Port IP Address [30.0.0.3]:VLAN ID [0]:Gateway IP Address [30.0.0.254]:hostname# hw-module module 1 recover bootThe module in slot 1 will be recovered. This mayerase all configuration and all data on that device andattempt to download a new image for it.Recover module in slot 1? [confirm]Recover issued for module in slot 1hostname#hostname# debug module-bootdebug module-boot enabled at level 1Step 2
After about a minute, the CSC-SSM drops into ROMMON, and prints messages similar to the following:
hostname# Slot-1 206> Cisco Systems ROMMON Version (1.0(10)0) #0: Sat Mar 26 00:13:50 PST 2005Slot-1 207> morlee@bowmore:/pixab/biosbuild/1.0.10.0/boot/rommonSlot-1 208> Platform ASA-SSM-AIP-10-K9Slot-1 209> GigabitEthernet0/0Slot-1 210> Link is UPSlot-1 211> MAC Address: 000b.fcf8.01b3Slot-1 212> ROMMON Variable Settings:Slot-1 213> ADDRESS=30.0.0.3Slot-1 214> SERVER=171.69.1.129Slot-1 215> GATEWAY=30.0.0.254Slot-1 216> PORT=GigabitEthernet0/0Slot-1 217> VLAN=untaggedSlot-1 218> IMAGE=dqu/sg-6.0-1345-tftp.imgSlot-1 219> CONFIG=Slot-1 220> LINKTIMEOUT=20Slot-1 221> PKTTIMEOUT=2Slot-1 222> RETRY=20Slot-1 223> tftp dqu/sg-6.0-1345-tftp.img@171.69.1.129 via 30.0.0.254Step 3
The SSM attempts to connect to the TFTP server to download the image. After several seconds, output similar to the following appears:
Slot-1 224> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 225> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 226> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 227> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 228> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!. . . [ output omitted ]. . .Slot-1 400> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 401> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 402> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 403> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 404> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 405> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Slot-1 406> Received 59501255 bytesStep 4
The TFTP download is complete. Note the number of received bytes, which should be the same size as your CSC SSM image. ROMMON then launches the image.
Slot-1 407> Launching TFTP Image...Step 5
The image is being unpacked and installed. After several minutes, CSC SSM reboots. Messages similar to the follow appear.
Slot-1 408> Cisco Systems ROMMON Version (1.0(10)0) #0: Sat Mar 26 00:13:50 PST 2005Slot-1 409> morlee@bowmore:/pixab/biosbuild/1.0.10.0/boot/rommonSlot-1 410> Platform ASA-SSM-AIP-10-K9Slot-1 411> Launching BootLoader...Step 6
After a minute or two, the CSC SSM boots up. Verify that the system has booted as follows:
hostname# show module 1Output similar to the following appears:
Mod Card Type Model Serial No.--- -------------------------------------------- ------------------ -----------1 ASA 5520/5530 AIP Security Service Module-10 ASA-SSM-AIP-10-K9 P00000000TTMod MAC Address Range Hw Version Fw Version Sw Version--- --------------------------------- ------------ ------------ ---------------1 000b.fcf8.01b3 to 000b.fcf8.01b3 1.0 1.0(10)0 CSC SSM 6.0 (Build#1345)Mod SSM Application Name Status SSM Application Version--- ------------------------------ ---------------- --------------------------1 CSC SSM Down 6.0 (Build#1345)Mod Status Data Plane Status Compatibility--- ------------------ --------------------- -------------1 Up UpLook for the two instances of "Up" in the Mod Status table (the last line of the output). The "Down" in the Status field of the SSM Application Name table indicates that the card is not yet activated.
What To Do If Installation Fails
Table 8-1 describes what to do if installation failure occurs during the steps described in the "Troubleshooting Installation" section.
Troubleshooting Activation
Before taking any other action, make sure that the clock is set correctly on ASA. See Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide for more information, as well as the ASDM online help.
Next, use the show module, show module 1, and show module 1 details commands to verify that the CSC SSM has been activated successfully. If you cannot resolve the problem using the output from these commands, contact Cisco TAC.
Troubleshooting Basic Functions
The following sections describe issues you may encounter with basic functions, such as logging on or password recovery:
•
Summary Status and Log Entries Out of Synch
•
Access to Some Websites Is Slow or Inaccessible
Cannot Log On
You specified an administrator password when you installed Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM with the setup wizard. You must use the password you created during installation to log in. This is not the same password that you use to access ASDM. Passwords are case-sensitive, so be sure you have entered the characters correctly.
If you forget your password, it can be recovered. See Recovering a Lost Password for more information.
Recovering a Lost Password
There are three passwords used to manage the ASDM/CSC SSM. They are:
•
The ASDM/Web interface password
•
The CLI password
•
The root account password
The default entry for all three passwords is "cisco."
The following describes how to recover your passwords in case you lose one or more of them:
•
If you have the ASDM/Web interface password, but have lost the cisco and root account passwords, you can continue to manage the CSC SSM via the Web interface. However, there is no way to use the command-line interface or root account if you should need to at some time in the future. To recover these two passwords, re-image the CSC SSM and restore your configuration using the steps described below.
•
If you have only the CLI password, you can log in to the CSC SSM and navigate to the "Restore Factory Defaults" option to reset the SSM, which has the same effect as re-imaging the device. Then import your saved configuration. See Restore Factory Defaults, page A-10 for more information about the Restore Factory Defaults option.
•
If you have only the root account password, log in and use the password command to set the CLI password. Then proceed as described in the previous paragraph.
CautionOnly access the root account under the supervision of Cisco TAC. Unauthorized modifications made through the root account are not supported and will require the device to be reimaged to guarantee proper operation.
•
If you have lost all three passwords you must re-image the device and restore your configuration as described below.
To re-image the CSC SSM and recover your configuration, follow these steps:
Step 1
Re-image the CSC SSM, which restores the factory default settings. Re-imaging transfers a factory default software image to the SSM. Transferring an image is described in the "Reimaging and Configuring the CSC SSM Using the Command Line" section on page A-1.
Step 2
After re-imaging, all passwords are restored to their default value. You can now log in using the default password "cisco" and create a new ASDM/Web interface password.
Step 3
Use the new ASDM/Web interface password to access the CSC SSM interface. Go to Administration > Configuration Backup.
Step 4
Import the most recent configuration backup to restore your configuration settings.
Step 5
Using the default password "cisco," access the command-line interface and the root account to update the default CLI and root account passwords as well.
Summary Status and Log Entries Out of Synch
You may occasionally notice that the counters displayed on the Mail (SMTP), Mail (POP3), Web (HTTP), and File Transfer (FTP) tabs of the Summary window do not synchronize to the statistics displayed in the log reports. (In the CSC SSM console, the logs are accessed by choosing Logs > Query.) This "mismatch" happens because:
•
The logs are reset by a reboot that occurs either because of a device error or a reboot following installation of a patch.
•
Logs may be purged because of limited memory storage on the SSM.
Delay in HTTP Connection
A delay of approximately 30 seconds can occur if you have URL filtering enabled on the CSC SSM, but the CSC SSM does not have access to the Internet via HTTP. Trend Micro maintains an online database that stores URLs in different categories. CSC SSM attempts to access the URL database when intercepting an HTTP request from a client. If you cannot grant Internet access to CSC SSM (either direct, or indirect via a proxy), disable URL filtering.
Access to Some Websites Is Slow or Inaccessible
There are some websites, such as banks, online shopping sites, or other special purpose servers that require extra backend processing before responding to a client request. The CSC SSM has a hard-coded 90 second timeout between the client request and the server response to prevent transactions from tying up resources on the CSC SSM for too long. This means that transactions that take a longer time to process fail.
The workaround is to exclude the site from scanning. To do so from the command-line interface, for example, for a site on the outside network with the IP address 192.168.10.10:
! exempt http traffic to 192.168.10.10access-list 101 deny tcp any host 192.168.10.10 eq http! catch everything elseaccess-list 101 permit tcp any eq httpclass-map my_csc_classmatch access-list 101policy-map my_csc_policyclass my_csc_classcsc fail-closeservice-policy my_csc_policy interface insideThe above configuration exempts HTTP traffic to 192.168.10.10 from being scanned by the CSC SSM.
Performing a Packet Capture
If there are sites you can access without going through CSC SSM, but cannot access when traffic is being scanned, report the URL to Cisco TAC. If possible, do a packet capture and send the information to Cisco TAC as well. For example, assuming the client has IP address 1.1.1.1, and the outside website has IP address 2.2.2.2:
access-list cap_acl permit tcp host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2access-list cap_acl permit tcp host 2.2.2.2 host 1.1.1.1capture cap access-list cap_acl interface insidecapture cap access-list cap_acl interface outsideFTP Download Does Not Work
If your FTP login works, but you cannot download via FTP, verify whether the inspect ftp setting is enabled on the ASA. See the Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide for more information.
Reimaging or Recovery of CSC Module
During reimaging or recovery of a CSC module, it is possible to type the address of the TFTP server or the file name incorrectly. If this occurs, the CSC module will continuously reboot, attempting the reimaging using the invalid configuration information provided. To stop the reimaging process and correct the configuration, enter the hw module 1 recover stop command in the specified configuration mode.
Troubleshooting Scanning Functions
The following sections describe issues you may encounter with scanning for viruses and/or spam.
•
Cannot Update the Pattern File
•
Cannot Create a Spam Stamp Identifier
•
Unacceptable Number of Spam False Positives
•
Cannot Accept Any Spam False Positives
•
Virus Is Detected but Cannot Be Cleaned
Cannot Update the Pattern File
If the pattern file is out of date, and you are unable to update it, the most likely cause is that your Maintenance Agreement has expired. Check the Expiration Date field on the Administration > Product License window. If the date shown is in the past, you cannot update the pattern file until you renew your Maintenance Agreement.
Another possible cause is that the Trend Micro ActiveUpdate server is temporarily down. Try to update again in a few minutes.
Spam Not Being Detected
If the anti-spam feature does not seem to be working, be sure that:
•
You have the Plus License installed.
•
You have enabled the feature; the anti-spam option is not enabled by default (See Enabling SMTP & POP3 Spam Filtering, page 3-6 for more information)
•
You have configured the incoming mail domain (See Configuring SMTP Message Filter, Disclaimer, & Incoming Mail Domain, page 3-5 for more information)
Cannot Create a Spam Stamp Identifier
A spam stamp identifier is a message that appears in the email message subject. For example, for a message titled "Q3 Report," if the spam stamp identifier is defined as "Spam:," the message subject would appear as "Spam:Q3 Report."
If you are having problems creating a spam identifier, make sure you are using only English upper and lowercase characters, digits 0-9, or the set of special characters shown in Figure 8-1.
Figure 8-1 Special characters for spam stamp identifier
If you attempt to use characters other than those specified, you cannot use the spam identifier for your SMTP and POP3 messages.
Unacceptable Number of Spam False Positives
Your spam filtering threshold may be set at a level that is too aggressive for your organization. Assuming you adjusted the threshold to Medium or High, try a lower setting in the threshold fields on the Mail (SMTP) > Anti-spam > SMTP Incoming Anti-spam window and the Mail (POP3) > Anti-spam > POP3 Anti-spam windows. Also enable the anti-spam "stamp message" feature on the SMTP Incoming Anti-spam window and the POP3 Anti-spam windows. See the online help for these two windows for more information.
Also, if users in your network are receiving newsletters, this type of message tends to trigger a high number of false positives. Add the newsletter email address or domain name to the approved senders list to bypass spam filtering on these messages.
Cannot Accept Any Spam False Positives
Some organizations, such as banks and other financial institutions, cannot risk any message being identified as a false positive. In this case, disable the anti-spam feature for SMTP and POP3.
Unacceptable Amount of Spam
You may have set your spam filtering threshold at a level that is too lenient for your organization. Try a higher setting in the threshold fields on the Mail (SMTP) > Anti-spam > SMTP Incoming Anti-spam window and the Mail (POP3) > Anti-spam > POP3 Anti-spam window.
Virus Is Detected but Cannot Be Cleaned
Not all virus-infected files are cleanable. For example, a password-protected file cannot be scanned or cleaned.
If you think you are infected with a virus that does not respond to cleaning, go to the following URL:
http://subwiz.trendmicro.com/SubWiz/Default.asp
This link takes you to the Trend Micro Submission Wizard, which includes information on what to do, including how to submit your suspected virus to TrendLabs for evaluation.
Virus Scanning Not Working
Ensure that no one has disabled the virus scanning feature on the SMTP Incoming, SMTP Outgoing, POP3, HTTP, and FTP Scanning windows. If scanning is enabled but viruses are not being detected, contact customer support for assistance.
Also, test the virus scanning feature by following the directions described in the "Test the Antivirus Feature" section on page 2-3.
Scanning Not Working Because of Incorrect ASA Firewall Policy Configuration
Another possible cause is that a file has not been scanned due to incorrect ASA firewall policy configuration. Use the ASA show service-policy csc command in the CLI to configure the SSM to process traffic. For example:
show service-policy flow tcp host [clientIP] host [server IP] eq [proto]For example:
hostname(config)# show service-policy flow tcp host 192.168.10.10 host 10.69.1.129 eq httpGlobal policy:Service-policy: global_policyClass-map: trendMatch: access-lit trendAccess rule: permit tcp any any eq wwwAction:Output flow: csc fail-closeInput flow set connection timeout tcp 0:05:00Class-map: perclientMatch: access-lit perclientAccess rule: permit IP any anyAction:Input flow: set connection per-client-max 5 per-client-embryonic-max 2Scanning Not Working Because the CSC SSM Is in a Failed State
If the CSC SSM is in the process of rebooting, or has experienced a software failure, a syslog error 421007 is generated. In the CLI, enter the following command to view the status of the SSM card:
hostname# show module 1The output appears in several tables, as shown in the following example. The third table (SSM Application Name) displays a status. In this example, the status of the SSM is "Down."
Mod Card Type Model Serial No.--- -------------------------------------------- -----------------------------1 ASA 5500 Series Security Services Module-10 ASA-SSM-10 JAB092400TXMod MAC Address Range Hw Version Fw Version Sw Version--- --------------------------------- ------------ ---------------------------1 0013.c480.ae4c to 0013.c480.ae4c 1.0 1.0(10)0 CSC SSM 6.0 (Build#1345)Mod SSM Application Name Status SSM Application Version--- ------------------------------ ------------------------------------------1 CSC SSM Down 6.0 (Build#1345)Mod Status Data Plane Status Compatibility--- ------------------ --------------------- -------------1 Up UpThere are three possible states that could display in the Status field for the third table:
•
Down—A permanent error, such as an invalid activation code was used, licensing has expired, or a file has been corrupted
•
Reload—Scanning is restarting, for example during a pattern file update
•
Up—A normal operating state
To view the state for each individual process, issue the following command in the CLI:
hostname# show module 1 detailThe output appears similar to the following:
Getting details from the Service Module, please wait...ASA 5500 Series Security Services Module-10Model: ASA-SSM-10Hardware version: 1.0Serial Number: JAB092400TXFirmware version: 1.0(10)0Software version: CSC SSM 6.0 (Build#1345)MAC Address Range: 0013.c480.ae4c to 0013.c480.ae4cApp. name: CSC SSMApp. Status: DownApp. Status Desc: CSC SSM scan services are not availableApp. version: 6.0 (Build#1345)Data plane Status: UpStatus: UpHTTP Service: DownMail Service: DownFTP Service: DownActivated: NoMgmt IP addr: <not available>Mgmt web port: 8443Peer IP addr: <not enabled>The status for the CSC SSM is shown in the App. Status field. In the example, the status is "Down." The possible states for this field are:
•
Not Present—The SSM card is not found
•
Init—The SSM card is booting
•
Up—The SSM card is up and running
•
Unresponsive—The SSM card is not responding
•
Reload—The SSM card is reloading
•
Shutting Down—The SSM card is shutting down
•
Down—The SSM card is down and can be safely removed from its slot
•
Recover—The SSM card is being reimaged
Downloading Large Files
Handling of very large files may be a potential issue for the HTTP and FTP protocols. On the Target tabs of the HTTP Scanning and FTP Scanning windows, you configured large file handling fields, which included a deferred scanning option.
If you did not enable deferred scanning, InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM must receive and scan the entire file before passing the file contents to the requesting user. Depending on the file size, this could:
•
Result in the file being downloaded, but very slowly at first with more rapid speed as the download progresses
•
Take longer than the automatic browser timeout period, with the result being that the user is unable to receive the file contents at all (because the browser times out before the download completes)
If you enabled deferred scanning, part of the content of the large file is delivered without scanning to prevent timeout. Subsequent portions of the content are being scanned in the background and are then downloaded if no threat is detected. If a threat is detected, the rest of the file is not downloaded, but the unscanned portion of the large file is already stored on the user's machine and may introduce a security risk.
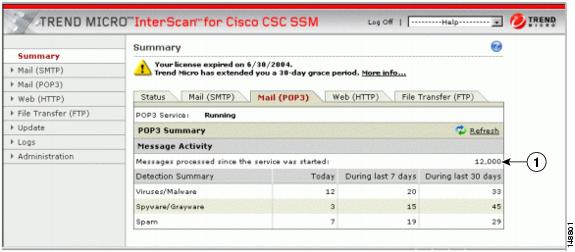
Restart Scanning Service
The Mail (SMTP and POP3) tabs on the Summary window display a count of Messages processed since the service was started in the Message Activity area of the window. For an example, see Figure 8-2.
Figure 8-2 Messages Processed Counter on the Mail (POP3) Tab of the Summary Window
Several events can cause these counters to reset to zero. The events are:
•
A pattern file or scan engine update
•
A configuration change
•
Application of a patch
The statistics in the Detection Summary area of the window do not reset; these statistics continue to update as trigger events occur, regardless of the above events.
There is nothing wrong when the counters reset. If, however, you have a continuous zero in the Messages processed... fields, this indicates that email traffic is not being scanned and you should investigate the situation.
Troubleshooting Performance
The following sections describe issues you may encounter with performance.
•
Status LED Flashing for Over a Minute
•
SSM Cannot Communicate with ASDM
•
Logging in Without Going Through ASDM
•
CSC SSM Throughput is Significantly Less Than ASA
•
CSC SSM Throughput is Significantly Less Than ASA
CSC SSM Console Timed Out
If you leave the CSC SSM console active and there is no activity detected for approximately 10 minutes, your session is timed out. Log in again to resume work. Unsaved changes to your work are lost. If you are called away, it's best to save your work and log off until your return.
Status LED Flashing for Over a Minute
If the Status LED continues flashing for more than a minute, the scanning service is not available. To resolve this problem, reboot the system from ASDM, or contact customer support for assistance.
CautionIf the file to be downloaded is larger than the size specified in the Do not scan files larger than... field, the file is delivered without scanning and may present a security risk.
SSM Cannot Communicate with ASDM
See the "Reset Management Port Access Control" section on page A-14 for information on resetting port access controls, which may solve this problem.
Logging in Without Going Through ASDM
If for some reason ASDM is unavailable, you can log directly into CSC SSM via a Web browser. To log in, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Type the following URL in a browser window:
https://{SSM IP addresss}:8443For example:
https://10.123.123.123:8443/Step 2
The Logon window displays. Type the password you created on the Password Configuration installation window in the setup wizard and click Log On.
Step 3
The default view of the CSC SSM console is the Status tab on the Summary window:
Figure 8-3 Status Tab of the Summary Screen on the CSC SSM Console
CSC SSM Throughput is Significantly Less Than ASA
Restoring files from TCP connections and scanning them is a processor-intensive operation, which involves much more overhead than the protocol-conformance checking that is usually done by firewall. The workaround is to divert only the connections that need to be scanned to CSC SSM to mitigate the performance mismatch.
For example, HTTP traffic can be divided into outbound traffic (an inside user accessing outside websites), inbound traffic (outside users are accessing inside servers), and intranet traffic (traffic between internal sites or trusted partners). You can configure CSC SSM to scan only outbound traffic for viruses, but skip the inbound ones.
Refer to the "Managing AIP SSM and CSC SSM" chapter of the Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide for more information.
Using Knowledge Base
You are welcome to search for more information in the Trend Micro online Knowledge Base. The Knowledge Base URL is:
http://esupport.trendmicro.com
The Knowledge Base search engine allows you to refine your search, by entering product name, problem category, and keywords. There are thousands of solutions available in the Knowledge Base, and more are added weekly.
Using the Security Information Center
Comprehensive security information is available 24x7 from the Trend Micro Security Information Center, which is a free online resource. The Security Information Center URL is:
The Security Information Center provides information such as the following:
•
Virus Encyclopedia—A compilation of knowledge about all known threats, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and others
•
Security Advisories—View malware alerts, risk ratings for the most prominent risks, the most current pattern file and scan engine versions, and other helpful information
•
Scams and Hoaxes—Information about malware hoaxes, scams such as chain letters or money-based hoaxes, and urban legends
•
Joke Programs—A repository of information about known joke programs that are detected by the Trend Micro scan engine
•
Spyware/Grayware—Information about the top ten spyware/grayware programs, and a searchable database of spyware/grayware programs
•
Phishing Encyclopedia—A list of known phishing scams and a description of the perpetration methods
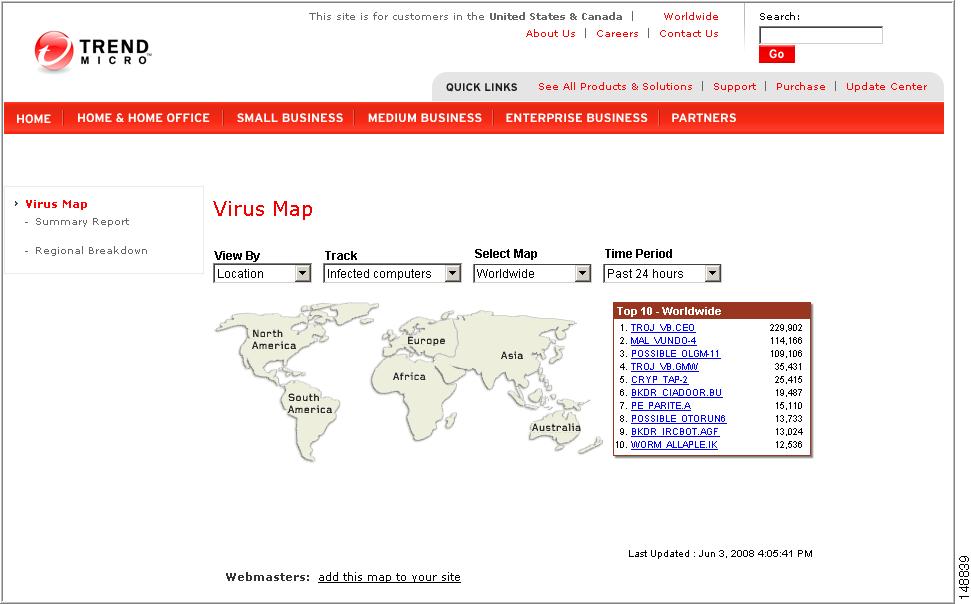
•
Virus Map—A description of threats by location worldwide
Figure 8-4 Virus Map
•
Weekly Virus Report —Current news about threats that have appeared in the past week (Subscribe to the Weekly Virus Report to automatically receive a copy each week via email.)
•
General virus information, including:
–
Virus Primer—An introduction to virus terminology and a description of the virus life cycle
–
Safe Computing Guide—A description of safety guidelines to reduce the risk of infections
–
Risk ratings—A description of how malware and spyware/grayware threats are classified as Very Low, Low, Medium, or High threats to the global IT community
•
White papers—Links to documents that explain security concepts with titles such as The Real Cost of a Virus Outbreak or The Spyware Battle—Privacy vs. Profits
•
Test files—A test file for testing Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM and instructions for performing the test
•
Webmaster tools—Free information and tools for Webmasters
•
TrendLabs—Information about TrendLabs, the ISO 9002-certified virus research and product support center
Understanding the CSC SSM Syslogs
CSC SSM-related syslog messages are listed and described as follows:
SSM Application Mismatch [1-105048]
Error Message %ASA-1-105048: (unit) Mate's service module (application) is different from mine (application)Explanation The failover process detected that different applications are running on the service modules in the active and standby units. The two failover units are incompatible if different service modules are used.
unit—Primary or secondary.
application—The name of the application, such as InterScan Security Card.
Recommended Action Make sure that both units have identical service modules before trying to re-enable failover.
Traffic Dropped Because of CSC Card Failure [3-421001]
Error Message %ASA-3-421001: TCP|UDP flow from interface_name:ip/port to interface_name:ip/port is dropped because application has failed.Explanation A packet was dropped because the CSC SSM application failed. By default, this message is rate limited to 1 message every 10 seconds.
interface_name—The interface name.
IP_address—The IP address.
port—The port number.
application—The CSC SSM is the only application supported in the current release.
Recommended Action Immediately investigate the problem with the service module.
Skip Non-applicable Traffic [6-421002]
Error Message %ASA-6-421002: TCP|UDP flow from interface_name:IP_address/port to interface_nam:IP_address/port bypassed application checking because the protocol is not supported.Explanation Connection bypassed service module security checking because the protocol it is using cannot be scanned by the service module. For example, the CSC SSM is not capable of scanning TELNET traffic. If the user configures TELNET traffic to be scanned, the traffic will bypass the scanning service. By default, this message is rate limited to 1 message every 10 seconds.
IP_address—The IP address.
port—The port number.
interface_name—The name of the interface on which the policy is applied.
application—The CSC SSM is the only application supported in the current release.
Recommended Action The configuration should be modified to only include protocols that are supported by the service module.
Drop ASDP Packet with Invalid Encapsulation[3-421003]
Error Message %ASA-3-421003: Invalid data plane encapsulation.Explanation A packet injected by the service module did not have the correct data plane header. Packets exchanged on data backplane adhere to a Cisco proprietary protocol called ASDP. Any packet that does not have the proper ASDP header is dropped.
Recommended Action Use the capture name type asp-drop [ssm-asdp-invalid-encap] command to capture the offending packets and contact Cisco TAC.
Failed to Inject Packet [7-421004]
Error Message %ASA-7-421004: Failed to inject {TCP|UDP} packet from IP_address/port to IP_address/portExplanation The security appliance has failed to inject a packet as instructed by the service module. This could happen if the security appliance tries to inject a packet into a flow that has already been released.
IP_address—The IP address.
port—The port number.
Recommended Action This could happen because the security appliance maintains its connection table independently from the service module. Normally it will not cause any problem. If this affects security appliance performance, contact Cisco TAC.
Account Host Toward License Limit [6-421005]
Error Message %ASA-6-421005: interface_name:IP_address is counted as a user of applicationExplanation A host has been counted toward the license limit. The specified host was counted as a user of application. The total number of users in 24 hours is calculated at midnight for license validation.
interface_name—The interface name.
IP_address—The IP address.
application—The CSC SSM is the only application supported in the current release.
Recommended Action No action required. However, if the overall count exceeds the user license you have purchased, contact Cisco to upgrade your license.
Daily Node Count [5-421006]
Error Message %ASA-6-421006: There are number users of application accounted during the past 24 hours.Explanation Identifies the total number of users who have used application for the past 24 hours. This message is generated every 24 hours to give the total number of hosts that have used services provided by the service module.
Recommended Action No action required. However, if the overall count exceeds the user license you have purchased, contact Cisco to upgrade your license.
Traffic Dropped Because of CSC Card Failure [6-421007]
Error Message %ASA-3-421007: TCP|UDP flow from interface_name:IP_address/port to interface_name:IP_address/port is skipped because application has failed.Explanation This message is generated when a flow is skipped because the service module application has failed. By default, this message is rate limited to 1 message every 10 seconds.
IP_address—The IP address.
port—The port number.
interface_name—The name of the interface on which the policy is applied.
application—the CSC SSM is the only application supported in the current release.
Recommended Action Immediately investigate the problem with the service module.
New Application Detected [5-505011]
Error Message %ASA-5-505011: Module in slot slot, application detected application, version version.Explanation A new application was detected on a 4GE SSM. This may occur when the system boots, when the 4GE SSM boots, or when the 4GE SSM starts a new application.
slot—The slot in which the application was detected.
application—The name of the application detected.
version—The application version detected.
Recommended Action No action required if the activity described is normal and expected.
Application Stopped [5-505012]
Error Message %ASA-5-505012: Module in slot slot, application stopped application, version versionExplanation This message is generated whenever an application is stopped or removed from a 4GE SSM. This may occur when the 4GE SSM upgrades an application or when an application on the 4GE SSM is stopped or uninstalled.
slot—The slot in which the application was stopped.
application—The name of the application stopped.
version—The application version stopped.
Recommended Action If an upgrade was not occurring on the 4GE SSM or the application was not intentionally stopped or uninstalled, review the logs from the 4GE SSM to determine why the application stopped.
Application Version Changes [5-505013]
Error Message %ASA-5-505013: Module in slot slot application changed from: application version version to: newapplication version newversion.Explanation This message is generated whenever an application version changes, such as after an upgrade. This occurs when a software update for the application on the module is complete.
slot—The slot in which the application was upgraded.
application—The name of the application that was upgraded.
version—The application version that was upgraded.
slot—The slot in which the application was upgraded.
application—The name of the application that was upgraded.
version—The application version that was upgraded.
newapplication—The new application name.
newversion—The new application version.
Recommended Action Verify that the upgrade was expected and that the new version is correct.
Data Channel Communication Failure [3-323006]
Error Message %ASA-3-323006: Module in slot slot experienced a data channel communication failure, data channel is DOWN.Explanation This message indicates that a data channel communication failure occurred and the system was unable to forward traffic to the 4GE SSM. This failure triggers a failover when it occurs on the active appliance in a failover pair. It also results in the configured fail open or fail closed policy being enforced on traffic that would normally be sent to the 4GE SSM. This message is generated whenever there is a communication problem over the security appliance dataplane between the system module and the 4GE SSM. This can be caused when the 4GE SSM stops, resets, or is removed.
slot—The slot in which the failure occurred.
Recommended Action If this is not the result of the 4GE SSM reloading or resetting and a corresponding message 5-505010 is not seen after the 4GE SSM returns to an UP state, the module may need to be reset using the hw-module module 1 reset command.
Data Channel Communication OK [5-505010]
Error Message %ASA-5-505010: Module in slot slot data channel communication is UP.Explanation This message is generated whenever the data channel communication recovers from a DOWN state. This message indicates that data channel communication is operating normally. It occurs after the data channel communication fails and then recovers.
slot—The slot that has established data channel communication.
Recommended Action No action required unless this message was generated as a result of a previous data channel communication failure (message 3-323006). In that case, check the 4GE SSM messages to determine the cause of the communication failure.
Virus detection event
Error Message is-protocol-virus: time|malware_name|malware_type|from_address| to_address|email_subject|action_on_the_content|action_on_the_email|Example:
is-protocol-virus: 2006/01/01 16:33:01| WORM_GREW.A|grayware|fromtester@trendmicro.com|totester@trendmicro.com|subject|Delete|Deli ver|Explanation This syslog message is generated when the CSC SSM detects a virus event in the connection. The infected file has been processed or blocked according to the policy setting.
protocol—The protocol involved.
time—Date and time of the event.
malware_name—Name of the malware.
malware_type—Type of malware.
from_address—From address of the e-mail.
to_address—To address of the -email.
action_on_the_content—Action taken on the e-mail content.
action_on_the_email—Action taken on the entire e-mail.
Recommended Action If the file is originated from an internal machine, perform virus scanning on that machine.
Spyware/Grayware detection event
Error Message is-mail-grayware: time|malware_name|malware_type|from_address| to_address|email_subject|action_on_the_content|action_on_the_email|Example:
is-mail-grayware: 2006/01/01 16:33:01| |Spyware|fromtester@trendmicro.com|totester@trendmicro.com|subject|Delete|Deliver|Explanation This syslog message is generated when the CSC SSM detects a spyware or grayware event in the connection. The suspicious file has been processed or blocked according to the policy setting.
mail—The e-mail message involved.
time—Date and time of the event.
malware_name—Name of the malware.
malware_type—Type of the malware.
from_address—From address of the -email.
to_address—To address of the e-mail.
action_on_the_content—Action taken on the e-mail content.
action_on_the_email—Action taken on the whole email.
Recommended Action If the file is originated from an internal machine, perform virus scanning on that machine.
SMTP/POP3 anti-spam event
Error Message is-anti-spam: time|from_email_address|to_email_address| email_subject|action_on_the_content|action_on_the_email|Example:
is-anti-spam: 2006/01/01 19:37:02|fromtester@trendmicro|totester@trendmicro.com|subject|Delete|Deliver|Explanation This syslog message is generated when the CSC SSM detects an anti-spam event in the SMTP or POP3 scanning. The spam mail has been processed or blocked according to the policy setting.
time—Date and time of the event
from_address—From address of the email
to_address—To address of the email
action_on_the_content—Action taken on the email content
action_on_the_email—Action taken on the whole email
Recommended Action No action is required. If the spam mail is generated from a similar source, you may add this source to the Blocked Sender list to reduce the email volume.
HTTP URL filtering event
Error Message is-url-filtering: time|filtered_url|client_ip|url_categoryExample:
is-url-filtering: 2006/01/01 17:10:59|forbidden.com/|10.2.3.4|Company Prohibited Sites|Explanation This syslog message is generated when the CSC SSM detects a URL filtering event in the HTTP scanning.
time—Date and time of the event
blocked_url—The URL that has been filtered
client_ip—IP address of the client
url_category—The category of URL blocking or filtering
Recommended Action No action is required. Adjust the URL filtering setting if you want this URL (category) to be allowed.
HTTP URL blocking event
Error Message is-url-blocking: time|blocked_url|client_ip|blocking_ruleExample:
is-url-blocking: 2006/01/01 17:10:59|blocked.com/|10.2.3.4|PhishTrap|Explanation This syslog message is generated when the CSC SSM detects a URL blocking event in the HTTP scanning.
time—Date and time of the event
blocked_url—The URL that has been blocked
client_ip—IP address of the client
blocking_rule—The rule that has blocked the URL
Recommended Action No action is required.
Syslog adaptor starting
Error Message is-syslog: ISSyslog Adaptor 1.0Example:
is-syslog: ISSyslog Adaptor 1.0Explanation This syslog message is generated when the CSC SSM starts the InterScan Syslog Adaptor.
Recommended Action No action is required.
License upgrade notice
Error Message license-upgrade-notice: Your daily node counts (daily_count) has exceeded your licensed seats (seats) by offset. Please upgrade your license.Example:
License-upgrade-notice: Your daily node counts (300) has exceeded your licensed seats (100) by 200. Please upgrade your license.Explanation This syslog message is generated when CSC SSM detects more nodes connected to the CSC SSM than are specified in the current license. In addition to this syslog, a notification email is sent to the administrator.
daily_count—The daily node count that has connected to the CSC SSM
seats—The number of seats of the CSC SSM license
offset—equals the daily count minus the number of seats
Recommended Action Contact a Trend Micro sales representative for a license upgrade.
Scan service failed
Error Message SysMonitor: INFO: service_title service is DOWN, count = counter, restartingExample:
SysMonitor: INFO: FTP service is DOWN, count = 1, restartingExplanation This syslog message is generated when a scan service stops; the counter increments for each restart attempt.
Recommended Action If a service goes down, restart all services by accessing the CSC SSM CLI Menu. If the failure persists, reset CSC SSM or contact Cisco TAC.
Scan service recovered
Error Message SysMonitor: INFO: service_title service is UP.Example:
SysMonitor: INFO: FTP service is UP.Explanation This syslog message is generated when a scan service recovers from a previous failure.
service_title—The name of the service.
Recommended Action No action is required.
CSC SSM status message
Error Message SysMonitor: INFO: Set CSC SSM Application Status to data_channel_status.Example:
SysMonitor: INFO: Set CSC SSM Application Status to UP.Explanation This syslog message is generated to indicate the current status of the CSC SSM. When the CSC SSM is healthy, the status is set to UP and traffic can be processed. When the CSC SSM is updating the configuration or an engine/pattern, the status is set to RELOAD and the ASA will perform fail-open or fail-close. When the CSC SSM is unable to process traffic, the status is set to DOWN and traffic bypasses CSC SSM processing. ASA will perform fail-open, fail-close or fail-over depending how it has been configured on the ASA.
data_channel_status—UP, RELOAD, and DOWN
Recommended Action No action is required for UP and RELOAD status. When the status is DOWN, either restart the services on the CSC SSM or contact Cisco TAC.
Resource availability of the CSC SSM falls below the desired level
Error Message SysMonitor: INFO: RESOURCE: resource_name free space current_free_space K is below desired_free_space KExample:
SysMonitor: INFO: RESOURCE: Compact Flash free space 1234K is below 5120K.Explanation This syslog message is generated when one of the storage spaces on the CSC SSM falls below the desired level.
resource_name—The name of the resource:
–
Compact Flash
–
Active Update Temp
–
Scanning TempDir
–
Log
current_free_space—Current free amount of the resource
desired_free_space—Desired free amount of the resource
Recommended Action If the message is sent more than once, contact Cisco TAC.
Resource availability of the CSC SSM has been restored
Error Message SysMonitor: INFO: RESOURCE: resource_title free space is back to normal (more than desired_free_space K)Example:
SysMonitor: INFO: RESOURCE: Compact Flash free space is back to normal (more than 5120K).Explanation This syslog message is generated when CSC SSM has recovered from a previous storage shortage.
resource_title—The name of the resource:
–
Compact Flash
–
Active Update Temp
–
Scanning TempDir
–
Log
desired_free_space—Desired free amount of the resource
Recommended Action No action is required.
System monitor started
Error Message SysMonitor: INFO: SysMonitor started.Example:
SysMonitor: INFO: SysMonitor started.Explanation This syslog message is generated when the system monitor has started.
Recommended Action No action is required.
CSC has actively disconnected a connection
Error Message CSCSSM: A protocol session has been disconnected from the client at client_ip to the server at server_ip due to internal error or timeout.Example:
CSCSSM: A HTTP session has been disconnected from the client at 1.1.1.1 to the server at 2.2.2.2 due to internal error or timeout.Explanation This syslog message is generated when a socket timeout is experienced when CSC SSM proxies a connection, or an internal problem is encountered.
protocol—The protocol involved
client_ip—IP address of the client
server_ip—IP address of the server
Recommended Action No action is required.
Connection capacity has been reached
Error Message The maximum number of connections for protocol has been reached. New connections will be kept in a backlog and may time out.Example:
The maximum number of connections for HTTP has been reached. New connections will be kept in a backlog and may time out.Explanation This syslog message is generated when CSC SSM reaches the maximum number of concurrent connections set for a given protocol.
protocol—The protocol involved
Recommended Action Configure ASA to bypass certain traffic from CSC SSM scanning or segment the network to another ASA device.
Connection capacity has been restored
Error Message The number of current protocol connections has returned to normal.Example:
ActiveUpdate: VirusScanEngine/uptodate, VirusPattern/3.189.00, AntiSpamEngine/failed, GraywarePattern/unlicensed, PhishTrap/187Explanation This syslog message is generated when the number of concurrent connections has returned to a range that CSC SSM can process promptly.
protocol—The protocol involved
Recommended Action No action is required.
Scheduled update report
Error Message ActiveUpdate: component/status component/status.Example:
ActiveUpdate: VirusScanEngine/uptodate, VirusPattern/3.189.00, AntiSpamEngine/failed, GraywarePattern/unlicensed, PhishTrap/187Explanation This syslog message is generated when a scheduled pattern/engine update occurs.
component—The component that is updated by ActiveUpdate
status—The status or version of the component
Recommended Action If you see consecutive update failures, either troubleshoot the Internet connectivity, the CSC SSM update settings, or contact Cisco TAC.
Failover service encountered an internal error
Error Message is-failover-daemon[process_id]: Could not create failover sync server socket; Could not open failover sync server socket; Could not create failover request handler thread; Could not create failover sync server thread; Could not create failover sync server; Could not create failover IPC server thread; Could not create failover IPC server; Cannot open IPC sockets; Could not create heartbeat threadExample:
is-failover-daemon[process_id]: Could not create failover sync server socketExplanation This syslog message is generated when the failover service encounters an unrecoverable internal error.
process_id—Process ID of the daemon
A list of possible failover daemon errors follows.
–
Could not create a TCP listening socket to accept connections.
–
Could not bind the SSM card management port IP address to the TCP listening socket.
–
Could not start listening for connections from peers.
–
Could not create a thread to service either a heartbeat or synchronization request from a peer.
–
Could not create a thread to accept connections from peers.
–
Could not create a server object to accept connections and handle requests from peers.
–
Could not create a thread to handle IPC requests from the CSC management system.
–
Could not create an IPC server object to handle IPC requests from the CSC management system.
–
Could not open the IPC FIFOs to receive a request from the CSC management system to send a heartbeat or a synchronization request to the peer.
–
Could not create a thread to send periodic heartbeats to a peer.
Recommended Action Restart all services on the CSC SSM, reload the CSC SSM, or contact Cisco TAC.
Failover service communication failed
Error Message is-failover-daemon[process_id]: request_type FAILED. Status code code; Status description: textExample:
is-failover-daemon[5532]: HEARTBEAT FAILED. Status code 403; Status description: Connection or request timed out.Explanation This syslog message is generated when the failover daemon could not send a heartbeat to its peer to verify network connectivity.
process_id—Process ID of the daemon
request_type—HELLO, HEARTBEAT, SYNCH
code—Status code
text—Status description
Recommended Action If this error occurs while configuring CSC failover, follow the recommended action display in the Device Failover Settings screen of the CSC management console. Otherwise, check all hardware connections between the ASA appliances or contact Cisco TAC.
Failover service email could not be sent
Error Message is-failover-daemon[process_id]: action_type failed notification could not be sentExample:
is-failover-daemon[5532]: HELLO failed notification could not be sent.Explanation This syslog message is generated when the automatic "heartbeat failure" notification emailed to the administrator cannot be sent.
process_id—Process ID of the daemon
action_type—HELLO, SYNCH
Recommended Action Restart all services on the CSC SSM, reload the CSC SSM, or contact Cisco TAC.
Service module informational report
Error Message is-service-module[process_id]: Software version: text; Increased process priority to -5; Application name: text; Application version: text; Application state: up/downExample:
is-service-module[553]: Software version: CSC SSM 6.0 (Build#1349)Explanation This syslog message displays the CSC application name, version and running state during Service Module start up.
process_id—Process ID of the daemon
text—Description of name or version
up/down—Service is up or down
Recommended Action No action is required.
Service module show module 1 details
Error Message is-service-module[process_id]: Syslog Number and Format: Software version: text; HTTP Service: up/down; Mail Service: up/down; FTP Service: up/down; Activated: Yes/No; Mgmt IP addr: IP_address; Mgmt web port: port; Peer IP addr: ip/not_enabledExample:
is-service-module[553]: Software version: CSC SSM 6.0 (Build#1349)Explanation This syslog message displays the output of the "show module 1 details" command produced by the Service Module.
process_id—Process ID of the service module
text—Description of name or version
up/down—Service is up or down
yes/no—Yes or No
ip_address—IP address
port—Port number
ip/not_enabled—IP address or not enabled
Recommended Action No action is required.
Time synchronization with the ASA chassis failed
Error Message is-service-module[process_id]: ASA time sync failedExample:
is-service-module[5532]: ASA time sync failed.Explanation This syslog message is generated when the Service Module is unable to synchronize the SSM system time with the PIX system time.
process_id—Process ID of the service module
Recommended Action No action is required.
Service module cannot create FIFO
Error Message is-service-module[process_id]: Cannot create fifo_name; Cannot open csc subsystem IPC fifosExample:
is-service-module[5532]: Cannot create /var/run/isvw/servmodfifo.1Explanation This syslog message is generated when the system is unable to create FIFOs for IPC with another CSC subsystem.
process_id—Process ID of the service module
fifo_name—Name of the FIFO
csc_subsystem—The name of CSC subsystem
Recommended Action Restart all services on the CSC SSM, reload the CSC SSM, or contact Cisco TAC.
Service module internal communication error
Error Message is-service-module[process_id]: Received unrecognized ipc_operation request; ipc_operation peer closed with no request sent; Bad ipc_operation request from InterScanExample:
is-service-module[5532]: Received unrecognized time sync requestExplanation This syslog message is generated when the IPC is unable to communicate with another CSC subsystem.
process_id—Process ID of the service module
ipc_operation—IPC (Inter-process Communication) operation
Recommended Action No action is required.
Service module encountered a problem when communicating with the ASA chassis
Error Message is-service-module[process_id]: Could not send the node count request to the ASA; Could not get time from the ASA; Could not send the time sync request to the ASA; ASA auto time sync failed on SSM reboot; Management port IP change report to the ASA failed; Management port IP change report failed; Could not increase the process priorityExample:
is-service-module[5532]: Could not send the node count request to the ASA.Explanation This syslog message is generated when the Service Module fails to communicate with the ASA chassis.
process_id—Process ID
Recommended Action No action is required.
Before Contacting Cisco TAC
Before you contact the Technical Assistance Center (TAC), check the documentation and online help to see if it contains the answer you are looking for. If you have checked the documentation, as well as Knowledge Base, and still need help, please be prepared to give the following information to speed the resolution of your problem:
•
Product Activation Code(s)
•
Version number of the product
•
Version number of the pattern file and scan engine
•
Number of users
•
Exact text of the error message, if you received one
•
Steps to reproduce the problem.

 Feedback
Feedback