Table Of Contents
C6576M Power Supply Dialog Box
C6576M Supervisor Module Dialog Box
System Flash Memory Inventory Area
C6576M Ethernet Module Dialog Box
C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
Packets/Octets Statistics Area
C6576M Switch Fabric Module Dialog Box
C6576M FlexWAN Module Dialog Box
C6576M Port Adapter Dialog Box
C6576M Optical Services Modules Dialog Box
C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
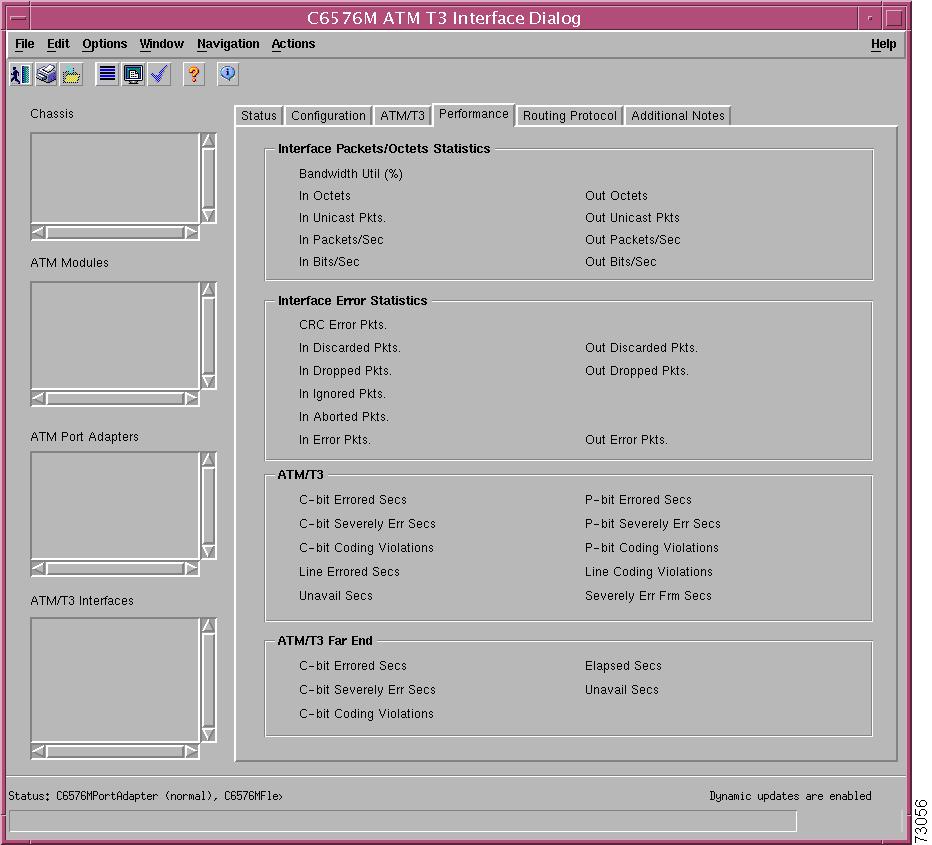
Interface Packets/Octets Statistics Area
Interface Error Statistics Area
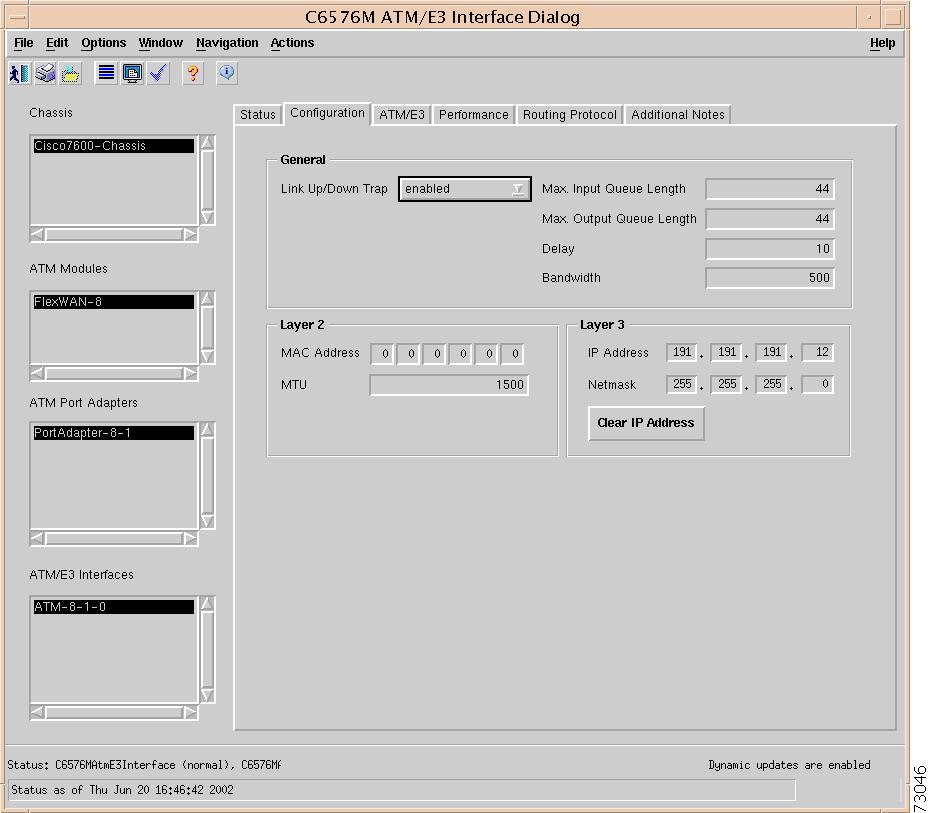
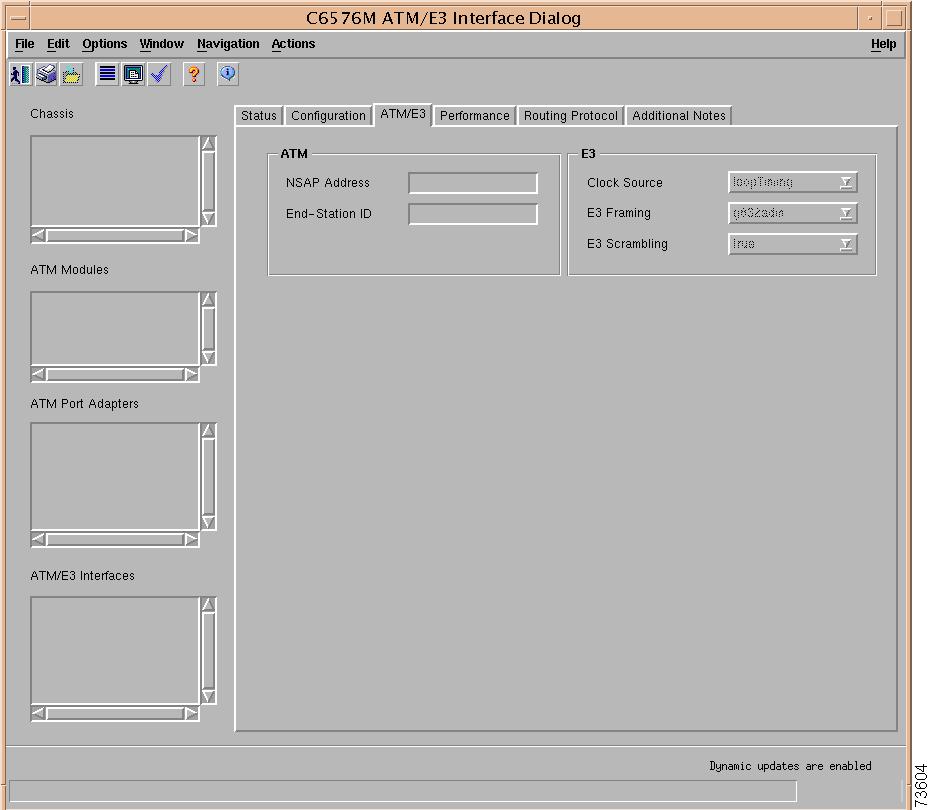
C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
Interface Packets / Octets Statistics Area
Interface Error Statistics Area
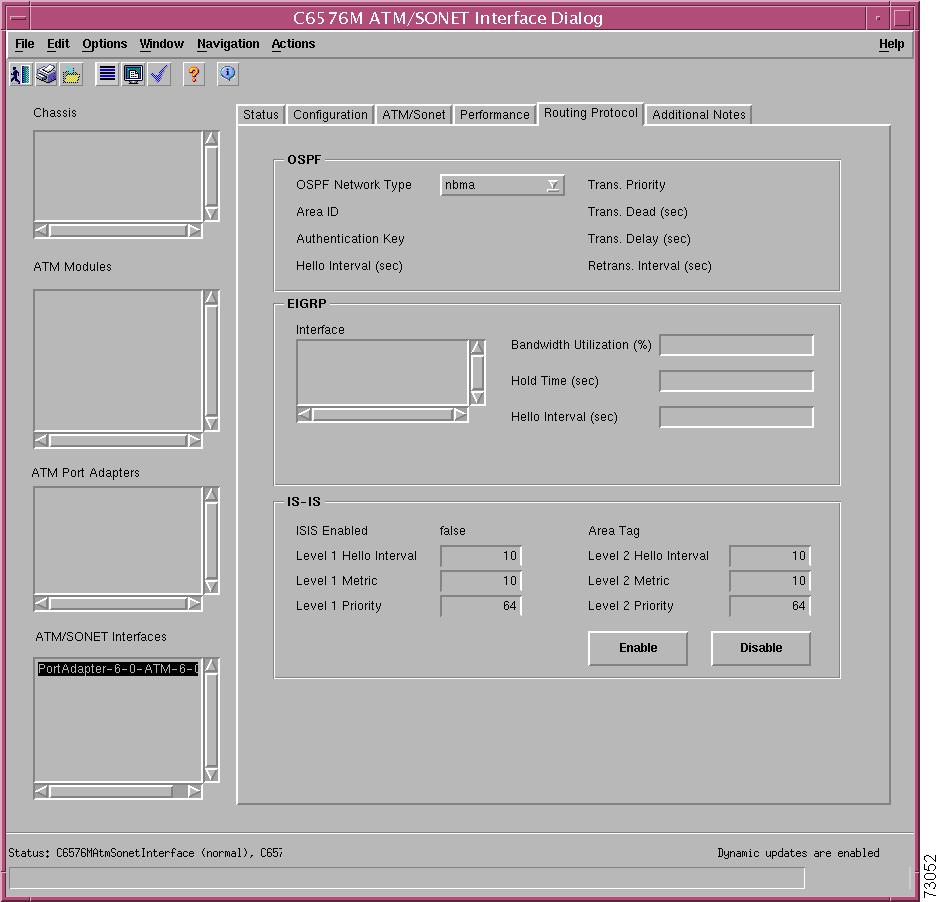
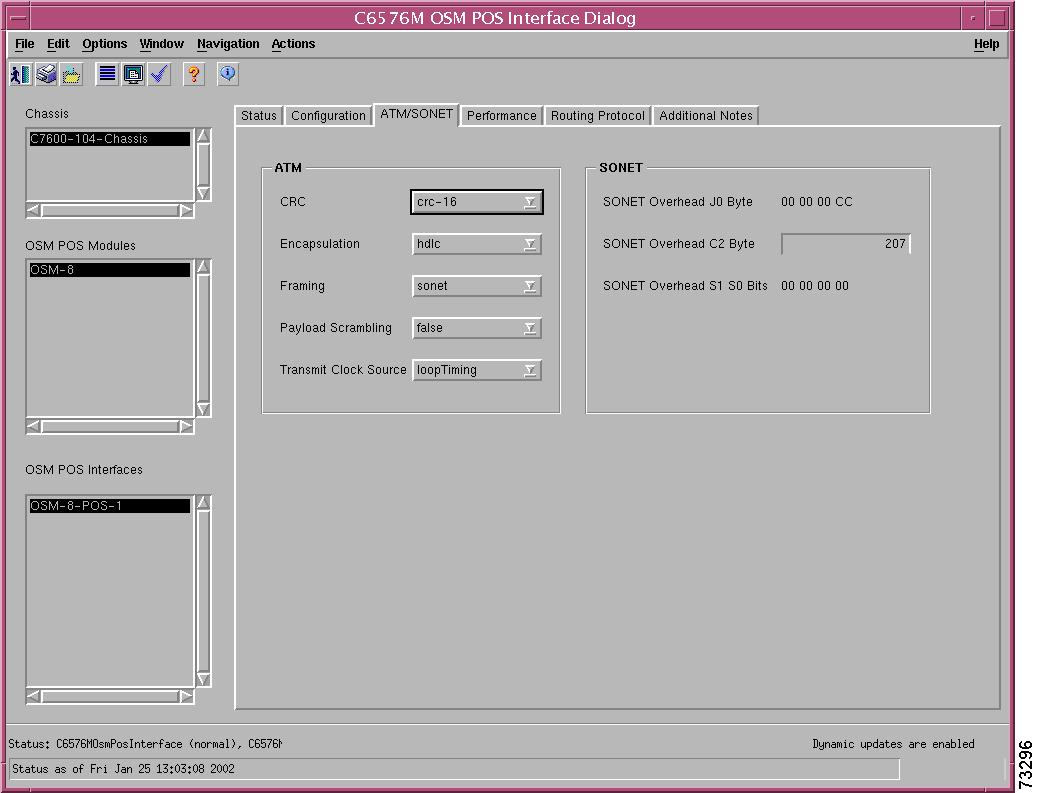
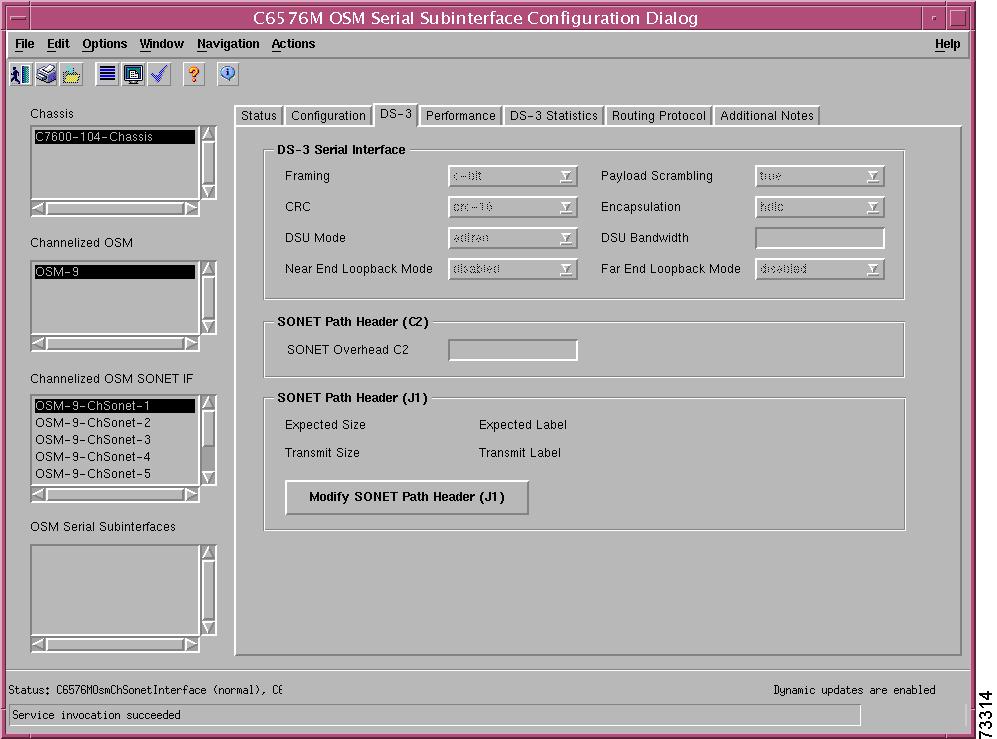
C6576M ATM SONET Interface Dialog Box
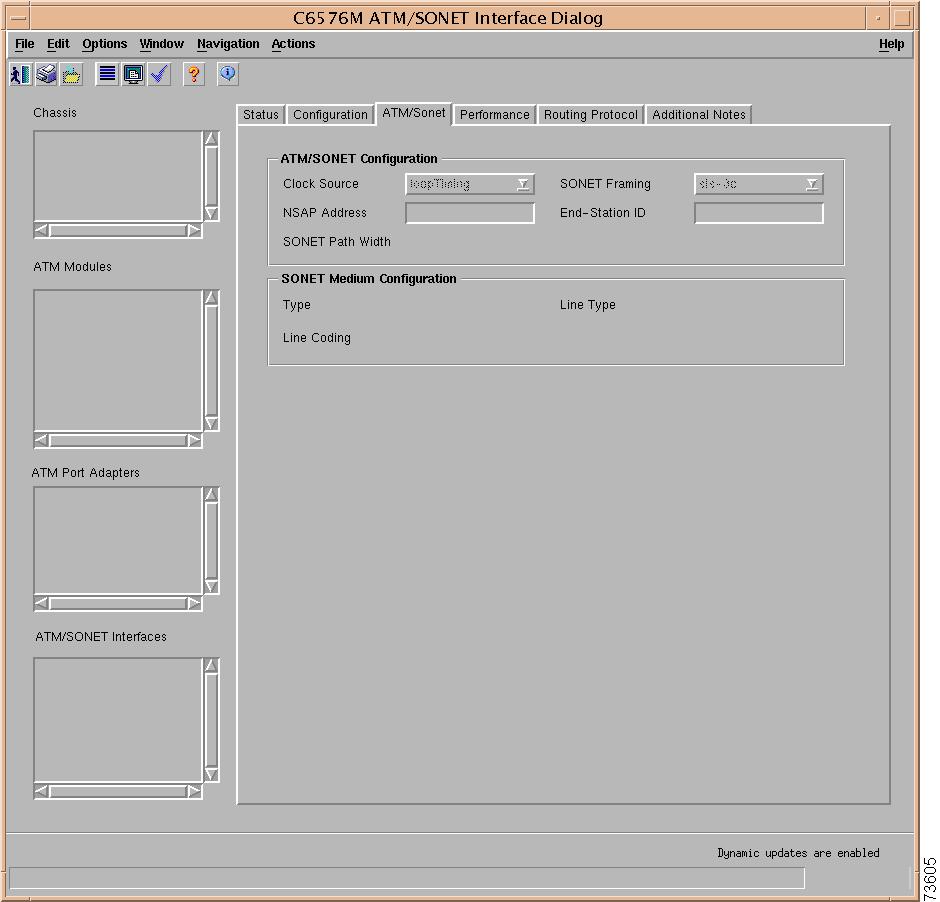
SONET Medium Configuration Area
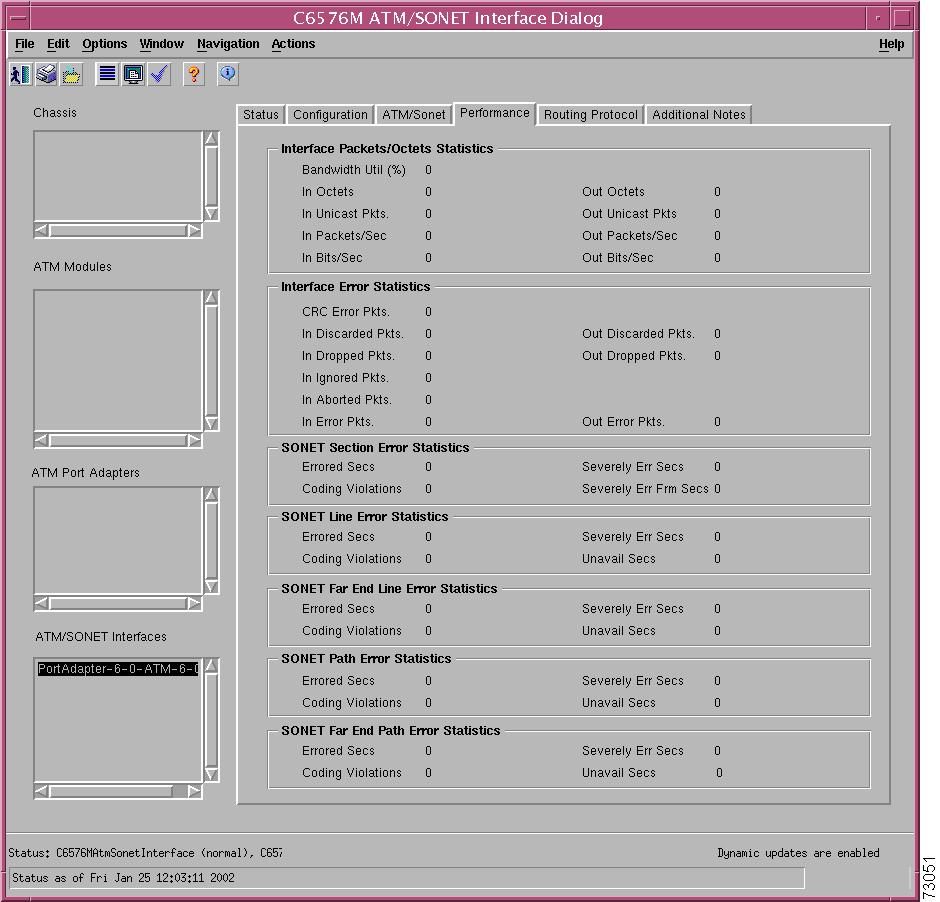
Interface Packets/Octets Statistics Area
Interface Error Statistics Area
SONET Section Error Statistics Area
SONET Line Error Statistics Area
SONET Far End Line Error Statistics Area
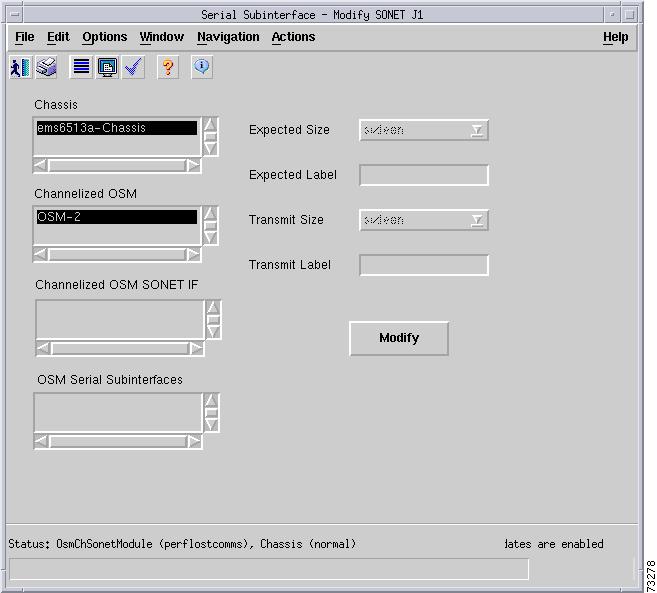
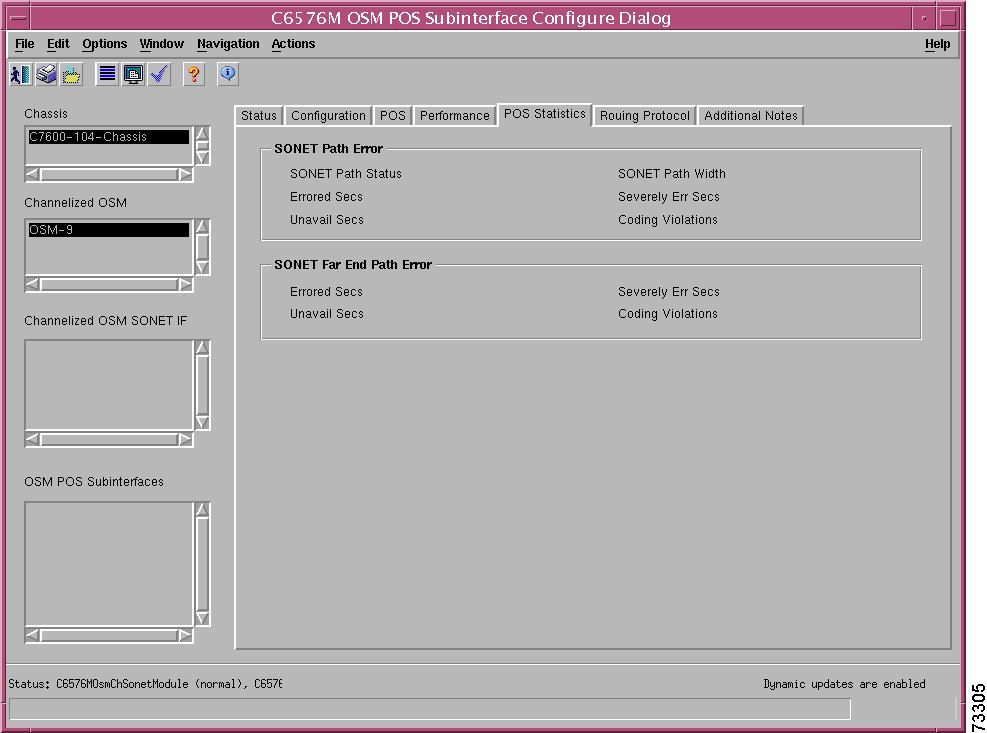
SONET Path Error Statistics Area
SONET Far End Path Error Statistics Area
C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
Packets/Octets Statistics Area
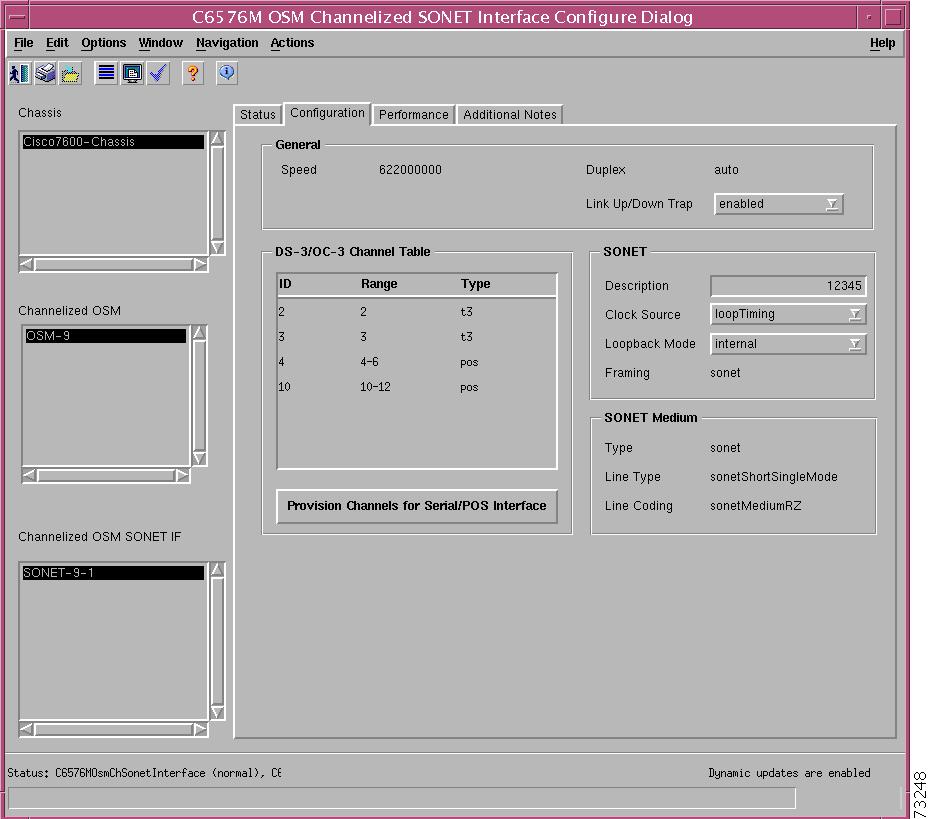
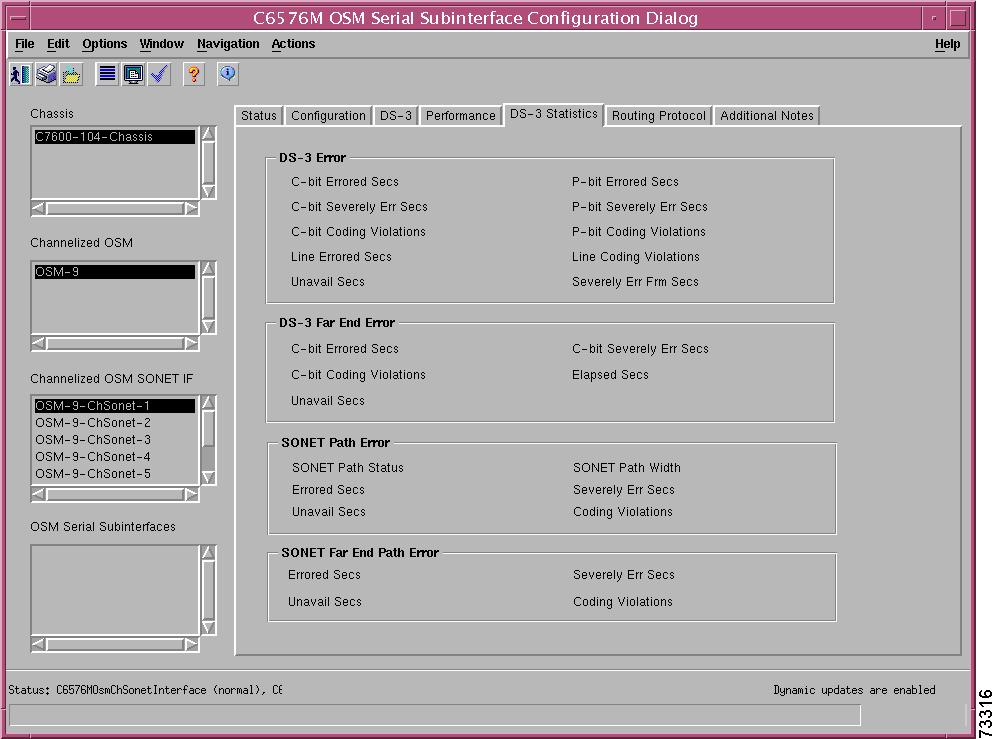
C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface Dialog Box
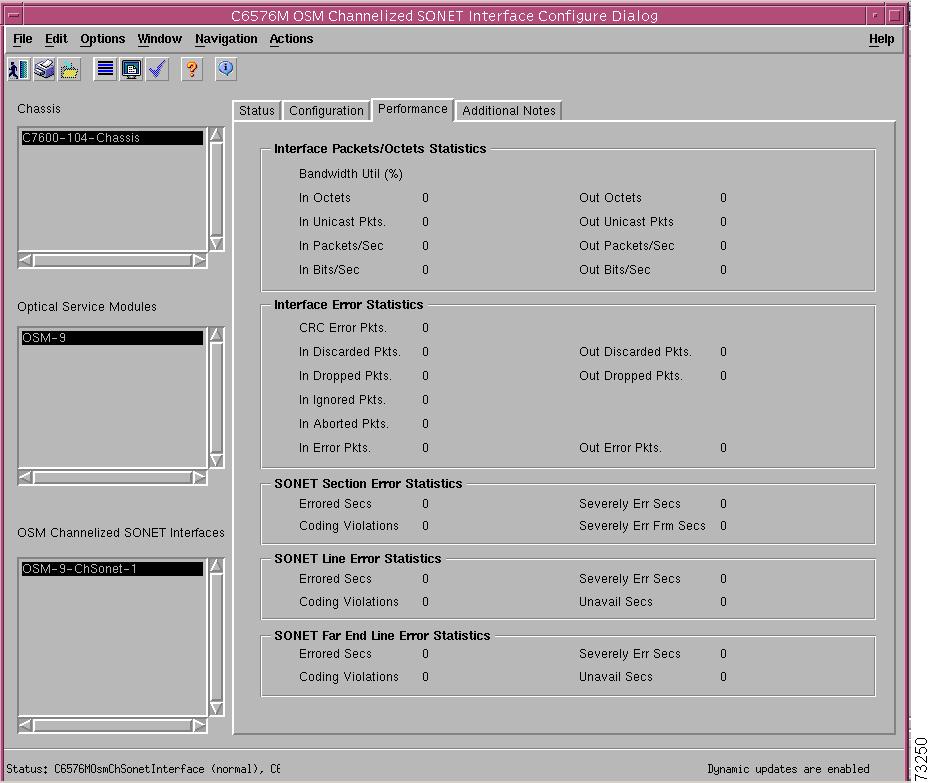
Interface Packets/ Octets Statistics Area
Interface Error Statistics Area
SONET Section Error Statistics Area
SONET Line Error Statistics Area
SONET Far End Line Error Statistics Area
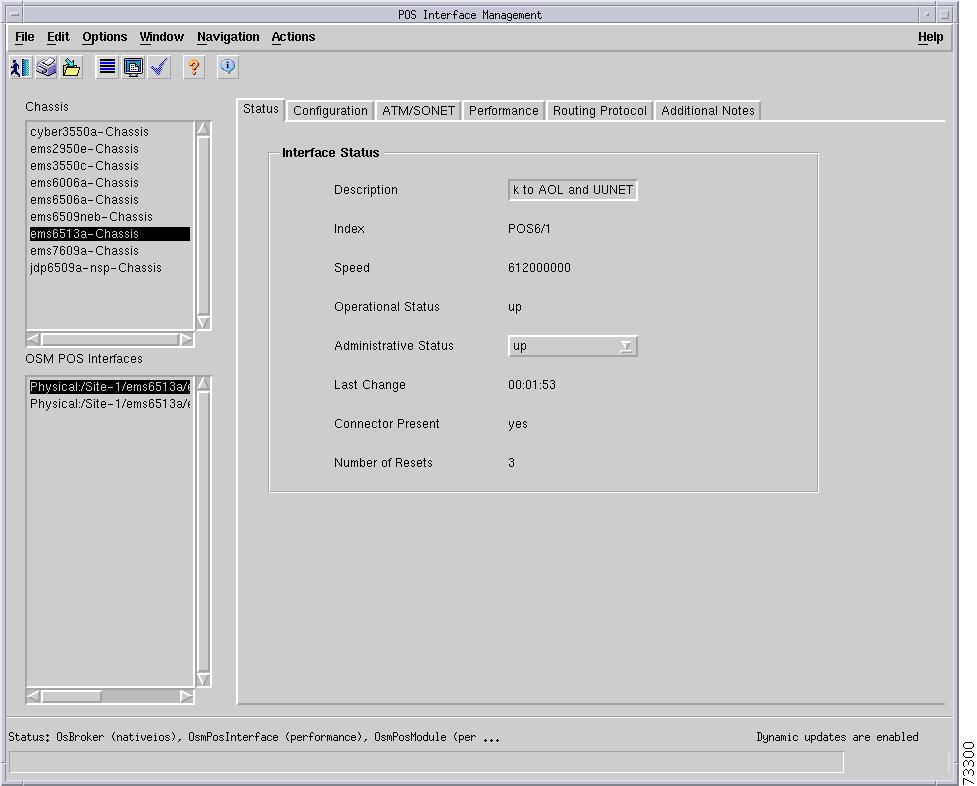
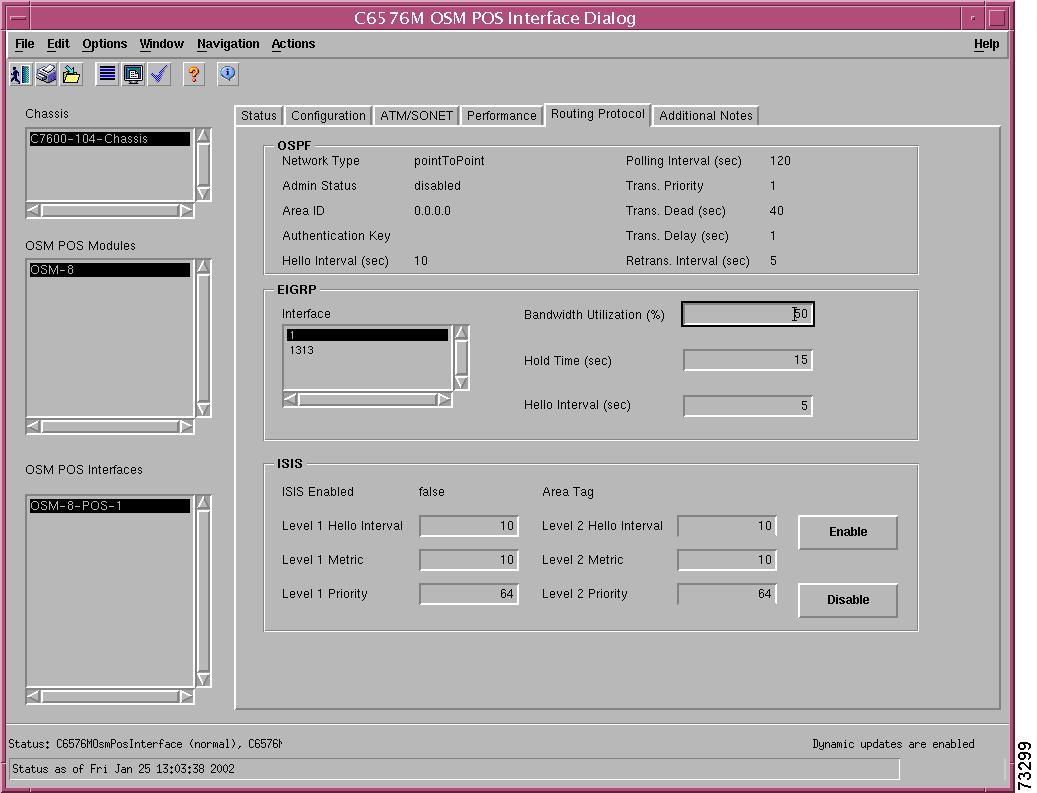
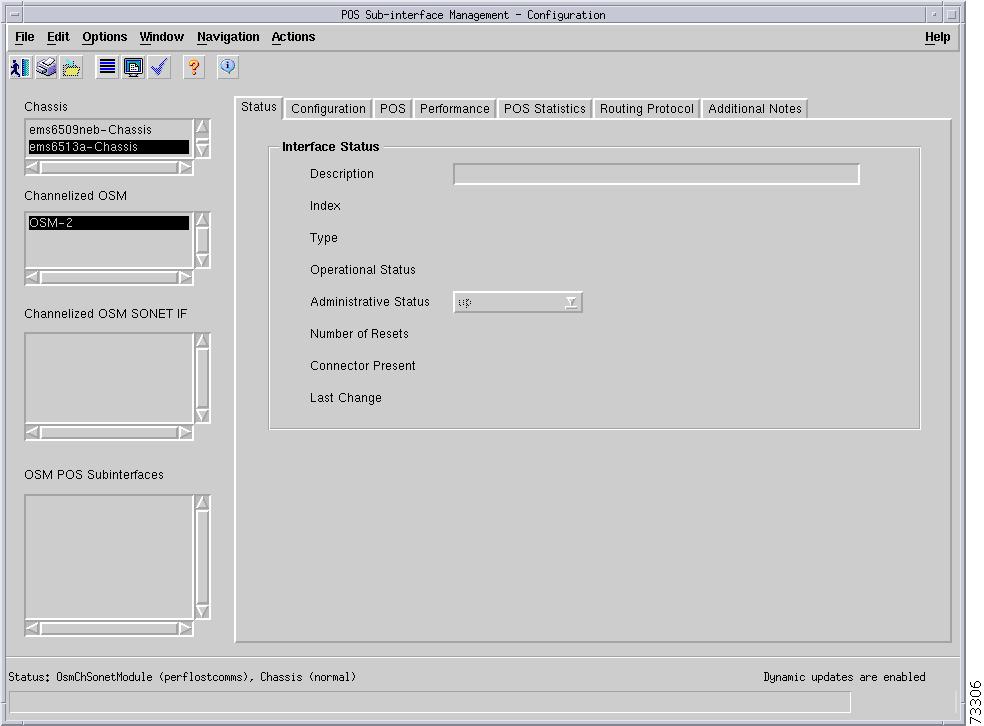
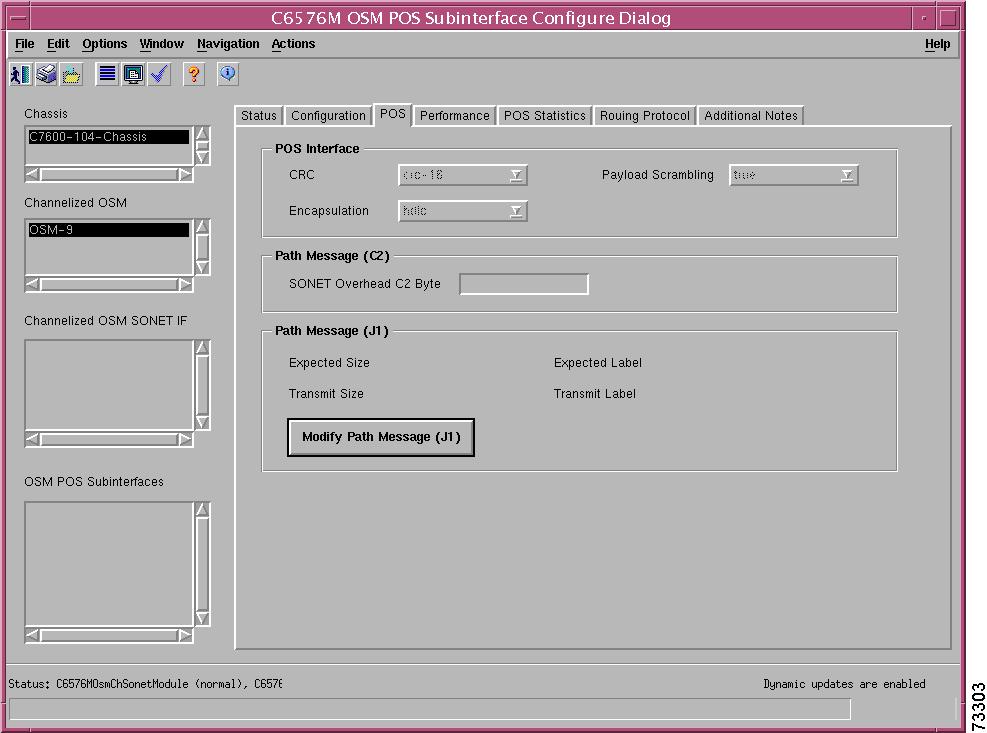
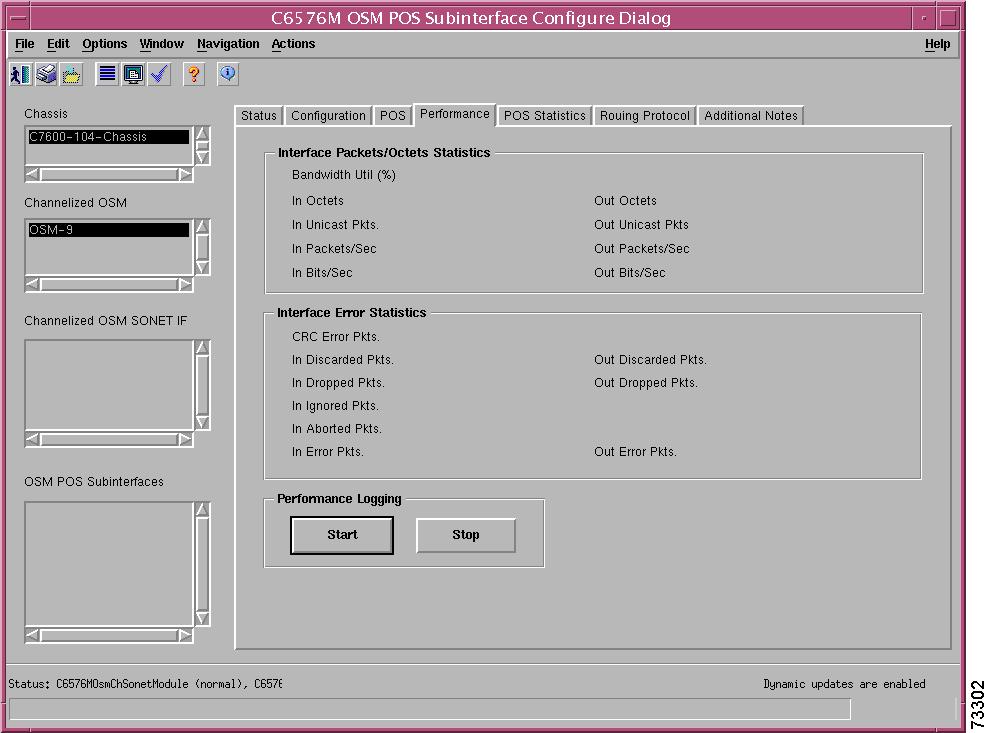
C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
Packets/Octets Statistics Area
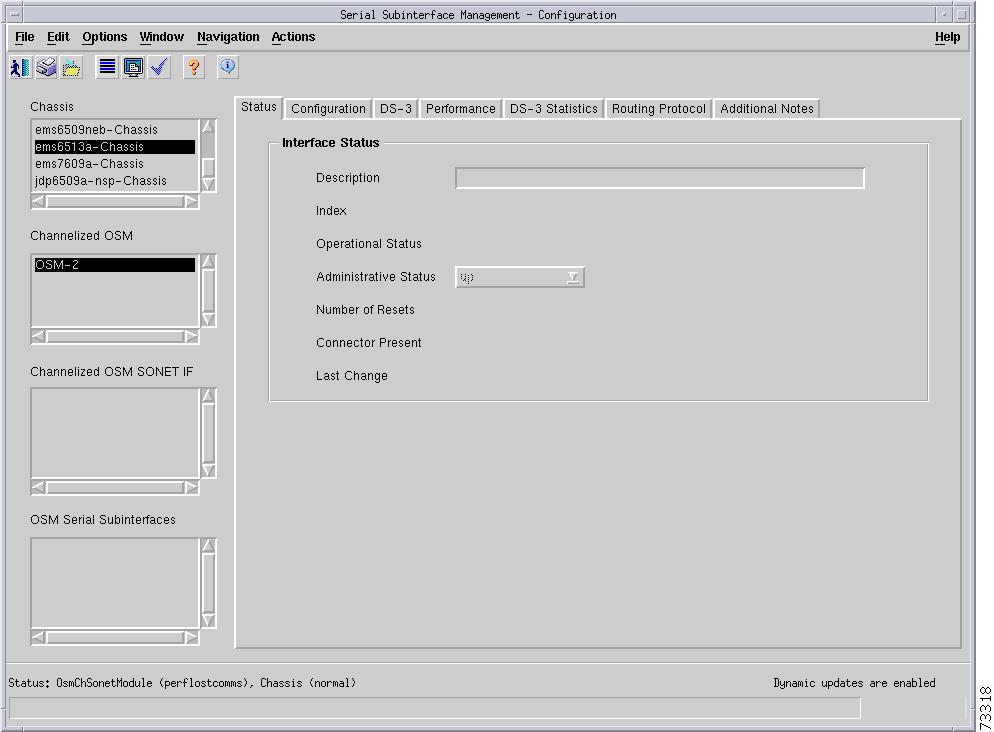
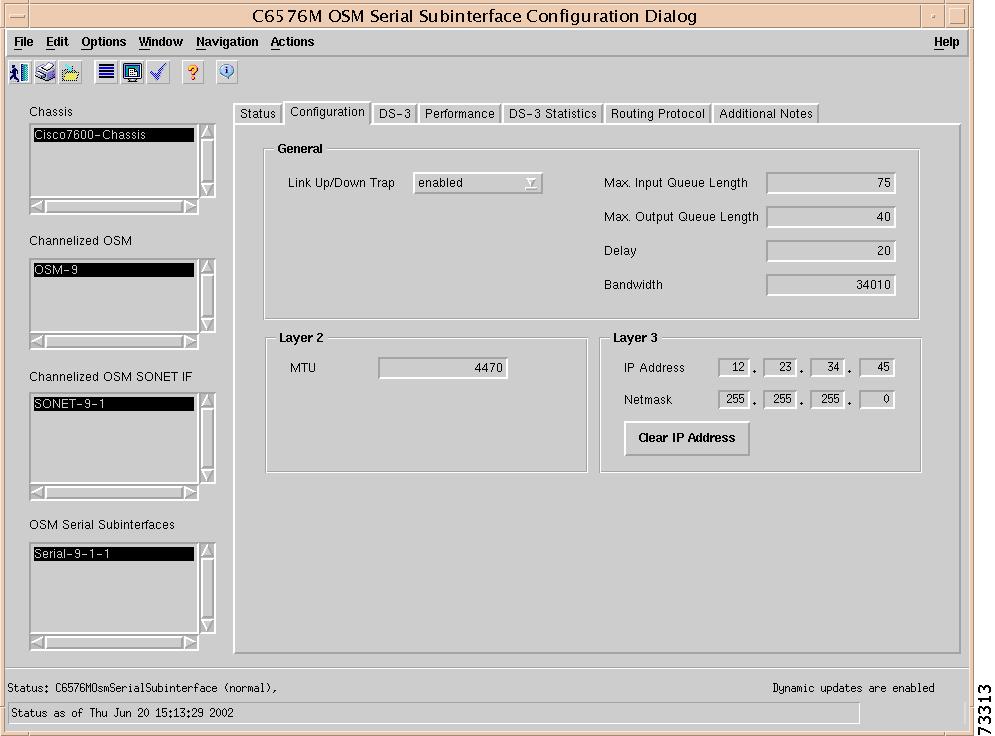
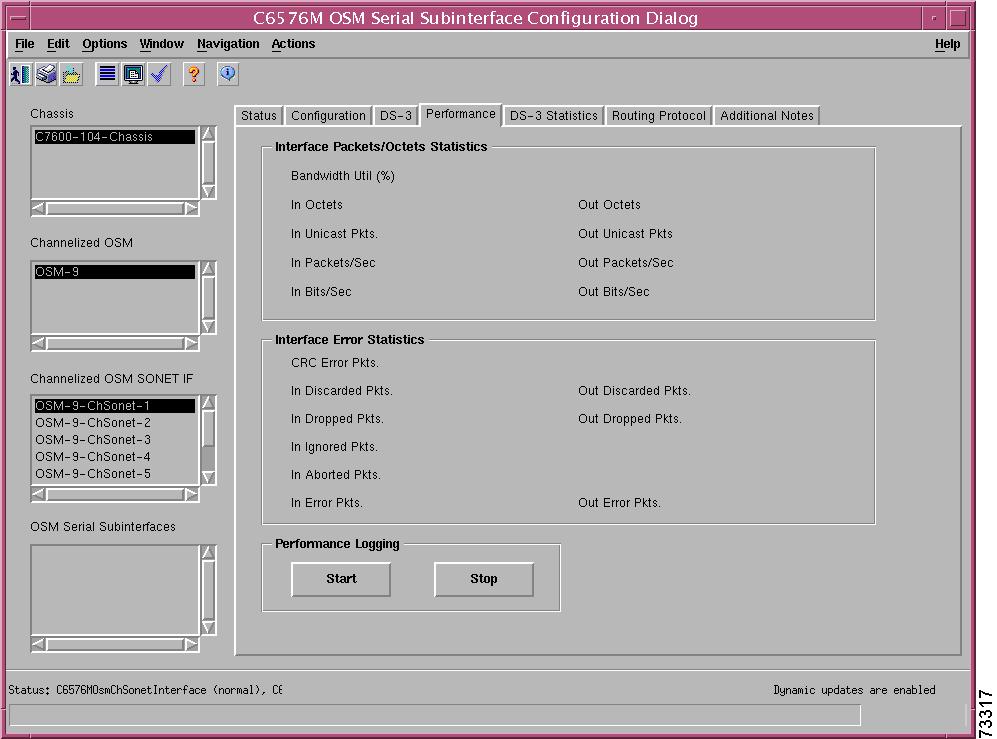
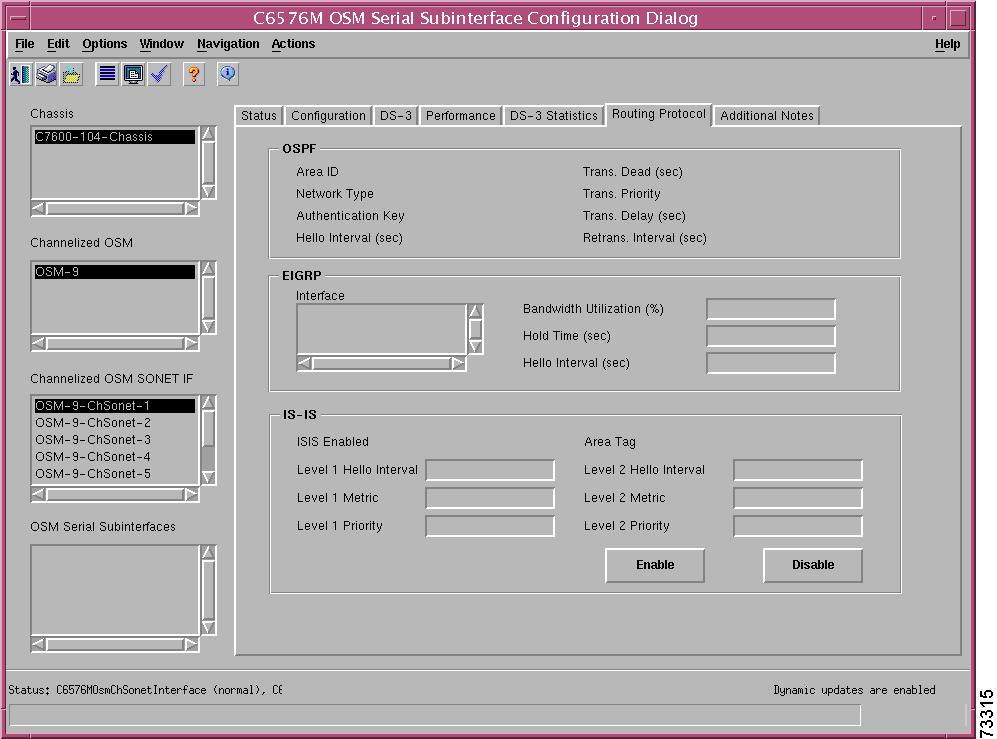
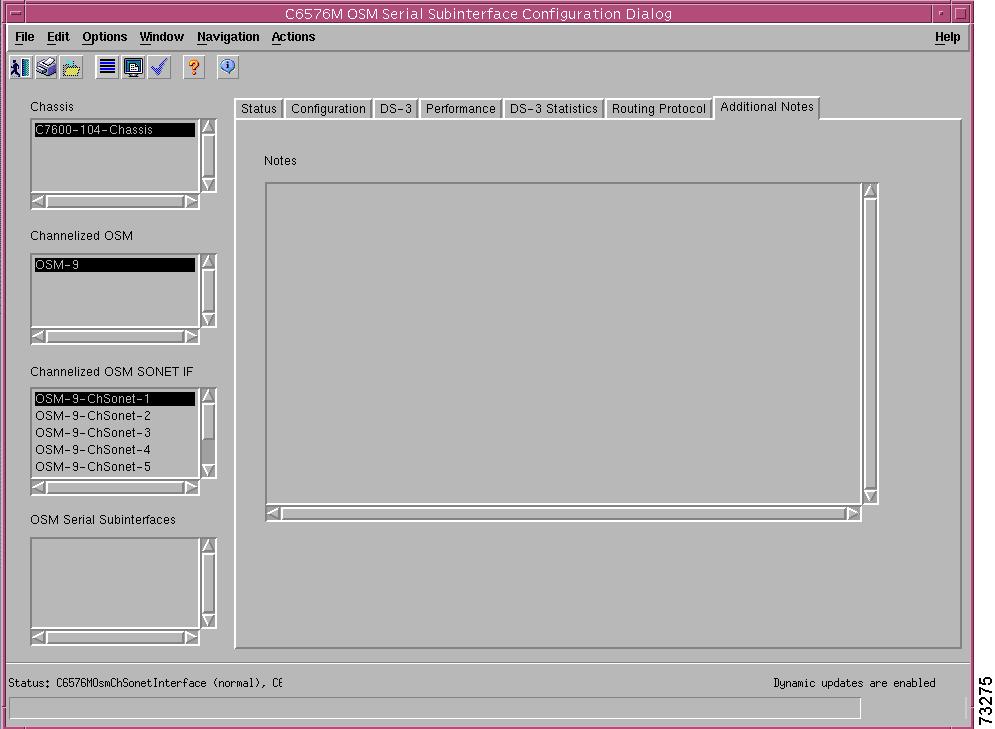
C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
Interface Packets/Octets Statistics Area
Interface Error Statistics Area
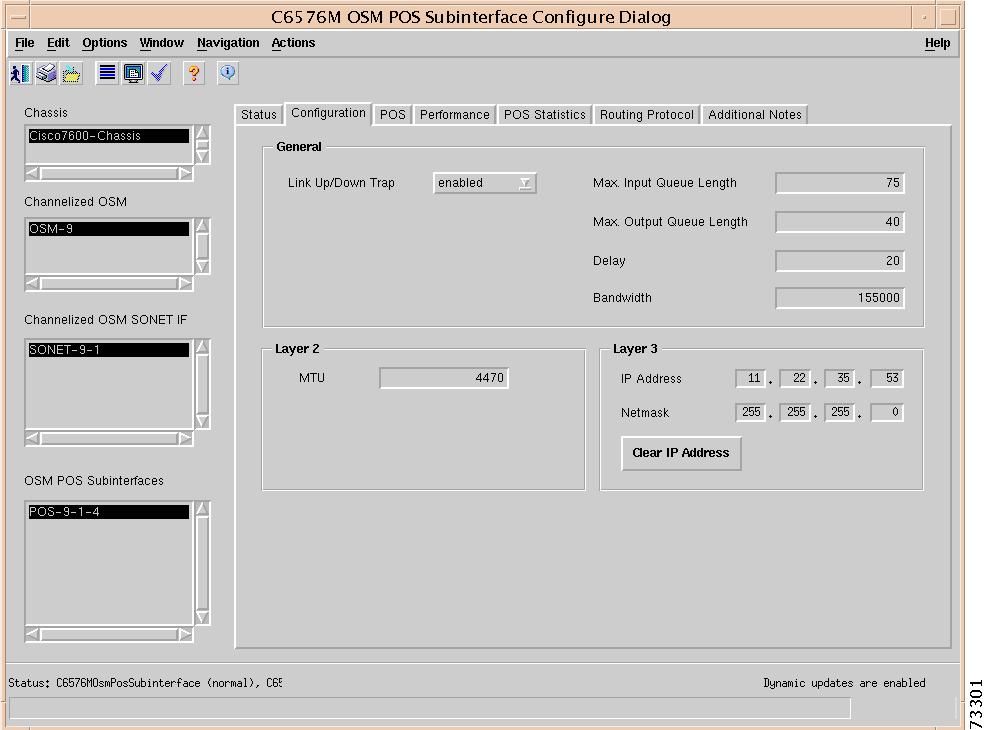
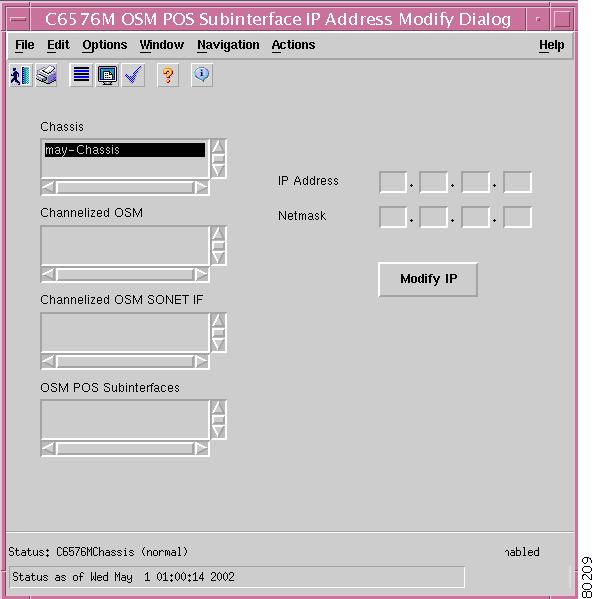
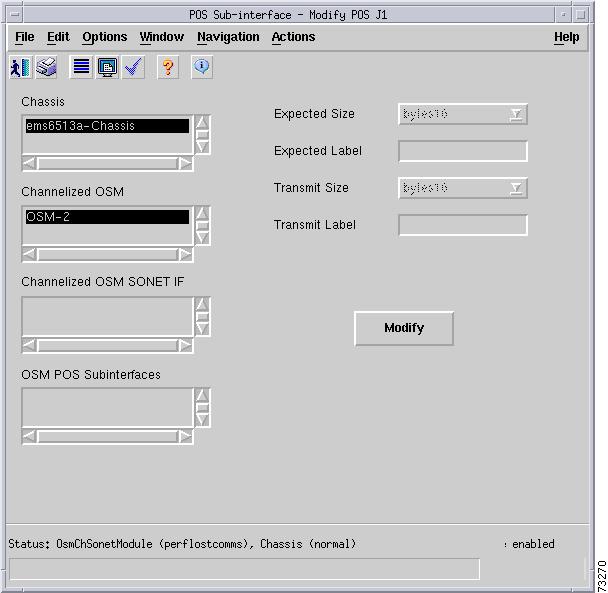
C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
Interface Packets/Octets Statistics Area
Interface Error Statistics Area
Physical Object Dialog Boxes
This chapter describes the Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager dialog boxes for the physical objects. The following physical object dialog boxes are available in the C65/76M:
•
C6576M Power Supply Dialog Box
•
C6576M Supervisor Module Dialog Box
•
C6576M Ethernet Module Dialog Box
•
C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
•
C6576M Switch Fabric Module Dialog Box
•
C6576M FlexWAN Module Dialog Box
•
C6576M Port Adapter Dialog Box
•
C6576M Optical Services Modules Dialog Box
•
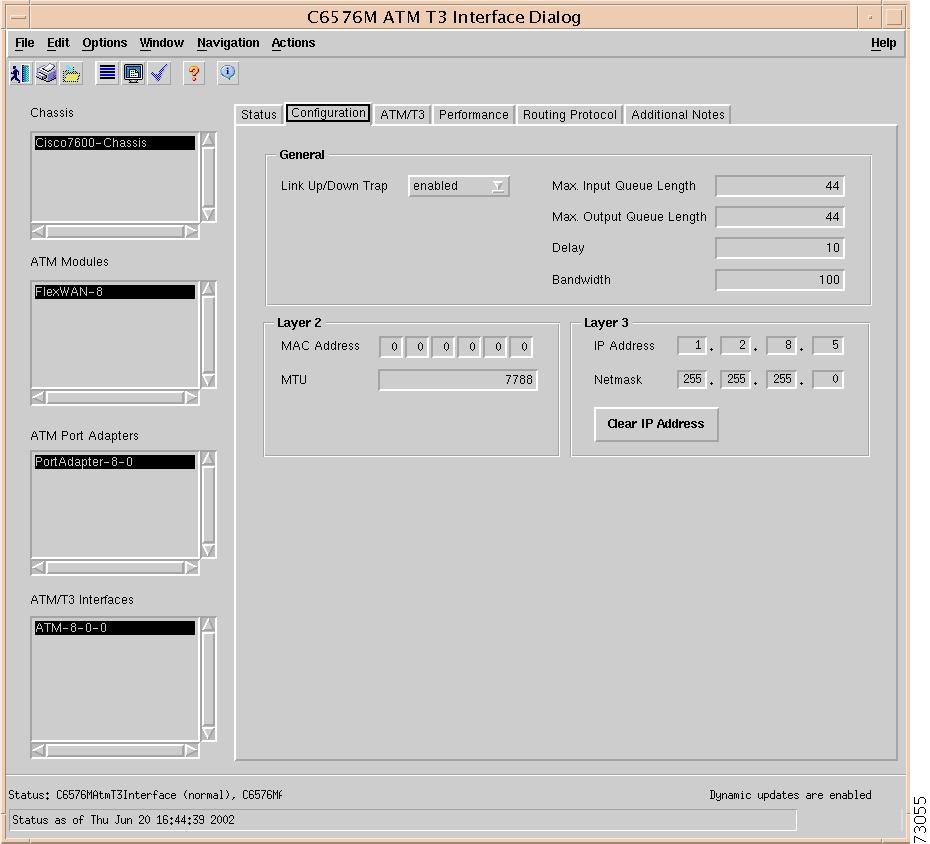
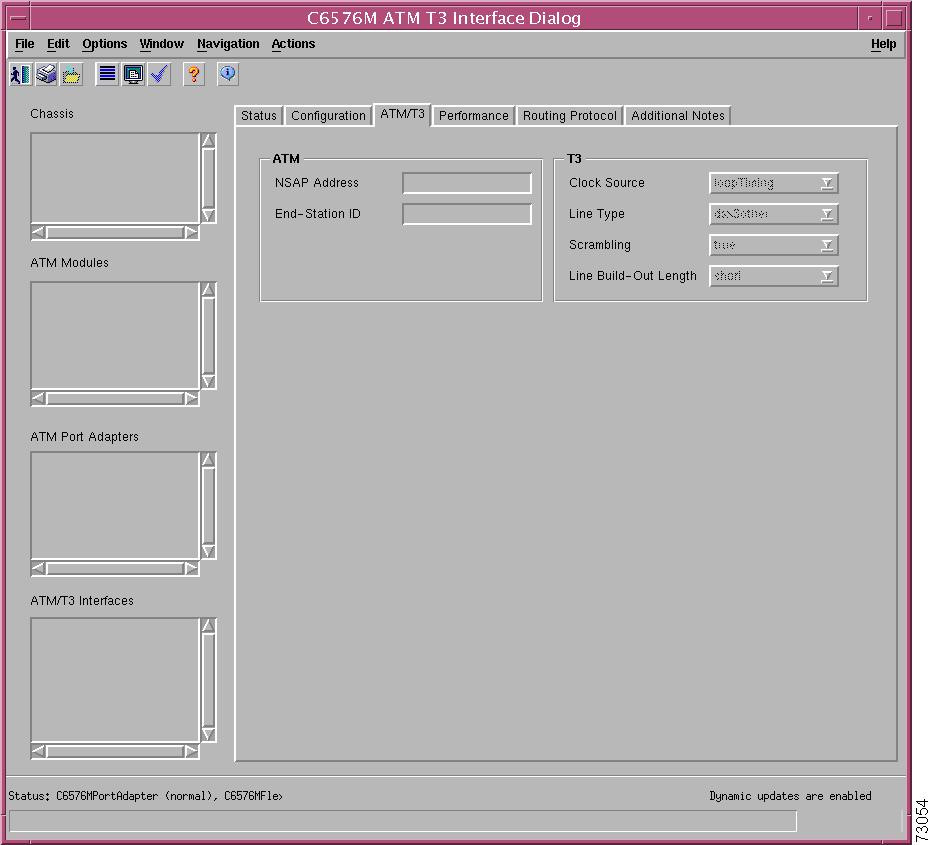
C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
•
C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
•
C6576M ATM SONET Interface Dialog Box
•
C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
•
C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface Dialog Box
•
C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
•
C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
•
C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
Table 5-1 lists the pop-up menu launch points for all C65/76M dialog boxes.
C6576M Chassis Dialog Box
This dialog box provides access to attributes for the physical chassis. This includes items such as the fan, temperature, and power supplies. This dialog box can be launched from a Network Element object or Chassis object within the Network or Physical containment views.
Only one Chassis object can be selected at a time from the Chassis object list on the left-hand side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
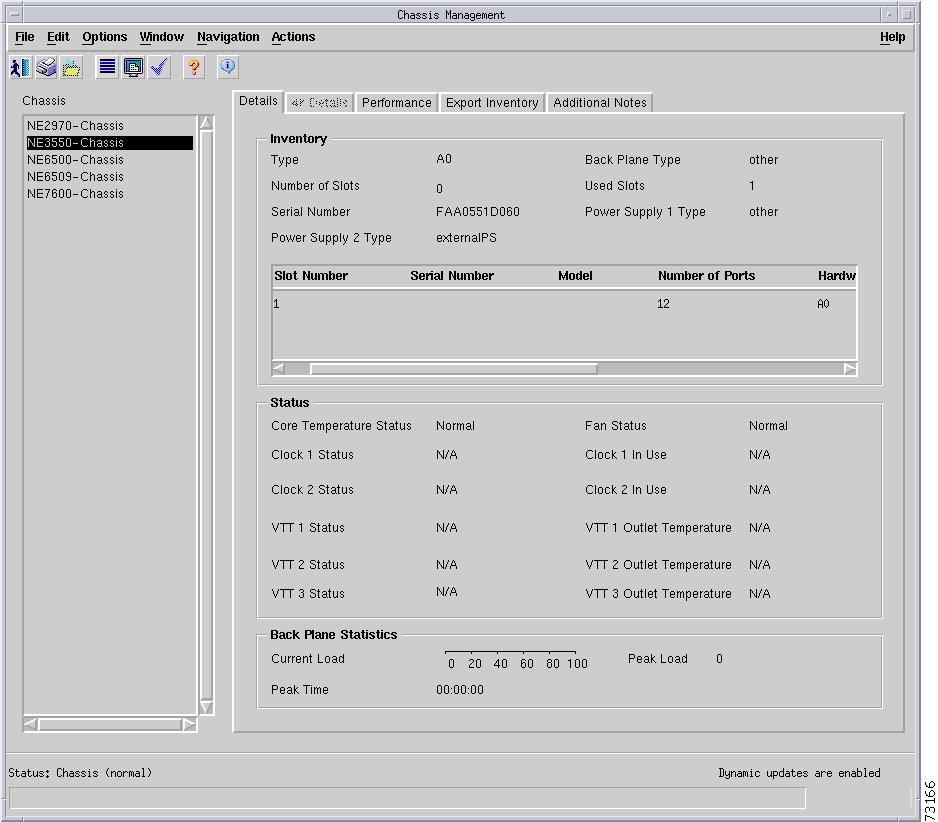
Figure 5-1 shows the Status tab of the C6576M Chassis dialog box.
Figure 5-1 Status Tab of the C6576M Chassis Dialog Box
General Area
The General area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box provides the following information:
•
Core Temperature Status—Status of the core of the chassis. This attribute can have the following values:
–
Excessive—The current temperature is within normal operating parameters.
–
Normal—The current temperature has exceeded the normal operating range.
–
High—The current temperature is dangerously high. The system will shutdown imminently.
Note
If this attribute has a value other than off, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
•
Fan Status—Status of the chassis fans. This attribute can have the following values:
–
other—The fan status is unknown.
–
Normal—Fan status is normal.
–
High—There is a minor problem.
–
Excessive—There is a major problem.
Note
If this attribute has a value other than ok, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
Clock Area
The Clock area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box provides the following information:
•
Clock 1 Status, Clock 2 Status—Operational statuses of clocks 1 and 2. These attributes can have the following values:
–
OK—Clock is operating.
–
failed—Clock is not operating.
•
Clock 1 In Use, Clock 2 In Use—Indicates which clock is in use. These attributes can have the following values:
–
in-use—Clock is in use.
–
not-in-use—Clock is not in use.
VTT Area
The VTT area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box provides the following information:
•
VTT 1 Status, VTT 2 Status, VTT 3 Status—Operational status of VTT 1, VTT 2, and VTT 3. These attributes can have the following values:
–
OK—VTT is operating.
–
failed—VTT is not operating.
•
VTT 1 Outlet Temperature, VTT 2 Outlet Temperature, VTT 3 Outlet Temperature—Outlet Temperatures of VTT 1, VTT 2, and VTT 3. These attributes can have the following values:
–
<n>C—Temperature in degrees Celsius.
–
N/O—Indicates that the sensor is not operational.
–
N/A—Indicates that the sensor value is not available.
Status Field
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
discovery—CEMF is trying to determine the contents and configuration of the Chassis object.
•
normal—Presence polling of the object.
•
performance—Attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the performance state.
•
discoverylostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device during discovery.
Note
To collect some of the statistics in the Performance tab, the running configuration of the switch is modified to add the following command to each interface: rmon collection stats <n> owner monitor
Inventory Tab
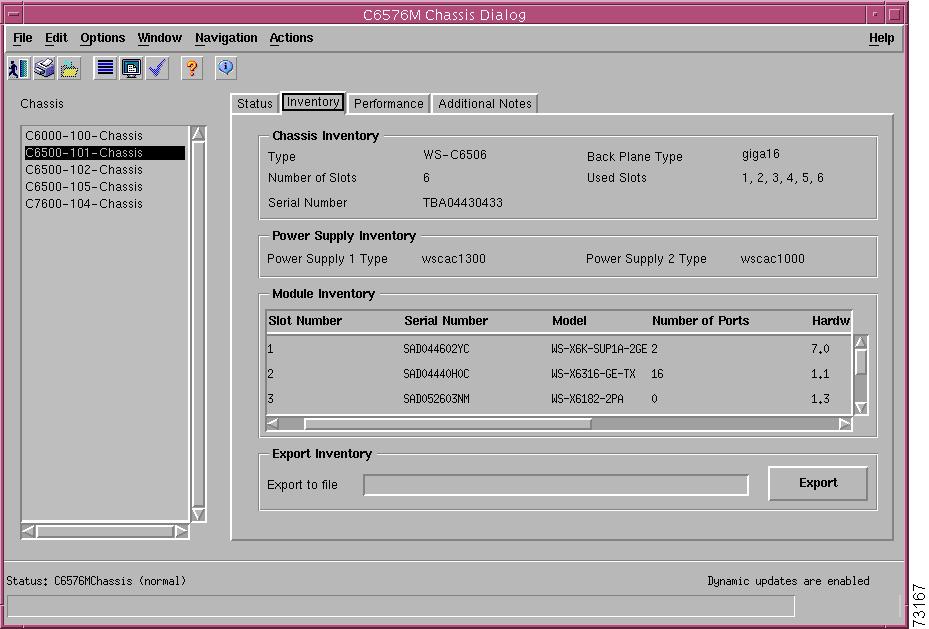
Figure 5-2 shows the Inventory tab of the C6576M Chassis dialog box.
Figure 5-2 Inventory Tab of the C6576M Chassis Dialog Box
Chassis Inventory Area
The Chassis Inventory area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box provides the following information:
•
Type—Displays the type of the chassis. One of the following values is displayed:
–
WS-C6006—6-slot Catalyst 6000 series switch
–
WS-C6009—9-slot Catalyst 6000 series switch
–
WS-C6506—6-slot Catalyst 6500 series switch
–
WS-C6509—9-slot Catalyst 6500 series switch
–
WS-C6509NEB— 9-slot vertical Catalyst 6500 series switch
–
WS-C6513—13-slot Catalyst 6500 series chassis
–
OSR-7603—3-slot Cisco 7600 series chassis
–
OSR-7606—6-slot Cisco 7600 series chassis
–
OSR-7609—9-slot Cisco 7600 series chassis
•
Number of Slots—Displays the total number of slots in the chassis. The values are 6 or 9.
•
Serial Number—Displays the serial number of the chassis.
•
Backplane Type—Indicates the chassis backplane type. For a Catalyst 6500 series switch or Cisco 7600 series Internet Router chassis, this attribute has the value "giga16 - 16 Gigabit switch."
•
Used Slots—Displays a comma-separated list indicating the slots that are occupied.
Note
If the Serial Number attribute changes, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
Power Supply Inventory Area
The Power Supply Inventory area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box provides the following information:
•
Power Supply 1 Type—Indicates the type of the first power supply.
•
Power Supply 2 Type—Indicates the type of the second power supply.
The possible types of power supplies are:
•
wscac1000—1000W AC power supply
•
wscac1300—1300W AC power supply
•
wscac2500w—2500W AC power supply
•
wscac4000w—4000W AC power supply
•
wscdc1300—1300W DC power supply
•
wscdc2500w—2500W DC power supply
•
pwr950ac—950W AC power supply
•
pwr950dc—950W DC power supply
•
pwr1900ac—1900W AC power supply
•
pwr1900dc—1900W DC power supply
•
pwr1900ac6—1900 watt supply AC/6 slots
Module Inventory Area
The Module Inventory area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box provides a list of occupied slots, including the following information:
•
Slot Number
•
Serial Number
•
Model number
•
Number of ports
•
Hardware version
•
Firmware version
•
Software version
Export Inventory Area
The Export Inventory area can be used to export the information on this tab to a CSV file on the CEMF server host.
•
Export to file—Enter the name of the file to which inventory is to be exported on the CEMF server host. If the file already exists, it will be overwritten.
•
Export Button—Exports the inventory list to a comma-separated file. The following data is exported from the Chassis object:
–
Type
–
Backplane Type
–
Number of Slots
–
Used Slots
–
Serial Number
–
Power Supply 1 Type
–
Power Supply 2 Type
The following data is exported for each installed module in the chassis:
–
Slot Number
–
Model
–
Number of Ports
–
Hardware Version
–
Firmware Version
–
Software Version
–
Serial Number
The inventory attributes are written in sections. Each section contains the attributes applicable to a particular class of object in the Cisco6500Manager containment hierarchy. Each section is preceded by the name of the object of that class in the Cisco6500Manager view hierarchy. If the object has not been deployed in the network model, a default name is used instead. The object name is delimited by the [ and ] characters.
The default section names are in this order:
–
[chassis]
–
[power supply 1]
–
[power supply 2]
–
[slot 1]
–
[slot2]
–
[slot3]
–
[slot4]
–
[slot 5]
–
[slot 6]
–
[slot 7]
–
[slot 8]
–
[slot 9]
The chassis and power supply sections are always printed. Each slot section is only printed if there is an installed module in that slot. The slot sections are always printed in order.
After each section name, the next line contains a comma-delimited list of attributes for that object class. The line of attributes is terminated by the end-of-line character. Each field is printed regardless of whether it is empty or not. If an attribute in the list has no value, a (nil) tab is written in its place.
The following is an example of the output:
[192.168.12.101-Chassis]WS-C6506,8,9,TBA04430433,1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6[power supply 1]2[PowerSupply-2]30[Supervisor-1]1,WS-X6K-SUP1A-2GE,2,7.0,,6.1(0.105)ORL 2000-06-15 06:07:10,SAD04510T8K[Ethernet-2]2,WS-X6316-GE-TX,16,1.1,5.4(2) 2000-03-17 10:18:33,6.1(0.105)ORL 2000-06-15 06:44:56,SAD04440H0C[Ethernet-3]3,WS-X6416-GBIC,16,1.2,5.4(2) 2000-03-17 10:18:33,6.1(0.105)ORL 2000-06-15 06:44:56,SAD04470EEK[Ethernet-4]4,WS-X6324-100FX-SM,24,1.1,5.4(2) 2000-03-17 10:18:33,6.1(0.105)ORL 2000-06-15 06:43:57,SAD04320F4X[Ethernet-5]5,WS-X6348-RJ-45,48,1.4,5.4(2) 2000-03-17 10:18:33,6.1(0.105)ORL 2000-06-15 06:43:57,SAD04310F9P[Ethernet-6]6,WS-X6248A-TEL,48,1.0,5.4(2) 2000-03-17 10:23:19,6.1(0.105)ORL 2000-06-15 06:43:36,SAD043608EHPerformance Tab
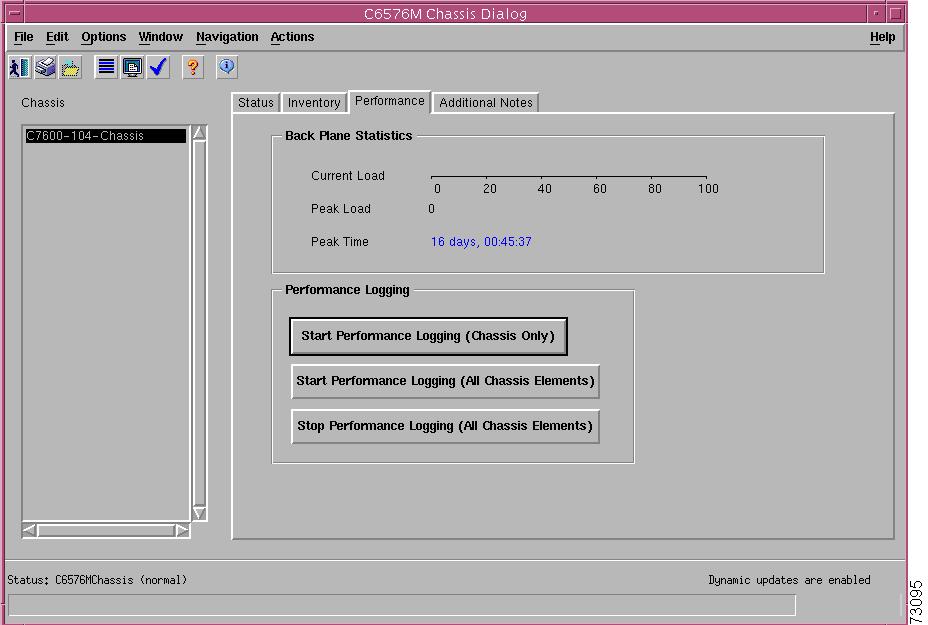
Figure 5-3 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M Chassis dialog box.
Figure 5-3 Performance Tab of the C6576M Chassis Dialog Box
Back Plane Statistics Area
The Back Plane Statistics area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box provides the following information:
•
Current Load—Displays the current traffic load on the backplane.
•
Peak Load—Displays the peak traffic load encountered.
•
Peak Time—Displays the time when the peak traffic load was encountered.
The Current Load and Peak Load attributes are polled at the specified interval when the Chassis object is in the Performance state.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box allows users to turn on performance logging for the chassis attributes as well as the attributes of all the chassis elements.
•
Start Performance Logging (Chassis Only) button—Turns performance data logging on the chassis object.
•
Start Performance Logging (All Chassis Elements) button—Turns performance data logging on all the chassis elements. This includes all chassis performance attributes, all supervisor performance attributes and all interface performance attributes.
•
Stop Performance Logging (All Chassis Elements) button—Turns performance data logging off for all the chassis elements.
Note
The logged data is available to the user through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
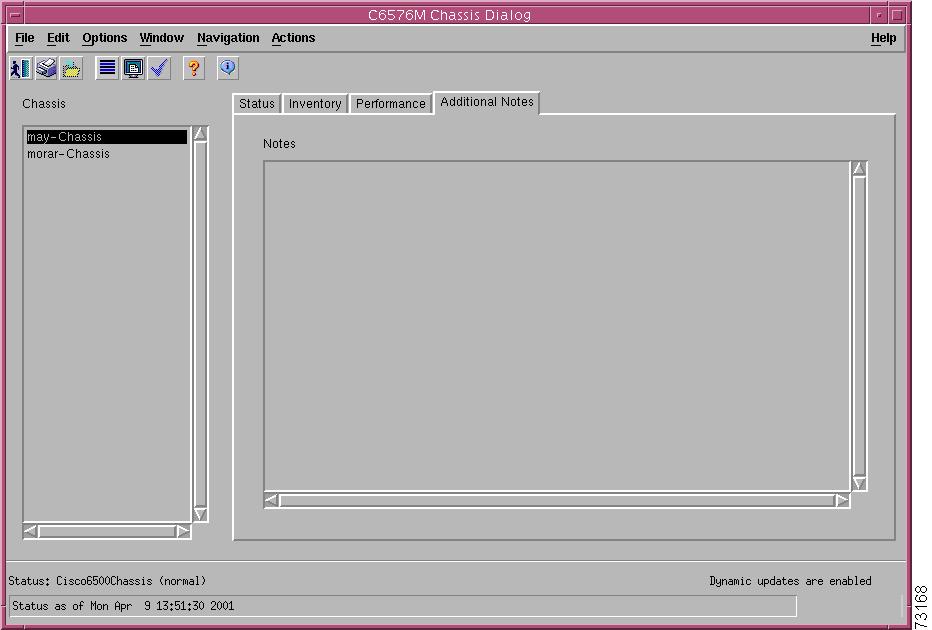
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-4 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Chassis dialog box.
Figure 5-4 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Chassis Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area of the C6576M Chassis dialog box is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for this chassis object. This can be used for providing notes, such as contact information, specifics of the chassis and/or network configurations, warnings, etc.
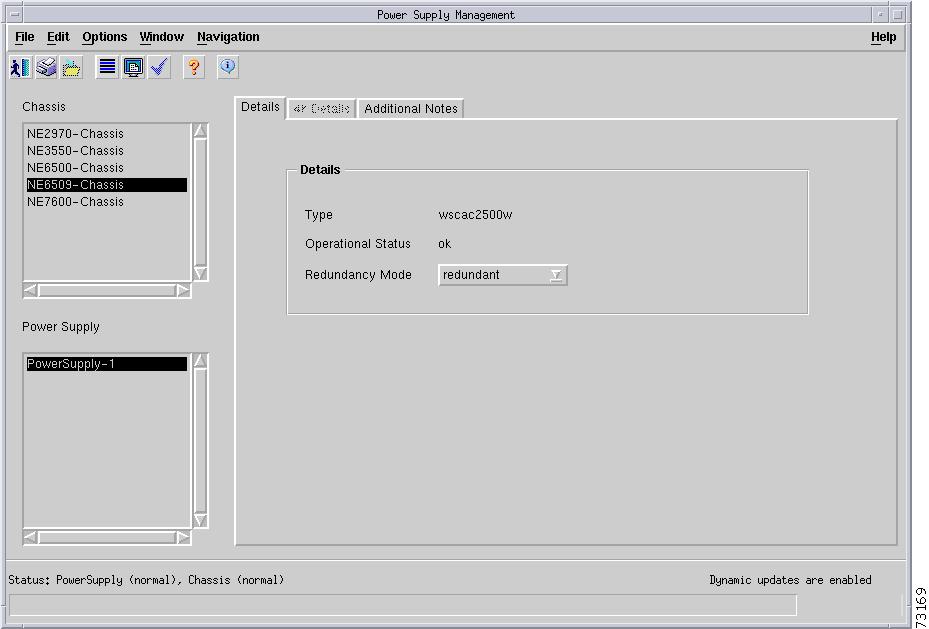
C6576M Power Supply Dialog Box
This dialog box provides access to attributes relating to the power supplies. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object or Power Supply objects within the Physical containment view.
You can select multiple Chassis and Power Supply objects at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Details Tab
Figure 5-5 shows the Details tab of the C6576M Power Supply dialog box.
Figure 5-5 Details Tab of the C6576M Power Supply Dialog Box
Details Area
The Details area of the C6576M Power Supply dialog box provides the following information:
•
Type—Displays the type of power supply. This field has one of the following values:
–
wscac1000—1000W AC power supply
–
wscac1300—1300W AC power supply
–
wscac2500w—2500W AC power supply
–
wscac4000w—4000W AC power supply
–
wscdc1300—1300W DC power supply
–
wscdc2500w—2500W DC power supply
–
pwr950ac—950W AC power supply
–
pwr950dc—950W DC power supply
–
pwr1900ac—1900W AC power supply
–
pwr1900dc—1900W DC power supply
–
pwr1900ac6—1900 watt supply AC/6 slots
Note
The WS-C6509-NEB chassis does not support the Type attribute. This attribute is displayed as `unknown' in the Power Supply Dialog.
•
Operational Status—Displays the operational status of the power supply. This field has the following values:
–
ok—The power supply status is normal.
–
other—The power supply operational status is unknown.
–
minorFault—There is a minor problem.
–
majorFault—There is a major problem.
Note
If this field has a value other than ok, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
•
Redundancy Mode—Displays the mode in which the power supply is operating. This is a drop-down list with the following values:
–
redundant—Power supply 1 is used as the primary supply. If power supply 1 fails, power supply 2 becomes the primary power supply.
–
combined—Both power supplies are used to supply power to the modules.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the power supply attributes.
•
normal—Data is being gathered periodically.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the power supply from the normal state.
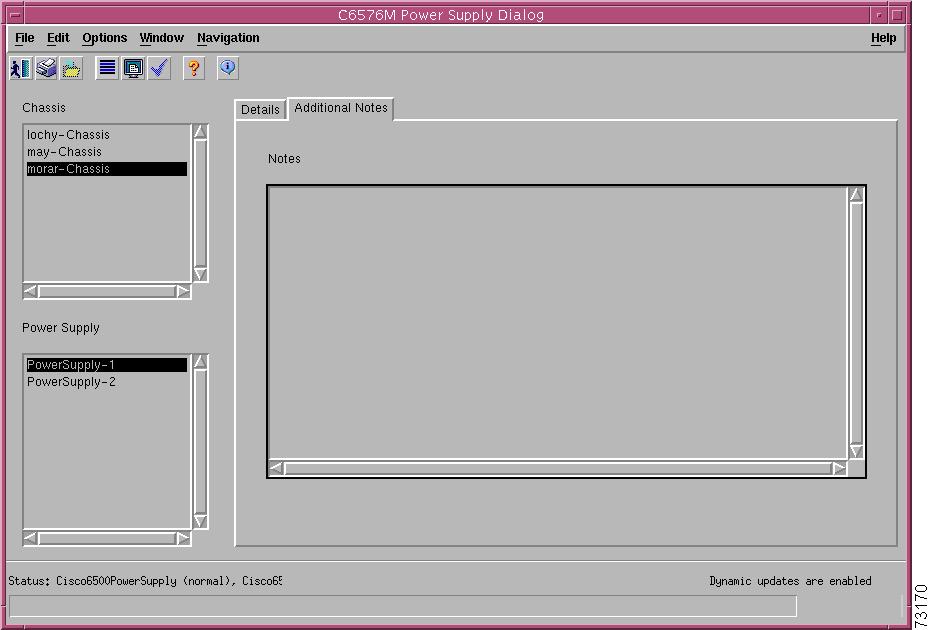
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-6 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Power Supply dialog box.
Figure 5-6 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Power Supply Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the power supply configuration. For example, the note might include the reason why the power supply is in redundant mode.
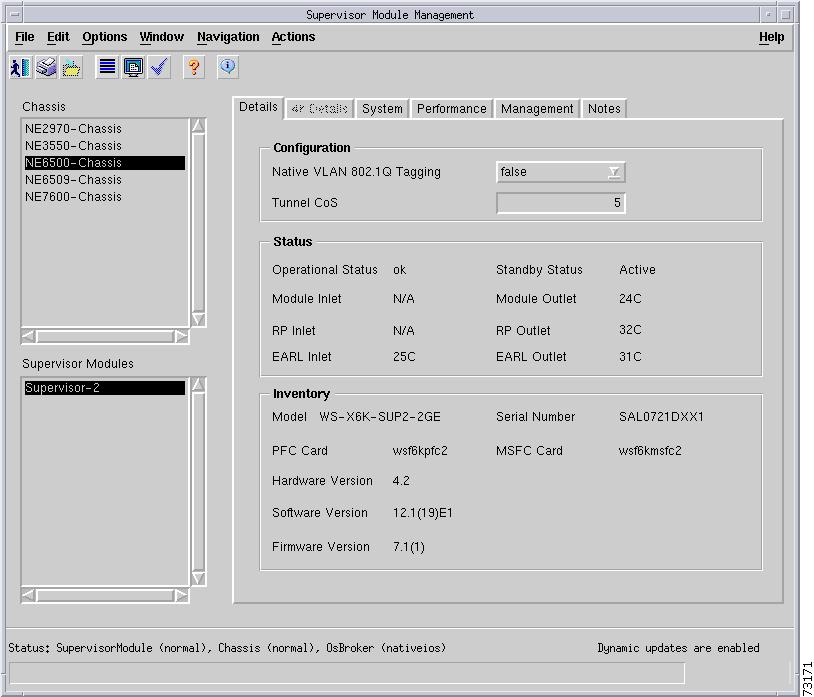
C6576M Supervisor Module Dialog Box
This dialog box provides access to attributes of the supervisor engine modules. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object or Supervisor Module object within the Physical view.
You can select one chassis and more than one supervisor engine module at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 5-7 shows the Status tab of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box.
Figure 5-7 Status Tab of the C6576M Supervisor Module Dialog Box
Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Operational Status—Displays the operational status of the supervisor engine module. The operation status can have one of the following values:
–
other—The status is unknown.
–
ok—The status is normal.
–
minorFault—There is a minor fault.
–
majorFault—There is a major fault.
Note
If this attribute has a value other than ok, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
•
Standby Status—Displays the status of the redundant Supervisor module if available. This attribute can have one of the following values:
–
other—Indicates a mode other than standby or active.
–
unknown—Indicates that mode cannot be detected.
–
standby—Indicates that the supervisor engine module status is in standby mode.
–
active—Indicates the supervisor engine module is being used to switch or route packets.
Temperature Area
The Temperature area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box provides the temperature for the following sensors:
•
Module Inlet—Inlet temperature of the module in degrees Celsius.
•
Module Outlet—Outlet temperature of the module in degrees Celsius.
•
RP Inlet—Inlet temperature of the MSFC daughter card in degrees Celsius.
•
RP Outlet—Outlet temperature of the MSFC daughter card in degrees Celsius.
•
EARL Inlet—Inlet temperature of the Policy Feature Card (PFC) daughter card in degrees Celsius.
•
EARL Outlet—Outlet temperature of the PFC daughter card in degrees Celsius.
Each of these sensor attributes can have the following values:
•
<n>C—Temperature in degrees Celsius.
•
N/O—Indicates that the sensor is not operational.
•
N/A—Indicates that the sensor value is not available.
Actions Area
The Actions area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Commission—This button is used to commission the object manually. This can only be done if the object is in a decommissioned state. By clicking this button, the two interface subobjects are also commissioned.
•
Decommission—This button is used to decommission the object manually. In the decommissioned state, the properties of the object are not monitored. As a result, data displayed in the configuration window is not guaranteed to be current. Decommissioning the Supervisor Module will also decommission its Ethernet Interface objects.
The decommission action is useful to allow a supervisor engine module to be removed and replaced without generating alarms.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the performance state.
•
mismatched—The type of supervisor engine module discovered does not match the predeployed supervisor engine module.
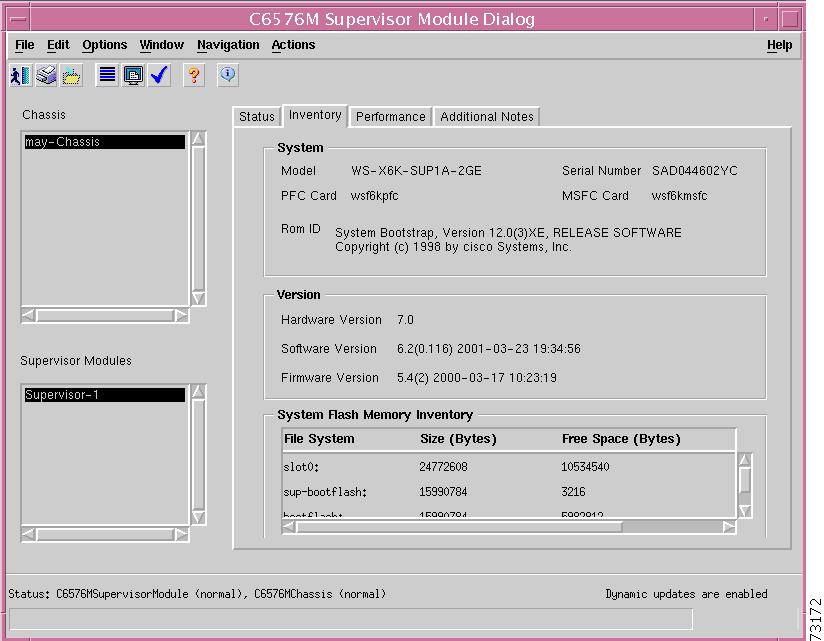
Inventory Tab
Figure 5-8 shows the Inventory tab of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box.
Figure 5-8 Inventory Tab of the C6576M Supervisor Module Dialog Box
System Area
The System area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Model—Displays the model description of supervisor engine module installed.
•
Serial Number—Displays the serial number for the supervisor engine module.
•
PFC Card—Displays the type of PFC daughter card installed on the Supervisor module.
–
empty—No card installed
–
wsf6kpfc—PFC installed
–
wsf6kpfc2—PFC2 installed
–
other—Card is not one of the above.
•
MSFC Card—Displays the type of MSFC daughter card installed on the Supervisor module. Not supported in Hybrid OS.
–
empty—No card installed
–
wsf6kmsfc—MSFC installed
–
wsf6kmsfc2—MSFC installed
–
other—Card is not one of the above
•
ROM ID—Displays the bootflash version information.
Version Area
The Version area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Hardware—Displays the hardware version of the supervisor engine module.
•
Software—Displays the software version of the supervisor engine module.
•
Firmware—Displays the firmware version of the supervisor engine module.
System Flash Memory Inventory Area
The System Flash Memory Inventory area lists the Flash memory information for the entire switch (including redundant supervisor engines, if available).
•
File System—Name used to refer to a partition by the system.
•
Size (Bytes)—Total size of Flash memory.
•
Free Space (Bytes)—Amount of free space available in the device.
•
File Count—Number of files on the device.
Performance Tab
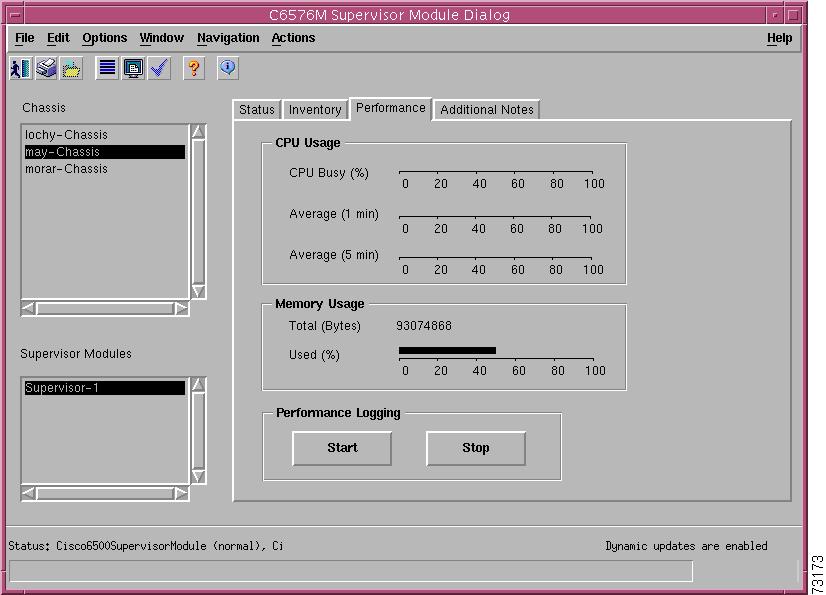
Figure 5-9 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box.
Figure 5-9 Performance Tab of the C6576M Supervisor Module Dialog Box
CPU Usage Area
The CPU Usage area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
CPU Busy (%)—Displays the current CPU load.
•
Average (1 min.)—Displays the 1-minute load average.
•
Average (5 min.)—Displays the 5-minute load average.
Memory Usage Area
The Memory Usage area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Total (Bytes)—Displays the total amount of processor memory.
•
Used (%)—Displays the current amount of processor memory used.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box allows users to turn on performance logging for the supervisor module attributes as well as the attributes of the two Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
•
Start—Turns performance data logging on the Supervisor object and its interfaces.
•
Stop—Turns performance data logging off for the Supervisor object and its interfaces.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
The following Supervisor attributes are polled in the Performance state:
•
CPU Usage Average (5 sec)
•
CPU Usage Average (1 min)
•
CPU Usage Average (5 min)
•
Memory Used (%)
•
Total amount of memory available (bytes)
•
Total amount of memory used (bytes)
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-10 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box.
Figure 5-10 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Supervisor Module Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the supervisor engine module.
C6576M Ethernet Module Dialog Box
This dialog box provides information on Ethernet modules, including standard Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, and Gigabit Ethernet modules. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object or Ethernet Module object within the Physical view.
You can select one chassis and more than one Ethernet module from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Details Tab
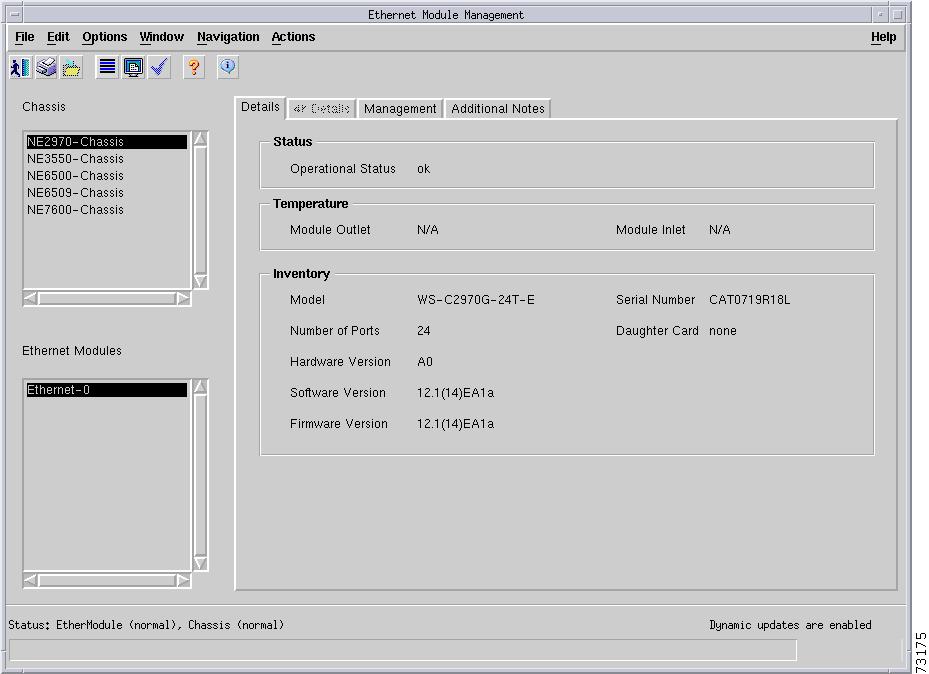
Figure 5-11 shows the Details tab of the C6576M Ethernet Module dialog box.
Figure 5-11 Details Tab of the C6576M Ethernet Module Dialog Box
Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M Ethernet Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Operational Status—Displays the operational status of the Ethernet module. This attribute can have one of the following values:
–
other—The status is unknown.
–
ok—The status is normal.
–
minorFault—There is a minor problem.
–
majorFault—There is a major problem.
Note
If this attribute has a value other than ok, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
Temperature Area
The Temperature area of the C6576M Supervisor Module dialog box provides information for the following sensors:
•
Module Inlet—Inlet temperature of the module in degrees Celsius.
•
Module Outlet—Outlet temperature of the module in degrees Celsius.
Each sensor can have the following values:
–
<n>C—Temperature in degrees Celsius.
–
N/O—Indicates that the sensor is not operational.
–
N/A—Indicates that the sensor value is not available.
Inventory Area
The Inventory area of the C6576M Ethernet Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Model—Type of Ethernet module. This attribute can have one of the following values:
–
WS-X6524-100FX-MM
–
WS-X6548-RJ-21
–
WS-X6548-RJ-45
–
WS-X6408-GBIC
–
WS-X6408A-GBIC
–
WS-X6416-GBIC
–
WS-X6416-GE-MT
–
WS-X6516-GBIC
–
WS-X6816-GBIC
–
WS-X6316-GE-TX
–
WS-X6501-10GEX4
–
WS-X6224-100FX-MT
–
WS-X6324-100FX-SM
–
WS-X6324-100FX-MM
–
WS-X6248-RJ-45
–
WS-X6248-TEL
–
WS-X6248-A-TEL
–
WS-X6348-RJ-45
–
WS-X6348-RJ-21
–
WS-X6516-GE-TX
–
WS-X6502-10GE
•
Serial Number—The serial number of the module.
•
Number of Ports—The total number of ports on the module.
•
Daughter Card—The type of daughter card installed on the module. The possible values of this attribute are:
–
none—No card installed.
–
WS-F6KDFC—Distributed Forwarding Card for WS-X6516-GBIC module.
–
WS-F6KVPWR—Inline Power Card.
–
unknown—Card installed is not one of the above.
•
Hardware Version—The hardware version on the module.
•
Software Version—The software version on the module.
•
Firmware Version—The firmware version on the module.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M Ethernet Module dialog box allows users to turn on performance data logging for all interfaces on the module:
•
Start—Turn performance data logging on for all interfaces.
•
Stop—Turn performance data logging off for all interfaces.
See the "C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box" section for a list of the interface attributes that are polled for performance data.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Actions Area
The Actions area of the C6576M Ethernet Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Commission—This button is used to commission the object manually. This can only be done if the object is in a decommissioned state. Clicking this button commissions all interfaces.
•
Decommission—This button is used to decommission the object manually. In the decommissioned state, the properties of the object are not monitored. As a result, data displayed in the configuration window is not guaranteed to be current. Clicking this button decommissions all interfaces.
The decommission action is useful to allow a Ethernet module to be removed and replaced without generating alarms.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the performance state.
•
mismatched—The type of Ethernet module discovered does not match the predeployed Ethernet module.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-12 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Ethernet Module dialog box.
Figure 5-12 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Ethernet Module Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the Ethernet module.
C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
This dialog box provides information for all Ethernet interface attributes, including Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object, Supervisor module object, Ethernet module object, or Ethernet Interface object within the Physical view.
You can select one chassis, more than one Ethernet module, and more than one interface at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
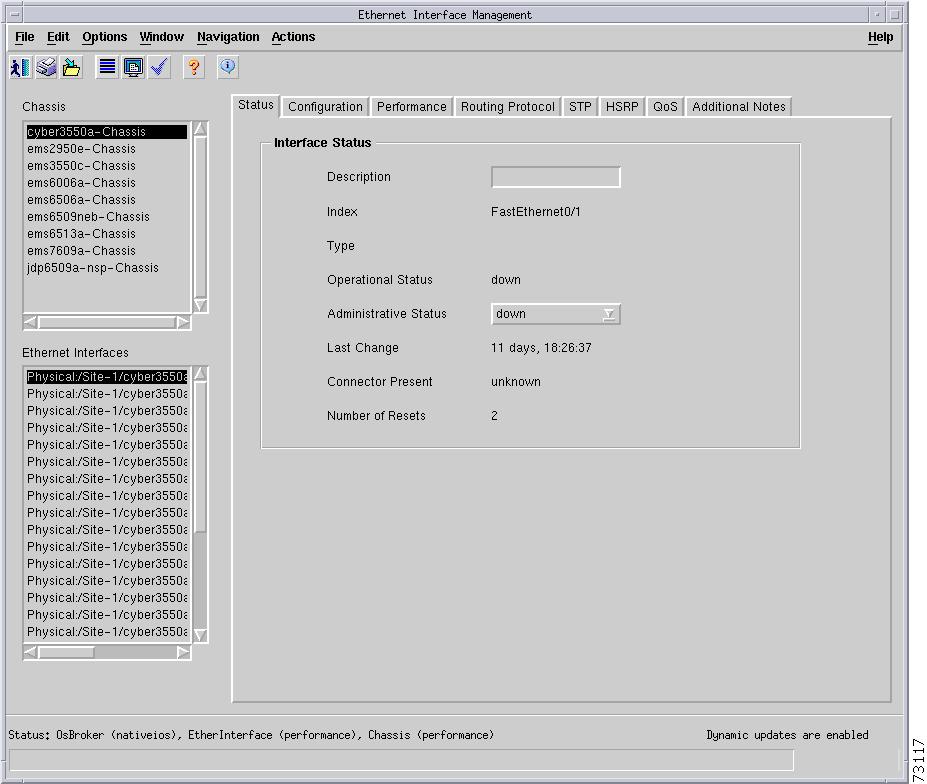
Figure 5-13 shows the Status tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-13 Status Tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Interface Status area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
Description—Descriptive name of the interface.
Note
The maximum number of characters allowed for Hybrid OS is 25.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Type—Displays the type of physical layer medium dependent interface on the port. This attribute is read-only. These are possible types:
–
e10BaseT
–
e10BaseF
–
e100BaseTX
–
e100BaseT4
–
e100BaseF
–
e100BaseFsm
–
e10a100BaseTX
–
mii
–
e1000BaseLX
–
e1000BaseSX
–
e1000BaseCX
–
e1000Empty
–
e1000BaseLH
–
e1000BaseT
–
e1000UnsupportedGbic
–
e1000BaseZX
•
Operational Status—Displays the operational status of the interface. This attribute is read-only and has one of the following values:
–
up—Interface is ready to transmit and receive packets.
–
down—No packets are being passed. The interface is in this state if there is a fault preventing it from going to the up state.
–
testing—No operational packages can be passed.
–
unknown
–
dormant—Interface is up but waiting for external actions.
–
notPresent—The interface is in this state if the interface has missing components (typically hardware).
–
lowerLayerDown—The interface in the lower layer is down.
•
Administrative Status—Displays the administrative status of the interface. These are the values:
–
up—The interface is up and operational.
–
down—The interface is in a down administrative status; this value causes the operational status to be set to down as well.
–
testing (read-only)—In this state, no operational packets can be transmitted or received. This value is read-only.
•
Last Change—The timestamp indicating when the configuration for this interface was last changed. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Connector Present—Displays if a cable is attached to the interface. These are the values:
–
yes
–
no
–
unknown—This value is used when the Administrative Status is not set to "up". In this case, it cannot be determined if a connection is present or not.
•
Number of Resets—The number of times this interface has been reset. This attribute is read-only.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates that current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Configuration Tab
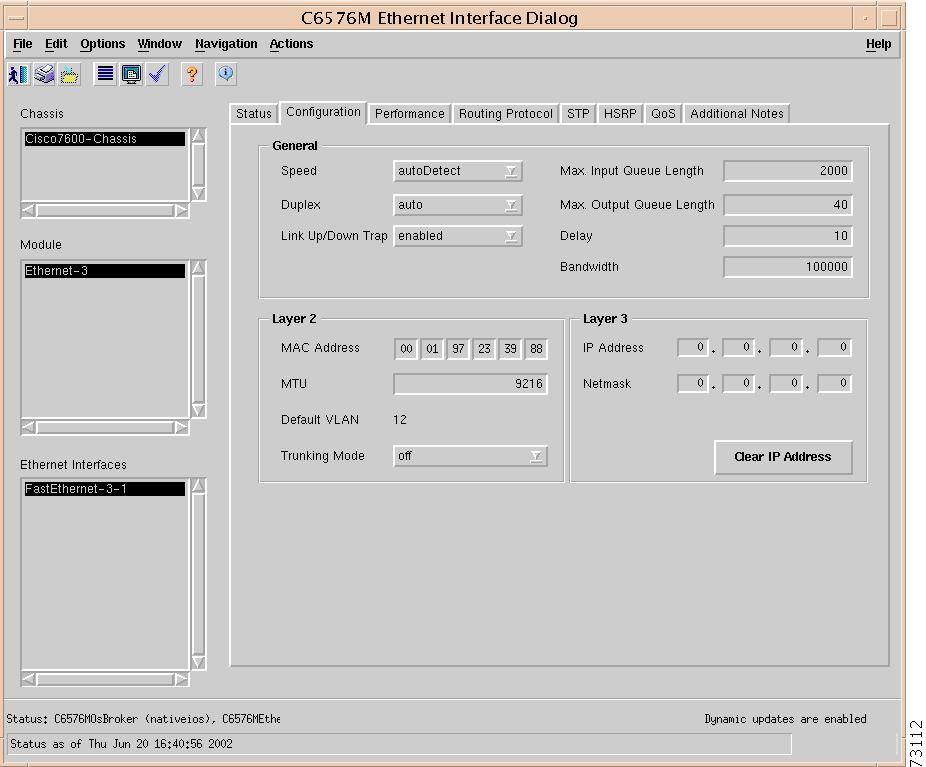
Figure 5-14 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-14 Configuration Tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
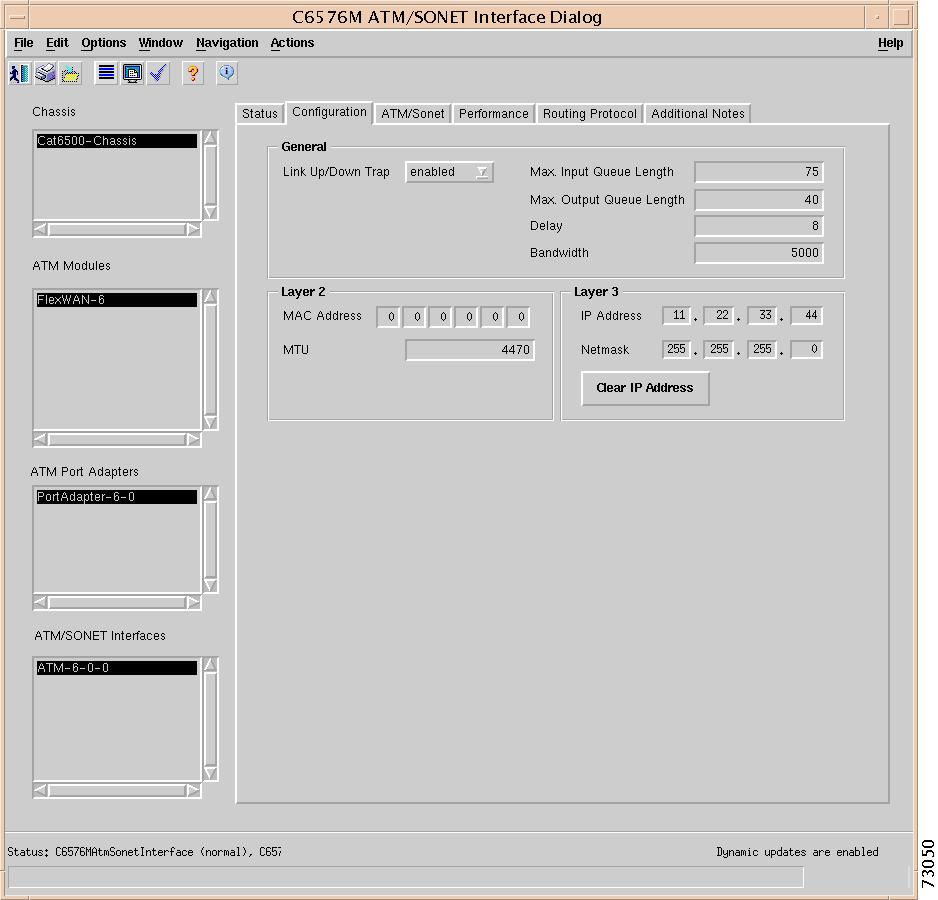
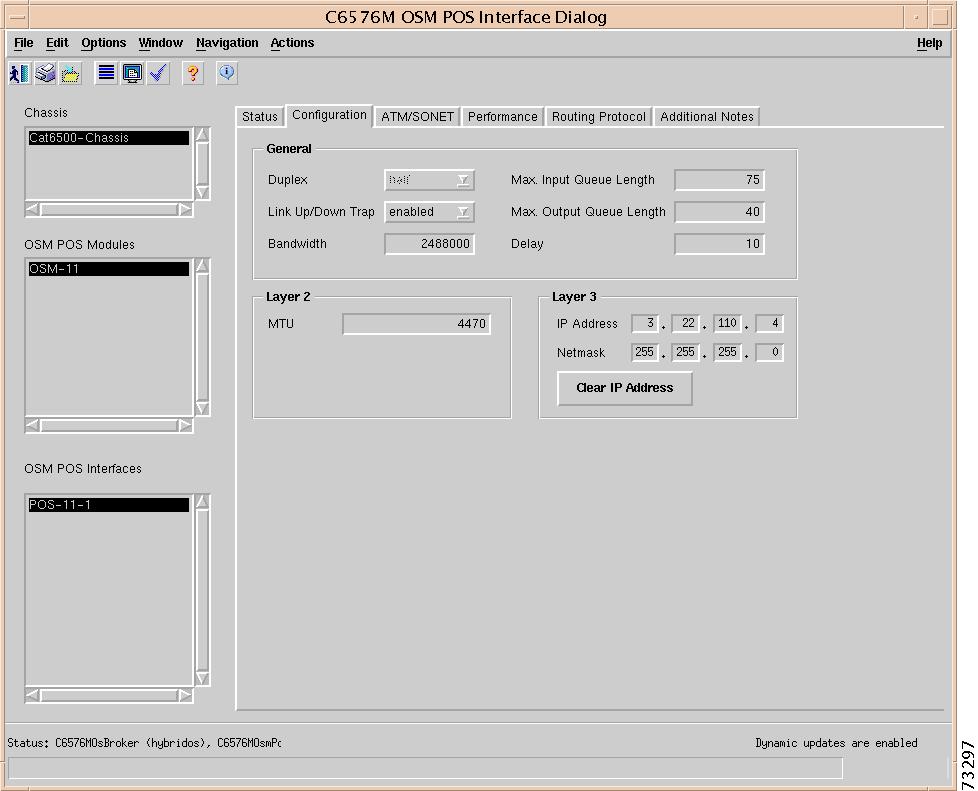
General Area
The General area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
Speed—The desired speed of this port in bits per second. This attribute is only editable if it is a Fast Ethernet interface. In this case, you can choose one of the following values:
–
autoDetect
–
10 Mb/s
–
100 Mb/s
–
1000 Mb/s
–
s10G
If set to autoDetect, the Duplex attribute is set to auto, which forces the interface to determine the speed and duplex mode for the interface automatically.
Note
If an unsupported speed is selected, an error is reported.
•
Duplex—Displays the duplex mode for the port. This attribute is only editable if it is a Fast Ethernet interface. In this case, you can choose one of the following modes:
–
half
–
full
–
disagree (read-only)
–
auto
If the Speed attribute is set to autoDetect, the Duplex will be set to auto.
•
Link Up/Down Trap—Indicates if link up or link down traps are being generated. This list contains the following values:
–
enabled
–
disabled
•
Input Queue Length—Displays the input queue length in packets.
•
Output Queue Length—Displays the output queue length in packets.
•
Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
Note
The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with this command.
•
Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
MAC Address—Displays the MAC address of the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
MTU—Displays the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size in bytes. The size of the largest packet which can be sent/received on the interface, specified in octets. For interfaces that are used for transmitting network datagrams, this is the size of the largest network datagram that can be sent on the interface.
Note
IOS 12.1(8a)E5 caveat: Jumbo frame support is incompatible with the IS-IS routing protocol. Leave the MTU size at the default value on any interface where IS-IS provides routing.
Note
For Native IOS, any value for the MTU will be accepted although it is recommeneded that only 1500 or 9600 bytes is configured. For Hybrid OS, if jumbo frames are enabled, the MTU will be reported as 9216 bytes. If jumbo frames are not enabled, the MTU will be reported as 1500 bytes. Any input value greater than or equal to 9216 bytes will be taken as 9216 bytes, and the jumbo frames will be enabled. Any input value less than 9216 bytes will be taken as 1500 bytes, and the jumbo frames will be disabled.
•
Default VLAN—Displays the VLAN to which this interface belongs if it stops trunking. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Trunking Mode—Indicates the administrative status set on the trunk port, while the operational status is the one that indicates whether the port is actually trunking or not. This mode is one of the following values:
–
off—The port is permanently set to be a non-trunk.
–
onNoNegotiate—The port is permanently set to be a trunk and no negotiation takes place with the far end to try to ensure consistent operation.
–
on—The port initiates a request to become a trunk and will become a trunk regardless of the response from the far end.
–
desirable—The port initiates a request to become a trunk and will become a trunk if the far end agrees.
–
auto—The port does not initiate a request to become a trunk but will do so if it receives a request to become a trunk from the far end.
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the layer 3 interface.
•
Netmask—Subnet mask of the interface IP address. Enabled bits indicate the network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Clear IP Address button— After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for this interface.
Performance Tab
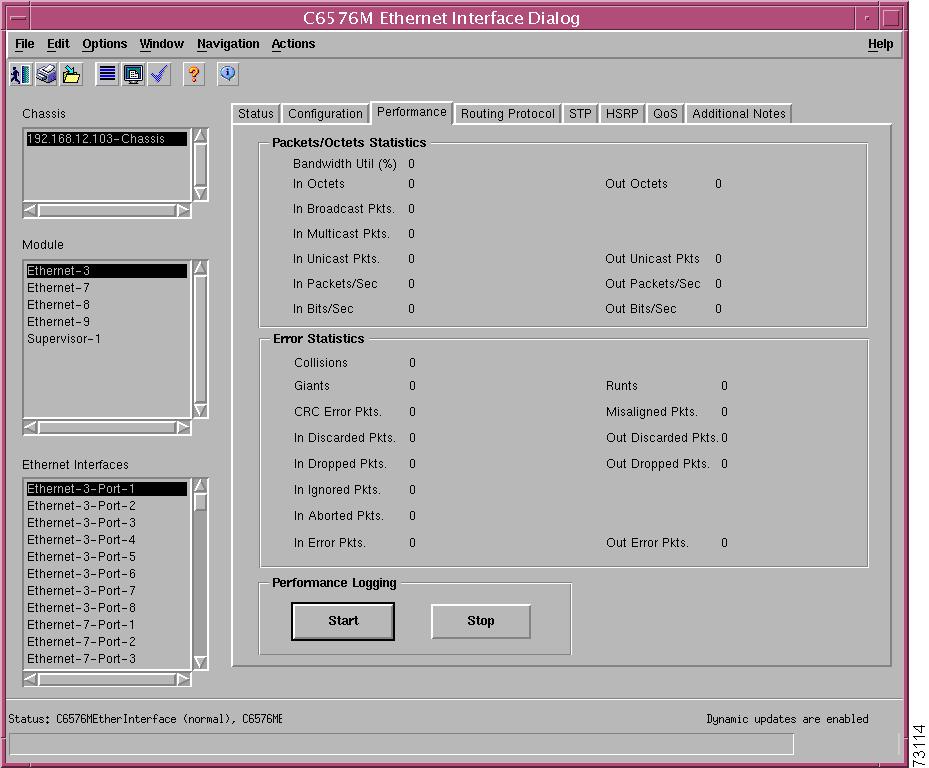
Figure 5-15 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-15 Performance Tab on the C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
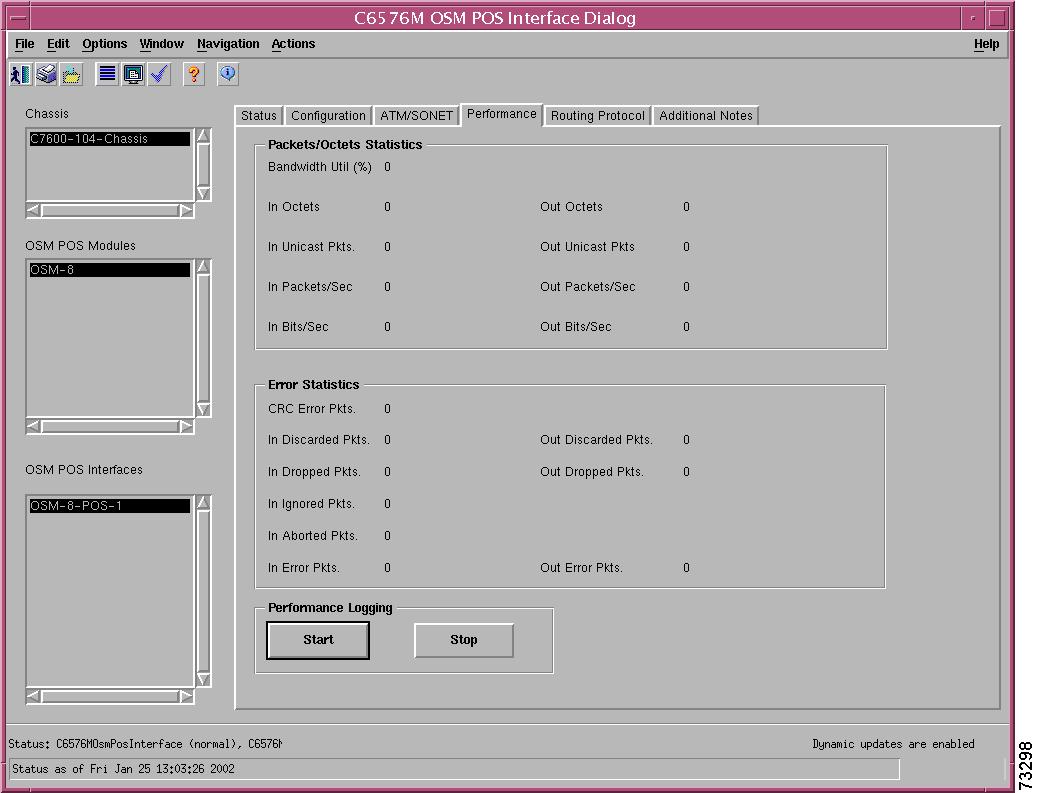
Packets/Octets Statistics Area
The Packets/Octets Statistics area C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization of the interface.
Note
This value will be disabled if the Chassis object is not in the normal or performance state.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
In Broadcast Pkts.—The total number of good packets received that were directed to the broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets.
•
In Multicast Pkts.—The total number of good packets received that were directed to a multicast address. Note that this number does not include packets directed to the broadcast address.
•
In Unicast Packets—The number of packets, delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
Out Unicast Pkts—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Error Statistics Area
The Error Statistics area C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
Collisions—Number of collisions on this segment.
•
Giants—Total number of packets received that were longer than 1518 octets (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were otherwise well formed.
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Packets received that had a length (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) of between 64 and 1518 octets, inclusive, but had either a bad Frame Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral number of octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a nonintegral number of octets (Alignment Error).
•
In Discarded Pkts.—Number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher layer protocol. One reason to discard such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—Number of events in which packets were dropped by the probe due to lack of resources. This number is not necessarily the number of packets dropped, but is the number of times this condition has been detected.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of packets ignored.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of packets aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—Number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Runts—Total number of packets received that were less than 64 octets long (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and were otherwise well formed.
•
Misaligned Pkts.—Alignment errors.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—Number of events in which outbound packets were dropped.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box allows users to turn on performance data logging for a single interface.
•
Start—Turns performance data logging on for this specific interface's attributes.
•
Stop—Turns performance data logging off for this specific interface's attributes.
All attributes in the Performance tab are logged when the object is placed into the Performance state.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
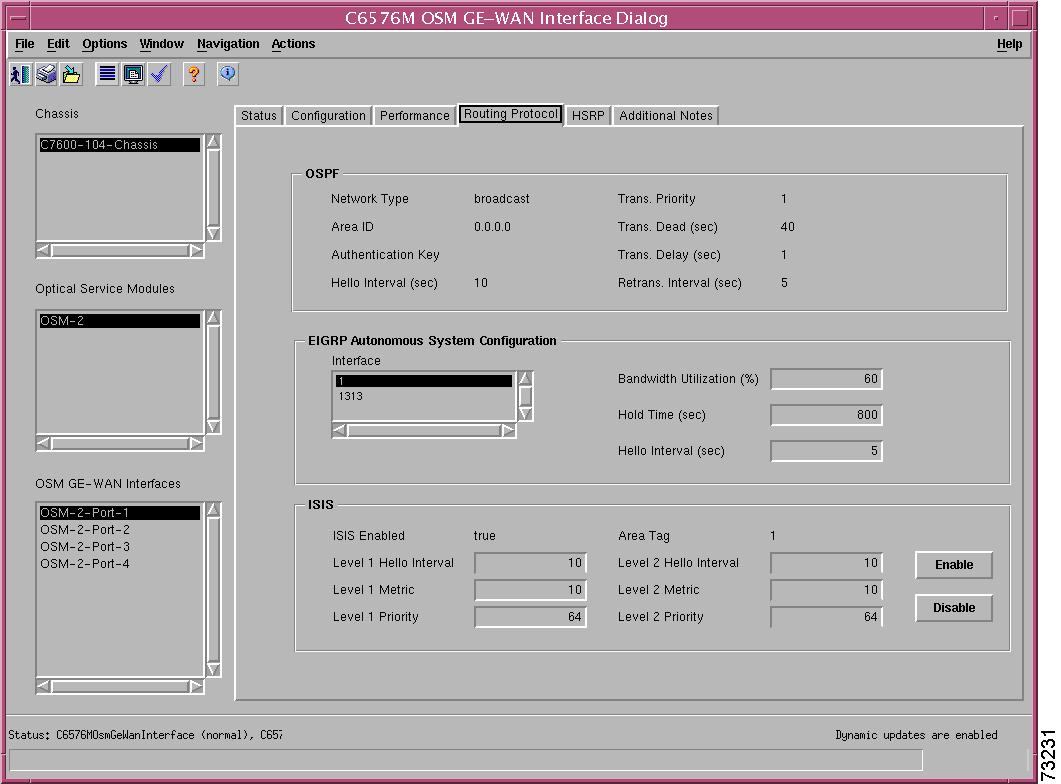
Routing Protocol Tab
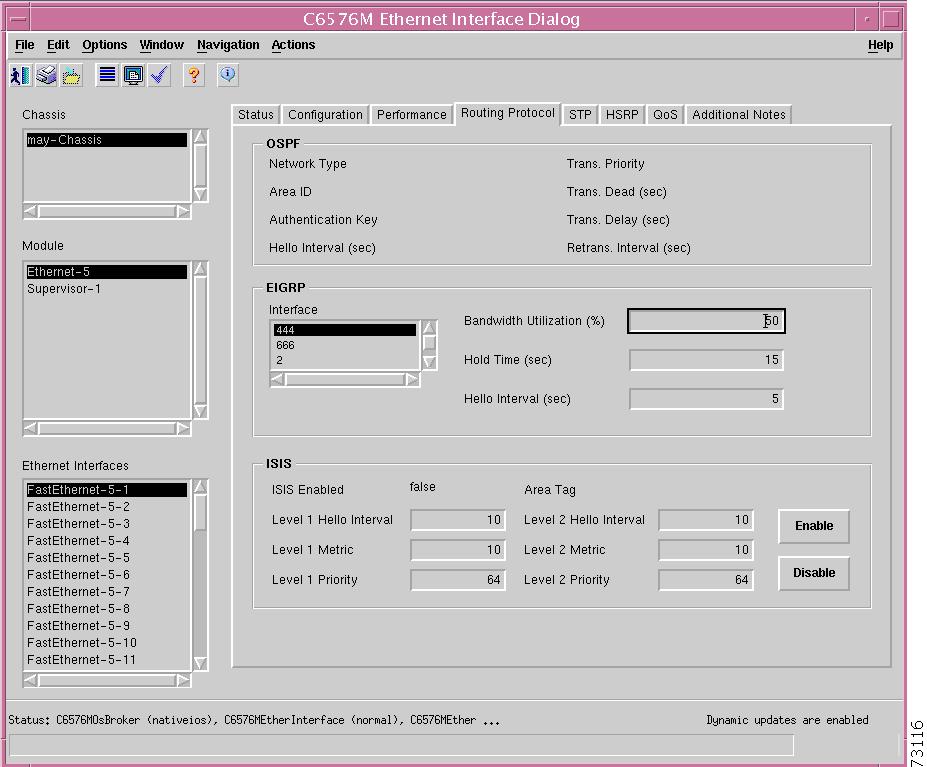
Figure 5-16 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-16 Routing Protocol Tab on the C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
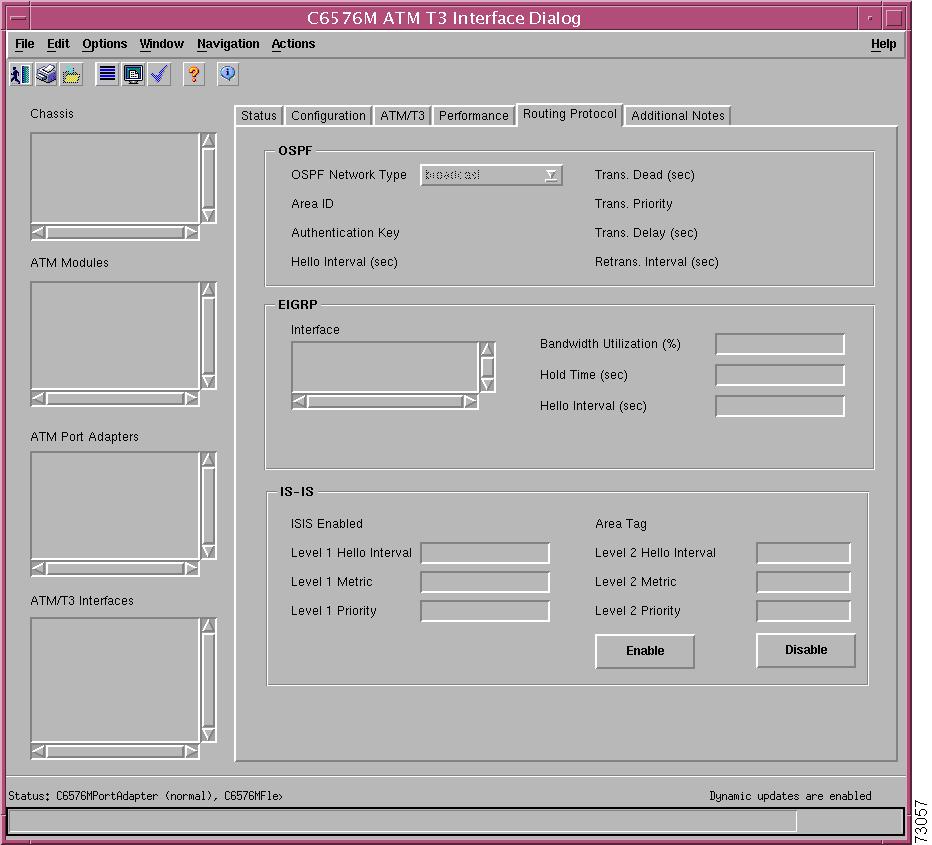
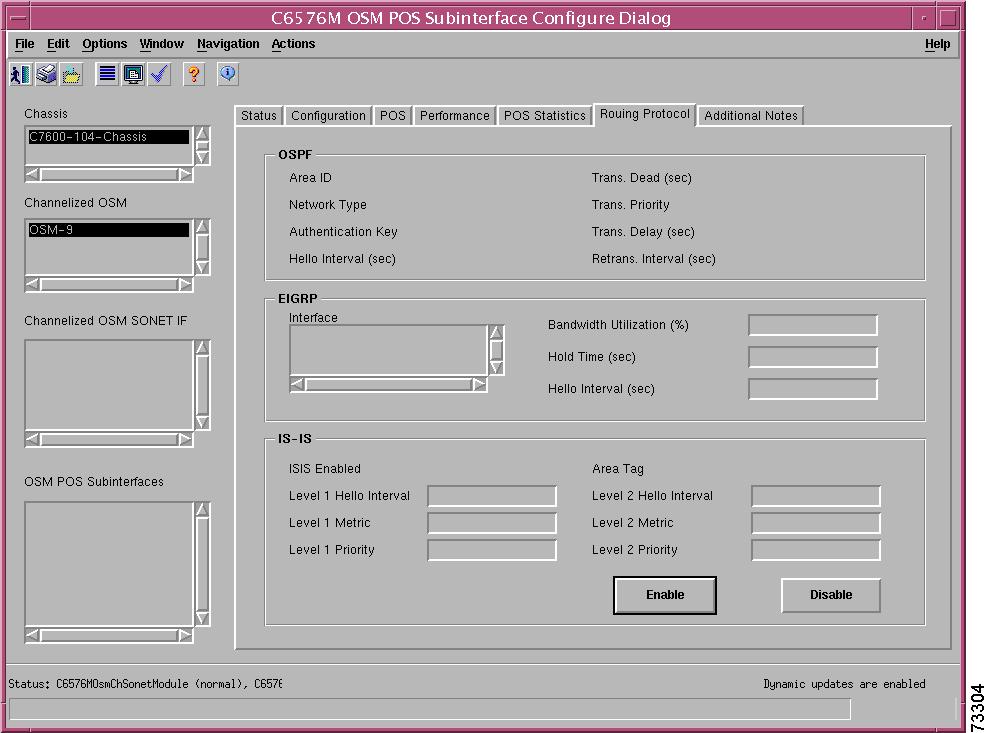
OSPF Area
The OSPF area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
Network Type—The OSPF interface type. For Ethernet interfaces, the type is always broadcast. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Area ID—The predefined ID uniquely identifying the area to which the interface connects. It can be specified as either a decimal value or as an IP address. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Authentication Key—The OSPF authentication key. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value is also used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular network. If more than one router has the same value for this field, the routers use their router ID as a tie breaker. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Trans. Dead (sec)—The number of seconds that a router's hello packets have not been seen before its neighbors declare the router down. This value should be a multiple of the hello interval. This value must be the same for all routers attached to a common network. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Trans. Delay (sec)—The estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state update packet over this interface. This is a read-only attribute.
EIGRP Area
The EIGRP Area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
EIGRP Interface Table—A list of the EIGRP processes. The following attributes can be configured for an EIGRP process:
–
Bandwidth Utilization (%) —The percentage of the interface bandwidth that the EIGRP protocol can use.
–
Hold Time (sec)—Hold time during which the device will wait for a hello packet to be received on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number. The hold time should be at least three times the hello interval.
–
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
ISIS Area
The ISIS area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface:
–
true—IS-IS routing is enabled.
–
false—IS-IS routing is disabled.
•
Area Tag—The IS-IS routing area in which the interface participates. If mutliarea IS-IS is configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named; otherwise, this value may be an implicit null tag.
•
Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1 routing.
•
Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2 routing.
•
Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
•
Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (inter-area) route calculation.
•
Level 1 Priority—The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or Designated Intermediate System (DIS).
•
Level 2 Priority—The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or Designated Intermediate System (DIS).
•
Enable button—Enables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
•
Disable button—Disables IS-IS routing on the interface.
STP Tab
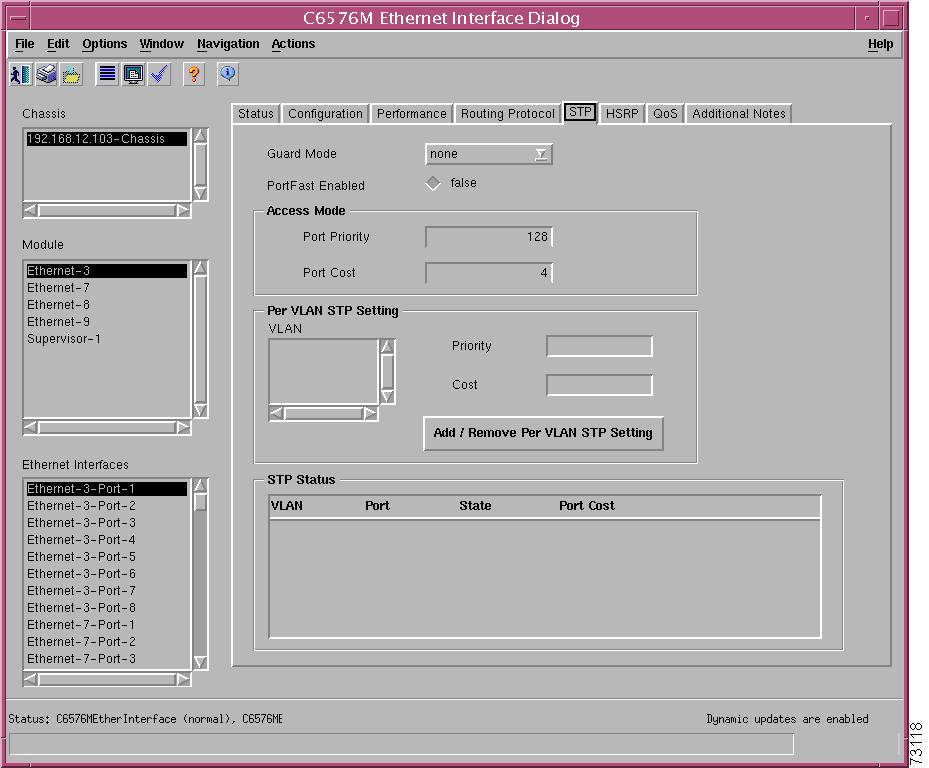
Figure 5-17 shows the STP tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-17 STP Tab on the C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
The area at the top of the STP tab provides the following information:
•
Guard Mode—Indicates whether or not STP guard mode is enabled on an interface. These are possible values:
–
root
–
none
–
loop (Hybrid OS only)
•
PortFast Enabled—Indicates whether or not an interface is enabled to move directly to the forwarding state on link up. This is a read-only attribute. Portfast can be configured on a trunking interface, but it only has an effect when the interface is in access mode. These are possible values:
–
true
–
false
Access Mode Area
The Access Mode area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
Port Priority—Describes the STP port priority of this interface. This is a metric used to represent the location of an interface in a network topology. It is used to determine which port will be placed in a blocking state when two or more ports are part of a loop. The default value is 128 in all versions of IOS, 32 in all versions of CatOS. The valid values are:
–
Native IOS 12.1(6)E and earlier:Integer (0..248) [increments of 8]
–
Native IOS 12.1(8a)E and later:Integer (0..252) [increments of 4]
–
CatOS 6.3:Integer(0..63)
–
CatOS 7.1:Integer(1..63)
•
Port Cost—Describes the STP port cost for this interface. The port cost is a metric used to represent the speed of the interface. STP will use this value in determining the preferred path when a loop is detected in the network.
Per VLAN STP Setting Area
The Per VLAN STP Setting area in the STP tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
STP VLAN Table—Describes the STP per-VLAN configurations of a trunking interface. There is one entry for each explicit per-VLAN spanning-tree configuration on the interface.
Note
The VLAN STP instance does not have to be currently carried on the trunk in order to configure the per-VLAN STP settings. The settings will take effect when the interface actually begins trunking the VLAN traffic.
•
Priority—Describes the STP VLAN port priority of this interface. The VLAN port priority is used on trunking interfaces. On any switchport that is not in trunking mode, the STP port priority is used instead. The default value is 128 in all versions of IOS, 32 in all versions of CatOS. The valid values are:
–
Native IOS 12.1(6)E and earlier:Integer (0..248) [increments of 8]
–
Native IOS 12.1(8a)E and later:Integer (0..252) [increments of 4]
–
CatOS 6.3:Integer(0..63)
–
CatOS 7.1:Integer(1..63)
•
Cost—Describes the STP VLAN path cost of this interface. The VLAN path cost is only used on trunking interfaces. On any switchport that is not in trunking mode, the STP port path cost is used instead.
Note
Default values for priority and cost will be used if one of these arguments is not provided by the user. The user must provide a nondefault value for at least one of these arguments; otherwise, the action will fail.
•
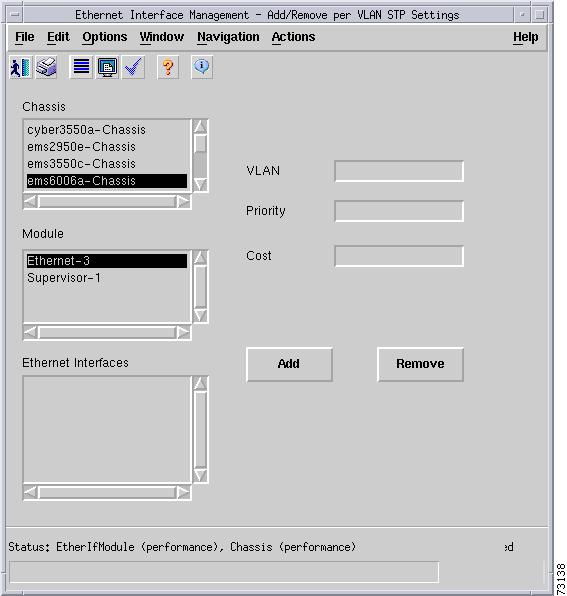
Add/Remove Per VLAN STP Setting button—Launches a subdialog box to add and remove an explicit STP VLAN configuration to the interface. The configuration will only have an effect if the interface is in trunking mode and the VLAN has an associated STP instance. The interface does not currently need to be configured as a trunking port, nor does the VLAN or the VLAN STP instance need to exist. Figure 5-18 shows the subdialog box that is displayed when the Add/Remove Per VLAN STP Setting button is selected. The subdialog box contain the following:
–
VLAN—Identifies the VLAN STP instance. This is the numeric identifier of the access mode VLAN or a VLAN that is carried on the trunk.
–
Priority—Describes the STP VLAN port priority of this interface.
Note
This value is the same as the Per VLAN STP Port Priority in the Per VLAN STP Setting Area.
–
Cost—Describes the STP VLAN path cost of this interface.
–
Add button—Adds an explicit STP VLAN configuration to the interface.
–
Remove button—Removes an explicit STP VLAN configuration to the interface.
Figure 5-18 Add/Remove Per VLAN STP Setting Subdialog Box
STP Status Area
The STP Status area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
STP VLAN Status Table—Describes the status of the active STP VLAN port configurations of the interface. No data is displayed if it is in the linkDown or STP misconfigured state. Data is displayed in the following columns:
–
VLAN—Identifies the VLAN STP instance that this status applies to. This is the numeric identifier of the access mode VLAN or a VLAN that is carried on the trunk.
–
Port—Unique port identifier for the interface in the STP instance. This identifier is unique for that port across all devices in the STP management domain.
–
State—Describes the interface state in the STP instance.
–
Port Cost—Indicates the current calculated port path cost of the interface in the STP instance.
HSRP Tab
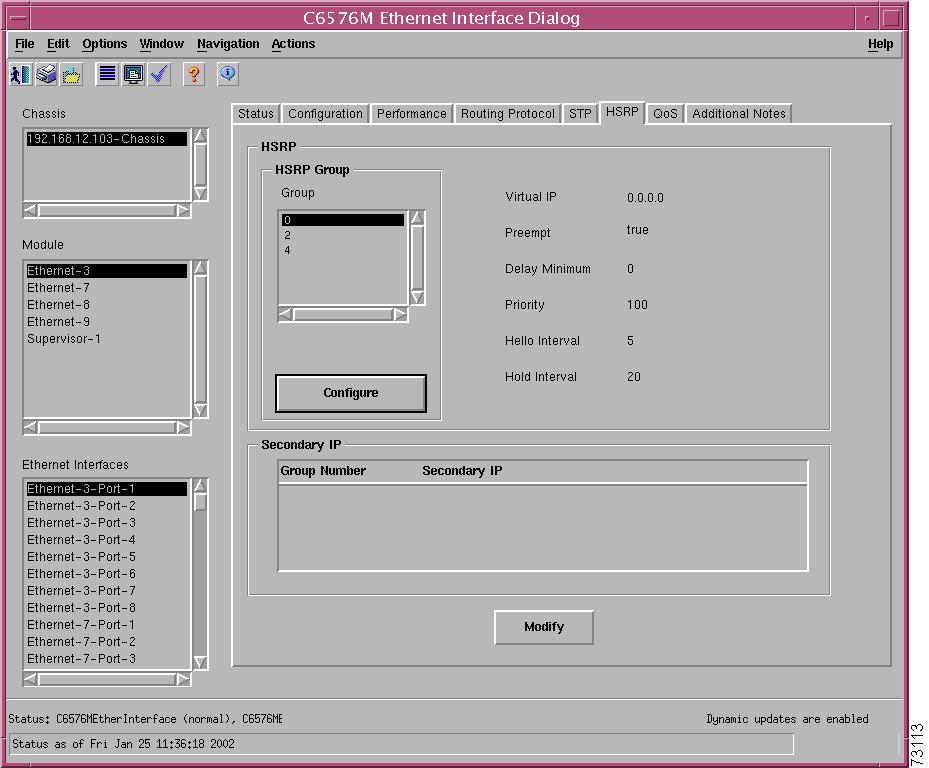
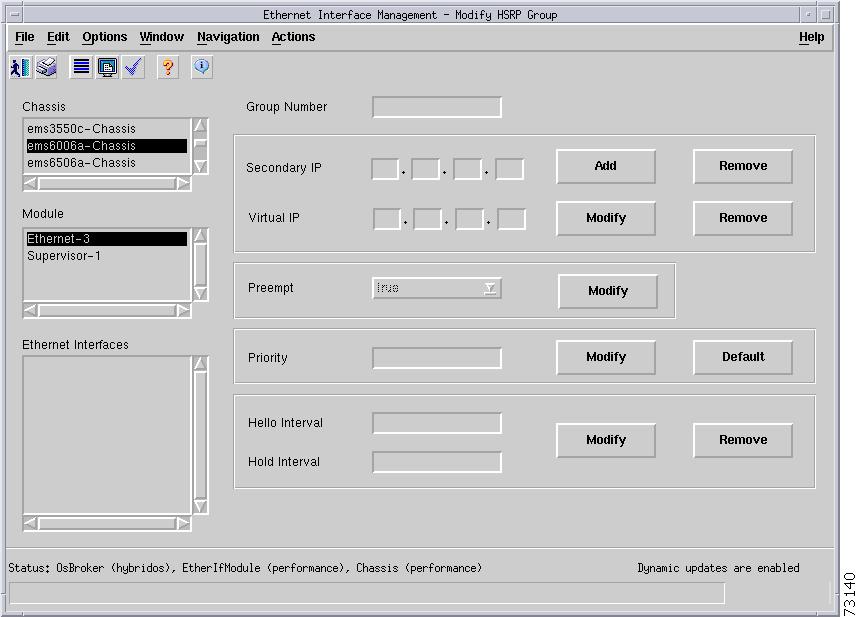
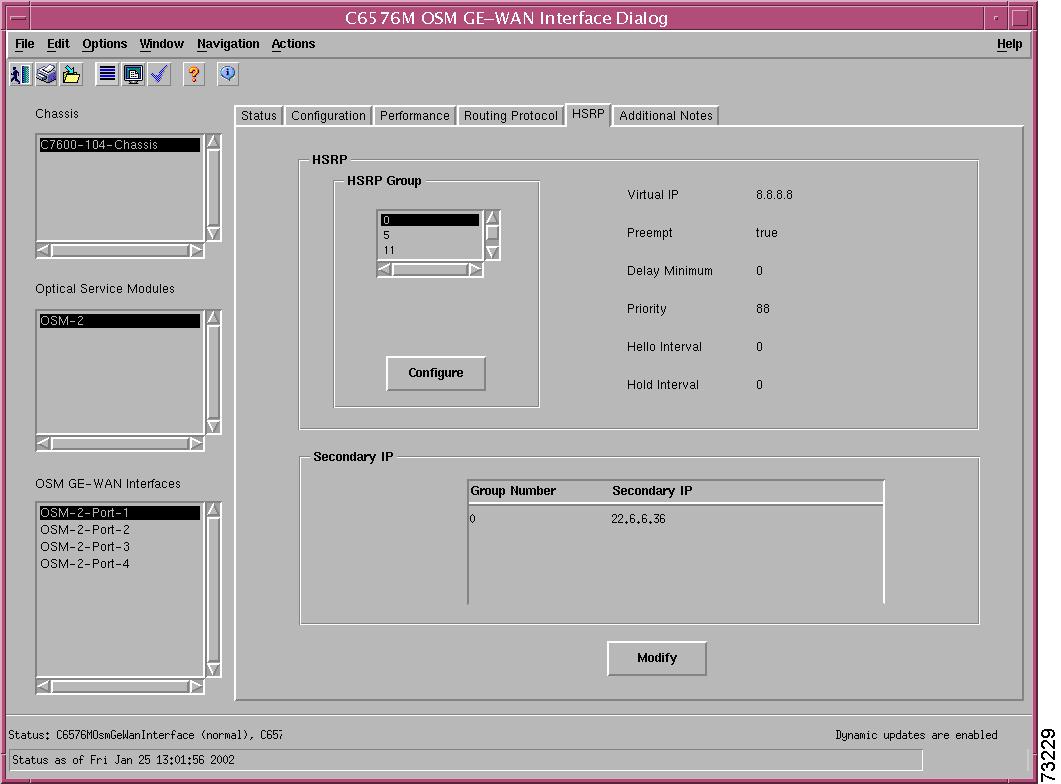
Figure 5-19 shows the HSRP tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-19 HSRP Tab on the C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
HSRP Area
The HSRP area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
HSRP Group Table—Describes HSRP groups deployed on an interface.
Note
There may be multiple groups deployed on an interface. Using a group number on one logical or physical interface does not preclude using it on another.
•
Virtual IP—Primary virtual IP address of the HSRP group. If this address is not configured, the agent attempts to discover the virtual address through a discovery process which scans the hello messages.
•
Preempt—If enabled, the current router attempts to overthrow a lower priority active router and attempt to become the active router. If disabled, this router becomes the active router only if there is no such router or the active router fails.
–
true—preempt enabled.
–
false—preempt disabled.
•
Delay Minimum—Time difference (in seconds) between a router power up and the time it can start preempting the currently active router. This value is only applicable when preemption is enabled.
•
Priority—Priority value that prioritizes a potential hot standby router. The range is 1 to 255, where 1 indicates the lowest priority and 255 indicates the highest priority. The default priority value is 100. The router in the HSRP group with the highest priority value becomes the active router.
•
Hello Interval—Hello interval in milliseconds. If this value is not configured, it can be learned from the active router.
•
Hold Interval—Hold interval in milliseconds. If this value is not configured, it can be learned from the active router.
•
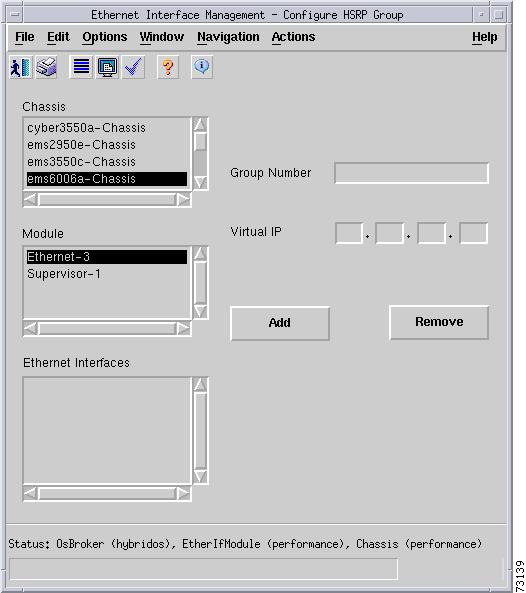
Configure button—Enable HSRP for IP on an interface. This action deploys an HSRP group on the interface. The HSRP group may optionally be assigned a primary IP address. If no address is explicitly assigned, the device attempts to discover the virtual IP address from the active server using Hello messages. Figure 5-20 shows the subdialog box displayed when the Add/Remove button is pressed.
Figure 5-20 HSRP Group Configure Subdialog Box
Secondary IP Area
The Secondary IP area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
HSRP Secondary Address Table—Describes secondary IP addresses of HSRP groups deployed on the interface. Data is displayed in the following columns:
–
Group Number—Unique identifier along of an HSRP group.
–
Secondary IP—Secondary IP address of HSRP group.
•
Modify button—Figure 5-21 shows the subdialog box that is displayed when the Modify button is pressed. This subdialog box is used to modify the following C6576M Ethernet Interface attributes of a given HSRP group:
–
Secondary IP
–
Virtual IP
–
Preempt
–
Delay Minimum
–
Priority
–
Hello Interval
–
Hold Interval
Figure 5-21 HSRP Secondary IP Modify Subdialog Box
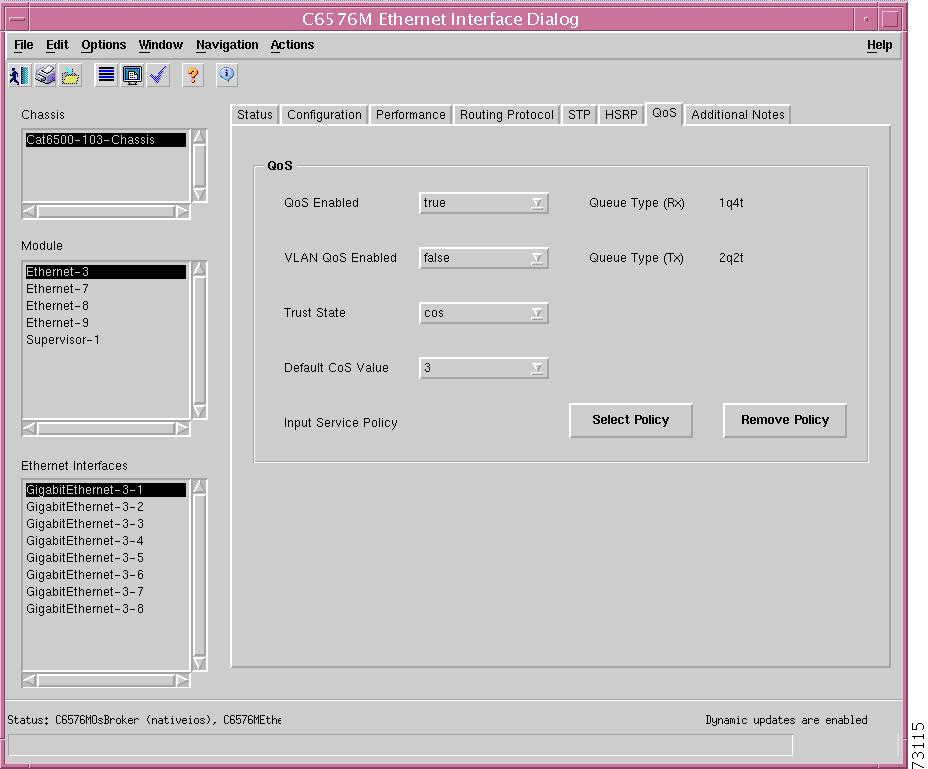
QoS Tab
Figure 5-22 shows the QoS tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-22 QoS Tab on the C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
QoS Area
The QoS area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
QoS Enabled—Enables or disables QoS on the interface.
–
true—QoS enabled.
–
false—QoS disabled.
Note
By default, if global QoS is enabled on the device, then the port QoS is also enabled unless explicitly disabled.
•
VLAN QoS Enabled—Enables/disables VLAN-based QoS on the interface.
–
true—VLAN-based QoS enabled.
–
false—VLAN-based QoS disabled.
•
Interface Trust State—The trust state of an interface determines how it marks, schedules, and classifies received L2 frames, and whether or not congestion avoidance is implemented. This attribute can have the following values:
–
untrusted—The interface is marked as untrusted.
–
DSCP—The DSCP value of the frame is trusted.
–
CoS—The CoS value of the frame is trusted.
–
IP-precedence—The IP-precedence value of the frame is trusted.
•
Default CoS Value—Interface class of service value. QoS assigns the CoS value to untagged frames from a trusted interface and to all frames of an untrusted interface.
•
Input Service Policy—The QoS policy map applied to the interface. This policy map is only applied if QoS is enabled on the interface and VLAN-based QoS is disabled on the interface.
•
Queue Type (RX)—Desribes the queue structure for traffic on an egress port.
•
Queue Type (TX)—Desribes the queue structure for traffic on an ingress port.
•
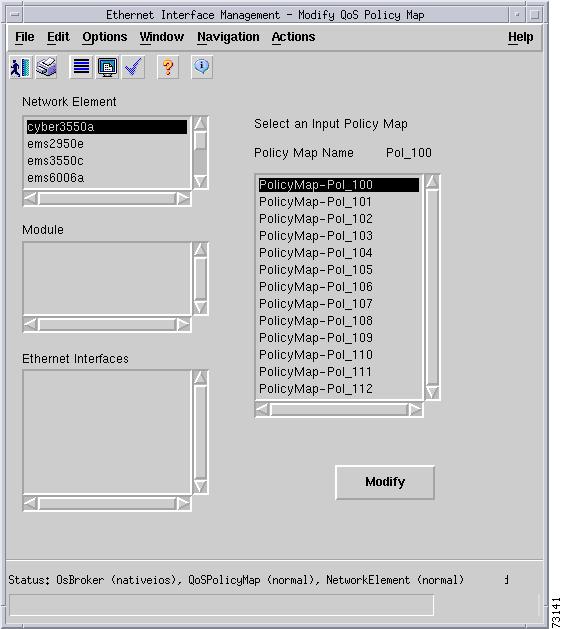
Select Policy button—Launches a subdialog box to attach an input QoS policy map to the interface. This action may fail if the specified policy map is not suitable for use with an Ethernet interface. Figure 5-23 shows subdialog box that is displayed when the Select Policy button is pressed. The subdialog box contains the following:
–
Input Policy Map Table—Lists the QoS policy maps to apply to the interface.
–
Modify button—Attaches an input QoS policy map to the interface
•
Remove Policy button—Detaches an input QoS policy map from the interface. When you click the Remove Policy button, a subdialog box is displayed prompting you to confirm the removal action.
Figure 5-23 Select Policy Subdialog Box
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-24 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-24 Additional Notes Tab on the C6576M Ethernet Interface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes tab is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the interface.
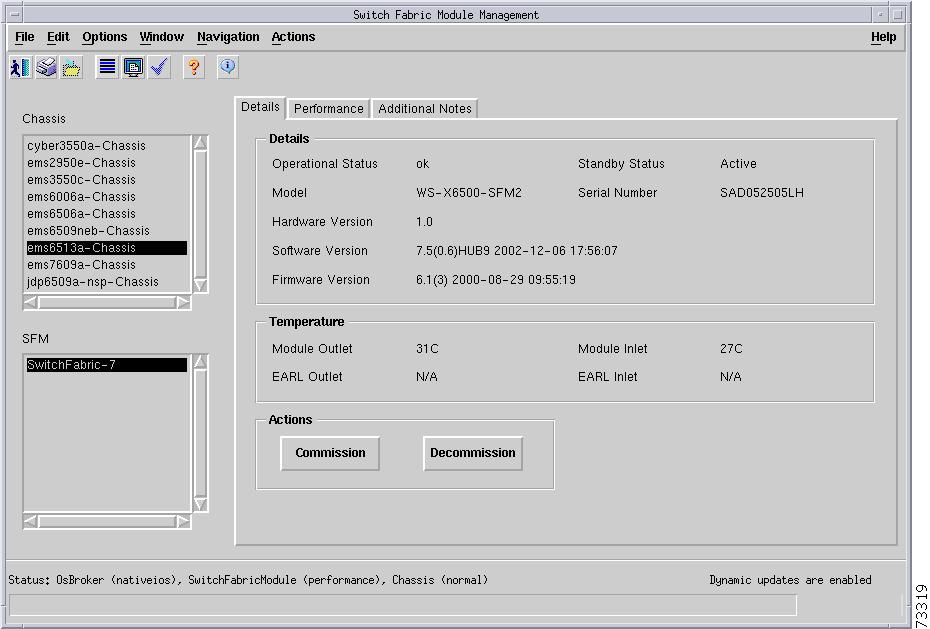
C6576M Switch Fabric Module Dialog Box
This dialog box provides information for the Switch Fabric Modules. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object or Switch Fabric Module object within the Physical view.
You can select one chassis and more than one Switch Fabric Module at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Details Tab
Figure 5-25 shows the Details tab of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module dialog box. All the attributes displayed in this tab are read-only.
Figure 5-25 Details Tab of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module Dialog Box
Details Area
The Details area of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Operational Status—Displays the operational status of the Switch Fabric Module. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
other—The status is unknown.
–
ok—The status is normal.
–
minorFault—There is a minor problem.
–
majorFault—There is a major problem.
Note
If this attribute has a value other than ok, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
•
Standby Status—Displays the status of the Switch Fabric Module. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
other (Hybrid OS only)
–
active
–
standby
–
error (Hybrid OS only)
•
Model—Model of the Switch Fabric Module. This attribute has the following value:
–
WS-X6500-SFM
–
WS-X6500-SFM2
•
Serial Number—The serial number of the module.
•
Hardware Version—The hardware version on the module.
•
Software Version—The software version on the module.
•
Firmware Version—The firmware version on the module.
Temperature Area
The Temperature area of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Module Outlet—The outlet temperature, in degrees Celsius, of the module.
•
Module Inlet—The inlet temperature, in degrees Celsius, of the module.
•
EARL Outlet—The outlet temperature, in degrees Celsius, of the Distributed Forwarding daughter card.
•
EARL Inlet—The inlet temperature, in degrees Celsius, of the Distributed Forwarding daughter card.
Actions Area
The Actions area of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module dialog box provides the following actions:
•
Commission—This button is used to commission the object manually. This can only be done if the object is in a decommissioned state.
•
Decommission—This button is used to decommission the object manually. In the decommissioned state, the properties of the object are not monitored. As a result, data displayed in the configuration window is not guaranteed to be current.
The decommission action allows a Switch Fabric Module to be removed and replaced without generating alarms.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
•
mismatched—The type of Switch Fabric Module discovered does not match the predeployed Switch Fabric Module.
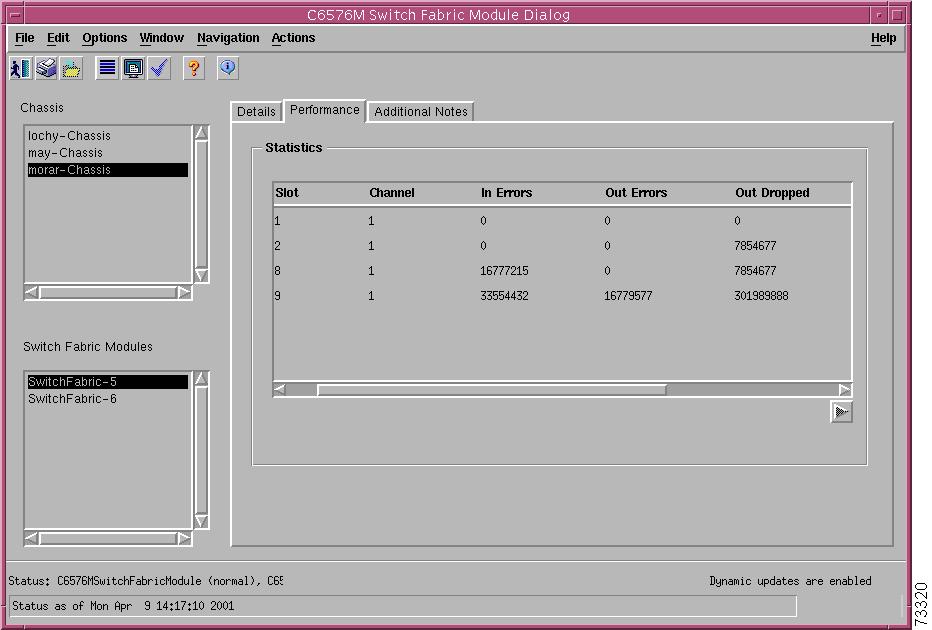
Performance Tab
Figure 5-26 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module dialog box.
Figure 5-26 Performance Tab of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module Dialog Box
Statistics Area
The Statistics Table of the Statistics area dialog box provides the fabric channel counters and utilization for the device. There is an entry in this table for each fabric-enabled module installed in the chassis.
•
Slot—Slot number of the fabric-enabled module.
•
Channel—Fabric channel number.
•
InErrors—Total number of error packets received on the module through the fabric channel since the entry was last initialized.
•
Out Errors—Total number of error packets transmitted on the module through the fabric channel since the entry was last initialized.
•
Out Dropped—Total number of dropped packets transmitted on the module through the fabric channel since the entry was last initialized.
•
In Util—Input utilization of the fabric channel for the module.
•
Out Util—Output utilization of the fabric channel for the module.
Note
This table is only supported in IOS versions 12.1(8a)EX and later; in earlier IOS versions, the table will be empty.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-27 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module dialog box.
Figure 5-27 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Switch Fabric Module Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the Switch Fabric Module.
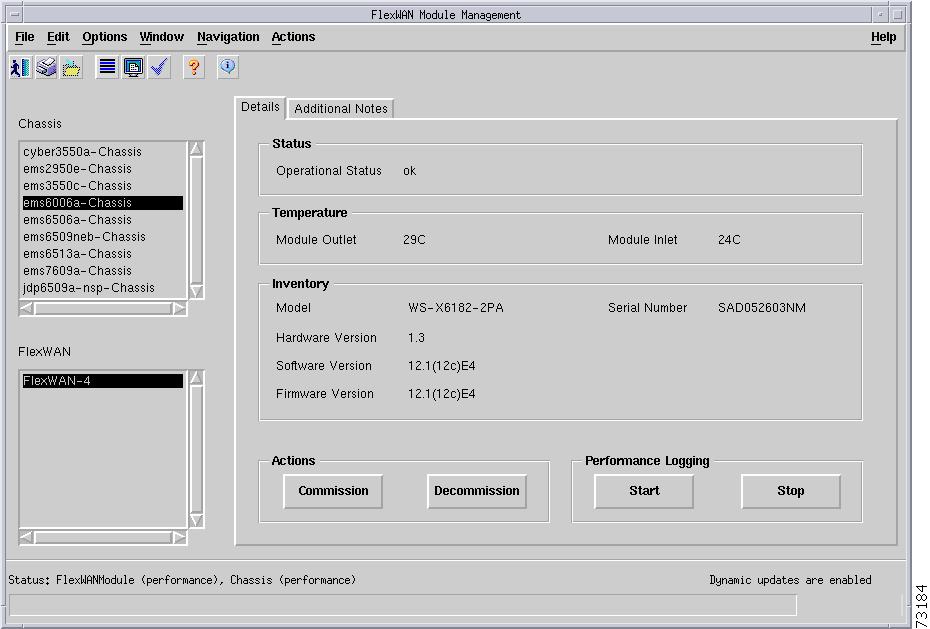
C6576M FlexWAN Module Dialog Box
This dialog box provides information for the FlexWAN modules. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object or FlexWAN module object within the Physical view.
You can select one chassis and more than one FlexWAN module at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Details Tab
Figure 5-28 shows the Details tab of the C6576M FlexWAN module dialog box.
Figure 5-28 Details Tab of the C6576M FlexWAN Module Dialog Box
Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M FlexWAN Module dialog box provides the following information:
•
Operational Status—Displays the operational status of the FlexWAN module. This attribute is read-only and has one of the following values:
–
other—The status is unknown.
–
ok—The status is normal.
–
minorFault—There is a minor problem.
–
majorFault—There is a major problem.
Note
If this attribute has a value other than ok, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
Inventory Area
The Inventory area of the C6576M FlexWAN Module dialog box provides the following information. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Model—Model of the FlexWAN module. This attribute has the following value:
–
WS-X6182-2PA
•
Serial Number—The serial number of the module.
•
Hardware Version—The hardware version on the module.
•
Software Version—The software version on the module.
•
Firmware Version—The firmware version on the module.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M FlexWAN Module dialog box contains these buttons to enable and disable performance logging of the interface attributes of the port adapters (if installed) on the FlexWAN module:
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to the user through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Actions Area
The Actions area of the C6576M FlexWAN Module dialog box provides the following actions:
•
Commission—This button is used to commission the object manually. This can only be done if the object is in a decommissioned state.
•
Decommission—This button is used to decommission the object manually. In the decommissioned state, the properties of the object are not monitored. As a result, data displayed in the configuration window is not guaranteed to be current.
The decommission action allows a FlexWAN module to be removed and replaced without generating alarms.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
•
mismatched—The type of FlexWAN module discovered does not match the predeployed FlexWAN module.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-29 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M FlexWAN Module dialog box.
Figure 5-29 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M FlexWAN Module Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the FlexWAN module.
C6576M Port Adapter Dialog Box
This dialog box provides information for the port adapters. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object or FlexWAN object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple chassis and port adapters at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Details Tab
Figure 5-30 shows the Details tab of the C6576M Port Adapter dialog box.
Figure 5-30 Details Tab of the C6576M Port Adapter Dialog Box
Inventory Area
The Inventory area of the C6576M Port Adapter dialog box provides the following information. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Model—Model of the port adapter. This attribute may have one of the following values:
–
PA-2E3—2-port serial E3 port adapter
–
PA-2H—2-port HSSI port adapter
–
PA-2T3—2-port serial T3 port adapter
–
PA-2T3+—Enhanced 2-port serial T3 port adapter
–
PA-4T+—Enhanced 4-port serial port adapter
–
PA-8T-232—8-port EIA/TIA-232 serial port adapter
–
PA-8T-V35—8-port V.35 serial port adapter
–
PA-8T-X21—8-port X.21 serial port adapter
–
PA-A3-E3—Enhanced ATM E3 port adapter
–
PA-A3-OC3MM—Enhanced ATM, OC-3 multimode port adapter
–
PA-A3-OC3SMI—Enhanced ATM, OC-3 single-mode intermediate reach port adapter
–
PA-A3-OC3SML—Enhanced ATM, OC-3 single-mode long reach port adapter
–
PA-A3-T3—Enhanced ATM T3 port adapter
–
PA-E3—1-port serial E3 port adapter
–
PA-H—1-port HSSI port adapter
–
PA-MC-2T3+—Dual interface multichannel T3 port adapter
–
PA-MC-8E1—8-port multichannel E1 port adapter
–
PA-MC-8T1—8-port multichannel T1 port adapter
–
PA-MC-E3—1-port multichannel E3 port adapter
–
PA-MC-T3—1-port multichannel T3 port adapter
–
PA-POS-OC3MM—Multimode PoS, OC3 port adapter
–
PA-POS-OC3SMI—Single-mode intermediate reach PoS, OC3 port adapter
–
PA-POS-OC3SML—Single-mode long reach PoS, OC3 port adapter
–
PA-T3—1-port T3 serial port adapter
–
PA-T3+—Enhanced 1-port T3 serial port adapter
•
Serial Number—The serial number of the port adapter.
Note
This attribute is unsupported for PA-ATMDX-E3 port adapter.
•
Number of Ports—The number of ports on the port adapter.
•
Hardware Version—The hardware version of the port adapter.
•
Software Version—The software version of the port adapter.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M ATM Interface dialog box contains the buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the port adapter.
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Actions Area
The Actions area of the C6576M Port Adapter dialog box provides the following actions:
•
Commission—This button is used to commission the object manually. This can only be done if the object is in a decommissioned state.
•
Decommission—This button is used to decommission the object manually. In the decommissioned state, the properties of the object are not monitored. As a result, data displayed in the configuration window is not guaranteed to be current.
The decommission action allows a port adapter to be removed and replaced without generating alarms.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
•
mismatched—The type of port adapter discovered does not match the predeployed port adapter.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-31 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Port Adapter dialog box.
Figure 5-31 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Port Adapter Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the port adapter.
C6576M Optical Services Modules Dialog Box
This dialog box describes the physical Gigabit Ethernet WAN OSM (OSM GE-WAN), Packet over Sonet OSM (OSM PoS), and channelized SONET OSM on a Cisco 7600 series Internet Router. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object or an OSM module object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple chassis and OSMs at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Details Tab
Figure 5-32 shows the Details tab of the C6576M OSM dialog box.
Figure 5-32 Details Tab of the C6576M OSM Dialog Box
Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M OSM dialog box provides the following information.
•
Operational Status—Displays the operational status of the OSM. This attribute has one of the following values. This is a read-only attribute.
–
other—The status is unknown.
–
ok—The status is normal.
–
minorFault—There is a minor problem.
–
majorFault—There is a major problem.
Note
If this attribute has a value other than ok, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
Temperature Area
The Temperature area of the C6576M OSM dialog box provides information for the following sensors. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Module Inlet—Inlet temperature of the module in degrees Celsius.
•
Module Outlet—Outlet temperature of the module in degrees Celsius.
Each sensor can have the following values:
–
<n>C—Temperature in degrees Celsius.
–
N/O—Indicates that the sensor is not operational.
–
N/A—Indicates that the sensor value is not available.
Inventory Area
The Inventory area of the C6576M OSM dialog box provides the following information. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Model—Model of the OSM. This attribute has the following value:
–
OSM-4GE-WAN-GBIC—4-port Gigabit Ethernet Optical Services Module, GBIC
–
OSM-4OC12-POS-MM—4-port OC-12/STM-4 SONET/SDH OSM, MM, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-4OC12-POS-SI—4-port OC-12/STM-4 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-IR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-4OC12-POS-SL—4-port OC-12/STM-4 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-LR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-1OC48-POS-SS—1-port OC-48/STM-16 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-SR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-1OC48-POS-SI—1-port OC-48/STM-16 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-IR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-1OC48-POS-SL—1-port OC-48/STM-16 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-LR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-16OC3-POS-MM—16-port OC-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH OSM, MM, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-16OC3-POS-SI—16-port OC-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-IR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-16OC3-POS-SL—16-port OC-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-LR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-2OC12-POS-MM—2-port OC-12/STM-4 SONET/SDH OSM, MM, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-2OC12-POS-SI—2-port OC-12/STM-4 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-IR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-2OC12-POS-SL—2-port OC-12/STM-4 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-LR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-8OC3-POS-MM—8-port OC-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH OSM, MM, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-8OC3-POS-SI—8-port OC-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-IR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-8OC3-POS-SL—8-port OC-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH OSM, SM-LR, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-1CHOC48/T3-SS—1-port Channelized OC48 to T3, Short Reach, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-1CHOC48/T3-SI—1-port Channelized OC48 to T3, Single-mode Intermediate Reach, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-2CHOC48/T3-SS—2-port Channelized OC48 to T3, Short Reach, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-2CHOC48/T3-SI—2-port Channelized OC48 to T3, Single-mode Intermediate Reach, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-4CHOC12/T3-MM—4-port Channelized OC12 to T3, Multi-mode, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-4CHOC12/T3-SI—4-port Channelized OC12 to T3, Single-mode Intermediate Reach, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-8CHOC12/T3-MM—8-port Channelized OC12 to T3, Multi-mode, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
–
OSM-8CHOC12/T3-SI—8-port Channelized OC12 to T3, Single-mode Intermediate Reach, with 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
•
Serial Number—The serial number of the module.
•
Hardware Version—The hardware version on the module.
•
Software Version—The software version on the module.
•
Firmware Version—The firmware version on the module.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M Port Adapter dialog box contains the buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the OSM.
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Actions Area
The Actions area of the C6576M OSM dialog box provides the following actions:
•
Commission—This button is used to commission the object manually. This can only be done if the object is in a decommissioned state.
•
Decommission—This button is used to decommission the object manually. In the decommissioned state, the properties of the object are not monitored. As a result, data displayed in the configuration window is not guaranteed to be current.
The decommission action allows a OSM to be removed and replaced without generating alarms.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
•
mismatched—The type of OSM discovered does not match the predeployed OSM.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-33 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M OSM dialog box.
Figure 5-33 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M OSM Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the OSM.
C6576M SLB Dialog Box
The Content Switching Module is a line card that provides server load balancing (SLB) of client traffic to server farms, firewalls, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) devices, or VPN termination devices. This dialog box provides information for SLB. This dialog box can be launched from a Chassis object or SLB object within the Physical view.
You can select one chassis and one SLB object at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Details Tab
Figure 5-34 shows the Details tab of the C6576M SLB dialog box.
Figure 5-34 Details Tab of the C6576M SLB Dialog Box
Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M SLB dialog box provides the following information:
•
Operational Status—Displays the operational status of the CSM. This attribute has one of the following values. This is a read-only attribute.
–
other—The status is unknown.
–
ok—The status is normal.
–
minorFault—There is a minor problem.
–
majorFault—There is a major problem.
Note
If this attribute has a value other than ok, an alarm is generated. (See Chapter 8, "Alarms and Alarm Management.")
Temperature Area
The Temperature area of the C6576M SLB dialog box provides information for the following sensors. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Module Inlet—Inlet temperature of the module in degrees Celsius.
•
Module Outlet—Outlet temperature of the module in degrees Celsius.
Each sensor can have the following values:
–
<n>C—Temperature in degrees Celsius.
–
N/O—Indicates that the sensor is not operational.
–
N/A—Indicates that the sensor value is not available.
Inventory Area
The Inventory area of the C6576M SLB dialog box provides the following information. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Model—Model of the Content Switching Module. This attribute has the following value:
–
WS-X6066-SLB-APC
•
Type—The type of module.
•
Number of Ports—The number of internal ports in the module.
•
Serial Number—The serial number of the module.
•
Hardware Version—The hardware version on the module.
•
Software Version—The software version on the module.
•
Firmware Version—The firmware version on the module.
SLB Setting Area
The Inventory area of the C6576M SLB dialog box provides the following information:
•
Forwarding Mode—The current SLB operating mode. This attribute has one of the following values. This is a read-only attribute.
–
csm(1)
–
rp(2)
•
Configured Mode—The current configured SLB mode. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
csm(1)
–
rp(2)
Note
The configured SLB mode does not take effect until the Content Switching Module is reloaded. The reload is performed manually by executing the IOS config mode command power cycle module slot_number.
Note
When changing the configured SLB mode from CSM to RP, the SLB configurations for CSM will be erased.
Actions Area
The Actions area of the C6576M SLB dialog box provides the following actions:
•
Commission—This button is used to commission the object manually. This can only be done if the object is in a decommissioned state.
•
Decommission—This button is used to decommission the object manually. In the decommissioned state, the properties of the object are not monitored. As a result, data displayed in the configuration window is not guaranteed to be current.
The decommission action allows a Content Switching Module to be removed and replaced without generating alarms.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field has the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
•
mismatched—The type of Content Switching Module discovered does not match the predeployed Content Switching Module.
Client Side VLAN Tab
Figure 5-35 shows the Client Side VLAN tab of the C6576M SLB module dialog box.
Figure 5-35 Client Side VLAN Tab of the C6576M SLB Module Dialog Box
Client Side VLAN Area
The Client Side VLAN area of the C6576M SLB dialog box provides the following information:
•
Client VLAN Table—Identifies the client VLANs used by the CSM. These are the VLANs on the device to which clients will connect. The following attributes are displayed for the selected client VLANs in the table:
–
IP Address—IP address of the client VLAN.
–
Netmask—Subnet mask of the client VLAN IP address. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Client VLAN Gateway Table—Describes the default gateways associated with the client VLANs. There may be multiple gateways associated with each client VLAN. The following columns are displayed in this table:
–
Client Side VLAN—Unique identifier of a client VLAN on the device.
–
Gateway—Default gateway of a client VLAN. A router to the client VLAN must have this gateway address configured and real servers must point their gateways to this address.
Client VLAN Config Area
The Client VLAN Config area of the C6576M SLB dialog box allows the user to add client side VLANs. The following attributes are configured:
•
Client Side VLAN field—Unique identifier of a client VLAN on the device.
Note
VLAN 1 is the default VLAN. VLAN identifiers greater than 1001 are reserved as the default VLANs for various media and for hidden VLANs generated by the device.
•
Client VLAN Add button—Adds the client VLAN specified in the client side VLAN field. If you do not specify a VLAN in the Client Side VLAN field, no action will take effect.
•
Client VLAN Remove button—Removes the client VLAN that is selected in the Client VLAN Table. A subdialog box is displayed asking the user to confirm the action.
Gateway Config Subarea
The Gateway Config subarea allows the user to add a default gateways associated with the client VLAN specified in the Client Side VLAN field. This VLAN must already be configured as a client side VLAN.
•
Gateway field—Default gateway associated with the client VLAN.
•
Gateway Remove button—Removes the default gateway specified by the Gateway field and the Client Side VLAN field. You need to specify a VLAN in the Client Side VLAN field and an IP address in the Gateway field for the action to take effect.
•
Gateway Add button—Adds the default gateway specified by the Gateway field and the Client Side VLAN field. You need to specify a VLAN in the Client Side VLAN field and an IP address in the Gateway field for the action to take effect.
Server Side VLAN Tab
Figure 5-36 shows the Server Side VLAN tab of the C6576M SLB dialog.
Figure 5-36 Server Side VLAN Tab of the C6576M SLB Dialog Box
Server Side VLAN Area
The Server Side VLAN area of the C6576M SLB dialog box provides the following information:
•
Server VLAN Table—Identifies the server VLANs used by the CSM. These are the VLANs on the device to which servers will connect. The following attributes are displayed for the selected server VLANs in the table:
–
IP Address—IP address of the server VLAN.
–
Netmask—Subnet mask of the server VLAN IP address. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Server VLAN Alias Table—Describes the aliases of a server VLAN. If the CSM is in a different subnet from the real servers, aliases may be used to eliminate the need for a router. Only used in server mode. There may be multiple aliases associated with each server VLAN. The following attributes are displayed in the table:
–
Server Side VLAN—Unique identifier of a server VLAN on the device.
–
IP Address—IP address of the server VLAN.
–
Netmask—Subnet mask of the server VLAN alias IP address. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Server VLAN Static Route Table—Describes the static routes of a server VLAN. A static route is configured to reach a real server if it is more than one network hop away from the CSM. There may be multiple static routes configured for a server VLAN. The following attributes are displayed in the table:
–
Server Side VLAN—Unique identifier of a server VLAN on the device.
–
Destination Network—IP address of network on the server VLAN.
–
Destination Netmask—Subnet mask of the network on the server VLAN. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
–
Gateway—Default gateway of a server VLAN. A router to the client VLAN must have this gateway address configured and real servers must point their gateways to this address.
Server VLAN Config Area
The Server VLAN Config area of the C6576M SLB dialog box allows you to add server side VLANs. The following attributes are configured:
•
Server Side VLAN field—Unique identifier of a server VLAN on the device.
•
Server VLAN Add button—Adds the server VLAN specified in the Server Side VLAN field. You need to specify a VLAN in the Server Side VLAN field for the action to take effect.
•
Server VLAN Remove button—Removes the server VLAN that is selected in the Server VLAN Table. A subdialog box is displayed asking the user to confirm the action.
Alias Config Subarea
This subarea allows you to add aliases associated with the server VLAN specified in the Server Side VLAN field. This VLAN must already be configured as a Server Side VLAN.
•
IP Address field—IP address of the server VLAN.
•
Netmask field—Subnet mask of the server VLAN alias IP address. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Alias Remove button—Removes the alias specified by the IP Address, Netmask, and Server Side VLAN fields. You need to specify a VLAN in the Server Side VLAN field, an IP address in the Alias IP Address field, and a subnet mask in the Alias Netmask field for the action to take effect.
•
Alias Add button—Adds the alias specified by the IP Address, Netmask, and Server Side VLAN fields. You need to specify a VLAN in the Server Side VLAN field, an IP address in the Alias IP Address field, and a subnet mask in the Alias Netmask field for the action to take effect.
Static Route Config Subarea
This subarea allows the user to add static routes of a server VLAN specified in the Server Side VLAN field. This VLAN must already be configured as a server side VLAN.
•
Destination Network field—IP address of network on the server VLAN.
•
Destination Netmask field—Subnet mask of the network on the server VLAN. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Gateway field—Default gateway of a server VLAN. A router to the client VLAN must have this gateway address configured and real servers must point their gateways to this address.
•
Static Route Remove button—Removes the static route specified by the Destination Network, Destination Netmask, Gateway, and Server Side VLAN fields.
•
Static Route Add button—Adds the static route specified by the Destination Network, Destination Netmask, Gateway, and Server Side VLAN fields.
For the Static Route Remove and Static Route Add button actions to take effect, you need to specify the static route using one of the following sets of attributes:
•
Option (A)
–
A VLAN in the Server Side VLAN field
–
An IP address in the Destination Network field
–
A Subnet Mask in the Destination Netmask field
•
Option (B)
–
A VLAN in the Server Side VLAN field
–
An IP address in the Gateway field
•
Option (C)
–
A VLAN in the Server Side VLAN field
–
An IP address in the Destination Network field
–
A Subnet Mask in the Destination Netmask field
–
An IP address in the Gateway field
Server Farms Tab
Figure 5-37 shows the Server Farms tab of the C6576M SLB dialog box.
Figure 5-37 Server Farms Tab of the C6576M SLB Dialog Box
Server Farm Area
The Server Farm area of the C6576M SLB dialog box provides the following information:
•
Server Farm Table—Describes the configured server farms. The following attributes are displayed for the selected server farm in the table:
–
Server Farm Index—Unique identifier of a server farm on the device.
–
Predictor—Load-balancing predictor algorithm. This attribute can have one of the following values:
•
roundrobin (1)
•
leastconns (2)
•
other (3) (not in write)
Note
A value of other (3) indicates the predictor algorithm is of a type unsupported by the C65/76M EMS. A value of other (3) is not supported for write operations.
•
Real Server Table—Describes the real servers in a server farm. The following columns are displayed in the table:
–
Server Farm Name—Unique identifier of a server farm on the device.
–
Real IP Address—IP address of the real server.
–
TCP Port—Optional TCP Port translation for the real server.
–
Current Connections—Number of current connections to the real server.
–
Operation Status—The operational status of the real server. This attribute can have the following values:
•
outOfService (1)
•
operational (2)
•
failed (3)
–
Admin Status—The administrative status of the real server. When the administrative status is changed to inService (2), it enables the real server for use by SLB. This attribute can have the following values:
•
outOfService (1)
•
inService (2)
–
Admin Weight—Configured weighting value to use for virtual server predictor algorithm.
–
Current Weight—Actual real server weighting factor.
–
Minimum Connections—When the maximum connections is exceeded, no more connections will be established to the real server until the number of connections falls below this value. The valid values range from 0 to 4294967295. This value must be less than the currently configured maximum connections.
–
Maximum Connections—Maximum number of active connections on the real server at any one point. If the value is set to the maximum of 4294967295, it indicates that the maximum is infinite (not monitored). This value must be greater than the currently configured minimum connections.
Server Farm Config Area
The Server Farm Config area of the C6576M SLB dialog box allows you to add and configure server farms. The following attributes are configured:
•
Server Farm Name field—Unique identifier of a server farm on the device.
•
Server Farm Add button—Adds the server farm specified in the Server Farm Name field. You need to specify a name in the Server Farm Name field for the action to take effect.
•
Server Farm Remove button—Removes the server farm that is selected in the Server Farm Table. A subdialog box is displayed asking the user to confirm the action.
Real Server Config Subarea
This subarea allows the user to add and remove real servers to the server farm specified in the Server Farm Name field.
•
Real IP Address field—IP address of the real server.
•
TCP Port—Optional TCP Port translation for the real server.
•
Real Server Add button—Adds the real server specified by the Real IP Address, TCP Port, and Server Farm Name fields. You need to specify a name in the Server Farm Name field, an IP address in the Real IP Address field, and a port number in the TCP Port field for the action to take effect.
•
Real Server Remove button—Removes the real server specified by the Real IP Address, TCP Port, and Server Farm Name fields. You need to specify a name in the Server Farm Name field, an IP address in the Real IP Address field, and a port number in the TCP Port field for the action to take effect.
Virtual Servers Tab
Figure 5-38 shows the Virtual Servers tab of the C6576M SLB dialog box.
Figure 5-38 Virtual Servers Tab of the C6576M SLB Dialog Box
Virtual Server Area
The Virtual Server area of the C6576M SLB dialog box allows the user to configure a virtual server to bring it into service.
Note
To modify attribute values, enter the desired value into the fields and press the Save icon in order for changes to take effect. Click Refresh to display the new settings.
The following information is provided:
•
Virtual Server Table—Describes the virtual servers. The following attributes are displayed for the selected virtual server in the table:
–
Virtual Server Index—Unique identifier of a virtual server on the device.
–
IP Address—IP address of the virtual server. A value of 0.0.0.0 indicates that no IP address is configured.
–
TCP Port—TCP port of the virtual server. A value of 0 indicates all ports are supported. Well known port numbers include:
•
dns (53)
•
ftp (21)
•
https (443)
•
matip-a (350)
•
nntp (119)
•
pop2 (109)
•
pop3 (110)
•
smtp (25)
•
telnet (23)
•
www (80)
•
xot (1998)
Note
This attribute cannot be nil if the virtual server IP address is set to a value other than 0.0.0.0. If virtual server IP address is set to 0.0.0.0, it indicates that no IP address has been configured and the value of the TCP port number is not applicable. On read, a value of 0 will always be returned.
–
Server Farm Name—Identifies the server farm associated with the virtual server. This referenced server farm must be unique on the device.
–
Idle Timer—The duration that connection information is maintained in the absence of packet activity for a connection.
–
Current Connections—Number of current connections to the virtual server.
–
Operation Status—The operational status of the virtual server. This attribute can have the following values:
•
outOfService (1)
•
operational (2)
•
failed (3)
–
Admin Status—The administrative status of the virtual server. This attribute can have the following values:
•
outOfService (1)
•
inService (2)
•
Virtual Server Client Table—Describes the restricted clients of a virtual server. Client ranges are configured to permit or deny clients using the virtual server. The following columns are displayed in the table:
–
Virtual Server Name field—Unique identifier of a virtual server on the device.
–
IP Address field—IP address of a virtual server restricted client range.
–
Netmask field—Subnet mask of a virtual server restricted client range. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
–
Mode—Indicates whether or not the restricted client range defines clients that may not use the virtual server.
Virtual Server Config Area
The Virtual Server Config area of the C6576M SLB dialog box allows the user to add and configure virtual servers. The following attributes are configured:
•
Virtual Server Name field—Unique identifier of a virtual server on the device.
•
Virtual Server Add button—Adds the virtual server specified in the Virtual Server Name field. You need to specify a name in the Virtual Server Name field for the action to take effect.
•
Virtual Server Remove button—Removes the virtual server that is selected in the Virtual Server Table. A subdialog box is displayed asking the user to confirm the action.
Client Config Subarea
•
This subarea allows the user to add a client range to a virtual server definition. This action is used to restrict which clients are allowed to connect to the virtual server. The following attributes can be configured:
–
IP Address field—IP address of a virtual server restricted client range.
–
Netmask field—Subnet mask of a virtual server restricted client range. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
Note
The IP address and netmask must specify a unique client range on the virtual server. The netmask must agree with the class of network address specified by the IP address.
–
Mode button—Indicates that the restricted client range defines clients that may not use the virtual server. The client is excluded.
–
Client Add button—Adds the client range to a virtual server definition. You need to specify a name in the Server Farm Name field, an IP address in the IP Address field, and a subnet mask in the Netmask field, and select a mode for the action to take effect.
–
Client Remove button—Removes the client range to a virtual server definition.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-39 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M SLB dialog box.
Figure 5-39 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M SLB Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the SLB.
C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
This dialog box describes a physical and logical enhanced ATM T3 interface of the PA-A3-T3 port adapter on the Catalyst 6000 family switches or Cisco 7600 series Internet Routers. This dialog box is launched from the ATM port adapter or the ATM T3 interface object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple ATM T3 interfaces, port adapters, FlexWAN modules, and chassis at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 5-40 shows the Status tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-40 Status Tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box provides the following information to describe the general characteristics of the interface.
•
Description—Comment or a description to help you remember what is attached to this interface. The description is only put in the configuration to help you remember what specific interfaces are used for.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Operational Status—The current operational state of the interface. This is a read-only attribute. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
testing—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
unknown
–
down
–
up
–
dormant—Interface is waiting for external actions (such as a serial line waiting for an incoming connection)
–
notPresent—Interface has missing (typically, hardware) components.
–
lowerLayerDown—The interface in the lower layer is down.
•
Administrative Status—The desired state of the interface. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
testing (read-only)—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
up
–
down
•
Last Change—The value (in seconds) of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state was entered prior to the last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value. This is a read-only attribute.
•
Connector Present—Indication if a cable is connected to the interface. If the ifAdminStatus is down, then this value cannot be determined and an "unknown" message is displayed. This is a read-only attribute. This attribute can have the following values:
–
yes—Cable is connected to the interface.
–
no—Cable is not connected to the interface.
–
unknown—Cannot determine if a cable is connected to the interface.
•
Number of Resets—Number of times the interface internally reset. This is a read-only attribute.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box contains the buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the interface.
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field has the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Configuration Tab
Figure 5-41 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-41 Configuration Tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
General Area
The General area contains the following information:
•
Link Up/Down Trap—Enables or disables linkUp and linkDown trap generation for the interface.
•
Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
Note
The Bandwidth attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF); you cannot adjust the actual bandwidth of an interface with this command.
•
Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
Note
The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP and EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with this command.
•
Input Queue Length—Input queue length in packets.
•
Output Queue Length—Output queue length in packets.
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area contains the following information:
•
MAC Address—Displays the MAC address of the interface.
•
MTU—The size of the largest packet which can be sent/received on the interface, specified in octets.
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area contains the following information:
•
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the layer 3 interface.
•
Netmask—Subnet mask of the interface IP address. Enabled bits indicate the network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Clear IP Address - After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for this interface.
ATM/T3 Tab
Figure 5-42 shows the ATM/T3 tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-42 ATM/T3 Tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
ATM Area
The ATM area contains the following information:
•
NSAP Address—Unique identifier of node in ATM network. This address is required if not implemented by ATM CM.
•
End-Station ID—End-station ID of node in ATM network. The NSAP address prefix is provided by the switch to the router through ILMI. There must be a PVC configured for ILMI communication with the switch. This address is required if not implemented by ATM CM.
T3 Area
The T3 area contains the following information:
•
Clock Source—Source of the transmit clock.
–
loopTiming—Indicates that the recovered receive clock is used as the transmit clock.
–
localTiming—Indicates that a local clock source is used or that an external clock is attached to the box containing the interface.
•
Line Type—Indicates DS-3 framing. The following values are possible:
–
dsx3other
–
dsx3M23
–
dsx3CbitParity
–
dsx3ClearChan
•
Scrambling—Indicates whether DS-3 scrambling is enabled on the interface. Scrambling assists recovery of the clock by the receiver.
•
Line Build-Out Length—Line build-out length.
–
short—0 to 50 feet
–
long—Greater than 50 feet
Performance Tab
Figure 5-43 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-43 Performance Tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
Interface Packets/Octets Statistics Area
The Interface Packets/Octets Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
In Unicast Pkts.—The number of packets, delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub-)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
Out Unicast Pkts.—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Interface Error Statistics Area
The Interface Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum errors.
•
In Discarded Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent them from being delivered to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—The number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent them from being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the output queue was full.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of input packets that were ignored by this interface.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of input packets that were aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that contained errors that prevented them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
ATM/T3 Area
The ATM/T3 area contains the following information:
•
C-bit Errored Secs—C-bit errored seconds.
•
C-bit Severely Err Secs—C-bit severely errored seconds.
•
C-bit Coding Violations—C-bit coding violations.
•
P-bit Errored Secs—P-bit errored seconds.
•
P-bit Severely Err Secs—P-bit severely errored seconds.
•
P-bit Coding Violations—P-bit coding violations.
•
Line Errored Secs—Line errored seconds.
•
Line Coding Violations—Line coding violations
•
Unavail Secs—Unavailable seconds.
•
Severely Err Frm Secs—Severely errored framing seconds.
ATM/T3 Far End Area
The ATM/T3 Far End area contains the following information:
•
C-bit Errored Secs—Far end C-bit errored seconds.
•
C-bit Severely Err Secs—Far end C-bit severely errored seconds.
•
C-bit Coding Violations—Far end C-bit coding violations.
•
Elapsed Secs—Number of seconds which have elapsed since the beginning of the far end current error-measurement period.
•
Unavail Secs—Far end unavailable seconds.
Routing Protocol Tab
Figure 5-44 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-44 Routing Protocol Tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
OSPF Area
The OSPF area contains the following information:
•
OSPF Network Type—OSPF network type. ATM is a point-to-point service; by default it is considered to be nonbroadcast by the OSPF routing process. An ATM interface can be configured as a broadcast interface. The OSPF network type also can be dependent on the ATM network configuration, whether or not the network is partially meshed or fully meshed.
•
Area ID—The predefined ID uniquely identifying the area to which the interface connects. It can be specified as either a decimal value or as an IP address. Value is 0.0.0.0 if interface is a layer 2 (no IP address assigned) interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Authentication Key—Password to be used by neighboring OSPF routers on a network segment that is using OSPF simple password authentication. It is ignored if OSPF Authentication Type is not "simple". This attribute is read-only.
•
Hello Interval—Length of time between the hello packets sent on an OSPF interface. Must be consistent between all routers on an attached network. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular network. In the event of a tie in this value, routers will use their router ID as a tie breaker. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Dead (sec)—Number of seconds that a device's hello packets must not have been seen before its neighbors declare the OSPF router down. Must be consistent among all routers on an attached network. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Delay (sec)—Estimated number of seconds it takes to send a link-state update packet this interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value also is used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets. This attribute is read-only.
EIGRP Area
The EIGRP area describes the EIGRP configuration of the interface on each active autonomous system. This area contains the following information:
•
EIGRP Interface Table—Lists the active EIGRP routing processes on the router. Each routing process handles routing updates for a single autonomous system. The routing process only is active if it is deployed on at least one network.
•
Hold Time (sec)—Hold time during which the device will wait for a hello packet to be received on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number. The hold time should be at least three times the hello interval.
•
Bandwidth Utilization (%)—Percentage of bandwidth that may be used by EIGRP on the interface. Values greater than 100 percent may be configured; this can be useful if the bandwidth is set artificially low for other reasons.
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
IS-IS Area
The IS-IS area contains the following information:
•
ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Area Tag—Identifies the IS-IS routing area that the interface participates in. If multiarea IS-IS is configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named; otherwise, this value may be an implicit null tag. This attribute is read-only.
•
Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1 routing. With smaller hello intervals, topological changes are detected faster, but there is more routing traffic.
•
Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
•
Level 1 Priority—Level 1 priority. The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or Designated Intermediate System (DIS). The router with the highest priority will become the DIS. In the case of equal priorities, the highest MAC address breaks the tie.
•
Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2 routing.
•
Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (inter-area) route calculation.
•
Level 2 Priority—Level 2 priority.
•
Enable button—Enables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
•
Disable button—Disables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
By default, all interfaces are configured as IS-IS Circuit-type Level 1-2.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-45 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-45 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the ATM T3 Interface.
C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
This dialog box describes a physical and logical enhanced ATM E3 interface of the PA-A3-E3 FlexWAN port adapter on the Catalyst 6000 family switches or Cisco 7600 series Internet Routers. This dialog box can be launched from the ATM port adapter or the ATM T3 interface object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple ATM E3 Interfaces, port adapters, FlexWAN modules, and chassis at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 5-46 shows the Status tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-46 Status Tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface dialog box provides the following information to describe the general characteristics of the interface:
•
Description—Comment or a description to help you remember what is attached to this interface. The description is only put in the configuration to help you remember what specific interfaces are used for.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Operational Status—The current operational state of the interface. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
testing—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
unknown
–
down
–
up
–
dormant—Interface is waiting for external actions (such as a serial line waiting for an incoming connection)
–
notPresent—Interface has missing (typically, hardware) components.
–
lowerLayerDown—The interface in the lower layer is down.
•
Administrative Status—The desired state of the interface. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
testing (read-only)—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
up
–
down
•
Last Change—The value (in seconds) of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state was entered prior to the last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value. This attribute is read-only.
•
Connector Present—Indication if a cable is connected to the interface. If the ifAdminStatus is down, then this value cannot be determined and an "unknown" message is given. This attribute is read-only. This attribute can have the following values:
–
yes—Cable is connected to the interface.
–
no—Cable is not connected to the interface.
–
unknown—Cannot determine if a cable is connected to the interface.
•
Number of Resets—Number of times the interface internally reset. This attribute is read-only.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface dialog box contains the buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the interface.
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to the user through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Configuration Tab
Figure 5-47 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-47 Configuration Tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
General Area
The General area contains the following information:
•
Link Up/Down Trap—Enables or disables linkUp and linkDown trap generation for the interface.
•
Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
Note
The Bandwidth attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF); you cannot adjust the actual bandwidth of an interface with this command.
•
Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
Note
The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP and EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with this command.
•
Input Queue Length—Input queue length in packets.
•
Output Queue Length—Output queue length in packets.
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area contains the following information:
•
MAC Address—Displays the MAC address of the interface.
•
MTU—The size of the largest packet which can be sent/received on the interface, specified in octets.
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area contains the following information:
•
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the layer 3 interface.
•
Netmask—Subnet mask of the interface IP address. Enabled bits indicate the network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Clear IP Address button— After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for this interface.
ATM/E3 Tab
Figure 5-48 shows the ATM/E3 tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-48 ATM/E3 Tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
ATM Area
The ATM area contains the following information:
•
NSAP Address—Unique identifier of node in ATM network. This address is required if not implemented by ATM CM.
•
End-Station ID—End-station ID of node in ATM network. The NSAP address prefix is provided by the switch to the router through ILMI. There must be a PVC configured for ILMI communication with the switch. This address is required if not implemented by ATM CM.
E3 Area
The E3 area contains the following information:
•
Clock Source—Source of the transmit clock.
–
loopTiming—Indicates that the recovered receive clock is used as the transmit clock.
–
localTiming—Indicates that a local clock source is used or that an external clock is attached to the box containing the interface.
•
E3 Framing—Describes E3 framing. The following values are possible:
–
g832adm
–
g751adm
–
g751plcp
•
E3 Scrambling—Indicates whether or not E3 scrambling is enabled on the interface. Scrambling assists recovery of the clock by the receiver.
Performance Tab
Figure 5-49 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface dialog box. All attributes shown in this tab are read-only.
Figure 5-49 Performance Tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
Interface Packets / Octets Statistics Area
The Interface Packets/Octets Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
In Unicast Pkts.—The number of packets, delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub-)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
Out Unicast Pkts.—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Interface Error Statistics Area
The Interface Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Number of input packets which had cyclic redundancy checksum errors.
•
In Discarded Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—The number of outbound packets which were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the output queue was full.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of input packets that were simply ignored by this interface.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of input packets that were aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
DX3 Current Area
The DX3 Current area contains the following information:
•
C-bit Errored Secs—C-bit errored seconds.
•
C-bit Severely Err Secs—C-bit severely errored seconds.
•
C-bit Coding Violations—C-bit coding violations.
•
P-bit Errored Secs—P-bit errored seconds.
•
P-bit Severely Err Secs—P-bit severely errored seconds.
•
P-bit Coding Violations—P-bit coding violations.
•
Line Errored Secs—Line errored seconds.
•
Line Coding Violations—Line coding violations
•
Unavail Secs—Unavailable seconds.
•
Severely Err Frm Secs—Severely errored framing seconds.
DX3 Far End Current Area
The DX3 Far End Current area contains the following information:
•
C-bit Errored Secs—Far end C-bit errored seconds.
•
C-bit Severely Err Secs—Far end C-bit severely errored seconds.
•
C-bit Coding Violations—Far end C-bit coding violations.
•
Elapsed Secs—Number of seconds that have elapsed since the beginning of the far end current error-measurement period.
•
Unavail Secs—Far end unavailable seconds.
Routing Protocol Tab
Figure 5-50 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-50 Routing Protocol Tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
OSPF Area
The OSPF area contains the following information:
•
OSPF Network Type—OSPF network type. ATM is a point-to-point service; by default it is considered to be nonbroadcast by the OSPF routing process. An ATM interface can, however, be configured as a broadcast interface. The OSPF network type can also be dependent on the ATM network configuration, whether the network is partially meshed or fully meshed.
•
Area ID—The predefined ID uniquely identifying the area to which the interface connects. It can be specified as either a decimal value or as an IP address. Value is 0.0.0.0 if interface is a layer 2 (no IP address assigned) interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Authentication Key—Password to be used by neighboring OSPF routers on a network segment that is using OSPF simple password authentication. This password is ignored if OSPF Authentication Type is not "simple". This attribute is read-only.
•
Hello Interval—Length of time between the hello packets sent on an OSPF interface. Must be consistent among all routers on an attached network. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular network. In the event of a tie in this value, routers will use their Router ID as a tie breaker. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Dead (sec)—Number of seconds that a device's hello packets must not have been seen before its neighbors declare the OSPF router down. Must be consistent among all routers on an attached network. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Delay (sec)—Estimated number of seconds it takes to send a link-state update packet this interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions, for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value is also used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets. This attribute is read-only.
EIGRP Area
The EIGRP area describes the EIGRP configuration of the interface on each active autonomous system. This area contains the following information:
•
EIGRP Interface Table—Lists the active EIGRP routing processes on the router. Each routing process handles routing updates for a single autonomous system. The routing process is only active if it is deployed on at least one network.
•
Hold Time (sec)—Hold time during which the device will wait for a hello packet to be received on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number. The hold time should be at least three times the hello interval.
•
Bandwidth Utilization (%)—Percentage of bandwidth that may be used by EIGRP on the interface. Values greater than 100 percent may be configured; this can be useful if the bandwidth is set artificially low for other reasons.
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
IS-IS Area
The IS-IS area contains the following information:
•
ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Area Tag—Identifies the IS-IS routing area that the interface participates in. If multiarea IS-IS is configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named; otherwise, this value may be an implicit null tag. This attribute is read-only.
•
Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1 routing. With smaller hello intervals, topological changes are detected faster, but there is more routing traffic.
•
Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
•
Level 1 Priority—Level 1 priority. The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or designated intermediate system (DIS). The router with the highest priority will become the DIS. In the case of equal priorities, the highest MAC address breaks the tie.
•
Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2 routing.
•
Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (inter-area) route calculation.
•
Level 2 Priority—Level 2 priority.
•
Enable button—Enable IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
•
Disable button—Disable IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
By default, all interfaces are configured as IS-IS Circuit-type Level 1-2.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-51 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-51 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M ATM E3 Interface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the ATM E3 Interface.
C6576M ATM SONET Interface Dialog Box
This dialog box describes a physical and logical enhanced ATM OC-3 interface of a FlexWAN port adapter on the Catalyst 6000 family switches or Cisco 7600 series Internet Routers. This dialog box can be launched from the ATM Port Adapter or ATM Sonet interface object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple ATM SONET interfaces, port adapters, FlexWAN modules, and chassis at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 5-52 shows the Status tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-52 Status Tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface dialog box provides the following information to describe the general characteristics of the interface:
•
Description—Comment or a description to help you remember what is attached to this interface. The description is only put in the configuration to help you remember what specific interfaces are used for.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Operational Status—The current operational state of the interface. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
testing—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
unknown
–
down
–
up
–
dormant—Interface is waiting for external actions (such as a serial line waiting for an incoming connection)
–
notPresent—Interface has missing (typically, hardware) components.
–
lowerLayerDown—The interface in the lower layer is down.
•
Administrative Status—The desired state of the interface. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
testing (read-only)—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
up
–
down
•
Last Change—The value (in seconds) of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state was entered before the last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value. This attribute is read-only.
•
Connector Present—Indication if a cable is connected to the interface. If the ifAdminStatus is down, then this value cannot be determined and an "unknown" message is given. This attribute is read-only. This attribute can have the following values:
–
yes—Cable is connected to the interface.
–
no—Cable is not connected to the interface.
–
unknown—Cannot determine if a cable is connected to the interface.
•
Number of Resets—Number of times the interface internally reset. This attribute is read-only.
ATM/SONET Area
The ATM/SONET area of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
SONET Section Status—Status of the SONET Section. This status may indicate multiple simultaneous defects. This has one of the following values:
–
sonetSectionNoDefect—No defect.
–
sonetSectionLOS—Error condition, Loss Of Signal.
–
sonetSectionLOF—Error condition, Loss Of Frame.
•
SONET Line Status—Status of the SONET Line. This status may indicate multiple simultaneous defects. This can have one of the following values:
–
sonetLineNoDefect—No defect.
–
sonetLineAIS—Line defect Alarm Indication Signal.
–
sonetLineRDI—Line defect Remote Defect Indication.
•
SONET Path Status—Status of the SONET Path. This status may indicate multiple simultaneous defects. This can have one of the following values:
–
sonetPathNoDefect—No defect.
–
sonetPathSTSLOP—STS-Path Loss of Pointer.
–
sonetPathSTSAIS—STS-Path Alarm Indication Signal.
–
sonetPathSTSRDI—STS-Path Remote Defect Indication.
–
sonetPathUnequipped—Unequipped.
–
sonetPathSignalLabelMismatch—Signal Label Mismatch.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M ATM T3 Interface dialog box contains buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the interface:
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field has the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Configuration Tab
Figure 5-53 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-53 Configuration Tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface Dialog Box
General Area
The General area contains the following information:
•
Link Up/Down Trap—Enables or disables linkUp and linkDown trap generation for the interface.
•
Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
Note
The Bandwidth attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF); you cannot adjust the actual bandwidth of an interface with this command.
•
Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
Note
The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP and EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with this command.
•
Input Queue Length—Input queue length in packets.
•
Output Queue Length—Output queue length in packets.
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area contains the following information:
•
MAC Address—Displays the MAC address of the interface.
•
MTU—The size of the largest packet which can be sent or received on the interface, specified in octets.
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area contains the following information:
•
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the Layer 3 interface.
•
Netmask—Subnet mask of the interface IP address. Enabled bits indicate the network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Clear IP Address button - After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for this interface.
ATM/Sonet Tab
Figure 5-54 shows the ATM/Sonet tab of the C6576M ATM/Sonet Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-54 ATM/Sonet Tab of the C6576M ATM /Sonet Interface Dialog Box
ATM/SONET Configuration Area
The ATM/SONET Configuration area contains the following information:
•
Clock Source—Source of the transmit clock.
–
loopTiming—Indicates that the recovered receive clock is used as the transmit clock.
–
localTiming—Indicates that a local clock source is used or that an external clock is attached to the box containing the interface.
•
SONET Framing—SONET framing for ATM cell transmission. The following values are possible:
–
sts-3c—Synchronous Transport Signal level 3 concatenated is the SONET (N. American) format that specifies the frame structure for a 155.52-Mbps line.
–
stm-1—Synchronous Transport Module level 1 is the SDH (European) format that specifies the frame structure for a 155.52-Mbps line.
•
NSAP Address—Unique identifier of node in ATM network. Required if not implemented by ATM CM.
•
End-Station ID—End-station ID of node in ATM network. The NSAP address prefix is provided by the switch to the router through ILMI. There must be a PVC configured for ILMI communication with the switch. Required if not implemented by ATM CM.
•
SONET Path Width—Width of the SONET path. This attribute is read-only. This is described by the STS-Nc SPE.
–
STS-3c/STM-1—For OC-3 signal (155.52 Mbps).
–
STS-12c/STM-4—For OC-12 signal (622.08 Mbps).
SONET Medium Configuration Area
The SONET Medium Configuration area contains the following information. All attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Type—Indicates whether or not a SONET or SDH signal is used on the interface.
•
Line Type—Line type of the interface. The following values are possible:
–
sonetShortSingleMode
–
sonetLongSingleMode
–
sonetMultiMode
•
Line Coding—Line coding for the interface:
–
sonetMediumB3ZS—For electrical SONET/SDH signals (STS-1 and STS-3).
–
sonetMediumCMI—For electrical SONET/SDH signals (STS-1 and STS-3).
–
sonetMediumNRZ—Non-return to Zero, which is used for optical SONET/SDH signals.
–
sonetMediumRZ—Return to Zero, which is used for optical SONET/SDH signals.
–
sonetMediumOther—Other.
Performance Tab
Figure 5-55 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface dialog box. All attributes in this area are read-only.
Figure 5-55 Performance Tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface Dialog Box
Interface Packets/Octets Statistics Area
The Interface Packets/Octets Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
In Unicast Pkts.—The number of packets delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
Out Unicast Pkts.—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Interface Error Statistics Area
The Interface Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum errors.
•
In Discarded Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—The number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent them from being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the output queue was full.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of input packets which were ignored by this interface.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of input packets that were aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
SONET Section Error Statistics Area
The SONET Section Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of errored seconds encountered by the SONET Section in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET Section in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of coding violations encountered by the SONET Section in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Frm Secs—Number of severely errored framing seconds encountered by the SONET Section in the current 15-minute interval.
SONET Line Error Statistics Area
The SONET Line Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of errored seconds encountered by the SONET Line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET Line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of coding violations encountered by the SONET Line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET Line in the current 15-minute interval.
SONET Far End Line Error Statistics Area
The SONET Far End Line Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of far end errored seconds encountered by the SONET Line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely far end errored seconds encountered by the SONET Line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of far end coding violations encountered by the SONET Line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of far end unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET Line in the current 15-minute interval.
SONET Path Error Statistics Area
The SONET Path Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of coding violations encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
SONET Far End Path Error Statistics Area
The SONET Far End Path Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of far end errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of far end severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of far end coding violations encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of far end unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
Routing Protocol Tab
Figure 5-56 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-56 Routing Protocol Tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface Dialog Box
OSPF Area
The OSPF area contains the following information:
•
OSPF Network Type—OSPF network type. ATM is a point-to-point service; by default it is considered to be nonbroadcast by the OSPF routing process. An ATM interface can be configured as a broadcast interface. The OSPF network type also can be dependent on the ATM network configuration, whether the network is partially meshed or fully meshed.
•
Area ID—The predefined ID uniquely identifying the area to which the interface connects. It can be specified as either a decimal value or as an IP address. Value is 0.0.0.0 if interface is a layer 2 (no IP address assigned) interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Authentication Key—Password to be used by neighboring OSPF routers on a network segment that is using OSPF simple password authentication. It is ignored if OSPF Authentication Type is not "simple". This attribute is read-only.
•
Hello Interval—Length of time between the hello packets sent on an OSPF interface. Must be consistent between all routers on an attached network. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular network. In the event of a tie in this value, routers will use their router ID as a tie breaker. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Dead (sec)—Number of seconds that a device's hello packets must not have been seen before its neighbors declare the OSPF router down. Must be consistent among all routers on an attached network. This attribute is read-only.
•
Trans. Delay (sec)—Estimated number of seconds it takes to send a link-state update packet this interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value also is used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets. This attribute is read-only.
EIGRP Area
The EIGRP area describes the EIGRP configuration of the interface on each active autonomous system. This area contains the following information:
•
EIGRP Interface Table—Lists the active EIGRP routing processes on the router. Each routing process handles routing updates for a single autonomous system. The routing process only is active if it is deployed on at least one network.
•
Hold Time (sec)—Hold time during which the device will wait for a hello packet to be received on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number. The hold time should be at least three times the hello interval.
•
Bandwidth Utilization (%)—Percentage of bandwidth that may be used by EIGRP on the interface. Values greater than 100 percent may be configured; this can be useful if the bandwidth is set artificially low for other reasons
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
IS-IS Area
The IS-IS area contains the following information:
•
ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Area Tag—Identifies the IS-IS routing area that the interface participates in. If multiyear IS-IS is configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named; otherwise, this value may be an implicit null tag. This attribute is read-only.
•
Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1 routing. With smaller hello intervals, topological changes are detected faster, but there is more routing traffic.
•
Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
•
Level 1 Priority—Level 1 priority. The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or designated intermediate system (DIS). The router with the highest priority will become the DIS. In the case of equal priorities, the highest MAC address breaks the tie.
•
Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2 routing.
•
Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (interarea) route calculation.
•
Level 2 Priority—Level 2 priority.
•
Enable button—Enables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
•
Disable button—Disables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
By default, all interfaces are configured as IS-IS Circuit-type Level 1-2.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-57 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-57 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M ATM SONET Interface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the ATM SONET Interface.
C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
This dialog box describes a physical and logical Gigabit Ethernet WAN (GE-WAN) interface on the OSM-4GE-WAN-GBIC module. This dialog box can be launched from the OSM object or OSM GE-WAN Interface object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple OSM GE-WAN Interfaces, OSMs, and chassis at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 5-58 shows the Status tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-58 Status Tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box provides the following information to describe the general characteristics of the interface:
•
Description—Comment or a description to help you remember what is attached to this interface. The description is only put in the configuration to help you remember what specific interfaces are used for.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Type—Describes the physical interface type. This attribute is read-only.
•
Operational Status—The current operational state of the interface. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
other
–
ok
–
minorFault
–
majorFault
•
Administrative Status—The desired state of the interface. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
testing (read-only)—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
up
–
down
•
Last Change—The value (in seconds) of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state was entered before the last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value. This attribute is read-only.
•
Connector Present—Indication if a cable is connected to the interface. If the ifAdminStatus is down, then this value cannot be determined and an "unknown" message is given. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has the following values:
–
yes—Cable is connected to the interface.
–
no—Cable is not connected to the interface.
–
unknown—Cannot determine if a cable is connected to the interface.
•
Number of Resets—Number of times the interface internally reset. This attribute is read-only.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field has the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Configuration Tab
Figure 5-59 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-59 Configuration Tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
General Area
The General area of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
Speed—The desired speed of this port in bits per second. This attribute should have this value:
–
1 Gb/s
Note
If an unsupported speed is selected, an error is reported.
•
Duplex—Displays the duplex mode for the port. This attribute should have this value:
–
full-duplex
•
Input Queue Length—Displays the input queue length in packets.
•
Output Queue Length—Displays the output queue length in packets.
•
Link Up/Down Trap—Indicates if link up or link down traps are being generated. This list contains the following values:
–
enabled
–
disabled
•
Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
Note
The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP and EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with this command.
•
Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
Note
The Bandwidth attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF); you cannot adjust the actual bandwidth of an interface with this command.
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
MAC Address—Displays the MAC address of the interface.
•
MTU—The size, specified in octets, of the largest datagram (frame) that can be sent on the interface.
Note
A GE interface that is using a nondefault MTU cannot be added to an EtherChannel with GE interfaces using the default MTU. If the interface MTU is changed for one interface, the change is applied to all interfaces (GE and GE EtherChannel) using a nondefault MTU.
Note
IOS 12.1(8a)E5 caveat: Jumbo frame support is incompatible with the IS-IS routing protocol. Leave the MTU size at the default value on any interface where IS-IS provides routing.
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the layer 3 interface.
•
Netmask—Subnet mask of the interface IP address. Enabled bits indicate the network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Clear IP Address button—After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for this interface.
Performance Tab
Figure 5-60 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box. All attributes in this area are read-only.
Figure 5-60 Performance Tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
Packets/Octets Statistics Area
The Interface Packets/Octets Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
In Unicast Pkts.—The number of packets, delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub-)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
Out Unicast Pkts.—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Error Statistics Area
The Interface Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum errors.
•
In Discarded Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being delivered to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—The number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the output queue was full.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of input packets that were ignored by this interface.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of input packets that were aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box contains buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the interface:
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Routing Protocol Tab
Figure 5-61 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M OSM GEWAN Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-61 Routing Protocol Tab on the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
OSPF Area
The OSPF area of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box provides the following information. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Network Type—OSPF interface type. OSPF network type can be nonbroadcast multiaddress (NBMA) even on a broadcast media such as Ethernet. This attribute can have one of the following values:
–
broadcast
–
nbma
–
pointToPoint
–
pointToMultipoint
•
Area ID—The predefined ID uniquely identifying the area to which the interface connects. It can be specified as either a decimal value or as an IP address. Value is 0.0.0.0 if interface is a layer 2 (no IP address assigned) interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Authentication Key—Password to be used by neighboring OSPF routers on a network segment that is using OSPF simple password authentication. It is ignored if Authentication Type is not "simple".
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value is also used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets.
•
Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular network. If more than one router has the same value for this field, the routers use their router ID as a tie breaker.
•
Trans. Dead (sec)—Number of seconds that a device's hello packets must not have been seen before its neighbors declare the OSPF router down. Must be consistent among all routers on an attached network.
•
Trans. Delay (sec)—The estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link-state update packet over this interface.
EIGRP Area
The EIGRP Area of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
EIGRP Interface Table—Describes the EIGRP configuration of the interface on each active autonomous system. The EIGRP parameters of the interface on an autonomous system may be explicitly configured even if EIGRP routing updates in the autonomous system are not currently carried on the interface.
•
Bandwidth Utilization (%) —The percentage of the interface bandwidth that the EIGRP protocol can use.
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Hold Time (sec)—Hold time during which the device will wait for a hello packet to be received on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number. The hold time should be at least three times the hello interval.
ISIS Area
The ISIS area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface. This attribute is read-only.
–
true—ISIS routing is enabled.
–
false—ISIS routing is disabled.
•
Area Tag—The IS-IS routing area in which the interface participates. If multiarea IS-IS is configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named; otherwise, this value may be an implicit null tag. This attribute is read-only.
•
Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1 routing.
•
Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2 routing.
•
Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
•
Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (inter-area) route calculation.
•
Level 1 Priority—The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or designated intermediate system (DIS).
•
Level 2 Priority—The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or DIS.
•
Enable button—Enable IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
•
Disable button—Disable IS-IS routing on the interface.
HSRP Tab
Figure 5-62 shows the HSRP tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box. The attributes in this tab are read-only. To modify the attributes, click the Modify button.
Figure 5-62 HSRP Tab on the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
•
Modify button—Figure 5-63 shows the subdialog box that is displayed when you click the Modify button. This subdialog box is used to modify the following C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface attributes of a given HSRP group:
–
Secondary IP
–
Virtual IP
–
Preempt
–
Delay Minimum
–
Priority
–
Hello Interval
–
Hold Interval
Figure 5-63 HSRP Secondary IP Modify Subdialog Box
HSRP Area
The HSRP area of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
HSRP Group Table—Describes HSRP groups deployed on an interface.
Note
There may be multiple groups deployed on an interface. Using a group number on one logical or physical interface does not preclude using it on another.
•
Virtual IP—Primary virtual IP address of the HSRP group. If this address is not configured, the agent attempts to discover the virtual address through a discovery process which scans the hello messages.
•
Preempt—If enabled, the current router attempts to overthrow a lower priority active router and attempts to become the active router. If disabled, this router becomes the active router only if there is no such router or the active router fails.
–
true—Preempt enabled.
–
false—Preempt disabled.
•
Delay Minimum—Time difference (in seconds) between a router power up and the time it can start preempting the currently active router. This value is only applicable when preemption is enabled.
•
Priority—Metric used to select the active and standby routers. 0 is lowest priority, 255 is highest. Router with highest priority is selected to be the active router.
•
Hello Interval—Hello interval in milliseconds. If this value is not configured, it can be learned from the active router.
•
Hold Interval—Hold interval in milliseconds. If this value is not configured, it can be learned from the active router.
•
Configure button—Enables HSRP for IP on an interface. Figure 5-64 shows the subdialog box displayed when you click the Configure button. The following is displayed in the subdialog box:
–
Group Number—Unique identifier of an HSRP group.
–
IP Address—The HSRP group may optionally be assigned a primary IP address. If no address is explicitly assigned, the device attempts to discover the virtual IP address from the active server using hello messages.
–
Add button—Adds an HSRP group on the interface.
–
Remove button—Removes an HSRP group on the interface.
Figure 5-64 HSRP Group Configure Subdialog Box
Secondary IP Area
The Secondary IP area of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
HSRP Secondary Address Table—Describes secondary IP addresses of HSRP groups deployed on the interface. Data is displayed in the following columns:
–
Group Number—Unique identifier of an HSRP group.
–
Secondary IP—Secondary IP address of HSRP group.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-65 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-65 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M OSM GE-WAN Interface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the OSM GE-WAN Interface.
C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface Dialog Box
This dialog box describes a physical and logical channelized OC-12 (Ch-OC12) or OC-48 (Ch-OC48) SONET interface on an OSM. This dialog box can be launched from the OSM Channelized SONET Module or Interface object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple OSM Channelized SONET Interfaces, OSMs, and chassis at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 5-66 shows the Status tab of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-66 Status Tab of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface dialog box provides the following information to describe the general characteristics of the interface.
•
Description—Comment or a description to help you remember what is attached to this interface. The description is only put in the configuration to help you remember what specific interfaces are used for.
•
Type—Describes the type of allocated channel. This attribute is read-only.
–
t3—A DS3 channel is provisioned as a serial subinterface with T3 (DS3) content formatting.
–
e3—A DS3 channel is provisioned as a serial subinterface with E3 (DS3) content formatting.
–
pos—An OC-3 channel is provisioned as a POS subinterface.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Operational Status—The current operational state of the interface. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
testing—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
unknown
–
down
–
up
–
dormant—Interface is waiting for external actions (such as a serial line waiting for an incoming connection)
–
notPresent—Interface has missing (typically, hardware) components.
–
lowerLayerDown—The interface in the lower layer is down.
•
Administrative Status—The desired state of the interface. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
up
–
down
•
Last Change—The value (in seconds) of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state was entered before the last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value. This attribute is read-only.
•
Connector Present—Indicates whether or not a cable is connected to the interface. If the ifAdminStatus is down, then this value cannot be determined and an "unknown" message is given. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has the following values:
–
yes—Cable is connected to the interface.
–
no—Cable is not connected to the interface.
–
unknown—Cannot determine if a cable is connected to the interface.
•
Number of Resets—Number of times the interface internally reset. This attribute is read-only.
SONET Status Area
The ATM/SONET area of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
SONET Section Status—Status of the SONET Section. This status may indicate multiple simultaneous defects. This attribute is read-only. This can have one of the following values:
–
sonetSectionNoDefect—No defect.
–
sonetSectionLOS—Error condition, Loss Of Signal.
–
sonetSectionLOF—Error condition, Loss Of Frame.
•
SONET Line Status—Status of the SONET Line. This status may indicate multiple simultaneous defects. This attribute is read-only. This can have one of the following values:
–
sonetLineNoDefect—No defect.
–
sonetLineAIS—Line defect Alarm Indication Signal.
–
sonetLineRDI—Line defect Remote Defect Indication.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface dialog box contains buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the interface:
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Configuration Tab
Figure 5-67 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-67 Configuration Tab of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface Dialog Box
General Area
The General area contains the following information:
•
Speed—The desired speed of the port in bits per second.
•
Duplex—SONET interfaces are by definition full duplex.
•
Link Up/Down Trap—Enables or disables linkUp and linkDown trap generation for the interface.
SONET Area
The SONET area contains the following information:
•
Description—Description of the SONET interface.
•
Clock Source—Source of the transmit clock.
–
loopTiming—Indicates that the recovered receive clock is used as the transmit clock.
–
loopTimingPrimary—Indicates that loop timing is used and the SONET controller provides the first priority clock for internal circuitry.
–
loopTimingSecondary—Indicates that loop timing is used and the SONET controller provides the clock if the primary clock source fails.
–
Primary—Indicates that the SONET controller provides the first priority clock for internal circuitry. Secondary indicates that the SONET controller provides the clock if the primary clock source fails.
–
localTiming—Indicates that the transmit clock source is generated internally.
–
localTimingPrimary—Indicates that local timing is used and the SONET controller provides the first priority clock for internal circuitry.
–
localTimingSecondary—Indicates that local timing is used and the SONET controller provides the clock if the primary clock source fails.
•
Loopback Mode—Indicates whether or not SONET loopback mode is enabled. The possible values are:
–
None—Indicates that the loopback is disabled.
–
Internal—Indicates data is looped from the transmit path to the receive path allowing diagnostics to send data to itself without relying on any external connections. To enable internal loopback, you must first set the clock source to internal.
–
Line—(external) Indicates data is looped from the external port to the transmit port and back out the external port.
•
Framing—Framing for optical digital transmission.
Note
SDH framing is currently unsupported on the channelized SONET modules even though IOS CLI allows the interface to be configured for SDH framing.
SONET Medium Area
The SONET Medium area contains the following information. All attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Type—Indicates whether a SONET or SDH signal is used on the interface.
•
Line Type—Line type of the interface. The following values are possible:
–
sonetShortSingleMode
–
sonetLongSingleMode
–
sonetMultiMode
•
Line Coding—Line coding for the interface.
–
sonetMediumB3ZS—For electrical SONET/SDH signals (STS-1 and STS-3).
–
sonetMediumCMI—For electrical SONET/SDH signals (STS-1 and STS-3).
–
sonetMediumNRZ—Non-return to zero, which is used for optical SONET/SDH signals.
–
sonetMediumRZ—Return to zero, which is used for optical SONET/SDH signals.
–
sonetMediumOther—Other.
DS-3/OC-3 Channel Table Area
•
DS-3/OC-3 Channel Table—Lists the DS3 and OC-3 channels that have been provisioned on the SONET interface. The following items are listed in the table:
–
ID—Unique identifier of a channel on the SONET interface. This coincides with the number of the first sts-1 service payload envelope (SPE) allocated in the channel. It is also the subinterface number of the serial or POS interface representing the DS3 or OC-3 channel. Numbering is 1-based.
–
Range—Range of allocated channels. Numbering is 1-based. A DS3 subinterface has a width of sts-1 and it occupies a single channel. An OC-3 subinterface has a width of sts-3c and it occupies three consecutive channels.
–
Type—Describes the type of allocated channel. A DS3 channel is provisioned as a serial subinterface with E3 or T3 (DS3) content formatting. An OC-3 channel is provisioned as a POS subinterface.
•
Provision Channels for Serial/PoS Interface button—Launches a subdialog box to provision a DS3 or OC-3 channel from the SONET interface's constituent sts-1 service payload envelopes (SPEs). Figure 5-68 shows the Channel Provision subdialog box of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface dialog box. The following items are displayed:
–
Channel ID field—Unique identifier of a channel on the SONET interface.
–
Channel Type field—Describes the type of allocated channel.
–
Free Channel button—Frees a provisioned DS3 or OC-3 channel from the SONET interface.
–
Provision Channel button—Provisions the interface.
Note
The provisioned sts-1 SPEs cannot be in use by any other channel on the interface.
Figure 5-68 Channel Provision Subdialog Box of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface Dialog Box
Performance Tab
Figure 5-69 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-69 Performance Tab of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface Dialog Box
Interface Packets/ Octets Statistics Area
The Interface Packets/Octets Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
In Unicast Pkts.—The number of packets delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
Out Unicast Pkts.—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Interface Error Statistics Area
The Interface Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum errors.
•
In Discarded Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—The number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because osteopath queue was full.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of input packets that were ignored by this interface.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of input packets that were aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
SONET Section Error Statistics Area
The SONET Section Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of errored seconds encountered by the SONET section in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET section in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of coding violations encountered by the SONET section in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Frm Secs—Number of severely errored framing seconds encountered by the SONET section in the current 15-minute interval.
SONET Line Error Statistics Area
The SONET Line Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of errored seconds encountered by the SONET line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of coding violations encountered by the SONET line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET line in the current 15-minute interval.
SONET Far End Line Error Statistics Area
The SONET Far End Line Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of far end errored seconds encountered by the SONET line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely far end errored seconds encountered by the SONET line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of far end coding violations encountered by the SONET line in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of far end unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET line in the current 15-minute interval.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-70 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-70 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M OSM Channelized SONET Interface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the OSM Channelized SONET Interface.
C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
This dialog box describes a physical and logical PoS interface on an OSM. This dialog box can be launched from the OSM POS Module or Interface object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple OSM POS Interfaces, OSMs, and chassis at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 5-71 shows the Status tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-71 Status Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box provides the following information to describe the general characteristics of the interface:
•
Description—Comment or a description to help you remember what is attached to this interface. The description is only put in the configuration to help you remember what specific interfaces are used for.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Type—Describes the physical interface type. This attribute is read-only. The possible values of this attribute are:
–
posOc12mm
–
posOc12smi
–
posOc12sml
–
posOc48mm
–
posOc48smi
–
posOc48sml
–
posOc3mm
–
posOc3smi
–
posOc3sml
•
Operational Status—The current operational state of the interface. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
other
–
ok
–
minorFault
–
majorFault
•
Administrative Status—The desired state of the interface. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
up
–
down
•
Last Change—The value (in seconds) of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state was entered before the last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value. This attribute is read-only.
•
Connector Present—Indicates whether or not a cable is connected to the interface. If the ifAdminStatus is down, then this value cannot be determined and an "unknown" message is given. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has the following values:
–
yes—Cable is connected to the interface.
–
no—Cable is not connected to the interface.
–
unknown—Cannot determine if a cable is connected to the interface.
•
Number of Resets—Number of times the interface internally reset. This attribute is read-only.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Configuration Tab
Figure 5-72 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-72 Configuration Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
General Area
The General area contains the following information:
•
Speed—The desired speed of the port in bits per second.
•
Duplex—SONET interfaces are by definition full duplex.
•
Link Up / Down Trap—Enables or disables linkUp and linkDown trap generation for the interface.
•
Input Queue Length—Displays the input queue length in packets.
•
Output Queue Length—Displays the output queue length in packets.
•
Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
Note
The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP and EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with this command.
•
Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
Note
The Bandwidth attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF); you cannot adjust the actual bandwidth of an interface with this command.
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area contains the following information:
•
MTU—The size of the largest datagram (frame) which can be sent or received on the interface, specified in octets.
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area contains the following information:
•
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the layer 3 interface.
•
Netmask—Subnet mask of the IP address. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Clear IP Address button—After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for this interface.
ATM/SONET Tab
Figure 5-73 shows the ATM/SONET tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-73 ATM/SONET Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
ATM Area
The ATM area contains the following information:
•
CRC—Cyclical redundancy check (CRC) word size. The CRC is an error-checking technique that uses a calculated numeric value to detect errors in transmitted data.
•
Encapsulation—Indicates whether HDLC or PPP encapsulation is used on the interface.
•
Framing—Framing for optical digital transmission. SONET is the North American standard, SDH is the European standard.
•
Payload Scrambling—Indicates whether or not SONET payload scrambling is enabled on the interface. Payload scrambling ensures that there is sufficient bit-transition density to maintain the transmit clock for synchronous signalling. Both ends of the connection must use the same scrambling algorithm.
•
Transmit Clock Source—Source of the transmit clock.
–
loopTiming—Indicates that the recovered receive clock is used as the transmit clock.
–
localTiming—Indicates that the transmit clock source is generated internally.
SONET Area
The SONET area contains the following information:
•
SONET Overhead J0 Byte—Value of the SONET overhead section trace byte. A value of 0x10 is for interoperability with some Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) devices in Japan. This attribute is read-only.
•
SONET Overhead C2 Byte—Value of the SONET overhead path signal identifier. This attribute is read-only. These are possible values:
–
0xCF = PPP or HDLC
–
0x13 = ATM
•
SONET Overhead S1 S0 Bits—Value of the SONET overhead S1 & S0 bits. These bits are part of the payload pointer byte. This attribute is read-only. These are possible values:
–
0 = OC-3c
–
2 = AU-4
Performance Tab
Figure 5-74 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box. All the attributes in this tab are read-only.
Figure 5-74 Performance Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
Packets/Octets Statistics Area
The Packets/Octets Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
In Unicast Pkts.—The number of packets delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
Out Unicast Pkts.—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Error Statistics Area
The Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum errors.
•
In Discarded Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—The number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet is to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the output queue was full.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of input packets that were ignored by this interface.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of input packets that were aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box contains buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the interface:
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
Routing Protocol Tab
Figure 5-75 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-75 Routing Protocol Tab on the C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
OSPF Area
The OSPF area of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box provides the following information. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Network Type—OSPF interface type. By default, a POS interface is point-to-point, however, the OSPF network type may be modified to accommodate different types of network configurations. This attribute can have one of the following values:
–
broadcast
–
nbma
–
pointToPoint
–
pointToMultipoint
•
Admin Status—The desired state of the interface.
•
Area ID—The predefined ID uniquely identifying the area to which the interface connects. It can be specified as either a decimal value or as an IP address. Value is 0.0.0.0 if interface is a layer 2 (no IP address assigned) interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Authentication Key—Password to be used by neighboring OSPF routers on a network segment that is using OSPF simple password authentication. It is ignored if Authentication Type is not "simple".
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Polling Interval—Polling interval in seconds.
•
Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular network. If more than one router has the same value for this field, the routers use their router ID as a tie breaker.
•
Trans. Dead (sec)—Number of seconds that a device's hello packets must not have been seen before its neighbors declare the OSPF router down. Must be consistent among all routers on an attached network.
•
Trans. Delay (sec)—The estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state update packet over this interface.
•
Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value is also used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets.
EIGRP Area
The EIGRP Area of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
EIGRP Interface Table—Describes the EIGRP configuration of the interface on each active autonomous system. The EIGRP parameters of the interface on an autonomous system may be explicitly configured even if EIGRP routing updates in the autonomous system are not currently carried on the interface.
•
Bandwidth Utilization (%) —The percentage of the interface bandwidth that the EIGRP protocol can use.
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Hold Time (sec)—Hold time during which the device will wait for a hello packet to be received on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number. The hold time should be at least three times the hello interval.
ISIS Area
The ISIS area of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface:
–
true—ISIS routing is enabled.
–
false—ISIS routing is disabled.
•
Area Tag—The IS-IS routing area in which the interface participates. If multiarea IS-IS is configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named; otherwise, this value may be an implicit null tag.
•
Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1 routing.
•
Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2 routing.
•
Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
•
Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (inter-area) route calculation.
•
Level 1 Priority—Determines which router on a LAN will be the designated router or Designated Intermediate System (DIS).
•
Level 2 Priority—Determines which router on a LAN will be the designated router or Designated Intermediate System (DIS).
•
Enable button—Enables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
•
Disable button—Disables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
By default, all interfaces are configured as IS-IS Circuit-type Level 1-2.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-76 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box.
Figure 5-76 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Interface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the OSM POS Interface.
C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
This dialog box describes a logical DS3 channel on a channelized OC-12 (ChOC-12) or OC-48 (ChOC-48) SONET interface of an Optical Service Module (OSM). A DS3 channel of a SONET interface is provisioned as a logical Serial interface. This dialog box can be launched from the OSM Channelized SONET Module or Interface object or the Serial Subinterface object within the Physical view.
You can select multiple OSM serial subinterfaces, OSM Channelized SONET interfaces, OSMs, and chassis at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Note
E3 serial subinterfaces can be configured through the CLI, but the OSM Channelized SONET cards do not support SDH (E3) content formatting. The EMS will discover these interfaces but does not support any operations against them.
Status Tab
Figure 5-77 shows the Status tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-77 Status Tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box provides the following information to describe the general characteristics of the interface:
•
Description—Comment or a description to help you remember what is attached to this interface. The description is put in the configuration to help you remember what specific interfaces are used for.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Operational Status—The current operational state of the interface. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
unknown
–
down
–
up
–
dormant—Interface is waiting for external actions (such as a serial line waiting for an incoming connection)
–
notPresent—Interface has missing components (typically hardware).
–
lowerLayerDown—Indicates that the primary channelized SONET interface has failed.
•
Administrative Status—The desired state of the interface. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
up
–
down
•
Number of Resets—Number of times the interface internally reset. This attribute is read-only.
•
Connector Present—Displays if a cable is attached to the parent interface (the OSM Channelized SONET Interface). These are the values:
–
yes
–
no
–
unknown—This value is used when the Administrative Status is not set to "up". In this case, it cannot be determined if a connection is present or not.
•
Last Change—The value (in seconds) of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state was entered before the last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value. This attribute is read-only.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field has the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Interface Configuration Tab
Figure 5-78 shows the Interface Configuration tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-78 Interface Configuration Tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
General Area
The General area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
Note
The Bandwidth attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF); you cannot adjust the actual bandwidth of an interface with this command.
•
Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
Note
The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP and EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with this command.
•
Input Queue Length—Displays the input queue length in packets.
•
Output Queue Length—Displays the output queue length in packets.
•
Link Up / Down Trap—Enables or disables linkUp and linkDown trap generation for the interface.
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area contains the following information:
•
MTU—The size of the largest datagram (frame) which can be sent or received on the interface, specified in octets.
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area contains the following information:
•
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the Layer 3 interface.
•
Netmask—Subnet mask of the IP address. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Clear IP Address button—After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for this interface.
DS-3 Configuration Tab
Figure 5-79 shows the DS-3 Configuration tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-79 DS-3 Configuration Tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
DS-3 Serial Interface Area
The DS-3 Serial Interface area contains the following information:
•
Framing—Framing for optical digital transmission. SONET is the North American standard; SDH is the European standard.
•
CRC—Cyclical redundancy check (CRC) word size. The CRC is an error-checking technique that uses a calculated numeric value to detect errors in transmitted data.
•
DSU Mode—Data Service Unit (DSU) mode. This enables interoperability with other DSUs. The local interface configuration must match the remote configuration. This attribute can have the following values:
–
adtran
–
cisco
–
digital-link
–
larscom
–
verilink
–
kentrox (6)
Note
The Kentrox DSU/CSU mode is configurable in the CLI but is currently not supported. The C6576M EMS will allow a user to configure this value, but it will log a warning message indicating that the value is unsupported by IOS.
•
Near End Loopback Mode—Near end channel loopback mode. This mode can have the following values:
–
disabled
–
local—Sets the loopback after going through the framer toward the terminal.
–
network—Puts the near end in network loopback.
•
Far End Loopback Mode—Far end channel loopback mode. If enabled, this mode puts the far end in loopback by sending far-end alarm control (FEAC). This mode has the following values:
–
disabled
–
remote
•
Payload Scrambling—Indicates whether or not SONET payload scrambling is enabled on the interface. Payload scrambling ensures that there is sufficient bit-transition density to maintain the transmit clock for synchronous signalling. Both ends of the connection must use the same scrambling algorithm.
•
Encapsulation—Indicates whether HDLC or PPP encapsulation is used on the interface.
•
DSU Bandwidth—DSU subrate bandwidth in kilobits per second. This attribute reduces the DS3 bandwidth by padding the T3 frame.
SONET Path Header (C2) Area
The SONET Path Header (C2) area contains the following information:
•
SONET Overhead C2 Byte—Value of the SONET overhead Path Signal Label (C2), which indicates the contents of the SONET STS-SPE Higher Order VC. This attribute is read-only. These are possible values:
–
207 (0xCF) = PPP or HDLC with no payload scrambling
–
22 (0x16) = PPP or HDLC with payload scrambling
SONET Path Header (J1) Area
The SONET Path Header (J1) area contains the following information:
•
Expected Size—Maximum length of the expected receive SONET Path overhead message in bytes.
•
Transmit Size—Maximum length of the transmitting SONET Path overhead message in bytes.
•
Expected Label—The expected receive SONET Path overhead message. If the expected label is longer than the expected size, it will be truncated.
•
Transmit Label—Transmitting SONET Path overhead message. If the transmitting label is longer than the transmitting size, it will be truncated.
•
Modify SONET Path Header (J1) button—Launches a subdialog box to modify the expected receive and transmit SONET Path overhead message. Figure 5-80 shows the subdialog box launched by this button. The following items are displayed in the subdialog box:
–
Expected Size
–
Transmit Size
–
Expected Label
–
Transmit Label
–
Modify button—Sets the specified values of the attributes given in the subdialog box.
Note
In 12.1(11b)E and later the values for the Expected Size and the Transmit Size should be the same since the Tx and Rx message sizes cannot be independently configured. If the received values are different, the J1 Path Overhead message size will be set to the larger of the two values.
Figure 5-80 SONET J1 Modify Subdialog Box of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
Performance Tab
Figure 5-81 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box. All the attributes shown in this tab are read-only.
Figure 5-81 Interface Performance Tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
Interface Packets/Octets Statistics Area
The Interface Packets/Octets Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
In Unicast Pkts.—The number of packets delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
Out Unicast Pkts.—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and that were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Interface Error Statistics Area
The Interface Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum errors.
•
In Discarded Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—The number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the output queue was full.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of input packets that were ignored by this interface.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of input packets that were aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being delivered to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box contains these buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the interface:
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
DS-3 Statistics Tab
Figure 5-82 shows the DS-3 Statistics tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-82 DS-3 Statistics Tab on the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
DS-3 Error Area
The DS-3 Error area contains the following information:
•
C-bit Errored Secs—C-bit errored seconds.
•
C-bit Severely Err Secs—C-bit severely errored seconds.
•
C-bit Coding Violations—C-bit coding violations.
•
P-bit Errored Secs—P-bit errored seconds.
•
P-bit Severely Err Secs—P-bit severely errored seconds.
•
P-bit Coding Violations—P-bit coding violations.
•
Line Errored Secs—Line errored seconds.
•
Line Coding Violations—Line coding violations.
•
Unavail Secs—Unavailable seconds.
•
Severely Err Frm Secs—Severely errored framing seconds.
DS-3 Far End Error Area
The DS-3 Far End Error area contains the following information:
•
C-bit Errored Secs—Far end C-bit errored seconds.
•
C-bit Severely Err Secs—Far end C-bit severely errored seconds.
•
C-bit Coding Violations—Far end C-bit coding violations.
•
Elapsed Secs—Number of seconds that have elapsed since the beginning of the far end current error-measurement period.
•
Unavail Secs—Far end unavailable seconds.
SONET Path Error Area
The SONET Path Error area contains the following information:
•
SONET Path Status—Status of the SONET Path. This status may indicate multiple simultaneous defects. There are possible Path defects:
–
STS-Path Loss of Pointer
–
STS-Path Alarm Indication Signal
–
STS-Path Remote Defect Indication
–
Unequipped
–
Signal Label Mismatch
•
SONET Path Width—Width of the SONET path. This is described by the STS-Nc SPE. A DS3 channel has a width of STS-1 (55.84 Mbps).
•
Errored Secs—Number of errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of coding violations encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
SONET Far End Path Error Area
The SONET Far End Path Error area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of far end errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of far end severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of far end coding violations encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of far end unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
Routing Protocol Tab
Figure 5-83 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-83 Routing Protocol Tab on the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
OSPF Area
The OSPF area of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box provides the following information. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Network Type—OSPF interface type. By default, a POS interface is point-to-point, however, the OSPF network type may be modified to accommodate different types of network configurations. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
broadcast
–
nbma
–
pointToPoint
–
pointToMultipoint
•
Area ID—The predefined ID uniquely identifying the area to which the interface connects. It can be specified as either a decimal value or as an IP address. Value is 0.0.0.0 if the interface is a Layer 2 (no IP address assigned) interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Authentication Key—Password to be used by neighboring OSPF routers on a network segment that is using OSPF simple password authentication. Ignored if Authentication Type is not "simple".
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular network. If more than one router has the same value for this field, the routers use their router ID as a tie breaker.
•
Trans. Dead (sec)—Number of seconds that a device's hello packets must not have been seen before its neighbors declare the OSPF router down. Must be consistent among all routers on an attached network.
•
Trans. Delay (sec)—The estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state update packet over this interface.
•
Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value is also used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets.
EIGRP Area
The EIGRP Area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
EIGRP Interface Table—Describes the EIGRP configuration of the interface on each active autonomous system. The EIGRP parameters of the interface on an autonomous system may be explicitly configured even if EIGRP routing updates in the autonomous system are not currently carried on the interface.
•
Bandwidth Utilization (%) —The percentage of the interface bandwidth that the EIGRP protocol can use.
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Hold Time (sec)—Hold time during which the device will wait for a hello packet to be received on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number. The hold time should be at least three times the hello interval.
ISIS Area
The ISIS area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface:
–
true—IS-IS routing is enabled.
–
false—IS-IS routing is disabled.
•
Area Tag—The IS-IS routing area in which the interface participates. If multiarea IS-IS is configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named; otherwise, this value may be an implicit null tag.
•
Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1 routing.
•
Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2 routing.
•
Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
•
Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (inter-area) route calculation.
•
Level 1 Priority—The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or designated intermediate system (DIS).
•
Level 2 Priority—The priority is used to determine which router on a LAN will be the designated router or DIS.
•
Enable button—Enables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
•
Disable button—Disables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
By default, all interfaces are configured as IS-IS Circuit-type Level 1-2.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-84 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-84 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M OSM Serial Subinterface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the OSM Serial Subinterface.
C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
This dialog box describes a logical OC-3 channel on a channelized OC-12 (ChOC-12) or OC-48 (ChOC-48) SONET interface of an Optical Service Module (OSM). An OC-3 channel of a SONET interface is provisioned as a logical packet over SONET (POS) interface. This dialog box can be launched from the OSM Channelized SONET Module or Interface object or the POS Subinterface within the Physical view.
You can select multiple OSM POS subinterfaces, OSM Channelized SONET interfaces, OSMs, and chassis at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 5-85 shows the Status tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-85 Status Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Status area of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box provides the following information to describe the general characteristics of the interface.
•
Description—Comment or a description to help you remember what is attached to this interface. The description is only put in the configuration to help you remember what specific interfaces are used for.
•
Index—String index of the interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Type—Indicates the type of interface distinguished by the physical and link layer protocols on the interface.
•
Operational Status—The current operational state of the interface. This attribute is read-only. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
unknown
–
down
–
up
–
dormant—Interface is waiting for external actions (such as a serial line waiting for an incoming connection)
–
notPresent—Interface has missing (typically, hardware) components.
–
lowerLayerDown—Indicates that the primary channelized SONET interface has failed.
•
Administrative Status—The desired state of the interface. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
up
–
down
•
Number of Resets—Number of times the interface internally reset. This attribute is read-only.
•
Connector Present—Displays if a cable is attached to the parent interface (the OSM Channelized SONET Interface). These are the values:
–
yes
–
no
–
unknown—This value is used when the Administrative Status is not set to "up". In this case, it cannot be determined if a connection is present or not.
•
Last Change—The value (in seconds) of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its current operational state. If the current state was entered before the last reinitialization of the local network management subsystem, then this object contains a zero value. This attribute is read-only.
Status Field
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object. This field can have the following values:
•
decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
•
normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
•
performance—Some attributes are collected periodically for trending purposes.
•
normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
•
perflostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the performance state.
Interface Configuration Tab
Figure 5-86 shows the Interface Configuration tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-86 Interface Configuration Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
General Area
The General area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
Note
The Bandwidth attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF); you cannot adjust the actual bandwidth of an interface with this command.
•
Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
Note
The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP and EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with this command.
•
Input Queue Length—Displays the input queue length in packets.
•
Output Queue Length—Displays the output queue length in packets.
•
Link Up/Down Trap—Enables or disables linkUp and linkDown trap generation for the interface.
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area contains the following information:
•
MTU—The size of the largest datagram (frame) which can be sent or received on the interface, specified in octets.
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area contains the following information:
•
IP Address—Displays the IP address of the Layer 3 interface.
•
IP MTU—Layer 3 MTU. The size of the largest datagram (packet) that can be sent/received on the interface. Cannot exceed the size of the largest layer 2 datagram on the interface. If the Layer 2 MTU is updated, the Layer 3 MTU must be adjusted so that it does not exceed the new Layer 2 MTU.
•
Netmask—Subnet mask of the IP address. Enabled bits indicate network addressing bits in the IP address.
•
Modify IP button—Launches a subdialog box to modify the IP address of the interface. Figure 5-87 shows the subdialog box that is displayed when the Modify IP button is selected. The subdialog box contain the following:
–
IP Address—Primary IP address of interface.
–
Netmask—Subnet mask for the interface.
–
Modify IP button—Modify the IP address.
Figure 5-87 Modify IP Subdialog Box
POS Tab
Figure 5-88 shows the POS tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-88 POS Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
POS Interface Area
The POS Serial Interface area contains the following information:
•
CRC—Cyclical redundancy check (CRC) word size. The CRC is an error-checking technique that uses a calculated numeric value to detect errors in transmitted data.
•
Payload Scrambling—Indicates whether or not SONET payload scrambling is enabled on the interface. Payload scrambling ensures that there is sufficient bit-transition density to maintain the transmit clock for synchronous signalling. Both ends of the connection must use the same scrambling algorithm.
•
Encapsulation—Indicates whether HDLC or PPP encapsulation is used on the interface.
Path Message (C2) Area
The Path Message (C2) area contains the following information:
•
SONET Overhead C2 Byte—Value of the SONET overhead Path Signal Label (C2), which indicates the contents of the SONET STS-SPE Higher Order VC. This attribute is read-only. These are possible values:
–
207 (0xCF) = PPP or HDLC with no payload scrambling
–
22 (0x16) = PPP or HDLC with payload scrambling
Path Message (J1) Area
The SONET Path Header (J1) area contains the following information:
•
Expected Size—Maximum length of the expected receive SONET Path overhead message in bytes.
•
Transmit Size—Maximum length of the transmitting SONET Path overhead message in bytes.
•
Expected Label—The expected receive SONET Path overhead message. If the expected label is longer than the expected size, it will be truncated.
•
Transmit Label—Transmitting SONET Path overhead message. If the transmitting label is longer than the transmitting size, it will be truncated.
•
Modify Path Message (J1) button—Launches a subdialog box to modify the expected receive and transmit SONET Path overhead message. Figure 5-89 shows the subdialog box launched by this button. The following items are displayed in the subdialog box:
–
Expected Size
–
Transmit Size
–
Expected Label
–
Transmit Label
–
Modify button—Sets the specified values of the attributes given in the subdialog box.
Note
In 12.1(11b)E and later the values for the Expected Size and the Transmit Size should be the same since the Tx and Rx message sizes cannot be independently configured. If the received values are different, the J1 Path Overhead message size will be set to the larger of the two values.
Figure 5-89 SONET J1 Modify Subdialog Box of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
Performance Tab
Figure 5-90 shows the Performance tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box. All the attributes shown in this tab are read-only.
Figure 5-90 Performance Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
Interface Packets/Octets Statistics Area
The Interface Packets/Octets Statistics area contains the following information:
•
Bandwidth Util (%)—Percentage of bandwidth utilization.
•
In Octets—Total number of received octets including framing characters.
•
Out Octets—Total number of transmitted octets including framing characters.
•
In Unicast Pkts.—The number of packets delivered by this sublayer to a higher (sub-)layer, which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer.
•
Out Unicast Pkts.—The total number of packets that higher-level protocols requested be transmitted, and which were not addressed to a multicast or broadcast address at this sublayer, including those that were discarded or not sent.
•
In Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input packets per second.
•
Out Packets/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output packets per second.
•
In Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of input bits per second.
•
Out Bits/Sec—Five-minute exponentially decayed moving average of output bits per second.
Interface Error Statistics Area
The Interface Error Statistics area contains the following information:
•
CRC Error Pkts.—Number of input packets that had cyclic redundancy checksum errors.
•
In Discarded Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space.
•
Out Discarded Pkts.—The number of outbound packets that were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space.
•
In Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the input queue was full.
•
Out Dropped Pkts.—The number of packets dropped because the output queue was full.
•
In Ignored Pkts.—Number of input packets that were ignored by this interface.
•
In Aborted Pkts.—Number of input packets that were aborted.
•
In Error Pkts.—The number of inbound packets that contained errors preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
•
Out Error Pkts.—Number of outbound packets that could not be transmitted because of errors.
Performance Logging Area
The Performance Logging area of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box contains buttons to enable data logging of all the interface attributes of the interface.
•
Start—Turns on performance data logging.
•
Stop—Turns off performance data logging.
Note
The logged data is available to you through the CEMF Performance Manager. Refer to the Cisco Element Management Framework User Guide for more information about the Performance Manager.
POS Statistics Tab
Figure 5-91 shows the POS Statistics tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-91 POS Statistics Tab on the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
SONET Path Error Area
The SONET Path Error area contains the following information:
•
SONET Path Status—Status of the SONET Path. This status may indicate multiple simultaneous defects. These are possible path defects (bitmask):
–
No defects (1)
–
STS-Path Loss of Pointer (2)
–
STS-Path Alarm Indication Signal (4)
–
STS-Path Remote Defect Indication (8)
–
Unequipped (16)
–
Signal Label Mismatch (32)
•
SONET Path Width—Width of the SONET path. This is described by the STS-Nc SPE. A DS3 channel has a width of STS-1 (55.84 Mbps).
•
Errored Secs—Number of errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of coding violations encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of Unavailable Seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
SONET Far End Path Error Area
The SONET Far End Path Error area contains the following information:
•
Errored Secs—Number of far end errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Severely Err Secs—Number of far end severely errored seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Coding Violations—Number of far end coding violations encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
•
Unavailable Secs—Number of far end unavailable seconds encountered by the SONET Path in the current 15-minute interval.
Routing Protocol Tab
Figure 5-92 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-92 Routing Protocol Tab on the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
OSPF Area
The OSPF area of the C6576M OSM POS Interface dialog box provides the following information. All the attributes in this area are read-only.
•
Network Type—OSPF interface type. By default, a POS interface is point-to-point, however, the OSPF network type may be modified to accommodate different types of network configurations. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
broadcast
–
nbma
–
pointToPoint
–
pointToMultipoint
•
Area ID—The predefined ID uniquely identifying the area to which the interface connects. It can be specified as either a decimal value or as an IP address. Value is 0.0.0.0 if interface is a Layer 2 (no IP address assigned) interface. This attribute is read-only.
•
Authentication Key—Password to be used by neighboring OSPF routers on a network segment that is using OSPF simple password authentication. It is ignored if Authentication Type is not "simple".
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at which the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular network. If more than one router has the same value for this field, the routers use their router ID as a tie breaker.
•
Trans. Dead (sec)—Number of seconds that a device's hello packets must not have been seen before its neighbors declare the OSPF router down. Must be consistent among all routers on an attached network.
•
Trans. Delay (sec)—The estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state update packet over this interface.
•
Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value is also used when retransmitting database description and link-state request packets.
EIGRP Area
The EIGRP Area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
EIGRP Interface Table—Describes the EIGRP configuration of the interface on each active autonomous system. The EIGRP parameters of the interface on an autonomous system may be explicitly configured even if EIGRP routing updates in the autonomous system are not currently carried on the interface.
•
Bandwidth Utilization (%) —The percentage of the interface bandwidth that the EIGRP protocol can use.
•
Hello Interval (sec)—Frequency at that the device will send hello packets on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number.
•
Hold Time (sec)—Hold time during that the device will wait for a hello packet to be received on the specified interface and EIGRP autonomous system number. The hold time should be at least three times the hello interval.
ISIS Area
The ISIS area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
•
ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface:
–
true—IS-IS routing is enabled.
–
false—IS-IS routing is disabled.
•
Area Tag—The IS-IS routing area in which the interface participates. If multiarea IS-IS is configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named; otherwise, this value may be an implicit null tag.
•
Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1 routing.
•
Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2 routing.
•
Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
•
Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (inter-area) route calculation.
•
Level 1 Priority—Determines which router on a LAN will be the designated router or designated intermediate system (DIS).
•
Level 2 Priority—Determines which router on a LAN will be the designated router or DIS.
•
Enable button—Enables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
•
Disable button—Disables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note
By default, all interfaces are configured as IS-IS Circuit-type Level 1-2.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 5-93 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface dialog box.
Figure 5-93 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M OSM POS Subinterface Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the OSM POS Subinterface.

 Feedback
Feedback