-
Cisco IP Solution Center Traffic Engineering Management User Guide, 4.1
-
Document Type Definition (DTD) File
-
Index
-
About This Guide
-
Introduction
-
Setting Up the Service
-
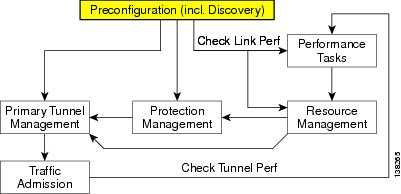
TE Network Discovery
-
TE Resource Management
-
Basic Tunnel Management
-
Primary Tunnel Management
-
Protection Planning
-
Traffic Admission
-
Administration
-
Task Monitoring
-
TE Topology
-
Traffic Engineering Management GUI
-
Managing Service Requests
-
Warnings and Violations
-
Table Of Contents
Memory Shortage on Large Networks
Setting Up Management Interfaces
TE Network Discovery
After completing the preconfiguration process and creating a seed router, you can discover the TE network for a particular TE provider. This populates the repository with the network topology. Also, you might need to set up the management interfaces. The necessary steps are described in this chapter.
This chapter includes the following sections:
–
Memory Shortage on Large Networks
•
Verifying a TE Discovery Task
•
Setting Up Management Interfaces
Overview
The purpose of the discovery process is to populate the repository with the network topology, tunnels, and static routes to tunnels present in the live network.
The discovery process uses a seed device to discover the MPLS TE network topology using either Telnet or SSH. All the Traffic Engineering routers in the network should be accessible via their TE ID if the device entry does not exist in the repository. The Management IP address will be used to access the device if the device entry exists in the Repository.
TE Discovery is a schedulable task that can be run once or on a periodic basis. Any inconsistencies between the repository and the network are reported in the Discovery log. The service state information is updated incrementally by logging tunnel in-use Label Switched Paths (LSPs) and updating the service request (SR) state.
TE Discovery Prerequisites
The following prequisites apply mainly to TE discovery.
For an overview of the general ISC TEM prerequisites, see Prerequisites and Limitations.
Accessibility
To successfully run a TE Discovery task, the seed router must be directly accessible from the management station.
ALL TE routers must be accessible from the ISC machine via their TE router ID. This is often the a loopback ip address, but not always.
For Telnet/SSH, there must be either direct Telnet/SSH access from the Cisco IP Solution Center Traffic Engineering Management (ISC TEM) management station to each device.
See Preconfiguration Process Overview for instructions on how to select Telnet or SSH when setting up a seed router.
Memory Shortage on Large Networks
When running discovery on a large network (250+ devices or 5000+ tunnels, for example) or an OutOfMemoryException is encountered, do the following:
Edit the watchdog.server.worker.java.flags property in the vpnsc.properties file to a value, for example -Xmx1024m, instead of the default value -Xmx512m. This increases the heap size of the discovery task, which will clear up the OutOfMemoryException problem.
Revert the watchdog.server.worker.java.flags property back to its original value to reduce the resource usage when no longer needed.
IOS-XR and Enable Passwords
If an IOS-XR device is to be used as a seed device, the enable password should be set in its device record even though IOS-XR does not require an enable password,for itself. That way IOS devices in the network, which do require an enable password, may be fully discovered
When creating an IOS-XR device through the Devices tab (Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Devices) to act as a seed device for an initial discovery, it is strictly speaking not necessary to specify the enable password - ISC TEM will be able to log in and get all the data it needs.
However, if there are other IOS devices in the same network, ISC TEM will not be able to enter enable mode for those devices. As a result, these are not fully discovered in the sense that the inability to enter e nable mode stops ISC TEM from gathering all the relevant data. These other IOS routers will show up as 'unknown' devices in the Devices window).
Creating a TE Discovery Task
To create a TE Discovery task on the TE network, use the following steps:
Step 1
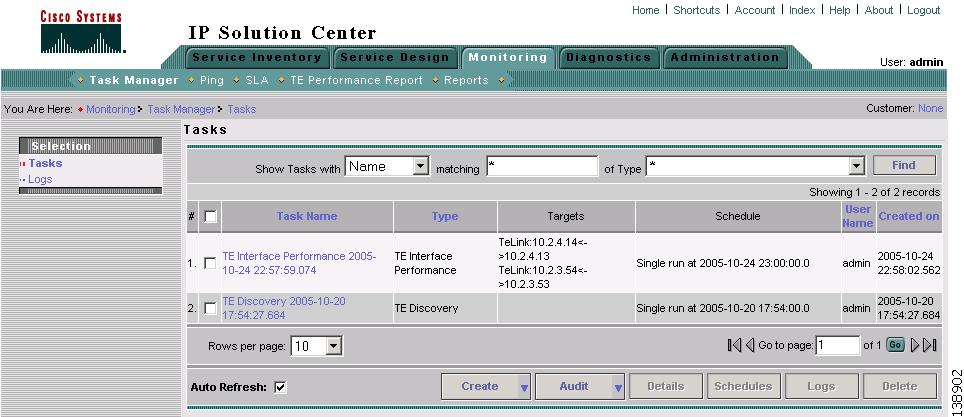
Navigate Monitoring > Task Manager. The window in Figure 3-1 appears.
Figure 3-1 Tasks
Step 2
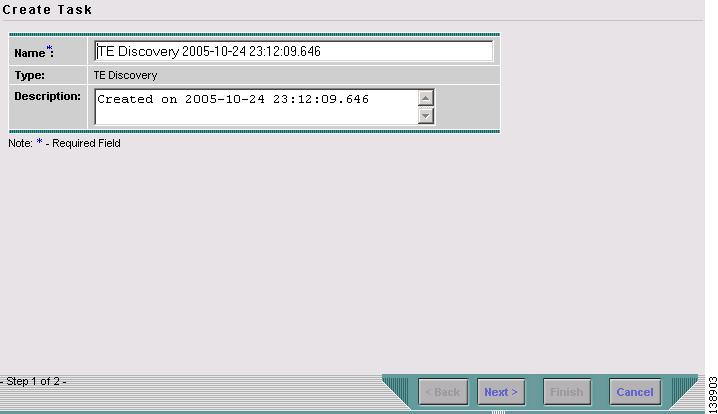
Create a new task by selecting Create > TE Discovery. The window in Figure 3-2 appears.
Figure 3-2 Create TE Discovery Task (Step 1)
Step 3
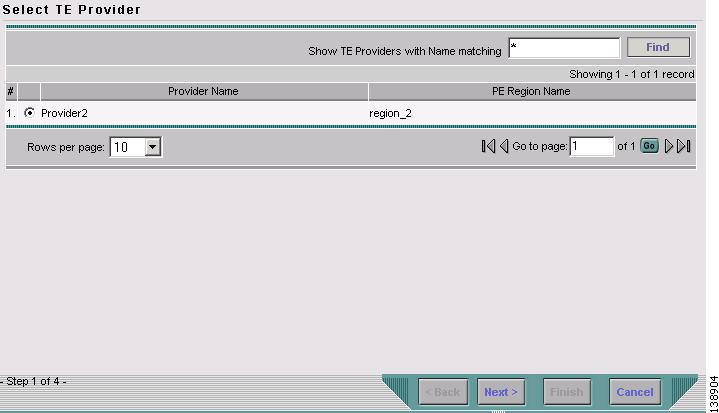
Optionally alter the Name and/or Description fields and click Next. The Select TE Provider window in Figure 3-3 appears.
Figure 3-3 Select TE Provider
Step 4
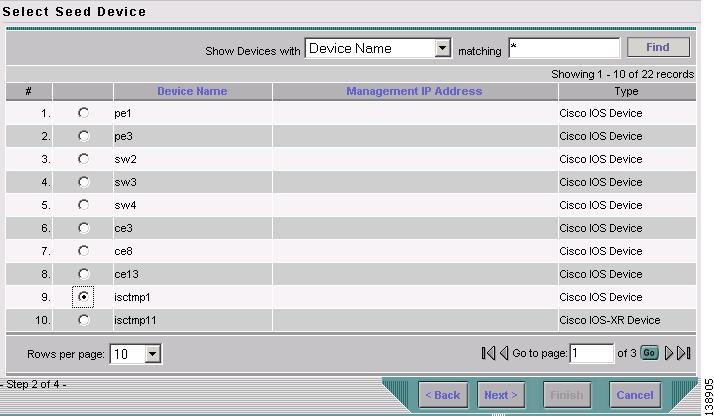
Select a TE provider and click Next. The Select Seed Device window in Figure 3-4 appears.
Non-Cisco devices, if any, are excluded from the list.
Figure 3-4 Select Seed Device
Step 5
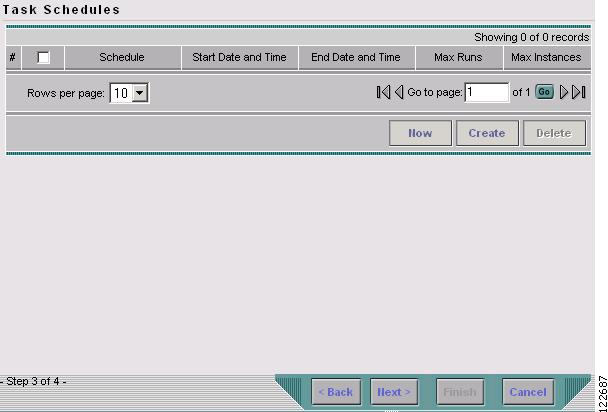
Select the seed device for discovery of the network and click Next. The Task Schedules window in Figure 3-5 appears.
Figure 3-5 TE Discovery Task Schedules Window Before Scheduling
Step 6
Create a task schedule in one of two ways:
•
Click Now to schedule the task to run immediately, in which case the schedule information is automatically filled into the Task Schedules list (Figure 3-7).
•
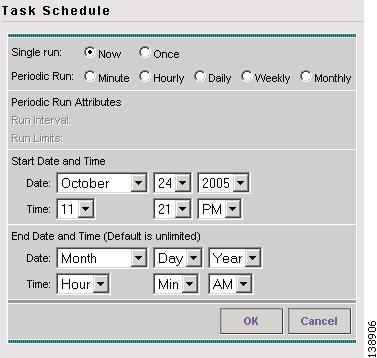
Click Create to create a scheduler for this task, in which case the Task Schedule window in Figure 3-6 appears.
Figure 3-6 Task Schedule
Step 7
In the Task Schedule window, make your selections to define when and how often the task should be run.
Note
The default setting is to schedule a single TE Discovery task to take place immediately ("Now").
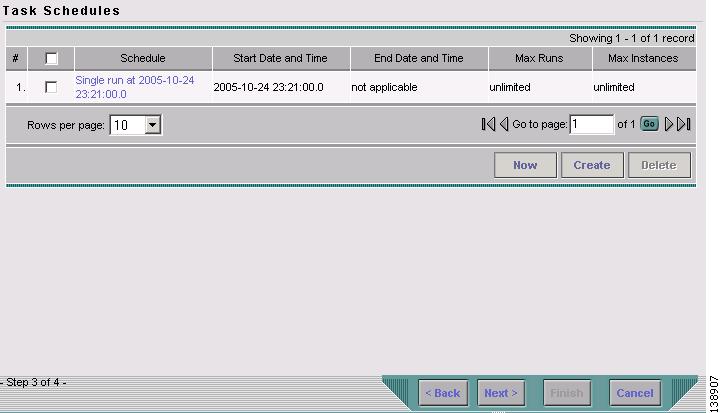
Step 8
Click OK. The scheduled task should now appear in the Task Schedules table as shown in Figure 3-7.
Figure 3-7 TE Discovery Task Schedules Window After Scheduling
Step 9
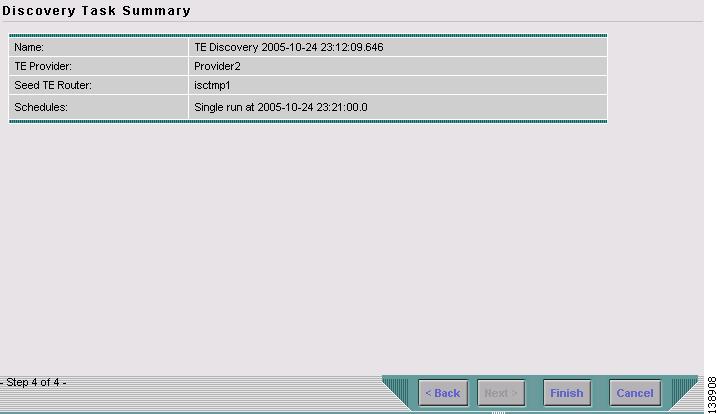
Click Next. A summary of the scheduled task in Figure 3-8 appears.
Figure 3-8 Discovery Task Summary
Step 10
Click Finish. This will add the task to the list of created tasks in the Tasks window (Figure 3-1).
Verifying a TE Discovery Task
The result of running the TE Discovery task can be assessed in three ways:
•
Task Logs—View a summary log of any changes that have occured in the network.
•
TE Topology—Display the latest TE Topology from the repository.
•
View Network Element Types—In the Traffic Engineering Management GUI, go to TE Nodes, TE Links, TE Primary Tunnels, and so on to verify the state of specific network element types.
Task Logs
The TE Discovery log captures the state of the network and compares it with the most recent snapshot of the repository.
To view the task log for a TE Discovery task, use the following steps:
Step 1
Navigate Monitoring > Task Manager.
Step 2
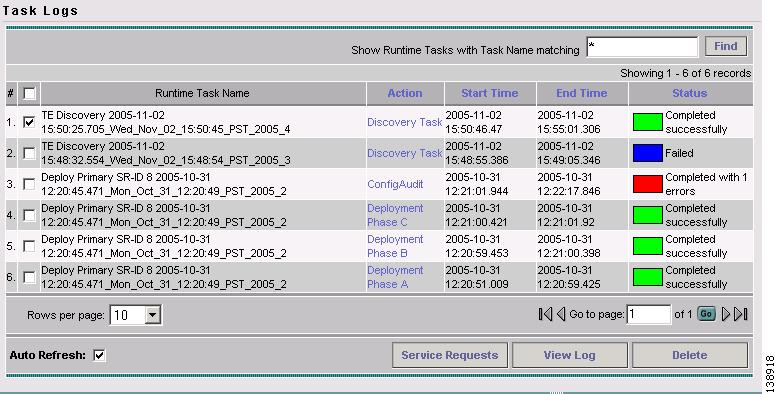
Select Logs in the table of contents on the left side of the Tasks window. The Task Logs window in Figure 3-9 appears.
Figure 3-9 Task Logs - TE Discovery
For an explanation of the various window elements, see Task Log.
The status of each task is shown in Status column. This updates automatically and indicates when the discovery process is complete.
If the task is not completed and Auto Refresh is selected, the table continues to update periodically until it is completed.
Step 3
To view the log for a particular task, click the log name in the Action column. A copy of a TE Discovery log is shown in the following screenshots, starting with Figure 3-10.
Note
To find the summary of changes in the network depicted in the following screenshots, scroll to the bottom of the log .
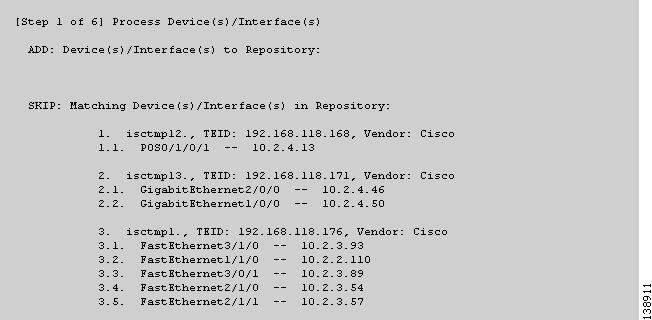
Figure 3-10 TE Discovery Task Log - Devices/Interfaces
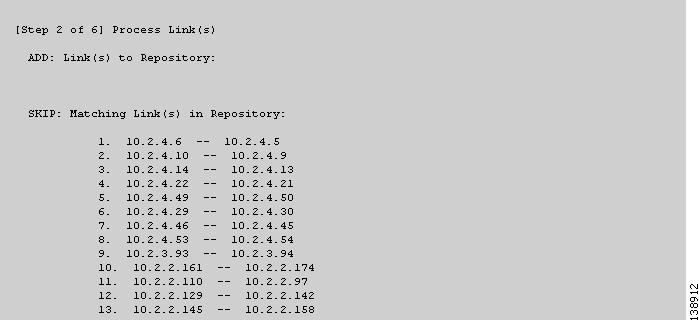
Figure 3-11 TE Discovery Task Log - Links
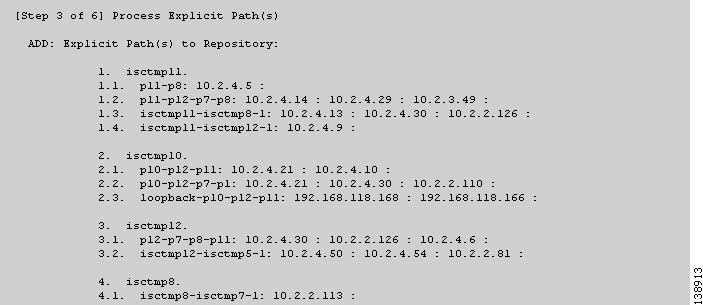
Figure 3-12 TE Discovery Task Log - Explicit Paths
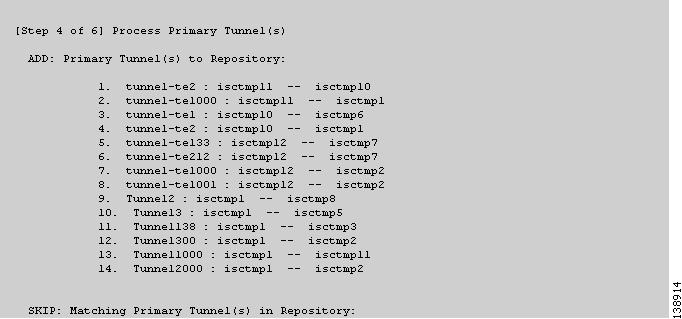
Figure 3-13 TE Discovery Task Log - Primary Tunnels
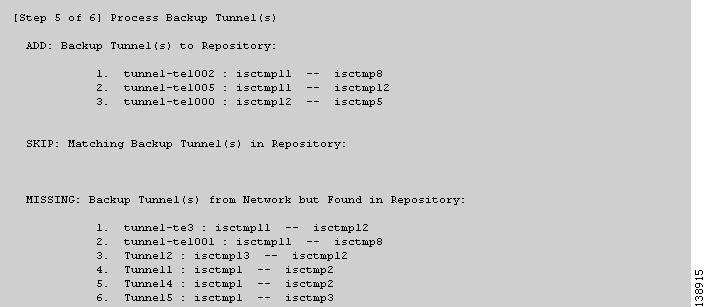
Figure 3-14 TE Discovery Task Log - Backup Tunnels
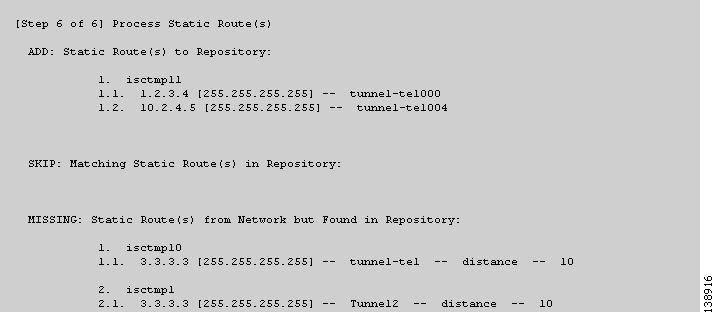
Figure 3-15 TE Discovery Task Log - Static Routes
The TE Discovery task log window is organized into sections that each describes particular events in the TE network:
•
either the state of the network as recorded in the repository the first time a TE Discovery task is run
•
or changes in the network since the last time the TE Discovery task was run (repository delta).
The summary of changes in the network is reported in six steps:
1.
Devices/Interfaces (Figure 3-10)
2.
Links (Figure 3-11)
3.
Explicit paths (Figure 3-12)
4.
Primary tunnels (Figure 3-13)
5.
Backup tunnels (Figure 3-14)
6.
Static routes (Figure 3-15).
As seen in the figures, in each step a log table reports the changes in the following reporting categories:
•
ADD—This section lists those elements that the TE Discovery task added to the repository. At the initial discovery, all elements should be in the ADD section as nothing existed in the repository beforehand. With every subsequent discovery, the ADD section will list elements that have been added to the network since the discovery independent of ISC TEM. Thus, the ADD function is synchronizing the repository with the network by adding these elements..
•
SKIP—This section lists those elements that exist both in the network and in the repository and have all attributes equal. This shows that these elements have not been deleted or modified independently of ISC TEM.
•
MISSING—This section lists those elements that exist in the repository but do not exist in the network, implying that they have been deleted independently of ISC TEM. This indicates that more investigation is required in order to correct the discrepancy.
•
MISMATCH—This section lists those elements that exist both in the network and in the repository, but have one or more attributes that are not equal. This implies that these elements have been modified independently of ISC TEM and that you need to investigate and correct the problem.
•
MODIFY—This section lists any network elements that have had attributes in the repository modified since the previous run of the TE Discovery task to synchronize with the network. These are usually dynamic attributes, such as the time when a tunnel was set up.
Step 4
Click Return to Logs to quit the current log with the option to open another log.
TE Topology
The TE Topology tool provides a visual snapshot of the current state of the network. It cannot be used to determine changes that have taken place in the network.
The steps required to generate a topology graph of the network are described in "TE Topology."
View Network Element Types
Another way to check the state of the network after running TE discovery is to go to the Traffic Engineering Management Services window and select the type of elements you want to verify.
For example, to check the status of the nodes after running TE discovery, navigate Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Traffic Engineering Management > TE Nodes. Look at the updated list of TE nodes to assess which nodes are in the network.
Do the same for TE Links, TE Primary Tunnels, TE Backup Tunnels, and so on.
Setting Up Management Interfaces
Before commencing tunnel management operations, you need to set up management interfaces. However, this step is only necessary if the network devices are not accessible by the hostname from the management station.
For a detailed description of how to set up management interfaces on specific devices, see Cisco IP Solution Center Infrastructure Reference, 4.1 in the section on creating devices.
MPLS-TE Management Process
The MPLS-TE management process involves the following steps:
1.
Enable MPLS-TE on the network devices and make sure that the IP addresses used as the devices TE IDs are accessible from the management station (this step is not supported by ISC TEM).
2.
Prepare the repository for discovering MPLS-TE network.
3.
Set up management interfaces for the discovered devices or update the server host file with resolution for all discovered devices. Again, this is not needed if the hostnames are already accessible from the management station.
4.
Discover the MPLS-TE network.
You will then be in a position to run the other MPLS-TE functions available in ISC TEM.
Note
When the repository is empty, or when the management IP addresses are not configured for current devices in the TE network, make sure that the router MPLS TE ID can be reached from the management station. In other words, the TE discovery process does not support seed passthrough.
Making SSH Work With IOS-XR
To make SSH work with IOS-XR, enter the following commands on the IOS-XR device:
(config)# domain name <domain name> # crypto key gen rsaVerify the crypto configuration by way of the following command:
# sh crypto key mypubkey rsaNext, configure all links as point-to-point as described in Configuring Ethernet Links.
Configuring Ethernet Links
Only point-to-point links are supported in ISC TEM. POS links are point-to-point by default but otherwise Ethernet links need to be configured as point-to-point.
For IOS, enter the following command:
# ip ospf network point-to-pointFor IOS-XR, enter the following command:
# router ospf <id> area 0 interface <name> network point-to-point

 Feedback
Feedback