-
Cisco Prime Network User Guide, 4.0
-
Preface
-
Setting Up Devices and Using the GUI Clients
-
Working with the Cisco Prime Network Vision Client
-
Viewing and Managing NE Properties
-
Device Configurations and Software Images
-
Working with Prime Network Vision Maps
-
Working with Links
-
Labeling NEs Using Business Tags
-
Tracking Faults Using Prime Network Events
-
Working with Tickets in Cisco Prime Network Vision
-
Working with Reports
-
Using Cisco PathTracer to Diagnose Problems
-
Monitoring Carrier Ethernet Services
-
Monitoring Carrier Grade NAT Properties
-
Monitoring DWDM Properties
-
Monitoring Ethernet Operations, Administration, and Maintenance Tool Properties
-
Monitoring Y.1731 IPSLA Configuration
-
IPv6 and IPv6 VPN over MPLS
-
Monitoring MPLS Services
-
Viewing IP and MPLS Multicast Configurations
-
Monitoring MToP Services
-
Viewing and Managing SBCs
-
Monitoring AAA Configurations
-
Monitoring IP Pools
-
Monitoring BNG Configurations
-
Monitoring Mobile Technologies
-
Monitoring Data Center Configurations
-
Monitoring the Cable Technologies
-
Monitoring ADSL2+ and VDSL2 Technology Enhancements
-
Icon and Button Reference
-
Glossary
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Working with Prime Network Vision Maps
User Roles Required for Working with Prime Network Vision Maps
Deleting Maps from the Database
Adding and Removing NEs from Maps
Finding NEs, Services, and Links, and Elements Affected by Tickets
Grouping Network Elements into Aggregations
Viewing an Aggregation Thumbnail
Adding Elements to an Existing Aggregation
Communicating with Devices Using Ping and Telnet
Working with Prime Network Vision Maps
The topological map is the main tool used by Cisco Prime Network Vision (Prime Network Vision) to display the links and relationships between the network elements and aggregations. The following topics describe how to work with the topological maps displayed in the content pane of the Prime Network Vision window:
•
User Roles Required for Working with Prime Network Vision Maps
•
Adding and Removing NEs from Maps
•
Finding NEs, Services, and Links, and Elements Affected by Tickets
•
Communicating with Devices Using Ping and Telnet
You can also perform the following functions from the map and list views if they are configured for your client:
•
Launch external applications or tools, such as an SSH client.
•
Launch available scripts and commands, depending on the NE device type, OS, supported technologies, and so forth. Those commands are documented throughout this guide (for example, Setting Up Devices and Validating Device Information). This also includes commands you create using Command Manager and Command Builder. A list of scripts is provided in Cisco Prime Network 4.0 Supported VNEs - Addendum.
User Roles Required for Working with Prime Network Vision Maps
This topic identifies the roles that are required to work with Prime Network Vision maps. Prime Network determines whether you are authorized to perform a task as follows:
•
For GUI-based tasks (tasks that do not affect elements), authorization is based on the default permission that is assigned to your user account.
•
For element-based tasks (tasks that do affect elements), authorization is based on the default permission that is assigned to your account. That is, whether the element is in one of your assigned scopes and whether you meet the minimum security level for that scope.
For more information on user authorization, see the Cisco Prime Network 4.0 Administrator Guide.
The following tables identify the tasks that you can perform:
•
Table 5-1 identifies the tasks that you can perform if a selected element is not in one of your assigned scopes.
•
Table 5-2 identifies the tasks that you can perform if a selected element is in one of your assigned scopes.
By default, users with the Administrator role have access to all managed elements. To change the Administrator user scope, see the topic on device scopes in the Cisco Prime Network 4.0 Administrator Guide.
Table 5-1 Default Permission/Security Level Required for Working with Prime Network Vision Maps - Element Not in User's Scope
Apply a background image
—
—
—
X
X
Create maps
—
—
X
X
X
Define a map layout
X
X
X
X
X
Delete maps
—
—
X
X
X
Open maps
X
X
X
X
X
Preview and print maps
X
X
X
X
X
Rename maps
—
—
X
X
X
Save as a new map
—
—
X
X
X
Save as an image
X
X
X
X
X
Save map appearance
—
—
X
X
X
Select viewing options
X
X
X
X
X
Use Overview window
X
X
X
X
X
View maps
X
X
X
X
X
Add elements to a map
—
—
X
X
X
Remove elements from a map
—
—
X
X
X
Resize elements in a map
X
X
X
X
X
Group and ungroup aggregations
—
—
X
X
X
Rename aggregations
X
X
X
X
X
View aggregation thumbnails
X
X
X
X
X
Find affected elements
—
—
—
—
X
Find an element or service
X
X
X
X
X
Find and select a link in a map1
X
X
X
X
X
Filter links
X
X
X
X
X
Apply an overlay
X
X
X
X
X
Hide or view an overlay
X
X
X
X
X
Remove an overlay
X
X
X
X
X
Open the CPU Usage Graph
—
—
—
—
X
Use Ping and Telnet to communicate with elements
—
—
—
—
X
1 This applies to links within the selected context, and not links identified as network links.
Table 5-2 Default Permission/Security Level Required for Working with Prime Network Vision Maps - Element in User's Scope
Apply a background image
—
—
—
X
X
Create maps
—
—
X
X
X
Define a map layout
X
X
X
X
X
Delete maps
—
—
X
X
X
Open maps
X
X
X
X
X
Preview and print maps
X
X
X
X
X
Rename maps
—
—
X
X
X
Save as a new map
—
—
X
X
X
Save as an image
X
X
X
X
X
Save map appearance
—
—
X
X
X
Select viewing options
X
X
X
X
X
Use Overview window
X
X
X
X
X
View maps
X
X
X
X
X
Add elements to a map
—
—
X
X
X
Remove elements from a map
—
—
X
X
X
Resize elements in a map
X
X
X
X
X
Group and ungroup aggregations
—
—
X
X
X
Rename aggregations
X
X
X
X
X
View aggregation thumbnails
X
X
X
X
X
Find affected elements
X
X
X
X
X
Find an element or service
X
X
X
X
X
Find and select a link in a map1
X
X
X
X
X
Filter links
X
X
X
X
X
Apply an overlay
X
X
X
X
X
Hide or view an overlay
X
X
X
X
X
Remove an overlay
X
X
X
X
X
Open the CPU Usage Graph
—
—
X
X
X
Use Ping and Telnet to communicate with devices
—
—
—
X
X
1 This applies to links within the selected context, and not links identified as network links.
Opening and Closing Maps
Whenever you open a map, the network information is automatically refreshed. For example, if a device was up the last time that the map was saved and closed, and then the device is moved to maintenance, the next time you open the map the management status of the device is updated accordingly and the device displays a maintenance status.
When you first log in, Prime Network Vision lists the maps you recently viewed but did not close when you exited the session. You can also open other maps by choosing File > Open, which displays the Open Map dialog.
By default, you can view and work on a maximum of five maps at any given time (per client instance) in the Prime Network Vision window. To change this default setting, contact your Cisco account representative. To create a new map or select a new map, close the required number of maps.
You can save maps as images or print them, if desired.
To close a map, choose File > Close. Prime Network Vision saves basic map information whether or not you manually save the map. This default information includes device and link additions, device and link removals, aggregations, and disaggregations. If you made any changes that will not be saved, Prime Network Vision prompts you to save the map.
Creating and Deleting Maps
You can create maps that cover specific network segments, customer networks, or any other mix of network elements required. Network maps provide a graphic display of active faults and alarms, and serve as access points for activating services. When you create a map, it is saved in the database and made available to other users if they have sufficient access and security privileges. When you delete a map, it is removed from the database. See these topics for more information:
•
Deleting Maps from the Database
Creating New Maps
To create a new map, choose File > New Map in the main menu. The following figures give examples of how you can create and manipulate maps. To add NEs to maps, see Adding and Removing NEs from Maps.
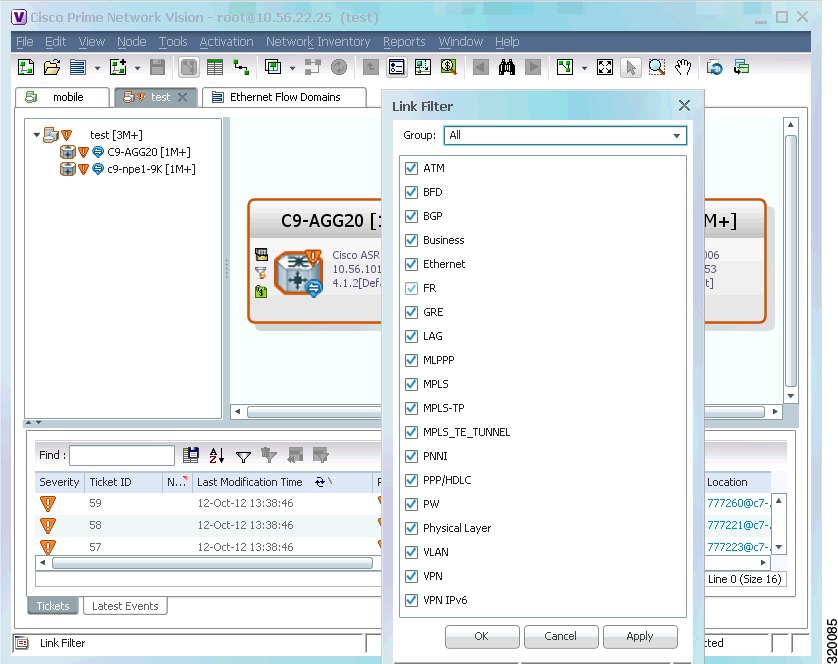
Link Filters
Link filters let you choose the links in which you are interested, and then build a map that only displays NEs using those link types. Examples are physical links, data links, MPLS, VLANs, and so forth. When you open the New Map dialog, click the Advanced button and choose the types you want to display.
Figure 5-1 Map with Link Filter
To create a map with link filters, see Figure 5-13.
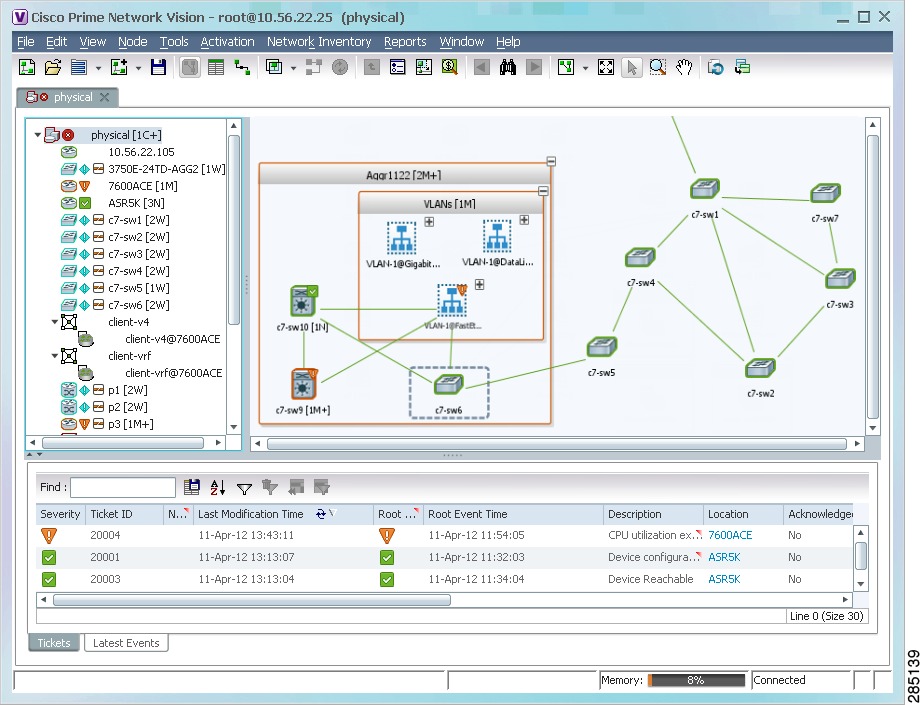
Aggregations
Aggregations are user-defined groups of elements. An aggregation can contain network elements, services, other aggregations, and so forth. Figure 5-2 shows an example of an aggregation.
Figure 5-2 Map with Aggregation (Thumbnail View)
When you delete an aggregation, the member devices are not deleted from Prime Network; only the aggregation definition is deleted. To create an aggregation, see Working with Aggregations.
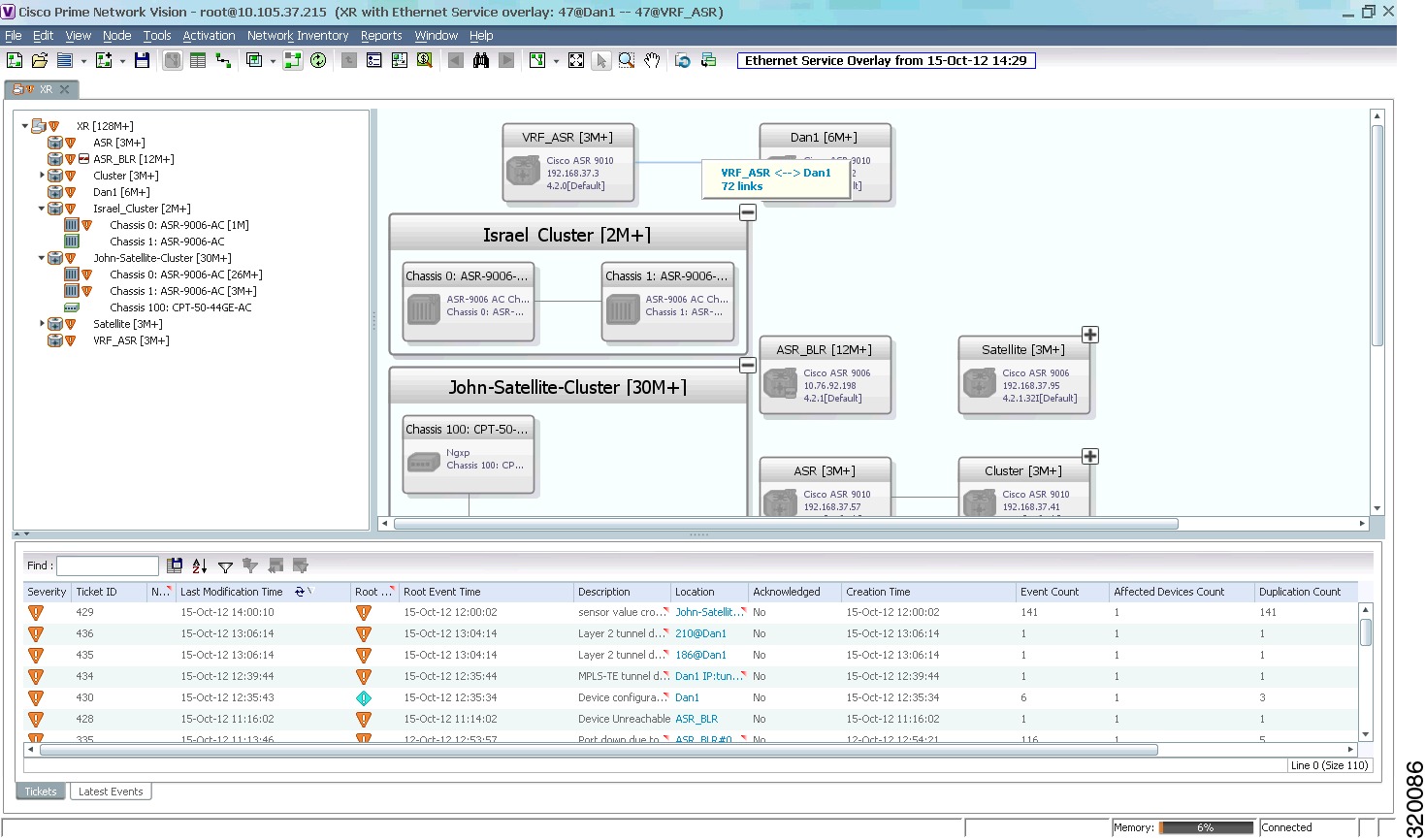
Overlays
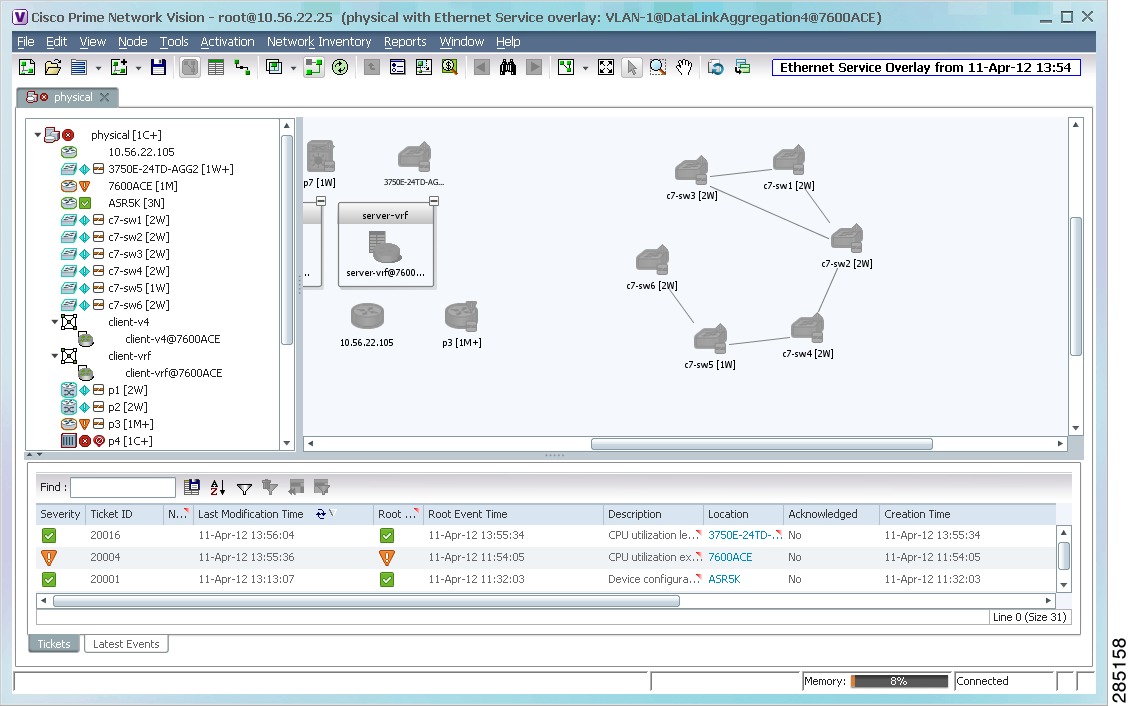
Overlays isolate the parts of a network that are being used by a specific service, such as an ethernet service or network clock. Figure 5-3 shows an example of an Ethernet Service overlay, where the ethernet link is using the service.
Figure 5-3 Map with Overlay
To create an overlay, see Working with Overlays.
Deleting Maps from the Database
If another client is using a map that you are deleting, Prime Network Vision displays a message to those clients advising them that the map is being closed and deleted from the database.
To delete a map from Prime Network Vision and the Prime Network Vision database:
Step 1
Open the Open Map dialog by choosing File > Open.
Step 2
In the Open Map dialog box, complete the following steps:
a.
Select the map you want to delete.
b.
In the toolbar, click Delete Map. A confirmation message is displayed.
c.
Click Yes. The selected map is deleted from the Open Map dialog box, the Prime Network Vision window, and the database. If the map is open when you click Yes, a message is displayed, stating that the map will be closed.
d.
Click OK to acknowledge that the map can be closed.
e.
Click Cancel to close the Open Map dialog box.
Adding and Removing NEs from Maps
When you add an element to a map, the map is automatically saved in the Prime Network Vision database
If the element you want to add is outside of your scope, it is not displayed if you enter a search string. You can display all NEs by selecting Show All in Step 2, but devices outside your scope will be displayed with a lock icon.
To add an element to a map:
Step 1
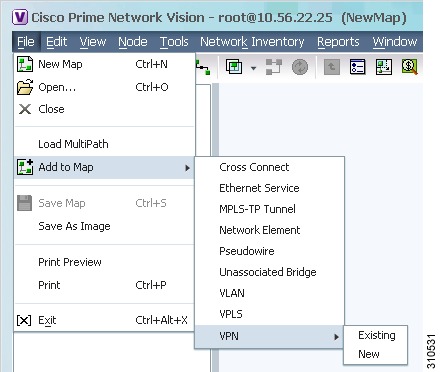
Choose File > Add to Map > element.
Figure 5-4 shows the type of elements you can add to maps.
Figure 5-4 Available Elements to Add to Maps
If you choose to add a new VPN, the Create VPN dialog box is displayed. For information on creating a VPN, see Creating a VPN.
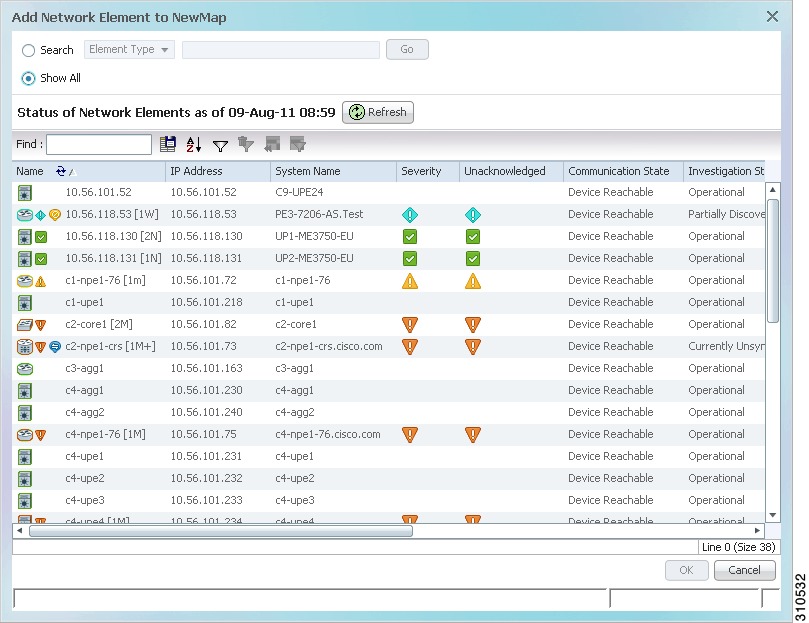
In all other instances, the Add element to map dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 5-5.
Figure 5-5 Add Element Dialog Box
Step 2
In the Add element dialog box, do one of the following:
If you are working with a very large number of network elements, keep these items in mind:
•
Search for the elements you want to add to the map. For example, you can search Ethernet Services by the system name, NEs element type, pseudowires by their role, and so forth.
Note
If you are working with a large number of NEs, using the search filter Otherwise, it may take some time for all of the NEs to be listed.
•
To view all available elements, choose Show All.
The available elements are displayed in the Add element dialog box in table format. The dialog box also displays the date and time at which the list was generated. To update the list, click Refresh.
If a network element is not included in your scope, it is displayed with the locked device icon.
Step 3
In the Add element dialog box, select the elements that you want to add. You can select and add multiple elements by pressing Ctrl while selecting individual network elements or by pressing Ctrl + Shift to select a group of elements.
Step 4
Click OK. If you selected a large number of elements (for example, more than 25 VLANs or VPLS instances), the action may take a while to complete.
The NEs are added to the map and are displayed in the navigation pane and content area. In addition, any associated tickets are displayed in the ticket pane.
Removing Elements from a Map
When you delete an element or aggregation from a map, it is removed from the map in the database, but the elements are still managed by Prime Network Vision.
Note
Based on the security level and access permissions assigned, this option might not be available to all users.
To remove a network element or aggregation from a map:
Step 1
In the navigation pane or map, select the element or aggregation that you want to delete.
Step 2
Right-click to display the right-click menu and choose Remove from Map. The selected element or aggregation is removed from the map.
The element is removed from the map in the database, but is still managed by Prime Network Vision and can be added again.
Managing Maps
The following topics describe how to manage maps in Prime Network Vision:
•
Selecting Map Viewing Options
Selecting Map Viewing Options
Table 5-3 describes the tools that you can use to view and manipulate maps in the Prime Network Vision map pane.
Applying a Background Image
Prime Network Vision allows you to apply a background image to the map view. You can also choose the same background image or different images for other subordinate windows, such as detailed views of aggregations, VLANs, and VPNs.
The supported file formats are GIF, JPG/JPEG, and PNG.
Note
Background images are not supported in thumbnail views.
To apply a background image to a map:
Step 1
Navigate to the required map in Prime Network Vision. The map can reside at the top level or in a subordinate window.
Step 2
Right-click the map background and choose Set Map Background.
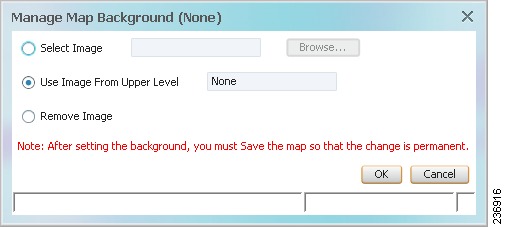
The Manage Map Background dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 5-6.
Figure 5-6 Manage Map Background Dialog Box
Step 3
Enter the required information as described in Table 5-4.
Table 5-4 Manage Map Background Options
Select Image
Applies the selected image to the current map background:
1.
Choose Select Image.
2.
Click Browse.
3.
In the Open dialog box, select the desired image and click OK.
The name of the selected image is displayed in the Manage Map Background dialog box.
4.
Click OK. The selected image is displayed as the map background.
Use Image From Upper Level
Indicates whether the selected subordinate map should use the same image as the parent map or a different image:
•
To use the same image that is used by the parent map, choose Use Image from Upper Level. The name of the image used by the parent map is displayed by default.
•
To use a different image than that used by the parent map, choose Select Image and complete the steps described for that option.
Remove Image
Removes the current image from the map background.
To remove an image from the current map, click Remove Image.
Step 4
Click OK. The current map background is updated as specified.
Step 5
To retain the background image for subsequent logins, do one of the following:
•
Click Save in the toolbar.
•
Choose File > Save.
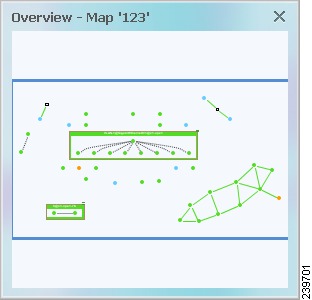
Using the Overview Window
The Prime Network Vision Overview window enables you to display the entire network map or any part of the map that you require in the map pane. The Overview window also enables you to see all the changes and alarms taking place in the network.
To open the network Overview window do either of the following:
•
Click Overview in the main toolbar.
•
Choose View > Overview from the main menu.
Figure 5-7 shows an example of the Overview window.
Figure 5-7 Overview Window
The Overview window can contain the following components:
•
Dot—Indicates an element. The dot color indicates the severity of an associated alarm.
•
Line—Indicates a link. The line color indicates the severity of an associated alarm.
•
Blue rectangle—Indicates the selection area. The area within the rectangle is displayed in the map pane. Handles on the corners enable you to resize the selection area.
•
Pan mode cursor—Displayed within the selection area. Use this cursor to move the selection area, and thereby view different elements in the map pane.
•
Zoom mode cursor—Displayed outside the selection area. Use this cursor to define a new selection area or to zoom in on an existing selection area.
Click the upper right corner to close the Overview window.
Saving Maps
By default, Prime Network Vision saves basic map information whether or not you manually save the map. This default information includes element additions and removals, link additions and removals, aggregations, and disaggregations. However, you must use the Save Map option if you want to retain the following information in the database:
•
Device location on the map
•
Thumbnails
•
Icon size
To save these changes, click Save Map Appearance in the main toolbar, then click OK. The map is saved as an image in the directory you specified.
Finding NEs, Services, and Links, and Elements Affected by Tickets
The following topics describe how to find network elements, services, links, or elements affected by a ticket in Prime Network Vision maps.
Working with Aggregations
Prime Network Vision enables you to group network elements and display them as an aggregation. Aggregations can contain network elements, services, other aggregations, and so forth.
Note
You cannot aggregate service entities that exist within a service. For example, you cannot aggregate VRFs that exist within a VLAN.
For more information on working with aggregations, see the following topics:
•
Grouping Network Elements into Aggregations
•
Adding Elements to an Existing Aggregation
•
Viewing an Aggregation Thumbnail
•
Viewing Multi-Chassis Devices
Grouping Network Elements into Aggregations
To aggregate network elements:
Step 1
Select the network elements. To select multiple items, press Ctrl.
Step 2
Aggregate the network elements by choosing Node > Aggregate.
Step 3
In the Aggregation dialog box, enter a unique name for the aggregation and click OK. The aggregation is displayed in the navigation pane and the map pane. Aggregations are displayed as a single entity with the Aggregation icon and a plus sign, as in the following examples:
The aggregation icon changes color according to the alarm severity. For more information about severity colors, see Alarm Indicators.
Viewing an Aggregation Thumbnail
You can view a thumbnail of a selected aggregation in the map pane, including all aggregated elements and any nested aggregations.
To display an aggregation thumbnail:
Step 1
Select the existing aggregation in the map pane.
Step 2
Open the thumbnail by right-clicking the aggregation, and choosing Show Thumbnail.
The thumbnail is displayed in the map pane as shown in Figure 5-8.
Figure 5-8 Aggregation Thumbnail
When a thumbnail is opened, neighboring nodes are moved aside by default to allow room for the thumbnail to expand. Similarly, when a thumbnail is closed, the neighboring nodes usually return to their original locations. This behavior of the neighboring nodes when a thumbnail is opened and closed is configured in the registry, and can be disabled, if required.
A dashed gray border around an icon indicates that the element resides within a thumbnail and not at the current map level.
Table 5-6 describes the options available when working with aggregation thumbnails.
Step 3
To close the aggregation thumbnail, right-click the thumbnail frame and choose Show As Aggregation.
Adding Elements to an Existing Aggregation
You can add elements to an existing aggregation at any time. When adding elements to an aggregation, keep in mind that certain restrictions exist. For example, you cannot add an EVC to a VLAN.
To add elements to an existing aggregation:
Step 1
Select the existing aggregation in the map pane.
Step 2
Open the thumbnail by right-clicking the aggregation, and choosing Show Thumbnail.
Step 3
Double-click the thumbnail frame to view the aggregation at the map level.
Step 4
Click Add to Map to add the required element to the aggregation.
Step 5
Return to the map by double-clicking the map background.
Ungrouping Aggregations
Aggregations can be ungrouped. If the aggregation that you ungroup contains nested aggregations, the nested aggregations move up one level, and the original aggregation is removed.
If an element in the aggregation that you ungroup also exists at the parent level, the element is represented only once after the aggregation is ungrouped. As a result, no elements are represented twice at the same level.
To ungroup an aggregation:
Step 1
Select the required aggregation in Prime Network Vision.
Step 2
Ungroup the node by selecting the aggregation in the map pane and choosing Node > Disaggregate.
If the aggregation contains elements that already exist at the parent level, a confirmation message is displayed, stating that any duplicate elements will be removed.
Step 3
Confirm the disaggregation. The node is disaggregated. Any aggregations in the selected node move up one level, and the original aggregation is removed.
Viewing Multi-Chassis Devices
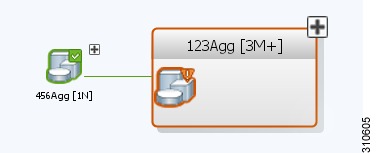
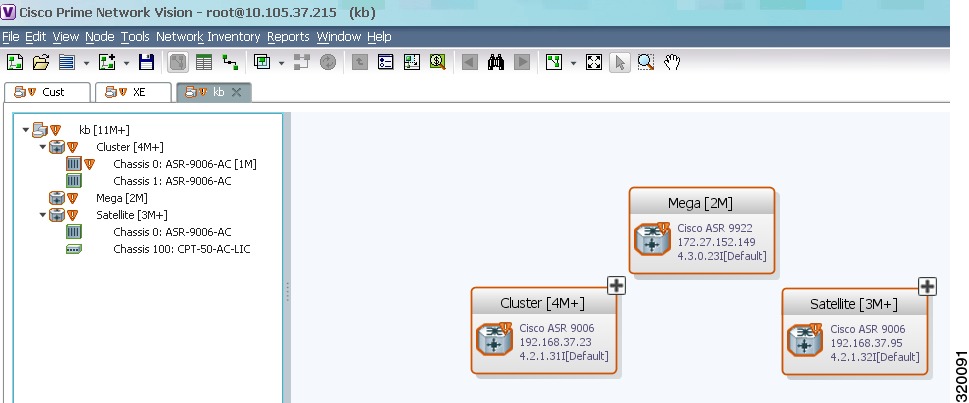
Using Prime Network Vision, you can view the physical layout and topology among the multi-chassis devices on the map. The multi chassis devices are grouped as an aggregation and are displayed as a single entity with a plus sign on the map as show in Figure 5-9. The plus sign can be expanded to display the devices under the group as shown in Figure 5-10.
You can see the multichassis grouping in the map view for network elements such as Cisco Aggregation Service Router (ASR) 9000 series network element and Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS). If satellites are configured for a Cisco ASR 9000 series network element, you can view the satellites grouped with the other chassis. For more information on how to view satellite properties, see Viewing Satellite Properties.
The physical ethernet links used for connecting the multi chassis devices are ICL (Inter Chassis Link) and IRL (Inter Rack Link). For more information on when each of these links are used, see Viewing Inter Rack Links and Viewing Inter Chassis Links.
Figure 5-9 Multichassis Devices in Map View
Viewing Inter Rack Links
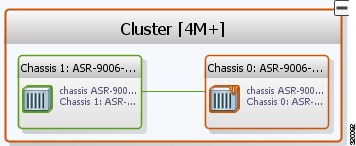
Inter Rack Links (IRLs) are used to represent connectivity between the cluster hosts, Cisco ASR 9000 network elements.
Figure 5-10 Multiple Chassis in a Cluster
To view the cluster IRLs:
Step 1
In Prime Network Vision, double-click the cluster device to open the Inventory Window for the device.
Step 2
Choose the Cluster IRL container in the logical inventory of the cluster device. The content pane displays a list of cluster IRLs with the following details:
•
A End Point—Device or site that is the source of the link, hyperlinked to the inventory of the device or site.
•
Z End Point—Device or site that is the destination of the link, hyperlinked to the relevant entry in the inventory.
Viewing Inter Chassis Links
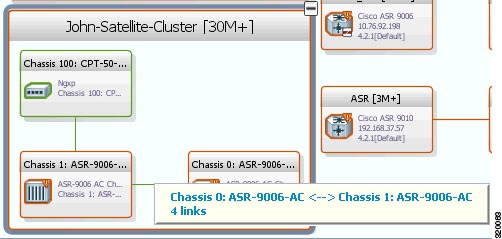
Inter Chassis Links (ICLs) are used to represent the connectivity between the host Cisco ASR 9000 network element and the satellites. One or more satellites are connected to the host Cisco ASR 9000 series network element by using the ICLs. Figure 5-11 shows an ICL in the map view.
Figure 5-11 ICL Connecting a Satellite with a Chassis
To view the satellite ICLs:
Step 1
In Prime Network Vision, double-click the satellite device to open the Inventory Window for the device.
Step 2
Choose the Satellite ICL container in the logical inventory of the cluster device. The content pane displays a list of Satellite ICLs with the following details:
Working with Overlays
When you apply an overlay to a map, you can isolate the parts of a network that are being used by a specific service.
Applying an Overlay
To apply an overlay:
Step 1
In Prime Network Vision, choose the map in which you want to apply an overlay.
Step 2
From the toolbar, choose Choose Overlay Type > overlay-type where overlay-type is one of the following options:
With the exception of the None option, a dialog box is displayed that allows you to select the specific overlay to apply.
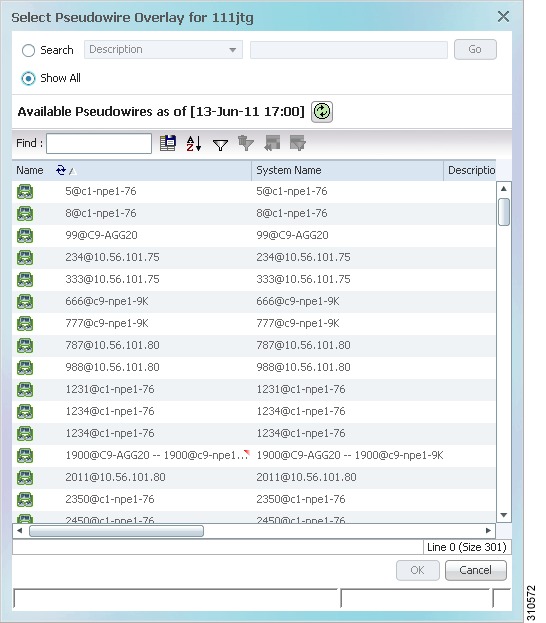
Figure 5-12 shows an example of the Select Pseudowire Overlay dialog box.
Figure 5-12 Select Pseudowire Overlay Dialog Box
Each overlay type allows you to search for specific overlays. Table 5-8 identifies the search fields available for each overlay type.
Step 3
In the Select Overlay dialog box, do either of the following:
•
To search for specific overlays:
a. Choose Search.
b. In the Search field, choose a search category.
c. Enter a search string to narrow the display to a range of overlays or to a specific overlay. Table 5-8 identifies the search categories available for each type of overlay.
d. Click Go.
Search strings are case-insensitive. If you choose Name and enter NET, the overlays that contain "net" in their names are displayed. If you choose System Name and enter System123, only the overlay with the system named System123 is displayed.
•
To view all available overlays, choose Show All.
The available overlays that meet the specified search criteria are displayed in the Select Overlay dialog box in table format. The dialog box also displays the date and time at which the list was generated. To update the list, click Refresh.
Step 4
Select the overlay that you want to apply to the map.
The elements and links that are used by the overlay are displayed in the map, and the overlay name and date are displayed in the toolbar, as shown in Figure 5-13.
Figure 5-13 Overlay Example
Note
The overlay is a snapshot taken at a specific point in time and does not reflect changes that occur in the service. As a result, the information in an overlay can become stale. To update the overlay, click Refresh Overlay in the toolbar.
Hiding and Viewing Overlays, and Removing Overlays from a Map
When an overlay is applied to a map, the Show Overlay/Hide Overlay button becomes active in the toolbar. To hide and view the overlay, click Hide Overlay/Show Overlay in the toolbar. The button toggles depending on whether the overlay is currently displayed or hidden.
To remove an overlay, choose Choose Overlay Type > None. The overlay is removed from the map.
Filtering Links in a Map
The links filter enables you to filter the links displayed in the map view and the links view. You can quickly select the types of links to be filtered by selecting from a predefined set of link types in the list, or by manually configuring a customized set of link types.
To filter links, do either of the following:
•
Create a new map, select a filter, and then add the devices to the map. This filter is applied to the new map and only the required link types are visible in the map view and the links view. For more information, see Filtering Links During Map Creation.
•
Create a map and add the devices with all links enabled and visible in the map view and links view. You can then filter (display or hide) the different types of links as required. For more information, see Filtering Links in an Existing Map.
The links filter applies to all aspects of Prime Network Vision: the map view, links view, ticket pane, severity calculation, and other items, such as memory consumption and thresholds. Prime Network Vision holds only the links that are relevant to the filter and synchronizes the links with the gateway according to that filter.
For more information about links in Prime Network Vision, see Chapter 6 "Working with Links."
Filtering Links During Map Creation
To filter links while creating a map:
Step 1
Open the Create Map dialog box by choosing File > New Map from the main menu. The Create Map dialog box is displayed. For more information, see Creating and Deleting Maps.
Step 2
Click Advanced. The Link Filter dialog box is displayed.
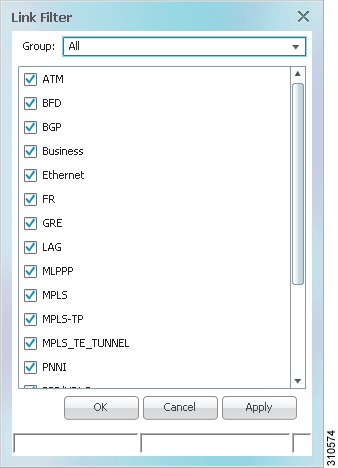
Figure 5-14 Link Filter Dialog Box
The Link Filter dialog box displays a list of all the types of links that you can filter in the map view and links view.
Note
By default all link types are selected in the Link Filter dialog box. That is, all links are displayed in the map view and links view.
Step 3
Select the required option from the Group drop-down list:
•
All—All the links are displayed in the map view and links view.
•
Custom—Only the links defined for the customized filter are displayed in the map view and links view.
•
Data Link—The data link layer class of links (ATM and Frame Relay) is displayed in the map view and links view.
•
None—None of the links are displayed in the map view and links view.
•
Physical—Only the physical links are displayed in the map view and links view.
•
VPN—Only VPN-related links (GRE, Pseudowire, VPN, and VPN IPv6) are displayed in the map view and links view.
Note
You can customize the Group drop-down list options by selecting an option and adding or removing the required link types. The next time the Link Filter dialog box is opened, the Custom option is displayed with the specified link types.
Step 4
Click Apply to apply the defined link filter settings and continue with more selections.
Step 5
Click OK when you have completed your selections.
Step 6
In the Create Map dialog box, enter a name for the new map and click OK. An empty new map is displayed in the navigation pane and content area, and the Link Filter Applied button is displayed in the to indicate that the links have been filtered.
Step 7
Add the required elements to the map. For more information, see Creating and Deleting Maps.
The links are displayed in the map view and links view according to your selections.
Filtering Links in an Existing Map
You can also create a map, add elements with all links enabled and visible in the map view and links view, and then filter (display or hide) the different types of links as required.
To filter links in an existing map:
Step 1
Click Link Filter in the main toolbar.
Step 2
In the Link Filter dialog box, uncheck the check boxes for the links that you do not want to display in the map view and links view.
Step 3
Click Apply to apply the defined link filter settings and continue with more selections.
Step 4
Click OK when you have completed your selections.
The links are displayed in the map view and links view according to the defined filter, and the Link Filter Applied button is displayed in the to indicate that the links are filtered.
Opening the CPU Usage Graph
Prime Network Vision enables you to display memory and CPU usage information for a device or network element, including its history.
To open the CPU usage graph:
Step 1
Right-click a network element in the navigation tree and choose Tools > CPU Usage.
The CPU Usage dialog box displays the following information:
•
CPU Usage—The CPU usage rate as a percentage.
•
CPU Usage History—The CPU usage rate history is graphically displayed.
•
Memory Usage—The memory usage rate as a percentage.
•
Memory Usage History—The memory usage rate history is graphically displayed.
Step 2
If desired, click Save to CSV File to export the displayed data.
Step 3
Click the upper right corner to close the CPU Usage dialog box.
Communicating with Devices Using Ping and Telnet
Prime Network Vision enables you to communicate with devices in the following ways:
Pinging a Device
Prime Network Vision enables you to ping a device to verify that the device is responding.
The ping is performed from the client to the device, and not from the Prime Network Vision unit hosting the VNE to the device.
To ping a device, right-click a device in the navigation tree or map, and choose Tools > Ping.
The results are displayed in a new window.
Telneting a Device
Prime Network Vision enables you to communicate with a device using the Telnet window.
The Telnet session is performed from the client to the device, and not from the Prime Network Vision unit hosting the VNE to the device.
Note
If you are using a Windows 7 system, you must enable the Windows Telnet Client before you can use the Prime Network Telnet option.
- For Windows 7 32-bit systems, enable the Windows Telnet Client to use the Prime Network Telnet option.
- For Windows 7 64-bit systems, a solution is available on the Cisco Developer Network at http://developer.cisco.com/web/prime-network/forums/-/message_boards/message/2780108.To telnet a device:
Step 1
Right-click a device in the navigation tree or map, and choose Tools > Telnet. A terminal window opens.
Step 2
Log in and use the Telnet window as needed.

 Feedback
Feedback