-
Cisco 7600 Series Router Software Configuration Guide Cisco IOS Release 15S
-
Preface
-
Product Overview
-
Configuring the Router for the First Time
-
Configuring a Supervisor Engine 720
-
Configuring a Route Switch Processor 720
-
Configuring NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy
-
ISSU and eFSU on Cisco 7600 Series Routers
-
Configuring RPR and RPR+ Supervisor Engine Redundancy
-
Configuring Interfaces
-
Configuring a Supervisor Engine 32
-
Configuring LAN Ports for Layer 2 Switching
-
Configuring Flex Links
-
Configuring EtherChannels
-
Configuring VTP
-
Configuring VLANs
-
Configuring Private VLANs
-
Configuring Cisco IP Phone Support
-
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
-
Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
-
Configuring L2TPv3
-
Configuring STP and MST
-
Configuring Optional STP Features
-
Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces
-
Configuring GTP-SLB IPV6 Support
-
IP Subscriber Awareness over Ethernet
-
Configuring UDE and UDLR
-
Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching on the PFC
-
Configuring IPv4 Multicast VPN Support
-
Configuring Multicast VPN Extranet Support
-
Configuring IP Unicast Layer 3 Switching
-
Configuring IPv6 Multicast PFC3 and DFC3 Layer 3 Switching
-
Configuring IPv4 Multicast Layer 3 Switching
-
Configuring MLDv2 Snooping for IPv6 Multicast Traffic
-
Configuring IGMP Snooping for IPv4 Multicast Traffic
-
Configuring PIM Snooping
-
Configuring Network Security
-
Understanding Cisco IOS ACL Support
-
Configuring VRF aware 6RD Tunnels
-
Configuring VLAN ACLs
-
Private Hosts (Using PACLs)
-
Configuring IPv6 PACL
-
IPv6 First-Hop Security Features
-
Configuring Online Diagnostics
-
Configuring Denial of Service Protection
-
Configuring DHCP Snooping
-
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
-
Configuring Traffic Storm Control
-
Unknown Unicast Flood Blocking
-
Configuring PFC QoS
-
Configuring PFC QoS Statistics Data Export
-
Configuring MPLS QoS on the PFC
-
Configuring LSM MLDP based MVPN Support
-
Configuring IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
-
Configuring IEEE 802.1ad
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring UDLD
-
Configuring NetFlow and NDE
-
Configuring Local SPAN, RSPAN, and ERSPAN
-
Configuring SNMP IfIndex Persistence
-
Power Management and Environmental Monitoring
-
Configuring Web Cache Services Using WCCP
-
Using the Top N Utility
-
Using the Layer 2 Traceroute Utility
-
Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding and Detection over Switched Virtual Interface
-
Configuring Call Home
-
Configuring IPv6 Policy Based Routing
-
Using the Mini Protocol Analyzer
-
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
-
Configuring Synchronous Ethernet
-
Configuring Link State Tracking
-
Configuring BGP PIC Edge and Core for IP and MPLS
-
Configuring VRF aware IPv6 tunnels over IPv4 transport
-
ISIS IPv4 Loop Free Alternate Fast Reroute (LFA FRR)
-
Multicast Service Reflection
-
Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
-
Online Diagnostic Tests
-
Acronyms
-
Cisco IOS Release 15S Software Images
-
Table Of Contents
Restrictions for IPv6 PACL feature
Configuring PACL mode and Applying IPv6 PACL
Configuring IPv6 PACL
This chapter describes how to configure the IPv6 Port based Access Control List (PACL).
This chapter includes the following sections:
Understanding IPv6 PACL
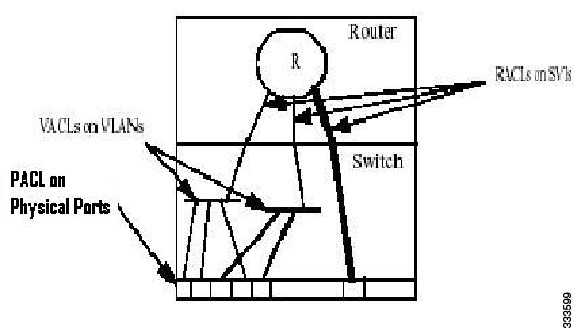
The c7600 has mechanisms to apply Access Control Lists (ACLs) at various levels such as Router, VLAN, and Port level. Router Access Control Lists (RACLs) are applied on a Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) or physical interface to filter out the layer 3 traffic. VLAN Access Control Lists (VACLs) are configured on VLANs, and are applicable on the layer 2 and the layer 3 packets passing through the VLAN.
PACLs help filter the incoming Layer 3 packets based on layer 2 and layer 4 parameters at the layer 2 switchports.
Figure 40-1 PACL on Physical Ports
Restrictions for IPv6 PACL feature
Following restrictions apply to the IPv6 PACL feature:
•
IPv6 PACL is not supported in the IOS software path.
•
IPv6 PACL is not supported in the egress direction.
•
IPv6 PACL logging is not supported.
•
IPv6 PACL does not support routing header match and Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) ACL match as these features do not have hardware support.
•
IPv6 supports fragment keyword and layer 4 information.
•
IPv6 PACL supports time-based ACLs.
•
When you configure the platform ipv6 acl icmp optimize neighbor-discovery command, a global Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Neighbor Discovery (ND) Value Mask Result (VMR) is appended at the top of the Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM). This ICMP entry overrides the applicable PACL configured on the interface.
•
IPv6 PACL is supported on the layer 2 etherchannel, but not on its member ports.
•
IPv6 PACL is supported on the trunk ports only in the port prefer mode.
•
IPv6 PACL does not support the access-list log and reflect/evaluate keywords. These keywords are ignored if you add them to the access list for a PACL.
•
Due to the limited size of the flow key in the TCAM, IPv6 addresses along with the layer 4 port information cannot be accommodated unless the IPv6 addresses are compressed. Use the mls ipv6 acl compress address unicast command to compress the IPv6 address. You cannot apply the IPv6 PACL to non-compressible addresses, if the filtering is based on layer 4 ports.
Configuring IPv6 PACL
The following sections describe how to configure IPv6 PACL on c7600:
•
Configuring PACL mode and Applying IPv6 PACL
Creating Access List
Complete the following steps to create an access list:
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1
enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Step 3
ipv6 access-list access-list-name
Step 4
{permit | deny} {protocol/ IPv6 source prefix} source [source-ipv6-address] destination [destination-ipv6-address]
Step 5
end
ETAILED STEPS
Configuration Example
This example shows how to create an IPv6 ACL:
Router# enableRouter# configure terminalRouter(config)# ipv6 access-list list1Router(config-ipv6-acl)# permit tcp 1000::1/64 anyRouter(config-ipv6-acl)# endConfiguring PACL mode and Applying IPv6 PACL
Complete the following steps to configure the PACL mode, and apply IPv6 PACL on a switchport interface:
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1
enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Step 3
interface type number
Step 4
switchport
Step 5
switchport mode {access | trunk}
Step 6
switchport access vlan vlan-id [or] switchport trunk allowed vlan vlan-list
Step 7
access-group mode {prefer {port | vlan} | merge}
Step 8
ipv6 traffic-filter access-list-name in
Step 9
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Example
This example shows how to configure a PACL mode and apply an IPv6 PACL on a switchport interface:
Router# enableRouter# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface gigabitethernet 3/24Router(config-if)# switchportRouter(config-if)# switchport mode accessRouter(config-if)# switchport access vlan 1000Router(config-if)# access-group mode prefer portRouter(config-if)# ipv6 traffic-filter list1 inRouter(config-if)# endVerifying IPv6 PACL
Use these commands to verify the configuration of IPv6 PACL on c7600:
•
The show ipv6 access-list command displays the details of all the IPv6 access lists created.
Router# show ipv6 access-listIPv6 access list PACLpermit ipv6 host 2001:410:1:0:200:FF:FE00:1 host 2001:410:2:0:200:FF:FE00:1 sequence 10deny ipv6 host 2001:410:1:0:200:FF:FE00:2 host 2001:410:2:0:200:FF:FE00:2 sequence 20permit ipv6 host 2001:410:1::3 host 2001:410:2::3 sequence 30•
The show run interface GigabitEthernet command displays the IOS interface configuration.
Router# show run interface GigabitEthernet 7/0/1Current configuration : 179 bytes!interface GigabitEthernet7/0/1switchportswitchport access vlan 10switchport mode accessipv6 traffic-filter PACL inend•
The show tcam interface GigabitEthernet acl in ipv6 command displays the following output when the IPv6 PACL is configured on an interface.
Router# show tcam interface GigabitEthernet 7/0/1 acl in ipv6* Global Defaults shared-------------------------------------------------------ICMP Neighbor Discovery Packet Types:na - neighbor advertisement ra - router advertisementns - neighbor solicit rs - router solicitr - redirectIPV6 Address Types:full - IPv6 Full eui - IPv6 EUIeipv4 - IPv6 embeded IPv4-------------------------------------------------------permit ipv6 host 0:2001:410:1:0:200:0:1(eui) host 0:2001:410:2:0:200:0:1(eui)deny ipv6 host 0:2001:410:1:0:200:0:2(eui) host 0:2001:410:2:0:200:0:2(eui)permit ipv6 host 2001:410:1::3(full) host 2001:410:2::3(full)permit icmp(nd-ra) any(eui) anypermit icmp(nd-na) any(eui) anypermit icmp(nd-rs) any(eui) anypermit icmp(nd-ra) any(full) anypermit icmp(nd-na) any(full) anypermit icmp(nd-rs) any(full) anydeny ipv6 any(eipv4) anydeny ipv6 any(eui) anydeny ipv6 any(full) any•
The show fm interface FastEthernet command displays all the features configured on a specific interface including the PACLs.
Router# show fm interface FastEthernet 2/1
Interface: FastEthernet2/1 IP is disabledhw_state[INGRESS] = not reduced, hw_state[EGRESS] = not reducedmcast = 0priority = 0flags = 0x0parent[INGRESS] = noneinbound label: 65Feature IPV6_PACL:ACL: test-----------------------------------------------------------------------------FM_FEATURE_IPV6_PACL - PACL Name: test Direction:Ingress=============================================================================DPort - Destination Port SPort - Source Port Pro - ProtocolPT - Packet Type DPT - Dst. Packet Type SPT - Src. Packet TypeX - XTAG TOS - TOS Value Res - VMR ResultRFM - R-Recirc. Flag MRTNPC - M-Multicast Flag R - Reflexive flag- F-Fragment flag - T-Tcp Control N - Non-cachable- M-More Fragments - P-Mask Priority(H-High, L-Low)Adj. - Adj. Index C - Capture Flag T - M(Mask)/V(Value)FM - Flow Mask NULL - Null FM SAO - Source Only FMDAO - Dest. Only FM SADA - Sour.& Dest. Only VSADA - Vlan SADA OnlyISADA - Intf. SADA FF - Full Flow VFF - Vlan Full FlowIFF - Intf. FF F-VFF - Either FF or VFF IFF-FF - Either IFF or FFA-VSD - Atleast VSADA A-FF - Atleast FF A-VFF - Atleast VFFA-SON - Atleast SAO A-DON - Atleast DAO A-SD - Atleast SADASHORT - Shortest ISADA-L- ISADA Least FF-L - FF LeastIFF-L - IFF Least A-SFF - Any short than FF A-EFF - Any except FFA-EVFF - Any except VFF SA-L - Source Least DA-L - Dest. LeastSADA-L - SADA Least FF-LESS- FF Less N-FF - Not FFN-IFF - Not IFF A-LVFF - Any less than VFF FULL - Full Pkt TypeEUI - EUI 64 Pkt Type EMBD - Embedded Pkt Type ELNK - EUI Link OverlapESIT - EUI Site Overlap LINK - Link Pkt Type SITE - Site Pkt TypeERR - Flowmask Error
Troubleshooting Tips
For troubleshooting information, contact Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/support/tsd_cisco_worldwide_contacts.html

 Feedback
Feedback