-
User Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager 6.1
-
Overview
-
Configuring Security
-
Setting Up Your Server
-
Getting Started
-
Basic Operations
-
Understanding Basic Object Functions
-
Managing Views
-
Understanding Detailed Object Functions
-
Managing Alarms and Events
-
Viewing Network Topology
-
Accessing Data From the Web Interface
-
Managing Reports
-
Editing an ITP Route Table File
-
Editing an ITP Global Title Translation Table
-
Editing ITP MLR Address Table Files
-
Client Object Map Reference
-
Command Reference
-
FAQs
-
Troubleshooting the MWTM and the Network
-
Status Definitions
-
MIB Reference
-
Trap Reference
-
Configuring MWTM to Run with Various Networking Options
-
MWTM Ports
-
Glossary
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Accessing Data from the Web Interface
Accessing the MWTM Web Interface
Overview of the MWTM Web Interface
MWTM Web Interface Navigation Tree
MWTM Web Interface Content Area
Downloading the MWTM Client from the Web
Downloading the Solaris Client
Downloading the Windows Client
Downloading the Linux Client (Unsupported)
Accessing Software Updates and Additional Information
Viewing the MWTM Technical Documentation
Displaying the Administrative Page
Viewing System Information for the MWTM
Viewing MWTM User Action Messages
Viewing All Archived MWTM Messages
Viewing System Status Information
Viewing the Event Automation Log
Viewing Web Configuration Properties
Viewing Trap Forwarding Properties
Displaying RAN-O Historical Statistics
Displaying Performance Statistics
Displaying Shorthaul Performance Statistics
Displaying Backhaul Performance Statistics
Displaying Shorthaul Error Statistics
Displaying Backhaul Error Statistics
Generating RAN Data Export Files
Displaying CSG2 Real-Time Statistics
Displaying BWG Real-Time Statistics
Creation and Deletion Statistics
Displaying HA Real-Time Statistics
Registrations Processed by AAA
Displaying GGSN Real-Time Statistics
Displaying PWE3 Real-Time Statistics
Displaying TDM Real-Time Statistics
Accessing Data from the Web Interface
This chapter provides information about accessing Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager (MWTM) data from the MWTM web interface by using a web browser. This chapter includes:
•
Accessing the MWTM Web Interface
•
Overview of the MWTM Web Interface
•
Displaying the Administrative Page
•
Displaying RAN-O Historical Statistics
•
Displaying CSG2 Real-Time Statistics
•
Displaying BWG Real-Time Statistics
•
Displaying HA Real-Time Statistics
•
Displaying GGSN Real-Time Statistics
•
Displaying PWE3 Real-Time Statistics
•
Displaying TDM Real-Time Statistics
Accessing the MWTM Web Interface
The home page of the MWTM web interface is the first window to appear when you launch the MWTM web interface.
To access the MWTM web interface, use one of these methods:
•
Open a browser and enter http://mwtm_server:1774 in the Address field. (1774 is the default port.)
Note
Accessing the MWTM web interface through a URL other than http://mwtm-server:1774 is not supported.
•
From the MWTM client interface, choose View > Web > Home.
The MWTM Home page window opens in the browser window. For details about the Home page, see Displaying the Home Page.
Overview of the MWTM Web Interface
The MWTM web interface shows basic information about the events and objects that the MWTM manages.
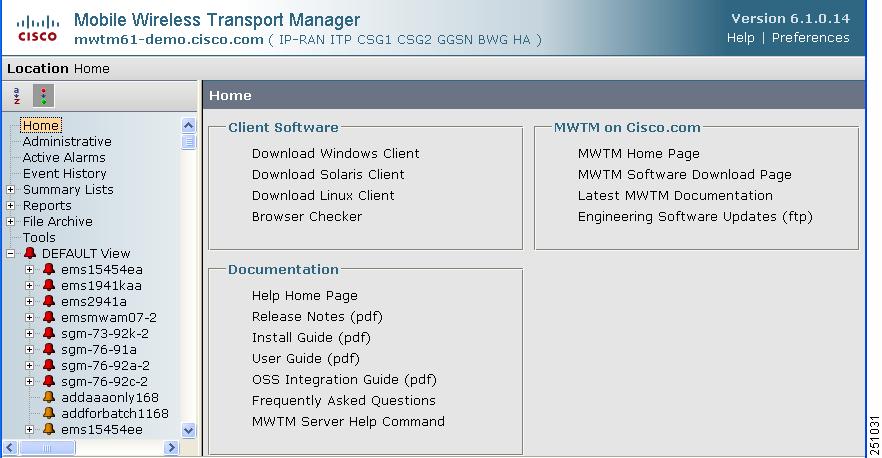
Figure 11-1 MWTM Web Interface
The MWTM web interface shows:
Title Bar
Shows:
•
Mobile Wireless Transport Manager, version, and server name
•
Managed networks (can be any combination of IPRAN, ITP, CSG1, CSG2, GGSN, BWG and/or HA)
•
Logout (appears only if you enable user access; see Configuring User Access, page 2-1)
•
Help—Click this link to access context-sensitive online help
•
Preferences—Click this link to access preferences that you can change from the web interface (see Changing Web Preference Settings, page 5-20)
Location bar
Shows where you currently are in the MWTM navigation tree.
Navigation Tree
In the left pane, shows a tree of information organized by categories (see MWTM Web Interface Navigation Tree).
Content Area
In the right pane, shows detailed information about the object chosen in the navigation tree (see MWTM Web Interface Content Area).
MWTM Web Interface Navigation Tree
You can easily navigate the features of the MWTM web interface by using the navigation tree in the left pane. By default, the navigation tree is sorted by alarm severity, with objects having the most severe alarms appearing at the top of the tree.
Note
To learn more about alarm severity, see Chapter 9, "Managing Alarms and Events."
To view detailed information about a selection in the navigation tree, click the item in the tree. The content area in the right pane shows details about the chosen item. A plus (+) or minus (-) just to the left of the item indicates whether the item has subtending items under its domain.
The MWTM automatically updates the navigation tree when changes occur to discovered nodes or to the network. When any changes occur in the MWTM client navigation tree, the MWTM web interface reflects these changes in its navigation tree. For example, if you delete a node in the MWTM client, the MWTM web interface removes that node from its navigation tree.
Note
For information about the navigation tree in the MWTM client interface, see MWTM Client Navigation Tree, page 4-19.
The MWTM web interface navigation tree contains:

Sort tree by name
Sorts all content in the navigation tree alphabetically by name.

Sort tree by status
Sorts all content in the navigation tree by status, from the highest alarms to the lowest.
Home
Shows links to MWTM client software, Cisco documentation, and information about the MWTM on the Cisco web (see Displaying the Home Page).
Administrative
Shows MWTM system information including messages, logs, status, and properties (see Displaying the Administrative Page).
If MWTM User-Based Access is enabled, only users with authentication level 3 (Network Operator) and higher can see all options. Users of all other levels see only the System Information and System Status panes.
Active Alarms
Shows alarms (see Displaying Alarms and Events).
Event History
Shows information about the events delivered by the MWTM event logger and event processor for events that the MWTM event logger and event processor deliver for all objects in the current network view (see Displaying Alarms and Events).
Summary Lists
Shows summaries of all objects that the MWTM manages (see Displaying Summary Lists).
Reports
For ITP and RAN-O networks:
•
Shows Event reports for RAN-O and ITP networks (see Setting an Alarm or Event Filter, page 9-18).
For ITP networks only:
•
Shows ITP historical reports for a specified time period (see Displaying Reports).
For RAN-O networks only:
•
Shows RAN-O shorthaul and backhaul performance and error reports (see Viewing RAN Reports, page 12-75).
If MWTM User-Based Access is enabled, only users with authentication level 4 (Network Administrator) and higher can see the Reports menu.
File Archive
Shows file archives (events and ITP reports). See Viewing Reports, page 12-6.
Tools
Provides tools for launching CiscoWorks, CiscoView, Device Center, CSG Service Manager, and GGSN Service Manager (if integrated with MWTM). Also provides a search tool for Home Agent (HA) subscribers (see Tools).
DEFAULT View
Shows a current list of nodes in the DEFAULT view (see Displaying Objects in a View).
MWTM Web Interface Content Area
The content area of the MWTM client interface is fully described in MWTM Client Content Area, page 4-19. That description also applies to the web interface. Additional navigational features that appear only in the web interface include:
Customizing the Date Range
Some windows require that you select date ranges for generating historical graphs (see Displaying RAN-O Historical Statistics). Standard date ranges (for example, Last 24 Hours or Last 7 Days) are available from a drop-down menu. However, if you want to customize the date range:
Step 1
Click the Customize Date and Time Range tool
in the toolbar of the content area. A dialog box appears.
Step 2
Enter a:
a.
Begin Date and End Date; or, select those dates by clicking the Calendar tool
.
b.
Begin Hour and End Hour from the drop-down menus, if they are available.
Note
The dialog box shows an error if the End Date is equal to or less than the Begin Date. Correct the error before proceeding.
Step 3
Click OK to accept the date and time changes; or, Cancel to cancel this operation.
The MWTM web interface generates a report for the specified time period.
Using the Toolbar
Depending upon the object you select in the navigation tree, the web interface toolbar provides these tools and options:
Last Updated
Date and time the MWTM last updated the information on the page.
Page
Shows where you are (page X of X total pages) and lists the total number of entries.
Refresh
Forces a refresh of the current web page. Click this icon to refresh the current page.
Status Refresh Interval
Allows you change the default refresh interval of 180 seconds. Enter a value between 180 and 900 seconds.
Note
Changes you make are temporary to the current page. Navigating away from the page sets the status refresh interval back to the default setting. To change the default setting, see Changing Web Preference Settings, page 5-20.
Page Size
Drop-down list of different page sizes (the number of table rows in the display). Click the drop-down arrow to select a different value. The value that you select becomes the default page size for all pages in the web interface.
CautionSetting the Page Size to Unlimited may cause your browser to stop responding if the number of table rows is large.
The title bar displays the current page and total number of table entries.
>
Advances the display to the next page of information.
>>
Advances the display to the last page of information.
<
Advances the display to the previous page of information.
<<
Advances the display to the first page of information.
Modify event filter
Opens the Event Filter dialog box. You can create a filter to display only the events in which you are interested (see Setting an Alarm or Event Filter, page 9-18).
Remove filter
Applies or removes a filter that you created.
Archived
Link that shows only archived alarms or events. This link appears when you select Event History or Active Alarms in the navigation tree. It also appears when you click the Alarms tab or Recent Events tab for a specific object.
CautionIn the Server.properties file, you can limit the number of rows in the archived events table with the MAX_ARCHIVED_EVENT
_DB_ROWS property. The default value is 200,000. Increasing this value can have severe impact on server performance and can cause the server to run out of memory.
Customize Date and Time Range
Opens the Customize Date and Time Range dialog box (see Customizing the Date Range).
Graph Series Editor
Opens the Graph Series Editor dialog box, which provides a check box for each shorthaul that is associated with the chosen RAN backhaul. To display a data series, check the check box. To hide a series, uncheck the check box.
If you uncheck all shorthauls and click OK, the graph shows the default series of shorthauls.
The MWTM displays no more than 12 series by default. To change this default setting, see Display Series Dialog Box, page 8-113.
Run
Runs the report type for the chosen duration.
Export
Exports the raw graph data to a report with comma-separated values (CSV file). You can save this file to disk or open it with an application that you choose (for example, Microsoft Excel).
Data Range
Label that shows the chosen time range for the historical statistics.
Type
Drop-down list of report types.
Duration
Drop-down list of default time ranges. Select one of these options, then click the Run tool
. To specify a nondefault time range, click the Customize Date and Time Range tool
.
Output Type
Drop-down menu that provides these options:
•
Graph—Displays statistical data in graphs and tables
•
Table—Presents statistical data in tabular format only
•
CSV—Exports statistical data using comma-separated values
Pause
Pauses the page refresh feature. Click Pause to disable the page refresh that would normally occur after the Status Refresh Interval. Click Pause again to re-enable the Status Refresh Interval.
Edit Notes
Enables you to edit or add notes for events.
Slow Poller Interval
Allows you to change the default slow poller interval of 60 seconds. Enter a value between 60 and 300 seconds.
Note
Changes you make are temporary to the current page. Navigating away from the page sets the status refresh interval back to the default setting. To change the default setting, see Changing Web Preference Settings, page 5-20.
Fast Poller Interval
Allows you to change the default fast poller interval of 15 seconds. Enter a value between 5 and 60 seconds.
Note
Changes you make are temporary to the current page. Navigating away from the page sets the status refresh interval back to the default setting. To change the default setting, see Changing Web Preference Settings, page 5-20.
Reset Counters
Enables you to modify the counter reset settings to one of the following:
•
Show counters since reboot
•
Show counters since last poll
•
Show counters since user reset
Launch
Drop-down list of applications you can launch:
•
CiscoView
•
Device Center
After you choose the application, click the
Run icon to launch it.
Severity
Drop-down list of the severities of alarms or events. Severity can be Critical, Major, Minor, Warning, Informational, Indeterminate, or Normal.
This drop-down list appears when you select Event History or Active Alarms in the navigation tree. It also appears when you click the Alarms tab or Recent Events tab for a specific object.
Change Severity
Button to change the severity level of an alarm or event.
To change the severity level, select one or more alarms or events by clicking the corresponding check boxes, choose a severity from the Severity drop-down list, then click Change Severity.
This button appears when you select Event History or Active Alarms in the navigation tree. It also appears when you click the Alarms tab or Recent Events tab for a specific object.
Clear Selection
Link to clear the selection of one or more events or alarms. To select one or more alarms or events, check the corresponding check boxes. To clear the selection, click the Clear Selection link.
This button appears when you select Event History or Active Alarms in the navigation tree. It also appears when you click the Alarms tab or Recent Events tab for a specific object.
Toolbar for alarms and events
The web interface provides the same toolbar for alarms and events as the client interface. For full descriptions of these tools, see Toolbar Buttons, page 9-14.
Displaying the Home Page
The MWTM web interface Home page provides access to MWTM client software, Cisco documentation, and information about the MWTM.
To access the Home page of the MWTM web interface, click Home under the navigation tree in the left pane.
The content area in the right pane shows these GUI elements:
Client Software
Download Windows Client
Download Solaris Client
Download Linux Client
Browser Checker
Shows the download instructions for the:
•
Windows client
•
Solaris client
•
Linux client
•
Information about the browser and screen display
For details, see Downloading the MWTM Client from the Web.
MWTM on Cisco.com
MWTM Home Page
Engineering Software Updates (FTP)
MWTM Software Download Page
Latest MWTM Documentation
Shows hyperlinks to:
•
MWTM information on the Cisco web
•
Software updates provided by Cisco Engineering
•
MWTM software download from Cisco.com
•
Most recent versions of MWTM documentation
For details, see Accessing Software Updates and Additional Information.
Documentation
Help Home Page
User Guide
Install Guide
Release Notes
Frequently Asked Questions
MWTM Server Help Command
Shows:
•
Online Help system for the MWTM
•
PDF versions1 of the:
–
User Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager
–
Installation Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager
–
Release Notes for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager
•
HTML version1 of the FAQs
•
CLI output of the mwtm help command
For details, see Viewing the MWTM Technical Documentation.
1 To access the latest versions, go to the parent index for Cisco MWTM user documents: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6472/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Downloading the MWTM Client from the Web
You can access the MWTM client installation software for Linux (unsupported), Solaris, and Windows from the MWTM web interface Home page. This access is useful if you do not have the CD-ROM, or if you prefer to download the software by using your web browser. Once you have downloaded the MWTM client installation software to your workstation, you must install the software on your local system.
For more information about installing the MWTM client software by using a web server, see the following chapters in the Installation Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager 6.1:
•
"Installing the MWTM on Solaris"
•
"Installing the MWTM on Windows"
•
"Installing the MWTM on Linux"
Downloading the Solaris Client
To access the MWTM Client for Solaris page, select Download Solaris Client.
The web interface shows the supported Solaris versions and instructions for downloading the Solaris client. See the Installation Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager 6.1 for a detailed procedure.
To start the client after installation, add the /opt/CSCOsgmClient/bin subdirectory to your path, then enter the mwtm client command from the command line.
Downloading the Windows Client
To access the MWTM Client for Windows page, select Download Windows Client.
The web interface shows supported Windows versions and instructions for downloading the Windows setup program. After downloading the setup program onto your desktop or other Windows directory, double-click the setup.exe icon to start the setup program and launch the installation wizard. See the Installation Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager 6.1 for detailed procedures.
To start the client after installation, launch it from the Windows Start menu or double-click the MWTM Client icon on your desktop.
Downloading the Linux Client (Unsupported)
To access the MWTM Client for Linux page, select Download Linux Client.
Note
The MWTM does not support the MWTM client for Linux. Use the MWTM Linux client under advisement.
The web interface shows the supported Linux versions and instructions for downloading the Linux client. See the Installation Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager 6.1 for a detailed procedure.
To start the client after installation, add the /opt/CSCOsgmClient/bin subdirectory to your path, then enter the mwtm client command from the command line.
Checking Your Browser
MWTM 6.1 supports the following browsers:
Windows
•
Internet Explorer 6
•
Internet Explorer 7
•
Firefox 3.01
Solaris 9
Solaris 10•
Firefox 2.0
Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS 4.0
1 The first time you attempt to connect to the MWTM server using Firefox 3.0, you must must add an exception to allow the connection. See the MWTM 6.1 Release Notes for more information.
Note
Opening the MWTM in an unsupported browser generates a warning. Also, if JavaScript is not enabled, the MWTM web interface cannot function.
To check your browser and screen settings, select Browser Checker.
The Browser Checker window contains:
Accessing Software Updates and Additional Information
You can access this information about the MWTM from the MWTM web interface Home page. To:
•
View information about the MWTM or any other Cisco product available on Cisco.com, select Cisco Home Page.
•
Read Cisco literature associated with the MWTM, including product data sheets, Q and As, and helpful presentations, select MWTM Home Page.
•
Access software updates for the MWTM from Cisco.com for FTP, select Engineering Software Updates (FTP). The Cisco Systems Engineering FTP server page appears.
•
Access software updates for the MWTM from Cisco.com, select MWTM Software Download Page. The Software Download page for the MWTM appears.
•
Access the most recent versions of customer documentation for the MWTM, select Latest MWTM Documentation. The Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager documentation page on Cisco.com appears. From this page, you can view the latest versions of MWTM release notes, installation guides, and end-user guides.
Note
If you cannot access Cisco.com from your location, you can always view the customer documentation that was delivered with the MWTM software. See the "Viewing the MWTM Technical Documentation" section.
Viewing the MWTM Technical Documentation
From the MWTM web interface Home page, you can view this MWTM technical documentation. To view the:
•
Entire Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager Help System, select Help Home Page.
•
Entire User Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager 6.1 as a PDF file on the web, using the Adobe Acrobat Reader, select User Guide (PDF).
•
Entire Installation Guide for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager 6.1 as a PDF file on the web, using the Adobe Acrobat Reader, select Install Guide (PDF).
•
Entire Release Notes for the Cisco Mobile Wireless Transport Manager 6.1 as a PDF file on the web, using the Adobe Acrobat Reader, select Release Notes (PDF).
•
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the MWTM, select Frequently Asked Questions.
•
Syntax for every MWTM command, select MWTM Server Help Command.
CautionThese PDF versions of technical documents might not be the latest versions. For the latest versions, go to: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6472/tsd_products_support_series_home.html.
Displaying the Administrative Page
The MWTM web interface Administrative page provides access to MWTM system information, including messages, logs, status, and properties.
To access the Administrative page of the MWTM web interface, click Administrative under the navigation tree in the left pane. The right pane displays the information indicated in Table 11-1.
Note
If MWTM User-Based Access is enabled, only users with authentication level 3 (Network Operator) and higher can see all options. Users of all other levels see only the System Information and System Status panes.
Table 11-1 Administrative Page Information
System Information
•
README
•
(ITP only)
ITP OS README•
(IPRAN only) IPRAN OS README
•
(mSEF, CSG1 only)
CSG1 OS README•
(mSEF, CSG2 only)
CSG2 OS README•
(mSEF, GGSN only)
GGSN OS README•
(mSEF, HA only)
HA OS README•
(mSEF, BWG only) BWG OS README
•
MIBs
•
README.txt file
•
MWTM-OS-Info-ITP file
•
MWTM-OS-Info-IPRAN file
•
MWTM-OS-Info-CSG1 file
•
MWTM-OS-Info-CSG2 file
•
MWTM-OS-Info-GGSN file
•
MWTM-OS-Info-HA file
•
MWTM-OS-Info-BWG file
•
Lists of MIBs, which may include:
–
(IPRAN only)
RAN MIBs–
(ITP only)
ITP MIBs–
(mSEF only)
CSG1 MIBs–
(mSEF only)
CSG2 MIBs–
(mSEF only)
GGSN MIBs–
(mSEF only)
BWG MIBs–
(mSEF only)
HA MIBs–
Common MIBs
For details, see Viewing System Information for the MWTM.
System Messages
•
Info Messages
•
Error Messages
•
User Actions
•
Message Archives
Shows tabular information about different types of system messages.
For details, see Viewing System Messages.
System Status
•
System Status
•
System Versions
•
Connected Clients
•
User Accounts
Shows the output of these system commands:
•
mwtm status
•
mwtm version
•
mwtm who
•
mwtm users
For details, see Viewing System Status Information.
System Logs
•
Console Log
•
Command Log
•
Event Automation Log
•
Security Log
•
Install Log
•
Web Access Log
•
Web Error Log
•
Report Log
Shows the contents of these system logs:
•
sgmConsoleLog.txt
•
sgmCommandLog.txt
•
eventAutomationLog.txt
•
sgmSecurityLog.txt
•
cisco_sgmsvr_install.log
•
access_log
•
error_log
•
sgmReportLog.txt
For details, see Viewing System Logs.
Properties
•
System
•
Server
•
WebConfig
•
Reports
•
Trap Forwarding
Shows the contents of these system property files:
•
System.properties
•
Server.properties
•
WebConfig.properties
•
Reports.properties
•
TrapForwarder.properties
For details, see Viewing System Properties.
Viewing System Information for the MWTM
Depending upon which type(s) of network you are managing, you can view this MWTM system information from the Administrative page:
•
README—Shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/install/README.txt file. This file provides a brief overview of the system requirements and the tasks that are necessary to install this software release.
To access the MWTM README page, choose README from the Administrative page.
•
(ITP only) ITP OS README—Shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/install/MWTM-OS-Info-ITP file. This file contains a list of the supported OS software images for:
–
ITP nodes
–
GTT encoding scheme
–
MLR address table configuration
–
GTT accounting statistics reports
–
Route table and GTT table deployment
–
MSU rates
–
ITP provisioning
To access the MWTM ITP OS README page, choose ITP OS README from the Administrative page.
•
(IPRAN only) IPRAN OS README—Shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/install/MWTM-OS-Info-IPRAN file. This file contains a list of the supported OS software images for:
–
MWR nodes
–
ONS nodes
–
RAN SVC cards
To access the MWTM IPRAN OS README page, choose IPRAN OS README from the Administrative page.
•
(mSEF, CSG1 only) CSG1 OS README—Shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/install/MWTM-OS-Info-CSG file. This file contains a list of the supported OS software images for CSG1.
To access the MWTM CSG1 OS README page, choose CSG1 OS README from the Administrative page.
•
(mSEF, CSG2 only) CSG2 OS README—Shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/install/MWTM-OS-Info-CSG2 file. This file contains a list of the supported OS software images for CSG2.
To access the MWTM CSG2 OS README page, choose CSG2 OS README from the Administrative page.
•
(mSEF, GGSN only) GGSN OS README—Shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/install/MWTM-OS-Info-GGSN file. This file contains a list of the supported OS software images for GGSN.
To access the MWTM GGSN OS README page, choose GGSN OS README from the Administrative page.
•
(mSEF, HA only) HA OS README—Shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/install/MWTM-OS-Info-HA file. This file contains a list of the supported OS software images for HA.
To access the MWTM HA OS README page, choose HA OS README from the Administrative page.
•
(mSEF, BWG only) BWG OS README—Shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/install/
MWTM-OS-Info-BWG file. This file contains a list of the supported OS software images for BWG.To access the MWTM BWG OS README page, choose BWG OS README from the Administrative page.
•
MIBs—Shows a list of the MIBs (categorized by product type) on the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM.
Each MIB appears in a list as a clickable link. You can open or download the contents of the MIB by clicking the MIB name. See Appendix F, "MIB Reference," for a complete list and high-level description of each supported MIB.
To access the MIBs page, choose MIBs from the Administrative page of the MWTM web interface.
Viewing System Messages
You can view these MWTM system messages from the Administrative page:
Note
These messages are related to the MWTM system itself, not to your network.
•
Viewing MWTM User Action Messages
•
Viewing All Archived MWTM Messages
Viewing Info Messages
The System Messages: Last number Info Messages page shows informational messages in the MWTM system log. These messages can be useful when diagnosing and correcting MWTM operational problems.
To access this page, click Info Messages from the Administrative page, or Info from the web page menu bar, if visible.
The Last Info Messages table contains:
Viewing Error Messages
The System Messages: Last number Error Messages page shows error messages stored in the MWTM system log. These messages can be useful when diagnosing and correcting MWTM operational problems.
To access this page, click:
•
Error Messages from the Administrative page.
•
Error from the web page menu bar, if visible.
The Last Error Messages table contains:
Viewing MWTM User Action Messages
The System Messages: Last number Action Messages page shows user action messages stored in the MWTM system log. These messages can be useful when diagnosing and correcting MWTM operational problems, and when monitoring audit trails of user actions.
To access this page, use one of these procedures. Click:
•
User Actions from the Administrative page.
•
Action from the web page menu bar, if visible.
The MWTM shows the System Messages: Last number Action Messages page. The System Messages: Last number Action Messages page has these sections:
Last Action Messages Menu
By default, the MWTM shows action messages of all classes on the System Messages: Last number Action Messages page. However, the MWTM provides menu options that enable you to display only messages of a specific class on the page.
The Last Action Messages menu contains:
Last Action Messages Table
The Last Action Messages table contains:
Viewing All Archived MWTM Messages
The System Message Archives: All Messages page shows all archived messages in the MWTM system logs, including:
•
error
•
informational
•
trace
•
debug
•
dump
•
messages
•
SNMP
To access the System Message Archives: All Messages page, use one of these options. Click:
•
Message Archives from the Administrative page.
•
Archives from the web page menu bar, if visible.
On the System Message Archives: All Messages page, messages are archived by timestamp. Each archived file contains all MWTM system messages for a single session for the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM server. (If you restart the server, the MWTM creates a new file.)
To view archived messages, click a timestamp. The System Messages Archive: Last number All Messages page appears, which shows all messages that were in the system log at the specified timestamp.
Note
You might observe an entry labeled messageLog-old among a list of files that have timestamps in the filenames. A daily cron job creates the files with the timestamps. The cron job, which runs at midnight, searches through the messageLog.txt and messageLog-old.txt files for all entries from the past day. The messageLog-old.txt file exists only if the size of messageLog.txt exceeds the limit set by the mwtm logsize command. The MWTM lists the contents of messageLog-old.txt because it could contain important data from the day the message log file rolled over.
The Last All Messages table contains this information (without column headers):
Viewing System Status Information
You can view this MWTM system status information from the Administrative page:
Viewing System Status
To access system status information, click System Status from the Administrative page. (The MWTM might take a few seconds to display this page.) This page shows the status of all MWTM servers, local clients, and processes.
Viewing System Versions
To access version information, click System Versions from the Administrative page. (The MWTM might take a few seconds to display this page.) This page shows version information for all MWTM servers, clients, and processes.
Viewing Connected Clients
To access connected client information, click Connected Clients from the Administrative page. This page lists all MWTM clients that are currently connected to the MWTM server. It also lists all Solaris and Linux users that are logged in to the MWTM server.
Viewing User Accounts
To access user account information, click User Accounts from the Administrative page. This page shows information about all user accounts that have been defined for the MWTM server. If no user accounts have been defined, the MWTM shows this message:
User Database is EmptyThe user accounts page displays the output of the mwtm users command. For example:
/opt/CSCOsgm/bin/mwtm usersUser Name Last Login Level Name & Number Status-----------------------------------------------------------------User1 Wed Jan 17 14:03:13 EST 2007 System Admin 5 [Account Enabled]User2 Unknown System Admin 5 [Account Enabled]User3 Wed Jan 17 13:43:30 EST 2007 System Admin 5 [Account Enabled]User Based Access Protection is Enabled.Authentication type = localThe the mwtm users command output contains:
User Name
The MWTM user for whom a User-Based Access account has been set up.
Last Login
Date and time the user last logged in to the MWTM.
Level Name & Number
Authentication level and number for the user. Valid levels and numbers are:
•
Basic User, 1
•
Power User, 2
•
Network Operator, 3
•
Network Administrator, 4
•
System Administrator, 5
Status
Current status of the user's account. Valid status settings are:
•
Account Enabled—The account has been enabled and is functioning normally.
•
Account Disabled—The account has been disabled for one of these reasons:
–
A System Administrator disabled the account. See the "mwtm disablepass" section on page B-25 and the "mwtm disableuser" section on page B-26 for more information.
–
The MWTM disabled the account as a result of too many failed attempts to log in using the account. See the "mwtm badlogindisable" section on page B-11 for more information.
–
The MWTM disabled the account because it was inactive for too many days. See the "mwtm inactiveuserdays" section on page B-32 for more information.
Viewing System Logs
From the Administrative page, you can view:
•
Viewing the Event Automation Log
Viewing the Console Log
The Console Log shows the contents of the MWTM system console log file for the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM. The console log file contains unexpected error and warning messages from the MWTM server, such as those that might occur if the MWTM server cannot start. It also provides a history of start-up messages for server processes and the time each message appeared.
To access the Console Log, click Console Log in the System Logs pane of the Administrative page. You can also view the Console Log with the mwtm console command.
Viewing the Command Log
The Command Log shows the contents of the MWTM system command log file for the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM server. The system command log lists all mwtm commands that have been entered for the MWTM server, the time each command was entered, and the user who entered the command.
To access the Command Log, click Command Log in the System Logs pane of the Administrative page. You can also view the Command Log with the mwtm cmdlog command.
The MWTM Command Log page appears. The Command Log table contains:
Viewing the Event Automation Log
The Event Automation Log shows the contents of the system event automation log file for the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM server. The system event automation log lists all messages that event automation scripts generate.
The default path and filename for the system event automation log file is /opt/CSCOsgm/logs/eventAutomationLog.txt. If you installed the MWTM in a directory other than /opt, then the system event automation log file is in that directory.
To access the Event Automation Log, click Event Automation Log in the System Logs pane of the Administrative page. You can also view the Event Automation Log with the mwtm eventautolog command.
Related Topic
Changing the Way the MWTM Processes Events, page 9-35.
Viewing the Security Log
The Security Log shows the contents of the MWTM system security log file for the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM server. The system security log lists:
•
All security events that have occurred for the MWTM server
•
The time each event occurred
•
The user and command that triggered the event
•
The text of any associated message
The default path and filename for the system security log file is /opt/CSCOsgm/logs/sgmSecurityLog.txt. If you installed the MWTM in a directory other than /opt, then the system security log file is in that directory.
To access the Security Log, click Security Log in the System Logs pane of the Administrative page. You can also view the Security Log with the mwtm seclog command.
The Last Security Entries table contains these columns:
Viewing the Install Log
The Install Log shows the contents of the MWTM system installation log. The installation log contains messages and other information recorded during installation, which can be useful when troubleshooting problems. The Install Log also records the installer's selections (for example, whether the installer chose to configure the MWTM to receive SNMP traps).
The default path and filename for the install log file is /opt/CSCOsgm/install/cisco_sgmsvr_install.log. If you installed the MWTM in a directory other than /opt, then the install log file is in that directory.
To access the Install Log, click Install Log in the System Logs pane of the Administrative page. You can also view the Install Log with the mwtm installlog command.
Viewing the Web Access Logs
The Web Access Logs page shows a list of web access log files for the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM server. The web access log lists all system web access messages that have been logged for the MWTM server, providing an audit trail of all access to the MWTM server through the MWTM web interface.
The default path and filename for the web access log file is /opt/CSCOsgm/apache/logs/access_log. If you installed the MWTM in a directory other than /opt, then the web access log file is in that directory.
To access the Web Access Logs page, click Web Access Logs from with the System Logs pane of the Administrative page. You can also view the Web Access Logs page using the mwtm webaccesslog command.
Viewing the Web Error Logs
The Web Error Logs page shows a list of web error log files for the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM server. The web server error log lists all system web error messages that have been logged for the MWTM web server. You can use the web error log to troubleshoot the source of problems that users may have encountered while navigating the MWTM web interface.
The default path and filename for the web error log file is /opt/CSCOsgm/apache/logs/error_log. If you installed the MWTM in a directory other than /opt, then the web error log file is in that directory.
To access the Web Error Logs page, click Web Error Logs in the System Logs pane of the Administrative page. You can also view the Web Error Logs page using the mwtm weberrorlog command.
Viewing the Report Log
The Report Log shows the message log for ITP reports for the server to which you are connected, and which is currently running the MWTM server. You can view this log to determine the beginning and finish times for report generation. The log also records errors that occurred during report generation (for example, server connection errors).
The default path and filename for the report log file is /opt/CSCOsgm/logs/sgmReportLog.txt. If you installed the MWTM in a directory other than /opt, then the report log file is in that directory.
To access the Report Log, click Report Log in the System Logs pane of the Administrative page. You can also view the Report Log with the mwtm replog command.
Viewing Properties
Property files for the MWTM are in the /opt/CSCOsgm/properties directory. You can view these MWTM properties from the Administrative page.
•
Viewing Web Configuration Properties
•
Viewing Trap Forwarding Properties
Viewing System Properties
To access the System Properties file, click System in the Properties pane of the Administrative page. The MWTM shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/properties/System.properties file.
The System Properties file contains MWTM server and client properties that control various MWTM configuration parameters.
You can change some of the system properties using MWTM commands:
For these system properties, you can view related documentation:
CLIENT_PORT
DATASERVER_PORT
LOGINSERVER_PORT
RMIREGISTRY_PORT
MAX_CHART_SERIES
Viewing Server Properties
To access the Server Properties file, click Server in the Properties pane of the Administrative page. The MWTM shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/properties/Server.properties file.
The Server Properties file contains various properties that control the MWTM server.
You can use MWTM commands to change these server properties:
DEMAND_POLLER_TIMELIMIT
SNMP_MAX_ROWS
UNKNOWN_AGING_TIMEOUT
To change poller parameters in the Server Properties file, see the "Changing MWTM Server Poller Settings" section on page 3-2.
Viewing Web Configuration Properties
To access the Web Configuration Properties file, click WebConfig in the Properties pane of the Administrative page. The MWTM shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/properties/
WebConfig.properties file.The Web Configuration Properties file contains properties that control the configuration of the MWTM web interface. For example:
MAX_ASCII_ROWS = 6000MAX_HTML_ROWS = 100# The selectable page sizes start at MIN_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE and doubles until# the MAX_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE value is reached# (e.g. 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800)MIN_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE = 25MAX_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE = 800LOG_UPDATE_INTERVAL = 300WEB_UTIL = percentWEB_NAMES = displayMAX_EV_HIST = 15000You can use the MWTM to change the web configuration properties:
LOG_UPDATE_INTERVAL
To control how often, in seconds, the MWTM updates certain web output, use the mwtm weblogupdate command. The valid range is 1 second to an unlimited number of seconds. The default value is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
MAX_ASCII_ROWS
To set the maximum number of rows for MWTM ASCII web output, such as displays of detailed debugging information, use the mwtm maxasciirows command. The valid range is 1 row to an unlimited number of rows. The default value is 6,000 rows.
MAX_EV_HIST
To set the maximum number of rows for MWTM to search in the event history logs, use the mwtm maxevhist command. The event history logs are the current and archived MWTM network status logs for status change and SNMP trap messages. The MWTM sends the results of the search to the web browser, where the results are further limited by the setting of the mwtm maxhtmlrows command. The valid range is 1 row to an unlimited number of rows. The default value is 15,000 rows.
MAX_HTML_ROWS
To set the maximum number of rows for MWTM HTML web output, such as displays of statistics reports, status change messages, or SNMP trap messages, use the mwtm maxhtmlrows command. This lets you select a page size (if you have not explicitly chosen a page size). Once you select a page size from any page, the MWTM remembers your preference until you delete your browser cookies. The default value is 100 rows.
MIN_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE
This setting determines the minimum page size for the user to select from the Page Size drop-down menu. The page size values start with the MIN_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE and double until they reach the MAX_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE.
MAX_SELECTABLE_
PAGE_SIZEThis setting determines the maximum page size for the user to select from the Page Size drop-down menu. The page size values start with the MIN_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE and double until they reach the MAX_SELECTABLE_PAGE_SIZE.
WEB_NAMES
To specify whether the MWTM should show real DNS names or display names in web pages, enter the mwtm webnames command. To show:
•
The real DNS names of nodes, as discovered by the MWTM, enter mwtm webnames real.
•
Display names, enter mwtm webnames display. Display names are new names that you specify for nodes. This is the default setting. For more information about display names, see the "Editing Properties" section on page 6-33.
WEB_UTIL
To specify whether the MWTM should display send and receive utilization as percentages or in Erlangs in web pages, enter the mwtm who command. To show:
•
Utilization as a percentage, enter mwtm webutil percent. This is the default setting.
•
Display utilization in Erlangs (E), enter mwtm webutil erlangs.
See Viewing RAN-O Performance Data, page 8-107 and Viewing RAN-O Error Data, page 8-115 for more information on send and receive utilization for shorthauls and backhauls.
See Chapter 12, "Managing Reports" for more information on send and receive utilization for linksets and links.
Each of the web configuration commands requires you to be logged in as the root user, as described in the "Becoming the Root User (Server Only)" section on page 4-2, or as a superuser, as described in the "Specifying a Super User (Server Only)" section on page 2-20.
Related Topic
Viewing Reports Properties
To access the Reports Properties file, click Reports in the Properties pane of the Administrative page. The MWTM shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/properties/Reports.properties file.
The Reports Properties file contains properties that control various aspects of the reports that are available in the MWTM web interface.
You can use MWTM commands to change these reports properties:
Viewing Trap Forwarding Properties
To access the Trap Forwarding Properties file, click TrapForwarding in the Properties pane of the Administrative page. The MWTM shows the contents of the /opt/CSCOsgm/properties/TrapForwarder.properties file.
The Trap Forwarder Properties file contains a list of the destination addresses for the trap forwarder. Enter each destination address on its own line and use this format:
SERVERxx=destination_IP_address[:port_number]
The port_number parameter is optional.
Displaying Alarms and Events
To display alarms in the web interface, click Active Alarms in the navigation tree, or select an object in the navigation tree and click the Alarms tab.
To display events in the web interface, click Event History in the navigation tree, or select an object in the navigation tree and click the Recent Events tab.
Viewing alarms and events in the web interface is essentially the same as viewing them in the MWTM client. Only minor differences exist:
•
A paging feature for paging through large tables.
•
A refresh interval that you can change.
•
An Archived link for viewing archived alarms.
•
Alarm selection by check box and a Clear Selection link.
•
Severity drop-down list and a Change Severity button.
For detailed descriptions of these tools, see the "Using the Toolbar" section
For descriptions of the columns, see the "Right-click Menus" section on page 9-16.
Displaying Summary Lists
Displaying Summary Lists in the web interface is essentially the same as displaying them in the MWTM client. Only minor differences exist. Clicking on an object under the Summary Lists in the web interface causes the content area to show information about the object.
For details on:
•
Navigating table columns, see Navigating Table Columns, page 5-24.
•
The toolbar, see Using the Toolbar.
For complete information about Summary Lists, see the "Displaying Object Windows" section on page 6-2.
Displaying Software Versions
The Software Versions table lists the software versions for each node the MWTM manages.
To access the Software Versions page:
•
From the Web interface navigation tree, select Summary Lists > Software Versions.
•
From the MWTM main window, select View > Web > Software Versions.
For details on:
•
Navigating the columns of the Software Versions table, see Navigating Table Columns, page 5-24.
•
The toolbar, see Using the Toolbar.
The Software Versions table contains:
Name
Name of the node.
Node Type
Type of node.
Software Version
Software version used by the node.
Software Description
Full software version information.
Tools
To access launch and search tools, click Tools in the navigation tree of the MWTM web interface. This action opens a Launch pane and a Search pane in the content area:
Launch Tools
If you have integrated with a CiscoWorks server, one or more of the following applications appears in the Launch pane as active links:
•
CiscoView
•
CiscoWorks LMS Portal
•
CSG Service Manager
•
Device Center
•
GGSN Service Manager
The name of the server appears in parentheses following the application names. To launch an application, click the application name. See Integrating the MWTM with Other Products, page 5-39.
Note
The MWTM attempts to launch the URL of the service manager that resides on the LMS server. If the service manager is not installed on the LMS server, you will receive an HTTP 404 error. To prevent this error, ensure that the service managers are installed on the LMS server, or remove the CSG or GGSN network setting with the mwtm manage, page B-40, command.
Search Tools
Note
You must have the Cisco Home Agent (HA) network enabled to use this tool (for details on enabling HA, see mwtm manage, page B-40).
The Search pane provides a tool that you use to search for a specific subscriber across one or more designated Cisco Home Agent (HA) routers. This tool is useful for troubleshooting problems that HA subscribers may report. To search for an HA subscriber:
Step 1
Click Search for Home Agent Subscriber in the Search pane.
Step 2
Click the Identifier Type radio button:
•
Network Access Identifier—Use this option if you know the subscriber's network access identifier (NAI); for example, jdoe@xyz.com.
•
IP Address—Use this option if you know the subscriber's IP address
Step 3
Depending on your selection in Step 2, enter the subscriber's NAI or IP address in the Mobile Node Identifier field.
Step 4
In the Select Home Agents to Search pane, check the check boxes of the Home Agents that you want to search. (The default setting is all Home Agents.)
Step 5
To conduct the search, click the Search button.
The Search Results popup window appears.
Step 6
If the search successfully locates the subscriber, and you want to troubleshoot the problem, click the Troubleshoot Subscriber button in the Search Results popup.
The MWTM automatically navigates to the Troubleshooting tab of the HA device.
Step 7
For more information about troubleshooting devices by using the Troubleshooting tab, see Viewing Troubleshooting, page 8-43.
Displaying Reports
Note
If MWTM User-Based Access is enabled, only users with authentication level 4 (Network Administrator) and higher can see the Reports menu.
You can display reports primarily for ITP objects in the MWTM Web interface. An overview and a complete list and description of these reports is available in Chapter 12, "Managing Reports."
Event reports are also available for both RAN-O and ITP networks, also available in the Reports menu. For details, see the "Viewing Archived Event Files on the Web" section on page 9-30 and the "Viewing the Event Metrics Report on the Web" section on page 9-30.
You can also display network-wide RAN-O reports in the Reports menu. For details, see Viewing RAN Reports, page 12-75.
Displaying Objects in a View
Displaying objects in a view in the MWTM web interface is essentially the same as viewing them in the MWTM client. Only minor differences exist. The MWTM web interface:
•
Shows a subset of the columns that the client interface shows.
•
Has a paging feature. See the "Using the Toolbar" section.
•
Has a refresh interval that you can change.
•
Displays a Statistics tab when you select a CSG2 or BWG Gateway node in the navigation tree. See Displaying CSG2 Real-Time Statistics, or Displaying BWG Real-Time Statistics. The Statistics tab appears only on the web interface for these node types.
•
When viewing CPU Utilization in the Performance tab, the MWTM web interface displays the data in tabular format instead of graph format. See CPU Utilization, page 8-59.
•
When viewing performance and error information for interfaces (in the Interface Performance and Interface Errors tabs), the MWTM web interface displays the data in tabular format only. The MWTM client interface displays the data in tabular and graph format. See Viewing Data for Interfaces, page 8-63.
For details on each object type, see the "Displaying Object Windows" section on page 6-2.
Displaying RAN-O Historical Statistics
The MWTM web interface provides access to RAN-O historical statistics in the MWTM database. You can use these statistics for capacity planning and trend analysis. For example, you can generate graphs, tables, or CSV files:
•
For a specified time range to display historical statistics for customer busy-hours.
•
To show the maximum send and receive traffic over a specified time period.
•
To show data on a 15-minute, daily, or hourly basis.
Using this information, you can perform detailed analysis of historical traffic utilization on the backhaul and shorthaul links to plan future facility upgrades.
Note
The MWTM client provides real-time (not historical) graphs depicting performance and error information occurring in real time. You use real-time statistics for troubleshooting active problem areas in your network. See Viewing RAN-O Performance Data, page 8-107 and Viewing RAN-O Error Data, page 8-115.
This section provides information about:
•
Displaying Performance Statistics
•
Generating RAN Data Export Files
Displaying Performance Statistics
You can view performance data for a shorthaul or backhaul interface in the MWTM:
•
Web interface by selecting a shorthaul or backhaul interface in the navigation tree and clicking the Shorthaul Performance or Performance tab in the right pane.
•
Client interface by right-clicking a shorthaul or backhaul interface in the navigation tree and clicking Performance History.
Note
If the CISCO-IP-RAN-BACKHAUL-MIB on the node is not compliant with the MWTM, the MWTM issues the message:
MIB not compliant for reportsInstall a version of IOS software on the node that is compatible with the MWTM. For a list of compatible IOS software, from the MWTM:
•
Web interface, choose Administrative > IPRAN OS README.
•
Client interface, choose View > Web > Administrative; then click IPRAN OS README.
The Performance tab shows one or more graphs depending on the type of report chosen. These graphs depict send and receive rates of optimized IP traffic over a specified time range. The graphs display the traffic in bits per second. Each data series shows maximum, minimum, and average rates of optimized traffic.
The Performance tab for a backhaul interface shows total rates for GSM and UMTS traffic, including total error rates.
This section provides information about:
•
Displaying Shorthaul Performance Statistics
•
Displaying Backhaul Performance Statistics
Displaying Shorthaul Performance Statistics
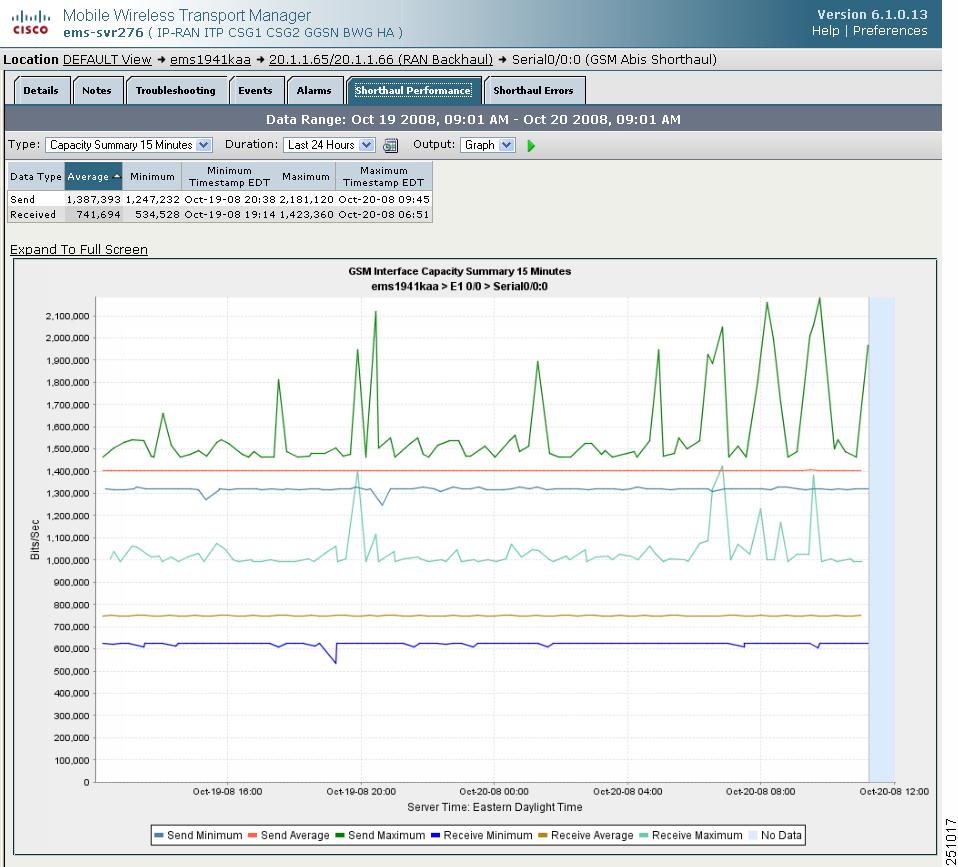
The Shorthaul Performance tab for a shorthaul interface shows the maximum, minimum, and average rates for send and receive traffic.
Figure 11-2 Performance Tab for Shorthaul Interface
The Shorthaul Performance tab for a shorthaul interface contains:
Toolbar
Provides functions to select a report type, duration, output type. See Using the Toolbar.
Type
A comprehensive summary of minimum, average, and maximum capacity statistics for send and receive traffic on a RAN shorthaul. You can choose from 15-minute, hourly, or daily capacity summary reports, or choose a custom range.
Table
If the Output Type is Graph, the table contains:
•
Data Type—Type of data, send or receive
•
Average—Average of the data across the chosen time range
•
Minimum—Minimum value across the chosen time range
•
Minimum Timestamp EDT—Time the minimum value occurred
•
Maximum—Maximum value across the chosen time range
•
Maximum Timestamp EDT—Time the maximum value occurred
Note
If the Output Type is Table or CSV, the same data is presented but the column headings are labeled by data type (for example, Send Average and Receive Average).
Expand to Full Screen
If Output Type is Graph, this text link that displays the graph in a new, full-screen window for easier viewing.
Bits/Sec
If Output Type is Graph, Y-axis label that shows traffic rate in bits per second. The Y axis automatically scales to the interface speed.
Note
If no data exists between any two data points, the graph displays a color-coded vertical bar to show the period for which no data is available.
Time
If Output Type is Graph, X-axis label that shows a historical time scale and the server time zone.
Legend
If Output Type is Graph, color-coded legend that shows labels for traffic rates.
Displaying Backhaul Performance Statistics
The Performance tab for a backhaul interface shows minimum, average, and maximum traffic rates for send and receive traffic. You can also determine the percentage of backhaul utilization that various traffic types occupy. Error rates appear, too.
Figure 11-3 Example of Performance Tab for Backhaul Interface
The Performance tab for a backhaul interface contains:
Toolbar
Provides functions to select a report type, duration, output type, and the Graph Series Editor. See the "Using the Toolbar" section.
Type
Report Type. If you choose a Capacity Summary report, the report shows a comprehensive summary of minimum, average, and maximum capacity statistics for total traffic (GSM-Abis and UMTS-Iub), total GSM-Abis traffic, and total UMTS-Iub traffic. You can choose from 15-minute, hourly, or daily capacity summary reports. Error rates appear, too.
If Output Type is Graph, statistics appear in three graphs:
•
Top—Capacity statistics for send traffic rates, including percentage of backhaul utilization (right side of graph).
•
Middle—Capacity statistics for receive traffic rates, including percentage of backhaul utilization (right side of graph).
•
Bottom—Error counts for send and receive traffic.
Type (continued)
If you choose a Minimum, Average, or Maximum Capacity report, the tables and graphs show capacity statistics for the backhaul interface. You can choose from 15-minute, hourly, or daily capacity reports.
If Output Type is Graph, send and receive rate statistics appear in separate panes. Each pane shows two fully expandable graphs:
•
Top—Shows total (GSM-Abis and UMTS-Iub), total GSM-Abis, and total UMTS-Iub traffic rates, including percentage of backhaul utilization (right side of graph).
•
Bottom—Shows traffic rates for each shorthaul interface that belongs to the backhaul.
Table
Note
Different tables appear depending on the report Type and Output Type selections.
If the Output Type is Graph, a table appears with these columns:
•
Data Type—Type of data, send or received
•
Average—Average of the data across the chosen time range
•
Minimum—Minimum value across the chosen time range
•
Minimum Timestamp EDT—Time the minimum value occurred
•
Maximum—Maximum value across the chosen time range
•
Maximum Timestamp EDT—Time the maximum value occurred
Note
If the Output Type is Table or CSV, similar data is presented but the column headings may vary. Also, if the value is N/A, that means no data is available.
Another table has these columns:
•
Data Type—Category of error for which statistics are gathered. Types include optimization, missed packets, and miscellaneous errors.
•
Total Counts—Total error count for each type of error.
•
Avg. Error Rate (Per Sec)—The calculated average error rate per second for each error type over the duration of the data range that you chose.
Note
You can sort the contents of the columns in ascending or descending order by clicking the column heading.
Expand to Full Screen
If Output Type is Graph, text link that shows a graph in a new, full-screen window for easier viewing.
Bits/Sec
If Output Type is Graph, primary Y-axis label (left side of graph) that shows traffic rate in bits per second. The Y axis automatically scales to the User Bandwidth. See the"Editing Properties for a RAN-O Backhaul" section on page 6-36.
Note
If no data exists between any two data points, the graph displays a color-coded vertical bar to show the period for which no data is available.
% Utilization
If Output Type is Graph, secondary Y-axis label (right side of graph) that shows the backhaul utilization as a percentage of the User Bandwidth. The graph background has three horizontal bars that are color-coded to indicate these thresholds:
•
Overloaded—Top portion of graph.
•
Warning—Middle portion of graph.
•
Acceptable—Bottom portion of graph.
For definitions of these thresholds, see the "Threshold Information (RAN-O Only)" section on page 8-43.
To change the threshold settings, see the "Editing Properties for a RAN-O Backhaul" section on page 6-36.
Note
If the % Utilization exceeds 100%, see Why does my backhaul utilization graph show greater than 100% for transmit traffic?, page C-22.
Time
X-axis label that shows a user-specified, historical time scale and the server time zone.
Legend
Color-coded legend that shows labels for traffic and error rates.
Displaying Error Statistics
You can view error data for a shorthaul or backhaul interface in the MWTM:
•
Web interface by selecting an interface in the navigation tree and clicking the Shorthaul Errors or Errors tab in the content area.
•
Client by right-clicking an interface in the navigation tree and clicking Error History.
Note
If the CISCO-IP-RAN-BACKHAUL-MIB on the node is not compliant with the MWTM, the MWTM issues the message:
MIB not compliant for reportsInstall a version of IOS software on the node that is compatible with the MWTM. For a list of compatible IOS software, from the MWTM:
•
Web interface, choose Administrative > IPRAN OS README.
•
Client interface, choose View > Web > Administrative; then click IPRAN OS README.
You view error data for a shorthaul or backhaul interface by selecting the interface in the navigation tree and clicking the Errors tab in the content area. The Errors tab shows total error counts and average error rates in table and graph format.
This section provides information about:
•
Displaying Shorthaul Error Statistics
•
Displaying Backhaul Error Statistics
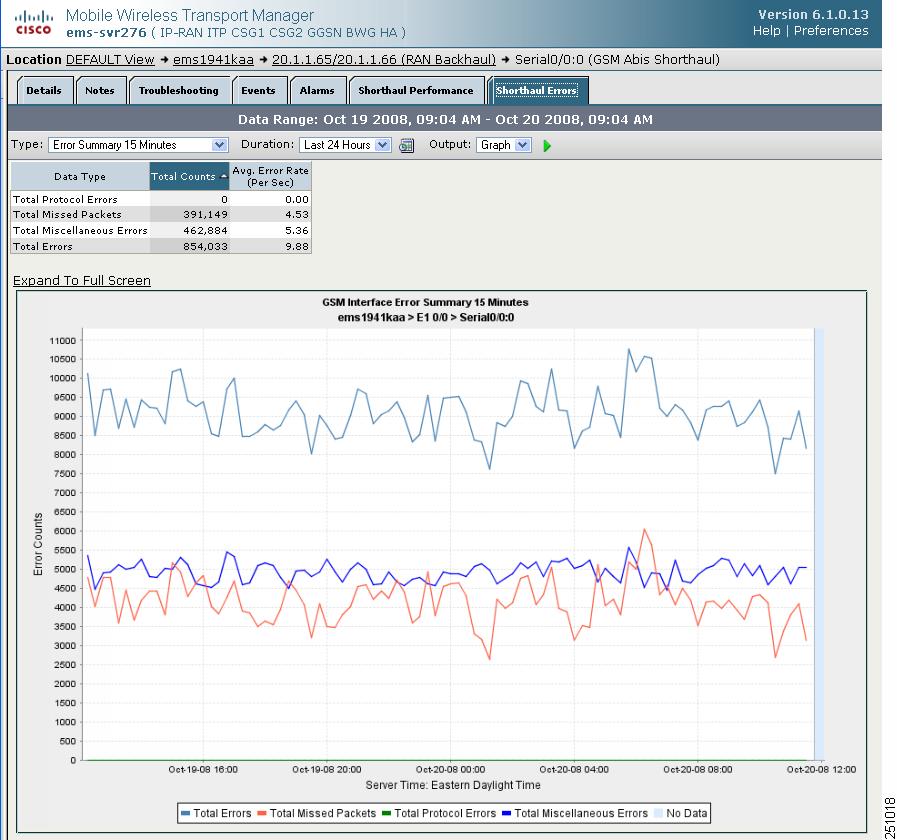
Displaying Shorthaul Error Statistics
The Shorthaul Errors tab for a shorthaul interface shows a single table and a graph that shows the error rates and counts for different types of GSM-Abis and UMTS-Iub errors.
Figure 11-4 Example of Errors Tab for Shorthaul Interface
The Shorthaul Errors tab for a shorthaul interface contains:
Toolbar
Provides functions to select report type, duration, and output type. See the "Using the Toolbar" section.
Type
Report Type. If you choose an Error Summary report, the table and graph display a comprehensive summary of total error counts and average error rates for protocol, missed-packet, and miscellaneous errors for the chosen shorthaul. You can choose from 15-minute, hourly, or daily error summary reports. Statistics appear in table and graph format.
Type (continued)
If you choose an error report that is not a summary report, the table and graph displays protocol, missed packet, or miscellaneous errors for the shorthaul interface. You can choose from 15-minute, hourly, or daily error reports. Statistics appear in table and graph format.
For definitions of these error types, see:
•
Protocol Failures, page 8-117
Table
Note
Different tables and column headings appear depending on the report Type and Output Type selections.
If Output Type is Graph, a table appears with these columns:
•
Data Type—Category of error for which statistics are gathered. Types include protocol, missed packets, and miscellaneous errors.
•
Total Counts—Total error count for each type of error.
•
Avg. Error Rate (Per Sec)—The calculated average error rate per second for each error type over the duration of the data range that you chose.
Note
If the value is N/A, that means no data is available.
Depending on the report Type selection, if the Output Type is Table or CSV, a table appears with multiple columns showing various error types and their counts. For definitions of these error types, see the:
•
Protocol Failures, page 8-117
Note
You can sort the contents of the columns in ascending or descending order by clicking the column heading.
Expand to Full Screen
If Output Type is Graph, this text link displays a graph in a new, full-screen window for easier viewing.
Error Counts
If Output Type is Graph, Y-axis label on left side of graph that shows traffic rate in bits per second.
Note
If no data exists between any two data points, the graph displays a color-coded vertical bar to show the period for which no data is available.
Time
If Output Type is Graph, X-axis label that shows a user-specified, historical time scale and the server time zone.
Legend
If Output Type is Graph, color-coded legend that shows labels for traffic and error rates.
Displaying Backhaul Error Statistics
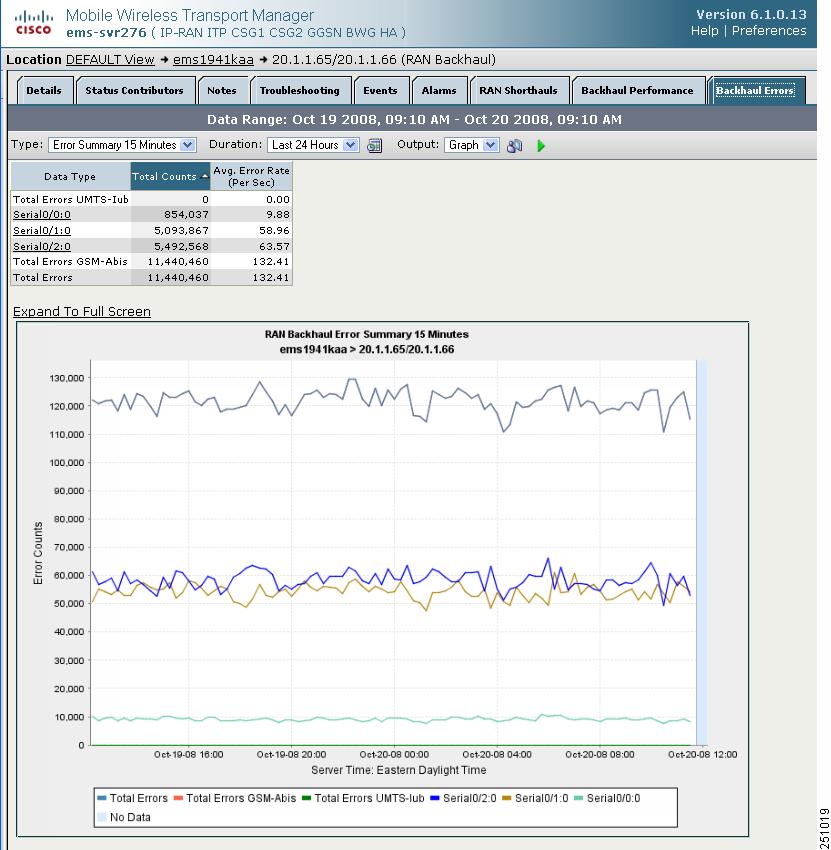
The Errors tab for a RAN backhaul interface shows a single table and a graph that shows the error rates and counts for different interfaces belonging to the backhaul.
Figure 11-5 Example of Errors Tab for Backhaul Interface
The Errors tab for a backhaul interface contains:
Toolbar
Provides functions to select a report type, duration, output type, and the Graph Series Editor. See the "Using the Toolbar" section.
Table
Note
Different tables and column headings appear depending on the report Type and Output Type selections.
If Output Type is Graph, a table appears with these columns:
•
Data Type—Category of error for which statistics are gathered. Types include optimization, missed packets, and miscellaneous errors.
•
Total Counts—Total error count for each type of error.
•
Avg. Error Rate (Per Sec)—The calculated average error rate per second for each error type over the duration of the data range that you chose.
Note
If the value is N/A, that means no data is available.
If Output Type is Table, a table appears with columns for total error counts for various error types (for example, total GSM-Abis errors).
Note
You can sort the contents of the columns in ascending or descending order by clicking the column heading.
Expand to Full Screen
If Output Type is Graph, text link that shows a graph in a new, full-screen window for easier viewing.
Error Counts
If Output Type is Graph, Y-axis label on left side of graph that shows traffic rate in bits per second.
Time
If Output Type is Graph, X-axis label that shows a user-specified, historical time scale and the server time zone.
Legend
If Output Type is Graph, color-coded legend that shows labels for traffic and error rates (for example, Total Errors UMTS-Iub).
Generating RAN Data Export Files
You can easily generate historical reports for RAN backhauls and shorthauls in the web interface. You can then export this data to a report with comma-separated values (CSV file). You can save this file to disk or open it with an application that you choose (for example, Microsoft Excel).
To export RAN data:
Step 1
Select a RAN backhaul or shorthaul in the navigation tree of the web interface.
Step 2
Click the Performance or Errors tab in the right pane.
Step 3
Generate a report.
Step 4
Click the Export the report as a CSV file icon
.
Displaying CSG2 Real-Time Statistics
The MWTM enables you to display real-time statistics for CSG2 nodes in the MWTM web interface. To display real-time statistics, select the node in the navigation tree and click the Statistics tab. Four categories of statistics appear:
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
Global Statistics
The Global Statistics pane contains:
Load Statistics
Load statistics are available only on CSG2, Release 2, for devices running IOS 12.4(15) or later.
The Load Statistics pane contains:
BMA Statistics
The Billing Mediation Agent (BMA) Statistics pane contains:
Quota Server Statistics
The Quota Server Statistics pane contains:
User Database Statistics
The user database is a service that translates a client IP address into a user identifier. The User Database Statistics pane contains:
Displaying BWG Real-Time Statistics
The MWTM enables you to display real-time statistics for Broadband Wireless Gateway (BWG) nodes in the MWTM web interface. To display BWG real-time statistics, select a BWG node in the navigation tree and click the Statistics tab. These four subtabs appear:
Global Statistics
The Global statistics subtab shows global statistics for BWG nodes and contains:
•
Creation and Deletion Statistics
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
Status
The Status pane shows:
Creation and Deletion Statistics
The Creation and Deletion Statistics pane shows:
Miscellaneous Statistics
The Miscellaneous Statistics pane shows:
Signaling Packet Statistics
The Signaling Packet Statistics pane shows:
DHCP Packet Statistics
The DHCP Packet Statistics pane shows:
Handoff Statistics
The Handoff Statistics pane shows:
Data Packet Statistics
The Data Packet Statistics pane shows:
Dropped Packet Statistics
The Dropped Packet Statistics pane shows:
Profile Statistics
The Profile Statistics pane shows:
Rejected Statistics
The Rejected Statistics pane shows:
Paths Statistics
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
The Paths statistics subtab shows information and statistics about each base station and contains:
User Groups Statistics
The User Groups statistics subtab shows information and statistics for user groups and contains:
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
Sessions and Flow Statistics
The Sessions and Flow Statistics pane shows:
Traffic Statistics
The Traffic Statistics pane shows:
Displaying HA Real-Time Statistics
The MWTM enables you to display real-time statistics for Home Agent (HA) nodes in the MWTM web interface. To display HA real-time statistics, select a HA node in the navigation tree and click the Statistics tab. These subtabs appear:
Global
The Global subtab shows global statistics for HA nodes and contains:
•
Registrations Processed by AAA
•
Registration Requests
•
Standby Synchronization
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
Registrations Processed by AAA
The Registrations Processed by AAA pane shows:
Registration Requests
The Registration Requests pane shows:
Standby Synchronization
The Standby Synchronization pane shows:
IP Local Pool Config
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
The IP Local Pool Config subtab shows IP addresses for HA nodes and contains:
IP Local Pool Stats
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
The IP Local Pool Stats subtab shows IP addresses and IP addresses in use for HA nodes and contains:
Displaying GGSN Real-Time Statistics
The MWTM enables you to display real-time statistics only in the MWTM web interface for Gateway GPRS Support Nodes (GGSNs) that reside on the Service and Application Module for IP (SAMI). To display GGSN real-time statistics, select a SAMI-based GGSN node in the navigation tree and click the Statistics tab. These subtabs appear:
Global
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
The Global subtab shows global statistics for GGSN nodes and contains:
GTP Statistics
The GTP Statistics pane displays statistics about the GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) and contains:
Charging Statistics
The Charging Statistics pane displays count and rate statistics for GGSN charging messages and contains:
G-CDR Messages Pending
GGSN Call Detail Records (CDRs) that are pending.
G-CDR Messages Sent
G-CDRs that were sent.
GTP Throughput Statistics
The GTP Throughput Statistics pane displays count and rate statistics about GTP throughput and contains:
PDP Context Statistics
The PDP Context Statistics pane shows count and rate values for these statistics:
AAA Statistics
The AAA Statistics pane shows:
IP and UDP Statistics
The IP and UDP Statistics pane shows:
SGSN Throughput
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
The SGSN Throughput subtab shows:
APN General
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
The APN General subtab contains:
APN Miscellaneous Statistics
To view the APN Miscellaneous Statistics table, choose this option from the Type drop-down menu. The GUI displays count and rate values for these statistics:
APN PDP Context Statistics
To view the APN PDP Context Statistics table, choose this option from the Type drop-down menu. The GUI displays the count and rate values for these statistics:
APN Throughput Statistics
To view the APN Throughput Statistics table, choose this option from the Type drop-down menu. The GUI displays the count and rate values for these statistics:
IP Local Pool Config
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
The IP Local Pool Config subtab shows IP addresses for GGSN nodes and contains:
IP Local Pool Stats
Note
For toolbar details, see Using the Toolbar.
The IP Local Pool Stats subtab shows IP addresses and IP addresses in use for GGSN nodes and contains:
Displaying PWE3 Real-Time Statistics
The MWTM enables you to display PWE3 real-time statistics in the MWTM web interface. Because the MWTM client also displays these statistics and the GUIs for the web and client interfaces are so similar, the PWE3 real-time statistics are described in Viewing PWE3 Statistics, page 8-121.
Displaying TDM Real-Time Statistics
The MWTM enables you to display TDM real-time statistics in the MWTM web interface. Because the MWTM client also displays these statistics and the GUIs for the web and client interfaces are so similar, the TDM real-time statistics are described in Viewing TDM Statistics, page 8-103.

 Feedback
Feedback