-
Cisco IP Solution Center MPLS VPN User Guide, 4.1
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Getting Started
-
Provisioning Unmanaged Multi-VRF CE
-
Creating Resource Pools
-
Defining VPNs and CERCs
-
MPLS VPN Service Policies
-
MPLS VPN Service Requests
-
Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
-
Provisioning MVRFCE PE-CE Links
-
Provisioning Management VPN
-
Provisioning Cable Services
-
Provisioning Carrier Supporting Carrier
-
Provisioning Multiple Devices
-
Spanning Multiple Autonomous Systems
-
Creating Custom MPLS Reports
-
IP Solution Center - MPLS VPN
-
Service Request Transition States
-
Troubleshooting MPLS VPN
-
Table Of Contents
Creating CE Routing Communities
Defining VPNs and CERCs
During service deployment, ISC generates the Cisco IOS commands to configure the logical VPN relationships.
At the beginning of the provisioning process, before creating a Service Policy, a VPN must be defined within ISC. The first element in a VPN definition is the name of the VPN.
This chapter describes how to define MPLS VPNs, IP Multicast VPNs, and CE Routing Communities (CERCs).
This chapter contain the following major sections:
•
Creating CE Routing Communities
Creating MPLS VPN
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Go to Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > VPNs.
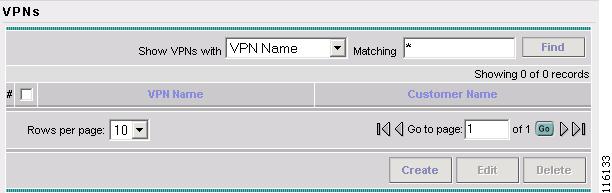
The VPN window appears, as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1 VPNs
Step 3
Click Create to create a VPN.
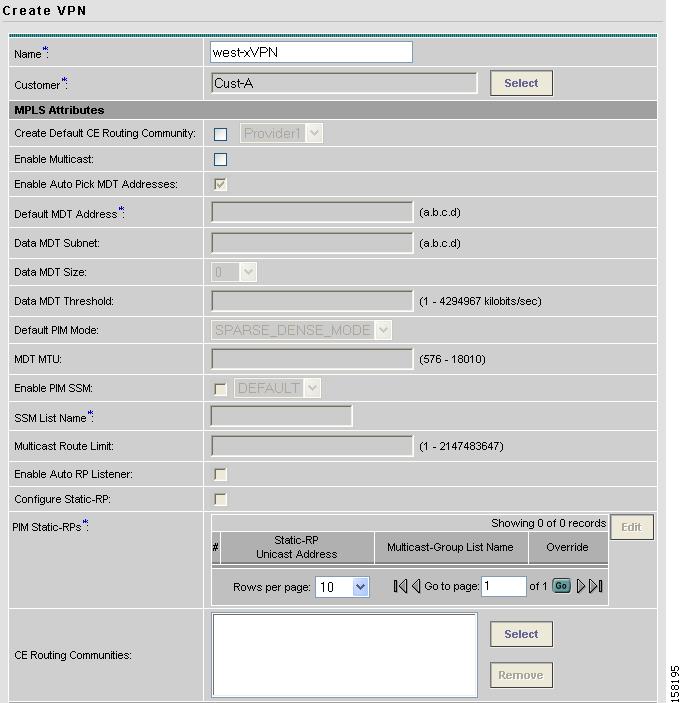
The Create VPN window appears, as shown in Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2 Create VPN
Step 4
Enter the VPN Name. (west-xVPN)
Step 5
For the Customer field, click Select.
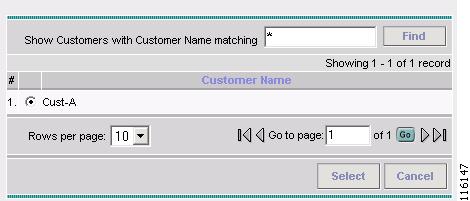
The Choose Customer window appears, as shown in Figure 4-3.
Figure 4-3 Choose Customer
Step 6
Choose a Customer and then click Select. (Cust-A)
The VPNs window reappears.
Step 7
To associate the VPN with a Provider, you have two options:
•
Go to Create Default CE Routing Community, then choose a Provider.
•
Choose a CE Routing Community, if one is already set up.
Note
To enable multicast for the VPN, see "Creating IP Multicast VPN".
Step 8
To save these changes, at the bottom of the window, click Save.
The VPN Name (west-xVPN) is associated with the Customer (Cust-A) in this new VPN definition.
Creating IP Multicast VPN
Step 1
To create an IP Multicast VPN, follow the procedure described in "Creating MPLS VPN" section to the place where you can enable multicast for the VPN.
Step 2
To enable multicast for the VPN, check Enable Multicast.
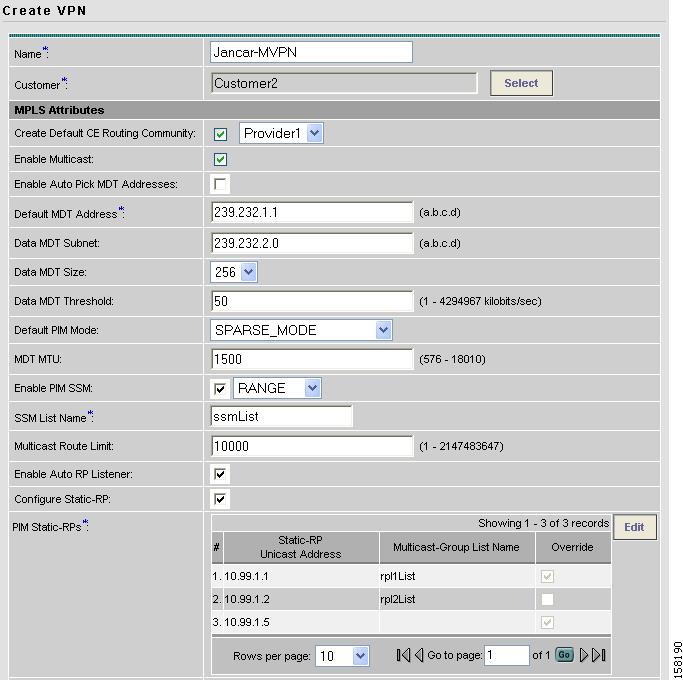
The current window will refresh with additional fields becoming active (see Figure 4-4).
Figure 4-4 Creating Multicast VPN
Step 3
For MDT (Multicast Distribution Tree) addresses, either accept the default (check box already checked) to enable the auto pick function, or uncheck the auto pick check box, then enter values in the next two fields:
Default MDT Address
Data MDT Subnet
Step 4
From the drop-down list, choose a value for Data MDT Size.
Step 5
In the next field, enter a valid value for Data MDT Threshold (1 - 4294967 kilobits/sec).
Step 6
For Default PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) Mode, choose a mode from the drop-down list:
SPARSE_MODE
SPARSE_DENSE_MODE
Tip
Multicast routing architecture allows the addition of IP multicast routing on existing IP networks. PIM is an independent unicast routing protocol. It can be operated in two modes: dense and sparse.
Step 7
In the next field, enter a valid value for MDT MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit).
Step 8
To enable PIM SSM (Source Specific Multicast), check the associated check box.
When you check the check box:
a.
The associated drop-down list goes active with the DEFAULT enumeration populated as the SSM default. This will create the following CLI: ip pim vrf <vrfName> ssm default.
b.
If you would like to associate an access-list number, or a named access-list, with SSM configuration, choose the RANGE enumeration from the SSM drop-down list instead of DEFAULT. This will create the following CLI: ip pim vrf <vrfName> ssm range {ACL# | named-ACL-name}.
Step 9
If you choose RANGE in the previous step, then the next field goes active for you to enter Access-list number or Access-list name.
Step 10
In the next field enter a valid value for the Multicast Route Limit (1 - 2147483647).
Step 11
To enable the auto RP (Rendezvous Point) listener function, check the associated check box.
Step 12
To configure Static-RPs, check the associated check box.
When you check this, the Edit option for PIM Static-RPs goes active.
Step 13
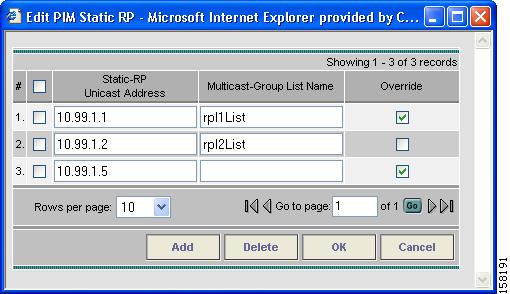
To edit, or add, PIM Static RPs (Rendezvous Points), click Edit.
The Edit PIM Static RPs window appears, see Figure 4-5).
Figure 4-5 Edit PIM Static RPs
Step 14
Complete all applicable fields in the Edit PIM Static RP window, then click OK.
These data now appear in the main Create VPN window (see Figure 4-4).
Step 15
To save your changes and add this Multicast VPN to you system, at the bottom of the window, click Save.
Creating CE Routing Communities
When you create a VPN, the ISC software creates one default CE routing community (CERC) for you. But if your network topology and configuration require customized CERC definitions, you can define CERCs customized for your network.
Tip
Customized CERCs should be defined only in consultation with the VPN network administrator.
To build complex topologies, it is necessary to break down the required connectivity between CEs into groups, where each group is either fully meshed, or has a hub-and-spoke pattern. A CE can be in more than one group at a time, so long as each group has one of the two basic configuration patterns.
Each subgroup in the VPN needs its own CERC. Any CE that is only in one group just joins the corresponding CERC (as a spoke if necessary). If a CE is in more than one group, then you can use the Advanced Setup choice during provisioning to add the CE to all the relevant groups in one service request. Given this information, ISC does the rest, assigning route target values and VRF tables to arrange the precise connectivity the customer requires.
To define a new CERC:
Step 1
Click the Service Inventory tab.
Step 2
Go to Inventory and Connection Manager.
The Inventory and Connection Manager window appears.
Step 3
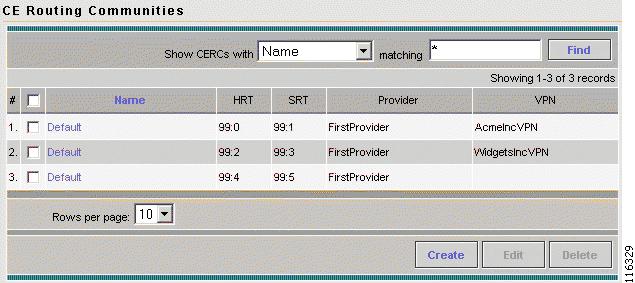
Go to CE Routing Communities.
The CE Routing Communities dialog box appears (see Figure 4-6).
Figure 4-6 CE Routing Communities Defined for This VPN
Step 4
From the CE Routing Communities dialog box, click Create.
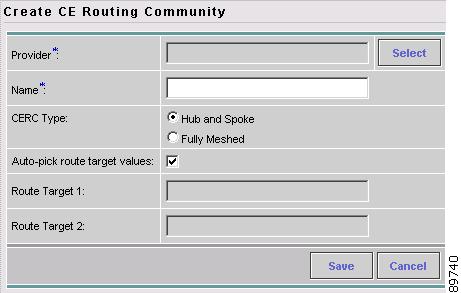
The Create CE Routing Community dialog box appears (see Figure 4-7).
Figure 4-7 Defining a New CE Routing Community
Step 5
Complete the CERC fields as required for the VPN:
c.
Provider: To specify the service provider associated with this CERC, click Select.
The Choose Provider dialog box appears.
d.
Choose the name of the service provider, then click Select.
e.
Name: Enter the name of the CERC.
f.
CERC Type: Specify the CERC type: Hub and Spoke or Fully Meshed.
g.
Auto-Pick Route Target Values: Choose to either let ISC automatically set the route target (RT) values or set the RT values manually.
By default, the Auto-pick route target values check box is checked. If you uncheck the check box, you can enter the Route Target values manually.
CautionIf you choose to bypass the Auto-pick route target values option and set the route target (RT) values manually, note that the RT values cannot be edited after they have been defined in the Cisco IP Solution Center software.
Step 6
When you have finished entering the information in the Create CE Routing Community dialog box, click Save.

 Feedback
Feedback