-
Cisco Prime Infrastructure 2.0 User Guide
-
Preface
- Getting Started
- Designing the Network
-
Operating the Network
-
Operating and Monitoring the Network
-
Monitoring Alarms
-
Updating Device Inventory
-
Configuring Device Features
-
Working With Device Configurations
-
Maintaining Software Images
-
Working with Wireless Operational Tools
-
Ensuring Consistent Application Experiences
-
Working with Wireless Mobility
-
Configuring the Cisco AppNav Solution
-
Configuring WAAS Container
-
Troubleshooting
-
Reports
-
-
Prime Infrastructure User Interface Reference
-
Table Of Contents
Adding Devices to Prime Infrastructure
Downloading Software Updates Without Cisco.com Access
Configuring Email Server Settings to Receive Notifications
Adding Devices Using Discovery
Understanding the Discovery Process
Sample IPv4 IP Addresses for Ping Sweep
Importing Devices from Another Source
CSV File Requirements for Importing Devices
Validating That Devices Were Added Successfully
Adding NAM HTTP/HTTPS Credentials
Adding Devices to Prime Infrastructure
Before You Add Devices
Before you add devices to Cisco Prime Infrastructure, complete the following tasks:
•
Configure the Prime Infrastructure server backup to prevent the loss of any data—See Configuring Server Backups.
•
Install any Prime Infrastructure updates—See Installing Software Updates.
•
Set up email notifications—See Configuring Email Server Settings to Receive Notifications.
Configuring Server Backups
To prevent the loss of any acquired data, configure a Prime Infrastructure server backup before you add devices.
To configure a server backup:
Step 1
Choose Administration > Background Tasks > Other Background Tasks > Prime Infrastructure Server Backup.
Step 2
Use the default repository, defaultRepo, or complete the required fields to create an external backup repository, then click Submit.
By default, the server is backed up weekly and is stored in the /localdisk/defaultRepo directory with the filename hostname-backup_date_time.tar.gpg. You can also specify a different backup schedule.
Note
You can configure SFTP as the defaultRepo repository through the CLI, and then select that repository in the user interface for the server backup. For more details, see "Backing Up and Restoring Prime Infrastructure" in the Cisco Prime Infrastructure 2.0 Administrator Guide.
Installing Software Updates
Make sure that you have installed any Prime Infrastructure updates by choosing Administration > Software Update. If your Prime Infrastructure server has access to cisco.com, you can view and install any updates. If your Prime Infrastructure server does not have access to Cisco.com, see Downloading Software Updates Without Cisco.com Access.
Step 1
Log in to the Prime Infrastructure server and choose Administration > Software Update.
Step 2
Click Check for Updates.
Step 3
Enter your cisco.com credentials and select the software updates you want to install.
You might be prompted to restart the Prime Infrastructure server to complete the update.
Downloading Software Updates Without Cisco.com Access
If your Prime Infrastructure server does not have access to cisco.com, you can download software updates by following these steps:
Step 1
Go to www.cisco.com/go/primeinfrastructure, then under Support, select Download Software for this Product, then select the required Cisco Prime Infrastructure version.
Step 2
Save the software update file, which has the file extension UBF.
Step 3
Log in to the Prime Infrastructure server and choose Administration > Software Update.
Step 4
Click Upload Update File and browse to the location where you saved the software update file.
Step 5
Confirm the name and description.
Step 6
Select the software updates you want to install, then click Install.
If required, you might be prompted to stop and restart the Prime Infrastructure server.
Configuring Email Server Settings to Receive Notifications
You can configure mail server settings to specify the email addresses that receive notifications when Prime Infrastructure has completed discovering the devices in your network, as well as notifications of alarms and reports.
To configure discovery email notifications:
Step 1
Choose Administration > System Settings > Mail Server Configuration.
Step 2
Enter the required information, then click Save.
Methods for Adding Devices
You can add devices to Prime Infrastructure in one of the following ways:
•
Use an automated process—See Adding Devices Using Discovery.
•
Import devices from a CSV file—See Importing Devices from Another Source.
•
Add devices manually by entering IP address and device credential information—See Adding Devices Manually.
Adding Devices Using Discovery
When you run discovery, Prime Infrastructure discovers the devices and, after obtaining access, collects device inventory data. We recommend that you run discovery when you are first getting started with Prime Infrastructure.
Prime Infrastructure uses SNMP polling to gather information about your network devices within the range of IP addresses you specify. If you have CDP enabled on your network devices, Prime Infrastructure uses the seed device you specify to discover the devices in your network.
You can discover your devices by:
•
Configuring discovery settings—This method is recommended if you want to specify settings and rerun discovery in the future using the same settings. See Running Discovery.
•
Running Quick Discovery—Quick Discovery quickly ping sweeps your network and uses SNMP polling to get details on the devices. See Running Quick Discovery.
Understanding the Discovery Process
Prime Infrastructure performs the following steps during the discovery process:
1.
Using ICMP ping, determine if each device is reachable. If Prime Infrastructure is unable to reach the device, the device status is Unreachable.
2.
Verify the SNMP credentials. If the SNMP credentials are not valid, the device status is Unreachable.
The device status is Reachable when Prime Infrastructure can reach the device and has verified that the SNMP credentials are correct.
3.
Verify Telnet and SSH credentials.
4.
Start the inventory collection process to gather all device information.
5.
Add the devices to the Device Work Center.
Running Discovery
Prime Infrastructure discovers devices with IPv4 addresses.
To run discovery:
Step 1
Choose Operate > Discovery, then click Discovery Settings.
Step 2
Click New.
Step 3
Enter the Protocol Settings as described in Table 3-1.
Step 4
Do one of the following:
•
Click Save to save your discovery settings and schedule your discovery to run at a specified time.
•
Click Run Now to run the discovery now.
Table 3-1 Discovery Protocol Settings
Ping Sweep Module
Prime Infrastructure gets a list of IP address ranges from a specified combination of IP address and subnet mask, then pings each IP address in the range to check the reachability of devices. See Sample IPv4 IP Addresses for Ping Sweep for more information.
CDP Module
Prime Infrastructure reads the cdpCacheAddress and cdpCacheAddressType MIB objects in the cdpCacheTable from CISCO-CDP-MIB on every newly found device as follows:
1.
The cdpCacheAddress MIB object is gathered from the current device. This provides a list of neighbor device addresses.
2.
If the neighbor device addresses do not already exist in the global device list, they are added to the local cache.
Check the Cross Router Boundary check box to specify that Prime Infrastructure should discover neighboring routers.
LLDP
Similar to CDP, but it allows the discovery of non-Cisco devices.
Routing Table
Queries and analyzes routing tables on seed routers to discover subnets and next-hop routers. This process discovers a router for every subnet on its list of known networks.
Address Resolution Protocol
The ARP Discovery Module depends on the Routing Table Discovery Module (RTDM), and is executed only when RTDM is processed. This precondition is identified based on the flags processed by the ARP Discovery Module, which are part of the DeviceObject.
The entries coming out of the ARP Discovery Module do not need to pass through RTDM because (per the router Discovery algorithm) active routers are those that RTDM must process and identify.
When the ARP table is fetched and the entries are not already discovered by RTDM, these entries (though they may represent routers) are not active routers and need not be passed on to RTDM. This is ensured by setting the ARP Discovery Module flag to Processed and leaving the RTDM flag set to Unprocessed.
When the RTDM comes across an entry with the RTDM flag unset and the ARP flag set, RTDM identifies the entry as a inactive router or other device and it leaves the entry as unprocessed. The ARP Discovery Module also ignores the entry according to the algorithm, based on the Processed flag set against the ARP Discovery Module.
When the ARP Discovery Module is checked, the device MAC address needs to be updated in the device information. Applications can retrieve this information in the adapter through the DeviceInfo object. By scanning the device MAC address, the applications can distinguish between Cisco and non-Cisco devices.
ARP cache from the device is collected using CidsARPInfoCollector. The MAC ID of the device is retrieved from this data and set in the DeviceInfo object.
Border Gateway Protocol
The BGP Discovery Module uses bgpPeerTable in the BGP4-MIB to find its BGP peer. The table contains its peers' IP addresses, which are added as clues to the local cache.
OSPF
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway routing protocol that uses the ospfNbrTable and ospfVirtNbrTable MIBs to find neighbor IP addresses.
IP Filter
Includes or excludes devices based on IP address. For example, you can enter any of the following strings and specify whether to include or exclude the devices found during discovery:
192.0.2.89
192.0.2.*192.0.
[16-32].89
[192-193].*.55.[16-32]System Location Filter
Includes or excludes devices based on System Location.
System Object ID Filter
Includes or excludes devices based on the sysObjectID string set on the device.
DNS Filter
Includes or excludes devices based on the domain name string set on the device.
SNMPv2 Credential
SNMP community string is a required parameter for discovering devices in the network using SNMPv2. You can enter multiple rows of credentials mapped to a specific IP address, or the IP address can be a wildcard; for example, *.*.*.*, 10.1.1.*. You cannot save or use the discovery settings if you do not specify SNMP credentials.
Telnet Credential
You can specify the Telnet credentials during discovery so that Prime Infrastructure can collect the device configurations and fully manage the devices. If you do not specify Telnet credentials in the discovery settings, Prime Infrastructure discovers the devices but is unable to manage the device until you specify the Telnet credentials.
SSH Credential
For full device support via SSH, you must use SSHv2 with a 1024 bit key. You can configure SSH before running discovery.
Note
We recommend that you select SSHv2 as the protocol for communicating with the device CLI because it allows the use of Web Services Management Agent (WSMA) for configuring devices. (For more information see, Configuring the Device using WSMA, page 13-1.)
SNMP V3 Credential
Prime Infrastructure supports SNMPv3 discovery for devices. The SNMP V3 modes are:
•
AuthPriv—Provides authentication based on the HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA algorithms. Provides DES 56-bit encryption in addition to authentication based on the CBC-DES (DES-56) standard.
•
AuthNoPriv—Provides authentication based on the HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA algorithms.
•
NoAuthNoPriv—Uses a user name match for authentication.
•
PrivType—Protocol used to secure the SNMP authentication request.
•
PrivPassword—Prefixed privacy passphrase for the SNMPv3 user.
Use Loopback IP
Prime Infrastructure uses the preferred management IP address from the loop back interface. If the device does not have a loopback interface, Prime Infrastructure uses similar logic to the OSPF algorithm to select the router's preferred management IP address.
Use SysName
Prime Infrastructure gets the preferred management IP address for the device using DNS lookup of the SysName for the device.
Use DNS Reverse Lookup
Prime Infrastructure gets the preferred management IP address by doing a reverse DNS lookup on the device IP address, followed by a forward DNS lookup.
After running discovery, click Device Work Center. See Device Work Center, page 10-4 for more information.
Sample IPv4 IP Addresses for Ping Sweep
Running Quick Discovery
If you want to quickly run discovery without specifying and saving your settings, you can use Quick Discovery.
To run Quick Discovery:
Step 1
Choose Operate > Discovery.
Step 2
On the top-right side of the page, click Quick Discovery.
Step 3
Complete the required fields, then click Run Now.
Verifying Discovery
When discovery has completed, you can verify that the process was successful.
To verify successful discovery:
Step 1
Choose Operate > Discovery.
Step 2
Choose the discovery job for which you want to view details.
Step 3
Under Discovery Job Instances, expand the arrow to view details about the devices that were discovered.
If devices are missing:
•
Change your discovery settings, then rerun the discovery. See Table 3-1 for information about discovery settings.
•
Add devices manually. See Adding Devices Manually for more information.
Importing Devices from Another Source
If you have another management system from which you want to import your devices, or if you want to import a spreadsheet that lists all of your devices and their attributes, you can add device information into Prime Infrastructure as explained in the following steps:
Step 1
Choose Operate > Device Work Center, then click Bulk Import.
Step 2
From the Operation drop-down menu, choose Device.
Step 3
Enter or browse to the CSV file that contains the devices that you want to import.
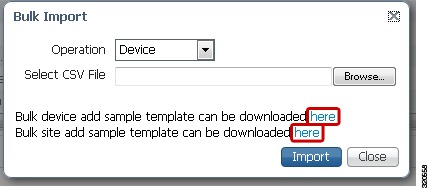
Step 4
Click the link to download a sample file that contains all of the fields and descriptions for the information that must be contained in your imported file. See Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Downloading a Sample Template for Importing Devices or Sites
Make sure that you retain the required information in the CSV file as explained in CSV File Requirements for Importing Devices.
Step 5
Click Import.
Step 6
Check the status of the import by choosing Administration > Jobs Dashboard.
Step 7
Click the arrow to expand the job details and view the details and history for the import job.
Note
If the importing CSV file contains any UDF parameters, ensure that UDF is configured in Administration > System Settings > User Defined Field prior to importing the devices. The UDF column in the CSV file must be begin with UDF: as indicated in the sample CSV template.
CSV File Requirements for Importing Devices
If you want to use a CSV file to import your devices or sites from another source into Prime Infrastructure, you can download a sample template by choosing Operate > Device Work Center, then clicking Bulk Import. Click the link to download a sample template as shown in Figure 3-1.
When you download a sample CSV template for importing devices or sites, the extent to which Prime Infrastructure can manage your devices depends on the information you provide in the CSV file. If you do not provide values for CLI user name, password, and enable password, Prime Infrastructure will have limited functionality and cannot modify device configurations, update device software images, and perform many other valuable functions.
•
For Prime Infrastructure to partially manage your devices, you must provide the following values in the CSV file:
–
Device IP address
–
SNMP version
–
SNMP read-only community strings
–
SNMP retry value
–
SNMP timeout value
•
For Prime Infrastructure to fully manage your devices, you must provide the following values in the CSV file:
–
Device IP address
–
SNMP version
–
SNMP read-only community strings
–
SNMP retry value
–
SNMP timeout value
–
Protocol
You must also provide values for the fields that correspond to the protocol you specify. For example, if you specify SNMPv3, you must specify values for the SNMPv3 fields in the sample CSV file such as the SNMPv3 user name and authorization password.
–
CLI user name
–
CLI password
–
CLI enable password
–
CLI timeout value
Adding Devices Manually
Adding devices manually is helpful if you want to add a single device. If you want to add all devices in your network, we recommend that you run discovery (see Running Discovery) or import devices from a CSV file (see Importing Devices from Another Source).
To add devices manually:
Step 1
Choose Operate > Device Work Center, then click Add.
Step 2
Complete the fields, then click Add to add the device with the settings you specified.
Note
User Defined Field (UDF) parameters are available only if you added them under Administration > System Settings > User Defined Field. Do not use the special characters : ; and # for UDF field parameters.
Validating That Devices Were Added Successfully
After collecting device information, Prime Infrastructure gathers and displays the configurations and the software images for the devices. To verify that your devices were successfully added to Prime Infrastructure, you can:
•
Choose Operate > Device Work Center and verify that the devices you added appear in the list. Hover your mouse over the Inventory Collection Status field and click the icon that appears to view details about the information that was collected for the device. Click a device name to view the device configurations and the software images that Prime Infrastructure collected from the devices.
Table 3-3 describes the possible Admin Status values.
•
Choose Administration > Jobs Dashboard, then click the arrow to expand the job details and view the details and history for the import job.
See Troubleshooting Unmanaged Devices, page 12-4 for information about how to resolve any errors.
Table 3-3 Descriptions of Device Admin Status
Managed
The inventory collection completed successfully and Prime Infrastructure is managing the device.
Unmanaged
You have exceeded the number of devices allowed by your license. Choose Administration > Licenses to view the status of your license. See the Cisco Prime Infrastructure 2.0 Administrator Guide for information about managing licenses, troubleshooting licensing issues, and verifying license details.
Verifying Device Credentials
In Prime infrastructure, whenever you are adding/editing the device, device credential verification will happen automatically as part of inventory collection and the report can be viewed at Report > Report Launch Pad > Device > Device Credential Verification.
Adding NAM HTTP/HTTPS Credentials
If you are using Cisco Network Analysis Modules (NAMs) to monitor your network, you must add HTTPS credentials so that Prime Infrastructure can retrieve data from them. This is especially important for users who have licensed Assurance features, as most Assurance features depend on NAM data to work.
Prime Infrastructure polls NAMs directly via HTTP (or HTTPS) to collect their data. This type of polling requires Prime Infrastructure to store each NAMs' HTTP credentials. Unlike with SNMP community strings and Telnet/SSH credentials, you cannot enter NAM HTTP credentials during the discovery process. You can only specify NAM HTTP credentials after the modules are discovered or added to inventory.
Follow these steps to add HTTP credentials for a single NAM. You can repeat this task for all NAMs from which you want Prime Infrastructure to collect data.
Step 1
Choose Operate > Device Work Center > Device Type > Cisco Interfaces and Modules > Network Analysis Modules.
Step 2
Select one of the NAMs and click Edit.
Step 3
In the Edit Device window, under Http Parameters:
•
Protocol—Select the HTTP protocol, HTTP or HTTPS. The TCP Port will change automatically to the default port for the protocol that you have selected.
•
TCP Port—Enter a different TCP Port if you want to override the default.
•
Username—Enter the name of a user who can access the NAM via HTTP or HTTPS.
•
Password—Enter the password for the user name you entered.
•
Confirm Password—Re-enter the password to confirm.
Step 4
Choose Update.
Exporting Devices
In Prime Infrastructure, you can export device information as a CSV file.
To export devices:
Step 1
Choose Operate > Device Work Center.
Step 2
Select devices and click Export Device.
Step 3
Enter an encryption password that will be used to open the exported CSV file.
Step 4
Confirm the encryption Password and click Export to export the device information.
Step 5
Double click the ExportDevice.zip file and enter the encryption password to open the ExportDevice.csv file.
Next Steps
Now that you have added devices to Prime Infrastructure, you can create device groups and port groups to simplify management, monitoring, and configuration of similar devices and ports. See Grouping Devices and Ports.
You might also want to:
•
Plan for devices that will be added to your network in the future—See Preconfiguring Devices to be Added Later, page 6-1.
•
Configure wired and wireless features on your devices using guided, step-by-step instructions—See Getting Help Setting Up Access Switches, page 6-6.

 Feedback
Feedback