

-
Cisco CPT Configuration Guide–CTC and Documentation Release 9.3 and Cisco IOS Release 15.1(01)SA
-
Preface
-
Understanding the Carrier Packet Transport System
-
Hardware
-
Configuring Ethernet Virtual Circuit
-
Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching
-
Configuring MPLS–Transport Profile
-
Configuring Pseudowire
-
Configuring Quality of Service
-
Configuring High Availability
-
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
-
Configuring Link Aggregation Group and Link Aggregation Control Protocol
-
Configuring MAC Learning
-
Configuring Multicast VLAN Registration
-
Configuring IGMP Snooping
-
Configuring Performance Monitoring, RMON, OTN, and Port Provisioning
-
Configuring Local Authentication
-
Configuring Cisco Discovery Protocol
-
Alarm Troubleshooting
-
SNMP
-
CPT Error Messages
-
Network Element Defaults
-
Index
-
Contents
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Understanding IGMP Snooping
- Joining a Multicast Group
- NTP-J64 Configuring IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J217 Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands
- Leaving a Multicast Group
- DLP-J218 Enabling or Disabling IGMP Immediate Leave Using Cisco IOS Commands
- IGMP Report Suppression
- DLP-J219 Disabling IGMP Report Suppression Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J220 Configuring a Static Multicast Router Port Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J230 Viewing IGMP Configuration Using Cisco IOS Commands
- NTP-J68 Configuring IGMP Snooping Using CTC
- IGMP Proxy Reporting
- L2 Address Aliasing Issue
- IGMP Snooping Interaction with LAG
- High Availability
- IGMP Statistics and Counters
- Alarms
Configuring IGMP Snooping
This chapter describes IGMP Snooping and procedures to configure IGMP Snooping.
- Understanding IGMP Snooping
- Joining a Multicast Group
- NTP-J64 Configuring IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands
- Leaving a Multicast Group
- IGMP Report Suppression
- NTP-J68 Configuring IGMP Snooping Using CTC
- IGMP Proxy Reporting
- L2 Address Aliasing Issue
- IGMP Snooping Interaction with LAG
- High Availability
- IGMP Statistics and Counters
- Alarms
Understanding IGMP Snooping
As networks increase in size, multicast routing becomes critically important as a means to determine which segments require multicast traffic and which do not. IP multicasting enables IP traffic to be propagated from one source to a number of destinations, or from many sources to many destinations. Rather than sending one packet to each destination, one packet is sent to the multicast group identified by a single IP destination group address.
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping restricts flooding of multicast traffic by sending multicast traffic only to the interfaces that are subscribed to a particular multicast group.
The Carrier Packet Transport (CPT) system can use IGMP snooping to constrain the flooding of multicast traffic by dynamically configuring Layer 2 interfaces so that multicast traffic is forwarded to only those interfaces associated with IP multicast devices. As the name implies, IGMP snooping requires the CPT system to snoop on the IGMP transmissions between the host and the router and to keep track of multicast groups and member ports. When the CPT system receives an IGMP report from a host for a particular multicast group, the CPT system adds the host port number to the forwarding table entry; when it receives an IGMP Leave Group message from a host, it removes the host port from the table entry. It also periodically deletes entries if it does not receive IGMP membership reports from the multicast clients.
NoteFor more information on IP multicast and IGMP, see RFC 1112, RFC 2236, and RFC 3376.
The CPT system forwards periodic general queries received from the multicast router in the bridge domain where IGMP snooping is enabled. All hosts interested in this multicast group send join requests and are added to the forwarding table entry. The CPT system creates one entry per bridge domain in the IGMP snooping IP multicast forwarding table for each group from which it receives an IGMP join request.
The IP multicast groups learned through IGMP snooping are dynamic.
If a port interface, EFP, and bridge domain state changes, the IGMP snooping-learned multicast groups from this port, EFP, and bridge domain in the bridge domain are deleted.
IGMP Versions
The CPT system supports IGMP version 1, IGMP version 2, and IGMP version 3 on a bridge domain level. The CPT system does snooping using L2 multicast address and not L3 IP address.
Note
The CPT system supports IGMPv3 snooping based only on the destination multicast MAC address and not on the the source IP address or on proxy reports.An IGMPv3 CPT system provides Basic IGMPv3 Snooping Support (BISS), which includes support for the snooping features on IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 switches and for IGMPv3 membership report messages. BISS constrains the flooding of multicast traffic when the network includes IGMPv3 hosts. It constrains traffic to approximately the same set of ports as the IGMP snooping feature on IGMPv1 or IGMPv2 hosts.
Joining a Multicast Group
When a host connected to the CPT system wants to join an IP multicast group and it is an IGMP version 2 or version 3 client, it sends an unsolicited IGMP join message, specifying the IP multicast group to join. Alternatively, when the CPT system receives a general query from the router, it forwards the query to all the EFPs in the bridge domain. IGMP hosts wanting to join the multicast group respond by sending a join message to the CPT system. The CPT system CPU creates a multicast forwarding-table entry for the group if it is not already present. The CPU also adds the interface where the join message was received to the forwarding-table entry. The host associated with that interface receives multicast traffic for that multicast group. See Figure 1.
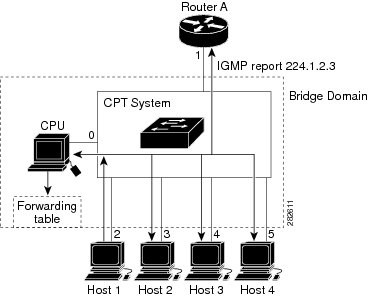 Router A sends a general query to the CPT system, which forwards the query to ports 2 through 5, which have EFPs configured in the same bridge domain. Host 1 wants to join multicast group 224.1.2.3 and multicasts an IGMP membership report (IGMP join message) to the group. The CPT system CPU uses the information in the IGMP report to set up a forwarding-table entry as shown in Table 1, which includes the port numbers connected to Host 1 and the router.
Router A sends a general query to the CPT system, which forwards the query to ports 2 through 5, which have EFPs configured in the same bridge domain. Host 1 wants to join multicast group 224.1.2.3 and multicasts an IGMP membership report (IGMP join message) to the group. The CPT system CPU uses the information in the IGMP report to set up a forwarding-table entry as shown in Table 1, which includes the port numbers connected to Host 1 and the router.The CPT system hardware can distinguish IGMP information packets from other packets for the multicast group. The information in the table enables the switching engine to send frames addressed to the 224.1.2.3 multicast IP address, which are not IGMP packets, to the router and to the host that has joined the group.
If another host (for example, Host 4) sends an unsolicited IGMP join message for the same group (Figure 2) the CPU receives that message and adds the port number of Host 4 to the forwarding table as shown in Table 2. Note that because the forwarding table directs IGMP messages only to the CPU, the message is not flooded to other ports on the CPT system. Any known multicast traffic is forwarded to the group and not to the CPU.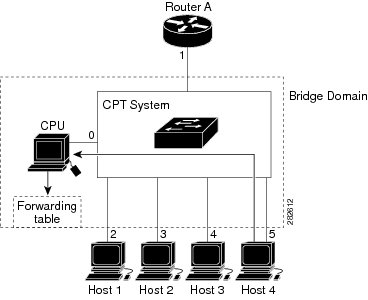
Table 2 Updated IGMP Snooping Forwarding Table Destination Address Type of Packet Ports 224.1.2.3 IGMP 1, 2, 5 IGMP Snooping Configuration Guidelines and Restrictions
- On a CPT system, IGMP snooping can be configured at the bridge domain level.
- IGMP immediate-leave and IGMP report-suppression commands can be configured at the bridge domain level.
- Static multicast router can be configured at the EFP level.
- It is mandatory to untag the packets before they enter the bridge domain. This is achieved using the rewrite pop configuration at the EFP level.
NTP-J64 Configuring IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands
Procedure
Step 1 Complete DLP-J217 Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands. Step 2 Complete the following tasks as necessary: Step 3 (Optional) Complete the DLP-J230 Viewing IGMP Configuration Using Cisco IOS Commands. Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-J217 Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands
ProcedureExamples:
The following example shows how to enable IGMP snooping on untagged Ethernet traffic on the bridge domain and how to configure the source and host ports:
! Configuration on the bridge-domain Router(config)# bridge-domain 30 Router(config-bdomain)# ip igmp snooping ! Configuration on port 1 Router(config)# interface gi 36/1 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation untagged Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 ! Configuration on port 2 Router(config)# interface gi 36/5 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation untagged Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 ! Configuration on port 3 Router(config)# interface gi 36/10 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation untagged Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domainThe following example shows how to enable IGMP snooping on single and double tagged Ethernet traffic on the bridge domain and how to configure the source and host ports:
! Configuration on the bridge-domain Router(config)# bridge-domain 30 Router(config-bdomain)# ip igmp snooping ! Configuration on port 1 Router(config)# interface gi 36/1 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 50 second-dot1q 10 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress pop 2 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 ! Configuration on port 2 Router(config)# interface gi 36/2 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 200 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress pop 1 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 ! Configuration on port 3 Router(config)# interface gi 36/5 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 100 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress pop 1 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30The following example shows how to enable IGMP snooping on double tagged Ethernet traffic on the bridge domain and how to configure the source and host ports::
! Configuration on the bridge-domain Router(config)# bridge-domain 30 Router(config-bdomain)# ip igmp snooping ! Configuration on port 1 Router(config)# interface gi 36/1 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 10 second-dot1q 20 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress pop 2 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 ! Configuration on port 2 Router(config)# interface gi 36/5 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 100 second-dot1q 20 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress pop 2 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 ! Configuration on port 3 Router(config)# interface gi 36/6 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 101 second-dot1q 20 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress pop 2 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30Leaving a Multicast Group
The router sends periodic multicast general queries, and the CPT system forwards these queries through all ports in the bridge domain. Interested hosts respond to the queries. If at least one host in the bridge domain wants to receive multicast traffic, the router continues forwarding the multicast traffic to the bridge domain. The CPT system forwards multicast group traffic only to those hosts listed in the forwarding table for that IP multicast group maintained by IGMP snooping.
When hosts want to leave a multicast group, they can leave without sending a message, or they can send a leave message. When the CPT system receives a leave message from a host, it sends a group-specific query to learn if any other devices connected to that interface are interested in traffic for the specific multicast group. The CPT system then updates the forwarding table for that MAC group so that only those hosts interested in receiving multicast traffic for the group are listed in the forwarding table. If the router receives no reports from a bridge domain, it removes the group for the bridge domain from its IGMP cache.
Immediate Leave
The Immediate Leave feature is only supported on IGMP version 2 hosts. The CPT system uses IGMP Snooping Immediate Leave feature to remove an interface from the forwarding table, which sends a leave message without the CPT system sending group-specific queries to the interface. The VLAN interface is pruned from the multicast tree for the multicast group specified in the original leave message. The Immediate Leave feature ensures optimal bandwidth management for all hosts on a switched network, even when multiple multicast groups are simultaneously in use.
NoteYou should only use the Immediate Leave feature on bridge domains where a single host is connected to each port. If this feature is enabled on bridge domains where more than one host is connected to a port, some hosts might get dropped.
DLP-J218 Enabling or Disabling IGMP Immediate Leave Using Cisco IOS Commands
ProcedureWhen you enable the IGMP Immediate Leave feature, the CPT system immediately removes a port when it detects an IGMP version 2 leave message on that port. You should use the Immediate Leave feature only when there is a single receiver present on every port in the bridge domain.
NoteThe Immediate Leave feature is supported only on IGMP version 2 hosts.
Purpose This procedure enables or disables IGMP Immediate Leave feature using Cisco IOS commands. Tools/Equipment None Prerequisite Procedures DLP-J217 Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands Required/As Needed As needed Onsite/Remote Remote Security Level None Examples:
To disable the IGMP Immediate Leave feature on a bridge domain, use the no ip igmp snooping immediate-leave global configuration command.
The following example shows how to enable IGMP Immediate Leave feature for bridge-domain130:
Router# configure terminal Router(config)# bridge-domain 130 Router(config-bdomain)# ip igmp snooping immediate-leave Router(config-bdomain)# endIGMP Report Suppression
NoteIGMP report suppression is supported only when the multicast query has IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 reports. This feature is not supported when the query includes IGMPv3 reports.
The CPT system uses IGMP report suppression to forward only one IGMP report per multicast router query, to multicast devices. When IGMP router suppression is enabled (the default), the CPT system sends the first IGMP report from all hosts for a group, to all the multicast routers. The CPT system does not send the remaining IGMP reports for the group to the multicast routers. This feature prevents duplicate reports from being sent to the multicast devices.
If the multicast router query includes requests only for IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 reports, the CPT system forwards only the first IGMPv1 or IGMPv2 report from all hosts for a group to all the multicast routers.
If the multicast router query also includes requests for IGMPv3 reports, the CPT system forwards all IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3 reports for a group to the multicast devices.
If you disable IGMP report suppression, all IGMP reports are forwarded to the multicast routers.
- DLP-J219 Disabling IGMP Report Suppression Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J220 Configuring a Static Multicast Router Port Using Cisco IOS Commands
- DLP-J230 Viewing IGMP Configuration Using Cisco IOS Commands
DLP-J219 Disabling IGMP Report Suppression Using Cisco IOS Commands
Procedure
NoteIGMP report suppression is supported only when the multicast query has IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 reports. This feature is not supported when the query includes IGMPv3 reports.
IGMP report suppression is enabled by default. When it is enabled, the CPT system forwards only one IGMP report per multicast router query. When report suppression is disabled, all IGMP reports are forwarded to the multicast routers. To re-enable IGMP report suppression, use the ip igmp snooping report-suppression command in the bridge domain configuration mode.
Purpose This procedure disables IGMP report suppression using Cisco IOS commands. Tools/Equipment None Prerequisite Procedures DLP-J217 Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands Required/As Needed As needed Onsite/Remote Remote Security Level None DLP-J220 Configuring a Static Multicast Router Port Using Cisco IOS Commands
ProcedureTo add a static connection to a multicast router port, use the ip igmp snooping mrouter EFP configuration command on the CPT system. To remove a static multicast router port from the bridge domain, use the no ip igmp snooping mrouter configuration command.
NoteStatic connections to multicast routers are supported only at the EFP.
Purpose This procedure enables a static connection to a multicast router using Cisco IOS commands. Tools/Equipment None Prerequisite Procedures DLP-J217 Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping Using Cisco IOS Commands Required/As Needed As needed Onsite/Remote Remote Security Level None Examples:
The following example shows how to enable a static connection to a multicast router:
Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet4/2 Router(config-if)# service instance 20 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 20 Router(config-if-srv)# ip igmp snooping mrouterThe following example shows how to disable a static connection to a multicast router:
Router(config)# interface TenGigabitEthernet4/2 Router(config-if)# service instance 20 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# no ip igmp snooping mrouter
NoteTo add a static multicast router port to the EFP using CTC, see Step 6.e of NTP-J68 Configuring IGMP Snooping Using CTC.
DLP-J230 Viewing IGMP Configuration Using Cisco IOS Commands
ProcedureExamples
The following example displays the output of the show ip igmp snooping [vlan bridge-domain ID ] command.
Router# show ip igmp sn vlan 2Global IGMP Snooping configuration: ------------------------------------------- IGMP snooping Oper State : Enabled IGMPv3 snooping (minimal) : Enabled Report suppression : Enabled TCN solicit query : Disabled Robustness variable : 2 Last member query count : 2 Last member query interval : 1000 Check TTL=1 : No Check Router-Alert-Option : No Vlan 2 ----------------------- IGMP snooping Admin State : Enabled IGMP snooping Oper State : Enabled IGMPv2 immediate leave : Disabled Report suppression : Enabled Robustness variable : 2 Last member query count : 2 Last member query interval : 1000 Check TTL=1 : Yes Check Router-Alert-Option : Yes Query Interval : 0 Max Response Time : 10000The following example displays the output of the show ip igmp snooping groups command.
Router# show ip igmp snooping groupsFlags: I -- IGMP snooping, S -- Static, P -- PIM snooping, A -- ASM mode Vlan Group/source Type Version Port List ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 224.1.1.1 I v2 Te7/4 Te5/2 Gi41/1 Gi41/44 Gi51/1 Gi51/44 Te4/2The following example displays the output of the show ip igmp snooping groups vlan command.
Router# show ip igmp snooping groups vlan 2Flags: I -- IGMP snooping, S -- Static, P -- PIM snooping, A -- ASM mode Vlan Group/source Type Version Port List ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 224.1.1.1 I v2 Te7/4 Te5/2 Gi41/1 Gi41/44 Gi51/1 Gi51/44 Te4/2The following example displays the output of the show ip igmp snooping groups vlan bridge-domain ID [ip_address] command.
Router# show ip igmp snooping groups vlan 2 224.1.1.1Flags: I -- IGMP snooping, S -- Static, P -- PIM snooping, A -- ASM mode Vlan Group/source Type Version Port List ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 224.1.1.1 I v2 Te7/4 Te5/2 Gi41/1 Gi41/44 Gi51/1 Gi51/44 Te4/2The following example displays the output of the show ip igmp snooping mrouter command.
Router# show ip igmp snooping mrouterVlan ports ---- ----- 2 Te4/4(dynamic)The following example displays the output of the show ip igmp snooping mrouter vlan 2 command.
Router# show ip igmp snooping mrouterVlan ports ---- ----- 2 Te4/4(dynamic)The following example shows the output of the show ip igmp snooping querier command.
Router# show ip igmp snooping querierVlan IP Address IGMP Version Port ------------------------------------------------------------- 2 10.10.10.1 v2 Te4/4The following example shows the output of the show ip igmp snooping querier [vlan bridge-domain ID ] command.
Router# show ip igmp snooping querier vlan 2IP address : 10.10.10.1 IGMP version : v2 Port : Te4/4 Max response time : 10sNTP-J68 Configuring IGMP Snooping Using CTC
Procedure
Purpose This procedure explains how to configure IGMP Snooping, Immediate Leave, Report Suppression, and IGMP Static Router Port using CTC. Tools/Equipment None Prerequisite Procedures Create an Ethernet Virtual Private LAN EVC circuit with the following conditions: To create an EVC circuit, see DLP-J2 Create an EVC Circuit Using CTC.
Required/As Needed As needed Onsite/Remote Remote Security Level None
Step 1 Complete the NTP-J22 Log into CTC procedure at a node where you want to configure IGMP snooping. Step 2 In node view, click the Layer2+ tab. Step 3 Click Carrier Ethernet. Step 4 From the list of Ethernet Virtual Circuits (EVCs), select an Ethernet Virtual Private LAN EVC circuit to configure IGMP snooping. Step 5 Click Edit. The Edit Circuit dialog box appears. Step 6 In the IGMP Snooping tab, specify the settings for the bridge domain.
Step 7 To view the IGMP configuration, refer to the procedure explained in DLP-J56 Open the Cisco IOS Configuration Mode and View the Feature Configuration Details Using CTC.
IGMP Proxy Reporting
IGMP supports proxy reporting for IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 messages to handle group-specific queries. These queries are not sent downstream, but the CPT system does respond to them directly. When the CPT system receives a group-specific query, the CPT system terminates the query and sends an IGMP proxy report if there is a receiver for the group. There is no proxy reporting for IGMPv3 messages. For IGMPv3, a group-specific query or a group source-specific query is flooded to all VLAN member ports. The database for the IGMPv3 membership report is built based on the reports received.
Host reports responding to a specific query can be suppressed by the report suppression feature. Report suppression is supported for IGMPv1, IGMPv2 and IGMPv3 messages. With report suppression enabled (by default), when the CPT system receives a general query, the CPT system starts a suppression cycle for reports from all hosts to each group or channel. Only the first report to the discovered multicast routers are forwarded; the rest of the reports are suppressed. For IGMPv1 and IGMPv2, the time of suppression is the report response time indicated in the general query message. For IGMPv3, suppression occurs for the entire general query interval.L2 Address Aliasing Issue
The IGMP snooping forwarding table is based on L2 address. Since multiple IP addresses can map to the same L2 address, an L2 address aliasing can occur. For example, IP addresses 225.1.1.1 and 226.1.1.1 map to the same MAC address 01005E010101 which results in L2 address aliasing.
IGMP Snooping Interaction with LAG
A link aggregation (LAG) interface can be added to a bridge domain, which has IGMP snooping enabled.
The following example shows how to configure the source port, which is part of the LAG interface that is a member of the bridge domain that has IGMP snooping enabled.
Configuration on the bridge-domain Router(config)# bridge-domain 30 Router(config-bdomain)# ip igmp snooping Configuration on port 1 Router(config)# interface port-channel 10 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 Router(config)# interface ten 6/1 Router(config-if)# channel-group 10 Router(config)# interface ten 6/2 Router(config-if)# channel-group 10 Configuration port 2 Router(config)# interface gi36/2 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 20 second-dot1q 30 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress pop 2 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 Configuration on port 3 Router(config)# interface gi36/3 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 40 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30The following example shows how to configure the receiver port, which is part of the LAG interface that is a member of the bridge domain that has IGMP snooping enabled.
Configuration on the bridge-domain Router(config)# bridge-domain 30 Router(config-bdomain)# ip igmp snooping Configuration on port 1 Router(config)# interface ten 6/1 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 10 second-dot1q 30 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress pop 2 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 Configuration port 2 Router(config)# interface port-channel 10 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30 Router(config)# interface gi36/1 Router(config-if)# channel-group 10 Router(config)# interface gi36/2 Router(config-if)# channel-group 10 Configuration on port 3 Router(config)# interface gi36/5 Router(config-if)# service instance 10 ethernet Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 40 Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 30High Availability
The multicast group tables are synchronized between the active and standby fabric cards. If an active fabric reloads, then the standby fabric card becomes active. Since, the multicast group tables are already synchronized, there is no traffic loss, unless the source or the receiver is not present on the card that reloaded.
NoteThe IGMP snooping feature does not interact with REP.
IGMP Statistics and Counters
An entry in a counter contains multicasting statistical information for the IGMP snooping capable CPT system. The equivalent IOS command to retrieve statistical information is show ip igmp snooping counters.
This information can be stored in the following counters:
- Tx General Queries—Number of general queries transmitted through an interface.
- Tx Group Specific Queries—Total group specific queries transmitted through an interface.
- Tx Reports—Total membership reports transmitted through an interface.
- Tx Leaves—Total leave messages transmitted through an interface.
- Rx General Queries—Total general queries received at an interface.
- Rx Group Specific Queries—Total group specific queries received at an interface.
- Rx Reports—Total membership reports received at an interface.
- Rx Leaves—Total leave messages received at an interface.
- Rx Valid Packets—Total valid IGMP packets received at an interface.
- Rx Invalid Packets—Total number of invalid IGMP packets that are received at an interface.
The following example shows the statistical information using the show ip igmp snooping counters command.
Router> show ip igmp snooping counterspacket queue maximum size: 20000 packet queue current size: 0 packet queue peak size: 0 packet queue drop count: 0 ---- Vlan 1 ---- Counters of group "IGMP snooping counters " overall there are 15 counters Type | Value | Ovr | Und ---------------------------------------------------+------------+-----+---- RX processed Query Count | 0 | | RX processed Group Specific Query | 0 | | RX processed Join | 787120 | | RX processed Leave | 0 | | RX processed Total Valid Packets | 782 | | RX processed Other Packets | 0 | | RX Packets dropped for sanity errors | 0 | | RX Packets dropped for checksum errors | 0 | | RX Packets dropped for header length errors | 0 | | RX Packets dropped for other errors | 0 | | RX processed Topology change notification | 0 | | TX processed Query Count | 0 | | TX processed Group Specific Query | 0 | | TX processed Join | 0 | | TX processed Leave | 0 | | Counters of group "IGMP snooping V3 counters " overall there are 18 counters RX processed V3 AllOW NEW | 0 | | RX processed V3 BLOCK OLD | 0 | | Type | Value | Ovr | Und ---------------------------------------------------+------------+-----+---- RX processed V3 MODE IS INCLUDE | 0 | | RX processed V3 MODE IS EXCLUDE | 0 | | RX processed V3 CHANGE TO INCLUDE | 0 | | RX processed V3 CHANGE TO EXCLUDE | 0 | | RX processed V3 Query | 782 | | RX processed V3 Group Specific Query | 0 | | RX processed V3 GSS Query | 0 | | TX processed V3 ALLOW NEW | 0 | | TX processed V3 BLOCK OLD | 0 | | TX processed V3 MODE IS INCLUDE | 0 | | TX processed V3 MODE IS EXCLUDE | 0 | | TX processed V3 CHANGE TO INCLUDE | 0 | | TX processed V3 CHANGE TO EXCLUDE | 0 | | TX processed V3 Query | 0 | | TX processed V3 Group Specific Query | 0 | | TX processed V3 GSS Query | 0 | |Alarms
The MCAST-MAC-TABLE-FULL condition is raised from IGMP snooping at the card level. The CPT system supports a maximum of 2000 multicast groups. The MCAST-MAC-TABLE-FULL condition is raised when the multicast table is full and a new join request is received. This table is cleared when at least one entry gets cleared from the multicast table after the alarm is raised.

 Feedback
Feedback