-
Basic Dial NMS Implementation Guide
-
Preface
-
Overview of Basic SNMP Building Blocks
-
Network Design for a Dial NMS Case Study
-
Task 1--Enabling SNMP in a Cisco IOS Device
-
Task 2-- Exploring SNMP Capabilities by Using UCD-SNMP
-
Task 3--Using MRTG to Monitor and Graph Traffic Loads
-
Task 4--Using Syslog, NTP, and Modem Call Records to Troubleshoot Faults
-
Task 5--Setting Up a Web Portal for the Dial NMS
-
Task 6--Managing IP Addresses by Using DNS
-
Task 7--Using HP OpenView to Create the SNMP Framework
-
Task 8--Using CiscoWorks 2000 Resource Manager Essentials
-
Dial MIBs and OIDs Used in the Case Study
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Task 5—Setting Up a Web Portal for the Dial NMS
Building a Device Linker Web Page
Troubleshooting a Cisco 2511 Console Connection
Using HTTP to Access CLI Commands
Task 5—Setting Up a Web Portal for the Dial NMS
About a Web Portal
A web portal for the dial NMS is a combination of CGI scripts and HTML links used to support a dial Internet access service.
As the number of devices and applications in a network increase, the operations support team may become inundated with a myriad of management products. To support a dial service, a web portal provides easy access to:
•
Product manuals, design guides, white papers, and troubleshooting guides.
•
Light-weight tools and scripts.
•
Network policies, procedures, and reports.
•
Periodic and just-in-time reporting.
–
The help desk can access operational information
(for example, current connected caller status).–
The operations staff can report on current service levels.
Tips
For more information on building a management intranet, go to http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/serv/mkt/nmps/ent/tech/bmi_wi.htm
Table 22 Utilities Provided by the Web Portal for the Dial NMS
Documentation Center
A web server used as an online-documentation hub to share network operations information.
Device Linker
A web page used for bookmarking URLs for quick device telnet and out of band (console) access.
Cisco IOS CLI Command Center
A web page that provides HTTP access to frequently used Cisco IOS CLI commands. The operations team and help desk can use this utility to troubleshoot connectivity problems.
IP Tracker
A web page that uses two scripts to keep track of IP address block assignments by using DNS reverse lookup zones.
SNMP Commander
A script that aids the MIB research task by enabling engineers to build web-based object identification (OIDs) bookmarks. You can poll for network statistics by using OID bookmarks and a web browser. No keyboard is required.
Syslog Viewer
A utility that uses FTP to access a syslog server and a web browser to view syslog messages. Migration to HTTP is straightforward after security issues are addressed. The use of non-wrapping text is useful when viewing debug messages and modem call records.
See the "Inspecting Syslog Messages in the Log File" section.
Modem Call Record Viewer
Light-weight scripts used to parse and view modem call records.
See the "About Syslog" section.
CiscoWorks 2000 Resource Manager Essentials
A utility used to remotely monitor and maintain devices through a web-based browser interface.
See the "Task 8—Using CiscoWorks 2000 Resource Manager Essentials" section.
Building a Device Linker Web Page
A device linker web page:
•
Simplifies access to the many device-management interfaces in the network.
•
Provides links to the telnet, console, and HTTP ports of Cisco IOS devices.
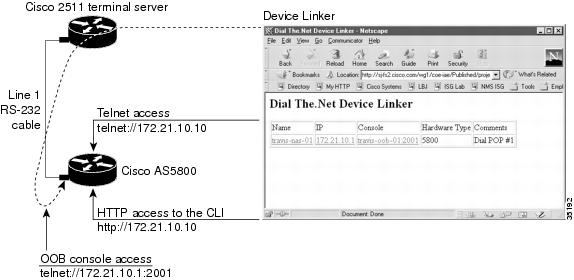
Figure 19
Device Linker Used to Access Devices
By using a Cisco terminal server for out-of-band console access, such as a Cisco 2511, the consoles are available at TCP port 20xx on a terminal server. The target line number replaces xx. For example to get to line 1, telnet to port 2001. The equivalent URL is telnet://172.21.101.250:2001
To build a device linker web page, follow these steps:
Step 1
Collect the IP addresses for the Cisco IOS devices.
Step 2
Collect the device console out-of-band (OOB) paths for the terminal server and the lines connected to Cisco IOS devices.
Step 3
Create a basic HTML table and enter the information for each device. The telnet and HTTP information is in bold in the following HTML code fragment. Step 4 shows what the table looks like in a web browser.
<html><head><title>Dial The.Net Device Linker</title></head><body><h2>Dial The.Net Device Linker</h2><table border="1"><tr><td>Name</td><td>IP</td><td>Console</td><td>Hardware Type</td><td>Comments</td></tr><tr><td><a href="http://172.21.10.1">travis-nas-01</a></td><td><a href="telnet://172.21.10.1">172.21.10.1</a></td><td><a href="telnet://172.21.101.250:2001">travis-oob-01:2001</a></td><td>5800</td><td>Dial POP #1</td></tr></table></body></html>
Step 4
Post the device linker web page to a WWW server in the NOC.
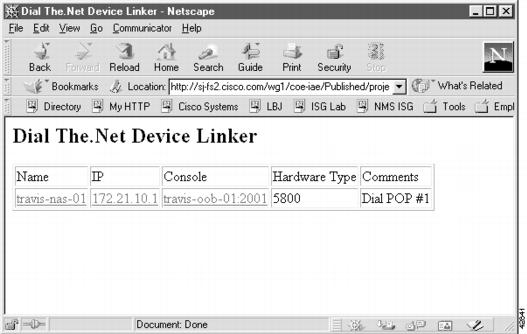
Figure 20
A Device Linker Management Page
Step 5
Click on an active device link. After a telnet session opens, log in.
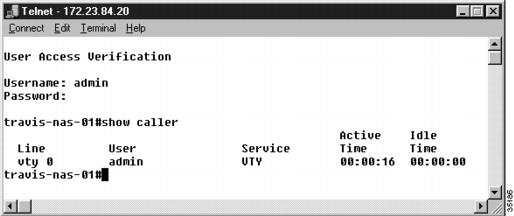
Figure 21
Console Port Login
Troubleshooting a Cisco 2511 Console Connection
If you cannot access the console of a device, follow these steps:
Step 1
Verify that the configuration on the terminal server is correct. Telnet is the only service that must be supported to access the lines. The following configuration fragment shows you how to configure 16 TTY lines on a Cisco 2511 terminal server.
!line 1 16no exectransport input telnet!Step 2
If the console port is blocked, you may need to telnet to the terminal server and clear the line. Enter the show users EXEC command followed by the clear line type number command.
c2511-oob#show usersLine User Host(s) Idle Location0 con 0 admin idle4 tty 4 admin incoming 0 dhcp-172-71-218-198.guessme.com* 10 vty 0 admin incoming 0 dhcp-172-71-218-198.guessme.comc2511-oob#clear line tty 4[confirm][OK]c2511-oob#show usersLine User Host(s) Idle Location0 con 0 admin idle* 10 vty 0 admin incoming 0 dhcp-172-71-218-198.guessme.comStep 3
(Optional) Sometimes administrators inadvertently leave lines in use. To make idle telnet sessions end after 30 minutes, enter the exec-timeout 30 0 command on all the lines.
!line 1 16no execexec-timeout 30 0transport input telnet!About HTTP Access to the CLI
Using web-based access to the CLI reduces the need for telnet sessions to monitor or verify network operations. Telnet sessions can be reserved for actions such as making configuration changes. Additionally, sending syslog to a syslog server prevents telnet sessions from becoming cluttered with debug output.
HTTP access to the CLI is:
•
Very difficult to secure. One way of securing a router is to use access-control lists on all VTY lines. Enable only devices in the NOC to access the VTY lines.
•
Not recommended for service providers. If used, you should weigh the perceived ease of use versus the additional security issues involved with HTTP access to a network device.
The Cisco IOS CLI Command Center is a web page utility that provides HTTP access to CLI commands on a router. HTTP access to the CLI simplifies the troubleshooting tasks for a help desk.
Using HTTP to Access CLI Commands
To manage a dial Internet access service by using HTTP access to CLI commands, follow these steps:
Step 1
Enable HTTP services on the Cisco IOS device by entering the following commands:
!ip http serverip http authentication aaa!
Step 2
Create a table in an HTML web page and enter your list of frequently used Cisco IOS CLI commands.
Note
To create the link for a CLI command, specify the IP address of the Cisco IOS device followed by the command. Remember to include the forward slashes (/) between each command mode and key word.
Table 25 Formula and Example for Linking a CLI Command
http://ip-address/exec/ios-key-word/.../cr
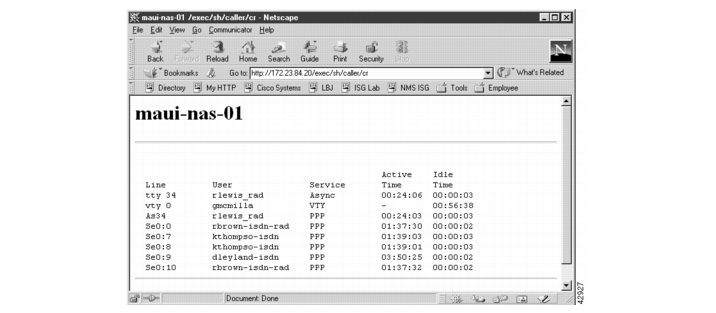
http:/172.23.84.20/exec/sh/caller/cr
The web page can include many types of commands useful for managing a dial Internet access service, including:
•
System commands (Table 26)
•
Interface commands (Table 27)
•
Call state commands (Table 28)
•
Debug commands (Table 29)
Table 26 System Commands
show running configuration
show file systems
show ip route
show version
dir
show ip route static
show modem version
show flash
show ip route connected
Table 27 Interface Commands
show controller t1
show ip interface brief
show interface Fast Ethernet0/0/0
show isdn service
show interface
show line
show isdn status
Table 28 Call State Commands
show modem
show caller
show users
show modem call-stats
show caller ip
show dialer
show modem ?
show caller timeout
show dialer map
show caller ?
Step 3
Post the HTML page that you created in Step 2 to a web server.
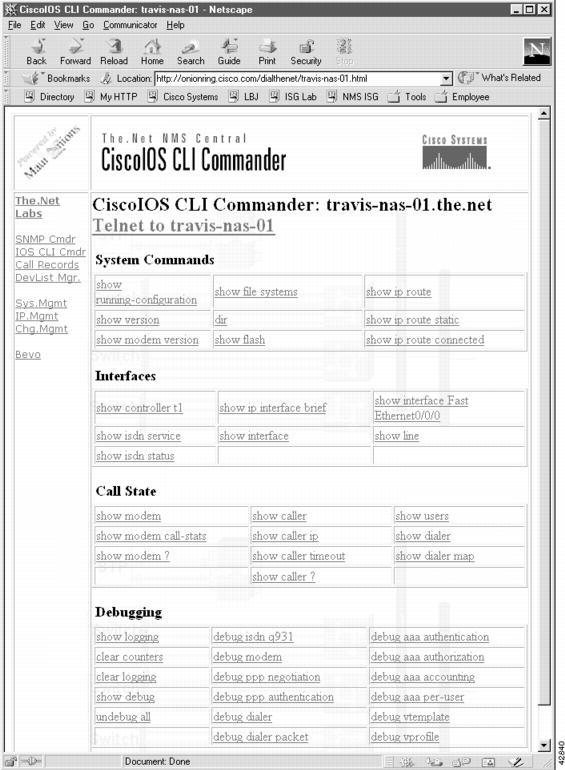
Figure 22
Cisco IOS CLI Commander
Table 30 shows the source code that created the Cisco IOS CLI Commander in Figure 22. Telnet to travis-nas-01.
Step 4
Click on a CLI command and view the command output in a web page.
Figure 23
Output for the Show Caller Command

 Feedback
Feedback