-
Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Configuration Guide, Release 12.2
-
About Cisco IOS Software Documentation
-
Using Cisco IOS Software
-
Voice, Video, and Fax Overview
-
Cisco Voice Telephony
-
Voice over IP Overview
-
Configuring Voice Ports
-
Configuring Dial Plans, Dial Peers, and Digit Manipulation
-
Configuring Quality of Service for Voice
-
H.323 Applications
-
Configuring H.323 Gateways
-
Configuring H.323 Gatekeepers
-
Configuring MGCP and Related Protocols
-
Configuring SIP for VoIP
-
Configuring Voice over Frame Relay
-
Configuring Voice over ATM
-
Configuring Tcl IVR Applications
-
Configuring Debit Card Applications
-
Configuring Settlement Applications
-
Configuring Trunk Connections and Conditioning Features
-
Configuring ISDN Interfaces for Voice
-
Configuring PBX Interconnectivity Features
-
Configuring Fax Applications
-
Configuring Modem Support for VoIP
-
Configuring Video Applications
-
Appendixes
-
Appendix A - Configuring Synchronized Clocking
-
Appendix B - Caller ID
-
Appendix C-Cisco Hoot and Holler over IP
-
Appendix D - Managing Cisco AS5300 Voice Feature Cards
-
Appendix E - Enhanced Voice Services for Japan for Cisco 800 Series Routers
-
Appendix F-Global System for Mobile Communications Full Rate and Enhanced Full Rate Codecs
-
Appendix G - Configuring the Cisco SS7/C7 Dial Access Solution System
-
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring ISDN Interfaces for Voice
Switch-Type Configuration Options
ISDN Voice Interface Limitations
ISDN Voice Interface Prerequisite Tasks
ISDN Voice Interface Configuration Task List
Configuring ISDN BRI Interfaces
Verifying ISDN BRI Interface Configuration
Monitoring and Maintaining ISDN BRI Interfaces
Configuring ISDN PRI Interfaces
Configuring ISDN PRI Voice Ports
Verifying ISDN PRI Configuration
Configuring Global QSIG Support for BRI or PRI
Configuring Controllers for QSIG over PRI
Configuring BRI Interfaces for QSIG
Configuring PRI Interfaces for QSIG
Verifying the QSIG Configuration
QSIG Support Troubleshooting Tips
Configuring ISDN PRI Q.931 Support
ISDN Voice Interface Configuration Examples
ISDN to PBX and ISDN to PSTN Configuration Examples
ISDN Connection to a PBX Configuration Example
ISDN Connection to the PSTN Configuration Example
QSIG Support Configuration Examples
QSIG Support on Cisco 3600 Series Routers Example
QSIG Support on Cisco 7200 Series Routers Example
QSIG Support on Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators Example
Q.931 Support Configuration Examples
Configuring ISDN Interfaces for Voice
This chapter explains how to configure ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI) ports for voice support and contains the following sections:
•
ISDN Voice Interface Overview
•
ISDN Voice Interface Prerequisite Tasks
•
ISDN Voice Interface Configuration Task List
•
ISDN Voice Interface Configuration Examples
For a complete description of the commands used to configure ISDN interfaces for voice, refer to the Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Command Reference and the Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Command Reference. To locate documentation of other commands that appear in this chapter, use the command reference master index or search online.
To identify the hardware platform or software image information associated with a feature in this chapter, use the Feature Navigator on Cisco.com to search for information about the feature or refer to the software release notes for a specific release. For more information, see the "Identifying Supported Platforms" section in the "Using Cisco IOS Software" chapter.
The following Cisco devices provide ISDN interfaces for voice applications:
•
Cisco 2600 series routers (ISDN BRI and PRI interfaces)
•
Cisco 3600 series routers (ISDN BRI and PRI interfaces)
•
Cisco 7200 series routers (ISDN PRI interfaces only)
•
Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator (ISDN BRI interfaces only)
•
Cisco AS5300 universal access servers (ISDN PRI interfaces only)
•
Cisco AS5800 universal access servers (ISDN PRI interfaces only)
The following documents provide additional information to help implement ISDN interfaces for voice:
•
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IOS IP Command Reference
•
Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Command Reference
•
Cisco IOS IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Command Reference
•
Voice Network Module and Voice Interface Card Configuration Note
•
Cisco Network Module Hardware Installation Guide
•
Cisco WAN Interface Cards Hardware Installation Guide
•
Update to Cisco WAN Interface Cards Hardware Installation Guide
•
Voice over IP for the Cisco 3600 and Cisco 2600 Series Software Configuration Guide
•
Cisco 7200 Series Port Adapter Hardware Configuration Guidelines
•
Cisco 7200 Series Configuration Notes
•
Quick Start Guide: Cisco MC3810 Installation and Startup
•
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrator Hardware Installation Guide
The following documents can help you troubleshoot ISDN, PRI, and BRI connections:
•
Internetwork Troubleshooting Guide
•
Cisco IOS Debug Command Reference
ISDN Voice Interface Overview
ISDN voice support provides the following benefits:
•
It allows you to bypass Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) tariffed services such as trunking and administration.
•
It allows your PBXs to be connected directly to a Cisco router so PBX station calls can be routed automatically to the WAN.
•
It allows you to configure a voice interface on a Cisco router to emulate either a Terminating Equipment (TE) or Network Termination (NT) interface. Customers with all types of PBXs can send calls through a Cisco router and deliver those calls across the customer network.
•
It allows you to configure Layer 2 operation as point-to-point (static terminal endpoint identifier [TEI]) or point-to-multipoint (automatic TEI).
Cisco routing devices support ISDN BRI and ISDN PRI. Both media types use bearer (B) channels and data (D) channels.
ISDN BRI provides two B channels, each capable of transferring voice or data at 64 kbps, and one 16-kbps D channel that carries signaling traffic. The D channel is used by the telephone network to carry instructions about how to handle each of the B channels. ISDN BRI (also referred to as "2 B + D") provides a maximum transmission speed of 128 kbps.
ISDN PRI provides 23 B channels plus a D channel (in North America and Japan) or 30 B channels plus a D channel (in the rest of the world). Similar to the ISDN BRI D channel, the ISDN PRI D channel carries signaling traffic. ISDN PRI is often referred to as "23 B + D" (in North America and Japan) or "30 B + D" (in the rest of the world). The D channel notifies the central office switch to send the incoming call to particular time slots on the Cisco access server or router. Each one of the B channels carries data or voice. The D channel carries signaling for the B channels. The D channel identifies if the call is a circuit-switched digital call or an analog modem call. Analog modem calls are decoded and then sent to the onboard modems. Circuit-switched digital calls are relayed directly to the ISDN processor in the router.
The ISDN BRI NT/TE voice interface card (VIC-2BRI-NT/TE) for the Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 series routers and the ISDN BRI voice module (BVM4-NT/TE) for the Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator enable Cisco IOS software to replicate the PSTN interface to a PBX that is compatible with European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) NET3 and QSIG switch types.
Prior to the release of these voice network modules and interface cards, customers with PBXs that implement only the BRI TE interface had to make substantial hardware and software changes on the PBX to implement the NT interface. The implementation of an NT interface on the router allows the customer to connect ISDN PBXs and key systems to a multiservice network with a minimum of configuration changes on the PBX.
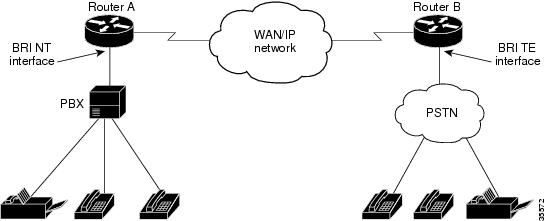
The typical application (see Figure 108) allows enterprise customers with a large installed base of legacy telephony equipment to bypass the PSTN.
Figure 108 Typical Application Using ISDN BRI NT/TE VICs or ISDN BVMs
QSIG Protocol Support
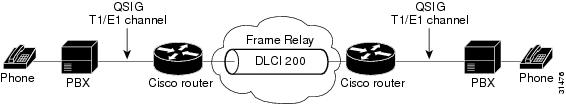
Integration of QSIG protocol support with Cisco voice switching services allows Cisco devices to connect PBXs, key systems (KTs), and central office switches (COs) that communicate by using the QSIG protocol. The QSIG protocol is becoming the standard for PBX interoperability in Europe and North America. QSIG is a variant of ISDN D-channel voice signaling that is based on the ISDN Q.921 and Q.931 standards. With QSIG, Cisco networks emulate the functionality of the PSTN, and QSIG signaling messages allow the dynamic establishment of voice connections across a Cisco WAN to a peer router, which can then transport the signaling and voice packets to a second PBX, as shown in Figure 109.
Figure 109 QSIG Signaling
The Cisco voice packet network appears to the traditional QSIG PBXs as a distributed transit PBX that can establish calls to any PBX, non-QSIG PBX, or other telephony endpoint served by a Cisco gateway, including non-QSIG endpoints.
When QSIG messages originate and terminate on QSIG endpoints, the QSIG messages are passed transparently across the network; the PBXs are responsible for processing and provisioning the supplementary services. When QSIG and non-QSIG endpoints are linked via a Cisco packet voice gateway, only basic calls are supported. In addition, all switched voice connections must be established and torn down in response to QSIG control messages.
QSIG voice signaling provides the following benefits:
•
It provides efficient and cost-effective services on permanent (virtual) circuits or leased lines.
•
It allows enterprise networks that include PBX networks to replace leased voice lines with a Cisco WAN.
•
It eliminates the need to route connections through multiple tandem PBX hops to reach the desired destination, thereby saving bandwidth, PBX hardware, and switching power.
•
It improves voice quality through the single-hop routing provided by voice switching while allowing voice to be compressed more aggressively, resulting in additional savings.
•
It supports PBX feature transparency across a WAN, permitting PBX networks to provide advanced features such as calling name and number display, camp-on/callback, network call forwarding, centralized attendant, and centralized message waiting. Usually these capabilities are available on only a single site where users are attached to the same PBX.
QSIG support includes the following capabilities:
•
It enables digit forwarding on POTS dial peers.
•
On Cisco 2600 series routers, it enables QSIG-switched calls over Voice over Frame Relay (VoFR) and Voice over IP (VoIP) for T1/E1 and BRI voice interface cards.
•
On Cisco 3600 series routers, it enables QSIG-switched calls over VoFR, VoIP, and Voice over ATM (VoATM) for T1/E1 and BRI voice interface cards.
•
On Cisco 7200 series routers, it enables QSIG-switched calls over VoFR and VoIP on T1/E1 voice interface cards.
•
On Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrators, it enables T1 or E1 PRI and BRI QSIG-switched calls over VoFR, VoIP, and VoATM for Cisco MC3810 digital voice modules (DVMs) and BRI voice module (BVM). QSIG support on the Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(2)T.
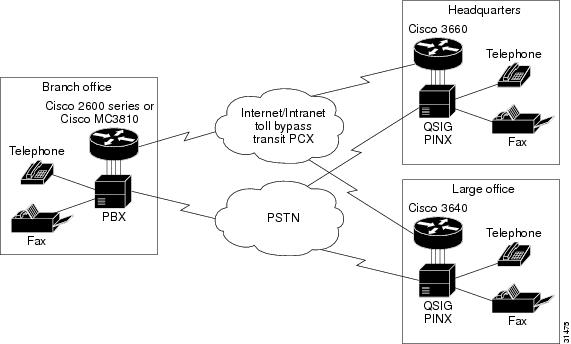
Figure 110 shows an example of how QSIG support can enable a toll-bypass application.
Figure 110 QSIG Toll-Bypass Application
QSIG Protocol Stack
QSIG is a variant of ISDN D-channel signaling. The protocol was originally specified by European Computer Manufacturers Association (ECMA), and then was adopted by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Table 46 identifies the ECMA standards and the OSI layer of the QSIG protocol stack to which they relate.
Switch-Type Configuration Options
To support QSIG at either the global configuration level or the interface configuration level, use the isdn switch-type command. For example, if you have a QSIG connection on one line and on the BRI or PRI port, you can configure the ISDN switch type in one of the following combinations:
•
Set the global isdn switch-type command to support QSIG by entering either the isdn switch-type basic-qsig command (BRI) or isdn switch-type primary-qsig command (PRI); and set the interface isdn switch-type command for the interfaces to a regular central office switch type such as those shown in Table 47.
•
Set the global isdn switch-type command to support the CO switch type (see Table 47), and set the interface isdn switch-type command for the interface to support QSIG.
•
Configure the global isdn switch-type command to another setting (see Table 47); then set the interface isdn switch-type command for interface bri to a BRI setting; set the interface isdn switch-type command for the serial interface to support QSIG.
Q.931 Support
Cisco platforms that support Q.931 offer both user- and network-side switch types for ISDN call processing, providing the following benefits:
•
User-side PRI enables the Cisco platform to provide a standard ISDN PRI user-side interface to the PSTN.
•
Network-side PRI enables the Cisco platform to provide a standard ISDN PRI network-side interface via digital T1/E1 packet voice trunk network modules on Cisco 2600 series and Cisco 3600 series routers.
ISDN Voice Interface Limitations
•
Basic-net3 and basic-qsig are the only ISDN switch types currently supported for an NT interface.
•
When the ISDN BRI port on the router is configured as an NT port, a "rolled" cable (one with the transmit and receive leads swapped) is needed to connect to a TE interface.
•
Layer 1 can be configured only as point-to-point (that is, with one TE connected to each NT). Automatic TEI support will issue only one TEI.
QSIG Support Limitations
The Cisco 2600 series routers do not support VoATM.
The following restrictions apply to the Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator:
•
QSIG data calls are not supported. All calls with bearer capability indicating a nonvoice type (such as for video telephony) are rejected.
•
A Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator supports only one T1/E1 interface with direct connectivity to a private integrated services network exchange (PINX).
•
The Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator supports a maximum of 24 B channels.
•
On the Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator, if the multiflex trunk module (MFT) is installed in slot 3 and QSIG is configured, the Cisco MC3810 requires a minimum revision of the system control board (SCB) in order to use ISDN and the serial 1 interface simultaneously. ISDN includes ISDN Q.SIG signaling on a digital voice module and the ISDN BRI port of a multiflex trunk module (MFT). (To display the revision of the SCB, use the show version command.) Otherwise, serial port 1 is inoperative when ISDN is active.
When using a newer SCB-06.07 board with QSIG features enabled or the BRI backup feature active, the following constraints are imposed:
–
Serial port 1 is limited to speeds of 3xDS0 (<= 192kbps or 168 kbps).
–
The serial ports does not support async, bisync, and half-duplex.
–
Serial port 0 cannot be set up to run the TDM cross-connect function if serial port 1 is in use, due to FIFO limitations.
–
If slot 3 is empty (no MFT installed) and QSIG features are enabled, serial port 1 cannot be used. This is because hardware on the MFT is used to enable the TDM sharing of serial port 1.
The following restrictions apply to the Cisco 7200 series routers:
•
VoATM is not supported.
•
BRI is not supported.
ISDN Voice Interface Prerequisite Tasks
Before you can configure a voice interface for ISDN, you must do the following:
•
Obtain PRI or BRI service and T1 or E1 service from your service provider, as required. Any BRI lines must be provisioned at the switch to support voice calls.
•
Establish a working IP, Frame Relay, or ATM network. At least one network module or WAN interface card must be installed in the router to provide the connection to the LAN or WAN. For more information on installing network modules and interface cards, see the list of documents at the beginning of this chapter.
–
For more information about configuring IP, see the chapter "Voice over IP Overview."
–
For more information about configuring Frame Relay, see the chapter "Configuring Voice over Frame Relay."
–
For more information about configuring ATM, see the chapter "Configuring Voice over ATM."
•
Complete your company's dial plan.
•
Establish a working telephony network based on your company's dial plan and configure the network for real-time voice traffic. This chapter describes only a portion of the process; for further information, see the chapter "Cisco Voice Telephony."
•
Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Routers—Install digital T1 or E1 packet voice trunk network modules, BRI voice interface cards, and other voice interface cards as required on your network.
•
Cisco 7200 Series Routers—Install a single-port 30-channel T1/E1 high-density voice port adapter.
•
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators—Install the required digital voice modules (DVMs), BRI voice module (BVM), and multiflex trunk modules.
•
All Platforms (As Required):
–
Configure voice card and controller settings.
–
Configure serial and LAN interfaces.
–
Configure voice ports.
–
Configure voice dial peers.
ISDN Voice Interface Configuration Task List
To configure your router for ISDN voice interface support, perform the tasks described in the following sections:
•
Configuring ISDN BRI Interfaces (required for BRI)
•
Configuring ISDN PRI Interfaces (required for PRI)
To configure your router for QSIG support, perform the tasks described in the following sections:
•
Configuring Global QSIG Support for BRI or PRI (required)
•
Configuring Controllers for QSIG over PRI (required for PRI)
•
Configuring BRI Interfaces for QSIG (required for BRI)
•
Configuring PRI Interfaces for QSIG (required for PRI)
To configure your router for Q.931 support, perform the tasks described in the following section:
•
Configuring ISDN PRI Q.931 Support (required)
Configuring ISDN BRI Interfaces
The steps in this section include commands for configuring an NT interface and a TE interface. To configure an ISDN BRI interface, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Configures the telephone company ISDN switch type. For a list of switch types, see Table 48.
Note
The only switch types currently supported for an NT interface are basic-net3 and basic-qsig.
Step 2
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators
Router(config)# interface bri numberOther Supported Routers
Router(config)# interface bri slot|portEnters interface configuration mode for the specified interface.
The arguments are as follows:
•
number—Voice module (1 to 4).
•
slot—Location of the voice network module in the router (1 to 6).
•
port—Location of the BRI voice interface card (VIC) in the voice network module. Valid values are 1 or 2.
Step 3
Router(config-if)# no ip addressSpecifies that there is no IP address for this interface. For information about IP addressing, refer to the Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide.
Step 4
Router(config-if)# isdn overlap-receiving(Optional) Activates overlap signaling to send to the destination PBX. In this mode, the interface waits for possible additional call-control information.
Step 5
Router(config-if)# isdn twait-disable(Optional) Delays a National ISDN BRI switch for a random length of time before activating the Layer 2 interface when the switch starts up. Use this command when the ISDN switch type is basic-ni1.
Step 6
(Optional; TE only) Specifies a service profile identifier (SPID) and optional local directory number for the B1 channel. Currently, only the DMS-100 and NI-1 switch types require SPIDs. Although some switch types might support a SPID, Cisco recommends that you set up ISDN service without SPIDs.
Step 7
(Optional; TE only) Specifies a SPID and optional local directory number for the B2 channel.
Step 8
Router(config-if)# isdn incoming-voice voiceConfigures the port for incoming voice calls.
Step 9
Router(config-if)# shutdownTurns off the port (prior to setting the port emulation).
Step 10
Configures the Layer 1 port mode emulation and clock settings.
The keywords are as follows:
•
user—Configures the port as TE and sets it to function as a clock slave. This is the default.
•
network—Configures the port as NT and sets it to function as a clock master.
Step 11
Router(config-if)# no shutdownTurns on the port.
Step 12
(Optional; TE only) Configures the priority of the network clock for this BRI voice port. If this port is configured as TE and you want it to be the first-priority BRI voice port for recovering the clock signal from the network NT device, enter high.
If this BRI voice port is configured as TE and you want it to be a low-priority BRI voice port for recovering the clock signal from the network NT device, enter low.
The default for the BRI voice module (BVM) is low.
The default for the BRI VIC is high.
Do not use this command if this port is configured as NT in Step 10 with the command isdn layer1-emulate network.
Step 13
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators Only
Router(config-if)# [no] line-powerControls the power supplied from an NT-configured port to a TE device. The line-power command turns the port power on; the no line-power command turns it off. The default is no line-power.
Step 14
Configures the Layer 2 and Layer 3 port protocol emulation.
The keywords are as follows:
•
user—Configures the port as TE; the PBX is the master. This is the default.
•
network—Configures the port as NT; the PBX is the slave.
Step 15
Router(config-if)# isdn sending-complete(Optional) Configures the voice port to include the "Sending Complete" information element in the outgoing call setup message. This command is used in some geographic locations, such as Hong Kong and Taiwan, where the "Sending Complete" information element is required in the outgoing call setup message.
Step 16
(Optional) Configures a static ISDN Layer 2 terminal endpoint identifier (TEI).
The value of tei-number can be from 0 to 64.
Step 17
Router(config-if)# isdn point-to-point-setup(Optional) Configures the ISDN port to send SETUP messages on the static TEI.
Note
A static TEI must be configured in order for this command to be effective.
Step 18
Router(config-if)# endExits interface configuration mode.
Step 19
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators
Router(config)# clear interface bri numberOther Supported Routers
Router# clear interface slot|port(Optional) Resets the specified interface. The interface needs to be reset if the static TEI number has been configured in Step 16.
The arguments are as follows:
•
number—Voice module (1 to 4).
•
slot—Location of the voice network module in the router (1 to 6).
•
port—Location of the BRI VIC in the voice network module. Valid values are 1 or 2.
When you have finished configuring one interface, you must repeat the appropriate steps above for the other interfaces.
Note
To complete voice configuration, you must set up your voice ports and dial peers. To do this, see the chapter "Configuring Voice Ports."
Table 48 lists the ISDN switch types.
Verifying ISDN BRI Interface Configuration
To verify the ISDN BRI interface configuration, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Enter the show running-config command in EXEC mode to show the current configuration running on the router.
Note
The examples show some of the command output that is relevant to BRI configuration tasks. The first example is from a Cisco 2600 series router.
Router# show running-configBuilding configuration...Current configuration:!version 12.2!no service udp-small-serversservice tcp-small-servers!hostname Router!username xxxx password x 11x5xx07no ip domain-lookupip host Labhost 172.22.66.11ip host Labhost2 172.22.66.12ip name-server 172.22.66.21!...interface BRI1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn overlap-receivingisdn T306 30000isdn skipsend-idverifyisdn incoming-voice voice!interface BRI1/1no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn overlap-receivingisdn T306 30000isdn skipsend-idverifyisdn incoming-voice voice!interface BRI2/0no ip addressisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn overlap-receivingisdn protocol-emulate networkisdn layer1-emulate networkisdn T306-30000isdn sending-completeisdn skipsend-idverifyisdn incoming-voice voice!interface BRI2/1no ip addressisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn overlap-receivingisdn protocol-emulate networkisdn layer1-emulate networkisdn T306-30000isdn sending-completeisdn skipsend-idverifyisdn incoming-voice voice!...The following example is from a Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator:
Router# show running-configBuilding configuration...Current configuration:!version 12.2service timestamps debug uptimeservice timestamps log uptimeno service password-encryption!hostname Router!no logging console!network-clock base-rate 56knetwork-clock-select 2 T1 0network-clock-select 3 system(SCB)network-clock-select 1 BVMip subnet-zero!isdn switch-type basic-net3isdn voice-call-failure 0call rsvp-sync!voice-card 0!controller T1 0mode atmframing esflinecode b8zs!interface BRI1no ip addressisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn protocol-emulate networkisdn layer1-emulate networkisdn incoming-voice voiceisdn T306 30000isdn skipsend-idverifyno cdp enable!interface BRI2no ip addressisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn protocol-emulate networkisdn layer1-emulate networkisdn incoming-voice voiceisdn T306 30000isdn skipsend-idverifyno cdp enable!interface BRI3no ip addressshutdownnetwork-clock-priority lowisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn T306 30000no cdp enable!interface BRI4no ip addressshutdownnetwork-clock-priority lowisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn T306 30000no cdp enable!...Step 2
Enter the show interfaces bri command to display information about the physical attributes of the ISDN BRI B and D channels. The term spoofing means that the interface is presenting itself to the IOS software as operational.
The following is sample output from the show interfaces bri command for a BRI voice port on a Cisco 2610 router:
router# show interfaces bri 1/0BRI3/1 is up, line protocol is up (spoofing)Hardware is Voice NT or TE BRIMTU 1500 bytes, BW 64 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec,reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255Encapsulation VOICE, loopback not setLast input 00:00:02, output never, output hang neverLast clearing of "show interface" counters neverInput queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0Queueing strategy: weighted fairOutput queue: 0/1000/64/0 (size/max total/threshold/drops)Conversations 0/0/16 (active/max active/max total)Reserved Conversations 0/0 (allocated/max allocated)5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec26110 packets input, 104781 bytes, 0 no bufferReceived 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort0 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns0 output errors, 0 collisions, 5 interface resets0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out9 carrier transitionsThe following is sample output from the show interfaces bri command for a BRI voice port on a Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator:
Router# show interfaces bri 1BRI1 is up, line protocol is up (spoofing)Hardware is BVMMTU 1500 bytes, BW 64 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec,reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not setLast input 19:32:19, output 19:32:27, output hang neverLast clearing of "show interface" counters neverInput queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0Queueing strategy: weighted fairOutput queue: 0/1000/64/0 (size/max total/threshold/drops)Conversations 0/1/16 (active/max active/max total)Reserved Conversations 0/0 (allocated/max allocated)5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec13282 packets input, 53486 bytes, 0 no bufferReceived 1 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort13292 packets output, 53515 bytes, 0 underruns0 output errors, 0 collisions, 4 interface resets0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out33 carrier transitions
Monitoring and Maintaining ISDN BRI Interfaces
To monitor ISDN interfaces, use these commands as needed:
Configuring ISDN PRI Interfaces
With ISDN PRI, signaling in VoIP is handled by ISDN PRI group configuration. After ISDN PRI has been configured, you must enter the isdn incoming-voice command on the serial interface (acting as the D channel) to ensure a dial tone.
To configure basic ISDN PRI interface parameters for T1 or E1, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Router(config)# isdn switch-type switch-type
Configures the telephone company ISDN switch type. For a list of switch types, see Table 48.
Note
The only switch types currently supported for an NT interface are basic-net3 and basic-qsig.
Step 2
Cisco AS5800 Access Servers
Router(config)# controller T1 1/0/0
Enters controller configuration mode and specifies the T1 0 controller on the T1 card.
or
Cisco AS5800 Access Servers
Router(config)# controller T1 1/0/0:1
Enters controller configuration mode and specifies the T1 1 controller on the T3 card.
or
Cisco AS5300 Access Servers
Router(config)# controller {T1 | E1} 0
Enters controller configuration mode and specifies the T1 0 or E1 0 controller.
Step 3
Router(config-controller)# framing esf
Defines the framing characteristics.
Step 4
Router(config-controller)# linecode {ami | b8zs | hdb3}
Sets the line-encoding method to match that of your telephone company service provider.
The keywords are as follows:
•
ami—Alternate mark inversion (AMI) as the line-code type. Valid for T1 or E1 controllers. This is the default for T1 lines.
•
b8zs— 8ZS as the line-code type. Valid for T1 controller only.
•
hdb3—High-density bipolar 3 (hdb3) as the line-code type. Valid for E1 controller only. This is the default for E1 lines.
Step 5
Router(config-controller)# pri-group timeslots range
Configures the ISDN PRI group.
The range argument specifies a range of time slots that make up the PRI group. The range is from 1 to 23.
Step 6
Router(config-controller)# exit
Exits controller configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode.
Step 7
Cisco AS5800 Access Servers
Router(config)# interface Serial1/0/0:23
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified first ISDN PRI line on the T1 card. (The ISDN serial interface is the D channel.)
or
Cisco AS5800 Access Servers
Router(config)# interface Serial1/0/0:1:23
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified first ISDN PRI line on the T3 card. (The ISDN serial interface is the D channel.)
or
Cisco AS5300 Access Servers
Router(config)# interface Serial0:23
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified first ISDN PRI line. (The ISDN serial interface is the D channel.)
Step 8
Cisco AS5xxx Access Servers
Router(config-if)# isdn incoming-voice modem
All Others
Router(config-if)# isdn incoming-voice voice
Enables incoming ISDN voice calls.
Configuring ISDN PRI Voice Ports
Under most circumstances, the default voice port command values are adequate to configure voice ports to transport voice data over your existing IP network. However, because of the inherent complexities of PBX networks, you might need to configure specific voice port values, depending on the specifications of the devices in your telephony network.
To configure specific voice port parameters, see the chapter "Configuring Voice Ports."
For more information on specific voice-port configuration commands and additional voice port commands, refer to the Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Command Reference.
Verifying ISDN PRI Configuration
You can check the validity of your voice port configuration by performing the following tasks:
•
To verify that the data configured is correct, use the show voice port command.
•
If you have not configured your device to support Direct Inward Dialing (DID), dial in to the router and verify that you have a dial tone.
•
Enter a dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) digit. If the dial tone stops, you have verified two-way voice connectivity with the router.
ISDN PRI Troubleshooting Tips
If you are having trouble connecting a call and you suspect that the problem is associated with voice port configuration, you can try to resolve the problem by performing the following tasks:
•
Ping the associated IP address to confirm connectivity. If you cannot successfully ping your destination, refer to the chapter "Configuring IP" in the Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide.
•
Determine if the voice feature card (VFC) has been correctly installed. For more information, refer to Installing Voice-over-IP Feature Cards in Cisco AS5300 Universal Access Servers, which came with your voice network module (VNM).
•
To learn if the VFC is operational, use the show vfc slot number command.
•
To view layer status information, use the show isdn status command. If you receive a status message stating that Layer 1 is deactivated, make sure the cable connection is not loose or disconnected. (This status message indicates a problem at the physical layer.)
•
With T1 lines, determine if your a-law setting is correct. With E1 lines, determine if your u-law setting is correct. To configure both a-law and u-law values, use the cptone command. For more information about the cptone command, refer to the Cisco IOS Voice, Video, and Fax Command Reference.
•
If dialing cannot occur, use the debug isdn q931 command to check the ISDN configuration.
Configuring Global QSIG Support for BRI or PRI
If you need additional guidance regarding switch-type configuration, see the section "Switch-Type Configuration Options." The steps in this section apply to both BRI and PRI, except as noted. To do the global configuration of QSIG signaling on the router, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
BRI Only on Cisco MC3810, 2600, and 3600 Series Routers
Router(config)# isdn switch-type basic-qsig
(Optional) Configures the global ISDN switch type.
PRI Only on Any Supported Router
Router(config)# isdn switch-type primary-qsig
(Optional) Configures the ISDN switch-type to support QSIG signaling.
Note
You can configure the ISDN switch type by using either this global command or the same command in interface configuration mode, depending on your configuration. If you configure the global isdn switch-type command for QSIG support, you do not need to configure the interface isdn switch-type command for QSIG.
For more information, see "Switch-Type Configuration Options" on page 588. For a list of CO switch types, see Table 47.
Step 2
Router(config)# dspinterface dspfarm slot/port
(Cisco 7200 series routers only) Configures the digital signal processor (DSP) farm interface.
Step 3
Router(config)# card type {t1 | e1} slot
(Cisco 7200 series routers only) Specifies the card type and slot number. Enter the card type as T1 or E1; specify the slot location by using a value from 1 to 6, depending on your router.
Configuring Controllers for QSIG over PRI
The steps in this section do not apply to BRI. To configure controllers for QSIG signaling over PRI, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Configuring BRI Interfaces for QSIG
To configure BRI interfaces for QSIG support, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators
Router(config)# interface bri number
Cisco 2600, and 3600 Series Routers
Router(config)# interface bri slot/port
Enters interface configuration mode for the specified interface.
The arguments are as follows:
•
number—Voice module (1 to 4).
•
slot—Location of the voice network module in the router (1 to 6).
•
port—Location of the BRI VIC in the voice network module. Valid values are 1 and 2.
Step 2
Cisco MC3810, 2600, and 3600 Series Routers Only
Router(config-if)# isdn static-tei 0
This command is required. (In previous releases, it was set automatically when the isdn switch-type basic-qsig command was issued.)
Step 3
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators Only
Router(config-if)# isdn layer1-emulate {user | network}
Configures the Layer 1 port mode emulation and the clock settings.
The keywords are as follows:
•
user—Configures the port as TE and sets it to function as a clock slave. This is the default. The term user is equivalent to the QSIG term slave.
•
network—Configures the port as NT and sets it to function as a clock master. The term network is equivalent to the QSIG term master.
Step 4
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators Only
Router(config-if)# network-clock-priority {low | high}
(TE only) Configures the priority of the network clock for this BRI voice port. If this port is configured as TE and you want it to be the first-priority BRI voice port for recovering the clock signal from the network NT device, enter high.
If this BRI voice port is configured as TE and you want it to be a low-priority BRI voice port for recovering the clock signal from the network NT device, enter low.
Do not use this command if this port is configured as NT in Step 3 with the command isdn layer1-emulate network.
Step 5
Cisco 2600 and 3600 Series Routers Only
Router(config-if)# isdn incoming-voice voiceRoutes incoming voice calls. This is set for voice-capable BRI interfaces by default, except for Cisco 2600 and 3600 series BRI S/T TE voice interface cards, where, unless this command is used, the isdn incoming-voice modem configuration setting is converted to isdn incoming-voice voice when it receives an incoming call.
Step 6
Router(config-if)# isdn sending-complete
(Optional) Configures the voice port to include the "Sending Complete" information element in the outgoing call setup message. This command is used in some geographic locations, such as Hong Kong and Taiwan, where the "Sending Complete" information element is required in the outgoing call setup message.
Step 7
Cisco MC3810, 2600, and 3600 Series Routers Only
Router(config-if)# isdn switch-type basic-qsig
(Optional) If the service provider switch type for this BRI port is different from the global ISDN switch type, configure the interface ISDN switch type to match the service provider switch type. The interface ISDN switch type overrides the global ISDN switch type on this interface.
See the section "Switch-Type Configuration Options."
Step 8
Router(config-if)# isdn protocol-emulate {user | network}
Configures the Layer 2 and Layer 3 port protocol emulation.
The keywords are as follows:
•
user—Configures the port as TE; the PINX is the master. This is the default. The term user is equivalent to the QSIG term slave.
•
network—Configures the port as NT; the PINX is the slave. The term network is equivalent to the QSIG term master.
Note
On the Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator, this command replaces the isdn switch-type [primary-qsig-slave | primary-qsig-master] command.
Step 9
Router(config-if)# isdn overlap-receiving value
(Optional) Activates overlap signaling to send to the destination PBX. In this mode, the interface waits for possible additional call-control information from the preceding PINX.
Note
You can leave the default mode of enbloc, in which all call establishment information is sent in the setup message without need for additional messages from the preceding PINX.
Step 10
Router(config-if)# isdn network-failure-cause value
(Optional) Specifies the cause code to pass to the PBX when a call cannot be placed or completed because of internal network failures. Possible values range from 1 to 127.
Configuring PRI Interfaces for QSIG
To configure PRI interfaces for QSIG support, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
Step 1
Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators
Router(config)# interface serial 1:channelnumber
Enters interface configuration mode for the ISDN PRI interface and the specified interface slot location and channel number. Enter the slot location as 1. For T1, enter the channel number as 23. For E1, enter 15.
Or
Other Supported Routers
Router(config)# interface serial slot/port:channel-number
Enters interface configuration mode for the ISDN PRI interface and the specified interface slot and port location and channel number. Enter a slot number from 1 to 6 and a port number of 1 or 2. For T1, enter the channel number as 23. For E1, enter 15.
Step 2
Router(config-if)# isdn switch-type primary-qsig
If you did not configure the global PRI ISDN switch type for QSIG support in global configuration mode, configure the interface ISDN switch type to support QSIG signaling.
See the section "Switch-Type Configuration Options."
The conditions that apply to this command in global configuration mode also apply to this command in interface configuration mode.
Note
For this interface, this interface configuration command overrides the setting of the isdn switch-type command entered in global configuration mode.
Step 3
Router(config-if)# isdn contiguous-bchan
(E1 only) Specifies contiguous bearer channel handling so that B channels 1 through 30 map to time slots 1 to 31, skipping time slot 16.
Step 4
Router(config-if)# isdn protocol-emulate {user | network}
Configures the Layer 2 and Layer 3 port protocol emulation.
The keywords are as follows:
•
user—Configures the port as TE; the PINX is the master. This is the default. The term user is equivalent to the QSIG term slave.
•
network—Configures the port as NT; the PINX is the slave. The term network is equivalent to the QSIG term master.
Note
On the Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator, this command replaces the isdn switch-type [primary-qsig-slave | primary-qsig-master] command.
Step 5
Router(config-if)# isdn overlap-receiving value
(Optional) Activates overlap signaling to send to the destination PBX. In this mode, the interface waits for possible additional call-control information from the preceding PINX.
Note
You can leave the default mode of enbloc, in which all call establishment information is sent in the setup message without need for additional messages from the preceding PINX.
Step 6
Router(config-if)# isdn network-failure-cause value
(Optional) Specifies the cause code to pass to the PBX when a call cannot be placed or completed because of internal network failures. Possible values range from 1 to 127.
Verifying the QSIG Configuration
To confirm the QSIG configuration, perform the following steps. The show running-config command displays PRI time slot group configuration and other details.
Step 1
To see information about switch type, memory, status, and Layer 2 and Layer 3 timers, enter the show isdn command.
For more information about this command, refer to the Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Command Reference.
The following sample output shows the results of the show isdn status command for a BRI voice port on a Cisco 3600 series router:
Router# show isdn statusGlobal ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsigISDN Serial3/1:15 interfacedsl 0, interface ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsig**** Master side configuration ****Layer 1 Status:ACTIVELayer 2 Status:TEI = 0, Ces = 1, SAPI = 0, State = MULTIPLE_FRAME_ESTABLISHEDLayer 3 Status:29 Active Layer 3 Call(s)Activated dsl 0 CCBs = 29CCB:callid=89BF, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=5, calltype=VOICE...CCB:callid=89C8, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=14, calltype=VOICE...CCB:callid=89D9, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=1, calltype=VOICECCB:callid=89DA, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=2, calltype=VOICECCB:callid=89DB, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=3, calltype=VOICEThe Free Channel Mask: 0x80000018ISDN Serial3/0:15 interfacedsl 1, interface ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsig**** Master side configuration ****Layer 1 Status:ACTIVELayer 2 Status:TEI = 0, Ces = 1, SAPI = 0, State = MULTIPLE_FRAME_ESTABLISHEDTEI = 0, Ces = 9, SAPI = 16, State = TEI_ASSIGNEDLayer 3 Status:28 Active Layer 3 Call(s)Activated dsl 1 CCBs = 28CCB:callid=BDF, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=2, calltype=VOICECCB:callid=BE0, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=1, calltype=VOICECCB:callid=BE1, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=3, calltype=VOICE...CCB:callid=BFA, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=31, calltype=VOICEThe Free Channel Mask: 0xB0000000Total Allocated ISDN CCBs = 54Total Allocated ISDN CCBs = 0...CCB:callid=89C8, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=14, calltype=VOICE...CCB:callid=89D9, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=1, calltype=VOICECCB:callid=89DA, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=2, calltype=VOICECCB:callid=89DB, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=3, calltype=VOICEThe Free Channel Mask: 0x80000018ISDN Serial3/0:15 interfacedsl 1, interface ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsig**** Master side configuration ****Layer 1 Status:ACTIVELayer 2 Status:TEI = 0, Ces = 1, SAPI = 0, State = MULTIPLE_FRAME_ESTABLISHEDTEI = 0, Ces = 9, SAPI = 16, State = TEI_ASSIGNEDLayer 3 Status:28 Active Layer 3 Call(s)Activated dsl 1 CCBs = 28CCB:callid=BDF, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=2, calltype=VOICECCB:callid=BE0, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=1, calltype=VOICECCB:callid=BE1, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=3, calltype=VOICE...CCB:callid=BFA, sapi=0, ces=0, B-chan=31, calltype=VOICEThe Free Channel Mask: 0xB0000000Total Allocated ISDN CCBs = 54The following sample output shows the results of the show isdn status command for a BRI voice port and a PRI voice port on a Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator:
Router# show isdn statusGlobal ISDN Switchtype = basic-qsigISDN BRI1 interfacedsl 1, interface ISDN Switchtype = basic-qsig**** Slave side configuration ****Layer 1 Status:DEACTIVATEDLayer 2 Status:TEI = 0, Ces = 1, SAPI = 0, State = TEI_ASSIGNEDLayer 3 Status:NLCB:callid=0x0, callref=0x0, state=31, ces=0 event=0x00 Active Layer 3 Call(s)Activated dsl 1 CCBs = 0ISDN BRI2 interface...Router# show isdn statusGlobal ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsigISDN Serial1:23 interfacedsl 0, interface ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsig**** Slave side configuration ****Layer 1 Status:DEACTIVATEDLayer 2 Status:TEI = 0, Ces = 1, SAPI = 0, State = TEI_ASSIGNEDLayer 3 Status:0 Active Layer 3 Call(s)Activated dsl 0 CCBs = 0The Free Channel Mask: 0x7FFFFFThe following sample output shows the results of the show isdn status command for a PRI voice port on a Cisco 7200 series router:
Router# show isdn statusGlobal ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsigISDN Serial1/0:15 interfacedsl 0, interface ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsig**** Slave side configuration ****Layer 1 Status:DEACTIVATEDLayer 2 Status:TEI = 0, Ces = 1, SAPI = 0, State = TEI_ASSIGNEDLayer 3 Status:0 Active Layer 3 Call(s)Activated dsl 0 CCBs = 0The Free Channel Mask: 0x7FFF7FFFISDN Serial1/1:15 interfacedsl 1, interface ISDN Switchtype = primary-qsig**** Slave side configuration ****Layer 1 Status:DEACTIVATEDLayer 2 Status:TEI = 0, Ces = 1, SAPI = 0, State = TEI_ASSIGNEDLayer 3 Status:0 Active Layer 3 Call(s)Activated dsl 1 CCBs = 0The Free Channel Mask: 0x7FFF7FFFTotal Allocated ISDN CCBs = 0Step 2
To display the state and the service status of each ISDN channel, enter the show isdn service command in privileged EXEC mode.
The following example shows sample output from the show isdn service command when PRI is configured on a T1 controller:
Router# show isdn servicePRI Channel Statistics:ISDN Se0:15, Channel (1-31)Activated dsl 8State (0=Idle 1=Propose 2=Busy 3=Reserved 4=Restart 5=Maint)0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0Channel (1-31) Service (0=Inservice 1=Maint 2=Outofservice)0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0Step 3
To display the Call Distributor Application Programming Interface (CDAPI) information, use the show cdapi command.
The following sample output shows the results of the show cdapi command for a PRI voice port on a Cisco 3660 series router:
Router# show cdapiRegistered CDAPI Applications/Stacks====================================Application: TSP CDAPI Application VoiceApplication Type(s) : Voice Facility SignalingApplication Level : TunnelApplication Mode : EnblocSignaling Stack: ISDNInterface: Se5/0:15Signaling Stack: ISDNInterface: Se5/1:15Signaling Stack: ISDNInterface: Se6/0:15Signaling Stack: ISDNInterface: Se6/1:15CDAPI Message Buffers=====================Used Msg Buffers: 0, Free Msg Buffers: 9600Used Raw Buffers: 0, Free Raw Buffers: 4800Used Large-Raw Buffers: 0, Free Large-Raw Buffers: 480The following sample output shows the results of the show cdapi command for a PRI voice port on a Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator:
Router# show cdapiRegistered CDAPI Applications/Stacks====================================Application: TSP CDAPI Application VoiceApplication Type(s) : Voice Facility SignalingApplication Level : TunnelApplication Mode : EnblocSignaling Stack: ISDNInterface: Se1:15CDAPI Message Buffers=====================Used Msg Buffers: 2, Free Msg Buffers: 1198Used Raw Buffers: 2, Free Raw Buffers: 598Used Large-Raw Buffers: 0, Free Large-Raw Buffers: 60
QSIG Support Troubleshooting Tips
Table 49 lists debug and show commands that can help you analyze problems with your QSIG configuration. The documents listed at the beginning of this chapter include information about these commands.
Configuring ISDN PRI Q.931 Support
To configure ISDN PRI Q.931 support on a Cisco 2600 or Cisco 3600 series router, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
ISDN Voice Interface Configuration Examples
This section provides specific configuration examples for ISDN interfaces in the following sections:
•
ISDN to PBX and ISDN to PSTN Configuration Examples
•
QSIG Support Configuration Examples
•
Q.931 Support Configuration Examples
ISDN to PBX and ISDN to PSTN Configuration Examples
This section includes the following configuration examples:
•
ISDN Connection to a PBX Configuration Example
•
ISDN Connection to the PSTN Configuration Example
The configuration examples included in this section correspond to the topology shown in Figure 111. The routers each include a BRI VIC and a 2-slot VNM, along with other voice interface cards and modules that are included for completeness. Router A is connected to a PBX through the BRI VIC and is connected to Router B by a serial Ethernet interface. Router B includes a BRI VIC for connection to the PSTN in order to process voice calls from off-premises terminal equipment.
For more information about IP configuration, refer to the Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide. For more information about VoIP, VoFR, and VoATM configuration, see the appropriate configuration information elsewhere in this configuration guide.
Figure 111 Configuration Example Topology
ISDN Connection to a PBX Configuration Example
The following configuration example illustrates the configuration of the BRI interfaces on a Cisco 3640 router (Router A in Figure 111) connected to a PBX:
interface BRI1/0no ip addressisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn overlap-receivingisdn protocol-emulate networkisdn layer1-emulate networkisdn T306-30000isdn sending-completeisdn skipsend-idverifyisdn incoming-voice voice!interface BRI1/1no ip addressisdn switch-type basic-net3isdn overlap-receivingisdn protocol-emulate networkisdn layer1-emulate networkisdn T306-30000isdn sending-completeisdn skipsend-idverifyisdn incoming-voice voice!ip default-gateway 1.14.0.1ip classlessip route 2.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Ethernet0/1ip route 2.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Serial0/1ip route 172.22.66.33 255.255.255.255 Ethernet0/0!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0transport input noneline aux 0line vty 0 4loginISDN Connection to the PSTN Configuration Example
The following configuration example illustrates the configuration of the BRI interfaces on a Cisco 2600 series router (Router B in Figure 111) connected to the public ISDN telephone network:
interface BRI1/0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastisdn switch-type basic-ni1isdn twait-disableisdn spid1 14085552111 5552111isdn spid2 14085552112 5552112isdn incoming-voice voiceinterface BRI1/1no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastisdn switch-type basic-ni1isdn twait-disableisdn spid1 14085552111 5552111isdn spid2 14085552112 5552112isdn incoming-voice voice!ip classlessip route 3.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Ethernet0/1ip route 3.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Serial0/1ip route 172.21.66.0 255.255.255.0 Ethernet0/0!!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0transport input noneline aux 0line vty 0 4loginQSIG Support Configuration Examples
The following configuration examples shows QSIG configuration on several supported routers:
•
QSIG Support on Cisco 3600 Series Routers Example
•
QSIG Support on Cisco 7200 Series Routers Example
•
QSIG Support on Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators Example
QSIG Support on Cisco 3600 Series Routers Example
The following configuration example shows how a Cisco 3660 series router can be configured for E1 and PRI with QSIG signaling support using VoIP and VoATM:
...hostname router3660!!!!!!memory-size iomem 20voice-card 5!voice-card 6!ip subnet-zero!isdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn voice-call-failure 0!!!!controller E1 5/0pri-group timeslots 1-5,16!controller E1 5/1pri-group timeslots 1-31!controller E1 6/0pri-group timeslots 1-31!controller E1 6/1pri-group timeslots 1-31!!!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.7.72.9 255.255.255.0speed autohalf-duplex!interface FastEthernet0/1ip address 10.100.100.7 255.255.255.0no keepaliveduplex autospeed autohold-queue 1000 in!interface Serial2/0no ip addressshutdown!interface Serial2/1no ip addressshutdown!interface Serial2/2no ip addressshutdown!interface Serial2/3no ip addressshutdown!interface ATM3/0no ip addressatm clock INTERNALno atm ilmi-keepalivepvc 10/40vbr-rt 155000 50000 64000encapsulation aal5mux voice!interface Serial5/0:15no ip addressip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn overlap-receivingisdn incoming-voice voiceno cdp enable!interface Serial5/1:15no ip addressip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn incoming-voice voicefair-queue 64 256 0no cdp enable!interface Serial6/0:15no ip addressip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn incoming-voice voicefair-queue 64 256 0no cdp enable!interface Serial6/1:15no ip addressip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn incoming-voice voicefair-queue 64 256 0no cdp enable!ip classlessip route 192.168.17.125 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0no ip http server!!map-class frame-relay frs0frame-relay voice bandwidth 1260000frame-relay fragment 200no frame-relay adaptive-shapingframe-relay cir 1260000frame-relay fair-queue!voice-port 1/0/0modem passthrough systemtiming hookflash-in 0!voice-port 1/0/1modem passthrough systemtiming hookflash-in 0!voice-port 5/0:15compand-type a-law!voice-port 5/1:15compand-type a-lawcptone DE!voice-port 6/0:15compand-type a-lawcptone DE!voice-port 6/1:15no echo-cancel enablecompand-type a-lawcptone DE!dial-peer voice 1 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 21...modem passthrough systemdirect-inward-dial!dial-peer voice 51 voipshutdowndestination-pattern 6504007modem passthrough systemsession target ipv4:100.100.100.3!dial-peer voice 2 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 21...modem passthrough systemdirect-inward-dialport 5/1:15!dial-peer voice 3 voipshutdowndestination-pattern 22...modem passthrough systemsession target ipv4:100.100.100.6!dial-peer voice 5 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 22...modem passthrough systemdirect-inward-dialprefix 4006!dial-peer voice 13 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 21...modem passthrough systemdirect-inward-dialport 6/0:15!dial-peer voice 6 potsdestination-pattern 21...modem passthrough systemdirect-inward-dialport 6/1:15!dial-peer voice 44 voatmdestination-pattern 22...modem passthrough systemsession target ATM3/0 pvc 10/40!dial-peer voice 20 potsincoming called-number 4...destination-pattern 4007modem passthrough systemdirect-inward-dialport 5/0:15prefix 4007!dial-peer voice 21 potsdestination-pattern 4006modem passthrough systemdirect-inward-dialport 5/0:15prefix 4006!!line con 0transport input noneline aux 0line vty 0 4login!endQSIG Support on Cisco 7200 Series Routers Example
The following configuration examples show how QSIG protocol support is configured with VoFR on Router A, where calls are originated, and Router B, where calls terminate:
QSIG Support on Cisco MC3810 Multiservice Concentrators Example
The following configuration example shows how a Cisco MC3810 multiservice concentrator can be configured for E1 and PRI with QSIG signaling support and VoIP and VoFR:
...hostname Router3810!!!!network-clock base-rate 56kip subnet-zero!isdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn voice-call-failure 0!!!!controller T1 0mode atmframing esfclock source internallinecode b8zs!controller E1 1pri-group timeslots 1-7,16!!!interface Ethernet0ip address 100.100.100.6 255.255.255.0no ip directed-broadcast!interface Serial0bandwidth 2000ip address 10.168.14.1 255.255.255.0no ip directed-broadcastencapsulation frame-relayno ip mroute-cacheno keepaliveclockrate 2000000cdp enableframe-relay traffic-shapingframe-relay interface-dlci 100class frs0vofr cisco!interface Serial1no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastshutdown!interface Serial1:15no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn overlap-receivingisdn incoming-voice voicefair-queue 64 256 0no cdp enable!interface ATM0no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastip mroute-cacheno atm ilmi-keepalivepvc 10/42encapsulation aal5mux voice!!interface FR-ATM20no ip addressno ip directed-broadcastshutdown!no ip http serverip classlessip route 223.255.254.0 255.255.255.0 Ethernet0!!map-class frame-relay frs0frame-relay voice bandwidth 1260000frame-relay fragment 200no frame-relay adaptive-shapingframe-relay cir 1260000frame-relay fair-queue!map-class frame-relay frsisco!voice-port 1:15compand-type a-law!dial-peer voice 100 voatmshutdowndestination-pattern 4...session target ATM0 pvc 10/42codec g729ar8no vad!dial-peer voice 1 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 3001!dial-peer voice 42 vofrdestination-pattern 4006session target Serial0 100signal-type ext-signal!dial-peer voice 21 potsdestination-pattern 4007direct-inward-dialport 1:15prefix 4007!dial-peer voice 12 voipshutdowndestination-pattern 4006session target ipv4:100.100.100.7...Q.931 Support Configuration Examples
The following configuration example shows how a Cisco 3660 router can be configured for E1 and PRI with network-side support using VoIP:
...hostname router3660!!memory-size iomem 20voice-card 5!voice-card 6!ip subnet-zero!isdn switch-type primary-net5isdn voice-call-failure 0!controller E1 3/0pri-group timeslots 1-5,16!controller E1 3/1pri-group timeslots 1-31!controller E1 4/0pri-group timeslots 1-31!controller E1 4/1pri-group timeslots 1-31!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.7.72.9 255.255.255.0speed autohalf-duplex!interface FastEthernet0/1ip address 10.100.100.7 255.255.255.0no keepaliveduplex autospeed autohold-queue 1000 in!interface Serial2/0no ip addressshutdown!interface Serial2/1no ip addressshutdown!interface Serial2/2no ip addressshutdown!interface Serial2/3no ip addressshutdown!interface Serial5/0:15no ip addressip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn overlap-receivingisdn incoming-voice voiceisdn protocol-emulate networkno cdp enable!interface Serial5/1:15no ip addressip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn incoming-voice voicefair-queue 64 256 0no cdp enable!interface Serial6/0:15no ip addressip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn incoming-voice voicefair-queue 64 256 0isdn protocol-emulate networkno cdp enable!interface Serial6/1:15no ip addressip mroute-cacheno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-qsigisdn incoming-voice voicefair-queue 64 256 0no cdp enable!ip classlessip route 223.255.254.254 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0no ip http server!!voice-port 1/0/0timing hookflash-in 0!voice-port 1/0/1timing hookflash-in 0!voice-port 5/0:15compand-type a-law!voice-port 5/1:15compand-type a-lawcptone DE!voice-port 6/0:15compand-type a-lawcptone DE!voice-port 6/1:15no echo-cancel enablecompand-type a-lawcptone DE!dial-peer voice 1 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 21...direct-inward-dial!dial-peer voice 51 voipshutdowndestination-pattern 6504007session target ipv4:100.100.100.3!dial-peer voice 2 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 21...direct-inward-dialport 5/1:15!dial-peer voice 3 voipshutdowndestination-pattern 22...session target ipv4:100.100.100.6!dial-peer voice 5 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 22...modem passthrough systemdirect-inward-dialprefix 4006!dial-peer voice 13 potsshutdowndestination-pattern 21...direct-inward-dialport 6/0:15!dial-peer voice 6 potsdestination-pattern 21...direct-inward-dialport 6/1:15!dial-peer voice 20 potsincoming called-number 4...destination-pattern 4007direct-inward-dialport 5/0:15prefix 4007!dial-peer voice 21 potsdestination-pattern 4006direct-inward-dialport 5/0:15prefix 4006!!line con 0transport input noneline aux 0line vty 0 4login!end

 Feedback
Feedback