-
Cisco IP Solution Center Traffic Engineering Management User Guide, 4.1
-
Document Type Definition (DTD) File
-
Index
-
About This Guide
-
Introduction
-
Setting Up the Service
-
TE Network Discovery
-
TE Resource Management
-
Basic Tunnel Management
-
Primary Tunnel Management
-
Protection Planning
-
Traffic Admission
-
Administration
-
Task Monitoring
-
TE Topology
-
Traffic Engineering Management GUI
-
Managing Service Requests
-
Warnings and Violations
-
Table Of Contents
Protection Planning
This chapter describes the process of creating and managing the protection of network elements using automated protection tools. See "Basic Tunnel Management" for a description of the process using the basic tools.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Overview
The purpose of protection planning is to protect selected elements in the network (links, routers, or SRLGs) against failure.
The first step is to identify the elements that must be protected and then invoke the protection tools to compute the protected tunnels. From the computation, the system responds for each element with either a set of tunnels that protect the element or a set of violations and warnings that help the user to determine why it could not be protected.
For successfully protected elements the tunnels can be deployed on the network. For elements that could not be protected, the protection is either ignored or the constraints are altered on the protection case. More specifically, this can involve changing the TE bandwidth settings of the links associated to the element and then rerunning the protection computation on the altered network.
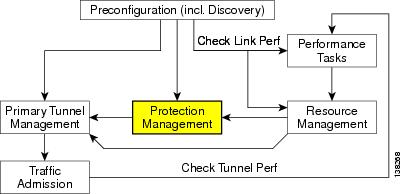
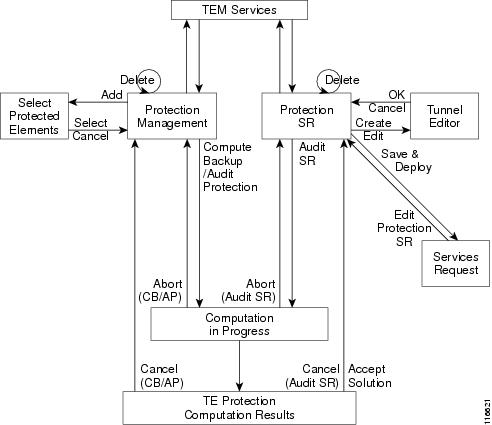
An overview of the protection management processes is provided in Figure 7-1.
Figure 7-1 Protection Management Processes
SRLG Operations
It is not uncommon for links to have identical physical characteristics, such as being physically located in the same conduit, or being connected to the same hardware. As a result, they could fail as a group during a single failure event. A Shared-Risk Link Group (SRLG) addesses this problem by identifying links that could fail together.
After SRLG modifications (create, edit, delete), use the protection planning functions in the TE Protection Management window to ensure that adequate protection is available on the network.
Note
If you include a non-POS interface of an IOS-XR device in an SRLG, the SRLG cannot be protected.
Create SRLG
Creating an SRLG is only necessary if a shared risk link group has been identified and it must be protected.
To create an SRLG, use the following steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Traffic Engineering Management.
Step 2
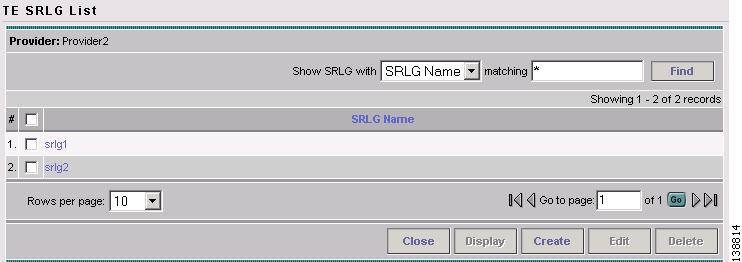
Click TE SRLGs. The TE SRLG List window in Figure 7-2 appears.
Figure 7-2 TE SRLG List
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Create/Edit TE SRLG.
Step 3
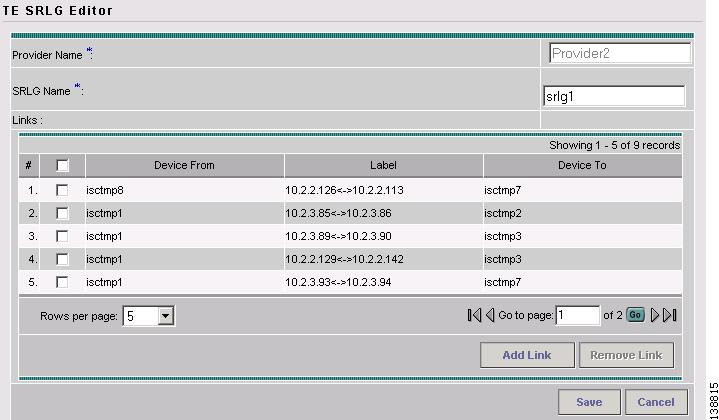
To create an SRLG in the TE SRLG List, click Create. The TE SRLG Editor window in Figure 7-3 appears.
Figure 7-3 TE SRLG Editor
For an explanation of the various window elements , see Create/Edit TE SRLG.
Step 4
Specify an SRLG Name.
Step 5
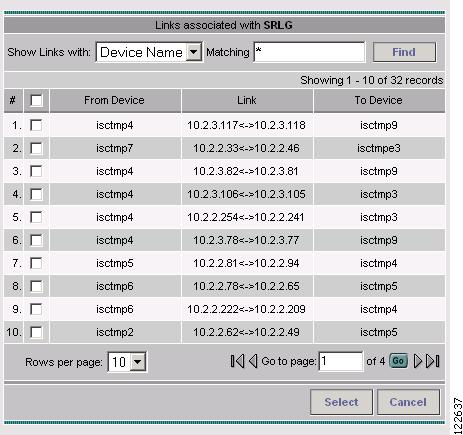
Click Add Link. The Links associated with SRLG window in Figure 7-4 appears.
Figure 7-4 Links associated with SRLG
For an explanation of the various window elements , see Create/Edit TE SRLG.
Step 6
Select one or more links and click Select. The corresponding link information is added to the link list and the Select window closes and returns to the SRLG editor.
Step 7
Click Save to save the SRLG. This closes the SRLG editor and brings back the TE SRLG List as the active window, where the newly created SRLG is listed.
Edit SRLG
To edit an SRLG, use the following steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Traffic Engineering Management.
Step 2
Click TE SRLGs. The TE SRLG List window in Figure 7-2 appears.
Step 3
To edit an SRLG in the TE SRLG List, from the TE SRLG List window select the SRLG that you want to modify and click Edit. The TE SRLG Editor window in Figure 7-3 appears
Step 4
Use Add Link and Remove Link to adjust to the desired set of links for the selected SRLG.
Step 5
Click Save to save the changes.
Delete SRLG
To delete an SRLG, use the following steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Traffic Engineering Management.
Step 2
Click TE SRLGs. The TE SRLG List window in Figure 7-2 appears.
Step 3
To delete an SRLG in the TE SRLG List, from the TE SRLG List window select the SRLG(s) that you want to delete and click Delete. The Delete Confirm window appears.
Step 4
Click Delete to confirm. The Delete Confirm window closes. After the TE SRLG List window has been updated, the deleted SRLG no longer appears in the SRLG list.
Configure Element Protection
Before a protection computation can be performed, it is necessary to configure the network element protection.
To do so, use the following steps:
Step 1
Navigate Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Traffic Engineering Management > TE Protected Elements.
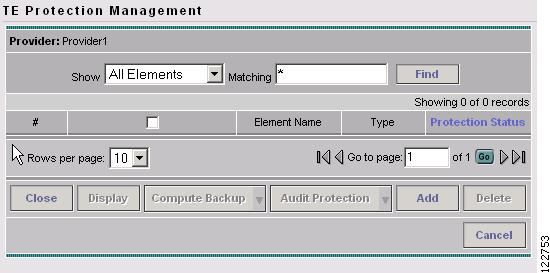
The TE Protection Management window in Figure 7-5 appears.
Figure 7-5 TE Protection Management
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Protection Management.
Step 2
First, decide which network elements must be protected.
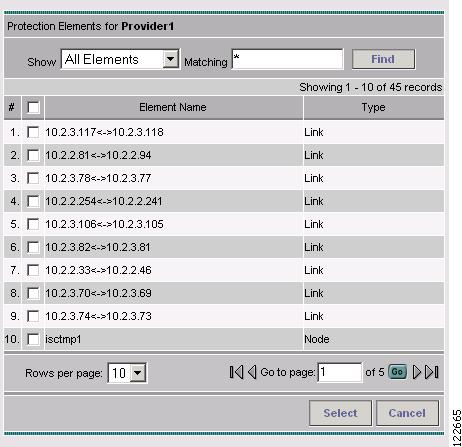
In the TE Protection Management window, click Add to add a protection element (link, node, or SRLG). The Select Protection Elements window in Figure 7-6 appears.
Note
If a link, node or SRLG contains a non-POS interface on an IOS-XR device, the element is selectable as a protected element and backup tunnels will be generated, but the deployment will fail due to a restriction is IOS-XR 3.2. For nodes, all nodes connected to an IOS-XR device must have POS interfaces. If even one node in an SRLG has a non-POS interface, that SRLG cannot be protected.
Links that are connected to non-Cisco devices cannot be protected and will, therefore, not show in the Select protection elements window. Likewise, non-Cisco devices and SRLGs that contain links to non-Cisco devices cannot be protected and are excluded from the selection.
Figure 7-6 Select Protection Elements
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Protection Management.
Step 3
Select one or more elements to be protected and click Select. The Select Protection Element window closes and the TE Protection Management window reappears.
Next, decide which protection tools should be applied.
Protection Tools
Relying on manual creation of backup tunnels as described in "Basic Tunnel Management" has its limitations, not just for larger and more complicated networks.
The protection tools available in ISC TEM provide a number of tools that automatically compute and verify protection of specified network elements.
Note
Certain attributes, such as Description, that do not impact the computation carried out by these tools and updates to these are, therefore, not displayed in the Computation Result Window.
Compute Backup
Compute Backup is used to let ISC TEM automatically compute the necessary backup tunnels to protect specified network elements. The manual process is described in "Basic Tunnel Management."
To run Compute Backup, use the following steps:
Step 1
Navigate Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Traffic Engineering Management > TE Protected Elements.
Step 2
Configure the necessary protection elements as described in Configure Element Protection.
Step 3
If you only want to perform Compute Backup on selected elements, select one or more elements on which to calculate a backup path.
Click Compute Backup and select one of the following:
•
All Elements
•
Selected Elements
The Computation In Progress window shown in Figure 7-7 appears.
Figure 7-7 FRR Computation In Progress - Compute Backup
To abort the computation and return to the previous window, click << Abort Computation.
Step 4
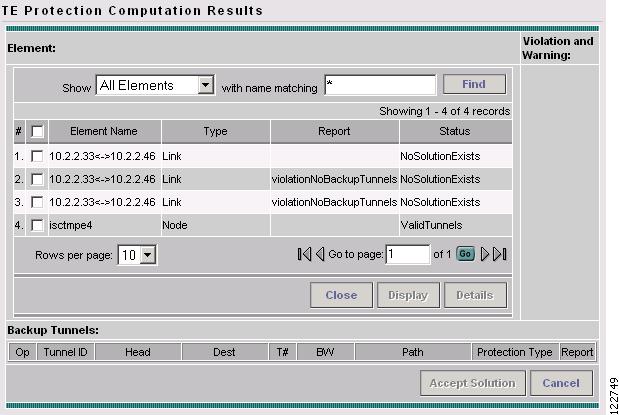
The TE Protection Computation window in Figure 7-8 appears.
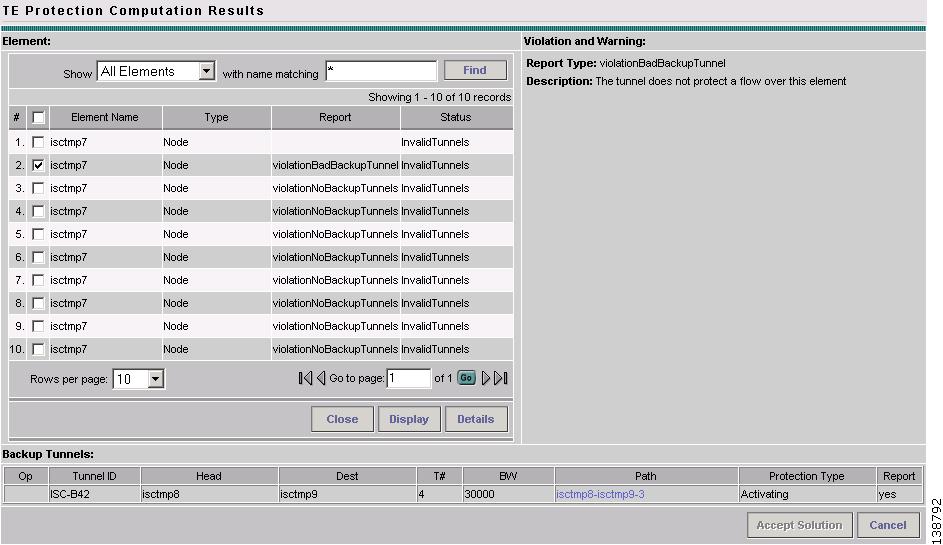
Figure 7-8 TE Protection Computation Results
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Compute Backup.
Note
Certain attributes, such as Description, that do not impact the computation carried out by the protection tools and updates to these are not displayed in the Computation Result Window.
Step 5
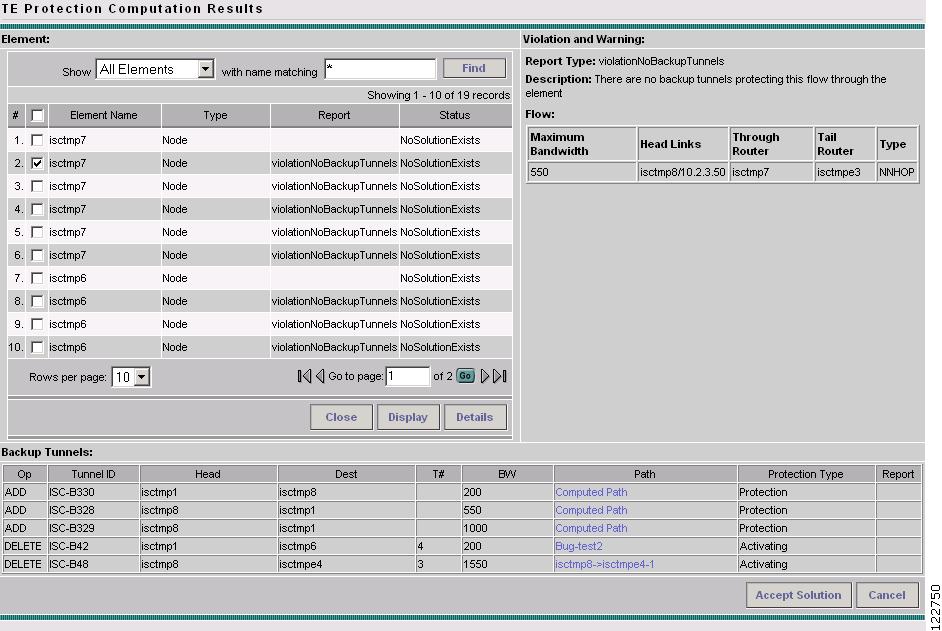
Select a row corresponding to a specific warning or violation and click Detail to display a detailed description in the right pane and backup tunnels associated with the selected item in the bottom pane as shown in Figure 7-9.
For a description of warnings and violations, see "Warnings and Violations."
Figure 7-9 TE Protection Computation Results with Backup Tunnels
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Compute Backup.
The Backup Tunnel table displays which new protection tunnels are required and any existing tunnels that should be kept or deleted for each element.
Step 6
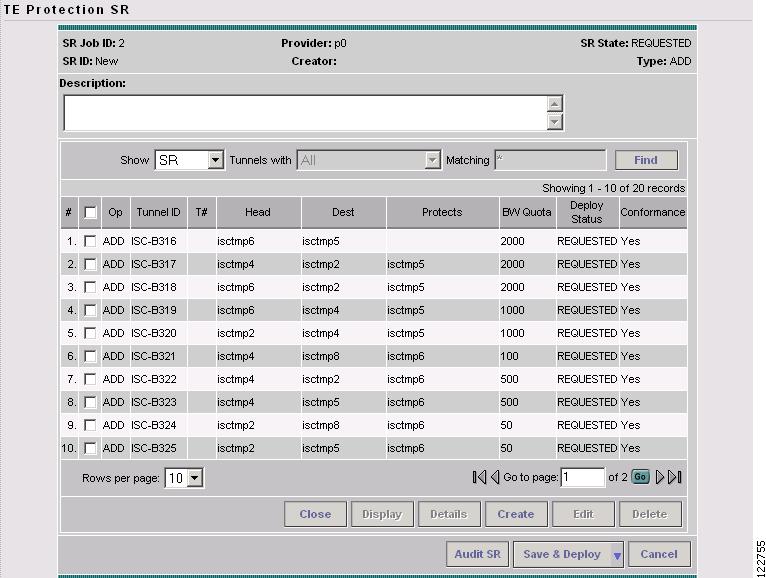
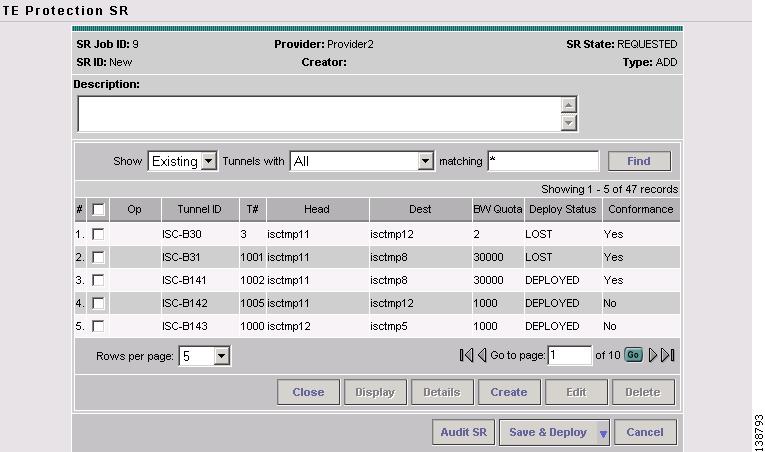
In the TE Protection Computation Results window, check whether the proposed protection solution is acceptable. It so, click Accept Solution. The TE Protection SR window in Figure 7-10 appears with all tunnel additions and deletions computed by the system.
Figure 7-10 TE Protection SR - Computed Path
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Create TE Backup Tunnel.
Optionally, you can make tunnel changes here and then run Audit SR to ensure that you have the desired level of protection before you deploy (see Audit SR).
Step 7
Click Save & Deploy to deploy the new tunnel SR to the network.
Note
When you click Save & Deploy, a background process is started. To avoid a potential conflict with another deployment, wait until the SR has completed the Requested and Pending states before deploying another SR with Save & Deploy. To see the state of deployment, go to the Service Request window under Inventory and Connection Manager or open the Task Manager under Monitoring.
Note
With the exception of TE Traffic Admission SRs, TE SRs are always deployed immediately from the specific TE SR screen, not from the Service Requests page in Inventory and Connection Manager.
Step 8
The Service Requests window (Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Service Requests) opens and displays the state of the deployed SR.
For more information on working with service requests, see "Managing Service Requests."
If the SR does not go to the Deployed state, go to the Task Logs screen to see the deployment log (Monitoring > Task Manager > Logs) as described in SR Deployment Logs.
Audit Protection
As opposed to the Compute Backup tool described on page 7, Audit Protection does not attempt to create a backup solution. It seeks to verify protection of specified network elements with the current set of backup tunnels and reports any warnings or violations that are discovered. It is recommended that any time a change has been committed on the TE topology such as resources on TE links or SRLG memebership, a protection audit be run to verify the protection status on all elements.
The computation will display the same computation result page as for Compute Backup. When you return from computation result page, the Protection Status column in the TE Protection Management window is updated to show the level of protection for each element.
This section describes the necessary steps to perform Audit Protection on one or more network elements.
To run Audit Protection, use the following steps:
Step 1
Navigate Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Traffic Engineering Management > TE Protected Elements.
The TE Protection Management window in Figure 7-5 appears.
Step 2
If you only want to perform Audit Protection on selected elements, select one or more tunnels on which to calculate a backup path.
Click Audit Protection and select one of the following:
•
All Elements
•
Selected Elements
The Computation In Progress window shown in Figure 7-7 appears.
Figure 7-11 FRR Audit Computation in Progress - Audit Protection
To abort the computation and return to the previous window, click << Abort Computation.
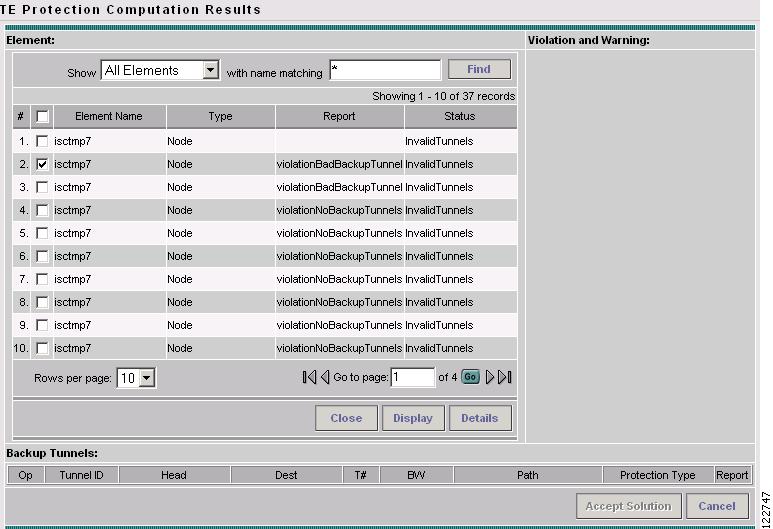
The TE Protection Computation Results window in Figure 7-12 appears.
Figure 7-12 TE Protection Computation Results
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Compute Backup.
Note
Certain attributes, such as Description, that do not impact the computation carried out by the protection tools and updates to these are not displayed in the Computation Result Window.
Step 3
To view the backup tunnels for a particular element, select the element and click Details.
The TE Protection Computation Results window in Figure 7-13 appears.
Figure 7-13 TE Protection Computation Results with Backup Tunnels
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Compute Backup.
Step 4
Select a row corresponding to a specific warning or violation and click Details to display a detailed description in the right pane and backup tunnels associated with the selected item in the bottom pane as shown in Figure 7-9.
Tunnels associated with a warning or violation are flagged in the Report column in the Backup Tunnels table in the bottom pane.
The Accept Solution button is greyed out because the audit does not provide a solution but rather an evaluation.
For a description of warnings and violations, see "Warnings and Violations."
Step 5
Click Cancel to return to the TE Protection Management window. The protection status is updated in the Protection Status column.
Audit SR
Audit SR audits protection of all elements in the TE Protection Management window against backup tunnels in the TE Protection SR window.
This feature can be used to audit the protection for manually added, modified, and deleted tunnels in the TE Protection SR window before deploying them.
To audit a TE backup tunnel SR, use the following steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Traffic Engineering Management.
Step 2
Click Create TE Backup Tunnel. The TE Protection SR window in Figure 7-14 appears.
Figure 7-14 TE Protection SR
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Create TE Backup Tunnel.
Step 3
To audit the protection SR, click Audit SR.
Note
Audit SR will only be enabled if there are elements in the TE Protection Management window. If this is not the case, the Audit SR button will be disabled (grayed out).
The FRR Audit process begins and the TE Protection Computation Results window in Figure 7-12 appears.
See Audit Protection for a description of the rest of the process. Detail and report windows are identical in these two processes.

 Feedback
Feedback