-
Deploying IPv6 in Unified Communications Networks with Cisco Unified Communications Manager
-
Preface
-
Introduction
-
IPv6 Basics
-
IPv6 Support in Cisco Unified Communications Devices
-
Unified Communications Deployment Models for IPv6
-
Network Infrastructure
-
Gateways
-
Trunks
-
Media Resources and Music on Hold
-
Call Processing and Call Admission Control
-
Dial Plan
-
Applications
-
IP Video Telephony
-
IP Telephony Migration Options
-
Security
-
Unified Communications Endpoints
-
Configuring IPv6 in Cisco Unified CM
-
Configuring Cisco Integrated Services Routers
-
Configuring Cisco VG224 Analog Voice Gateway
-
Configuring Cisco IOS Gateways
-
Table Of Contents
Unified Communications Endpoints
IPv6 Support on Analog Gateways
Cisco VG224 Analog Voice Gateway
Cisco Integrated Services Router (ISR) Analog FXS Ports
IPv6 Support on Cisco Unified IP Phones
Common Device Configuration Profile
Default Common Device Configuration Profile
Unified Communications Endpoints
Revised: June 08, 2010; OL-19142-02
This chapter describes the Cisco Unified Communications endpoints and their IPv6 capabilities. Table 15-1 lists the endpoint types and summarizes their IPv6 capabilities.
As indicated in Table 15-1, IPv6 support extends to only a subset of the Cisco analogue gateways and IP phones. The following sections discuss these devices in more detail.
IPv6 Support on Analog Gateways
The following analog gateways support IPv6:
•
Cisco VG224 Analog Voice Gateway
•
Analogue FXS ports on Cisco 2800 Series and 3800 Series Integrated Services Routers
Cisco VG224 Analog Voice Gateway
The Cisco VG224 Analog Voice Gateway is a Cisco IOS high-density 24-port gateway for connecting analog devices to the Cisco Unified Communications network. In Cisco IOS Release 12.4(22)T and later releases, the Cisco VG224 can act as an IPv6-capable Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) endpoint with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM). Once added as a gateway in Unified CM, the FXS ports on the VG224 gateway register as individual devices with Unified CM.
For configuration details about the Cisco VG224, see Configuring Cisco VG224 Analog Voice Gateway, page C-1.
Cisco Integrated Services Router (ISR) Analog FXS Ports
Analogue FXS ports on Cisco 2800 Series and 3800 Series Integrated Services Routers can act as IPv6-capable Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) endpoints with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM). Once added as a gateway in Unified CM, the FXS ports on the router register as individual devices with Unified CM.
For configuration details about the Cisco 2800 and 3800 Series Integrated Services Router FXS ports, see Configuring Cisco Integrated Services Routers, page B-1. Use the Cisco IOS command line interface (CLI) and the Unified CM Administration graphical user interface to configure the analogue FXS ports.
IPv6 Support on Cisco Unified IP Phones
The following SCCP-based Cisco Unified IP Phone models support IPv6:
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7906G
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7911G
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931G
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7941G and Cisco Unified IP Phone 7941GE
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7942G
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7945G
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7961G and Cisco Unified IP Phone 7961GE
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7962G
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7965G
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7970G
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7971G-GE
•
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7975G
These phones models can be configured to support the following addressing modes:
•
A single IPv4 address
•
A single IPv6 address
•
Both an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address (also known as dual-stack configuration)
For phones that support both an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address, the following conditions apply:
•
For call control signaling to Unified CM, the phone can be configured to use either its IPv4 address or its IPv6 address.
•
For voice media between two dual-stack devices, the devices may choose to use either their IPv4 addresses or their IPv6 addresses to transport RTP voice streams.
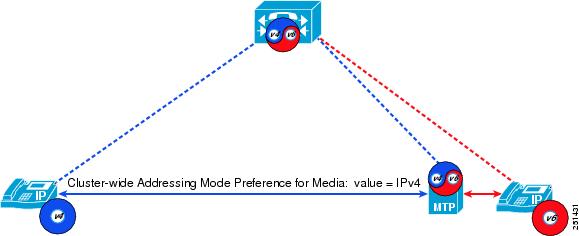
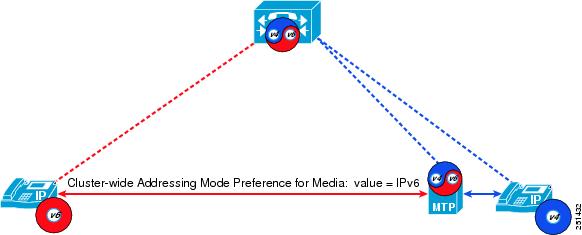
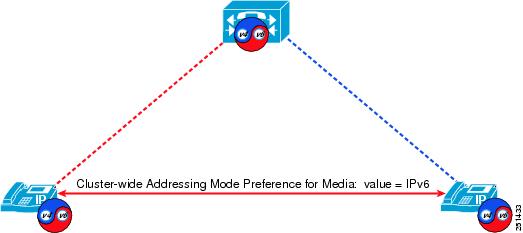
When a phone with a single IPv4 address needs to communicate with a phone with a single IPv6 address, an IP addressing version incompatibility exists. To resolve this media addressing incompatibility, Unified CM dynamically inserts a media termination point (MTP) to convert the media stream from IPv4 to IPv6 (and vice versa).
IP Phone Deployment Considerations in an IPv6 Network
The PC Voice LAN Access setting on IP phones is typically used to allow the monitoring of IP phone traffic by monitoring and recording applications and by network monitoring software. This setting also allows multicast traffic to be propagated from the voice VLAN to the IP phone's PC port. By default, the PC Voice VLAN Access setting is enabled on IP phones.
In IPv6-enabled networks, this default PC Voice VLAN Access setting allows Router Advertisement (RA) multicast messages to be sent from the voice VLAN to the IP phone's PC port. Ordinarily, the PC should drop any packets that it receives with a voice VLAN tag because it is not configured for the voice VLAN and does not understand 802.1g tagging. However, if the PC does accept packets with a voice VLAN tag and uses an RA from the voice VLAN, this can cause an IPv6 address from the voice VLAN to be assigned to the PC.
If you encounter the above issue of incorrect IPv6 address assignment for PC port devices, use either of the following techniques to resolve this issue:
•
Set the prefix lifetime of RAs sent by routers in the voice VLAN to a significantly shorter lifetime value than the RAs sent by routers in the data VLAN, and also ensure that routers in the data VLAN have higher priority than those in the voice VLAN. IPv6 devices in the data VLAN using the Address Selection Algorithm (RFC 3484) will pick the Network Prefix included in RAs with the longest lifetime, and will thus prefer routers in the data VLAN.
•
For all IP phones with connected devices that are affected by the above issue, set the IP phone's PC Voice VLAN Access setting to disabled. For large numbers of phones, this configuration change can be bulk-provisioned through the Unified CM Bulk Administration Tool (BAT).
Common Device Configuration Profile
The process for configuring IPv6 on the phones is similar to that for SIP trunks. In Cisco Unified CM Administration, select Device > Device Settings > Common Device Configuration to create and configure a Common Device Configuration Profile and associated it with one or more IP phones. The Common Device Configuration Profile contains the following IPv6 configuration information:
•
IP Addressing Mode
•
IP Addressing Mode Preference for Signaling
•
Allow Auto-Configuration for Phones
IP Addressing Mode
The phone IP Addressing Mode has three settings:
•
IPv4 only
In this mode, the phone acquires and uses only one IPv4 address for all signaling and media. If the phone has previously acquired an IPv6 address, it releases that address.
•
IPv6 only
In this mode, the phone acquires and uses only one IPv6 address for all signaling and media. If the phone has previously acquired an IPv4 address, it releases that address.
•
IPv4 and IPv6
In this mode, the phone acquires and uses one IPv4 address and one IPv6 address. It can use the IPv4 and the IPv6 address as required for media. It uses either the IPv4 address or the IPv6 address for call control signaling to Unified CM.
If IPv6 is enabled in the Unified CM cluster, the default phone setting for IP Addressing Mode is IPv4 and IPv6. If the IP phone supports both IPv4 and IPv6, it will adopt this setting, but all IPv4-only phones will ignore this setting.
Cisco recommends setting the phone IP Addressing Mode to IPv4 and IPv6. A setting of IPv6 only is not recommended and should be used only in test environments. For more information on IPv6-only phone functionality, see IPv6-Only Phones.
IP Addressing Mode Preference for Signaling
The phone IP Addressing Mode Preference for Signaling has three settings:
•
IPv4
If the phone has an IPv4 address, it uses that IPv4 address for call control signaling to Unified CM.
•
IPv6
If the phone has an IPv6 address, it uses that IPv6 address for call control signaling to Unified CM.
•
Use System Default
In this case, the phone uses the cluster-wide Enterprise Parameter configuration value for its IP Addressing Mode for Signaling.
If IPv6 is enabled in the Unified CM cluster, the default phone setting for IP Addressing Mode for Signaling is Use System Default. If the IP phone supports either IPv6 or both IPv4 and IPv6, it will adopt the cluster-wide setting for IP Addressing Mode for Signaling, but all IPv4-only phones will ignore this setting.
Allow Auto-Configuration for Phones
Allow Auto-Configuration for Phones has three settings:
•
On
With this setting, the phone is allowed to use Stateless Auto Address Configuration (SLAAC) to acquire an IPv6 address. Whether or not the phone uses SLAAC depends on the link-local router's O and M bit configuration for router advertisements (RAs), as follows:
–
If the O bit is set in the router's RAs, the phone uses SLAAC to acquire an IPv6 address and uses the DHCP server to acquire other information such as the TFTP server address.
–
If the M bit is set in the router's RAs, the phone does not use SLAAC. Instead, it uses the DHCP server to acquire its IP address and other information (Stateful DHCP).
–
If neither the M bit nor the O bits is set, the phone uses SLAAC to acquire an IP address and does not use DHCP for other information. The phone also requires a TFTP server address to download its configuration file and register to Unified CM. This TFTP server address can be configured manually through the phone's user interface (UI).
•
Off
With this setting, the phone does not use Stateless Auto Address Configuration (SLAAC) to acquire an IPv6 address. In this case, the phone can either be configured manually or use Stateful DHCPv6 to acquire an IPv6 address and TFTP server address.
•
Default
With this setting, the phone uses the cluster-wide Enterprise Parameter configuration value for Allow Auto-Configuration for Phones.
If IPv6 is enabled in the Unified CM cluster, the phone's default setting of Allow Auto-Configuration for Phones is Default. If the IP phone supports either IPv6 only or both IPv4 and IPv6, it will adopt the cluster-wide setting for Allow Auto-Configuration for Phones, but all IPv4-only phones will ignore this setting.
Default Common Device Configuration Profile
By default, there are no Common Device Configuration profiles configured, and each device is associated with a <None> Common Device Configuration. If IPv6 is enabled in the Unified CM cluster with this default configuration, IPv6-capable devices adopt the following settings:
•
IP Addressing Mode = IPv4 and IPv6
•
IP Addressing Mode Preference for Signaling = Use System Default
•
Allow Auto-Configuration for Phones = Default
Figure 15-1 Effect of IP Addressing Mode for Media on MTP Usage for IP Phones
Other IP Phone Functions
The following functions also affect the use of IPv6 on Cisco Unified IP Phones.
TFTP
As previously described, TFTP servers support both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. IPv4-only phones use their received IPv4 TFTP address to reach the TFTP server, and IPv6-only phones use their received IPv6 TFTP address to reach the TFTP server. Dual-stack phones can use either their IPv4 or IPv6 TFTP address to reach the TFTP server.
The following IPv6 information is sent to the phone in its configuration file from the TFTP server:
•
Unified CM IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
•
The setting for IP Addressing Mode
•
The setting for IP Addressing Mode Preference for Signaling
•
The setting for Allow Auto-Configuration for Phones
Unified CM Registration for Dual-Stack IP Phones
Dual-stack phones attempt to connect to Unified CM by using the preferred (IPv4 or IPv6) address specified in the IP Addressing Mode Preference for Signaling parameter found in the TFTP configuration file. If the first attempt at connection fails due to a TCP timeout, the phone will then attempt to connect to Unified CM using its other address.
IP Phone HTTP Server Functionality
The HTTP server function of all IP phones uses IPv4 only. The HTTP server provides several functions, including:
•
Telephone User Interface access to:
–
Directory search functions
–
Call history
–
All IP Phone Services
–
Extension Mobility
–
Quality Report Tool (QRT)
•
Web access to the phone through the Unified CM phone administration graphical user interface
CDP and LLDP
IP phones support the sending and receiving of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses in data link layer Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) and Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) messages. Currently, Cisco applications do not use any of the IPv6 addresses sent in CDP or LLDP messages.
IPv6-Only Phones
IP phones configured with an IP addressing mode of IPv6 Only are subject to a number of functional limitations and are therefore not recommended for production deployments. Those limitations are described here:
•
Because the phone's HTTP server uses IPv4 only, the following functions are not available to IPv6-only phones:
–
Directory search functions
–
Call history
–
All IP Phones Services
–
Extension Mobility
–
Quality Report Tool (QRT)
–
Web access to the phone through the Unified CM phone administration graphical user interface
•
Device mobility uses IP subnet information to locate mobile devices. Only IPv4 subnets are supported for device mobility, and this function is not supported for IPv6-only phones.
•
Peer Firmware Sharing for the distribution of files between like phones is not supported for IPv6-only phones. IPv6-capable phones do support a load server using an IPv6 address.

 Feedback
Feedback