-
Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000, Release 8.6(1)
-
Preface
- Introduction to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
- Checklists for Common Configuration Tasks
-
Field Descriptions for the Graphical User Interfaces
-
Administrator Settings
-
Auto Attendant Settings
-
Backup Settings
-
Call Detail Reports
-
Locale Settings
-
Cisco Extension Mobility Report
-
Configuration Export Settings
-
Date and Time Settings
-
Department Settings
-
Device Settings
-
Diagnostic Settings
-
Dial Plan Settings
-
Hunt List Settings
-
Health Summary
-
License Settings
-
Music on Hold Settings
-
Network Settings
-
Phone Settings
-
Phone Application Settings
-
Hunt List Settings
-
PSTN Connection Settings
-
Restart Settings
-
Restore Settings
-
Search Settings
-
Setup Mode Settings
-
Sites Settings
-
Summary Settings
-
Upgrade Settings
-
Usage Profile Settings
-
User Settings
-
User Preferences Settings
-
Voice Feature Settings
-
- Troubleshooting in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
Benefits of Deploying Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
Components of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 System
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Server
Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File
DHCP Usage for Acquiring IP Addresses
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines
Example of Typical Deployment Model
Overview of Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
This chapter contains information on the following topics:
•
Benefits of Deploying Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
•
Components of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 System
–
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Server
–
Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File
–
DHCP Usage for Acquiring IP Addresses
•
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
–
Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines
•
Example of Typical Deployment Model
Benefits of Deploying Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000, a system under the Cisco Unified Communications family of products, provides an IP telephony solution that enables:
•
Easy setup of deployments
•
Easy provisioning of users, phones, lines, and phone features
•
Easy monitoring and troubleshooting
•
Easy maintenance of your system (simplified backups, simplified restores, and so on)
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 software is preinstalled on the server that is supported with your system so that you do not have to perform a software installation to get your server up and running. Deployment of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server, phones, and the gateway across an IP network provides a distributed, virtual telephony network. Quality of service is maintained across constricted WAN links, internet, or VPN connections.
Your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 system is designed to support up to 300 users and 400 phones. Supplementary and enhanced services such as hold, transfer, forward, conference, multiple-line appearances, speed dials, last-number redial, and other features extend to the phones.
Web-browser interfaces allow configuration of the system. These interfaces also provide access to online help.
Components of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 System
Your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 system consists of the following components:
•
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Server
•
Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File
•
DHCP Usage for Acquiring IP Addresses
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Server
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 is installed for you on a standalone Cisco MCS 7816-I5 or MCS7890-C1 with 4GB of RAM. When you plug in the server, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 software is installed and ready for use. Cisco Unified Communications Manager, an internal component of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 software that provides call processing for your system, resides on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server. Cisco Unity Connection, an internal component of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 software that provides voicemail support for your system, also resides on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server also contains the database where your configuration records are stored. Internal services that are part of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 software allow you to troubleshoot, monitor, and perform maintenance tasks, such as backups, upgrades, and so on.
Tip
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server must use a static IP address.
Because you use web-browsable graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting, you need not connect a keyboard and mouse to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server. The following graphical user interfaces (GUIs) exist on the server so that you can perform tasks to support your system:
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard guides you through the deployment steps that are necessary to complete an initial configuration. From this wizard, you can upload a Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file that contains data that you can use to configure your system, or you can manually configure settings by moving throughout the wizard. After you log in to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server for the first time, the First Time Setup guides you through the set up of the application through prompts that display in the main content area. You complete the set up by clicking the appropriate responses. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard supports forward and back capability through Back and Next buttons that display on every page of the wizard.
Tip
If you click Next throughout the wizard without updating any of the settings, your system uses the default settings.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface
After you complete the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, the next time that you log in to the server, you can access the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface allows you to perform the tasks that are described in this chapter. For example, in this graphical user interface, you can monitor and troubleshoot the system, add, edit, delete configuration data, such as phones, users, sites, and so on, and perform maintenance tasks, such as backups, restorations, upgrades, add and view licenses, and so on.
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface uses a three-section layout, which consists of a top-level header, navigation menus that display on the left of the page that expand and collapse to display individual menu options, and a content section that displays on the right of the page where you can view, add, update, and delete data.
When you click an arrow next to a navigation menu, the navigation section displays the items that the belong to the navigation menu. To display the contents of an item in the navigation menu, click the item. The contents of that item display on the right side of the graphical user interface.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface
When users that exist in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface log in to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface, a web page displays where the user can manage user preferences for phone features; for example, the user can update Reach Me Anywhere, call forwarding, speed dials, the phone PIN for Cisco Extension Mobility, and the password for the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface. In addition, the user can use Cisco Web Dialer to place a call to an extension in the corporate directory.
Users can manage their user preferences settings for phone features by selecting check boxes and entering the appropriate information in the provided fields. Each user accesses his own Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface page, and this page is not shared by users.
Most settings that display in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface are dynamic; the settings display only if the user is allowed to use the feature (as configured by you, the system administrator). For example, if you do not enable Reach Me Anywhere in the usage profile that is assigned to the user, the user cannot see the Reach Me Anywhere setting in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface.
USB Support
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 gives you the option of using USB keys or a USB hard disk for the following functionality:
•
Performing a reimage of the server through a USB DVD drive—Perform a reimage of the server only when your technical support team advises that you do so. You can copy the answer file, platformConfig.xml (www.cisco.com), to the USB DVD drive key and perform a reimage.
Tip
For MCS7890-C1, the default Answer File (platformConfig.xml) required for install configuration is packaged within the DVD.
•
Updating the network parameters—You can copy the configure.xml file to a USB key to update the network parameters. The temporary network address allows you to log in to the First Time Setup Wizard through a browser. This is also an alternative method to connect a laptop to the server using a cable. You must update the network parameters before you can access the graphical user interfaces.
Note
After you run the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, designate a single USB DVD drive key for this function.
•
Uploading a Cisco-provided country pack—You copy the Cisco-provided country pack to the USB key and then install the country pack through the Country/Locale page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
•
Uploading the Cisco-provided.xls data configuration file—You can copy the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file to the USB key and then upload the spreadsheet to the system through the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
•
Backing Up and Restoring Your Data—You may store your backup tar file to a USB hard disk, and if you must restore you data for any reason, you can access the backup tar file on the USB hard disk to restore the data through the Restore page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
•
Uploading an audio source file for Music On Hold—You can copy the .wav file that you want to use for music on hold to the USB key; after you insert the USB key in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server, you can upload the file through the Music On Hold page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
•
Uploading Cisco User Connect licenses—Cisco User Connect license allow you to track the users and phones that are in your system. You may use a USB key to upload licenses.
Note
Some operating systems do not allow you to copy an entire file that is larger than 4 GB to the USB key. The system silently copies only 4 GB of the file to the USB key. Hence, Cisco recommends that you use USB keys that are formatted as FAT32 in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000.
Linux platform supports USB keys formatted with FAT32.•
Exporting your configured data—By using the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, you can export all of your configured data to a storage device that is connected to a USB port or to a SFTP server. You may store the exported configuration to a USB key or USB hard disk.
•
Using the Cisco Diagnostic Tool—The Cisco Diagnostic Tool allows you to diagnose your system if you cannot access the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. You copy the diagnose.xml file that is used with the Cisco Diagnostic Tool to a USB key.
Note
Make sure that you designate a USB key just for this purpose. Do not use the USB key for other functions.
For More Information
•
What is a country pack, and where do I install it?, page 2-7
•
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 3-1
•
Using the Cisco Network Configuration USB Key, page 6-4
•
Troubleshooting When You Cannot Access the Graphical User Interfaces, page 43-6
Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File
The data configuration file, which is a Cisco-provided .xls spreadsheet template where you can enter the majority of your configuration data, provides the following support:
•
Allows you to plan your configuration before you begin your first day of deployment.
•
Allows you to insert users and phones in bulk through the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface after your initial deployment.
To quickly import (add) your configuration data to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 after you plug in your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server, you can enter your data and then upload the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file to the server from a USB key or your desktop when you run the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard. If you upload the file, you bypass the configuration pages in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, and the wizard immediately takes you to the Summary page where you can confirm your data.
After the server restarts at the end of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, you can log into the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface and verify that you data got added to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000. If you include user and phone data in the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface allows you to import the users and phones and then informs you of import errors for users and phones.
Tip
If you do not want to upload the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file when you run the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard, consider entering your data in the file and using it as a guide when you manually enter the information in the graphical user interfaces.
For example, during your initial deployment, you inserted 25 users and phones; now, you must insert 25 more users and phones. To accomplish this task, you can modify the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file that you used for automatic set up during the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard or you can obtain a new Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file and add your new users and phones to that new spreadsheet.
CautionDo not use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file to modify your configuration data. Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 only supports the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file for the initial deployment and for bulk insertion (adding) of users and phones after the initial deployment. For example, if you attempt to update existing user and phone information through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file, the updates fail.
For More Information
•
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 3-1
Phones
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 supports a variety of phones that are available through Cisco. If the phone model can support either SIP or SCCP, Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 uses SIP with the phone.
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server sends a phone-specific configuration file to each phone in your system. (This file is not the same as the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file that is described in the "Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File" section.) This configuration file contains data that your phone requires to work; for example, the configuration file specifies whether the phone can use barge, whether phones can use phone applications, what the locale is for the system, and so on.
You can configure the phone for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 by using the following methods:
•
Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
•
Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial deployment)
•
Under Users/Phones > Phones in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial deployment)
Your phone requires an IP address and other network settings to work. For information on how your phone obtains its IP address and other network settings, refer to your phone administration documentation.
For your phone to work, you must install licenses. You cannot add a phone to the system if the appropriate license is not installed and available for use.
All features that are available with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 are not supported on all phone models. Before you configure your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000, determine which features are supported on your phone by obtaining the phone administration documentation that is available with your phone and this version of Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000.
For More Information
•
Sites (for information on how phones get associated with a site)
•
DHCP Usage for Acquiring IP Addresses
•
Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines
•
Cisco User Connect Licensing, page 4-1
•
Checklists for Users, Departments, Lines, and Phones, page 8-1
Voicemail
Cisco Unity Connection, an internal component of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 software that provides voicemail support for your system, resides on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server. With Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000, users can perform the following tasks:
•
Call into the voice messaging system
•
Send voice messages by using the phone keypad
•
Check voice messages by using the phone keypad
•
Reply to voice messages by using the phone keypad
•
Forward voice messages by using the phone keypad
•
Manage receipts by using the phone keypad—Receipts indicate when a voice message was played by an intended recipient, when it was received by the intended recipient, and if it was received by the intended recipient.
Tip
Voicemail support requires the use of voicemail licenses. You must install one voicemail license for each user that requires voicemail.
For More Information
•
Setting Up Voicemail, page 8-12
•
Cisco User Connect Licensing, page 4-1
Auto Attendant
In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000, the auto attendant serves as the "virtual receptionist;" that is, the caller receives an automated greeting and series of prompts in order to successfully transfer the call to a user without the assistance of an operator. The following options describe the auto attendant support.
Note
Auto attendant uses the same internal components as voicemail. Auto attendant is turned on by default, and you cannot turn it off. The system can handle up to 12 simultaneous calls to voicemail and auto attendant.
•
The auto attendant uses a single menu for both business and closed hours (default); the auto attendant plays the same greeting and set of prompts during both business and nonbusiness hours. Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 automatically comes with a sample menu that provides the following functionality. If you do not want to use the sample menu, you can upload another menu that can be used by the system.
–
The auto attendant plays a greeting announcing that the corporate directory has been reached.
–
The auto attendant requests that the caller enter the extension on the phone to transfer the call.
–
If the caller does not enter the extension quickly, the auto attendant requests that the caller enter the extension again.
–
The auto attendant transfers the call to the user of the extension.
–
The auto attendant requests that the caller reenter the extension of the user when the system cannot find the extension.
–
The auto attendant plays a farewell prompt.
•
The auto attendant uses a different menu for business hours and for closed hours; for example, the auto attendant plays a greeting and set of prompts during regular business hours, but, when the company is closed, the auto attendant plays an announcement that the business is closed and then automatically ends the call. (On the Auto Attendant page, you specify when the company is closed and when it is open.) For this option, you must upload a file that contains your greeting, set of prompts, and your message for nonbusiness hours.
Tip
The auto attendant does not support a different menu for holidays.
To use the auto attendant, you must first configure the Voicemail and Auto Attendant Extension setting in the dial plan. You can configure this setting
•
Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
•
On the Dial Plan page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (during initial deployment if you do not use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file)
•
Under System Settings > Dial Plan in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial deployment)
After you configure the Voicemail and Auto Attendant Extension setting in the dial plan, configure the Auto Attendant page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. (Select System Settings > Auto Attendant.) After you set it up, remember to test your auto attendant functionality.
Note
Auto attendant uses an internal user called operator. You cannot edit or delete this user, and it does not display in the Search User page. In addition, you cannot add a user with the user ID of operator. (User IDs should indicate who the user is, not the functions or tasks that the user perform.)
Do not assign the Voicemail and Auto Attendant Extension that you configure in the dial plan to the user that is your operator.For More Information
•
Auto Attendant Settings, page 11-1
•
Setting Up Auto Attendant, page 8-13
•
Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Operator, page 8-13
•
Setting Up the System So that Incoming Calls Reach the Auto Attendant, page 8-14
Gateway
For all calls that go through the PSTN, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 uses two gateways:
•
Gateway built in to Cisco Media Convergence Server 7890C1 (MCS7890-C1)
•
Cisco 2901 Integrated Services Router (ISR2901)
Both ISR2901 and MCS7890-C1 serve as your connection to the PSTN; that is, the gateway allows all of your users to place and receive calls that go through the PSTN.
For all calls that go through the PSTN, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 system uses Cisco ISR2901 or Cisco MCS7890-C1 gateways. Both gateways have two PSTN ports.
Note
For Cisco ISR2901, ensure that you connect the T1/E1 PSTN connections to slot 0 only.
The Cisco ISR2901 that you use with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 cannot be used for any IP routing functions other than those that are supported with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000.
The Cisco ISR2901 provides transcoding and conferencing features for Cisco MCS7816-I5 only.
The Cisco Unified Communications (UC) Technology Package License must be purchased with the order of Cisco ISR2901.
Note
Install the Cisco Unified Communications Technology Package License before you configure any Voice features on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000.
When you order a new router, it is shipped preinstalled with the software image and the corresponding permanent licenses for the packages and features that you specified. You do not need to activate or register the software before use. For more informations, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html#wp1057952.
To verify if the Cisco Unified Communications Technology Package License is installed and activated, refer to Chapter 24, "License Settings".
The Cisco MCS7890-C1 supports approximately 300 users and 400 devices.
For MCS78901-C1, you can create an internal gateway during the First Time Setup using the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard.
For the Cisco MCS7890-C1 gateway, you can configure the general settings, such as the Media Resource IP address and the hostname. The settings that you configure for the gateway allows the gateway, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server, and the phones to interact with each other for calls that go through the PSTN connection.
Ensure that you assign a static IP address for the Cisco MCS7890-C1 internal gateway. However, there is no such restriction of a static IP address for ISR2901 gateways. If you plan to use DHCP, see the "DHCP Usage for Acquiring IP Addresses" section.
You can configure the gateway for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 by using one of the following methods:
•
Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (for initial deployment).
•
On the Gateway page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (during initial deployment if you do not use the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file).
Under Connections > PSTN Connections > Add PSTN Connection > Connection Type > Device > Device > Add Device in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial deployment).
Tip
After you add the Cisco ISR2901 gateway configuration to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000, you must update the gateway with the appropriate CLI commands. See Generate CLI Commands, page 19-1.
For More Information
•
DHCP Usage for Acquiring IP Addresses
•
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 3-1
•
Checklists for Configuring the Gateway, page 7-1
DHCP Usage for Acquiring IP Addresses
This document does not provide detailed information on DHCP; you should have a thorough understanding of DHCP before you use it with your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 system. Typically, the IT support staff for the company or the internet service provider handles your DHCP setup. DHCP may be run on a computer or on a router. Before you implement DHCP with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000, consider the following information:
•
Use custom option 150 or option 66.
•
You can use a DHCP server to issue IP addresses to the phones.
If DHCP is enabled on a phone, which is the default for the phone, DHCP automatically assigns an IP address to the phone after you connect it to the network. The DHCP server directs the phone to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server, which serves a phone-specific configuration file to the phone.
If DHCP is not enabled on a phone, you must manually assign an IP address to the phone and configure the IP address or the hostname of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server locally on the phone (configure it under the TFTP server option on the phone).
•
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server must use a static IP address that you assign to it. If you use a DHCP server to issue IP addresses to computers and other network devices, make sure that the IP address for the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server is not in the active range of IP addresses on the DHCP server. Make sure that you configure your DHCP server so that it does not hand out the IP address for the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server to a different network device.
•
Cisco strongly recommends that you assign a static IP address to the gateway. If you use a DHCP server to issue IP addresses to computers and other network devices, make sure that the IP address for the gateway is not in the active range of IP addresses on the DHCP server. Make sure that you configure your DHCP server so that it does not hand out the IP address for the gateway to a different network device.
If DHCP is enabled on a gateway, DHCP automatically assigns an IP address to the gateway after you connect it to the network.
•
Before you configure your sites and DHCP, Cisco strongly recommends that you determine the number of sites that you need and determine how many phones will be located at each site. Configure your DHCP server so that it correctly distributes the IP addresses to the phones at the various sites.
For More Information
•
Phone administration documentation that supports your phone model
•
Sites (for subnet and subnet mask information for sites)
IP Addressing
The Cisco MCS7890-C1 uses two external IP addresses. The main IP address is the published IP address on the MCS7890-C1 device. This is the system IP address of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000. This IP address is set by your administrator during the First Time Setup of Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000. You can configure this IP address using DHCP or static. The second IP address is the IP address of the media resource used for transcoding and conferencing. Cisco recommends that the media resource IP address be static and unique for MCS7890-C1.
Note
For Cisco ISR2901 gateway, the media resource IP address is the same as the ISR2901 gateway IP address.
DNS and Hostname Resolution
This document does not provide detailed information on DNS. You should have a thorough understanding of DNS before you use it with your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 system. DNS is optional; you do not have to use a DNS server unless you plan to resolve hostnames for your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server or gateway. If you include a hostname for the server or gateway on the Network or Gateway page and you must use DNS, make sure that you map the hostname(s) to the IP address(es) on the DNS server for both forward and reverse DNS resolution. Cisco recommends that you perform this task before you add or edit the hostname in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 GUIs.
The current version of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 does not require a DNS server; however, it is configured for future requirements such as SIP trunks.
Note
Cisco recommends that you do not configure Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 to use DNS.
SFTP Server
Cisco allows you to use any SFTP server product but recommends SFTP products that are certified with Cisco through the Cisco Technology Developer Partner program (CTDP). CTDP partners, such as GlobalSCAPE, certify their products with a specified release of your software. For information on which vendors have certified their products with your version of software, refer to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/ctdp/Search.pl
For information on using GlobalSCAPE with supported Cisco Unified Communications versions, refer to the following URL:
http://www.globalscape.com/gsftps/cisco.aspx
Cisco uses the following servers for internal testing. You may use one of the servers, but you must contact the vendor for support:
•
Open SSH (refer to http://sshwindows.sourceforge.net/)
•
Cygwin (refer to http://www.cygwin.com/)
•
Titan (refer to http://www.titanftp.com/)
CautionCisco does not support using the SFTP product, freeFTPd, because of the file size limit on this SFTP product. For issues with third-party products that have not been certified through the CTDP process, contact the third-party vendor for support.
You can use a SFTP server to complete the following tasks:
•
Upload the upgrade file from the SFTP server to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server before you perform an upgrade
•
Store your backup file to a SFTP server, and if you must restore your data, restore the data from the SFTP server
•
Export your configuration data to a SFTP server
Common Configuration Concepts in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000
This section describes common configuration concepts in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000. In addition, this section describes considerations that you should review before you configure the items:
•
Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines
•
Example of Typical Deployment Model
Network Settings
Your network settings include the IPv4 address or hostname of the server, the subnet mask and default gateway for the server, the primary and secondary DNS server (if you use DNS), the link speed for the Network Interface Controller (NIC) on the server, and the Message Transmission Units (Maximum Transmission Units, MTU) for the network.
•
Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
•
On the Network page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (if you are not using the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file during initial deployment)
•
Under System Settings > Network in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial deployment)
•
Through the configure.xml file (used primarily for troubleshooting when you cannot access the graphical user interfaces)
For More Information
•
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 3-1
•
Network Settings, page 26-1 (for the Network page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface)
•
Using the Cisco Network Configuration USB Key, page 6-4
Dial Plans
Your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Dial Plan allows you to allocate phone numbers and translation rules for your system. You can choose the country where you are installing the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 installs a Dial Plan based on the regulations in your country.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 supports a local gateway in every site and multiple gateways in any site; therefore the installation of Routing Dial Plan is required.
For load balancing and backup purposes, the routing is set up such that if a local gateway is not available, the calls can be routed to the gateway on the other site.
You can install or update the Dial Plan during the following instances:
•
First Time Setup
•
Upgrade
•
Country Pack installation
•
Site creation, update and deletion
Information about Dial Plans is available in the following files:
•
Numbering Plan file—Specifies information about Dial Plan tags.
•
Cisco-provided .xml file—Specifies the metadata information to set up a Dial Plan for your country. It includes XML elements for Route Filters, Route Filter Members, Translation Patterns, Route Patterns, and Called and Calling Party Transformation Patterns.
•
Route Filters .xsd—Specifies XML definition.
For the default countries, the United States, India, and Canada, the dial plans are available with the installation file. For all other countries, you can install Dial Plans using the Country Pack.
For more information, see Country/Locale Settings, page 14-1.
Phone Numbers
For your dial plan, you specify the main business number, the area codes, the length of the extension, the extension ranges, and dialing prefixes for the outside dialing code (access code), operator dialing code, and the feature codes, which a user presses on the phone for certain features, including Meet Me Conferences, call pickup, and so on.
After you set up your default extension range, you cannot change it. You can change other settings for your dial plan in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
The extension length and range that you set in the dial plan impact the extensions that you can assign to your users, departments, and pilot extensions for your hunt lists and voicemail and auto attendant. You cannot add an extension to a user or department that does not belong in the extension range. (Pilot extensions for hunt lists must also be in the extension range, but pilot extensions do not get assigned to users or departments.)
Your system can support internal, local, long distance, and international calls. Toll-free calls are also supported. You can set the level of access for a site on the Sites page; you can set the level of access authorized for the user in the Usage Profile. When a user places a call from a phone in a particular site, the call gets connected if the phone at that site is allowed to make that level of call and if the user that owns the line is also authorized to make that level of call.
Translation Rules
Translation rules allow Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 to manipulate an incoming phone number that is part of your system and transform it to an extension before routing the call. The following list provides examples of when you would configure translation rules:
•
To translate the Meet Me conference number to an extension
•
To translate a toll-free number, such as an 800 number, to an extension
•
To translate an extension to a pilot extension in a hunt list
For More Information
•
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 3-1
•
Dial Plan Settings, page 21-1 (for the Dial Plan page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface)
•
Checklists for Users, Departments, Lines, and Phones, page 8-1
Sites
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 supports PSTN calls from every site through a local Gateway or a gateway located in other sites.
Your Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 system may contain multiple sites, which are geographical locations that define where the users are working.
•
Central Site—The central site contains the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 server and the gateway that allows access to the PSTN. In most cases, the central site is the location where the majority of users work; in most cases, the company headquarters is the central site. You can have only one central site, and you cannot delete the central site.
•
Remote Sites—Remote sites are branch offices that work with the central site; a dedicated WAN link or Internet connection must exist between the remote and central sites. You can have up to nine remote sites.
•
Teleworker Site—The teleworker site is for workers who do not work only at the central site or branch offices; these employees (users) use VPN connections to connect to the central site. A router is not required to contact the central site because their Internet connection provides access to the central site. You can have only one teleworker site.
When you configure a site, you must specify the maximum bandwidth that is required between sites, the maximum bandwidth that is required for internal calls that take place within the site, calling privileges for the site as a whole, and so on. You can configure the bandwidth between the remote site and the central site.
You can configure a site through the following methods:
•
Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
•
On the Sites page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (if you are not using the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file during initial deployment)
•
Under Connections > Sites in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial deployment)
A phone gets associated with a site through the subnet and subnet masks that are configured on the Sites page. If you are using DHCP to assign IP addresses to the phones, the values that you enter for the subnet and subnet mask depend on your DHCP configuration. In this case, the subnet and subnet mask translate to a range of IP addresses that get distributed to the phones that are associated with the site.
Considerations for Configuring Sites
Before you configure your sites and DHCP, Cisco strongly recommends that you determine the number of sites that you need and how many phones will be located at each site. Configure your DHCP server so that it correctly distributes the IP addresses to the phones at the various sites.
If you do not configure the subnet and subnet masks for any site, the phones automatically get assigned to the central site.
If no teleworker site exists and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 cannot determine where the phone is located, Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 automatically places the phone in the central site.
By default, subnet address 192.168.1.0 with a subnet mask of 24 are displayed on the central site page. You may update this information if it does not apply to your setup.
If you enable Reach Me Anywhere in the usage profile, the call privileges for the Reach Me Anywhere call are always based on the highest calling privileges that are selected for the central site.
To associate phones with the remote sites, you must configure the subnet and subnet masks on the Sites pages for the remote sites.
If you have a teleworker site, you must configure the subnet and subnet masks for the central site and all remote sites. For the teleworker site, you cannot specify the subnet and subnet masks.
You cannot enter the same subnet and subnet mask for multiple sites. In addition, Cisco recommends that your subnet and subnet masks do not overlap. If you configure multiple subnet and subnet masks on the Sites page, Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 selects the subnet and subnet mask that is most clearly defined and associates the phone with that site.
It is not uncommon to disallow emergency calls for the teleworker site. If you disallow emergency calls for the teleworker site, make sure that the users understand that they cannot place emergency calls from their work phone that is outside of the office.
Device Mobility
When you do not configure any remote site in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000, the endpoints will register with the central site even when the endpoint is situated in a different subnet. The gateway configured in a different subnet will not register with the central site automatically. You can configure the gateway manually in the central site.
Routing Calls Through Gateways
The calls are routed through the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 sites based on the PSTN access settings at Connections > Sites > Add Site > PSTN Access. Setting the gateway usage allows you to control the routing of PSTN calls through various gateways.
You can select certain local gateways or all the gateways to route the PSTN calls as required. You can also custom select the gateways. The selected gateways are ordered based on the gateway description. The PSTN calls are routed in a top down order among the gateway group.
When All Gateways is selected, the order of the gateways for routing the PSTN calls is as follows:
1.
Local Site gateways
2.
Nonlocal gateways
3.
Multiple gateways of the same type will be ordered based on Connection Description
Note
Ensure that you understand the regulations of your country before you configure call routing. Configuring call routing incorrectly may violate the toll bypass rules in your country.
The list of the gateways selected is sorted in the following order of precedence:
1.
Site
2.
Connection
3.
Description
Note
The connection and the description that correspond to a gateway are input in the PSTN Connection flow while provisioning PSTN Connections.
Logical Partitioning
The Logical Partitioning feature is required for countries with telecom restrictions, such as India.
Logical Partitioning prevents toll bypass of the PSTN calls through the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 for countries that adhere to telecom regulations. Logical Partitioning is enabled in the Country Pack for countries that have regulations.
The Logical Partitioning feature is not available for countries that do not have regulations. Currently, the Logical Partitioning feature is enabled for India.
You can select one of the following features for Logical Partitioning:
•
Default—Allows you to enable default policies such that each site can route calls using the local gateway. This is a basic requirement for deployments and is provided by default.
•
Custom—Allows you to choose the required gateways such that multiple sites located in the same trunk area can share a common gateway. This allows provisioning of a Policy matrix between any sites.
For More Information
•
DHCP Usage for Acquiring IP Addresses
•
Example of Typical Deployment Model
•
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 3-1
•
Sites Settings, page 35-1 (for the Sites page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface)
Usage Profiles
A usage profile allows you to configure most of the user settings for a phone in one place. You can edit an existing usage profile, duplicate an existing usage profile to create a new profile, or add an entirely new usage profile. Each usage profile has a unique name. After you configure your usage profiles, you can assign them to users or to departments, so that the settings in the usage profile apply to the phones that belong to an individual user or to a department.
In the usage profile, you can configure calling privileges for users, phone features, such as barge, Cisco Extension Mobility, and so on, phone hardware functionality, phone applications that may display on the phone, and the phone button template, which controls the order of the buttons and the feature buttons that display on the phone.
You can configure a usage profile through the following methods:
•
Through the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (for initial deployment)
•
On the Usage Profile page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (if you are not using the Cisco-provided .xls data configuration file during initial deployment)
•
Under Users/Phones > Usage Profiles in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface (after initial deployment)
The usage profiles are not phone model specific; all settings that are available in the usage profile do not support all phone models. Before you add or edit an existing usage profile and assign it to a user, determine whether the phone model that is assigned to the user supports the features and functionality that is available in the usage profile. If you configure a setting that is not supported by the phone, the phone ignores the value in the configuration file, and the user cannot use the feature or functionality on the phone.
Note
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 supports a maximum of 30 usage profiles.
The usage profiles in Table 1-1 come with your system by default; that is, they display on the Usage Profile page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard (and in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface, unless you delete them from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard). You can delete these usage profiles, you can edit these profiles, or you assign them to your users without modification.
For More Information
•
Working with the Cisco-Provided .xls Data Configuration File, page 3-1
•
Usage Profiles Settings, page 38-1 (for the Usage Profile page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 First Time Setup Wizard and Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface)
•
Checklists for Users, Departments, Lines, and Phones, page 8-1
Users, Departments, Phones, and Lines
Phones, users, and lines are closely related in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000. A user, which is an employee from the company, uses the usage profile on a phone that is supported in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000. Because phones and users are closely related, you cannot configure a phone without first configuring a user or department that has an extension (line) from the dial plan assigned to it.
In the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 system, a user becomes an owner of a phone when you assign the user extension to line 1 on the phone. If the user is an owner of the phone, the phone uses the usage profile that is assigned to the user.
Tip
A department is a special kind of user that is reserved for public-space phones; this user is reserved for phones in cafeterias, lobbies, break rooms, and so on. A public-space phone cannot support Reach Me Anywhere. You do not configure passwords or phone PINs for departments, unlike users (Users/Phones > Users).
Example of How User or Department Ownership Works for a Phone
Step 1
If you have not already done so, add the user or department configuration; for example, add the user by selecting Users/Phones > Users (or Department) in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface.
•
When you add the user or department, you must assign a usage profile that you want to be available to the phone.
•
When you add the user or department, assign an extension to the user or department, based on the dial plan that is set up for your system.
Step 2
Add the phone and assign the extension to line 1 on the phone. The user or department becomes the owner of the phone, and a user can use the features and functionality from the usage profile on the phone if the phone supports the functionality.
Tip
You can create a shared line between an IP phone and an analog phone using the same user extension.
Note
Refer to http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/vg224/software/configuration/guide/scgvoip.html for information on VG224 configuration.
On the User or Department page, you create lines for the user or department based on the dial plan that you set up; for example, if your dial plan is set up for 4-digit dialing with an extension range of 2000-2999, you can assign an extension such as 2555 to the user or department. You can set up to 6 extensions in a prioritized list for each user or department. The usage profile that you assign to the user or department applies to all extensions that are in the prioritized list.
You assign user extensions (lines) to the phone on the Phone page. You can set up to 6 lines as a prioritized list on the Phone page, even if the phone does not support 6 lines. For each line, you can define Call Forward All and External Caller ID.
The phone button template that is configured in the usage profile determines the order of line buttons and the types of functionality that displays next to the line buttons on the phone; for example, for all lines except line 1, which must be a line because of user-phone ownership, you can designate a line as a speed dial, line, or feature button (Mobility, Meet Me Conference, and so on). When the phone button template that is configured in the usage profile designates the buttons as lines, the system orders the lines that are assigned on the Phone page based on the prioritized list, with the first line being designated for line 1, the second line in the list being used for the next button on the phone that is designated as line 2, and so on. In the Usage Profile, you must establish the purpose for 12 line buttons on the phone, even when the phone does not support 12 buttons.
The users can create up to 12 speed dials in a prioritized list in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 User Preferences Interface, even when the phone does not support 12 speed dials.
Hunt Lists
A hunt list consists of a group of extensions that can answer calls. You set up hunt lists for the purpose of distributing calls amongst the users that belong to the group. For example, if the company does not have a receptionist and several users must answer calls, consider setting up a hunt list to ensure that calls are evenly distributed amongst the users that belong to the hunt list. For example, if several administrative assistants must share the call load for several managers, consider setting up a hunt list to ensure that all calls are answered quickly. You configure hunt lists on the Hunt Lists page in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 Administrative Interface. (Select Users/Phones > Hunt Lists.) You can create as many hunt lists as you want.
Extensions in a hunt list can belong to users or departments. You can assign any user or department extension to a hunt list, but only those extensions that are assigned to phones can actually answer the calls. An extension may belong to more than one hunt list.
Pilot extensions for hunt lists must be in the extension range(s), but pilot extensions do not get assigned to users or departments.
For the members (extensions) that belong to the group, you can select one of the following distribution methods:
Tip
An idle member is not servicing any calls. An available member is on an active call but is available to accept a new call. A busy member cannot accept calls.
•
Top Down—Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 distributes a call to idle or available members (extensions) starting from the first idle or available member of a hunt list to the last idle or available member.
•
Circular—Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 distributes a call to idle or available members starting from the (n+1)th member of a hunt list, where the nth member is the member to which Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 most recently extended a call. If the nth member is the last member of a hunt list, Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 distributes a call starting from the top of the hunt list.
•
Longest Idle Time—Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 only distributes a call to idle members, starting from the longest idle member to the least idle member of a hunt list.
•
Broadcast—Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 distributes a call to all idle or available members of a hunt list simultaneously.
CautionDo not put extensions that are shared lines in a hunt list that uses the Broadcast distribution algorithm. Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition 3000 cannot display shared lines correctly on the phone if the extensions are members of a hunt list that uses the Broadcast distribution algorithm.
For More Information
Example of Typical Deployment Model
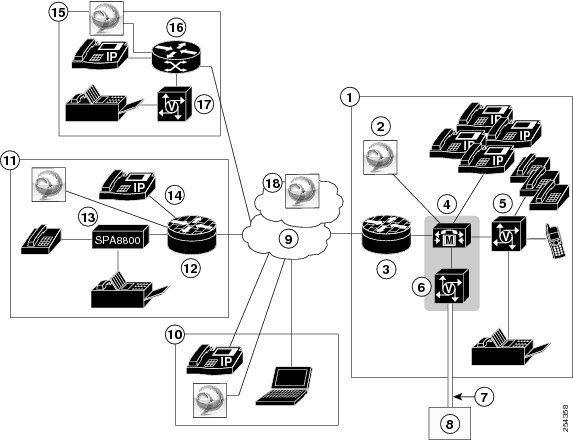
Figure 1-1 shows an example of a typical deployment model that includes the central site, two remote sites, and the teleworker site. The central site includes the gateway, server, several routers, a Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway, and IP and analog phones. The remote sites include phones and routers. For more information on the example, see the following:
Figure 1-1 Example of a Typical Deployment Model
Central Site (Example)
Figure 1-1 illustrates that the central site is where your server, gateway, and the majority of your phones/users are located. To use fax or analog phones at the central site, the Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway is set up specifically for the central site. The gateway allows access to the PSTN through a dual T1/E1 connection that is provided by the service provider (telecommunications company).
Although not included in Figure 1-1, a switch exists between the server and the Cisco Unified IP Phones.
Teleworker Site (Example)
Figure 1-1 illustrates that the teleworker site has phones and personal computers that connect to the central site through the Internet. A router that supports VPN connects the teleworker site to the central site.
Tip
Quality of service (QoS) may not be available for the teleworker site.
Remote Site 1 (Example)
Figure 1-1 illustrates that remote site 1 connects to the central site through a router that supports VPN (and connects to the Internet). Analog phones and fax are used at remote site 1, so the Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway is set up for these phones and functionality specifically for this site. Fewer phones are included in remote site 1 than at the central site.
Remote Site 2 (Example)
Figure 1-1 illustrates that remote site 2 connects to the central site through a dedicated WAN link. Analog phones are used at remote site 2, so the Cisco VG224 Analog Phone Gateway is set up to support the analog phones at this site.

 Feedback
Feedback