-
Cisco IP Solution Center Infrastructure Reference, 4.0
-
Index
-
About This Guide
-
Getting Started
-
WatchDog Commands
-
Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager
-
Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Inventory Manager
-
Service Inventory > Device Console
-
Service Design
-
Monitoring
-
Administration
-
Cisco CNS IE2100 Appliances
-
Property Settings
-
Glossary
-
Table Of Contents
Creating a Cisco CNS IE2100 Appliance
Creating a Cisco IOS Device Using the Cisco CNS Device Access Protocol
Cisco CNS IE2100 Appliances
Cisco IP Solution Center (ISC) supports the Cisco CNS IE2100 Device Access Protocol for communication with any Cisco IOS device, such as uploading a configuration file from a device, downloading a configlet to a device, or executing a command on a device and obtaining a result. ISC also supports CNS Plug-and-Play.
To use the Cisco CNS IE2100 functionality on ISC, you must first set up the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance and the ISC workstation as explained in an appendix in Cisco IP Solution Center Installation Guide, 4.0.
This appendix includes the following sections. Implement these sections in sequence:
Note
The "Using Plug-and-Play" section is optional.
1.
Creating a Cisco CNS IE2100 Appliance
2.
Creating a Cisco IOS Device Using the Cisco CNS Device Access Protocol
Creating a Cisco CNS IE2100 Appliance
ISC supports multiple Cisco CNS IE2100 appliances. To create a Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance, follow these steps:
Note
For more information, see the Devices section of "Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager".
Step 1
Navigate Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Devices.
Step 2
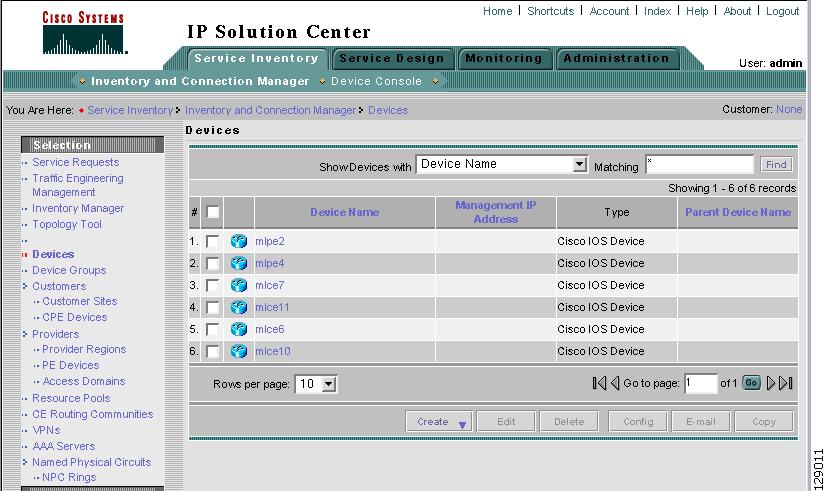
A window appears as shown in Figure A-1, "Devices Window."
Figure A-1 Devices Window
Step 3
Click the Create button.
Step 4
From the Create menu, click IE2100.
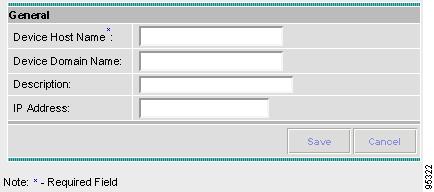
A window appears as shown in Figure A-2, "Create IE2100 Device Window".
Figure A-2 Create IE2100 Device Window
Step 5
Enter the Device Host Name and if applicable, the IE2100 Device Domain Name. If the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance is not registered with DNS, then you must enter the IP Address of the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance. Click Save.
Figure A-1 reappears with the IE2100 listed as a device.
Creating a Cisco IOS Device Using the Cisco CNS Device Access Protocol
Each Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance can serve multiple Cisco IOS devices. A Cisco IOS device can only be served by one Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance.To create a Cisco IOS device using the Cisco CNS Device Access Protocol, follow these steps:
Note
For more information, see the Devices section of "Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager".
Step 1
Navigate Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Devices.
Step 2
A window appears as shown in Figure A-1, "Devices Window."
Step 3
Click the Create button.
Step 4
From the Create menu, click Cisco IOS Device.
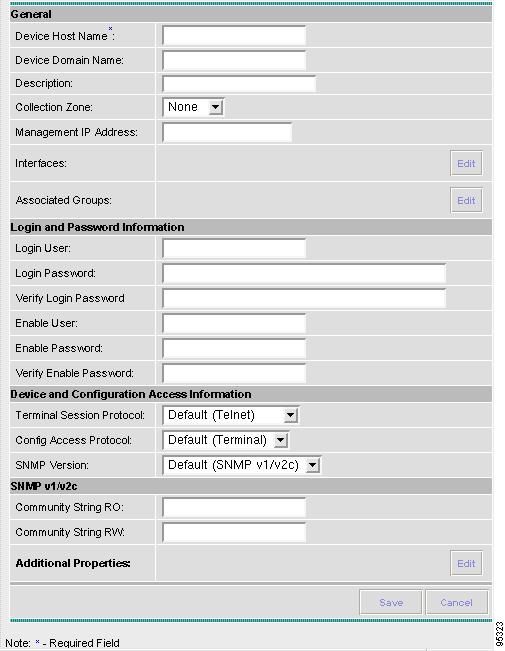
A window appears as shown in Figure A-3, "Create Cisco IOS Device Window."
Figure A-3 Create Cisco IOS Device Window
Step 5
In the General section, enter the Device Host Name and Device Domain Name.
For CNS Device Access Protocol, you do not need to define the parameters in the Login User and Login Password sections.
For the Device and Configuration Access Information section, you must select CNS for the Terminal Session Protocol. Defining Cisco IOS Device Properties
Step 6
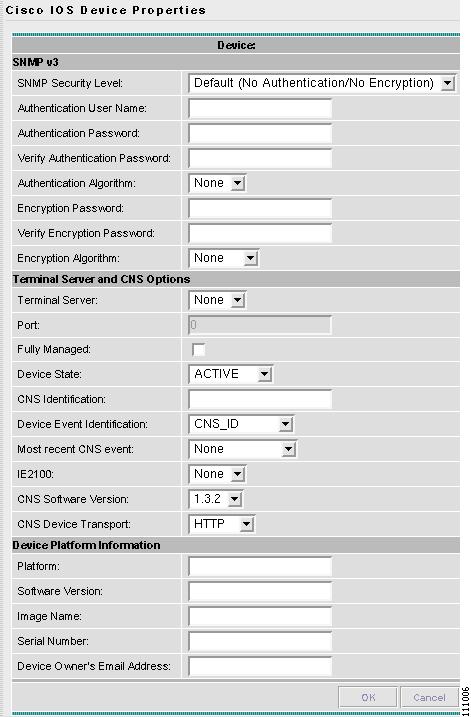
Click the Edit button for Additional Properties at the bottom of the window. A window as shown in Figure A-4, "Cisco IOS Device Additional Properties," appears.
Figure A-4 Cisco IOS Device Additional Properties
Step 7
The following steps pertain to the Terminal Server and CNS Options section.
Step 8
Select the Fully Managed check box if you want the device to become a fully managed device. For fully managed devices, ISC sends e-mail notifications upon receipt of device configuration changes originated outside ISC and schedules enforcement audit tasks upon detection of possible intrusion.
Note
Be sure to set the DCPL parameters for e-mail and Fully Managed, as explained in the "Config" section. Navigate Administration > Control Center. Select a Host and then click Config. Then in the TOC in the left column, be sure to enter appropriate information in the following four fields: SYSTEM > email > from; SYSTEM > email > smtpHost; SYSTEM > fullyManaged > enforcementAuditScript; and SYSTEM > fullyManaged > externalEventsEmailRecipients.
Note
Verify that the cns config notify command is configured for the IOS device.
Step 9
Specify the Device State, as follows:
•
Select ACTIVE (the default) if the router is physically present on the network.
•
Select INACTIVE if the router is not yet physically present on the network.
Step 10
Specify the Device Event Identification, as follows:
•
Select HOST_NAME if the Device Host Name as defined in Step 5 is to be used as the CNS Identification for this device.
•
Select CNS_ID if the device CNS Identification string is other than the Device Host Name.
•
If you have selected CNS_ID as the Device Event Identification, you must enter the CNS Identification parameter in the field labeled CNS Identification. This must be a unique argument. It is used to create the device in the corresponding Cisco CNS IE2100 repository and to listen to events pertaining to this device.
Note
Verify that the cns id string {CNS_ID} event command is configured for the IOS device.
Step 11
Select the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance that serves this Cisco IOS device. Select one entry from the drop-down menu of IE2100 devices already defined in the repository.
Step 12
Use the drop-down menu for CNS Software Version to choose the version of Cisco CNS Configuration Engine that manages the IOS device (1.3, 1.3.1, 1.3.2, or 1.4).
Step 13
Use the drop-down menu for CNS Device Transport to choose HTTP or HTTPS as the transport mechanism used by ISC to create, delete, or edit devices in the IE2100 repository. If HTTPS is used, the Cisco CNS Configuration Engine must be running in secure mode.
Step 14
Click OK. Figure A-1 reappears with the Cisco IOS device listed.
Using Plug-and-Play
ISC supports the Plug-and-Play device configuration through a Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance. ISC supports devices not physically present on the network.
The procedures for using Plug-and-Play when the Cisco IOS device is not physically present on the network vary depending on whether there is an initial configuration file for the device.
Follow these steps if the Cisco IOS device does not have an initial configuration file:
Step 1
Create a Cisco IOS Device as described in the "Creating a Cisco IOS Device Using the Cisco CNS Device Access Protocol" section.
Step 2
Define the Cisco IOS device properties as shown in Figure A-4.
Be sure to specify the Device State as INACTIVE because the device is not physically present on the network
Step 3
Click Save.
A Cisco IOS Device entry is created in the ISC repository and in the corresponding Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance repository.
Follow this step if the Cisco IOS device does have an initial configuration file:
Step 1
Import the initial configuration file into ISC using the Inventory Manager functionality, explained in Chapter 4, "Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Inventory Manager" in this manual.
Be sure to specify the Device State as INACTIVE because the device is not physically present on the network.
The Inventory Manager create a Cisco IOS Device entry in the ISC repository. Also, it creates an entry in the corresponding Cisco CNS IE2100 repository, and associates the specified initial configuration file with this new device in the Cisco CNS IE2100 repository.
You can provision the newly created inactive Cisco IOS Device for different services. Because the device is not physically present on the network, ISC saves the configlets associated with these services in its repository and tries to download them to the device only after the device has come up. Until the device is physically present on the network, the service request goes into the WAIT_DEPLOY state. The service requests are explained in the user guides for each of the services.
After the device comes up and connects to its corresponding Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance, the device retrieves and applies its initial configuration if there is one waiting for it in the Cisco CNS IE2100 repository.
ISC detects that the device has come onto the network and performs the following actions:
•
Changes the Cisco IOS Device state from INACTIVE to ACTIVE.
ISC performs a collect config of the IOS device and stores it in the ISC repository.
•
Verifies whether any ISC service has been waiting for this device to come up and tries to download the corresponding configlets to the device to complete the service request.

 Feedback
Feedback