-
Cisco Content Security and Control SSM Administrator Guide, 6.1
-
Preface
-
Introducing the Content Security and Control SSM
-
Verifying Initial Setup
-
Configuring Mail Traffic (SMTP and POP3)
-
Configuring Web (HTTP) and File Transfer (FTP) Traffic
-
Managing Updates and Log Queries
-
Administering Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM
-
Monitoring Content Security
-
Troubleshooting Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM
-
Reimaging and Configuring the CSC SSM Using the Command Line
-
Using CSC SSM with Trend Micro Control Manager
-
Glossary
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring Mail Traffic (SMTP and POP3)
Default Mail Scanning Settings
Defining Incoming/Outgoing SMTP Mail
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Spyware/Grayware Detection
Reviewing SMTP & POP3 Notifications
Configuring SMTP Message Filter, Disclaimer, & Incoming Mail Domain
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Spam Filtering
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Content Filtering
Enabling Network Reputation Services
Configuring Mail Traffic (SMTP and POP3)
After installation, assuming you have configured the ASA to send traffic to the SSM, your SMTP and POP3 traffic is being scanned for viruses and other malware such as worms and Trojans. This chapter describes additional configuration required to detect security risks such as spyware or to add an organizational disclaimer to incoming and outgoing messages, and includes the following sections:
•
Default Mail Scanning Settings
•
Defining Incoming/Outgoing SMTP Mail
•
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Spyware/Grayware Detection
•
Reviewing SMTP & POP3 Notifications
•
Configuring SMTP Message Filter, Disclaimer, & Incoming Mail Domain
•
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Spam Filtering
•
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Content Filtering
Default Mail Scanning Settings
Table 3-1 summarizes the mail configuration settings, and the default values that are in operation after installation.
These default settings give you some protection for your email traffic after you install Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM. You may change these settings. Review the online help carefully for more information about these selections before making changes.
There are additional configuration settings that you may want to update post-installation to get the maximum protection for your email traffic. These additional settings are described in the remaining pages of this chapter.
If you purchased the Plus License, which entitles you to receive anti-spam and content-filtering functionality, you must configure these features; they are not operable by default.
Defining Incoming/Outgoing SMTP Mail
When an email message is addressed to multiple recipients, one or more of which is an incoming message (addressed to someone within the same organization with the same domain name) and one of which is outgoing (addressed to someone in a different organization with a different domain name), the incoming rules apply. For example, a message from psmith@example.com is addressed to jdoe@example.com and gwood@example.net.
Assume that incoming SMTP messages are scanned via the "scan all" option, whereas outgoing messages are scanned via IntelliScan. Also assume that spyware/grayware detection is enabled for incoming messages only.
The message from psmith to jdoe and gwood would be treated as an incoming message for both recipients, even though gwood is an "outgoing" recipient.
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Spyware/Grayware Detection
Grayware is a category of software that may be legitimate, unwanted, or malicious. Unlike threats such as viruses, worms, and Trojans, grayware does not infect, replicate, or destroy data, but it may violate your privacy. Examples of grayware include spyware, adware, and remote access tools.
Spyware/grayware detection is not enabled by default. To begin detecting spyware and other forms of grayware in your email traffic, configure this feature on the following windows:
•
Click the Configure Incoming Scan link on Configuration > Trend Micro Content Security > Mail in ASDM to display the SMTP Incoming Message Scan/Target window
•
Click the Configure Outgoing Scan link on Configuration > Trend Micro Content Security > Mail in ASDM to display the SMTP Outgoing Message Scan/Target window
•
In the CSC SSM console, click Mail (POP3) > Scanning > POP3 Scanning/Target to display the POP3 Scanning/Target window
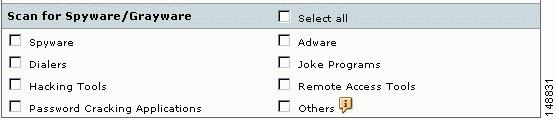
In the Scan for Spyware/Grayware section of these windows (shown in Figure 3-1), choose the types of grayware you want detected by Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM.
Figure 3-1 Spyware/grayware Scanning Configuration
See the specific online help for the above-mentioned windows to read a description of each of these types of grayware. After you specify the types of grayware to be detected, be sure to click Save to enable the new configuration.
Reviewing SMTP & POP3 Notifications
If you are satisfied with the default notification setup, no further action is required. However, you might want to review the notification options and decide whether you want to change the defaults. For example:
•
You may want to send a notification to the administrator when a security risk has been detected in an email message (for SMTP, you can also notify the sender and/or recipient)
•
You may want to tailor the default text in the notification message to something more appropriate for your organization
To review and possibly reconfigure email notifications, go to the following windows in the CSC SSM console:
•
Mail (SMTP) > Scanning > Incoming > SMTP Incoming Message Scan/Notification
•
Mail (SMTP) > Scanning > Outgoing > SMTP Outgoing Message Scan/Notification
•
Mail (POP3) > Scanning > POP3 Scanning/Notification
Types of Notifications
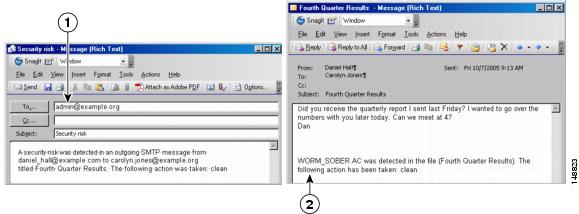
There are two types of notifications available in email traffic; email notifications and inline notifications, as shown in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 Examples of Notifications
Notifications use variables called tokens to supply information that makes the notification more meaningful. For example, a token called %VIRUSNAME% is replaced with the text WORM_SOBER.AC in the inline notification example on the right.
For more information about tokens, see the online help topic "Using Tokens in Notifications."
Modifying Notifications
To send a notification to additional recipients, or to change the default text of the notification message that is sent when a trigger event occurs, go to the message scanning notification window to be updated. For example, Figure 3-3 shows the notification fields on the Mail (SMTP) > Scanning > Outgoing > SMTP Outgoing Message Scan/Notification window.
Figure 3-3 Configure Notifications for Outgoing SMTP
By default, the only notification is an inline notification to the message recipient, which means neither the sender or the administrator of the originating organization are aware that a security threat was detected and cleaned. To make changes:
•
In the Email Notifications section of the window, click additional people to receive a notification via email
•
In the Inline Notifications section of the window, choose whether you want only the risk-free inline notification, the default "risk detected and action taken" message, neither, or both
•
To change the text of any of the notifications, highlight the existing text and type your own message in the text box provided; be sure to click Save when you are finished
Configuring SMTP Message Filter, Disclaimer, & Incoming Mail Domain
Note
These settings apply to SMTP protocol only.
Review the configuration settings available from Mail (SMTP) > Configuration > SMTP Configuration. There are four tabs on the SMTP Configuration window:
•
Message Filter
•
Disclaimer
•
Incoming Mail Domain
•
Advanced Settings
To configure these settings, perform the following steps:
Step 1
On the Message Filter tab of the SMTP Configuration window, Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM is already configured to reject messages larger than 20 MB and addressed to more than 100 recipients. These settings help protect you from an assault on your network that consumes CPU time while your email server tries to handle huge bogus messages addressed to hundreds of recipients. The default settings are recommended, and if you want to continue to use them, no action is required on this window.
Step 2
On the Message Filter tab of the SMTP Configuration window, you may add an organizational disclaimer that appears at the beginning or end of SMTP messages. Click the Add this disclaimer... check box to enable this feature, or leave the page as-is if you do not want to use this feature. To customize the disclaimer text, highlight and type over the default message.
Step 3
On the Incoming Mail tab of the SMTP Configuration window, you can define additional incoming mail domains for the purpose of:
•
scanning for viruses and other threats
•
anti-spam
•
content-filtering
The Incoming mail domains field should already contain the incoming email domain name you entered (on the Host Configuration installation window) during installation. If you have additions, enter the second level domain name only. For example, enter only example.com, not subsidiary domains such as ex1.example.com, ex2.example.com, and so on. If there are no other incoming domains, no further action is needed on this window.
Step 4
The Advanced Settings tab of the SMTP Configuration window contains fields that allow you to:
•
Set a more aggressive (or permissive) timeout for messages that appear to be from an attacker
•
Enable settings that place selected, temporary restrictions on the SMTP traffic. If you suspect you may be under attack, these restrictions make it more difficult for the traffic that has the characteristics of a suspicious message from an attacker to move through system because you have
–
Set a shorter timeout for sending an email (often an email that takes longer to send is part of an intentional attempt to occupy resources)
–
Limited the allowed number of errors triggered, indicative of someone resending a message over and over
–
Limitied the number of times the sender resets the conditions for attempting to send the same email
See the online help for more information.
Step 5
If you made any changes, click Save to activate your updated SMTP configuration.
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Spam Filtering
Note
This feature requires the Plus License.
The SMTP and POP3 anti-spam feature is disabled by default and must be configured.
Tip
Anti-spam is disabled by default whether you purchase the Base and Plus licenses together, or add the Plus license at a later time. You must enable and configure the anti-spam feature to begin using it.
To configure anti-spam functionality:
•
Click the Configure Anti-spam link on Configuration > Trend Micro Content Security > Mail in ASDM to display the SMTP Incoming Anti-spam window
•
In the CSC SSM console, click Mail (POP3) > Anti-spam > POP3 Anti-spam to display the POP3 Anti-spam window
To enable anti-spam, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Click Enable on the Target view of the above windows.
Step 2
Reset the anti-spam threshold to Medium or High if you do not want to use the default value of Low.
Tip
You might want to adjust this setting at a later time after you have some experience with blocking spam in your organization. If the threshold is too low, a high incidence of spam occurs. If the threshold is too high, high incidence of false positives (messages identified as spam that are legitimate messages) occurs.
Step 3
Add approved senders in the Approved Senders section of the SMTP Incoming Anti-spam and POP3 Anti-spam/Target windows. Mail from approved senders is always accepted without being evaluated as spam.
Note
Approved senders added and saved in either window appear in the other. For example, assume you add robert_li@example.com to the Approved Senders list on the POP3 Anti-spam window. Now open the SMTP Incoming Anti-spam window. The address for robert_li@example.com is already added to the list of Approved Senders on the SMTP Incoming Anti-spam window as well.
The Blocked Senders list is also matched—a blocked sender created on either window appears in both.Step 4
Add blocked senders in the Blocked Senders section of the SMTP Incoming Anti-spam and POP3 Anti-spam/Target windows. Mail from blocked senders is always rejected. Blocked senders added and saved in either window appear in the other.
Step 5
Configure the action for messages identified as spam on the SMTP Incoming Anti-spam and POP3 Anti-spam/Action windows. Choices are:
•
Stamp the message with a spam identifier, such as "Spam:" and deliver it anyway (The spam identifier acts as a prefix to the message subject, for example, "Spam:Designer luggage at a fraction of the cost!"
•
Delete the message
Step 6
Click Save to activate anti-spam per your configuration.
Enabling SMTP & POP3 Content Filtering
Note
This feature requires the Plus License.
The SMTP and POP3 content filtering feature is disabled by default and must be configured. To configure content filtering functionality, go to the following windows:
•
Click the Configure Incoming Filtering link on Configuration > Trend Micro Content Security > Mail in ASDM to display the SMTP Incoming Content Filtering/Target window
•
Click the Configure Outgoing Filtering link on Configuration > Trend Micro Content Security > Mail in ASDM to display the SMTP Outgoing Content Filtering/Target window
•
In the CSC SSM console, click Mail (POP3) > Content Filtering > POP3 Content Filtering/Target to display the POP3 Content Filtering/Target window
To enable content filtering, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Click Enable on the Target view of the above windows.
Step 2
Decide whether to use a message size filtering criteria, and if so, set the parameters in the Message size is field. For example, if you specify message filtering for messages and attachments greater than 5 MB, messages with attachments less than 5 MB are not filtered. If you do not specify a message size, all messages are filtered, regardless of their size.
Step 3
In the Message Subject and Body section of the windows, specify words that if present in the message subject and/or body trigger the content filtering action.
Step 4
In the Message Attachment section of the windows, specify characters or words that if present in the attachment name trigger the content filtering action. You can also choose content filtering by file types in this section of the window. For example, if you choose Microsoft Office file types for filtering, attachments created with Microsoft Office tools are filtered for content.
Step 5
Click the Action tab of the above listed windows to specify action when content filtering is triggered. For email messages, the choices are:
•
Delete messages that violate one of the content filtering policies
•
Deliver messages anyway
For attachments, the choices are:
•
Allow violating attachments to pass (in which case, do not make any changes in the For messages that match the attachment criteria section of the window)
•
Delete the attachment and insert an inline notification in the message body
Step 6
Click the Notification tab of the above listed window to specify whether a notification is sent to the administrator for a content-filtering violation. (For SMTP, you can also notify the sender and/or recipient.) Change the default text in the notification message box(es) by highlighting and typing over the default message.
Step 7
Click Save to activate content filtering per your configuration.
Enabling Network Reputation Services
In addition to filtering spam on the basis of content, CSC SSM provides Network Reputation Services (NRS), which allow you to determine spam based on the reputation of the originating MTA (off-loads the task from the CSC SSM server). With NRS enabled, all inbound SMTP traffic will be checked against the IP databases to see whether the originating IP address is clean or if it has been black-listed for being a known spam vector.
•
In the CSC SSM console, click Mail (SMTP) > Network Reputation Services to open the Target window.
About RBL+ and QIL
The Realtime Blackhole List (RBL+) is a database that tracks the reputation of some 2 billion IP addresses. IP addresses that have been consistently associated with the delivery of spam messages are added to the database and only seldom removed. The Quick IP Lookup (QIL) list is another database for tracking the reputation of IP addresses, but with QIL, IPs are added and removed more frequently (and thus can be considered more current).
When an IP address is found in either database, NRS "marks" the connection and CSC SSM will take the action you have selected for such IPs.
For example, say an MTA has been hijacked or an open relay exploited and used by a 3rd party to deliver spam messages. The system admin may discover the exploit after a few hours or days and correct it, but in the meantime millions of spam messages are being and have been sent by the server. The tainted IP may be added to the QIL database after only a few reports of spam, but then removed once the reports have trailed off (the admin regains control of the MTA). On the other hand, because it takes longer for an IP address to be added to the RBL+, many IPs that are only temporarily problematic (but nonetheless may be responsible for millions of spam) will not be flagged by RBL+. Once added to the RBL+, however, it is harder to remove an IP address from the database -- there is a higher degree of certainty that IPs in the RBL+ are inveterate spam MTAs.
Both services are applied to the message before the message is delivered to your MTA, freeing it from the overhead of processing complex heuristics and analysis while at the same time routing the mail.
To enable and configure NRS filtering, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Click Enable on the Target view of the above windows.
Step 2
Choose the level of service you want to employ: High or Low. High service level uses both the Realtime Blackhole List (RBL+) and Quick IP Lookup services to check the reputation of the MTA from which the email is received.
Step 3
In the Approved IP Address field, add the IP address, or a range of IP addresses, for any machines you want to exempt from the lookup.
Step 4
Click the Action tab to make that page active, and then choose the action you want CSC SSM to take on messages found to match an entry in the RBL+ or QIL databases. Actions are described below:
•
Intelligent action - Spam messages are rejected at the MTA with a brief message
•
Connection closed with no error - Spam messages are rejected but no message is sent (Note: this may trigger a series of automatic retries on the part of the originating MTA, and can increase traffic volume)
•
Detect, log, then pass - Spam incidents are logged and then delivered to the intended recipient (other scanning rules will be applied). This action is typically used only for troubleshooting.

 Feedback
Feedback