-
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI, 8.2
-
About This Guide
-
Glossary
- Getting Started and General Information
- Configuring Access Lists
- Configuring IP Routing
- Configuring NAT
- Configuring High Availability
- Configuring Access Control
- Configuring Application Layer Procotol Inspection
- Configuring Unified Communications
- Configuring Advanced Connection Settings
- Configuring Applications on SSMs and SSCs
-
Configuring VPN
-
Configuring IPSec and ISAKMP
-
Configuring L2TP over IPSec
-
Setting General VPN Parameters
-
Configuring Tunnel Groups, Group Policies, and Users
-
Configuring IP Addresses for VPN
-
Configuring Remote Access VPNs
-
Configuring Network Admission Control
-
Configuring Easy VPN on the ASA 5505
-
Configuring the PPPoE Client
-
Configuring LAN-to-LAN VPNs
-
Configuring Clientless SSL VPN
-
Configuring AnyConnect VPN Client Connections
-
Configuring Certificates
-
- Monitoring
- System Administration
- Reference
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
Configuring Neighbor Solicitation Messages
Configuring Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
Information About Neighbor Solicitation Messages
Licensing Requirements for Neighbor Solicitation Messages
Guidelines and Limitations for the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
Default Settings for the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
Configuring the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
Monitoring Neighbor Solicitation Message Intervals
Feature History for Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
Configuring the Neighbor Reachable Time
Information About Neighbor Reachable Time
Licensing Requirements for Neighbor Reachable Time
Guidelines and Limitations for Neighbor Reachable Time
Default Settings for Neighbor Reachable Time
Configuring Neighbor Reachable Time
Monitoring Neighbor Reachable Time
Feature History for Neighbor Reachable Time
Configuring Router Advertisement Messages
Information About Router Advertisement Messages
Configuring the Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Licensing Requirements for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Guidelines and Limitations for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Default Settings for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Configuring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Monitoring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Feature History for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Configuring the Router Lifetime Value
Licensing Requirements for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Guidelines and Limitations for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Default Settings for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Configuring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Monitoring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Feature History for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Licensing Requirements for IPv6 Prefixes
Guidelines and Limitations for IPv6 Prefixes
Default Settings for IPv6 Prefixes
Feature History for IPv6 Prefixes
Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Licensing Requirements for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Guidelines and Limitations for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Default Settings for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Monitoring Router Advertisement Messages
Feature History for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
Information About a Static IPv6 Neighbor
Licensing Requirements for Static IPv6 Neighbor
Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
Monitoring Neighbor Solicitation Messages
Feature History for Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
Configuring IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses ICMPv6 messages and solicited-node multicast addresses to determine the link-layer address of a neighbor on the same network (local link), verify the readability of a neighbor, and keep track of neighboring routers.
This chapter describes how to enable and configure IPv6 neighbor discovery on the security appliance, and it includes the following topics:
•
Configuring Neighbor Solicitation Messages
•
Configuring Router Advertisement Messages
•
Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
Configuring Neighbor Solicitation Messages
This section includes the following configuration task topics:
•
Configuring Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
•
Configuring the Neighbor Reachable Time
Configuring Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
•
Information About Neighbor Solicitation Messages
•
Licensing Requirements for Neighbor Solicitation Messages
•
Guidelines and Limitations for the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
•
Default Settings for the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
•
Configuring the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
•
Monitoring Neighbor Solicitation Message Intervals
•
Feature History for Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
Information About Neighbor Solicitation Messages
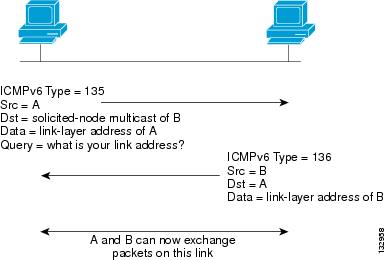
Neighbor solicitation messages (ICMPv6 Type 135) are sent on the local link by nodes attempting to discover the link-layer addresses of other nodes on the local link. The neighbor solicitation message is sent to the solicited-node multicast address.The source address in the neighbor solicitation message is the IPv6 address of the node sending the neighbor solicitation message. The neighbor solicitation message also includes the link-layer address of the source node.
After receiving a neighbor solicitation message, the destination node replies by sending a neighbor advertisement message (ICPMv6 Type 136) on the local link. The source address in the neighbor advertisement message is the IPv6 address of the node sending the neighbor advertisement message; the destination address is the IPv6 address of the node that sent the neighbor solicitation message. The data portion of the neighbor advertisement message includes the link-layer address of the node sending the neighbor advertisement message.
After the source node receives the neighbor advertisement, the source node and destination node can communicate. Figure 25-1 shows the neighbor solicitation and response process.
Figure 25-1 IPv6 Neighbor Discovery—Neighbor Solicitation Message
Neighbor solicitation messages are also used to verify the reachability of a neighbor after the link-layer address of a neighbor is identified. When a node wants to verifying the reachability of a neighbor, the destination address in a neighbor solicitation message is the unicast address of the neighbor.
Neighbor advertisement messages are also sent when there is a change in the link-layer address of a node on a local link. When there is such a change, the destination address for the neighbor advertisement is the all-nodes multicast address.
This section shows how you can configure the neighbor solicitation message interval and neighbor reachable time on a per-interface basis.
Licensing Requirements for Neighbor Solicitation Messages
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
Guidelines and Limitations for the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature:
•
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
Context Mode Guidelines
Supported in single and multiple context mode.
Firewall Mode Guidelines
Supported in routed firewall mode only. Transparent mode is not supported.
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
The interval value is included in all IPv6 router advertisements sent out this interface.
Default Settings for the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
Table 25-13 lists the default settings for neighbor solicitation message parameters.
Table 25-1 Default Neighbor Solicitation Messages Parameters
value (transmission interval)
1000 seconds between neighbor solicitation transmissions
Configuring the Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
To configure the interval between IPv6 neighbor solicitation retransmissions on an interface, enter the following command:
Example
The following example configures an IPv6 neighbor solicitation transmission interval of 9000 milliseconds for Gigabitethernet 0/0:
hostname (config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
hostname (config-if)# ipv6 nd ns-interval 9000
Monitoring Neighbor Solicitation Message Intervals
To monitor IPv6 neighbor solicitation message intervals, perform one of the following tasks:
Feature History for Neighbor Solicitation Message Interval
Table 25-14 lists the release history for this feature.
Configuring the Neighbor Reachable Time
This section includes the following topics:
•
Information About Neighbor Reachable Time
•
Licensing Requirements for Neighbor Reachable Time
•
Guidelines and Limitations for Neighbor Reachable Time
•
Default Settings for Neighbor Reachable Time
•
Configuring Neighbor Reachable Time
•
Monitoring Neighbor Reachable Time
•
Feature History for Neighbor Reachable Time
Information About Neighbor Reachable Time
The neighbor reachable time enables detecting unavailable neighbors. Shorter configured times enable detecting unavailable neighbors more quickly, however, shorter times consume more IPv6 network bandwidth and processing resources in all IPv6 network devices. Very short configured times are not recommended in normal IPv6 operation.
Licensing Requirements for Neighbor Reachable Time
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
Guidelines and Limitations for Neighbor Reachable Time
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature:
•
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
Context Mode Guidelines
Supported in single and multiple context mode.
Firewall Mode Guidelines
Supported in routed firewall mode only. Transparent mode is not supported.
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
•
The interval value is included in all IPv6 router advertisements sent out this interface.
•
The configured time enables detecting unavailable neighbors. Shorter configured times enable detecting unavailable neighbors more quickly; however, shorter times consume more IPv6 network bandwidth and processing resources in all IPv6 network devices. Very short configured times are not recommended in normal IPv6 operation.
Default Settings for Neighbor Reachable Time
Table 25-3 lists the default settings for neighbor reachable time parameters.
Table 25-3 Default Neighbor Reachable Time Parameters
value (time mode is reachable)
The default is 0.
Configuring Neighbor Reachable Time
To configure the amount of time that a remote IPv6 node is considered reachable after a reachability confirmation event has occurred, enter the following command:
Example
The following example configures an IPv6 reachable time of 1700000 milliseconds for the selected interface, Gigabitethernet 0/0:
hostname (config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
hostname (config-if)# ipv6 nd reachable-time 1700000
Monitoring Neighbor Reachable Time
To monitor IPv6 neighbor reachable time, perform one of the following tasks:
Feature History for Neighbor Reachable Time
Table 25-4 lists the release history for this feature.
Configuring Router Advertisement Messages
A security appliance can participate in router advertisements so that neighboring devices can dynamically learn a default router address.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Information About Router Advertisement Messages
•
Configuring the Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Configuring the Router Lifetime Value
•
Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Information About Router Advertisement Messages
A security appliance can participate in router advertisements so that neighboring devices can dynamically learn a default router address. Router advertisement messages (ICMPv6 Type 134) are periodically sent out each IPv6 configured interface of the ASA. The router advertisement messages are sent to the all-nodes multicast address.
Figure 25-2 IPv6 Neighbor Discovery—Router Advertisement Message
Router advertisement messages typically include the following information:
•
One or more IPv6 prefix that nodes on the local link can use to automatically configure their IPv6 addresses.
•
Lifetime information for each prefix included in the advertisement.
•
Sets of flags that indicate the type of autoconfiguration (stateless or stateful) that can be completed.
•
Default router information (whether the router sending the advertisement should be used as a default router and, if so, the amount of time (in seconds) the router should be used as a default router).
•
Additional information for hosts, such as the hop limit and MTU a host should use in packets that it originates.
•
The amount of time between neighbor solicitation message retransmissions on a given link.
•
The amount of time a node considers a neighbor reachable.
Router advertisements are also sent in response to router solicitation messages (ICMPv6 Type 133). Router solicitation messages are sent by hosts at system startup so that the host can immediately autoconfigure without needing to wait for the next scheduled router advertisement message. Because router solicitation messages are usually sent by hosts at system startup, and the host does not have a configured unicast address, the source address in router solicitation messages is usually the unspecified IPv6 address (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0). If the host has a configured unicast address, the unicast address of the interface sending the router solicitation message is used as the source address in the message. The destination address in router solicitation messages is the all-routers multicast address with a scope of the link. When a router advertisement is sent in response to a router solicitation, the destination address in the router advertisement message is the unicast address of the source of the router solicitation message.
You can configure the following settings for router advertisement messages:
•
The time interval between periodic router advertisement messages.
•
The router lifetime value, which indicates the amount of time IPv6 nodes should consider the ASA to be the default router.
•
The IPv6 network prefixes in use on the link.
•
Whether or not an interface transmits router advertisement messages.
Unless otherwise noted, the router advertisement message settings are specific to an interface and are entered in interface configuration mode. See the following topics for information about changing these settings:
•
Configuring the Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Configuring the Router Lifetime Value
•
Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Configuring the Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
This section shows how to configure the interval between IPv6 router advertisement transmissions on an interface.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Licensing Requirements for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Guidelines and Limitations for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Default Settings for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Configuring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Monitoring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Feature History for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Licensing Requirements for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
Guidelines and Limitations for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature:
•
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
Context Mode Guidelines
Supported in single and multiple context mode.
Firewall Mode Guidelines
Supported in routed firewall mode only. Transparent mode is not supported.
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
The interval between transmissions should be less than or equal to the IPv6 router advertisement lifetime if the security appliance is configured as a default router by using the ipv6 nd ra-lifetime command. To prevent synchronization with other IPv6 nodes, randomly adjust the actual value used to within 20 percent of the specified value.
Default Settings for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Table 25-5 lists the default settings for neighbor reachable time parameters.
Table 25-5 Default Router Advertisement Transmission Interval Parameters
value (interval between transmissions)
The default is 200 seconds.
Configuring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
To configure the interval between IPv6 router advertisement transmissions on an interface, enter the following command:
Example
The following example configures an IPv6 router advertisement interval of 201 seconds for the selected interface, Gigabitethernet 0/0:
hostname (config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
hostname (config-if)# ipv6 nd ra-interval 201
Monitoring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
To monitor IPv6 neighbor reachable time, perform one of the following tasks:
Feature History for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Table 25-6 lists the release history for this feature.
Configuring the Router Lifetime Value
This section shows how to configure the interval between IPv6 router advertisement transmissions on an interface.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Licensing Requirements for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Guidelines and Limitations for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Default Settings for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Configuring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Monitoring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
•
Feature History for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Licensing Requirements for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
Guidelines and Limitations for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature:
•
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
Context Mode Guidelines
Supported in single and multiple context mode.
Firewall Mode Guidelines
Supported in routed firewall mode only. Transparent mode is not supported.
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
The interval between transmissions should be less than or equal to the IPv6 router advertisement lifetime if the security appliance is configured as a default router by using the ipv6 nd ra-lifetime command. To prevent synchronization with other IPv6 nodes, randomly adjust the actual value used to within 20 percent of the specified value.
Default Settings for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Table 25-7 lists the default settings for neighbor reachable time parameters.
Table 25-7 Default Router Advertisement Transmission Interval Parameters
value (interval between transmissions)
The default is 200 seconds.
Configuring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
To configure the interval between IPv6 router advertisement transmissions on an interface, enter the following command:
Example
The following example configures an IPv6 router advertisement interval of 201 seconds for the selected interface, Gigabitethernet 0/0:
hostname (config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
hostname (config-if)# ipv6 nd ra-interval 201
Monitoring Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
To monitor IPv6 neighbor reachable time, perform one of the following tasks:
Where to Go Next
Configure the "router lifetime" value in IPv6 router advertisements on an interface with the ipv6 nd ra-lifetime command.
Feature History for Router Advertisement Transmission Interval
Table 25-8 lists the release history for this feature.
Configuring the IPv6 Prefix
Stateless autoconfiguration uses IPv6 prefixes provided in router advertisement messages to create the global unicast address from the link-local address. The prefix advertisement can be used by neighboring devices to autoconfigure their interface addresses. You can configure which IPv6 prefixes ar e included in IPv6 router advertisements.
This section shows how to configure IPv6 prefixes and includes the following topics:
•
Licensing Requirements for IPv6 Prefixes
•
Guidelines and Limitations for IPv6 Prefixes
•
Default Settings for IPv6 Prefixes
•
Feature History for IPv6 Prefixes
Licensing Requirements for IPv6 Prefixes
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
Guidelines and Limitations for IPv6 Prefixes
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature:
•
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
Context Mode Guidelines
Supported in single and multiple context mode.
Firewall Mode Guidelines
Supported in routed firewall mode only. Transparent mode is not supported.
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
The ipv6 nd prefix command allows control over the individual parameters per prefix, including whether or not the prefix should be advertised.
By default, prefixes configured as addresses on an interface using the ipv6 address command are advertised in router advertisements. If you configure prefixes for advertisement using the ipv6 nd prefix command, then only these prefixes are advertised.
The default keyword can be used to set default parameters for all prefixes.
A date can be set to specify the expiration of a prefix. The valid and preferred lifetimes are counted down in real time. When the expiration date is reached, the prefix will no longer be advertised.
When onlink is "on" (by default), the specified prefix is assigned to the link. Nodes sending traffic to such addresses that contain the specified prefix consider the destination to be locally reachable on the link.
When autoconfig is "on" (by default), it indicates to hosts on the local link that the specified prefix can be used for IPv6 autoconfiguration.
For stateless autoconfiguration to work properly, the advertised prefix length in router advertisement messages must always be 64 bits.
Default Settings for IPv6 Prefixes
Table 25-9 lists the default settings for neighbor reachable time parameters.
Configuring IPv6 Prefixes
To configure the which IPv6 prefixes are included in IPv6 router advertisements, enter the following command:
Example
The following example includes the IPv6 prefix 2001:200::/35, with a valid lifetime of 1000 seconds and a preferred lifetime of 900 seconds, in router advertisements sent out on the specified interface, which is Gigabitethernet 0/0:
hostname (config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
hostname (config-if)# ipv6 nd prefix 2001:200:200::/35 1000 900
Monitoring IPv6 Prefixes
To monitor IPv6 neighbor reachable time, perform one of the following tasks:
Additional References
For additional information related to implementing IPv6 router advertisement messages, see the following sections:
•
Related Documents for IPv6 Prefixes
Related Documents for IPv6 Prefixes
RFCs for IPv6 Prefixes
Feature History for IPv6 Prefixes
Table 25-10 lists the release history for this feature.
Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Router advertisement messages are automatically sent in response to router solicitation messages. You may want to disable these messages on any interface for which you do not want the security appliance to supply the IPv6 prefix (for example, the outside interface).
This section shows how to suppress IPv6 router advertisement transmissions on an interface, and it includes the following topics:
•
Licensing Requirements for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
•
Guidelines and Limitations for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
•
Default Settings for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
•
Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
•
Monitoring Router Advertisement Messages
•
Feature History for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Licensing Requirements for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
Guidelines and Limitations for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature:
•
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
Context Mode Guidelines
Supported in single and multiple context mode.
Firewall Mode Guidelines
Supported in routed firewall mode only. Transparent mode is not supported.
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
The "router lifetime" value is included in all IPv6 router advertisements sent out the interface. The value indicates the usefulness of the security appliance as a default router on this interface.
Setting the value to a non-zero value indicates that the security appliance should be considered a default router on this interface. The no-zero value for the "router lifetime" value should not be less than the router advertisement interval.
Default Settings for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Table 25-11 lists the default settings for neighbor reachable time parameters.
Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
To configure the "router lifetime" value in IPv6 router advertisements on an interface, enter the following command. Entering this command causes the security appliance to appear as a regular IPv6 neighbor on the link and not as an IPv6 router.
Example
The following example configures an IPv6 router advertisement lifetime of 1801 seconds for the specified interface, which is Gigabitethernet 0/0:
hostname (config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
hostname (config-if)# ipv6 nd ra-lifetime 1801
Monitoring Router Advertisement Messages
To monitor IPv6 neighbor reachable time, perform one of the following tasks:
Feature History for Suppressing Router Advertisement Messages
Table 25-12 lists the release history for this feature.
Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
This section includes the following topics:
•
Information About a Static IPv6 Neighbor
•
Licensing Requirements for Static IPv6 Neighbor
•
Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
•
Monitoring Neighbor Solicitation Messages
•
Feature History for Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
Information About a Static IPv6 Neighbor
You can manually define a neighbor in the IPv6 neighbor cache. If an entry for the specified IPv6 address already exists in the neighbor discovery cache—learned through the IPv6 neighbor discovery process—the entry is automatically converted to a static entry. Static entries in the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache are not modified by the neighbor discovery process.
Licensing Requirements for Static IPv6 Neighbor
The following table shows the licensing requirements for this feature:
Guidelines and Limitations
This section includes the guidelines and limitations for this feature:
•
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
Context Mode Guidelines
Supported in single and multiple context mode.
Firewall Mode Guidelines
Supported in routed firewall mode only. Transparent mode is not supported.
Additional Guidelines and Limitations
The following guidelines and limitations apply for configuring a static IPv6 neighbor:
•
The ipv6 neighbor command is similar to the arp command. If an entry for the specified IPv6 address already exists in the neighbor discovery cache—learned through the IPv6 neighbor discovery process—the entry is automatically converted to a static entry. These entries are stored in the configuration when the copy command is used to store the configuration.
•
Use the show ipv6 neighbor command to view static entries in the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache.
•
The clear ipv6 neighbor command deletes all entries in the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache except static entries. The no ipv6 neighbor command deletes a specified static entry from the neighbor discovery cache; the command does not remove dynamic entries—entries learned from the IPv6 neighbor discovery process—from the cache. Disabling IPv6 on an interface by using the no ipv6 enable command deletes all IPv6 neighbor discovery cache entries configured for that interface except static entries (the state of the entry changes to INCMP [Incomplete]).
•
Static entries in the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache are not modified by the neighbor discovery process.
•
The clear ipv6 neighbor command does not remove static entries from the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache; it only clears the dynamic entries.
•
The ICMP syslogs generated are caused by a regular refresh of IPv6 neighbor entries. The ASA default timer for IPv6 neighbor entry is 30 seconds, so the ASA would generate ICMPv6 neighbor discovery and response packets about every 30 seconds. If the ASA has both failover LAN and state interfaces configured with IPv6 addresses, then every 30 seconds, ICMPv6 neighbor discovery and response packets will be generated by both ASAs for both configured and link-local IPv6 addresses. In addition, each packet will generate several syslogs (ICMP connection and local-host creation or teardown), so it may appear that constant ICMP syslogs are being generated. The refresh time for IPV6 neighbor entry is configurable on the regular data interface, but not configurable on the failover interface. However, the CPU impact for this ICMP neighbor discovery traffic is minimal.
Default Settings
Table 25-13 lists the default settings for static IPv6 neighbor parameters.
Table 25-13 Default Static IPv6 Neighbor Parameters
Static IPv6 neighbor
Static entries are not configured in the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache.
Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
To configure a static entry in the IPv6 neighbor discovery cache, enter the following command:
Example
The following example adds a static entry for an inside host with an IPv6 address of 3001:1::45A and a MAC address of 002.7D1a.9472 to the neighbor discovery cache:
hostname)config-if)# ipv6 neighbor 3001:1::45A inside 002.7D1A.9472Monitoring Neighbor Solicitation Messages
To monitor IPv6 neighbor discovery, perform the following task:
Feature History for Configuring a Static IPv6 Neighbor
Table 25-14 lists the release history for this feature.

 Feedback
Feedback