-
Cisco 7600 Series Router Software Configuration Guide Cisco IOS Release 15S
-
Preface
-
Product Overview
-
Configuring the Router for the First Time
-
Configuring a Supervisor Engine 720
-
Configuring a Route Switch Processor 720
-
Configuring NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy
-
ISSU and eFSU on Cisco 7600 Series Routers
-
Configuring RPR and RPR+ Supervisor Engine Redundancy
-
Configuring Interfaces
-
Configuring a Supervisor Engine 32
-
Configuring LAN Ports for Layer 2 Switching
-
Configuring Flex Links
-
Configuring EtherChannels
-
Configuring VTP
-
Configuring VLANs
-
Configuring Private VLANs
-
Configuring Cisco IP Phone Support
-
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
-
Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
-
Configuring L2TPv3
-
Configuring STP and MST
-
Configuring Optional STP Features
-
Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces
-
Configuring GTP-SLB IPV6 Support
-
IP Subscriber Awareness over Ethernet
-
Configuring UDE and UDLR
-
Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching on the PFC
-
Configuring IPv4 Multicast VPN Support
-
Configuring Multicast VPN Extranet Support
-
Configuring IP Unicast Layer 3 Switching
-
Configuring IPv6 Multicast PFC3 and DFC3 Layer 3 Switching
-
Configuring IPv4 Multicast Layer 3 Switching
-
Configuring MLDv2 Snooping for IPv6 Multicast Traffic
-
Configuring IGMP Snooping for IPv4 Multicast Traffic
-
Configuring PIM Snooping
-
Configuring Network Security
-
Understanding Cisco IOS ACL Support
-
Configuring VRF aware 6RD Tunnels
-
Configuring VLAN ACLs
-
Private Hosts (Using PACLs)
-
Configuring IPv6 PACL
-
IPv6 First-Hop Security Features
-
Configuring Online Diagnostics
-
Configuring Denial of Service Protection
-
Configuring DHCP Snooping
-
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
-
Configuring Traffic Storm Control
-
Unknown Unicast Flood Blocking
-
Configuring PFC QoS
-
Configuring PFC QoS Statistics Data Export
-
Configuring MPLS QoS on the PFC
-
Configuring LSM MLDP based MVPN Support
-
Configuring IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
-
Configuring IEEE 802.1ad
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring UDLD
-
Configuring NetFlow and NDE
-
Configuring Local SPAN, RSPAN, and ERSPAN
-
Configuring SNMP IfIndex Persistence
-
Power Management and Environmental Monitoring
-
Configuring Web Cache Services Using WCCP
-
Using the Top N Utility
-
Using the Layer 2 Traceroute Utility
-
Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding and Detection over Switched Virtual Interface
-
Configuring Call Home
-
Configuring IPv6 Policy Based Routing
-
Using the Mini Protocol Analyzer
-
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
-
Configuring Synchronous Ethernet
-
Configuring Link State Tracking
-
Configuring BGP PIC Edge and Core for IP and MPLS
-
Configuring VRF aware IPv6 tunnels over IPv4 transport
-
ISIS IPv4 Loop Free Alternate Fast Reroute (LFA FRR)
-
Multicast Service Reflection
-
Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
-
Online Diagnostic Tests
-
Acronyms
-
Cisco IOS Release 15S Software Images
-
Table Of Contents
Multicast Service Reflection Working Architecture
Restrictions for Multicast Service Reflection
Configuring Multicast Service Reflection
Multicast Service Reflection
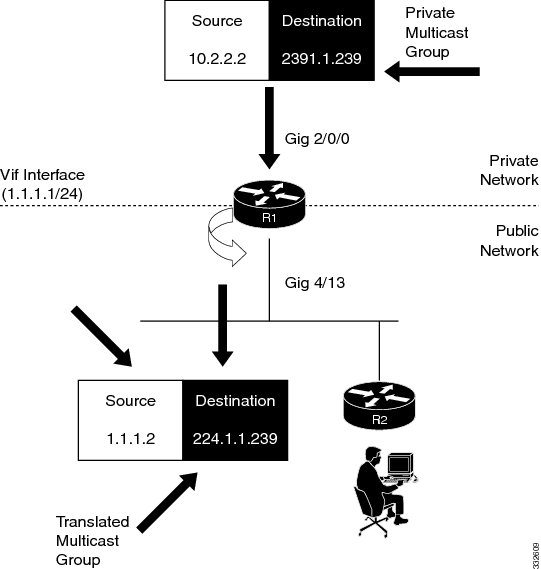
Multicast service reflection feature enables the users to translate externally received multicast destination addresses to addresses that conform to the organization's internal addressing policy. With this feature, users need not redistribute routes at the translation boundary into their network infrastructure for the Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) to work properly. Also, users can receive identical feeds from two ingress points in the network and route them independently.
The multicast service reflection feature is configured on the virtual interface. When a packet is forwarded to a virtual interface (original IP), this feature maps the original IP address to an internal IP address and the traffic is directed to the internal IP address. Therefore, it enables an organization to logically separate the private and public multicast networks.
Multicast Service Reflection Working Architecture
For multicast service reflection, the virtual interface is configured to statically join the group that needs to be translated to build a multicast tree. The virtual interface maintains information about:
•
Input interface
•
Private-to-public multicast group mappings
•
Mask length to define the pool range
•
Source of translated packet
When a packet is forwarded to a virtual interface, it is reflected for translation. The source IP address is changed to the IP address of the virtual interface subnet, which prevents RPF failures. Finally, the destination IP address is translated to a new multicast group IP address.
Figure 74-1 shows the multicast service reflection working architecture.
Figure 74-1 Multicast Service Reflection Working Architecture
Restrictions for Multicast Service Reflection
Following restrictions apply for multicast service reflection feature:
•
The virtual interface should be installed on the border router.
•
Multicast service reflection does not support bidirectional multicast.
•
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)/IGMP control packets are not translated.
•
Multicast service reflection does not support P2P GRE tunnelling.
•
Multicast service reflection does not support IPv6 multicasting.
•
Only 1000 service reflection translations are supported.
•
Multicast service reflection is not supported in the PIM-Dense mode.
Configuring Multicast Service Reflection
Complete these steps to configure multicast service reflection feature.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ip multicast-routing [distributed]
4.
interface loopback loopback_id
5.
description description
6.
ip address ip_address subnet_mask
7.
ip pim sparse-mode
8.
exit
9.
interface gigabitEthernet slot/port
10.
ip address ip_address subnet_mask
11.
ip pim sparse-mode
12.
exit
13.
interface gigabitEthernet slot/port
14.
ip address ip_address subnet_mask
15.
ip pim sparse-mode
16.
exit
17.
interface vif_id
18.
ip address ip_address subnet_mask
19.
ip pim sparse-mode
20.
ip service reflect interface_id destination destination_ip1 to destination_ip2 mask-len subnet_mask_length source source_ip
21.
ip igmp static-group {* | group-address [source {source-address | ssm-map}]}
22.
exit
23.
ip pim rp-address rp_address
24.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Example
This example describes how to configure multicast service reflection.
R11>enableR11#configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.R11(config)#ip multicast-routingR11(config)#interface Loopback0R11(config-if)#description Rendezvous Point for Public NetR11(config-if)#ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255R11(config-if)#ip pim sparse-mode
R11>exit
R11#interface GigabitEthernet2/0/0
R11(config)#ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.0.0R11(config-if)#ip pim sparse-mode
R11(config)#exitR11(config)#interface GigabitEthernet4/13R11(config-if)#ip address 23.1.1.2 255.255.0.0R11(config-if)#ip pim sparse-mode
R11(config-if)#exitR11(config)#interface Vif1R11(config-if)#ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.0.0R11(config-if)#ip pim sparse-modeR1(config-if)#ip service reflect GigabitEthernet2/0/0 destination 239.1.1.100 to 225.1.1.100 mask-len 32 source 1.1.1.2R1(config-if)#ip igmp static-group 239.1.1.100R1(config-if)#exitR1(config)#ip pim rp-address 22.22.22.22
R11(config-if)#exitFor more information on configuring multicast service reflection, see Configuring Multicast Service Reflection.

 Feedback
Feedback