Table Of Contents
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting with the Multicast Manager Tool
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting with the Multicast Manager Tool
This chapter covers:
Managing Diagnostics
The Diagnostics tool gives you a global view and a router-specific view of your network. The following sections describe global diagnostics:
The following section describes router-specific diagnostics:
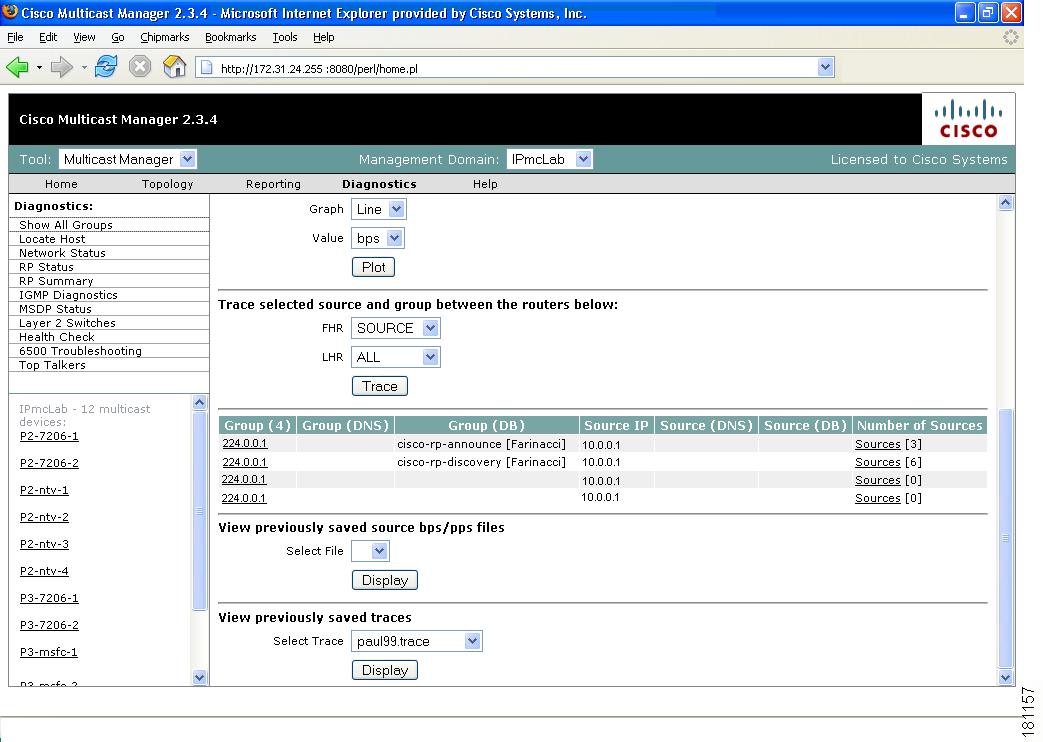
Show All Groups
With the Show All Groups page, you can:
1.
View all the active sources and groups in the network in tabular format. Groups are listed in numerical order, and the number of sources for each group appears in the last column. If there is more than one source for a group, select Sources to view them all.
2.
Draw complete graphical trees by clicking on a group.
3.
Draw filtered graphical trees by selecting the Source, Group, FHR and LHR.
4.
Plot the pps/bps for a particular source and group.
Figure 4-1 Multicast Diagnostics
(Optional) If you are using S,G caching, the cache contents appear. Click Refresh Cache to refresh the table of sources and groups.
If there are a lot of sources and groups present, you can filter the display to show only those you are interested in:
•
Source—Enter or select the IP address of the source to monitor.
•
Filter Groups—Filters the output to contain only the relevant groups.
•
Group—Enter or select the IP address of the group to monitor.
•
Filter Sources—Filters the output to contain only the relevant sources.
•
Reset SG Lists—Clears any entries and refreshes the source and group lists.
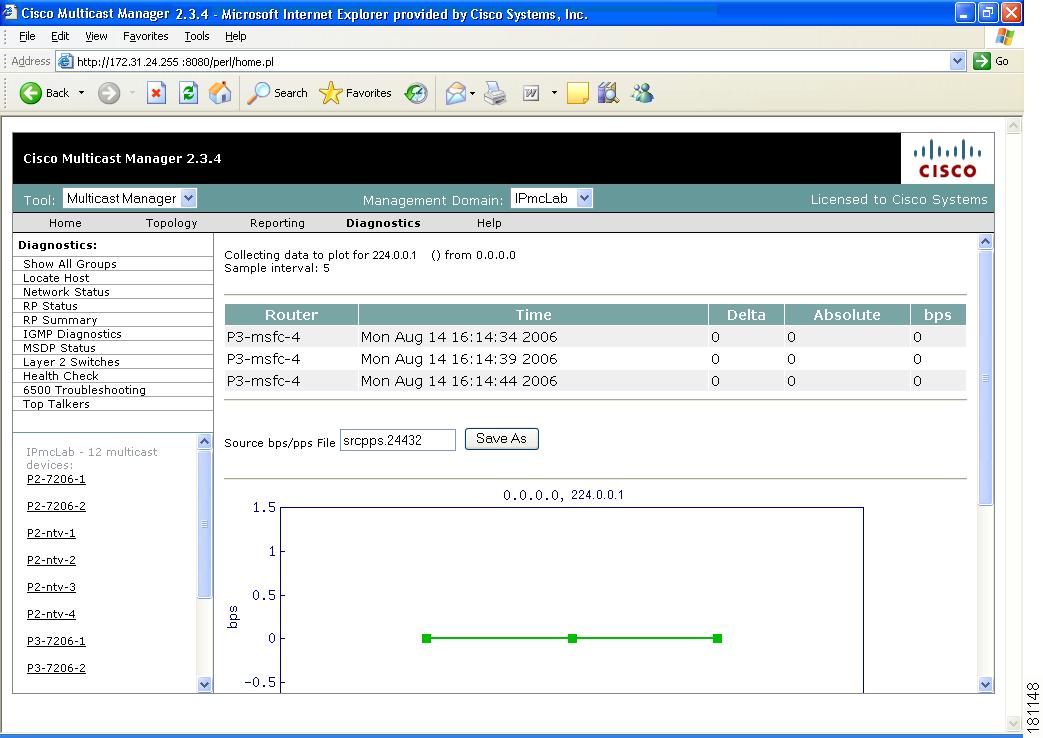
To ensure a source is sending data, you can plot traffic over a period of time:
•
Select Router—Select the router to take the sample from.
•
Samples—Enter the number of samples (1-50).
Note
If the device is a 6500, you may need to adjust the sampling period in order to generate useful data.
•
Interval—Enter the interval between samples (1-90s).
•
Graph—Select the type of graph, line or bar.
•
Value—Select the value, bps or pps.
•
Click Plot. This produces a graph for the currently selected S,G on the selected router. You can also save this graph on the server.
Note
This option is not meant for long term polling, but rather as an immediate troubleshooting tool. For long term polling of PPS data, the S,G should be configured under S,G Threshold polling.
Figure 4-2 Multicast Diagnostics—Plotting Traffic
To draw a graphical tree between two particular routers:
•
FHR—Select the first hop router that the trace should start under.
•
LHR—Select the last hop router that the trace should end under.
•
Click Trace. The CMM draws a tree of the source and group selected from the router in FHR to the router in LHR.
To list all of the active sources and groups, within the Show All Groups page, simply scroll down to see all entries.
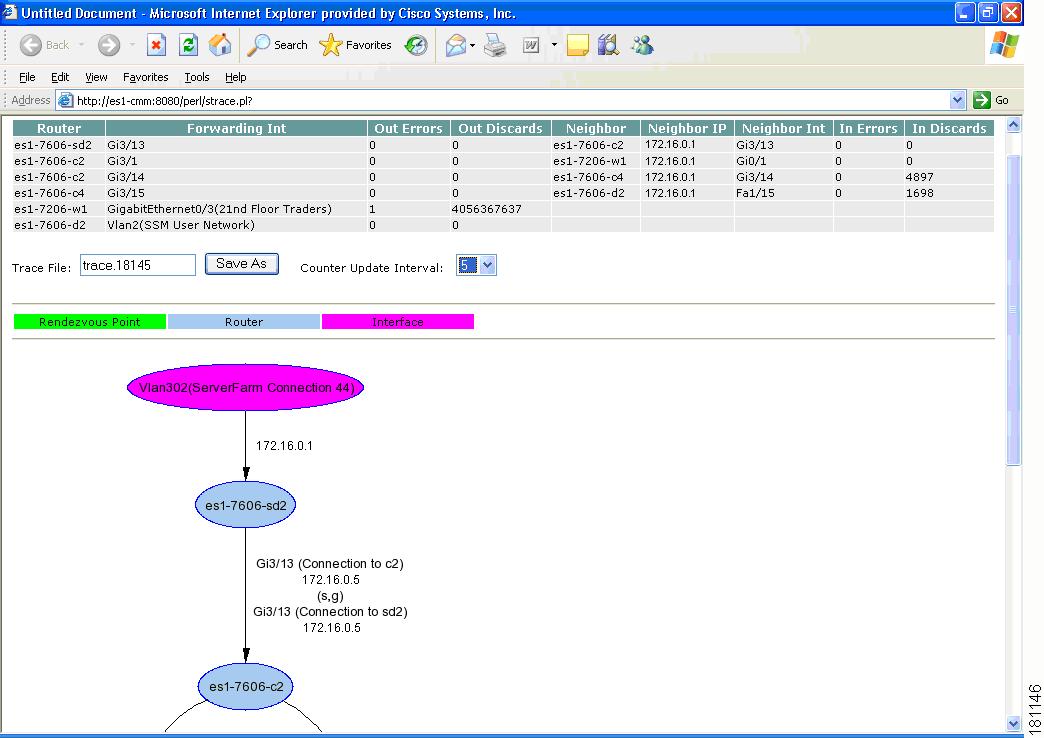
To draw a multicast tree, select a Group. A new page appears with the multicast tree in tabular and graphical format. Routers known as RPs to the source router appear green.
Note
If there is more than one source for the group, select Sources under Number of Sources and select the source you want to draw the tree from.
Figure 4-3 Drawing a Multicast Tree (Baseline)
•
To display packet error counters, select a Counter Update Interval. These counters are updated each period.
•
To save the multicast tree as a baseline, enter a name within Trace File, and click Save As. The window closes. You can use the saved baseline for tree polling (see Tree Polling, page 2-28).
Note
You can also save the tree as a .jpeg, .bmp, or .png file by right-clicking it.
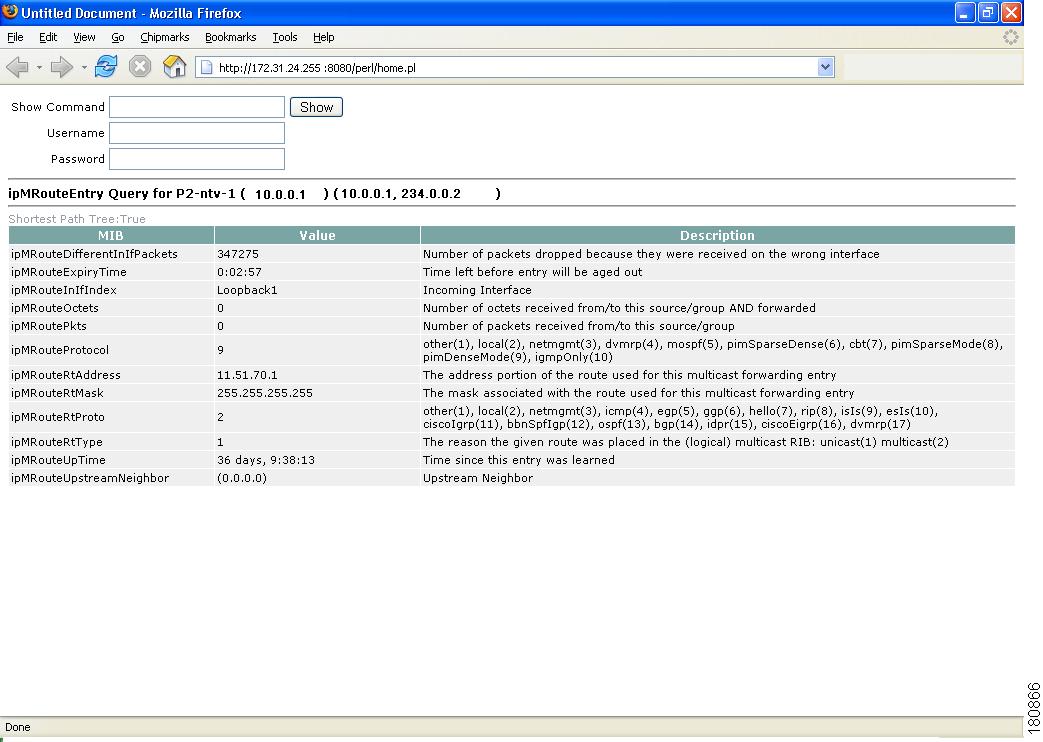
Figure 4-4 Viewing IP Multicast Routing Information
•
(Optional) Clicking on a router in the multicast tree opens another page that contains IP multicast routing information for the S,G that has been traced:
–
Show Command—Enter any show commands on the router. A new window opens that contains multicast route information for the selected router.
–
Username—Enter your username.
–
Password—Enter your password.
–
MIB
–
Value
–
Description
Figure 4-5 Multicast Diagnostics
•
Group (DNS)—Name given to this group in DNS.
•
Group (DB)—Name given to this group in the address database.
•
Source IP—IP address of the source.
•
Source (DNS)—Name given to this source in DNS.
Note
The Source (DNS) field is populated only if DNS is configured, and if Resolve Sources is selected on the Device Configuration page. It should be noted that resolving thousands of addresses via DNS can be extremely slow.
•
Source (DB)—Name given to this source in the address database.
•
Number of Sources—Number of sources in this group.
•
To view previously saved source bps/pps files, select the file, and click Display.
•
To view previously saved traces, select the trace, and click Display.
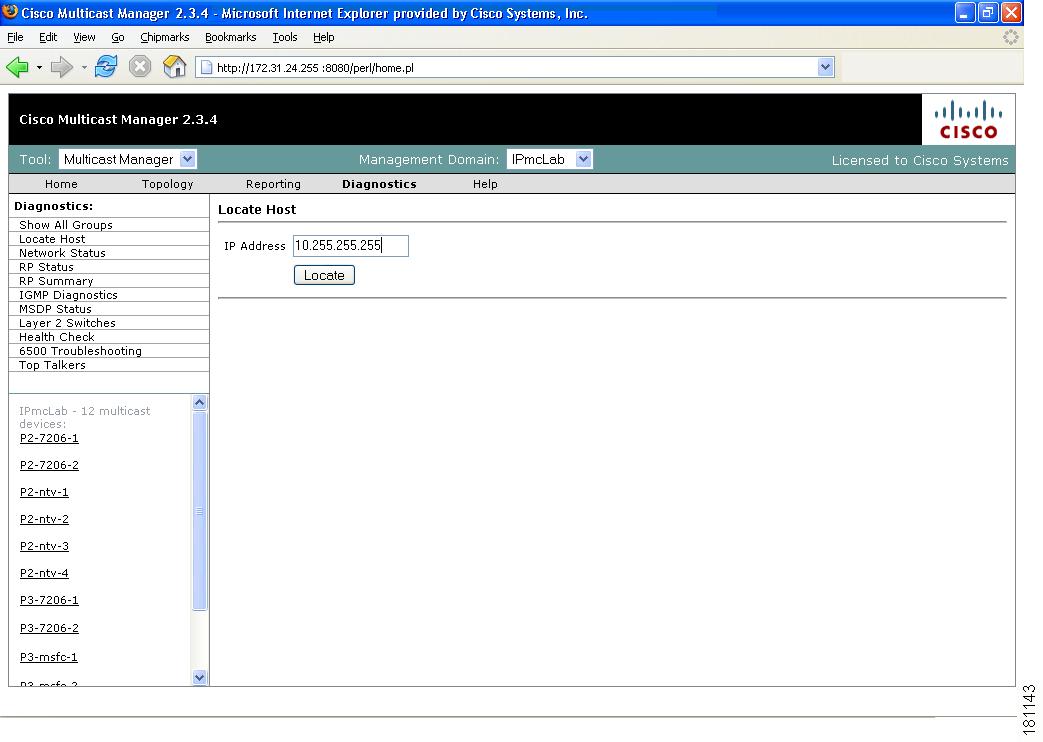
Locate Host
Using the Locate Host page, you can find sources and receivers in the network. Enter the IP Address or hostname (if DNS is configured) and click Locate.
Figure 4-6 Locate Host
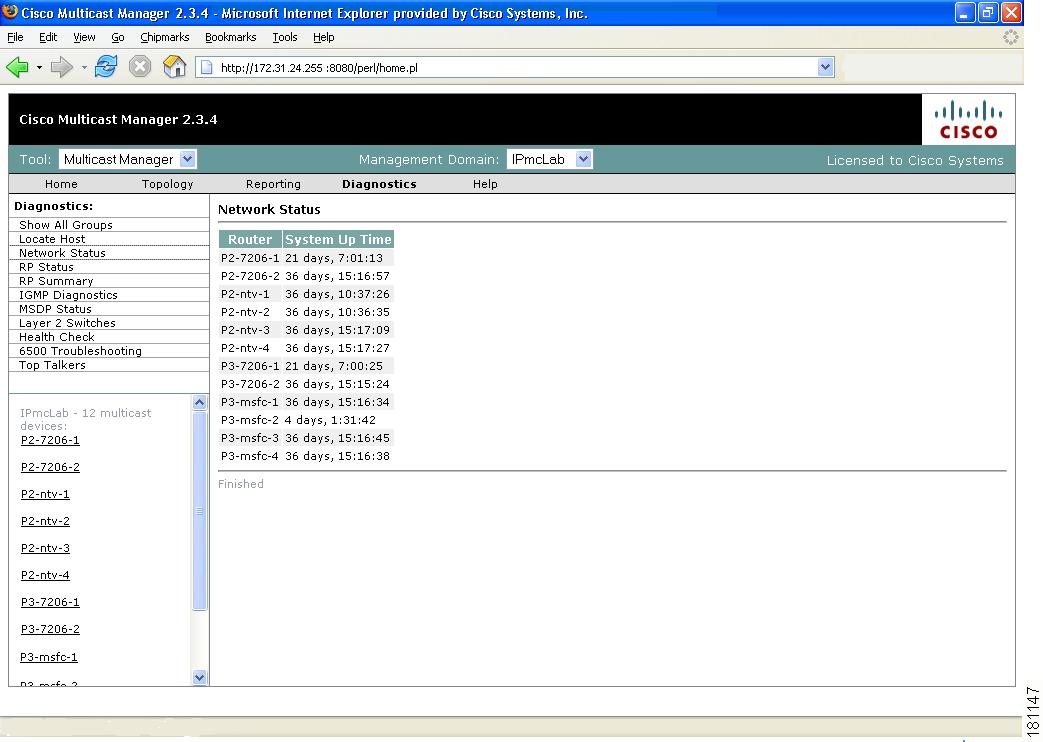
Network Status
Using the Network Status page, you can view the status of all devices in the current multicast domain. The System Up Time appears for all devices that are up. Devices that are down or unreachable appear in red.
Figure 4-7 Network Status
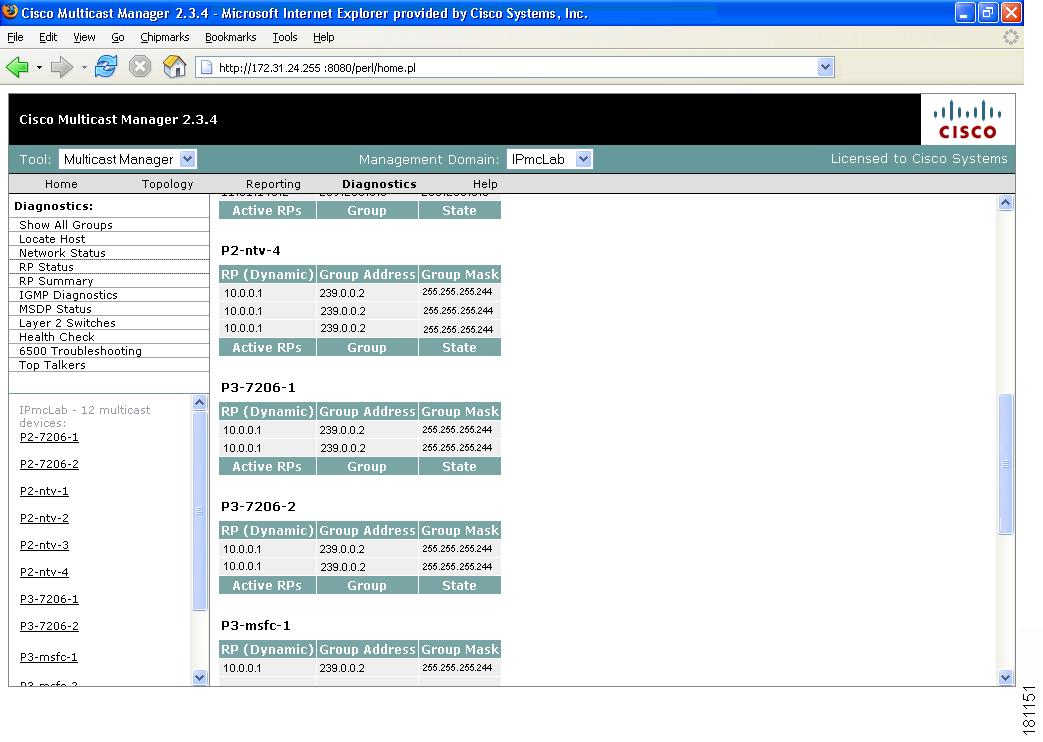
RP Status
Using the RP Status page, you can view all routers in the database, their RPs, and the active groups. In a large network with, many S,Gs, it may take some time for this data to appear, because each router in the multicast domain is queried.
Figure 4-8 RP Status
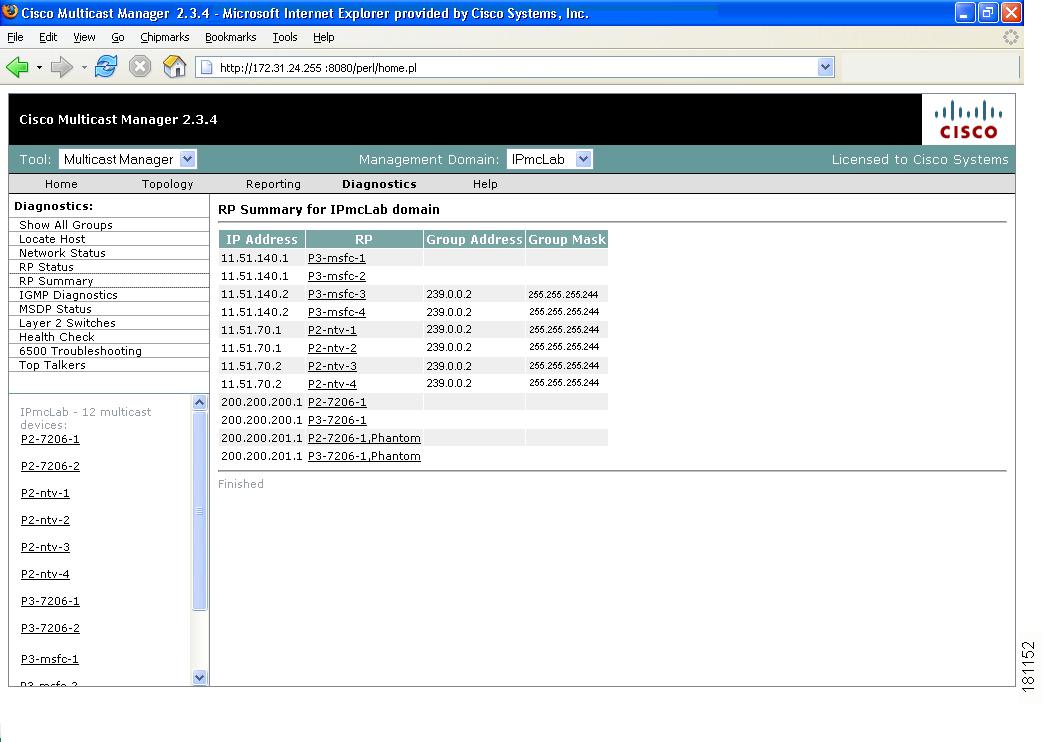
RP Summary
Using the RP Summary, you can view all the RPs that the CMM is aware of, based upon the discovery.
Figure 4-9 RP Summary
For details on clicking on an RP, see Viewing Topology, page 3-2.
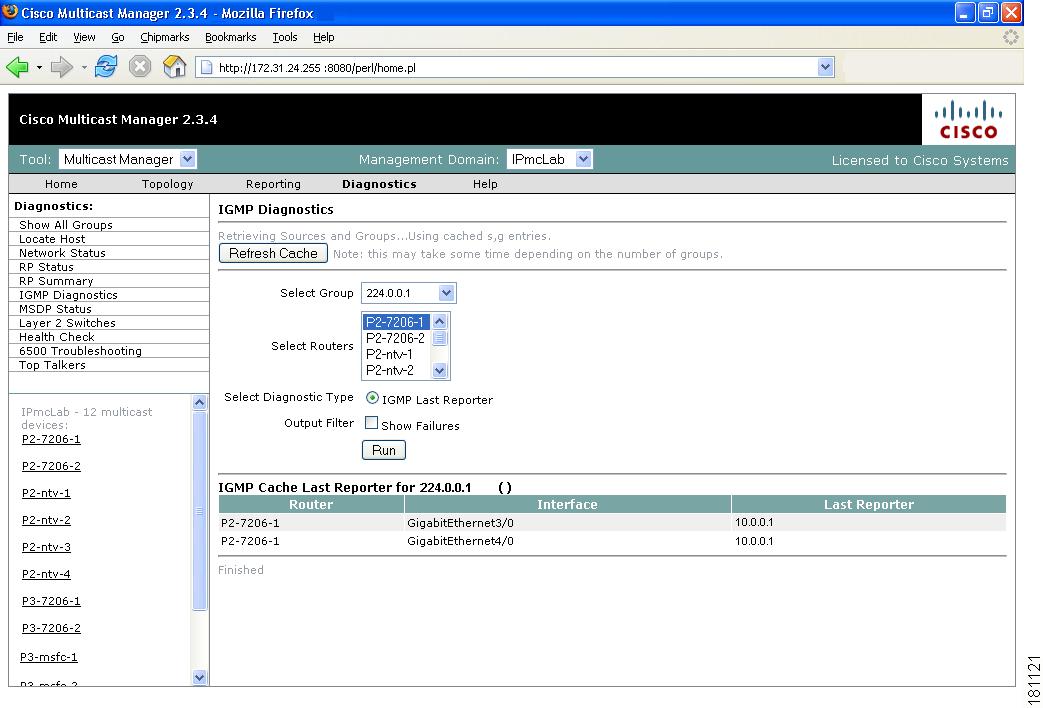
IGMP Diagnostics
Note
IGMP Diagnostics does not work for IOS 12.0S devices.
Using the IGMP Diagnostics page, you can see the interfaces that have joined onto a particular group:
Step 1
Select the router(s) you want to query.
Step 2
Select Diagnostic Type is alays set to IGMP Last Reporter.
Step 3
Select Show Failures to display all interfaces on the router.
Step 4
Click Run.
Figure 4-10 IGMP Diagnostics
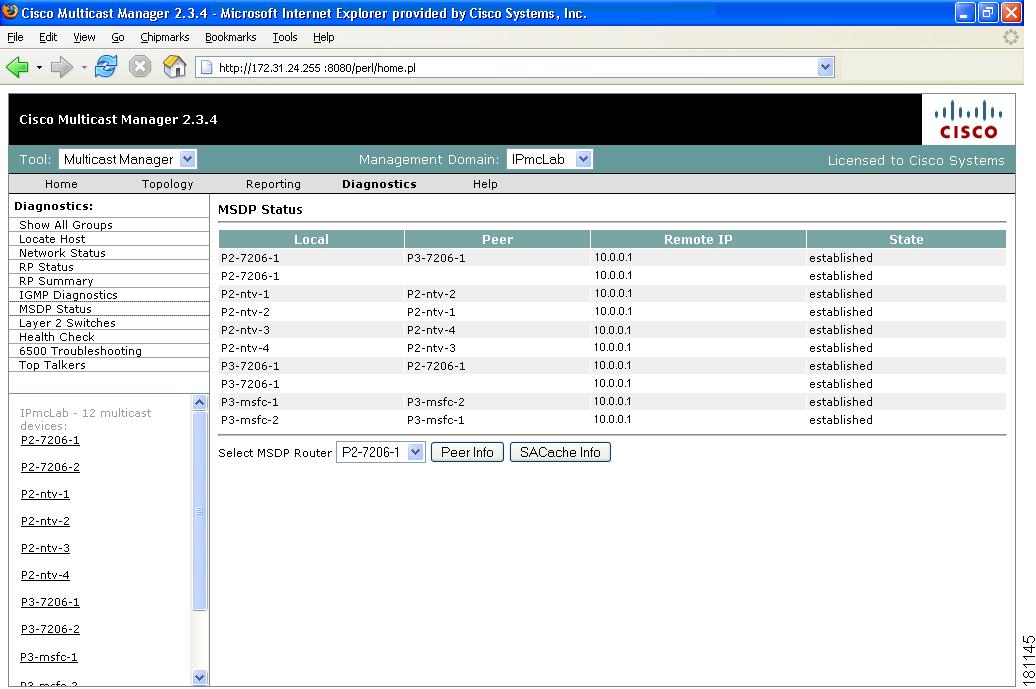
MSDP Status
Using the MSPD Status page, you can view all routers running MSDP and their peering connectivity. You can also view details for a specific router, such as peering information and the SA cache.
Note
The MSDP MIB is supported only in IOS releases 12.0S, 12.1T (12.2) and 12.3. Version 12.1(x) does not support this MIB. Therefore, any RP running 12.1(x) with MSDP configured does not appear on this table.
To view peer information or SA cache information, select a router from the list and click the corresponding button.
Figure 4-11 MSDP Status
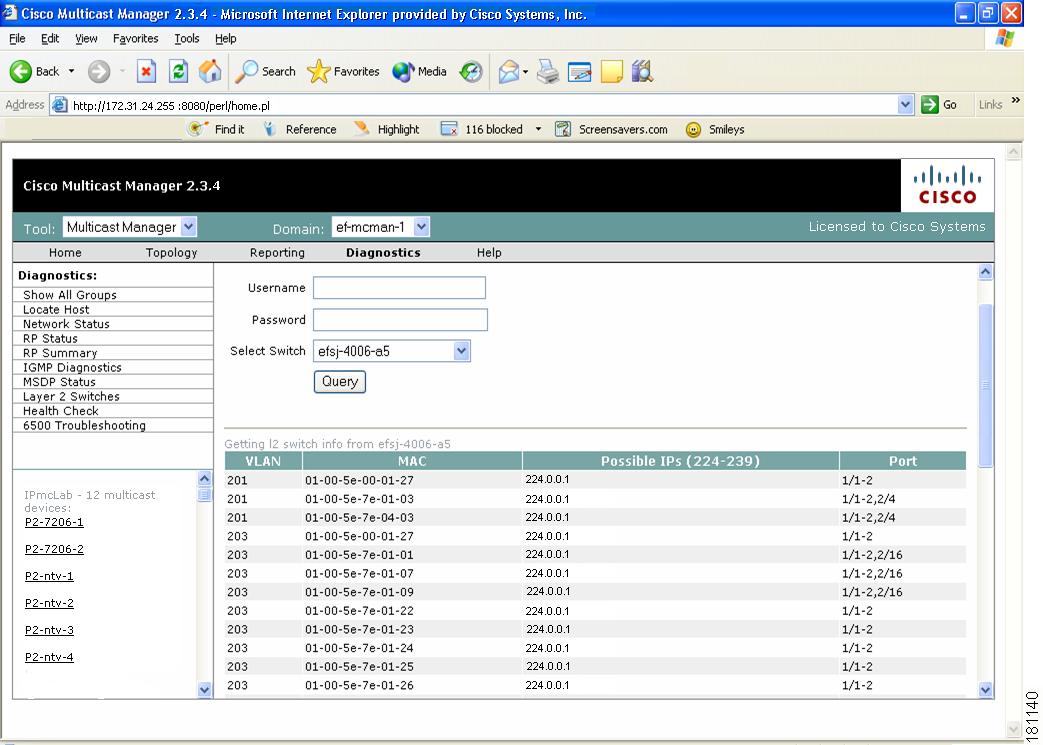
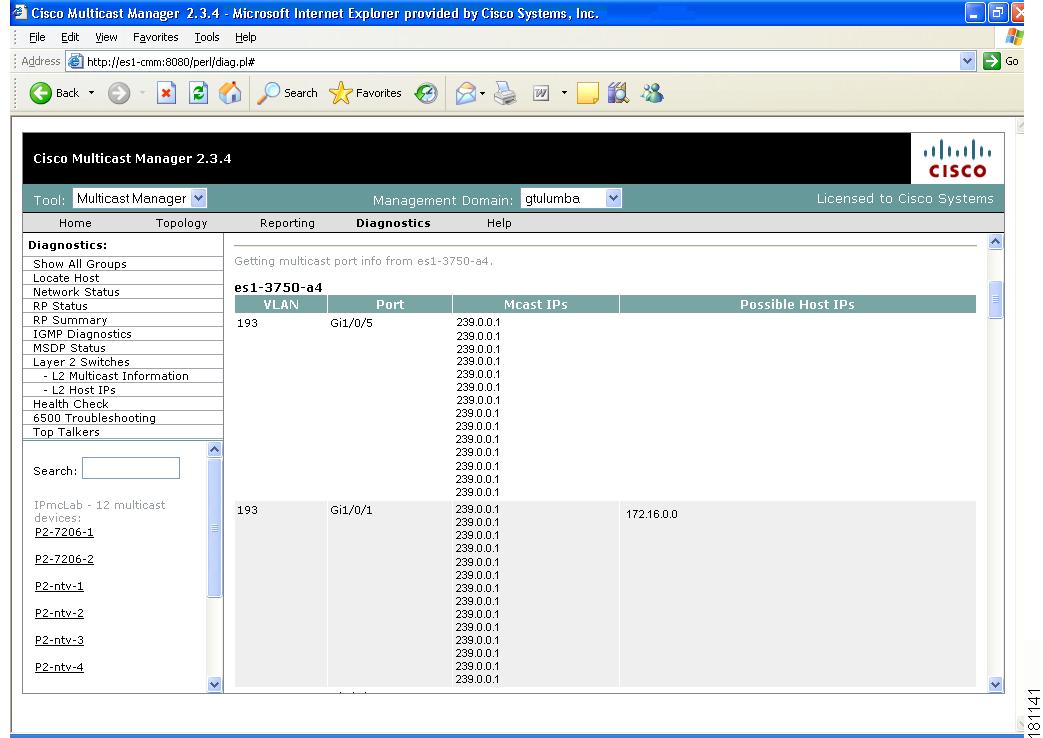
Layer 2 Switches
Using the Layer 2 Switches pages, you can view:
•
Layer 2 Multicast Information
•
Layer 2 Host IPs
Note
These queries require the VTY password, or a TACACS username/password. The table that is generated, shows, from a Layer 2 perspective, which multicast groups are being forwarded out which interfaces.
To view Layer 2 multicast information or host IPs:
Step 1
Enter your username.
Step 2
Enter your password.
Step 3
Select the switch(es) you want to view.
Step 4
Click Query.
The possible IP addresses that can be mapped to the MAC address are also shown.
Figure 4-12 Layer 2 Multicast Information
Figure 4-13 Layer 2 Host IPs
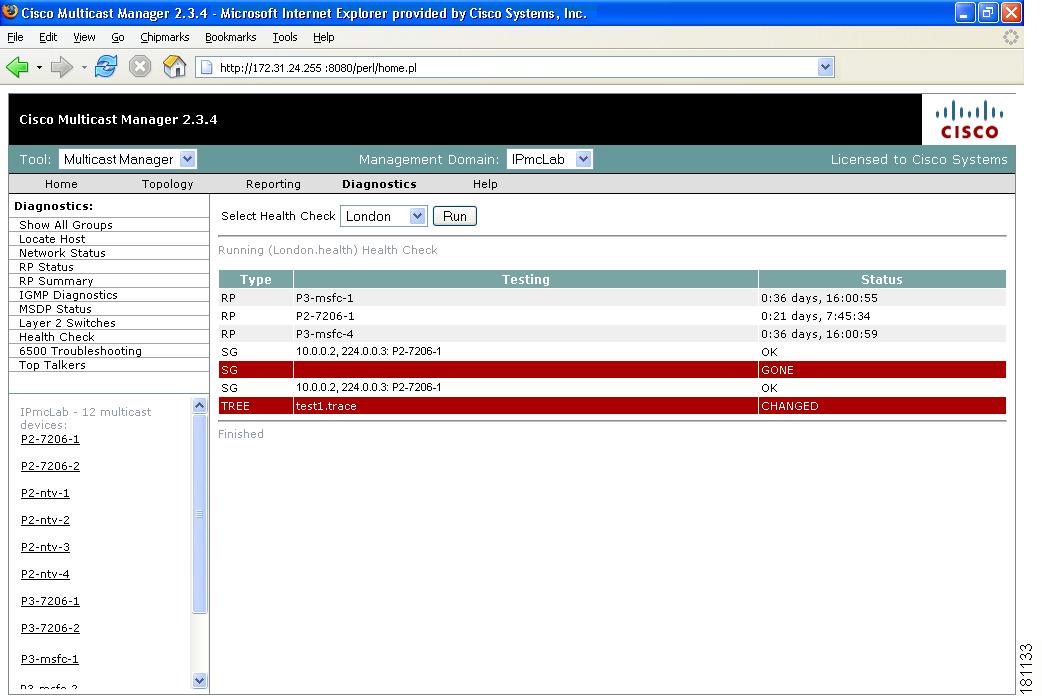
Health Check
Using the Health Check page, you can run a health check on a domain. To run a health check, select it from the list, and click Run.
Figure 4-14 Health Check
•
Gray = normal
•
White = normal
•
Red = error condition
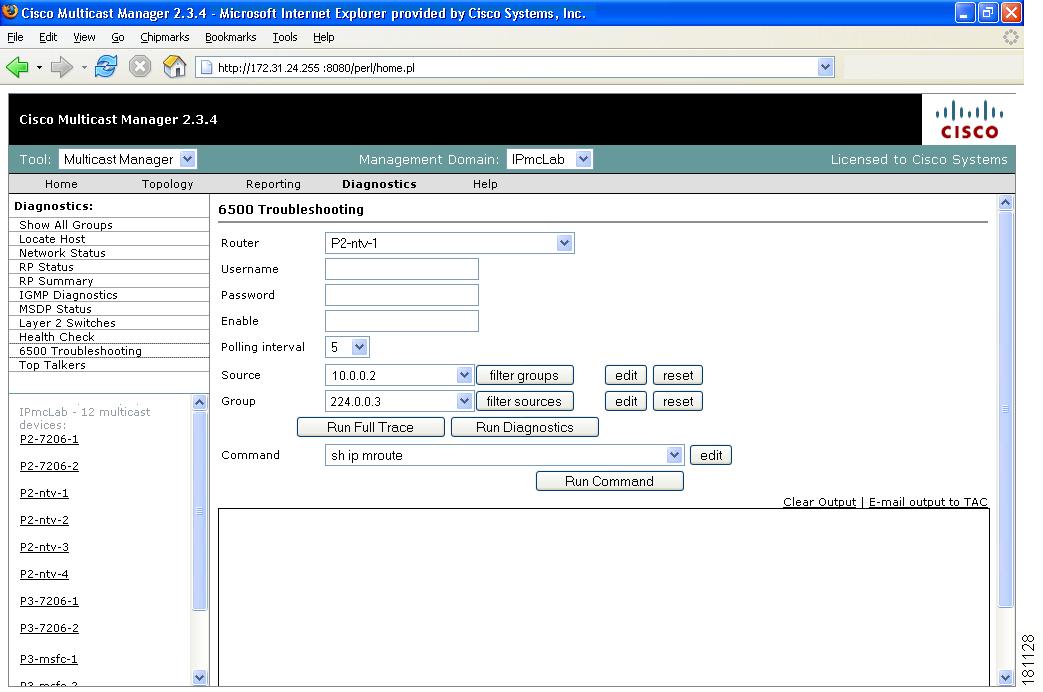
6500 Troubleshooting
Using the 6500 Troubleshooting page, you can enable the CMM to gather accurate packet forwarding statistics and other information in a timely manner. This option initiates a remote login session into the PFC. A persistent Telnet session issues show commands and displays live statistics. These sessions are terminated when the windows are closed.
Tip
All important sources and groups should be proactively monitored. Use the 6500 Troubleshooting tool to investigate a current problem.
Figure 4-15 6500 Troubleshooting
Router
Select a 6500 or 7600 router.
Username
Enter your username.
Password
Enter the MSFC password.
Enable
Enter the enable password.
Polling Interval
Interval at which the statistics are updated.
Source
IP address of the source.
Group
IP address of the group.
Edit
Lets you manually type in a group or source address.
Reset
Populates the source and group lists again.
Run Full Trace
Starts the tree at the source instead of the selected router. For details, see Show All Groups.
Run Diagnostics
Draws a graphical tree of the source and group selected, starting at the router selected. Live traffic statistics also appear for this source and group at this router. You can click any other router in the picture to see live packets statistics for them (see Show All Groups).
Ensure pop-up blockers are disabled.
Command
Provides a list of show commands.
Edit
Add your own command by clicking Edit, typing in your command, then click Run Command.
Run Command
Runs the selected show command. Output appears in the text box below.
Clear Output
Clears the output.
E-mail output to TAC
Emails the output to the Cisco TAC.
Note
Your server must have email set up.
When troubleshooting a problem, you can keep a record of the command output:
Step 1
Right-click in the output.
Step 2
Choose Select All.
Step 3
Copy and paste the content.
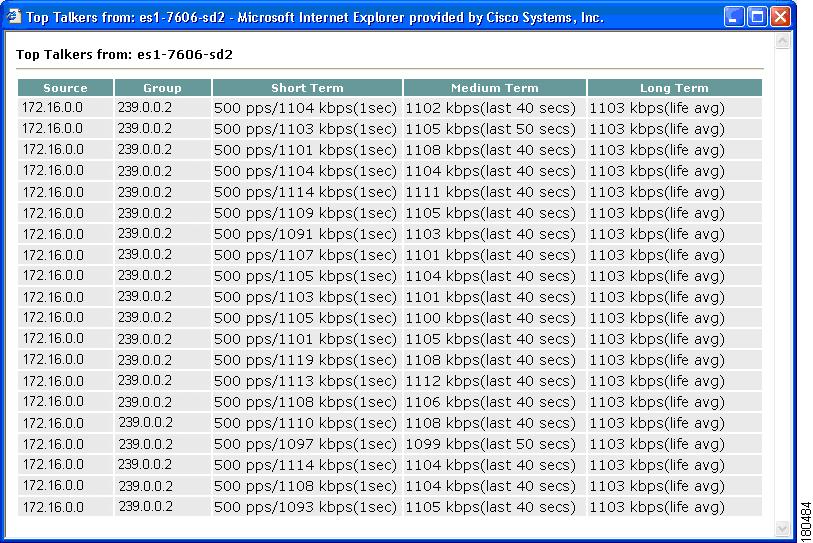
Top Talkers
Using the Top Talkers page, you can view the top 20 talkers, sorted by long term. The top 20 talkers are dynamically updated at every polling interval.
Step 1
Select a router to monitor.
Step 2
Enter your username and password.
Step 3
Select a polling interval, indicating the period (in seconds) for the window to update.
Step 4
Click Top Talkers.
Figure 4-16 Top Talkers
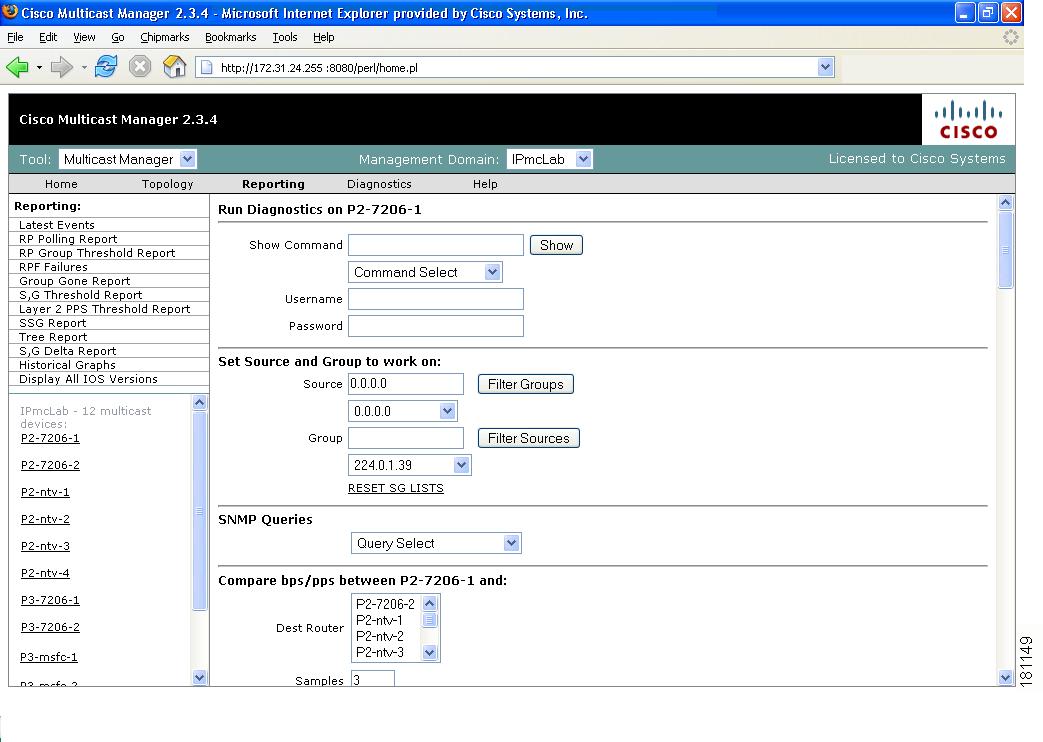
Managing Router Diagnostics
You can view specific multicast diagnostics on a router by clicking the router in the lower left pane.
Figure 4-17 Router Diagnostics
The Router Diagnostics page is similar to the Multicast Diagnostics page (under Show All Groups), except data is for the selected router only.
•
From the Show Command field, you can issue a show, ping, trace, or mtrace command. Scroll down to see all the sources and groups active on this router.
•
From the SNMP Queries pane, for a selected router, you can view:
–
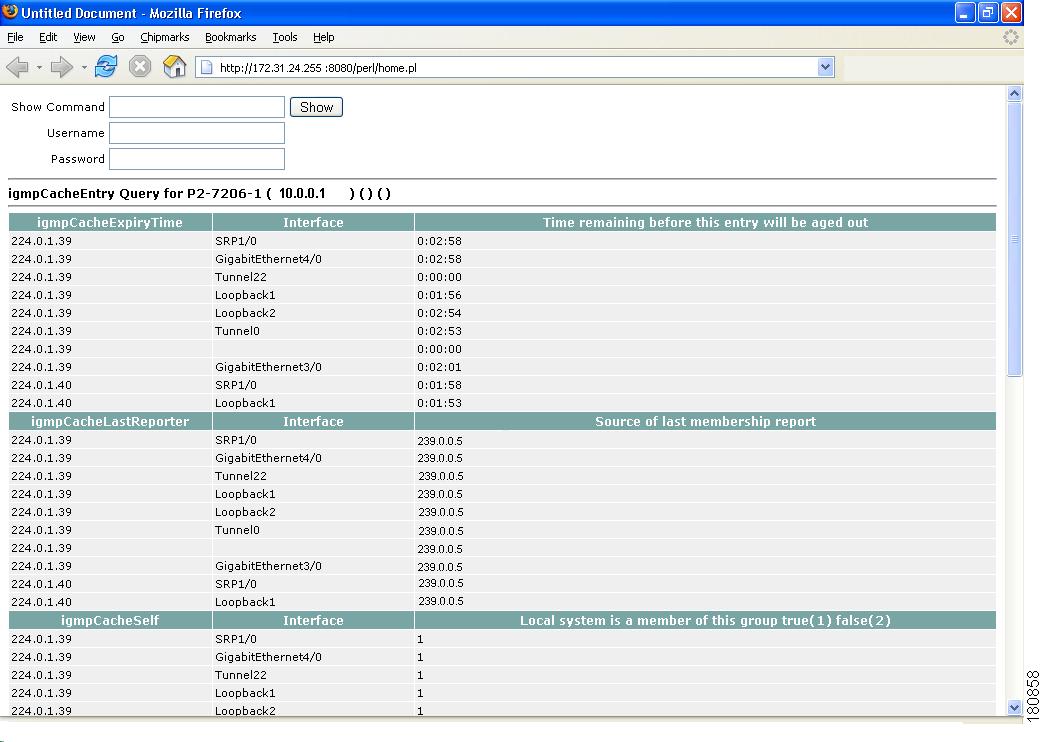
IGMP Cache Entries—Shows IGMP cache information.
Figure 4-18 IGMP Cache Entries
–
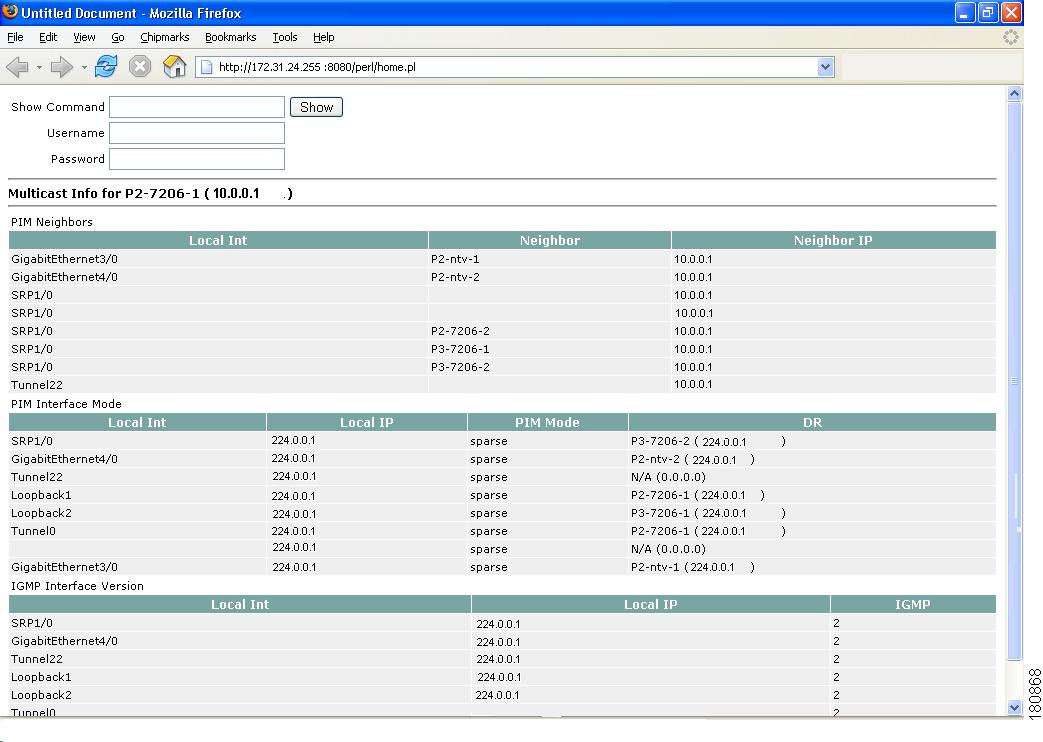
Multicast Information—Shows multicast topology information.
Figure 4-19 Multicast Information
–
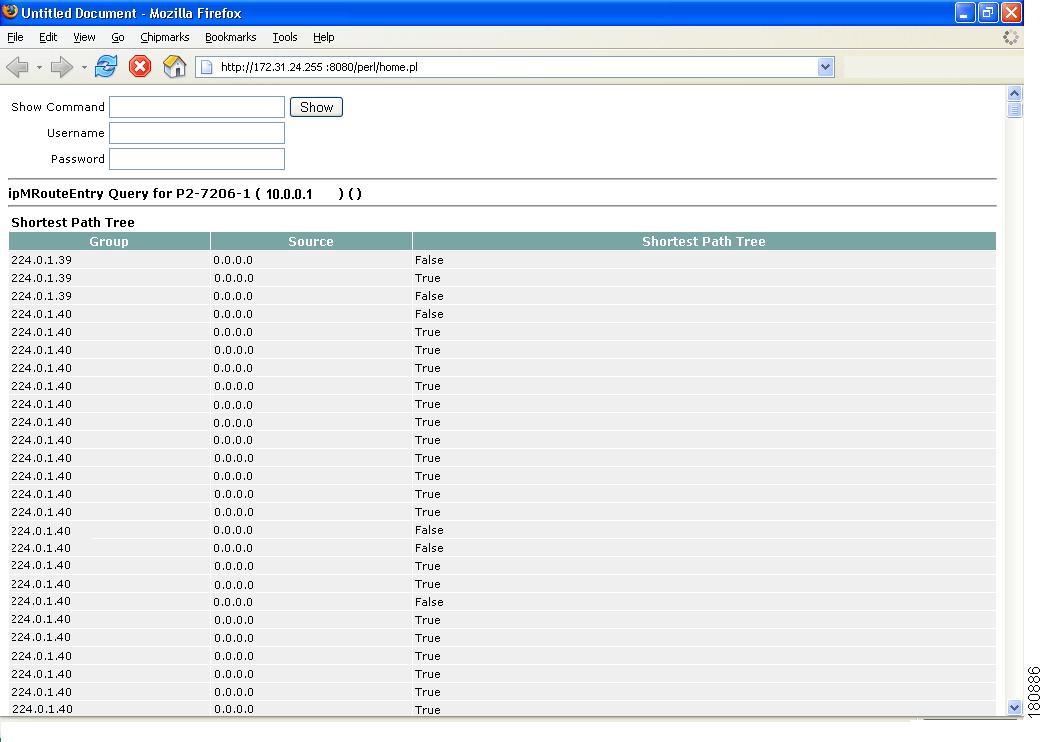
Multicast Routing Table—Shows the multicast routing table.
Figure 4-20 Multicast Routing Table
–
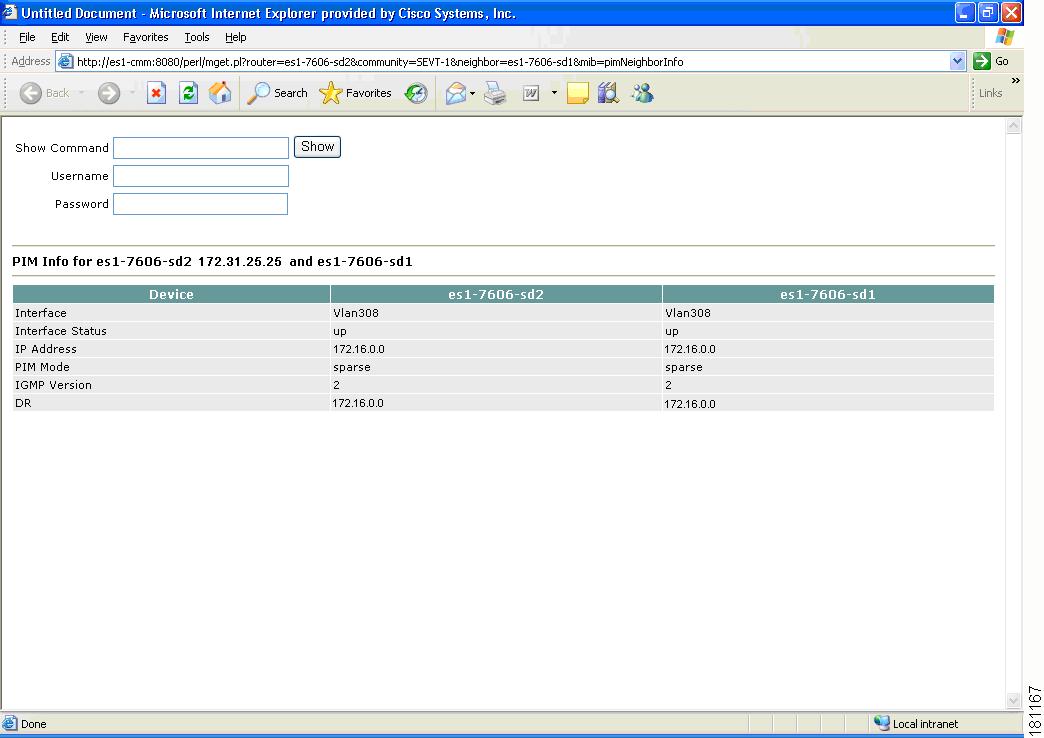
PIM Neighbor Information—Check that a PIM neighbor exists and compare a router's PIM neighbor information. Select the PIM neighbor you want to query.
Figure 4-21 PIM Neighbor Information
Viewing User Guide Help
You can view the Cisco Multicast Manager 2.3.4 User Guide PDF by selecting Help.

 Feedback
Feedback