-
Cisco IP Solution Center MPLS VPN User Guide, 4.1
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Getting Started
-
Provisioning Unmanaged Multi-VRF CE
-
Creating Resource Pools
-
Defining VPNs and CERCs
-
MPLS VPN Service Policies
-
MPLS VPN Service Requests
-
Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
-
Provisioning MVRFCE PE-CE Links
-
Provisioning Management VPN
-
Provisioning Cable Services
-
Provisioning Carrier Supporting Carrier
-
Provisioning Multiple Devices
-
Spanning Multiple Autonomous Systems
-
Creating Custom MPLS Reports
-
IP Solution Center - MPLS VPN
-
Service Request Transition States
-
Troubleshooting MPLS VPN
-
Table Of Contents
Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
Defining a VPN for the PE-CE Link
Creating MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Policies
Creating a PE-CE Service Policy
Creating a PE-NoCE Service Policy
Creating MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Requests
Creating a PE-CE Service Request
Creating a PE-NoCE Service Request
Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
This chapter describes how to configure MPLS VPN PE-CE links in the IP Solution Center (ISC) provisioning process. This chapter contains the following major sections:
•
Creating MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Policies
•
Creating MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Requests
MPLS VPN PE-CE Link Overview
This section contains the following sections:
To provision an MPLS VPN service in ISC, you must first create an MPLS VPN Service Policy. In ISC, a Service Policy is a set of default configurations for creating and deploying a Service Request.
ISC supports two MPLS VPN Service Policy Types: Regular PE-CE and MVRFCE PE-CE. The following scenarios focus on the Regular PE-CE Policy Type.
The Regular PE-CE Policy Type is a normal PE to CE link between two devices. This Policy Type has two options:
•
CE Present enabled (One PE with one CE; two devices)
•
CE Present disabled (PE Only with no CE; one device)
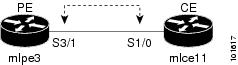
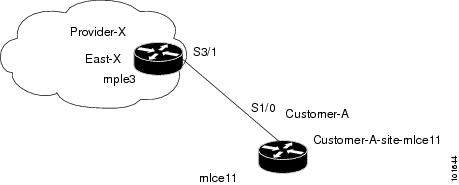
Figure 7-1 shows an example of a normal PE to CE link between two devices.
Figure 7-1 PE to CE link with CE Present
In a PE to CE link with CE Present enabled, interfaces S3/1 and S1/0 are configured as an MPLS VPN link in the Service Request process.
Figure 7-2 shows an example of a PE Only link with no CE.
Figure 7-2 PE to CE link with No CE
In a PE to CE link with CE Present disabled, interface FE0/0 is configured as an MPLS VPN link in the Service Request process.
Network Topology
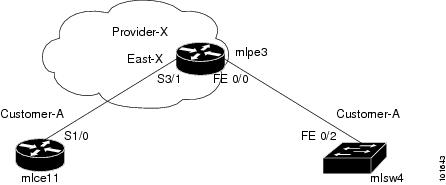
Figure 7-3 shows an overview of the network topology in which the MPLS VPN PE-CE links are created.
Figure 7-3 Network Topology for MPLS VPN PE-CE Scenarios.
The network topology in Figure 7-3 illustrates the lab environment of a service provider (Provider-X) and one customer (Cust-A). There is one Region (East-X) and one PE (mlpe3.cisco.com). Each customer device (one CE and one CLE) represents a Site (mlce11-Site and mlsw4-Site).
Prerequisite Tasks
Before you can create a Service Policy in ISC, you must complete the following Inventory Management tasks:
Step 1
Set up a Customer with a Site.
Step 2
Setup a Provider with a Region.
Step 3
Import, create, or discover Devices.
Step 4
Create CPE and PE.
Step 5
Collect Configurations.
Step 6
Create Resource Pools and CE routing communities (CERC).
Step 7
Define a VPN.
Infrastructure Data
In the subsequent PE-CE scenarios, the following infrastructure data is used:
•
Provider: Provider-X
•
Region: East-X
•
AS#: 99
•
PE: mlpe3.cisco.com
•
Device Role: PE POP
•
Customer: Cust-A
•
Site: Cust-A-Site- mlce11
•
CE: mlce11.cisco.com
•
Device Role: CPE
•
IP Address Pool:
–
Name: Provider-X-East-X
–
Type: Region
–
Start: 25.5.0.0
–
Mask: 30
–
Size: 16384
•
Route Distinguisher Pool:
–
Name: 99:PROVIDER-X
–
Start: 50000
–
Size: 10000
•
Route Target Pool:
–
Name: 99:PROVIDER-X
–
Start: 50000
–
Size: 10000
•
VPN
–
Definition: east-xVPN
–
See: Defining a VPN for the PE-CE Link
Defining a VPN for the PE-CE Link
During service deployment, ISC generates the Cisco IOS commands to configure the logical VPN relationships.
At the beginning of the provisioning process, before creating a Service Policy, a VPN must be defined within ISC. The first element in a VPN definition is the name of the VPN.
To create a VPN Name, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to ISC.
Step 2
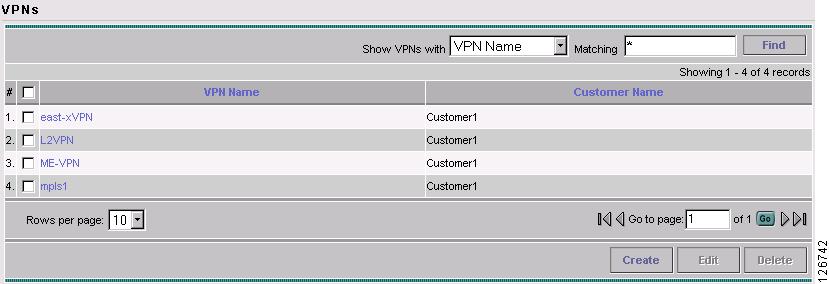
Go to Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > VPNs.
The VPN window appears, as shown in Figure 7-4.
Figure 7-4 VPNs
Step 3
Click Create to create a VPN.
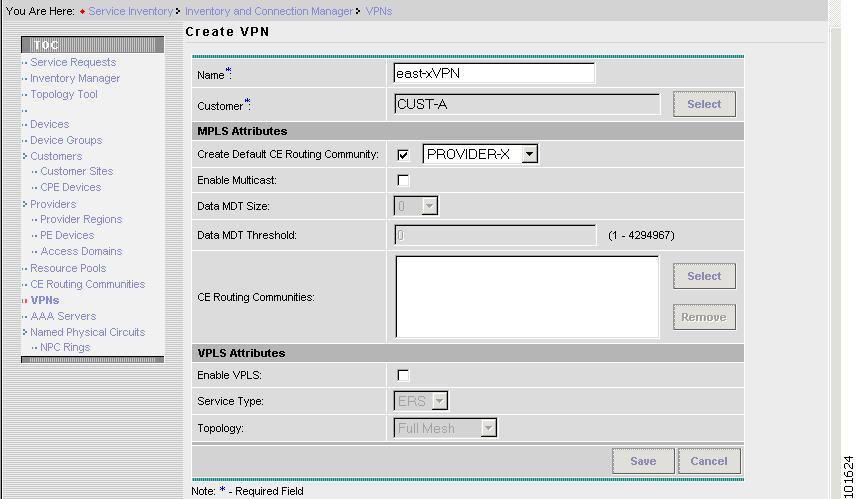
The Create VPN window appears, as shown in Figure 7-5.
Figure 7-5 Create VPN
Step 4
Edit the following attributes:
•
Name: Enter the vpn name. (east-xVPN)
•
Customer: Click Select.
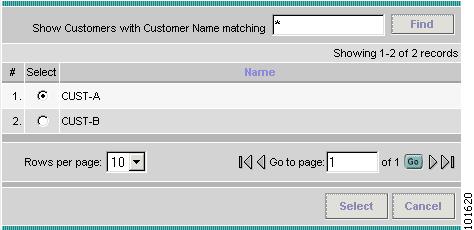
The Select Customer window appears, as shown in Figure 7-6.
Figure 7-6 Choose Customer
Step 5
Choose a customer and click Select.
Step 6
Click Save.
The VPNs window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-7.
Figure 7-7 VPNs
The VPN Name (east-xVPN) is associated with the Customer (Cust-A) in this new VPN definition.
Creating MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Policies
This section contains the following sections:
•
PE-CE Service Policy Overview
•
Creating a PE-CE Service Policy
•
Creating a PE-NoCE Service Policy
PE-CE Service Policy Overview
Figure 7-8 shows an example of the PE-CE link that is defined in the PE-CE Service Policy scenario.
Figure 7-8 PE-CE Topology
Creating a PE-CE Service Policy
To create a PE-CE Service Policy, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to ISC.
Step 2
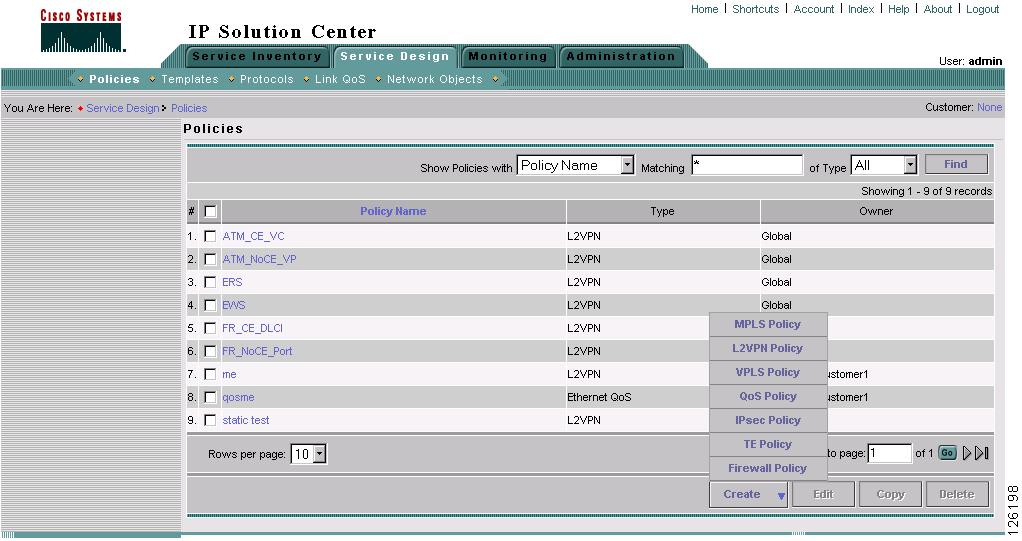
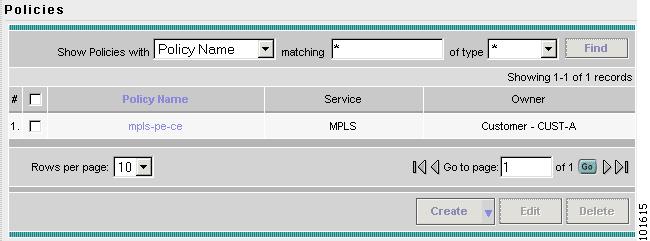
Go to Service Design > Policies.
The Policies window appears, as shown in Figure 7-9.
Figure 7-9 Policies
Step 3
From the Create drop-down list, choose MPLS Policy.
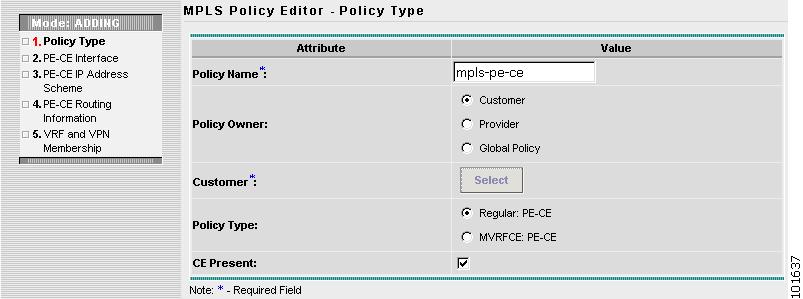
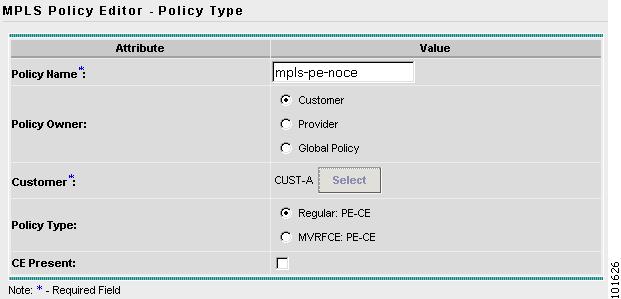
The MPLS Policy Editor - Policy Type window appears, as shown in Figure 7-10.
Figure 7-10 MPLS Policy Editor - Policy Type
Step 4
Edit the following attributes:
•
Policy Name: Enter the policy name.
•
Policy Owner: Choose the Policy Owner.
•
Customer: See Step 5.
•
Policy Type: Choose the Policy Type.
•
CE Present: Choose CE Present.
Step 5
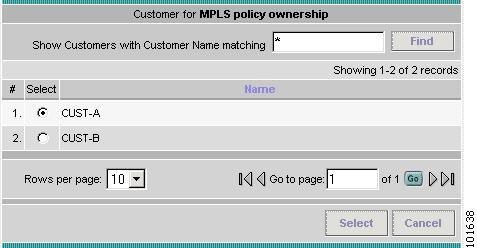
Click Select to specify a Customer.
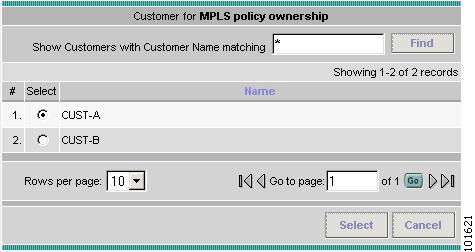
The Customer for MPLS Policy ownership window appears, as shown in Figure 7-11.
Figure 7-11 Customer for MPLS Policy
Step 6
Choose a customer and click Select. (Cust-A)
Step 7
Click Next.
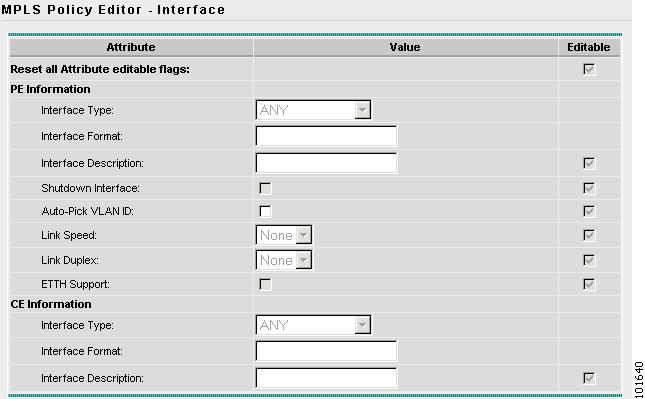
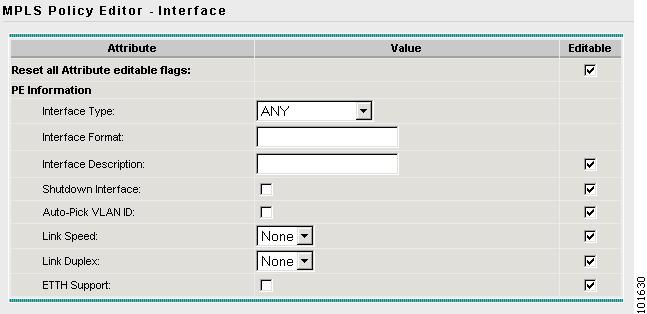
The MPLS Policy Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 7-12.
Figure 7-12 The MPLS Policy Editor - Interface
Step 8
Click Next to accept the defaults.
Note
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the Service Request process.
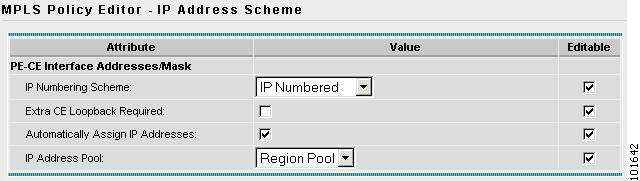
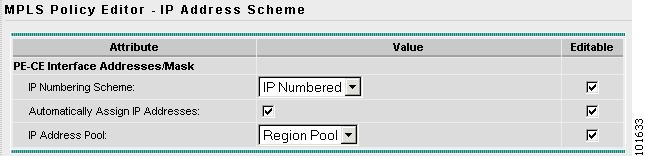
The MPLS Policy Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears, as shown in Figure 7-13.
Figure 7-13 The MPLS Policy Editor - IP Address Scheme
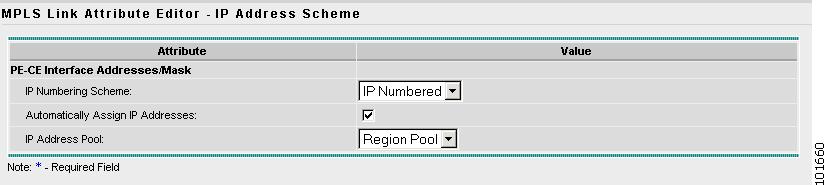
Step 9
Edit the following attributes:
•
IP Numbering Scheme: Choose an IP Numbering Scheme.
•
Automatically Assign IP Address: To have ISC automatically assign IP Addresses, click the check box.
•
IP Address Pool: Choose the IP Address Pool.
Step 10
Click Next.
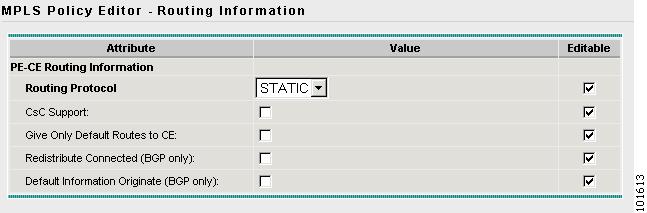
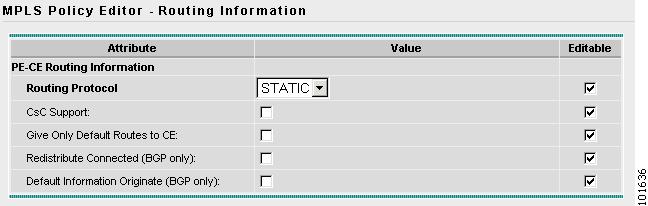
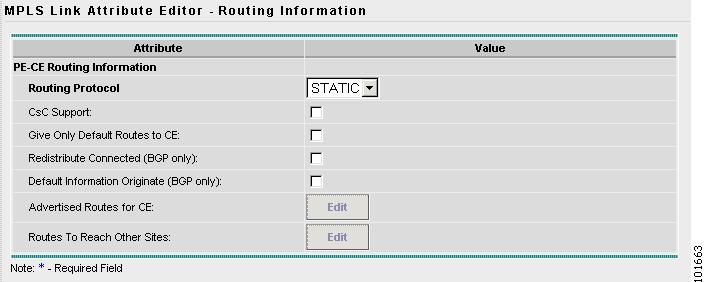
The MPLS Policy Editor - Routing Information window appears, as shown in Figure 7-14.
Figure 7-14 The MPLS Policy Editor - Routing Information
Step 11
Click Next to accept the defaults.
Note
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the Service Request process.
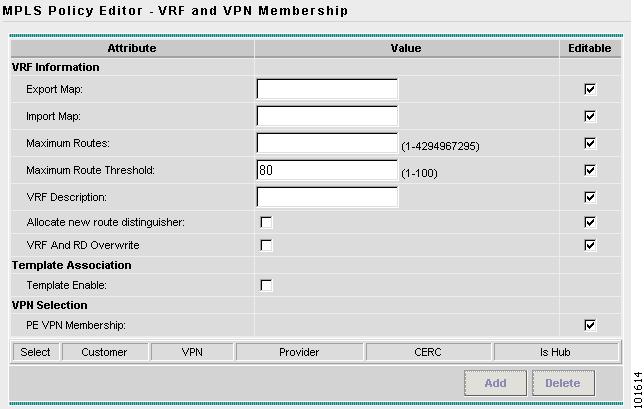
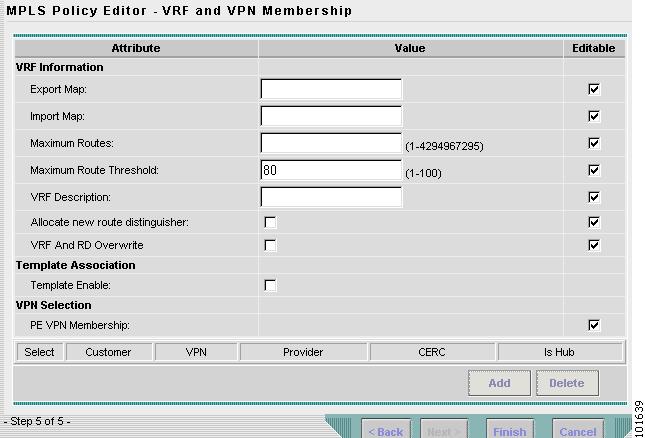
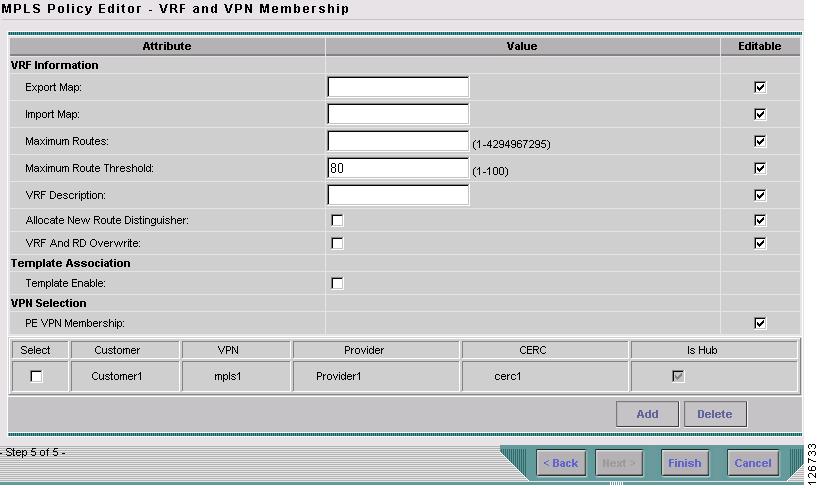
The MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window appears, as shown in Figure 7-15.
Figure 7-15 The MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership
Step 12
Click Next to accept the defaults.
Note
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the Service Request process.
Step 13
Click Finish.
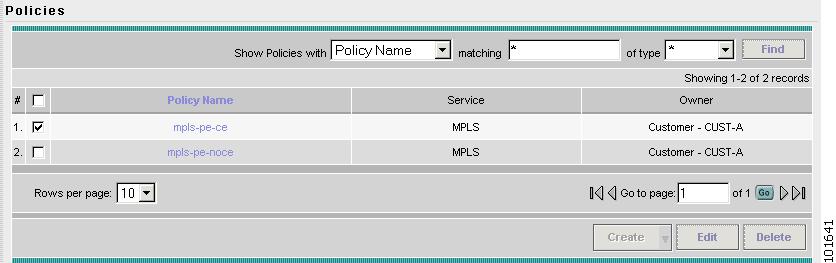
The Policies window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-16.
Figure 7-16 Policies
The MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Policy is complete.
Creating a PE-NoCE Service Policy
To create a PE-NoCE Service Policy, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to ISC.
Step 2
Go to Service Design > Policies.
The Policies window appears, as shown in Figure 7-17.
Figure 7-17 Policies
Step 3
From the Create drop-down list, choose MPLS Policy.
The MPLS Policy Editor - Policy Type window appears, as shown in Figure 7-18.
Figure 7-18 MPLS Policy Editor - Policy Type
Step 4
Edit the following attributes:
•
Policy Name: Enter the policy name.
•
Policy Owner: Choose the Policy Owner.
•
Customer: See Step 5.
•
Policy Type: Choose the Policy Type.
•
CE Present: Do not choose CE Present.
Step 5
Click Select to specify a Customer.
The Customer for MPLS Policy window appears, as shown in Figure 7-19.
Figure 7-19 Customer for MPLS Policy
Step 6
Choose a customer and click Select.
Step 7
Click Next.
The MPLS Policy Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 7-20.
Figure 7-20 The MPLS Policy Editor - Interface
Step 8
Click Next to accept the defaults.
Note
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the Service Request process.
The MPLS Policy Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears, as shown in Figure 7-21.
Figure 7-21 The MPLS Policy Editor - IP Address Scheme
Step 9
Edit the following attributes:
•
IP Numbering Scheme: Choose the IP Numbering Scheme.
•
Automatically Assign IP Address: To have ISC automatically assign IP Addresses, click the check box.
•
IP Address Pool: Choose the IP Address Pool.
•
Click Next.
Step 10
Click Next.
The MPLS Policy Editor - Routing Information window appears, as shown in Figure 7-22.
Figure 7-22 The MPLS Policy Editor - Routing Information
Step 11
Click Next to accept the defaults.
Note
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the Service Request process.
The MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window appears, as shown in Figure 7-23.
Figure 7-23 The MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership
Step 12
Accept the default attributes and choose Finish.
The Policies window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-24.
Figure 7-24 Policies
The MPLS VPN PE-NoCE Service Policy is complete.
Creating MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Requests
This section contains the following sections:
•
Creating a PE-CE Service Request
•
Creating a PE-NoCE Service Request
Creating a PE-CE Service Request
To create a PE-CE Service Request, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to ISC.
Step 2
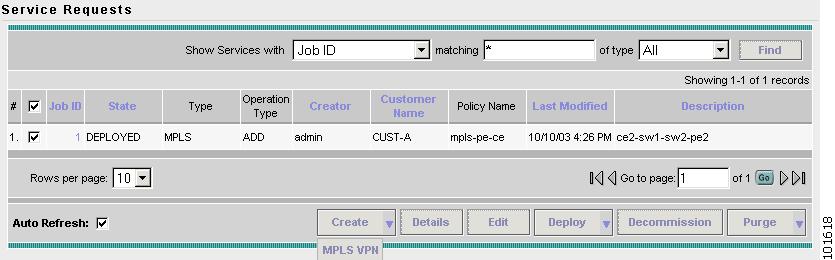
Go to Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Service Requests.
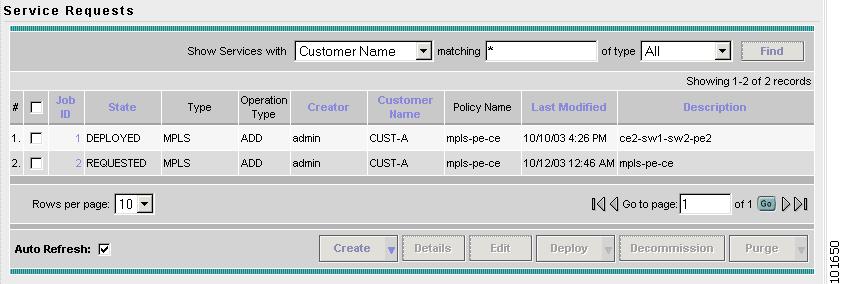
The Service Requests window appears, as shown in Figure 7-25.
Figure 7-25 Service Requests
Step 3
From the Create drop-down list, choose MPLS VPN.
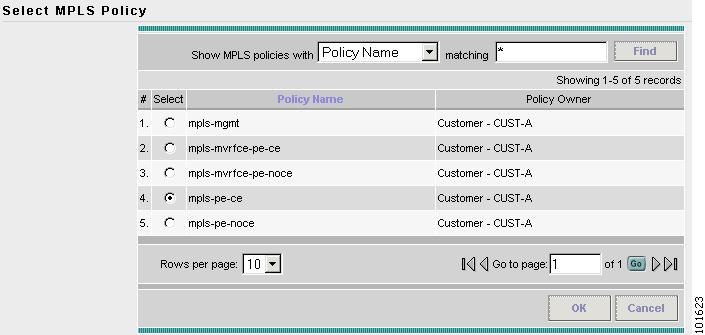
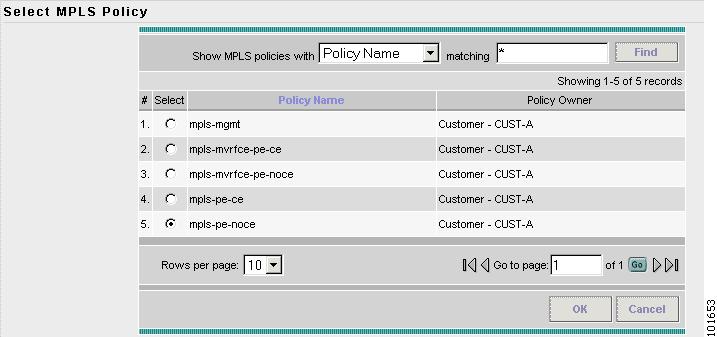
The Select MPLS Policy window appears, as shown in Figure 7-26.
Figure 7-26 Choose MPLS Policy
Step 4
Choose the MPLS Policy. (mpls-pe-ce)
Step 5
Click OK.
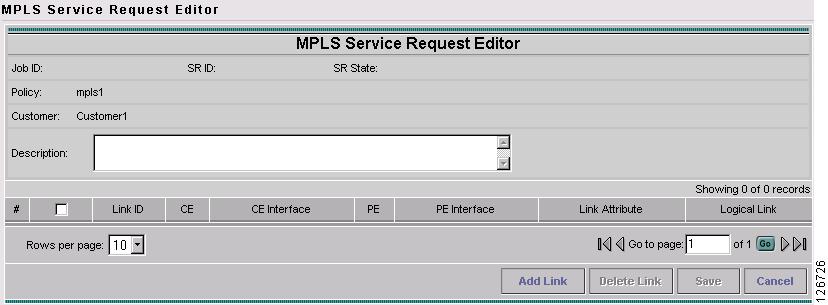
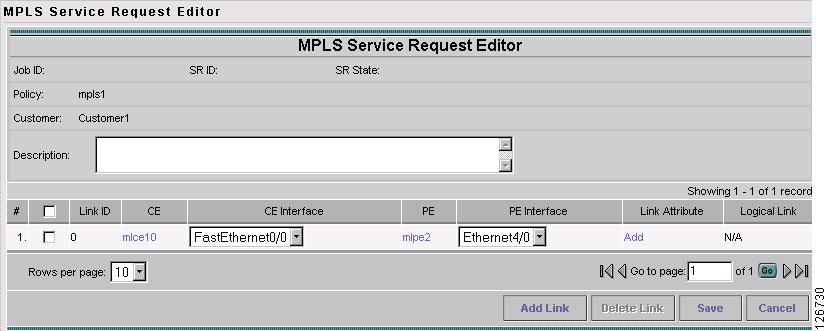
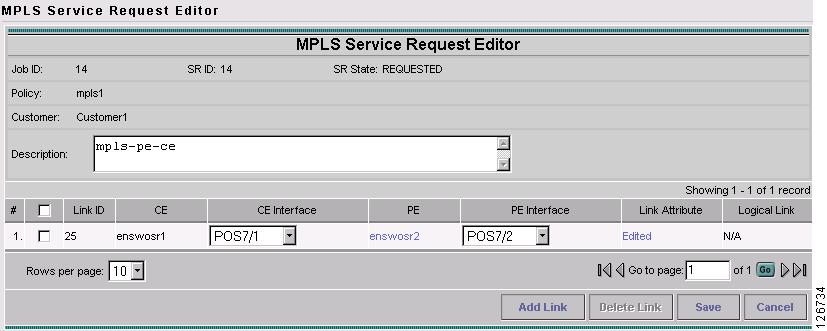
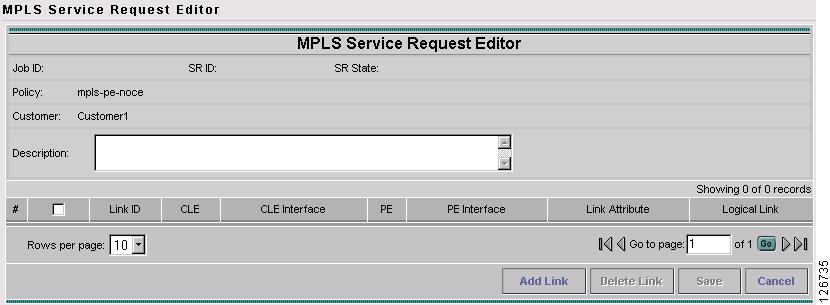
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 7-27.
Figure 7-27 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 6
Click Add Link.
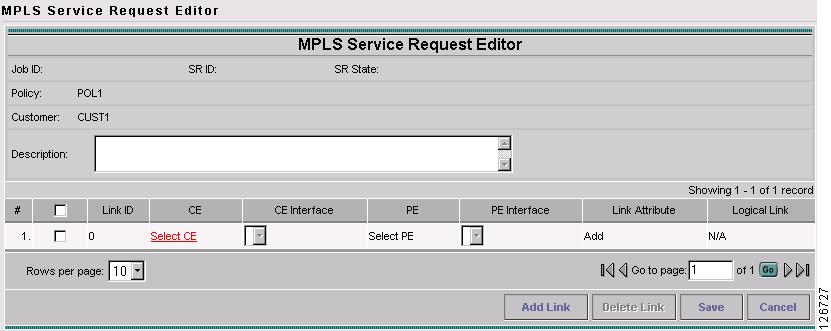
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 7-28.
Figure 7-28 MPLS Service Request Editor - Select CE
Step 7
Click Select CE.
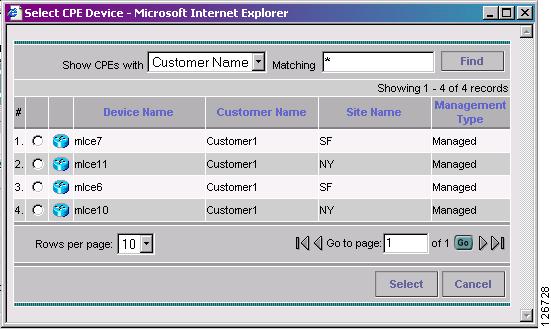
The CPE for MPLS VPN Link window appears, as shown in Figure 7-29.
Figure 7-29 CPE for MPLS VPN Link
Step 8
Choose the CPE device and click Select.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 9
Choose the CE Interface from the drop-down box.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 10
Click Select PE.
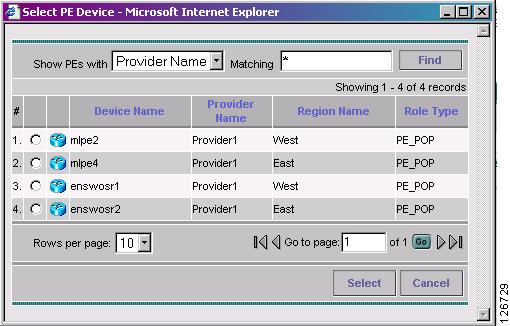
The PE for MPLS VPN Link window appears, as shown in Figure 7-30.
Figure 7-30 PE for MPLS VPN Link
Step 11
Choose the PE device and click Select.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 12
Choose the PE Interface from the drop-down box.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 13
Click Select PE.
The PE for MPLS VPN Link window appears, as shown in Figure 7-31.
Figure 7-31 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 14
Click Add in the Link Attribute cell.
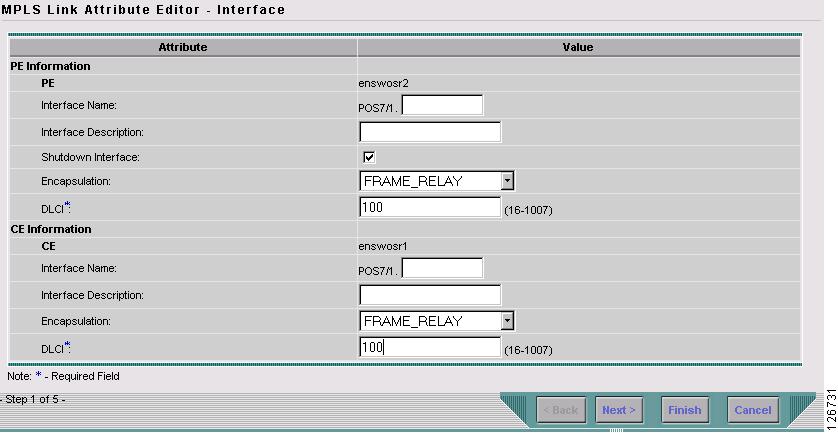
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 7-32.
Figure 7-32 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface
PE Information
Step 15
Encapsulation: Choose the PE Encapsulation from the drop-down box.
Step 16
DLCI: Enter the CE DLCI. (100)
CE Information
Step 17
Encapsulation: Choose the PE Encapsulation from the drop-down box.
Step 18
DLCI: Enter the PE DLCI. (100)
Step 19
Click Next.
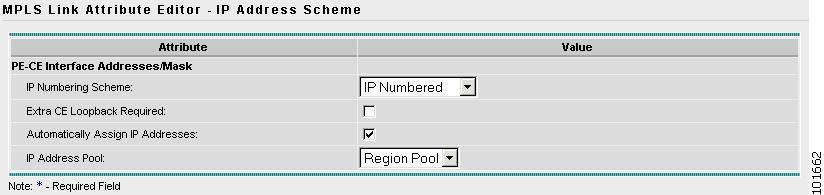
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears, as shown in Figure 7-33.
Figure 7-33 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme
Step 20
Accept the defaults and click Next.
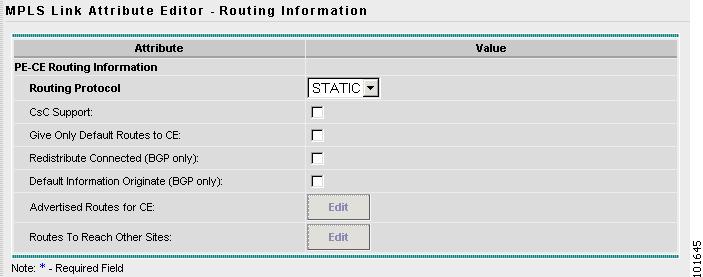
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-34.
Figure 7-34 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information
Step 21
Accept the defaults and click Next.
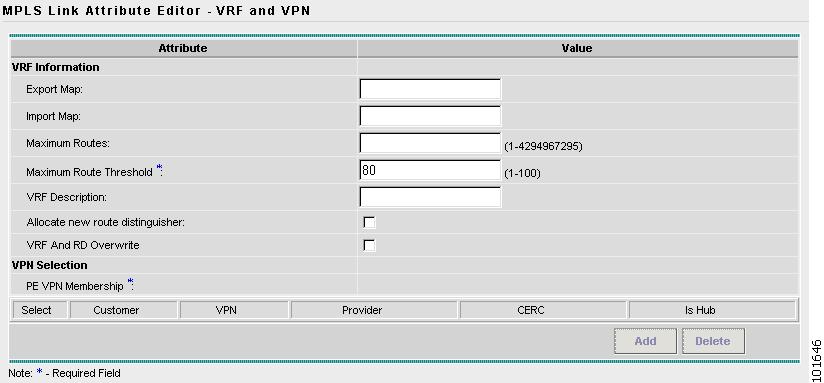
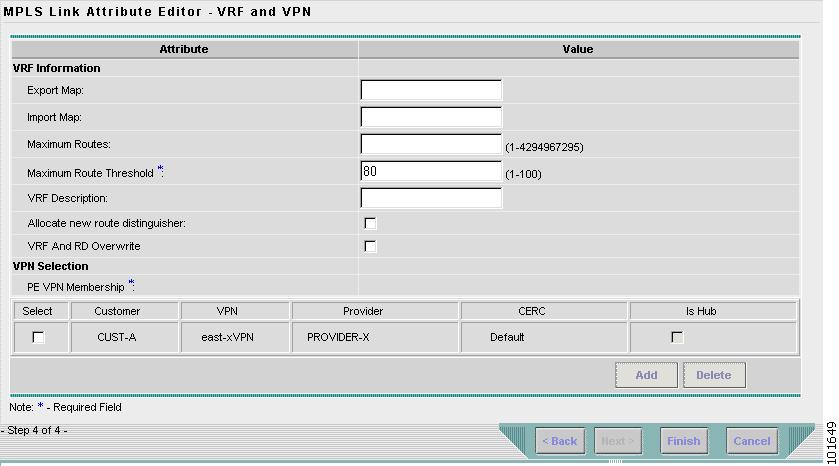
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN window appears, as shown in Figure 7-35.
Figure 7-35 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN
Step 22
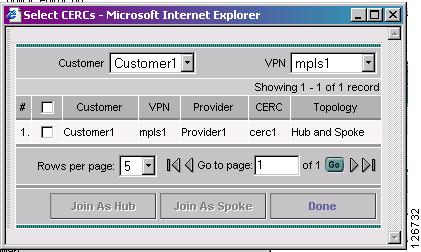
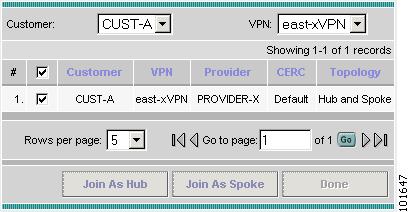
Click Add to join VPN. The Select CERCs window appears as show in Figure 7-36.
Figure 7-36 Select CERCs Window
Step 23
Choose a customer from the drop-down list.
Step 24
Choose a VPN from the drop-down lidt.
Step 25
Choose a VPN from the list.
Step 26
Click Join As Hub or Join As Spoke.
Step 27
Click Done. The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-37.
Figure 7-37 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 28
Click Finish.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-38.
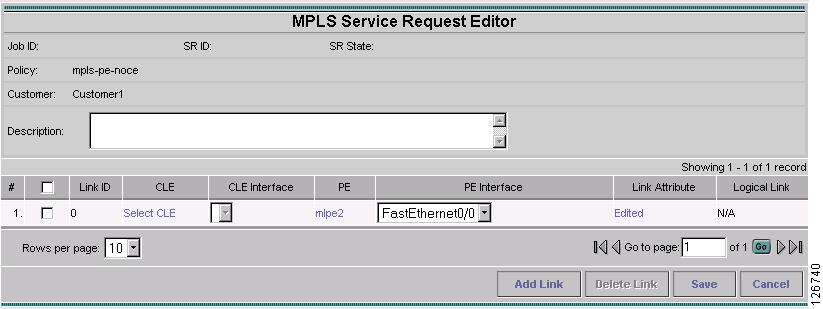
Figure 7-38 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 29
Enter the Service Request description and click Save. (mpls-pe-ce)
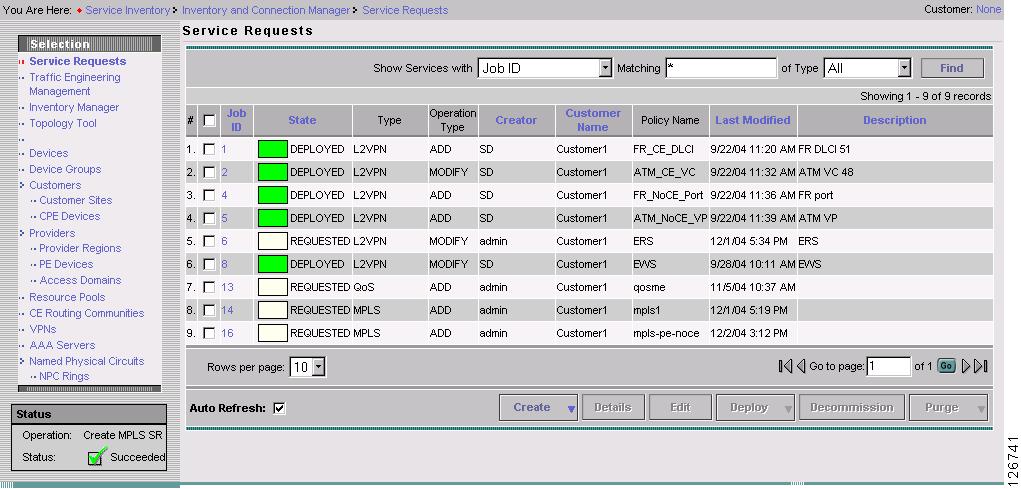
The MPLS Service Requests window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-39.
Figure 7-39 Service Request
The MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Request is in the Requested state and ready to deploy.
Creating a PE-NoCE Service Request
To create a PE-NoCE Service Request, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to ISC.
Step 2
Go to Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Service Requests.
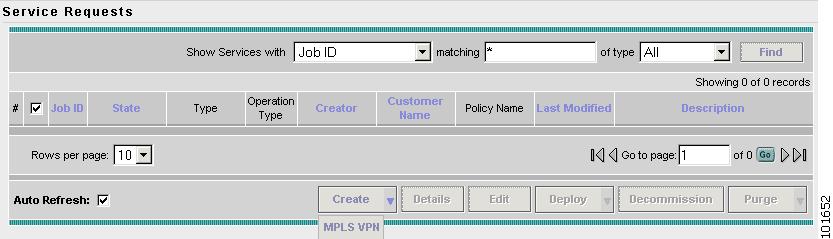
The Service Requests window appears, as shown in Figure 7-40.
Figure 7-40 Service Requests
Step 3
From the Create drop-down list, choose MPLS VPN.
The Select MPLS Policy window appears, as shown in Figure 7-41.
Figure 7-41 Select MPLS Policy
Step 4
Choose the MPLS Policy.
Step 5
Click OK.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 7-42.
Figure 7-42 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 6
Click Add Link.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 7-43.
Figure 7-43 MPLS Service Request Editor - Select CE
Step 7
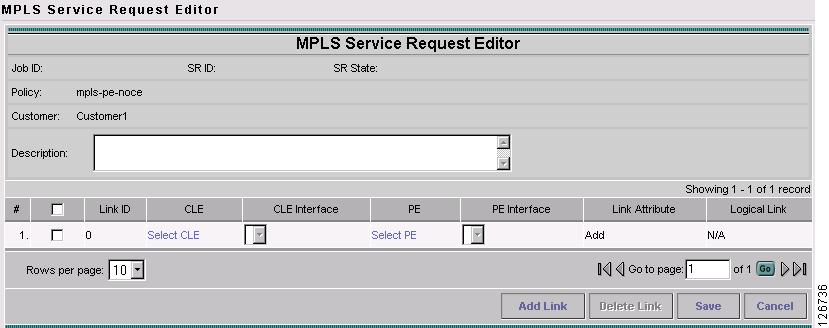
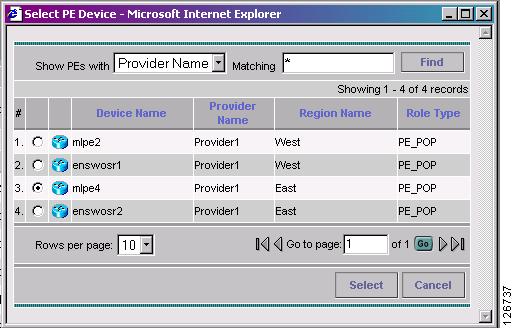
Click Select PE.
The PE for MPLS VPN Link window appears, as shown in Figure 7-44.
Figure 7-44 PE for MPLS VPN Link
Step 8
Choose the PE device and click Select.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
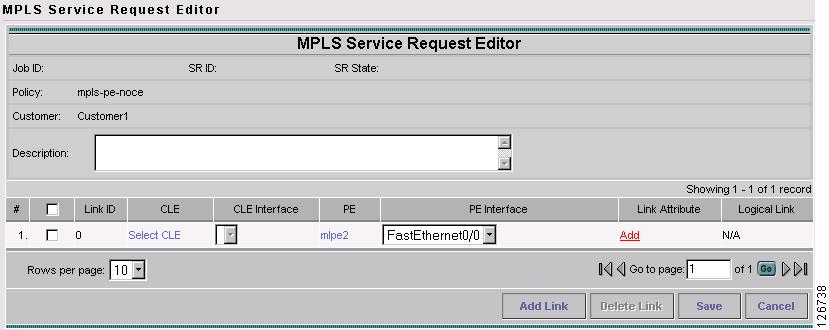
Step 9
Choose the PE Interface from the drop-down box.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 7-45.
Figure 7-45 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 10
Click Add in the Link Attribute cell.
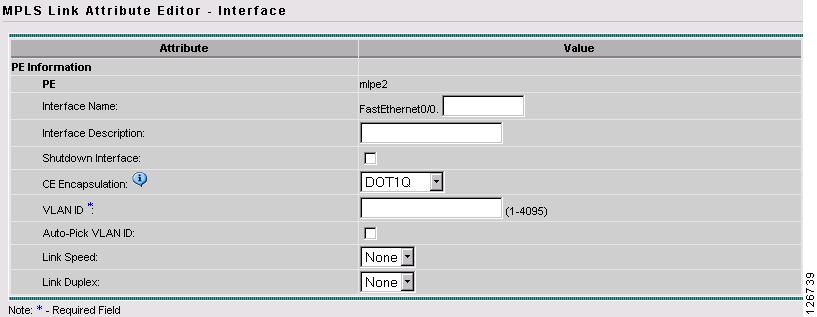
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 7-46.
Figure 7-46 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface
Step 11
Choose the CE Encapsulation from the drop-down list. (DOT1Q)
Note
This field is needed for deciding PE/UNI encapsulation.
Step 12
Click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears, as shown in Figure 7-47.
Figure 7-47 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme
Step 13
Accept the defaults and click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-48.
Figure 7-48 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information
Step 14
Accept the defaults and click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-49.
Figure 7-49 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN
Click Add to join the VPN.
The Join VPN dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 7-50.
Figure 7-50 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 15
Click the check box to choose the VPN. (Cust-A east-xVPN)
Step 16
Click Join as Hub or Join as Spoke. (Join as Spoke)
Click Done.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-51.
Figure 7-51 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 17
Click Finish.
The MPLS Service Requests Editor window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-52.
Figure 7-52 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 18
Enter the Service Request description and click Save. (mpls-pe-noce)
The MPLS Service Requests window reappears, as shown in Figure 7-53.
Figure 7-53 Service Request
The MPLS VPN PE-NoCE Service Request is ready to deploy.

 Feedback
Feedback