-
Cisco MWR 2941 Mobile Wireless Edge Router Software Configuration Guide, Release 15.0(1)MR
-
About This Guide
-
Cisco MWR 2941 Router Overview
-
Cisco IOS Software Basics
-
First-Time Configuration
-
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
-
Configuring Layer 2 Interfaces
-
Configuring HWIC-9ESW Interfaces
-
Configuring VLANs
-
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling, VLAN Mapping, 802.1ad, and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
-
Configuring STP
-
Configuring MSTP
-
Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
-
Managing the MAC Address Table
-
Configuring Cisco Express Forwarding
-
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
-
Configuring Ethernet Link Operations, Administration, and Maintenance
-
Configuring Clocking and Timing
-
Configuring Synchronous Ethernet ESMC and SSM
-
Configuring MLPPP Backhaul
-
Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching
-
Configuring Routing Protocols
-
Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
-
Configuring Pseudowire
-
Configuring Layer 3 Virtual Private Networks
-
Configuring Quality of Service
-
Configuring Link Noise Monitor
-
Configuring Cisco Discovery Protocol
-
Monitoring and Managing the Cisco MWR 2941 Router
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Understanding the Cisco MWR 2941 Router Interface Numbering
Verifying the Cisco IOS Software Version
Configuring the Hostname and Password
Verifying the Hostname and Password
First-Time Configuration
This chapter describes the actions to take before turning on your router for the first time. This chapter includes the following sections:
•
Understanding the Cisco MWR 2941 Router Interface Numbering
•
Verifying the Cisco IOS Software Version
•
Configuring the Hostname and Password
Understanding the Cisco MWR 2941 Router Interface Numbering
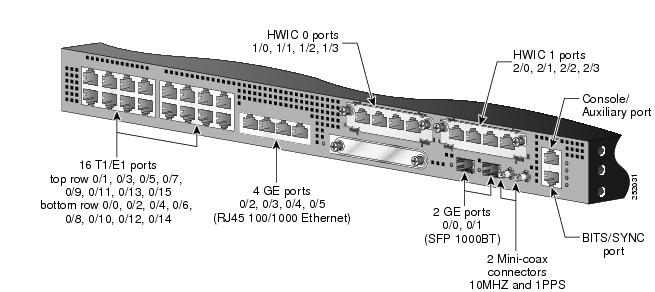
Each network interface on a Cisco MWR 2941 router is identified by a slot number and a port number.
Figure 3-1 shows an example of interface numbering on a Cisco MWR 2941 router:
•
Two HWIC ports (HWICs are ordered separately)
•
Two built-in Gigabit Ethernet small form-factor pluggable (SFP) interfaces (labeled GE0 and GE1)
•
Four built-in Gigabit Ethernet interfaces (labeled L2-L5)
•
16 E1/T1 ports (labeled C1AL-C15AL)
Note
The two HWIC cards shown in Figure 3-1 are not included with the Cisco MWR 2941 router; you must order them separately.
Note
The mini-coax timing connectors shown in Figure 3-1 only apply to the Cisco MWR 2941-DC-A router; the Cisco MWR 2941-DC does not have these ports.
Figure 3-1 Cisco MWR 2941 Router Port Numbers
Slot and Port Numbering
The Cisco MWR 2941 router chassis contains the following interface types:
•
16 T1/E1 ports, labeled "T1/E1"
•
4 RJ-45 jacks for copper Ethernet ports, labeled "100/1000" Ethernet
•
2 HWIC slots, labeled "HWIC0" and "HWIC1"
•
1 compact FLASH Type-II connector, labeled "Compact Flash"
•
2 SFP connectors for optical GE ports, labeled "GE0" and "GE1"
•
2 miniature coaxial connectors for 10MHZ and 1PPS timing
Note
Miniature coaxial timing connectors are not included on all versions of the Cisco MWR 2941. You can verify your hardware version with the VID label on the back of the router; routers labeled with a VID of V01 or V02 do not include the timing connectors, while routers with VID V03 and higher include the connectors.
•
1 RJ-45 connector for Console/Auxiliary, labeled "CON/AUX"
•
1 RJ-45 jack for BITS interface, labeled "BITS"
The logical slot numbers are 0 for all built-in interfaces.
The numbering format is:
Interface type Slot number/Interface numberInterface (port) numbers begin at logical 0 for each interface type.
Following is an explanation of the slot/port numbering:
•
Logical interface numbering for the built-in T1/E1 ports runs from 0/0 through 0/15. Interfaces are hardwired; therefore, port 0 is always logical interface 0/0, port 1 is always logical interface 0/1, and so on. Built-in T1/E1 ports are numbered bottom to top, left to right (bottom row numbered 0-2-4-6-8-10-12-14, top row numbered 1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15).
•
When the 2 HWIC slots are used to expand the T1/E1 port density to 20 or 24 ports, logical interface numbering continues from 1/0 through 1/3 and 2/0 through 2/3. Logical interfaces for HWIC0 are always 1/0 through 1/3 and logical interfaces for HWIC1 are always 2/0 through 2/3. Because the interfaces are hardwired, HWIC0 port 0 is always logical interface 1/0, HWIC0 port 1 is always logical interface 1/1, HWIC1 port 0 is always logical interface 2/0, HWIC1 port 1 is always logical interface 2/1, and so on. Ports are numbered left to right for each HWIC.
•
Logical interface numbering for the built-in Ethernet ports runs from 0/0 through 0/5. Because the interfaces are hard-wired, ports correspond to logical interface numbers. For example, port 0 is always logical interface 0/0, and port 1 is always logical interface 0/1. SFP ports are numbered left to right, 0 and 1; 100/1000 Ethernet ports are numbered left to right, 2 through 5.
•
Cisco IOS Setup Mode
Setup Mode
The setup mode guides you through creating a basic router configuration. If you prefer to configure the router manually or to configure a module or interface that is not included in setup mode, go to "Chapter 2 "Cisco IOS Software Basics" to familiarize yourself with the command-line interface (CLI).
Note
Cisco Networking Services (CNS) is a collection of services that can provide remote configuration of Cisco IOS networking devices and remote execution of some command-line interface (CLI) commands. CNS allows a Cisco MWR 2941 deployed and powered on in the field to automatically download its configuration. For more information about CNS, see Cisco Networking Services (CNS).
Before Starting Your Router
Before you power on your router and begin using the setup mode, follow these steps:
Step 1
Set up the hardware and connect the console and network cables as described in the "Connecting Cables" section of the Cisco MWR 2941-DC Router Hardware Installation Guide.
Step 2
Configure your PC terminal emulation program for 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit.
Using Setup Mode
The setup command facility appears in your PC terminal emulation program window. To create a basic configuration for your router, do the following:
•
Complete the steps in the "Configuring Global Parameters" section
•
Complete the steps in the "Completing the Configuration" section
Note
If you make a mistake while using the setup command facility, you can exit the facility and run it again. Press Ctrl-C, and type setup at the enable mode prompt (
1900#).
Configuring Global Parameters
Use the following procedure to configure global parameters.
Step 1
Power on the router. Messages appear in the terminal emulation program window.
CautionDo not press any keys on the keyboard until the messages stop. Any keys that you press during this time are interpreted as the first command entered after the messages stop, which might cause the router to power off and start over. Wait a few minutes. The messages stop automatically.
The messages look similar to the following:
Note
The messages vary, depending on the Cisco IOS software image and interface modules in your router. This section is for reference only, and output might not match the messages on your console.
rommon 1 >bootprogram load complete, entry point:0x80008000, size:0xc200Initializing ATA monitor library.......program load complete, entry point:0x80008000, size:0xc200Initializing ATA monitor library.......program load complete, entry point:0x80008000, size:0xc35eecSelf decompressing the image:########################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################### [OK]Smart Init is enabledsmart init is sizing iomemID MEMORY_REQ TYPE0035C 0X005F3C00 MWR2941 Mainboard0X000F3BB0 public buffer pools0X00843000 public particle poolsTOTAL: 0X06894CB0If any of the above Memory requirements are "UNKNOWN", you may be using anunsupported configuration or there is a software problem and system operationmay be compromised.Rounded IOMEM up to: 104Mb.Using 20 percent iomem. [104Mb/512Mb]Restricted Rights LegendUse, duplication, or disclosure by the Government issubject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph(c) of the Commercial Computer Software - RestrictedRights clause at FAR sec. 52.227-19 and subparagraph(c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and ComputerSoftware clause at DFARS sec. 252.227-7013.cisco Systems, Inc.170 West Tasman DriveSan Jose, California 95134-1706Cisco IOS Software, 2900 Software (MWR2900-IPRAN-M),Experimental Version 12.4(20050412:070057),Copyright (c) 1986-2009 by Cisco Systems, Inc.Compiled Sat 10-Jan-09 03:19 by cbrezoveImage text-base:0x60008F60, data-base:0x6106A000Cisco Systems, Inc. MWR-2941-DC (MPC8347E) processor (revision 0x400) with 417196K/107092K bytes of memory.Processor board IDMPC8347E CPU Rev: Part Number 0x8032, Revision ID 0x3001 RTM Module: ASM-M2900-TOP daughter card6 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces1 terminal line128K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.125440K bytes of ATA CompactFlash (Read/Write)--- System Configuration Dialog ---Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: yesAt any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.Step 2
To begin the initial configuration dialog, enter yes when the following message appears:
Basic management setup configures only enough connectivityfor management of the system, extended setup will ask youto configure each interface on the systemWould you like to enter basic management setup? [yes/no]:yesConfiguring global parameters:Step 3
Enter a hostname for the router (this example uses 2941-1).
Configuring global parameters:Enter host name [Router]: 2941-1Step 4
Enter an enable secret password. This password is encrypted (more secure) and cannot be seen when viewing the configuration.
The enable secret is a password used to protect access toprivileged EXEC and configuration modes. This password, afterentered, becomes encrypted in the configuration.Enter enable secret: ciscoenable
Note
When you enter the enable secret password, the password is visible while you type the it. After you enter the password, it becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Step 5
Enter an enable password that is different from the enable secret password. This password is not encrypted (less secure) and can be seen when viewing the configuration.
The enable password is used when you do not specify anenable secret password, with some older software versions, andsome boot images.Enter enable password: ciscoenableStep 6
To prevent unauthenticated access to the router through ports other than the console port, enter the virtual terminal password.
The virtual terminal password is used to protectaccess to the router over a network interface.Enter virtual terminal password: ciscoterminalStep 7
Respond to the following prompts as appropriate for your network:
Configure SNMP Network Management? [yes]:Community string [public]: publicStep 8
The summary of interfaces appears. This list varies, depending on the network modules installed in your router.
Current interface summaryAny interface listed with OK? value "NO" does not have a valid configurationInterface IP-Address OK? Method Status ProtocolGigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned NO unset up upGigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned NO unset up upStep 9
Specify the interface to be used to connect to the network management system.
Enter interface name used to connect to themanagement network from the above interface summary: GigabitEthernet0/0Step 10
Configure the specified interface as prompted.
Configuring interface GigabitEthernet0/0:Configure IP on this interface? [no]:
Completing the Configuration
When you have provided all of the information prompted for by the setup command facility, the configuration appears. Messages similar to the following appear:
The following configuration command script was created:!hostname 2941-1enable secret 5 $1$5fH0$Z6Pr5EgtR5iNJ2nBg3i6y1 enable password ciscoenable line vty 0 4password ciscoenablesnmp-server community public !no ip routing!interface GigabitEthernet0/1shutdown!endTo complete your router configuration, do the following:
Step 1
The setup command facility displays the following prompt.
[0] Go to the IOS command prompt without saving this config.[1] Return back to the setup without saving this config.[2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit.Enter your selection [2]: 2Building configuration...[OK]Use the enabled mode 'configure' command to modify this configuration.Press RETURN to get started!If you answer:
•
no—The configuration information that you entered is not saved, and you return to the router enable prompt. To return to the system configuration dialog, enter setup.
•
yes—The configuration is saved, and you return to the EXEC prompt.
Step 2
When the messages stop displaying in your window, press Return to view the command line prompt.
The
2941-1>prompt indicates that you are now at the CLI and you have just completed a basic router configuration.
Note
The basic configuration is not a complete configuration.
Verifying the Cisco IOS Software Version
To verify the version of Cisco IOS software, use the show version command. The show version command displays the configuration of the system hardware, the software version, the names and sources of the configuration files, and the boot images.
Configuring the Hostname and Password
First configure the hostname and set an encrypted password. Configuring a hostname allows you to distinguish multiple Cisco routers from each other. Setting an encrypted password allows you to prevent unauthorized configuration changes.
Note
In the following procedure, press the Return key after each step unless otherwise noted. At any time, you can exit the privileged level and return to the user level by entering disable at the Router# prompt.
To configure a hostname and to set an encrypted password, follow these steps:
Step 1
Enter enable mode.
Router> enableThe Password prompt appears. Enter your password.
Password: passwordWhen the prompt changes to
Router,you have entered enable mode.Step 2
Enter global configuration mode.
Router#configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.When the prompt changes to
Router#,Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.you have entered global configuration mode.Router(config)#Step 3
Change the name of the router to a meaningful name. Substitute your hostname for
Router(config).Router(config)#hostname RouterRouter(config)#Step 4
Enter an enable secret password. This password provides access to privileged EXEC mode. When you type enable at the EXEC prompt (
), you must enter the enable secret password to access configuration mode. Enter your secret password.Router(config)#enable secret secret passwordStep 5
Exit back to global configuration mode.
Router(config)#exit
Verifying the Hostname and Password
To verify that you have correctly configured the hostname and password, follow these steps.
Step 1
Enter the show config command:
Router# show configUsing 1888 out of 126968 bytes!version XX.X...!hostname Router!enable secret 5 $1$60L4$X2JYOwoDc0.kqa1loO/w8/...Step 2
Check the hostname and encrypted password, which appear near the top of the command output.
Step 3
Exit global configuration mode and attempt to re-enter it using the new enable password:
Router# exit..Router con0 is now availablePress RETURN to get started.Router> enablePassword: passwordRouter#

 Feedback
Feedback