-
Cisco IP Solution Center MPLS VPN User Guide, 4.0
-
Index
-
About This Guide
-
IP Solution Center - MPLS VPN
-
Provisioning an Unmanaged Multi-VRF CE
-
MPLS VPN Service Policies
-
MPLS VPN Service Requests
-
Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
-
Provisioning MVRFCE PE-CE Links
-
Provisioning Management VPN
-
Provisioning Cable Services
-
Provisioning Carrier Supporting Carrier
-
Spanning Multiple Autonomous Systems
-
Setting Up the Network
-
Service Request Transition States
-
Troubleshooting MPLS VPN
-
Table Of Contents
Provisioning an Unmanaged Multi-VRF CE
Creating a Customer, Site, and CPE
Collect the Latest Configuration
Create a Route Distinguisher Pool
Defining an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Policy
Creating an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Request
Provisioning an Unmanaged Multi-VRF CE
This chapter describes how to implement a new, Unmanaged Multi-VRF (MVRF) CE with all the required infrastructure data, define an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Policy, and create an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Request, using the Cisco IP Solution Center (ISC).
This chapter contains the following major sections:
•
Defining an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Policy
•
Creating an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Request
Unmanaged MVRFCE Overview
The unmanaged MVRFCE feature is similar to the unmanaged CE feature in so far as the service provider does not use ISC to upload or download configurations to the CPE. This feature is similar to the managed MVRFCE feature in so far as ISC creates a link with three devices: a PE, an MVRFCE, and a CE.
In the unmanaged scenarios, the customer configures the CPE manually. To automate the process of configuring the unmanaged MVRFCE, the service provider can use ISC to generate the configuration and then send it to the customer for manual implementation.
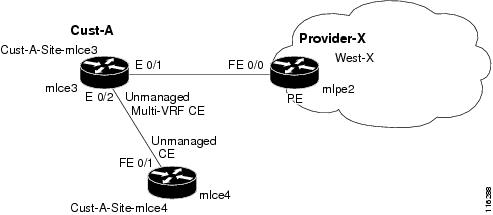
Figure 2-1 shows an overview of a network topology with MPLS VPN MVRFCE PE-CE links.
Figure 2-1 Unmanaged MVRFCE PE-CE Network Topology
The network topology in Figure 2-1 shows a service provider (Provider-X) and a customer (Cust-A). The Provider contains one Region (West-X) and one PE (mlpe2). The Customer contains an MVRFCE (mlce3) and a CE (mlce4). Both of these CPEs are unmanaged.
This section contains the following sections:
Process Overview
To configure MPLS VPN services with ISC, you must understand three key concepts:
Network Inventory
The purpose of preparing network inventory in ISC is to populate the Repository with infrastructure data. If multiple devices are involved, you can use Inventory Manager for importing devices and creating PE or CPE. Otherwise, you can use Inventory and Connection Manager to create the devices and infrastructure data.
To create an MPLS VPN Service Request, you must create the following infrastructure data:
•
Devices
A Device in ISC is a logical representation of a physical device in the network. You can import devices (configurations) into ISC by using Inventory Manager or the ISC GUI. You can also use the Auto Discovery feature of Inventory Manager to import devices into the Repository.
•
Customers
A customer is typically an enterprise or large corporation that receives network services from a service provider. A Customer is also a key logical component of ISC.
–
Sites
A Site is a logical component of ISC that connects a Customer with a CE. It can also represent a physical customer site.
–
CPE/CE Devices
A CPE is "customer premises equipment," typically a customer edge router (CE). It is also a logical component of ISC. You can create CPE in ISC by associating a device with a Customer Site.
•
Providers
A provider is typically a "service provider" or large corporation that provides network services to a customer. A Provider is also a key logical component of ISC.
–
Regions
A Region is a logical component of ISC that connects a Provider with a PE. It can also represent a physical provider region.
–
PE Devices
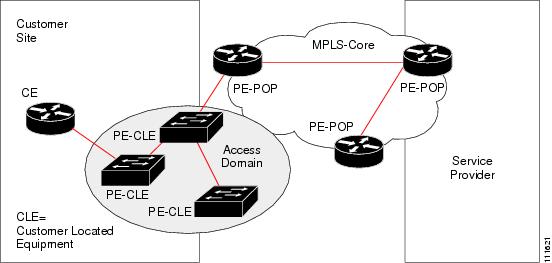
A PE is a provider edge router or switch. It is also a logical component of ISC. You can create PE in ISC by associating a Device with a Provider Region. In ISC, a PE can be a "point of presence" router (POP) or a Layer 2 switch (CLE).
•
Access Domains (for Layer 2 Access)
The Layer 2 Ethernet switching domain that connects a PE to a CE is called an Access Domain. All the switches attached to the PE-POP belong to this Access Domain. These switches belong to the Provider and are defined in ISC as PE-CLE.
•
Resource Pools
–
IP Addresses
–
Multicast
–
Route Distinguisher
–
Route Target
–
VLANs (for Layer 2 Access)
•
CE Routing Communities (CERC is optional)
•
VPN
Before creating a Service Policy, a VPN name must be defined within ISC.
Service Policy
To create an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Policy, you must set up the following items:
1.
Policy Type
2.
PE-MVRFCE Interface
3.
MVRFCE-CE Interface
4.
PE-MVRFCE IP Address Scheme
5.
MVRFCE-CE IP Address Scheme
6.
PE-MVRFCE Routing Information
7.
MVRFCE-CE Routing Information
8.
VRF and VPN Membership
Service Request
To create an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Request, you must complete the following items:
1.
PE-MVRFCE Interface
2.
MVRFCE-CE Interface
3.
PE-MVRFCE IP Address Scheme
4.
MVRFCE-CE IP Address Scheme
5.
PE-MVRFCE Routing Information
6.
MVRFCE-CE Routing Information
7.
VRF and VPN Membership
MVRFCE PE-CE Policy Type
An MVRFCE PE-CE Policy Type is a PE to CE link with three devices:
•
PE
•
MVRF CE
•
CE
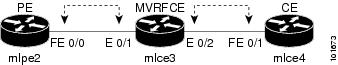
Figure 2-2 shows an example of an MVRFCE PE-CE link with three devices.
Figure 2-2 MVRFCE PE-CE Link
In an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Policy with CE Present enabled, interfaces FE 0/0, E 0/1, E 0/2 and FE 0/1 are configured as an MPLS VPN link in the Service Request process.
Infrastructure Data
In this MVRFCE PE-CE scenario, the following infrastructure data is used:
•
Provider: Provider-X
•
Region: West-X
•
AS#: 99
•
PE: mlpe2
•
Device Role: PE POP
•
Customer: Cust-A
•
Site: Cust-A-Site- mlce3
•
CE: mlce3
•
Site: Cust-A-Site- mlce4
•
CE: mlce4
•
Device Role: CPE
•
IP Address Pool:
–
Name: Provider-X-West-X
–
Type: Region
–
Start: 25.7.0.0
–
Mask: 30
–
Size: 16384
•
Route Distinguisher Pool:
–
Name: 99:PROVIDER-X
–
Start: 50000
–
Size: 10000
•
Route Target Pool:
–
Name: 99:PROVIDER-X
–
Start: 50000
–
Size: 10000
•
VPN
–
Definition: west-xVPN
Adding a New Customer CPE
This section describes how to create a new CPE with an Unmanaged Multi-VRF management Type using the Cisco IP Solution Center (ISC) GUI. It contains the following sections:
•
Creating a Customer, Site, and CPE
Overview of an ISC Customer
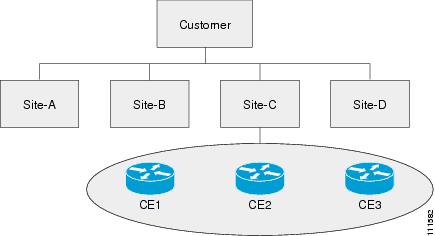
In ISC, a Customer is defined by the following three logical components:
•
Customer Name
•
Customer Site
•
Customer Device (CPE)
In ISC, a Customer is a logical container for Sites and CEs.
Within a Customer, there can be one or more Sites. Sites are logical entities that can be defined in any way that makes sense to a service provider.
Figure 2-3 shows an overview of an ISC Customer.
Figure 2-3 Overview of an ISC Customer
Creating a Device
This section describes how to create a Device with the ISC GUI, connect to a Cisco IOS router in the network, collect the live configuration, and populate the Repository. This section contains the following sections:
Create a Device
This section describes how to create a logical Device with the ISC GUI. To create a Device with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Devices.
The Devices window appears, as shown in Figure 2-4.
Figure 2-4 Devices
Step 3
Click Create.
Step 4
Select Cisco IOS Device.
The Create Cisco IOS Device window appears (not shown).
Step 5
Enter the following information:
•
General
–
Device Host Name (mlce3)
–
Management IP Address (172.29.146.26)
•
Login and Password Information
–
Login Password (*******)
–
Verify Login Password (*******)
–
Enable Password (*******)
–
Verify Enable Password (*******)
•
Device and Configuration Access Information
–
Terminal Session Protocol: Default (Telnet)
–
Config Access Protocol: Default (Terminal)
–
SNMP Version: Default (SNMP v1/v2c)
•
SNMP v1/v2c
–
Community String RO (Public)
–
Community String RW (Private)
Step 6
Click Save.
Note
You have saved a Device in the Repository.
Collect the Configuration
This section describes how to connect to the physical device in the network, collect the device information from the router, and populate the Repository.
To collect the configuration, follow these steps:
Step 1
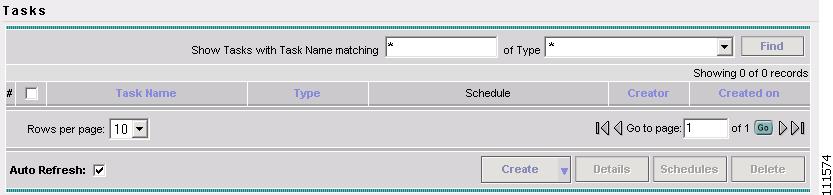
Select Monitoring > Task Manager.
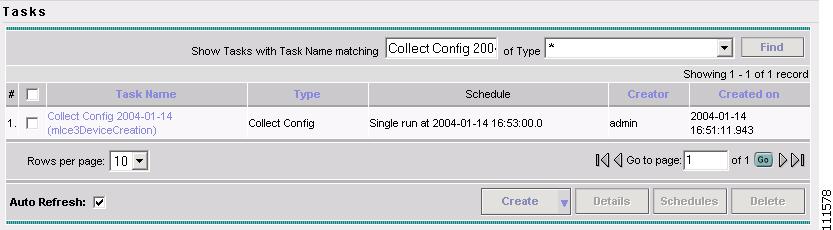
The Tasks window appears, as shown in Figure 2-5.
Figure 2-5 Tasks
Step 2
Click Create.
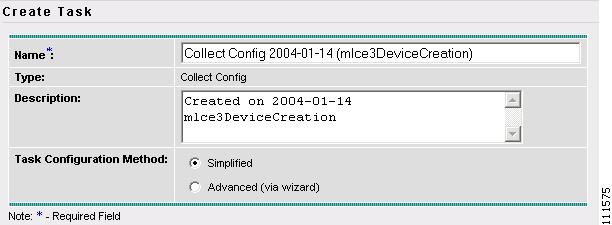
Step 3
Select Collect Config (not shown).
The Create Task window appears, as shown in Figure 2-6.
Note
You might want to change the default Name and Description for this task, so you can more easily identify it in the task log. For example, by adding: mlce3DeviceCreation.
Figure 2-6 Create Task
Step 4
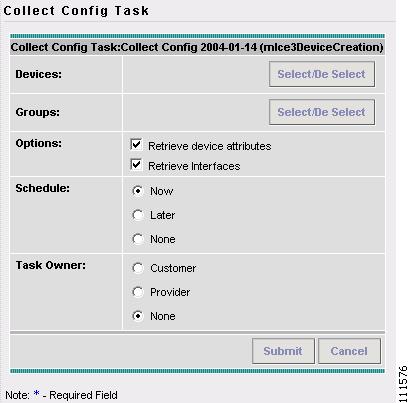
Click Next (not shown).
The Collect Config Task window appears, as shown in Figure 2-7.
Figure 2-7 Collect Config Task
Step 5
Click Select/De Select at Devices.
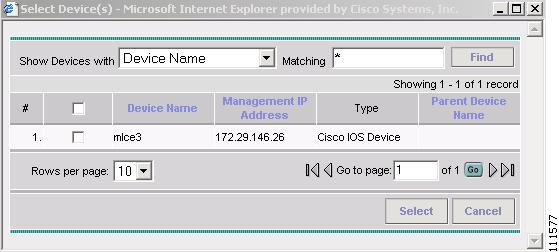
The Select Device window appears, as shown in Figure 2-8.
Figure 2-8 Select Device
Step 6
Select the device, which you created in the previous section, Creating a Device, and then click Select. (mlce3)
The Collect Config Task window appears (not shown).
Step 7
Click Submit.
The Task window appears, as shown in Figure 2-9.
Figure 2-9 Tasks
Step 8
Select your task in the Task Name column and then click Details to view more information.
Note
You have created a Task in the Repository.
Monitor Task Logs
To monitor the logs for your task, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Monitoring > Task Manager.
The Tasks window appears (not shown).
Step 2
Click Logs in the Selection window (not shown).
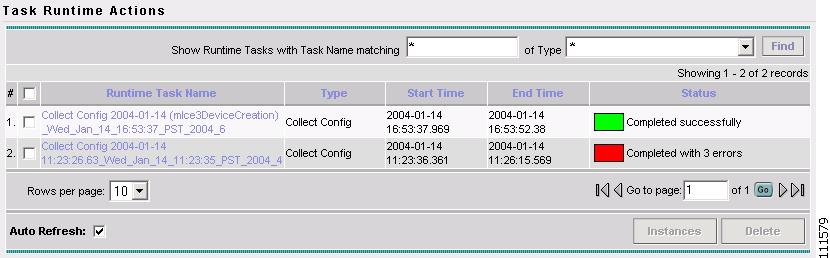
The Task Runtime Actions window appears, as shown in Figure 2-10.
Figure 2-10 Task Runtime Actions
Note
The Status field shows the task has completed successfully. You have collected the configuration for a device and saved it in the Repository.
Step 3
Select your task and then click Instances to view more information.
Creating a Customer, Site, and CPE
This section describes how to create a Customer with the ISC GUI, create a Site for the Customer, and associate a Device with the Site. This section contains the following sections:
Create a Customer
To create a Customer with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Customers.
The Customers window appears (not shown).
Step 2
Click Create.
The Create Customer window appears (not shown).
Step 3
Enter a Customer Name and then click Save. (Cust-A)
Note
You have saved a Customer in the Repository.
The Customers window appears (not shown).
Create a Site
To create a Site, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager.
Step 2
Click Customer Sites in the Selection window.
The Customer Site window appears (not shown).
Step 3
Click Create.
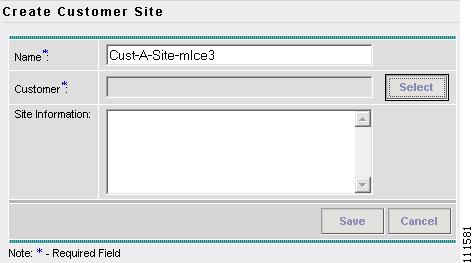
The Create Customer Site window appears, as shown in Figure 2-11.
Figure 2-11 Create Customer Site
Step 4
Enter a Site Name. (Cust-A-Site-mlce3)
Step 5
Click Select.
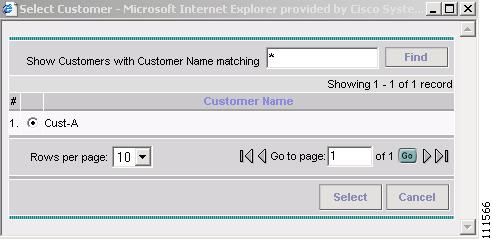
The Select Customer window appears, as shown in Figure 2-12.
Figure 2-12 Select Customer
Step 6
Select a Customer. (Cust-A)
Step 7
Click Select.
The Create Customer Site window appears.
Click Save.
Note
You have saved a Customer Site in the Repository.
Create a CPE
To create a CPE, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager.
Step 2
Click CPE Devices in the Selection window.
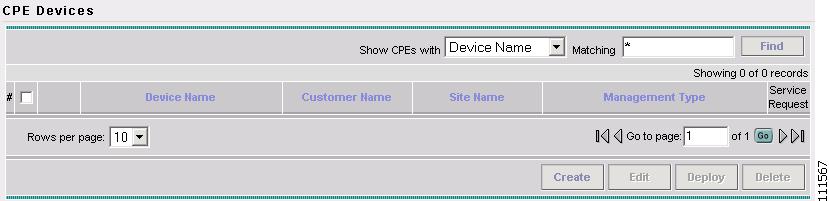
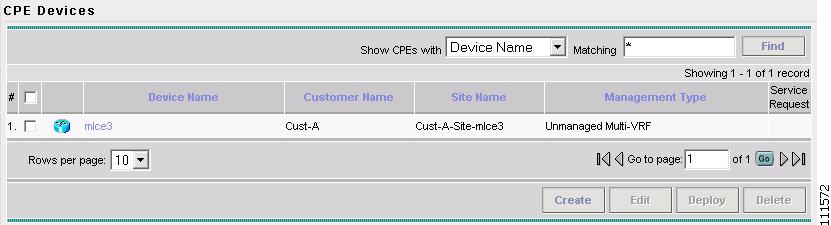
The CPE Devices window appears, as shown in Figure 2-13.
Figure 2-13 CPE Devices
Step 3
Click Create.
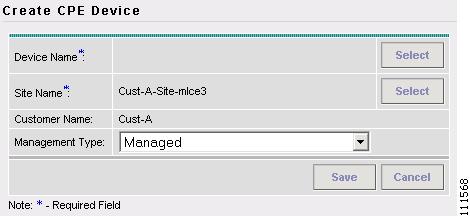
The Create CPE Device window appears, as shown in Figure 2-14.
Figure 2-14 Create CPE Device
Step 4
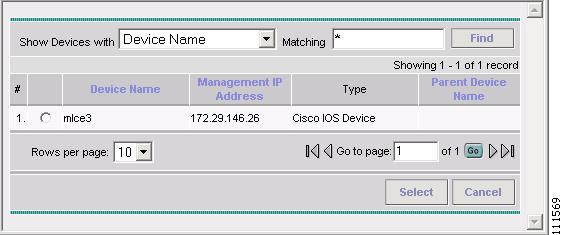
Click Select to Select a Device.
The Select Device window appears, as shown in Figure 2-15.
Figure 2-15 Select Device
Step 5
Select a Device and then click Select. (mlce3)
The Create CPE Device window appears, as shown in Figure 2-16.
Figure 2-16 Create CPE Device
Step 6
Select Management Type. (Unmanaged Multi-VRF)
Step 7
Click Save.
The Create CPE Device window appears, as shown in Figure 2-17.
Figure 2-17 CPE Devices
Note
You have saved a CPE in the Repository.
Adding a New Provider PE
This section describes how to use Cisco IP Solution Center (ISC) Inventory Manager to create a PE from a Device and configure a Provider in the process.
This section contains the following sections:
•
Collect the Latest Configuration
Overview of an ISC Provider
In ISC, a Provider is defined by the following three logical components:
•
Provider Name and BGP Autonomous System (AS) number
•
Provider Region
•
Provider Device (PE)
In ISC, a provider administrative domain (PAD) is a single AS. It is not a specific service provider, rather it is a logical container for Regions and PEs.
Within a single PAD, there must be one or more Regions. Regions are logical entities that can be defined in any way that makes sense to a service provider.
Within a Region, a Provider can contain one or more PEs. The PEs can be a PE-POP ("router") or a PE-CLE ("switch").
Figure 2-3 shows an overview of an ISC Provider.
Figure 2-18 Overview of an ISC Provider
Create a Device Group
This section describes how to create a Device Group with Inventory Manager. To create a Device Group, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Inventory Manager.
The Inventory Manager Java Web Start window appears (not shown).
Step 3
Click Inventory Manager.
The Inventory Manager task bar appears, as shown in Figure 2-19.
Figure 2-19 Inventory Manager Task Bar
Step 4
Select File > New > New Device Group.
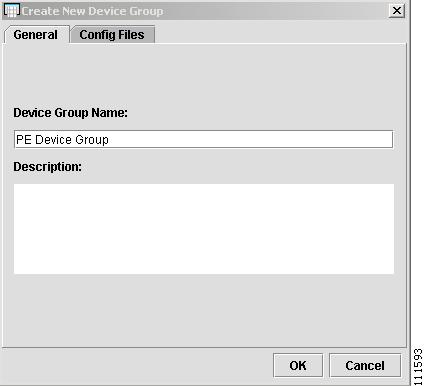
The Create New Device Group window appears, as shown in Figure 2-20.
Figure 2-20 Create New Device Group
Step 5
Enter the Device Group Name (PE Device Group) and a Description (optional).
Step 6
Click OK.
The No Config Files Specified for Import window appears (not shown).
Step 7
Click Yes.
The Choose Config Files for Device Group window appears (not shown).
Note
This process is continued in Import Configuration Files.
Import Configuration Files
This section describes how to import configuration files with Inventory Manager.
To import configuration files, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the Choose Config Files for Device Group window in the previous section (Step 7), click Add.
The Open window appears, as shown in Figure 2-21.
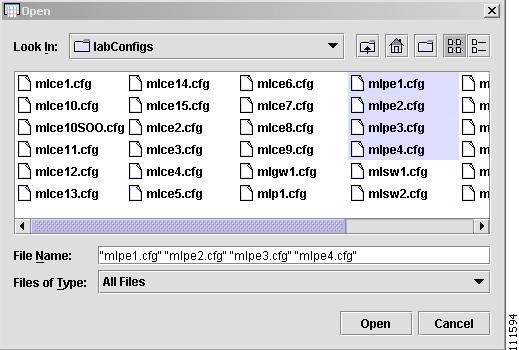
Figure 2-21 Open Config Files
Step 2
Browse to the directory where your configuration files are located and select the appropriate configuration file. Use Ctrl+Click to select multiple devices.
Step 3
Click Open.
The Choose Config Files for Device Group window appears (not shown).
Step 4
Click OK.
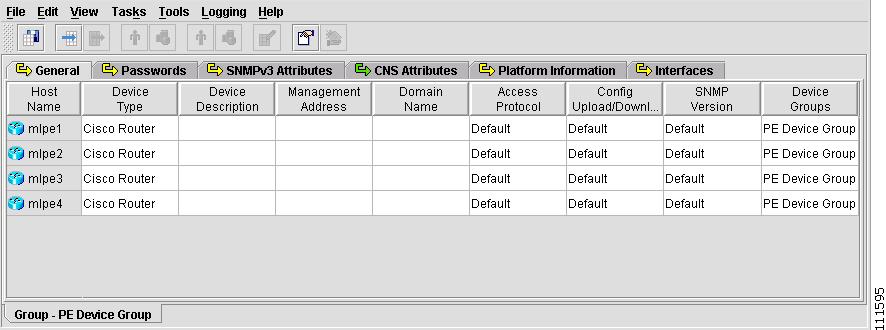
The Group spreadsheet appears, as shown in Figure 2-22.
Figure 2-22 Group Spreadsheet
Step 5
Select File > Save.
Note
You have now saved this Device Group, with the logical Devices and configuration data, in the Repository.
Open a Device
Note
Inventory Manager is designed to configure multiple Devices in a single operation. To facilitate understanding of this process, this scenario focuses on only one Device.
This section describes how to open a Device with Inventory Manager.
To open a Device, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the Inventory Manager task bar (not shown), select File > Open > Open Devices.
The Open Devices window appears, as shown in Figure 2-23.
Figure 2-23 Open Devices
Step 2
Click Find.
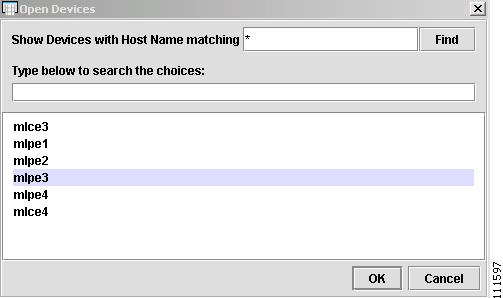
The Open Devices window appears, as shown in Figure 2-24.
Figure 2-24 Open Devices
Step 3
Select a Device and then click OK. (mlpe3)
The Devices spreadsheet appears, as shown in Figure 2-25.
Figure 2-25 Devices Spreadsheet
Note
This process is continued in Collect the Latest Configuration.
Collect the Latest Configuration
This section describes how to connect to a physical device in the network, and collect the latest configuration, with Inventory Manager.
To collect a configuration, follow these steps:
Step 1
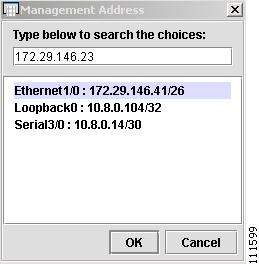
Click the cell in the Management Address column of the Device spreadsheet shown above in Figure 2-25.
The Management Address window appears, as shown in Figure 2-26.
Note
The three IP addresses in the lower window were imported previously in the section, Import Configuration Files. These interface addresses could also be used as the Management Address.
Figure 2-26 Management Address
Step 2
Enter the Management Address and then click OK. (172.29.146.23)
The Devices spreadsheet appears (not shown).
Step 3
Click the Passwords tab.
The Passwords spreadsheet appears (not shown).
Step 4
Click the Login Password cell.
The Login Password window appears (not shown).
Step 5
Enter the Password (*******).
Step 6
Enter the Verify Password (*******).
Step 7
Click OK.
Step 8
Click the Enable Password cell.
The Enable Password window appears (not shown).
Step 9
Enter the Password (*******).
Step 10
Enter the Verify Password (*******).
Step 11
Click OK.
Step 12
Select File > Save.
Step 13
Select Task > Collect Latest Config Files.
Step 14
Accept the prompt to proceed.
You are notified if the task completes successfully.
Step 15
Click the Platform Information tab to view the newly collected configuration information.
The Platform Information spreadsheet appears, as shown in Figure 2-27 below.
Step 16
Select File > Save.
Note
You have now saved this Device information in the Repository. This process is continued in Create a Provider and a PE.
Create a Provider and a PE
This section describes how to create a Provider and a PE from a Device, using Inventory Manager.
To create a Provider and a PE, follow these steps:
Step 1
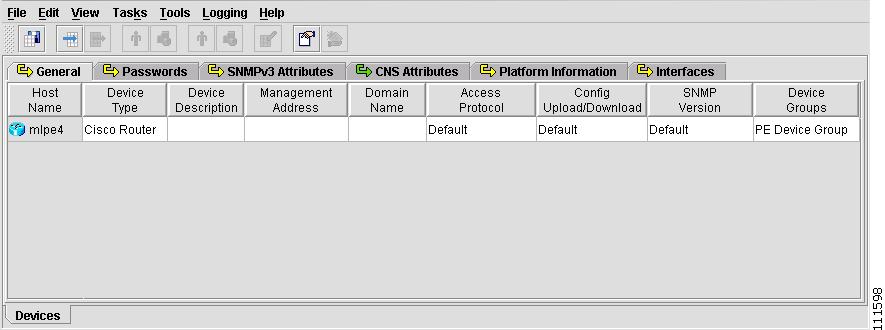
From the Devices spreadsheet shown in Figure 2-27, click the cell in the Host column to select the Device.
Figure 2-27 Platform Information
Step 2
From the Inventory Manager task bar, select Edit > Move to New Provider, as shown in Figure 2-28.
Figure 2-28 Move to New Customer
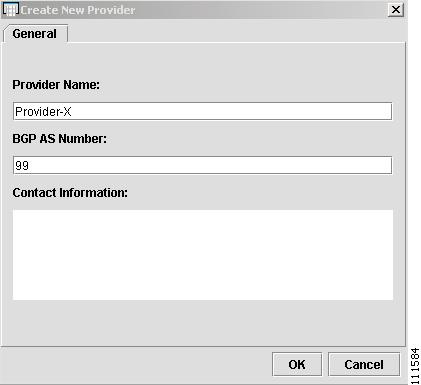
The Create New Provider window appears, as shown in Figure 2-29.
Figure 2-29 Create New Provider
Enter the Provider Name and BGP AS Number. (Provider-X, 99)
Step 3
Click OK.
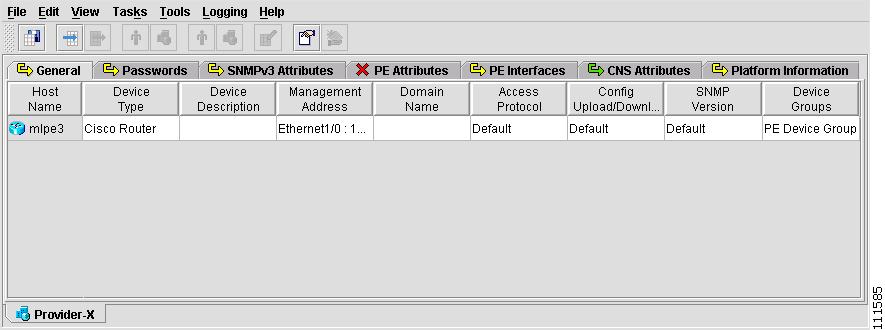
The Provider spreadsheet appears with a PE, as shown in Figure 2-30.
Figure 2-30 Provider Spreadsheet
Step 4
Select File > Save.
Note
The Provider spreadsheet contains two new tabs, PE Attributes and PE Interfaces. This process is continued in Create a Region for the PE.
Create a Region for the PE
This section describes how to create a Region for the PE with Inventory Manager.
To create a Region, follow these steps:
Step 1
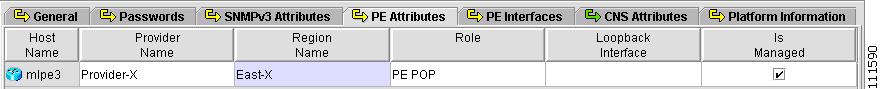
From the Provider spreadsheet, shown in Figure 2-30, click the PE Attributes tab.
The PE Attributes spreadsheet appears, as shown in Figure 2-31.
Figure 2-31 PE Attributes
Step 2
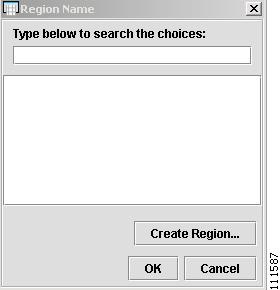
Click the cell in the Region Name column.
The Region Name window appears, as shown in Figure 2-32.
Figure 2-32 Region Name
Step 3
Click Create Region.
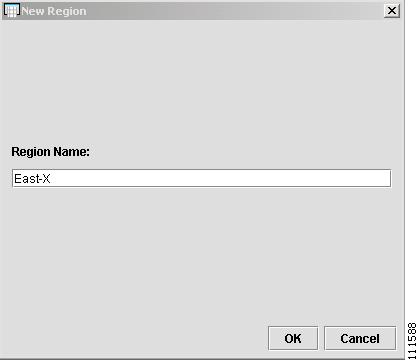
The New Region window appears, as shown in Figure 2-33.
Figure 2-33 New Region
Step 4
Enter the Region Name and then click OK. (East-X)
The Region Name window appears, as shown in Figure 2-34.
Figure 2-34 Region Name
Step 5
Click OK.
The PE Attributes spreadsheet appears, as shown in Figure 2-35.
Figure 2-35 PE Attributes
Step 6
Click File > Save.
Note
The process of adding a PE to a Provider Region is complete. To view or edit the PE in the ISC GUI, continue to Edit a PE with the ISC GUI.
Edit a PE with the ISC GUI
This section describes how to view or edit a PE with the ISC GUI.
To view a PE with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Open a new browser and log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager.
Step 3
Click PE Devices in the Selection window.
The PE Devices window appears, as shown in Figure 2-36.
Figure 2-36 PE Devices
Step 4
Select the PE Device.
Step 5
Click Edit.
Creating an Access Domain
Note
This section is only required for Layer 2 access to MPLS VPN.
This section describes how to create an Access Domain using the Cisco IP Solution Center (ISC) GUI. This section contains the following sections:
Overview of an Access Domain
Any Transport over MPLS (AToM) is the Cisco solution for transporting Layer 2 traffic over an IP/MPLS backbone. AToM is required for supporting legacy services over MPLS infrastructures and for supporting new connectivity options, including Layer 2 VPNs and Layer 2 virtual leased lines.
AToM supports three types of Ethernet-based L2VPNs (EoMPLS):
•
Point-to-Point Ethernet Wire Service (EWS)
•
Point-to-Point Ethernet Relay Service (ERS)
•
Multipoint TLS Service
The Layer 2 Ethernet switching domain that connects a PE to a CE is called an Access Domain. All the switches attached to the PE-POP belong to this Access Domain. These switches belong to the Provider and are defined in ISC as PE-CLE.
Note
To have ISC automatically assign VLAN links from a VLAN pool, you must create an Access Domain.
ISC supports multiple PE-POPs per Access Domain and multiple PE-CLE devices can be included.
Figure 2-37 shows an overview of an ISC Access Domain.
Figure 2-37 Overview of an Access Domain
Create an Access Domain
This section describes how to create a Device with the ISC GUI.
To create a Device with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager.
Step 3
Click Access Domains in the Selection window.
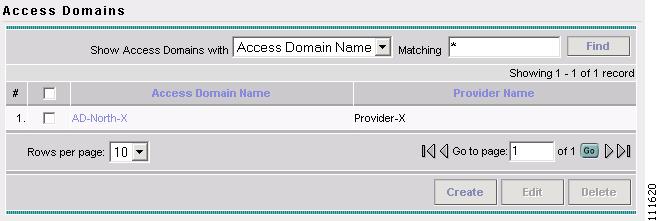
The Access Domains window appears, as shown in Figure 2-38.
Figure 2-38 Access Domains
Step 4
Click Create.
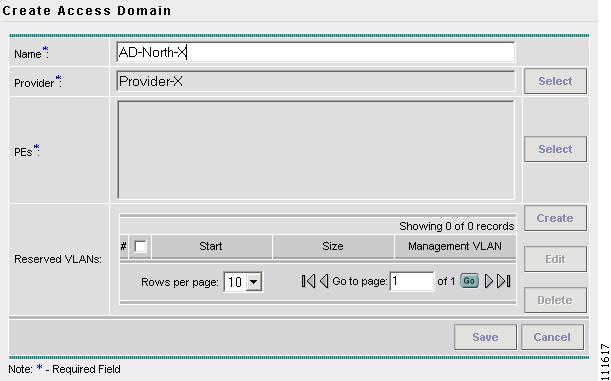
The Create Access Domain window appears, as shown in Figure 2-39.
Figure 2-39 Create Access Domain
Step 5
Enter an Access Domain Name.
Step 6
Select a Provider (not shown).
Step 7
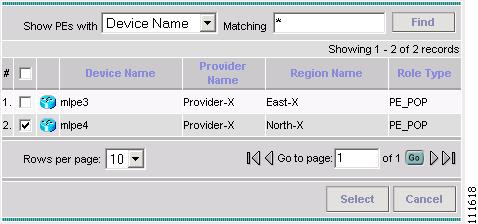
Click Select to show PEs.
The Show PEs window appears, as shown in Figure 2-40.
Figure 2-40 Show PEs
Step 8
Select a PE.
Step 9
Click Select.
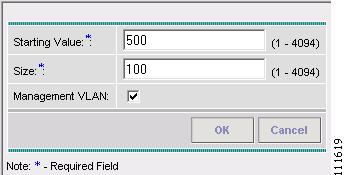
The Create Reserved VLAN window appears, as shown in Figure 2-41.
Figure 2-41 Create Reserved VLAN
Step 10
Enter a Starting Value.
Step 11
Enter a Size.
Step 12
Select Management VLAN.
Step 13
Click OK.
The Access Domains window appears, as shown in Figure 2-8.
Figure 2-42 Access Domains
The Access Domain has been saved in the Repository.
Creating Resource Pools
This section describes how to create Resource Pools using the Cisco IP Solution Center (ISC) GUI.
This section contains the following sections:
•
Create a Route Distinguisher Pool
Overview of Resource Pools
Before creating a service in ISC, you must define your Resource Pools. From these Resource Pools, ISC can automatically assign some values during the provisioning process. You can also manually assign these values during the provisioning process, but it is not recommended.
ISC allocates numbers from the following pools during the provisioning process:
•
IP Address—Connects PE and CE interfaces, when you define addresses in a Service Request.
•
Multicast—Class D addresses used with multicast, when building PE to multiple CE links.
•
Route Distinguisher (RD)—A 64-bit number composed of the Provider AS number and an index number that is prepended to a VPN route. The RD allows the route subnet to be unique across the entire provider MPLS VPN network. It is carried by MP-BGPv4 as a 96-bit VPNv4 address as part of the extended community string.
•
Route Target (RT)—An import and export feature of a VRF, the RT allows VPN routes to be forwarded between VRFs. It is a 64-bit number, also carried as part of the MP-BGPv4 extended community string, and directly related to each VPNv4 route and its VPN-related IPv4 route.
•
Site of Origin—Indicates the origin of a BGP update. Depending on the use of two Cisco IOS BGP commands, the Site of Origin will be used by BGP to preclude routing loops.
•
VC ID (Virtual Circuit)—Used as a Layer 2 circuit identifier across a provider network.
•
VLAN—Used in a Layer 2 VPN as a circuit identifier within the provider Access Domain.
Create an IP Address Pool
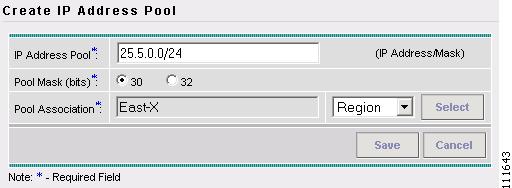
This section describes how to create an IP Address Pool with the ISC GUI.
To create an IP Address Pool with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Resource Pools.
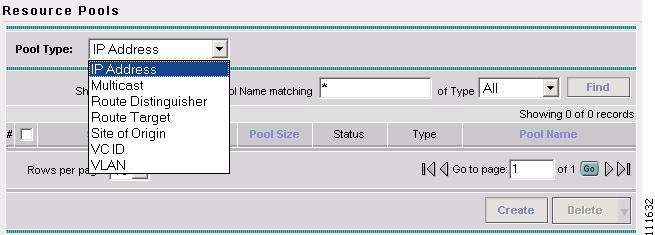
The Resource Pools window appears, as shown in Figure 2-43.
Figure 2-43 Resource Pools
Step 3
Select IP Address from the Pool Type window.
Step 4
Click Create.
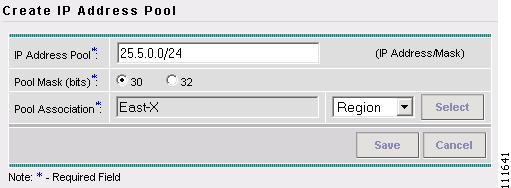
The Create IP Address Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-44.
Figure 2-44 Create IP Address Pool
Step 5
Enter an IP Address and Mask. (25.5.0.0/24)
Step 6
Select the Pool Mask (bits) value. (30)
Note
Use 32 for loopback addresses.
Step 7
Click Select to associate the pool with a Region.
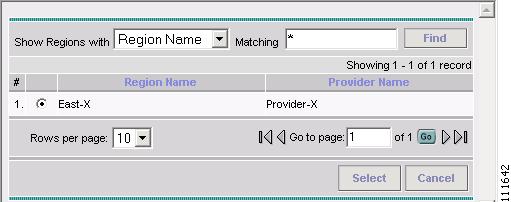
The Select Region window appears, as shown in Figure 2-45.
Figure 2-45 Select Region
Step 8
Select a Region.
Step 9
Click Select.
The Create IP Address Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-46 Create IP Address Pool
Step 10
Click Save.
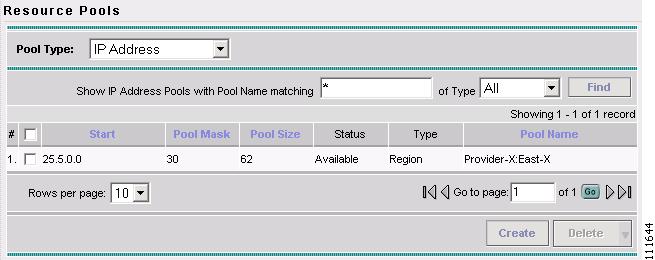
The Resource Pools - IP Address window appears, as shown in Figure 2-47.
Figure 2-47 Resource Pools - IP Address
You have saved an IP Address Pool in the Repository.
Create a Multicast Pool
This section describes how to create a Multicast Address Pool with the ISC GUI.
To create a Multicast Pool with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Resource Pools.
The Resource Pools window appears (not shown).
Step 3
Select Multicast from the Pool Type window.
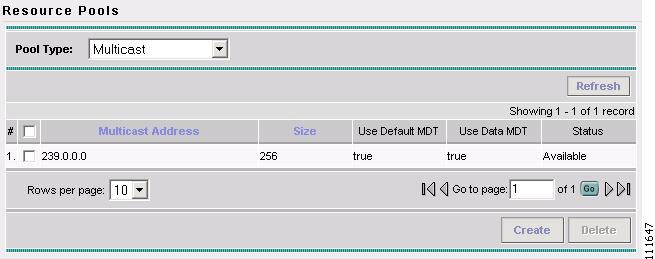
The Resource Pools - Multicast window appears, as shown in Figure 2-8.
Figure 2-48 Resource Pools - Multicast
Step 4
Click Create.
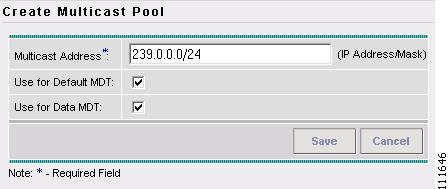
The Create Multicast Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-49.
Figure 2-49 Create Multicast Pool
Step 5
Enter an IP Address and Mask. (239.0.0.0/24)
Step 6
Select the defaults. (Default MDT and Data MDT).
Step 7
Click Save.
The Resource Pools - Multicast window appears, as shown in Figure 2-48.
Figure 2-50 Resource Pools - Multicast
You have saved a Multicast Address Pool in the Repository.
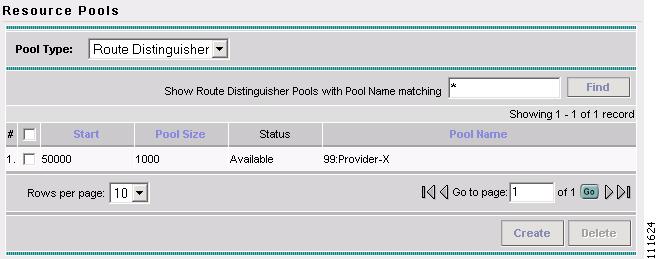
Create a Route Distinguisher Pool
This section describes how to create a Route Distinguisher Pool with the ISC GUI.
To create a Route Distinguisher Pool with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Resource Pools.
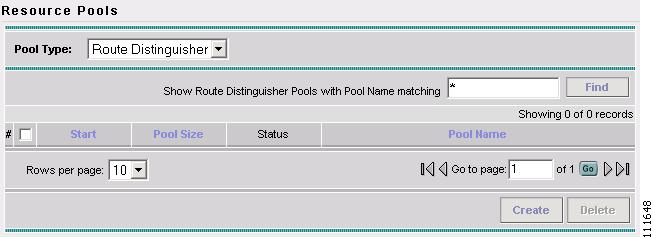
The Resource Pools window appears (not shown).
Step 3
Select Route Distinguisher from the Pool Type window.
The Resource Pools - Route Distinguisher window appears, as shown in Figure 2-11.
Figure 2-51 Resource Pools - Route Distinguisher
Step 4
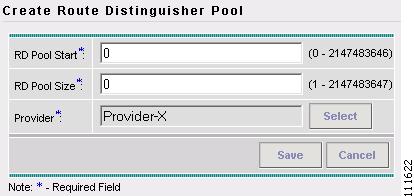
Click Create.
The Create Route Distinguisher Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-52.
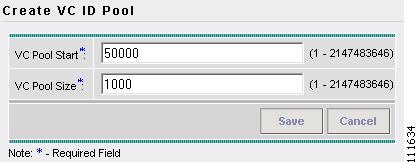
Figure 2-52 Create Route Distinguisher Pool
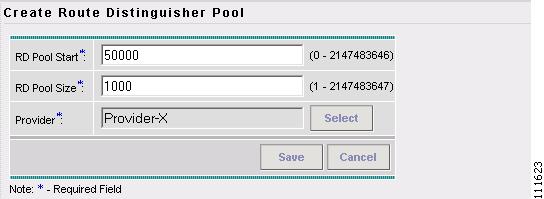
Step 5
Enter an RD Pool Start. (50000)
Step 6
Enter an RD Pool Size. (1000)
Step 7
Click Select.
The Select Provider window appears (not shown).
Step 8
Select a Provider.
The Create Route Distinguisher Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-53.
Figure 2-53 Create Route Distinguisher Pool
Step 9
Click Save.
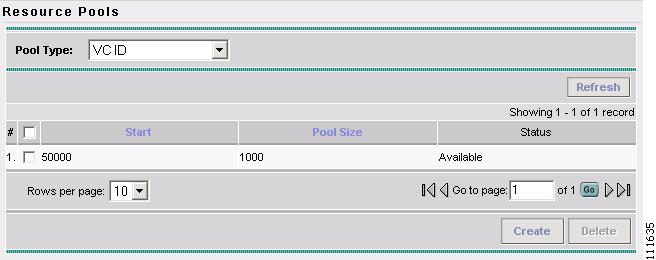
The Resource Pools - Route Distinguisher window appears, as shown in Figure 2-15.
Figure 2-54 Create Route Distinguisher Pool
You have saved a Route Distinguisher Pool in the Repository.
Create a Route Target Pool
This section describes how to create a Route Target Pool with the ISC GUI.
To create a Route Target Pool with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Resource Pools.
The Resource Pools window appears (not shown).
Step 3
Select Route Target from the Pool Type window.
The Resource Pools - Route Target window appears, as shown in Figure 2-55.
Figure 2-55 Create Route Target Pool
Step 4
Click Create.
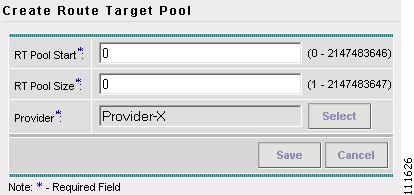
The Create Route Target Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-56.
Figure 2-56 Create Route Target Pool
Step 5
Enter an RT Pool Start. (50000)
Step 6
Enter an RT Pool Size. (1000)
Step 7
Click Select.
The Select Provider window appears (not shown).
Step 8
Select a Provider.
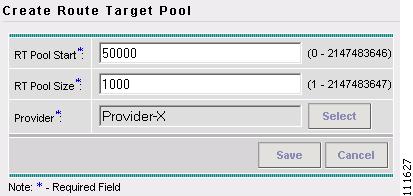
The Create Route Target Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-57.
Figure 2-57 Create Route Target Pool
Step 9
Click Save.
The Resource Pools - Route Target window appears, as shown in Figure 2-58.
Figure 2-58 Resource Pools - Route Target
You have saved a Route Target Pool in the Repository.
Create a Site of Origin Pool
This section describes how to create a Site of Origin Pool with the ISC GUI.
To create a Site of Origin Pool with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Resource Pools.
The Resource Pools window appears (not shown).
Step 3
Select Site of Origin from the Pool Type window.
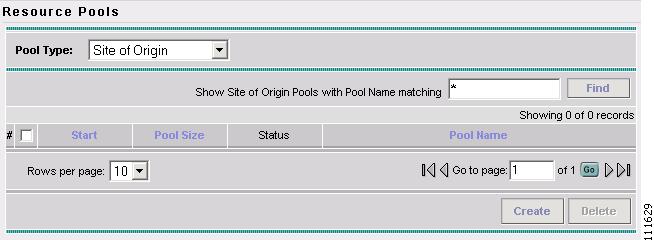
The Resource Pools - Site of Origin window appears, as shown in Figure 2-59.
Figure 2-59 Resource Pools - Site of Origin
Step 4
Click Create.
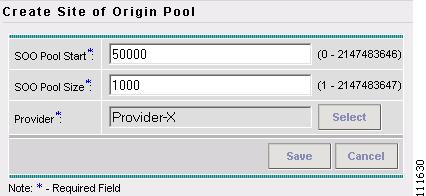
The Create Site of Origin Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-60.
Figure 2-60 Create Site of Origin Pool
Step 5
Enter an SOO Pool Start. (50000)
Step 6
Enter an SOO Pool Size. (1000)
Step 7
Click Select.
The Select Provider window appears (not shown).
Step 8
Select a Provider.
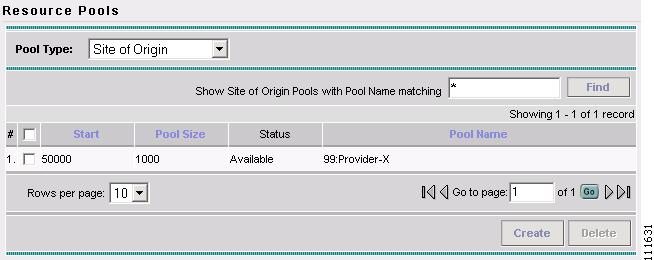
The Create Route Target Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-61.
Figure 2-61 Resource Pools - Site of Origin
You have saved a Site of Origin Pool in the Repository.
Create a VC ID Pool
This section describes how to create a Virtual Circuit ID (VC ID) Pool with the ISC GUI.
To create a VC ID Pool with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Resource Pools.
The Resource Pools window appears (not shown).
Step 3
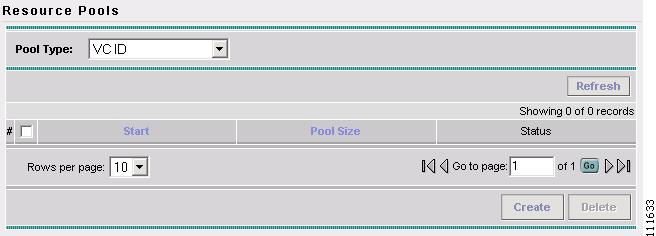
Select VC ID from the Pool Type window.
The Resource Pools - VC ID window appears, as shown in Figure 2-62.
Figure 2-62 Resource Pools - VC ID
Step 4
Click Create.
The Create VC ID Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-63.
Figure 2-63 Create VC ID Pool
Step 5
Enter an VC Pool Start. (50000).
Step 6
Enter an VC Pool Size. (1000).
Step 7
Click Save.
The Resource Pools - VC ID window appears, as shown in Figure 2-64.
Figure 2-64 Resource Pools - VC ID
You have saved a VC ID Pool in the Repository.
Create a VLAN Pool
This section describes how to create a VLAN (VC ID) Pool with the ISC GUI.
To create a VLAN Pool with the ISC GUI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Resource Pools.
The Resource Pools window appears (not shown).
Step 3
Select VLAN from the Pool Type window.
The Resource Pools - VLAN window appears, as shown in Figure 2-65.
Figure 2-65 Resource Pools - VLAN
Step 4
Click Create.
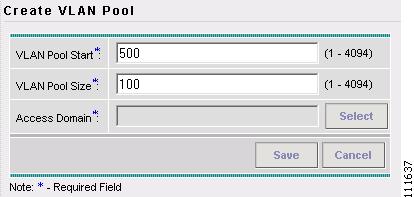
The Create VLAN Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-66.
Figure 2-66 Select Device
Step 5
Enter an VLAN Pool Start. (500)
Step 6
Enter an VLAN Pool Size. (100)
Step 7
Click Select.
The Select Access Domain window appears, as shown in Figure 2-67.
Figure 2-67 Select Access Domain
Step 8
Select an Access Domain.
Step 9
Click Select.
The Create VLAN Pool window appears, as shown in Figure 2-68.
Figure 2-68 Create VLAN Pool
Step 10
Click Save.
The Resource Pools - VLAN window appears, as shown in Figure 2-69.
Figure 2-69 Resource Pools - VLAN
You have saved a VLAN Pool in the Repository.
Defining a VPN
During service deployment, ISC generates the Cisco IOS commands to configure the logical VPN relationships.
At the beginning of the provisioning process, before creating a Service Policy, a VPN must be defined within ISC. The first element in a VPN definition is the name of the VPN.
To create a VPN Name, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > VPNs.
The VPN window appears, as shown in Figure 2-70.
Figure 2-70 VPNs
Step 3
Click Create to create a VPN.
The Create VPN window appears, as shown in Figure 2-71.
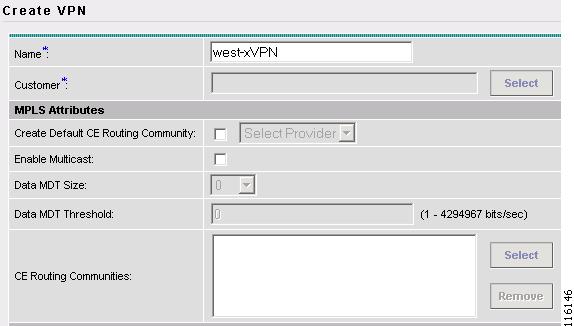
Figure 2-71 Create VPN
Step 4
Enter the VPN Name. (west-xVPN)
Step 5
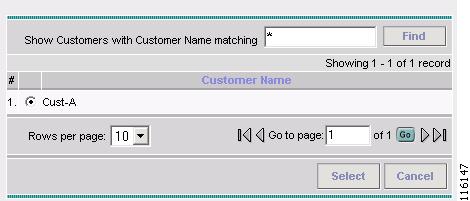
Click Select.
The Select Customer window appears, as shown in Figure 2-72.
Figure 2-72 Select Customer
Step 6
Select a Customer and then click Select. (Cust-A)
Step 7
Click Next.
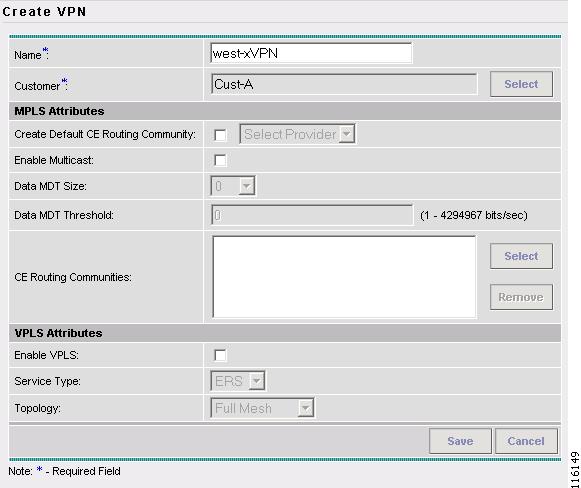
The VPNs window reappears, as shown in Figure 2-73.
Figure 2-73 VPNs
Step 8
To associate the VPN with a Provider, you have two options:
•
Select Create Default CE Routing Community and then Select a Provider.
•
Select a CE Routing Community, if one is already set up.
Step 9
Click Save.
The VPN Name (west-xVPN) is associated with the Customer (Cust-A) in this new VPN definition.
Defining an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Policy
To define an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Policy, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
Select Service Design > Policies.
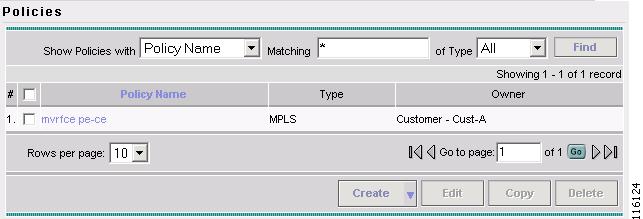
The Policies window appears, as shown in Figure 2-74.
Figure 2-74 Policies
Step 3
From the Create drop-down list, select MPLS Policy.
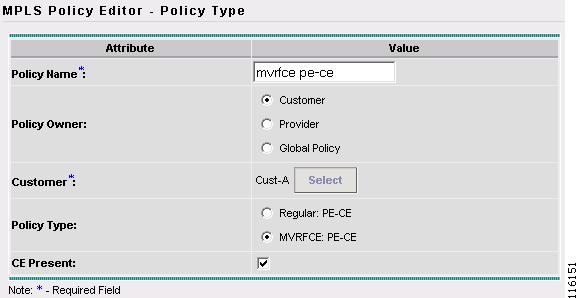
The MPLS Policy Editor - Policy Type window appears, as shown in Figure 2-75.
Figure 2-75 MPLS Policy Editor - Policy Type
Step 4
Edit the following attributes:
Step 5
Enter the policy name. (mvrfce pe-ce)
Step 6
Select the Policy Type. (Regular MVRFCE PE-CE)
Step 7
Select CE Present. (CE Present)
Step 8
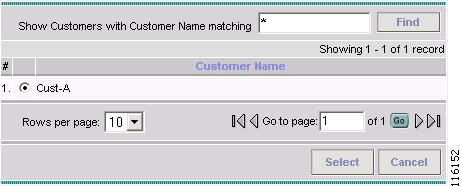
Click Select to specify a Customer.
The Customer for MPLS Policy ownership window appears, as shown in Figure 2-76.
Figure 2-76 Customer for MPLS Policy
Step 9
Select a Customer and then click Select. (Cust-A)
Step 10
Click Next.
The MPLS Policy Editor - PE Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 2-77.
Figure 2-77 The MPLS Policy Editor - PE Interface
Step 11
Click Next.
The MPLS Policy Editor - CE Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 2-78.
Figure 2-78 The MPLS Policy Editor - CE Interface
Step 12
Click Next to accept the defaults.
Note
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the Service Request process.
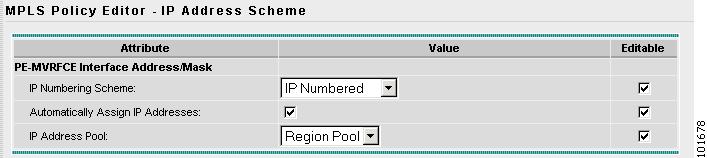
The MPLS Policy Editor - PE IP Address Scheme window appears, as shown in Figure 2-79.
Figure 2-79 The MPLS Policy Editor - PE IP Address Scheme
Step 13
Select Automatically Assign IP Addresses.
The IP Address Pool appears with the Region Pool in the window.
Step 14
Click Next.
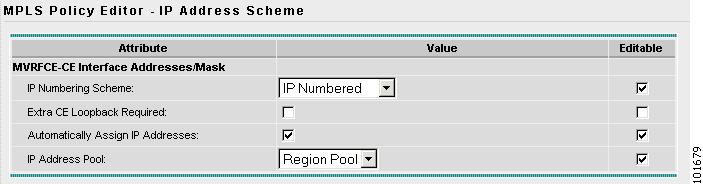
The MPLS Policy Editor - CE IP Address Scheme window appears, as shown in Figure 2-79.
Figure 2-80 The MPLS Policy Editor - CE IP Address Scheme
Step 15
Select Automatically Assign IP Address.
Step 16
Click Next.
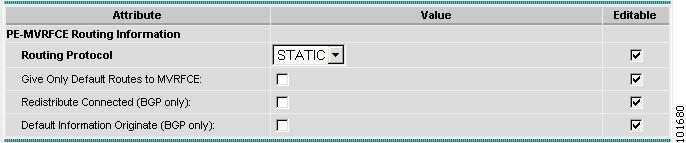
The MPLS Policy Editor - PE Routing Information window appears, as shown in Figure 2-81.
Figure 2-81 The MPLS Policy Editor - PE Routing Information
Step 17
Click Next to accept the defaults.
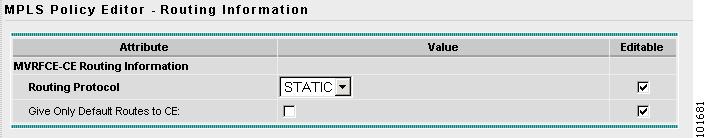
The MPLS Policy Editor - CE Routing Information window appears, as shown in Figure 2-82.
Figure 2-82 The MPLS Policy Editor - CE Routing Information
Step 18
Click Next to accept the defaults.
Note
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the Service Request process.
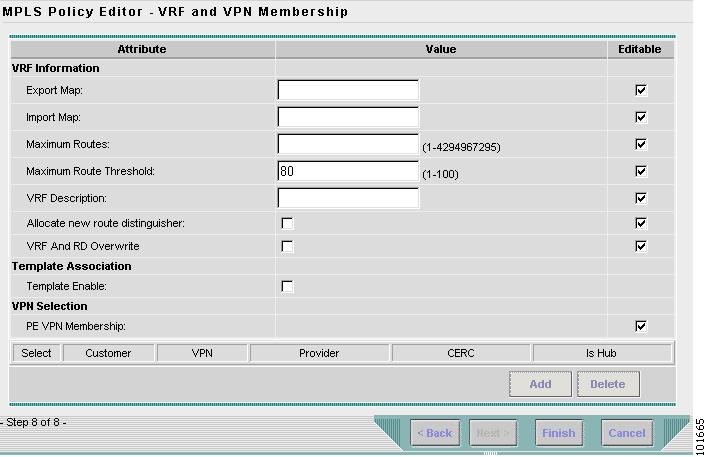
The MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window appears, as shown in Figure 2-83.
Figure 2-83 The MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership
Step 19
Click Next to accept the defaults.
Note
You could add the VPN here, but in this scenario you add the VPN in the Service Request process. Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the Service Request process.
Step 20
Click Finish:
The Policies window reappears, as shown in Figure 2-84.
Figure 2-84 Policies
The MVRFCE PE-CE Service Policy is complete.
Creating an MVRFCE PE-CE Service Request
To create a MVRFCE PE-CE Service Request, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into ISC.
Step 2
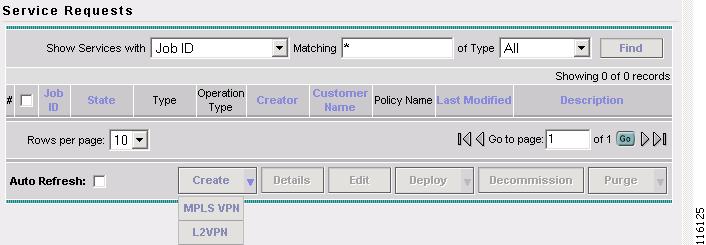
Select Service Inventory > Inventory and Connection Manager > Service Requests.
The Service Requests window appears, as shown in Figure 2-85.
Figure 2-85 Service Requests
Step 3
From the Create drop-down list, select MPLS VPN.
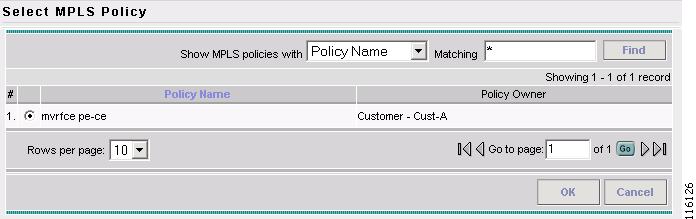
The Select MPLS Policy window appears, as shown in Figure 2-86.
Figure 2-86 Select MPLS Policy
Step 4
Select the MPLS Policy. (mvrfce pe-ce)
Step 5
Click OK.
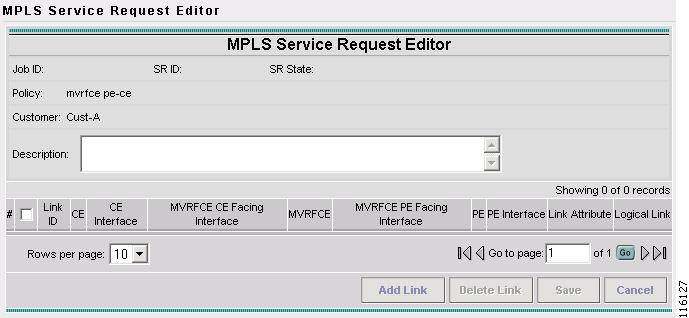
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 2-87.
Figure 2-87 MPLS Service Request Editor
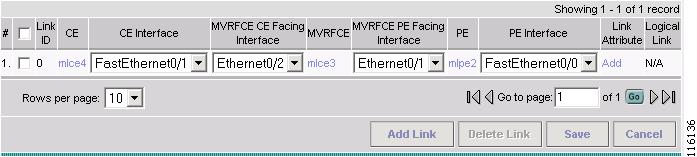
Step 6
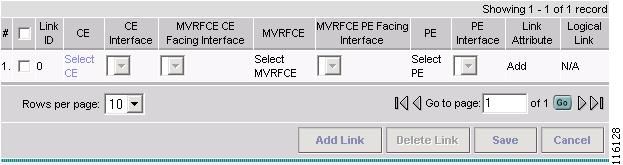
Click Add Link.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 2-88.
Figure 2-88 MPLS Service Request Editor - Select CE
Step 7
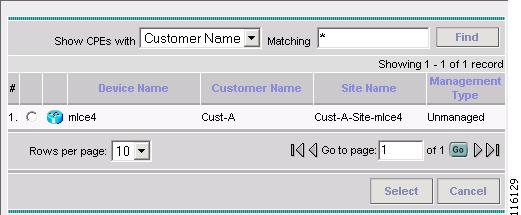
Click Select CE.
The Select CPE Device - CE window appears, as shown in Figure 2-89.
Figure 2-89 Select CPE Device - CE
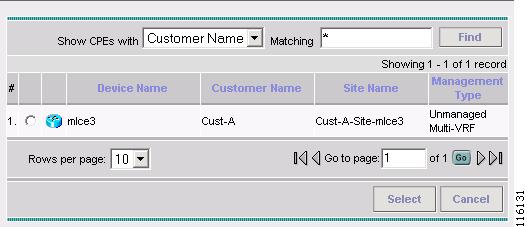
Step 8
Select the CPE Device and then click Select. (mlce4)
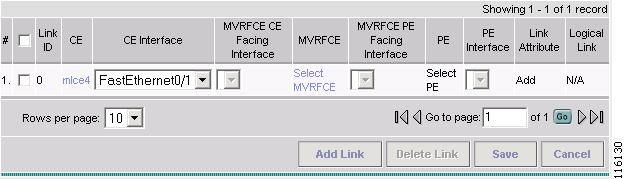
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 2-90.
Figure 2-90 MPLS Service Request Editor - CE Interface
Step 9
Select the CE Interface from the drop-down box. (FE0/1)
Step 10
Click Select MVRFCE.
The Select CPE Device - MVRFCE window appears, as shown in Figure 2-91.
Figure 2-91 Select CPE Device - MVRFCE
Step 11
Select the MVRFCE and then click Select. (mlce3)
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 2-92.
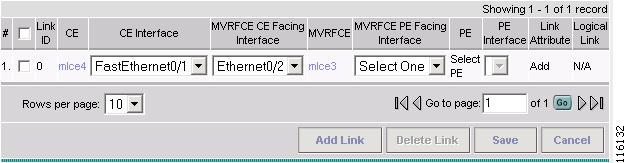
Figure 2-92 MPLS Service Request Editor - MVRFCE CE Facing Interface
Step 12
Select the MVRFCE CE Facing Interface from the drop-down box. (E0/2)
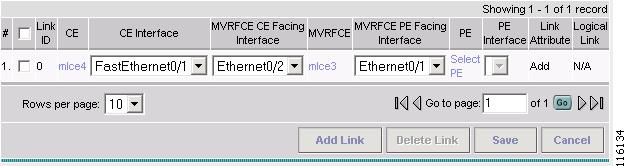
Step 13
Select the MVRFCE PE Facing Interface from the drop-down box. (E0/1)
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 2-93.
Figure 2-93 MPLS Service Request Editor - Select MVRFCE PE Facing Interface
Step 14
Select PE.
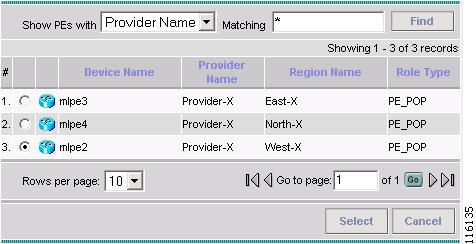
The Select PE Device window appears, as shown in Figure 2-94.
Figure 2-94 Select PE Device
Step 15
Select the PE and then click Select.
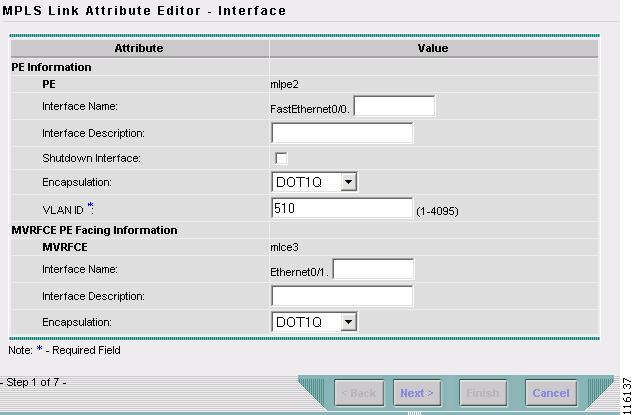
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 2-95.
Figure 2-95 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface
Step 16
Select the PE Interface from the drop-down box. (FE0/0)
Step 17
Click Add in the Link Attribute cell.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 2-95.
Figure 2-96 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface
Step 18
Enter the VLAN ID for the PE. (510)
Step 19
Click Next.
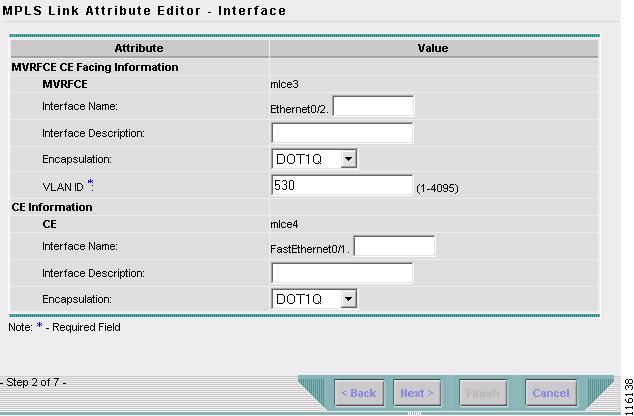
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 2-97.
Figure 2-97 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface
Step 20
Enter the VLAN ID for the MVRFCE. (530)
Click Next.
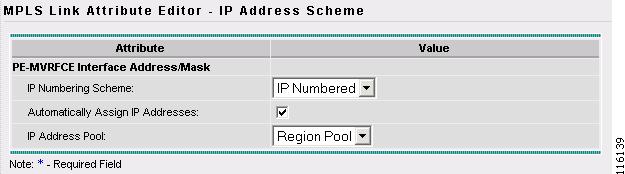
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears, as shown in Figure 2-98.
Figure 2-98 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme
Step 21
Keep the defaults and click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears, as shown in Figure 2-99.
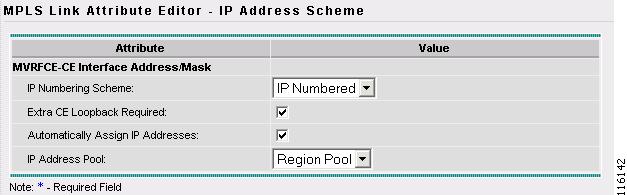
Figure 2-99 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme
Step 22
Keep the defaults and click Next.
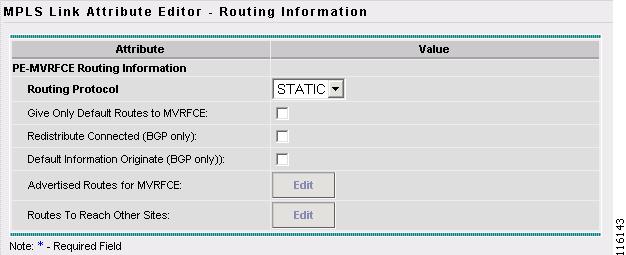
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information window reappears, as shown in Figure 2-100.
Figure 2-100 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - PE Routing Information
Step 23
Keep the defaults and click Next.
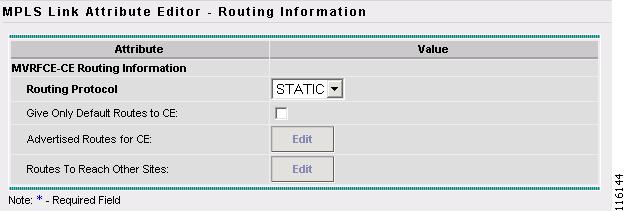
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information window reappears, as shown in Figure 2-101.
Figure 2-101 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - MVRFCE Routing Information
Step 24
Keep the defaults and click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN window appears (not shown).
Step 25
Click Add to select a VPN.
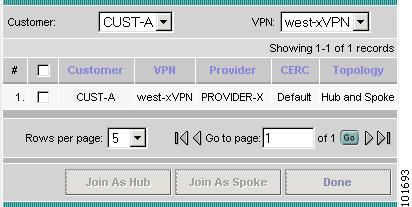
The Select VPN window appears, as shown in Figure 2-102.
Figure 2-102 Select VPN
Step 26
Select a VPN.
Step 27
Click Join as Hub or Join as Spoke to join the CERC.
Step 28
Click Done.
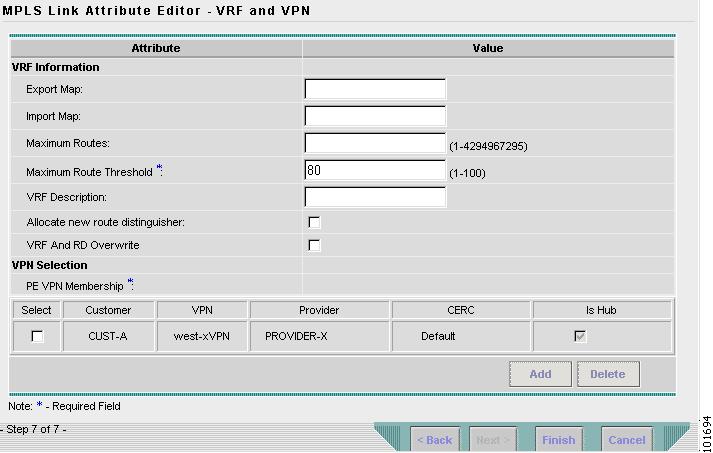
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN window reappears, as shown in Figure 2-103.
Figure 2-103 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 29
Click Finish.
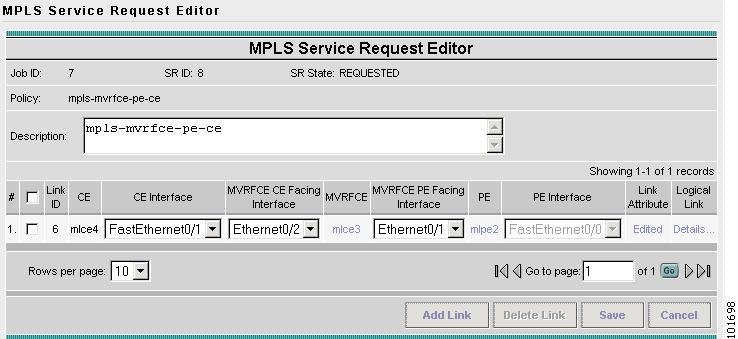
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears, as shown in Figure 2-104.
Figure 2-104 MPLS Service Request Editor
Step 30
Enter the Service Request description and then click Save. (mpls-mvrfce-pe-ce)
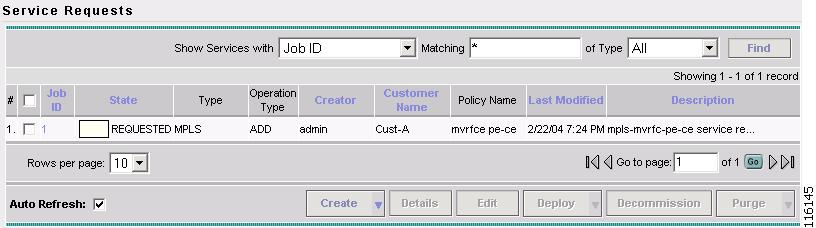
The MPLS Service Requests window appears, as shown in Figure 2-105.
Figure 2-105 Service Request
The MPLS VPN MVRFCE PE-CE Service Request is in the Requested state and ready to deploy.

 Feedback
Feedback