Table Of Contents
Command Line Interface Routing
Basic Subscriber Routingthe following
Command Line Interface Routing Examples
Carrier 9999 Use Dial-Plan "N"
Command Line Interface Routing
Revised: December 9, 2008, OL-8001-10Introduction
This chapter provides a basic understanding of how the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Command Line Interface (CLI) functions with of the routing types and call types. This chapter is divided into the following sections:
•
Command Line Interface Routing Examples
Routing Types
This section provides the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch CLI routing type information. The following topics are covered in this section:
•
Basic Subscriber Routingthe following
Basic Subscriber Routingthe following
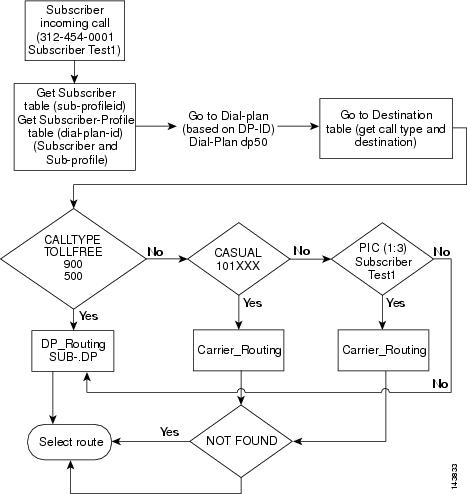
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch basic subscriber routing and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-1 for visual representation of basic subscriber routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step basic subscriber routing flow.
Step 1
Subscriber incoming received or placed.
Example:
Step 2
Get the subscriber table (sub-profile identification (ID)).
Step 3
Get the subscriber-profile table (dial-plan-identification (DP-ID)).
Example:
Step 4
Go to the dial-plan (based on DP-ID).
Step 5
Go to destination table and get the call type and destination.
Example:
Step 6
Determine the call type. If the call type is toll free, 900, or 500, proceed to Step 7. If the call type is casual, proceed to Step 8. If the call type is via a presubscribed interexchange carrier (PIC), proceed to Step 9.
Examples:
Step 7
If the call type is toll free, 900, or 500, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the dial plan to select the call route and to route the call.
Step 8
If the call type is casual, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the carrier routing information to select the call route and to route the call.
Step 9
If the call type is via a PIC, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will user the PIC carrier routing information to select the call route and to route the call.
Figure 4-1 Basic Subscriber Routing
Basic Trunk Routing
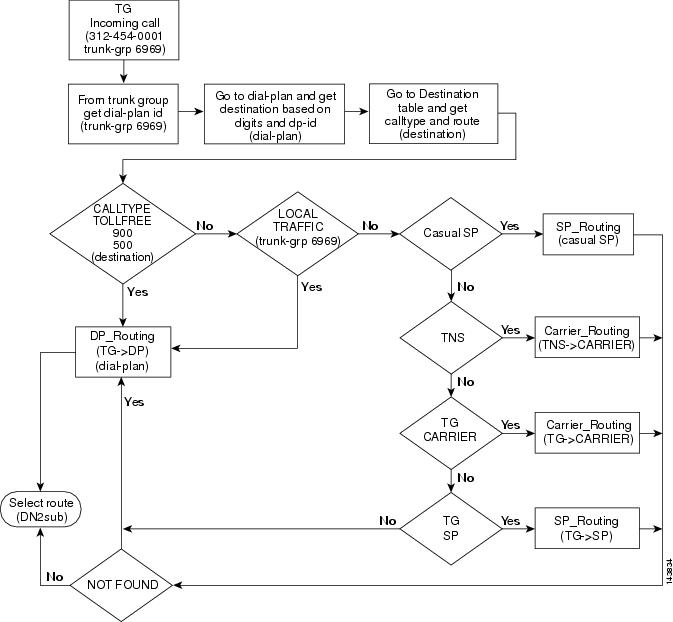
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch basic trunk routing and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-2 for visual representation of basic trunk routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step basic trunk routing flow.
Step 1
Trunk group (TG) call received or placed.
Example:
Step 2
Get the DP-ID from the TG.
Example:
Step 3
Go to the dial-plan and get the destination based on the digits and DP-ID.
Example:
Step 4
Go to the destination table and get the call type and the route.
Example:
Step 5
Determine the call type. If the call type is toll free, 900, or 500, proceed to Step 6. If the call type is local traffic, proceed to the Step 7. If the call type is casual service provider (SP), proceed to Step 8. If the call type is transit network selection (TNS), proceed to Step 9. If the call type is TG carrier, proceed to Step 10. If the call type is TG SP, proceed to Step 11.
Example:
Step 6
If the call type is toll free, 900, or 500, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the dial plan to select the call route and to route the call.
Examples:
Step 7
If the call type is local traffic, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the dial plan to select the call route and to route the call.
Examples:
Step 8
If the call type is casual SP, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the SP routing to select the call route and to route the call. If the SP routing is not found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will user the dial plan to select the call route and to route the call.
Examples:
Step 9
If the call type is TNS, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the carrier routing to select the call route and to select the call route and to route the call. If the carrier routing is not found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will user the dial plan to select the call route and to route the call.
Examples:
Step 10
If the call type is TG carrier, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the carrier routing to select the call route and to route the call. If the carrier routing is not found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will user the dial plan to select the call route and to route the call.
Step 11
If the call type is TG SP, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will the SP routing to select the call route and to route the call. If the SP routing is not found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will user the dial plan to select the call route and to route the call.
Examples:
Figure 4-2 Basic Trunk Routing
Carrier Based Routing
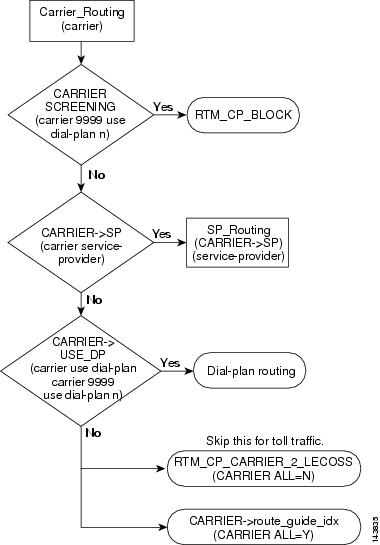
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch carrier based routing and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-3 for visual representation of carrier based routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step carrier based routing flow. Additionally, LNP-QUERY has been added to the call flow. LNP-QUERY specifies whether to perform an local number portability (LNP) query on the call type. Applies only if the ALL-CALL-QUERY flag in the LNP-PROFILE table is set to Y and the ACQ-LNP-QUERY token in the Destination table is set to ACQ-BASED-ON-CALL-TYPE.
Step 1
Carrier based routing call is received.
Step 2
Determine if the carrier is being screened. If the carrier is being screened, proceed to Step 3. If the carrier is not being screened, proceed to Step 4.
Example:
Carrier 9999 Use Dial-Plan "N"
Step 3
If the carrier is being screened, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will determine if the carrier call processing is being remotely blocked (RTM_CP_BLOCK). If the carrier call processing is being remotely blocked, the call can not be completed and will be dropped.
Step 4
If the carrier is not being screened, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will determine if the carrier is a recognized service provider. If the carrier is a recognized service provider, proceed to Step 5. If the carrier is not a recognized service provider, proceed to Step 6.
Example:
Step 5
If the carrier is a recognized service provider, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the service provider routing to select the call route and to route the call.
Example:
Step 6
If the carrier is not a recognized service provider, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will determine if a carrier dial plan is configured. If a carrier dial plan is configured, proceed to Step 7. If a carrier dial plan, is not configured proceed to Step 8.
Example:
Carrier 9999 Use Dial-Plan "N"
Step 7
If a carrier dial plan is configured, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the carrier dial plan to select the call route and to route the call.
Step 8
If a carrier dial plan is not configured, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will determine if a carrier remote call processing to local exchange carrier operations support system is available (RTM_CP_CARRIER_2_LECOSS). If the RTM_CP_CARRIER_2_LECOSS is available, proceed to Step 9. If the RTM_CP_CARRIER_2_LECOSS is not available, proceed to Step 10.
Note
Step 8 is skipped for toll traffic. If the traffic is toll traffic, proceed to Step 10.
Step 9
If the RTM_CP_CARRIER_2_LECOSS is available and if the traffic is not toll traffic, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the RTM_CP_CARRIER_2_LECOSS to select the call route and to route the call.
Example:
Step 10
If the RTM_CP_CARRIER_2_LECOSS is not available, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the carrier guide index to select the call route and to route the call.
Example:
Figure 4-3 Carrier Based Routing
Basic Dial Plan Routing
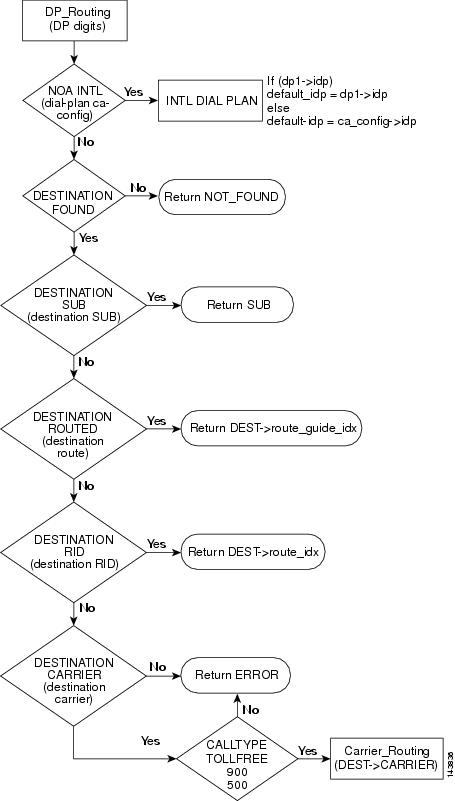
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch basic dial plan routing and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-4 for visual representation of basic dial plan routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step basic dial plan routing flow.
Step 1
Basic dial plan routing call received.
Step 2
Determine if the nature of address (NOA) for the received call is an international call. If the call is an international call, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will use the the international dial plan to select the call route and to route the call. If the call is not an international call, proceed to Step 3.
Example:
Step 3
Determine if the call destination is found. If the call destination is not found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will return a destination not found response (NOT FOUND) and will drop the call. If the call destination is found, proceed to the Step 4.
Step 4
Determine if a call destination subscriber is found. If a call destination subscriber is found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will return a subscriber (SUB) response and will use the subscriber information to select the call route and to route the call. If a call destination subscriber is not found, proceed to Step 5.
Example:
Step 5
Determine if a call destination route is found. If a call destination route is found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will return a destination (DEST) response and will use the route guide index to select the call route and to route the call. If a call destination route is not found, proceed to Step 6.
Example:
Step 6
Determine if a call destination route identification (RID) is found. If a call destination RID is found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will return a DEST response and will user the route index to select the call route and to route the call. If a call destination RID is not found, proceed to Step 7.
Example:
Step 7
Determine if a destination carrier is found. If a destination carrier is found, proceed to the Step 8. If a destination carrier is not found, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will return an error and will drop the call.
Example:
Step 8
Determine the call type. If the call type is toll free, 900, or 500, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and to route the call using the destination carrier routing. If the call type is not toll free, 900, or 500, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will return an error and will drop the call.
Figure 4-4 Basic Dial Plan Routing
Call Types
This section provides detailed information on the CLI usage for the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch call types. CLI information on the following call types is provided:
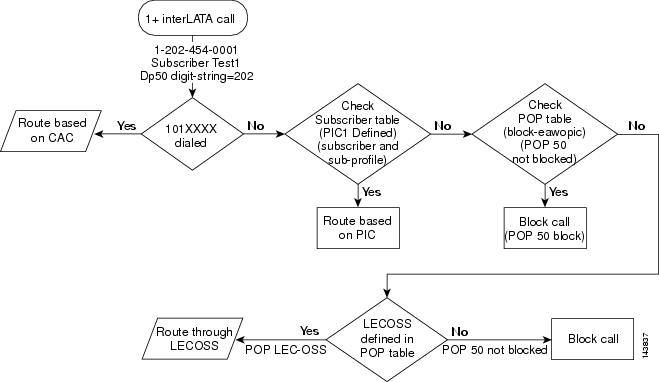
1+ Interlata Call
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch routing and call flow for 1+ interlata calls and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-5 for visual representation of the 1+ interlata call routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step 1+ interlata call routing flow.
Step 1
A 1+ interlata call is received.
Examples:
Step 2
Determine if a 101XXXX number has been dialed. If a 101XXXX number has been dialed, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call based on the carrier access code (CAC). If a 101XXXX number has not been dialed, proceed to Step 3.
Step 3
Check the subscriber table to determine if a PIC is defined. If a PIC is defined, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call based on the PIC information. If a PIC is not defined, proceed to Step 4.
Example:
Step 4
Check the point of presence (POP) table and verify if a block-eawopic is configured. If the a block-eawopic is configured, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call. If a block-eawopic is not configured, proceed to Step 5.
Examples:
Step 5
Determine if a local exchange carrier operations support system (LECOSS) is defined in the POP table. If a LECOSS is defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select route the call via the LECOSS. If a LECOSS is not defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call.
Examples:
Figure 4-5 1+ Interlata Call
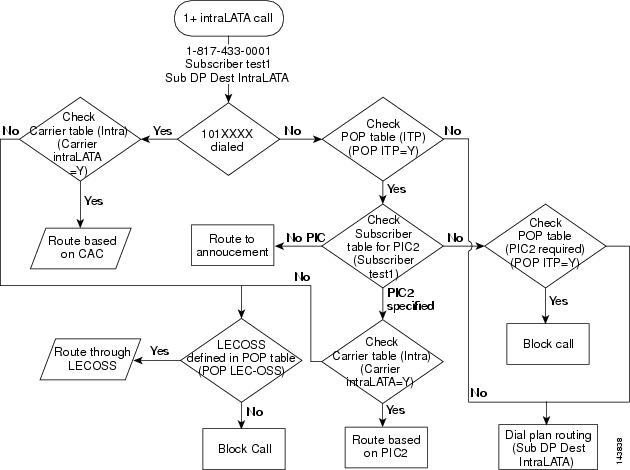
1+ Intralata Call
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch routing and call flow for 1+ intralata calls and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-6 for visual representation of the 1+ intralata call routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step 1+ intralata call routing flow.
Step 1
An 1+ intralata call is received.
Examples:
Step 2
Determine if 101XXXX number has been dialed. If a 101XXXX number has been dialed proceed to Step 3. If a 101XXXX number has not been dialed, proceed to Step 4.
Step 3
Check the carrier table for a CAC. If a CAC is available, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call based on the CAC. If a CAC is not available, proceed to Step 3a.
Example:
a.
Determine if a LECOSS is defined in the POP table. If a LECOSS is defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call via the LECOSS. If a LECOSS is not defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call.
Step 4
Check the POP table for a configured IP transfer point (ITP). If an ITP is configured, proceed to Step 4a. If an ITP is not configured, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will route the call via dial plan routing.
Example:
a.
Check the subscriber table for a specified PIC. If a PIC is specified, proceed to Step 4b. If a PIC is not specified, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will route the call to the announcement server and will check the POP table for a specified PIC. If a PIC is not specified, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call or if a dial plan is available, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call according to the dial plan routing information.
Examples:
b.
Check the intra carrier table for a specified PIC. If a PIC is specified in the intra carrier table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call based on the PIC information. If a PIC is not specified in the intra carrier table, proceed to Step 4c.
Example:
c.
Determine if a LECOSS is defined in the POP table. If a LECOSS is defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call via the LECOSS. If a LECOSS is not defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call.
Example:
Figure 4-6 1+ Intralata Call
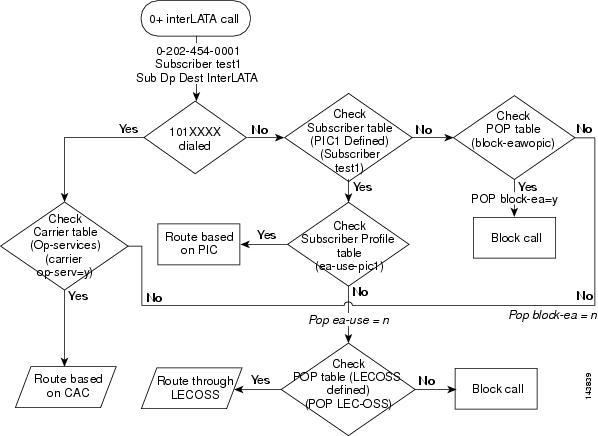
0+ Interlata Call
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch routing and call flow for 0+ interlata calls and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-7 for visual representation of the 0+ interlata call routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step 0+ interlata call routing flow.
Step 1
A 0+ interlata call is received.
Examples:
Step 2
Determine if a 101XXXX number has been dialed. If a 101XXXX number has been dialed proceed to Step 3. If a 101XXXX number has not been dialed proceed to Step 5.
Step 3
Check the carrier table for a CAC. If a CAC is available, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call based on the CAC. If a CAC is not available, proceed to Step 4.
Example:
Step 4
Check the POP table for a defined LECOSS. If a LECOSS is defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will route the call via the LECOSS. If a LECOSS is not defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call.
Example:
Step 5
Check the subscriber table for a defined PIC. If a PIC is defined in the subscriber table, proceed to Step 6. If a PIC is not defined in the subscriber table, proceed to Step 7.
Example:
Step 6
Check the subscriber profile for ea-use-pic entry. If the subscriber profile contains an ea-use-pic entry, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call based on the PIC information. If the subscriber profile does not contained an ea-use-pic entry, return to Step 4.
Examples:
Step 7
Check the POP table for a block-eawopic entry. If the POP table contains a block-eawopic entry, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call. If the POP table does not contain a block-eawopic entry, return to Step 4.
Examples:
Figure 4-7 0+ Interlata Call
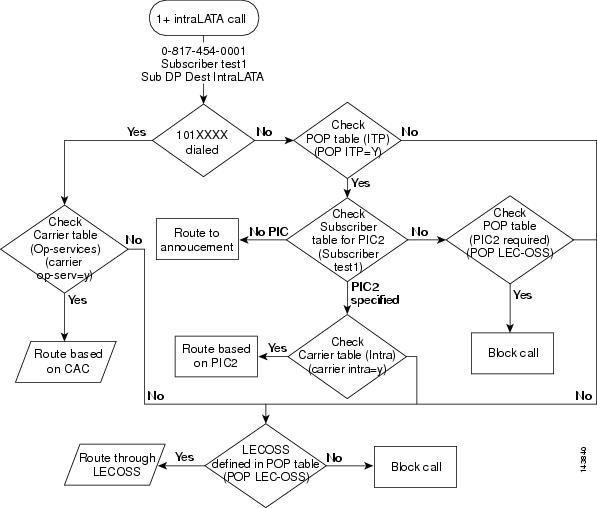
0+ Intralata Call
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch routing and call flow for 0+ intralata calls and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-8 for visual representation of the 0+ intralata call routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step 0+ intralata call routing flow.
Step 1
A 0+ intralata call is received.
Examples:
Step 2
Determine if a 101XXXX number was dialed. If a 101XXXX number was dialed, proceed to Step 3. If a 101XXXX number was not dialed, proceed to Step 5.
Step 3
Check the carrier table for a CAC. If a CAC is available, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call based on the CAC. If a CAC is not available, proceed to Step 4.
Example:
Step 4
Check the POP table for a defined LECOSS. If a LECOSS is defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will route the call via the LECOSS. If a LECOSS is not defined in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call.
Example:
Step 5
Check the POP table for a configured ITP. If an ITP is configured, proceed to Step 6. If an ITP is not configured return to Step 4.
Example:
Step 6
Check the subscriber table for a specified PIC. If a PIC is specified, proceed to Step 7. If a PIC is not specified, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will route the call to the announcement server. Additionally, if a PIC is not specified in the subscriber table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will check the POP table for a specified PIC. If a PIC is specified in the POP table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will block the call. If a PIC is not specified in the POP table, return to Step 4.
Examples:
Step 7
Check the intra carrier table for the specified PIC. If the specified PIC is included in the intra carrier table, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will select the call route and route the call based on the PIC information. If the specified PIC is not included in the intra carrier table, return to Step 4.
Example:
Figure 4-8 0+ Intralata Call
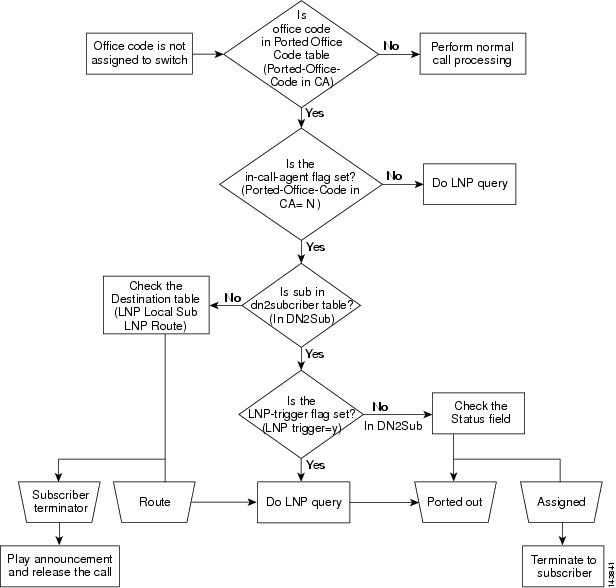
Ported-In Call Processing
This section provides a detailed description of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch routing and call flow for ported-in call processing calls and provides CLI example references. Refer to Figure 4-9 for visual representation of the ported-in call processing call routing flow while reviewing the following detailed step-by-step ported-in call processing call routing flow.
Step 1
A ported-in call is received.
Step 2
The office code is not assigned to the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch.
Step 3
Determine if the office code is in the ported-in office code table. If the office code is in the ported-in office code table, proceed to Step 4. if the office code is not in the ported-in office code table, perform normal call processing.
Example:
Step 4
Determine if the in-call agent flag is set. If the in-call agent flag is set, proceed to Step 5. If the in-call agent flag is not set, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will perform an local number portability (LNP) query.
Examples:
Step 5
Determine if the subscriber is included the dn2subscriber table. If the subscriber is included in the dn2sunscriber table, proceed to Step 6. If the subscriber is not included in dn2subscriber table, proceed to Step 7.
Examples:
Step 6
Determine if the LNP trigger flag is set. If the LNP trigger flag is set, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will perform an LNP query and port out the call. If the LNP trigger flag is not set, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will check the status field to determine if a LNP trigger has been assigned and will port out the call or terminate the call to the subscriber.
Examples:
Step 7
Check the destination table for the subscriber information. Based on the destination table information, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will route the call or issue a subscriber terminator, release the call, and play the released call announcement. As part of routing the call, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch will perform an LNP query and , if necessary, port out the call.
Examples:
Figure 4-9 Ported-In Call Processing
Command Line Interface Routing Examples
This section provides CLI routing examples. The following CLI examples are provided:
•
Carrier 9999 Use Dial-Plan "N"
Carrier - Service-Provider
The Carrier - Service-Provider CLI example is used in the Carrier Based Routing routing example.
Carrier - Service-Provider Example:
CLI>show carrier id=7777Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=7777STATUS=INSINTER=YINTRA=NINTL=NCASUAL=YCUT_THRU=YOP_SERVICES=YSEND_CN=NSEND_CSP=NUSE_DIAL_PLAN=NROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testSP_ID=testNETWORK_TYPE=NOTUSEDNATIONAL_NETWORK_PLAN=NOTUSEDCarrier 9999 Use Dial-Plan "N"
The Carrier 9999 Use Dial-Plan "N" CLI example is used in the Carrier Based Routing routing example.
Carrier 9999 Use Dial-Plan "N" Example:
CLI>show carrier id=9999Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=9999STATUS=INSINTER=YINTRA=NINTL=NCASUAL=YCUT_THRU=YOP_SERVICES=YSEND_CN=NSEND_CSP=NUSE_DIAL_PLAN=NNETWORK_TYPE=NOTUSEDNATIONAL_NETWORK_PLAN=NOTUSEDCarrier All = N
The Carrier All = N CLI example is used in the Carrier Based Routing routing examples.
Carrier All = N Example:
CLI>show carrier id=7777Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=7777STATUS=INSINTER=NINTRA=NINTL=NCASUAL=NCUT_THRU=NOP_SERVICES=NSEND_CN=NSEND_CSP=NUSE_DIAL_PLAN=NROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testNETWORK_TYPE=NOTUSEDNATIONAL_NETWORK_PLAN=NOTUSEDCarrier All = Y
The Carrier All = Y CLI example is used in the Carrier Based Routing routing examples.
Carrier All = Y Example:
CLI>show carrier id=7777Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=7777STATUS=INSINTER=YINTRA=YINTL=YCASUAL=YCUT_THRU=YOP_SERVICES=YSEND_CN=NSEND_CSP=NUSE_DIAL_PLAN=NROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testNETWORK_TYPE=NOTUSEDNATIONAL_NETWORK_PLAN=NOTUSEDCarrier Intra = Y
The Carrier Intra = Y CLI example is used in the 1+ Intralata Call and 0+ Intralata Call routing examples.
Carrier Intra = Y Example:
CLI>show carrier id=9999Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=9999STATUS=INSINTER=YINTRA=YINTL=NCASUAL=YCUT_THRU=YOP_SERVICES=YSEND_CN=NSEND_CSP=NUSE_DIAL_PLAN=YNETWORK_TYPE=NOTUSEDNATIONAL_NETWORK_PLAN=NOTUSEDCarrier Op-Serv = Y
The Carrier Op-Serv = Y CLI example is used in the 0+ Interlata Call and 0+ Intralata Call routing examples.
Carrier Op-Serv = Y Example:
CLI>show carrier id=7777Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=7777STATUS=INSINTER=YINTRA=NINTL=NCASUAL=YCUT_THRU=YOP_SERVICES=YSEND_CN=NSEND_CSP=NUSE_DIAL_PLAN=NROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testSP_ID=testNETWORK_TYPE=NOTUSEDNATIONAL_NETWORK_PLAN=NOTUSEDCarrier Use Dial-Plan "Y"
The Carrier Use Dial-Plan "Y" CLI example is used in the Carrier Based Routing routing example.
Carrier Use Dial-Plan "Y" Example:
CLI>show carrier id=8888Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=8888STATUS=INSINTER=YINTRA=NINTL=NCASUAL=YCUT_THRU=YOP_SERVICES=YSEND_CN=NSEND_CSP=NUSE_DIAL_PLAN=YDESCRIPTION=TESTNETWORK_TYPE=NOTUSEDNATIONAL_NETWORK_PLAN=NOTUSEDDestination
The Destination CLI example is used in the Basic Subscriber Routingthe following and Basic Trunk Routing routing examples.
Destination Example:
CLI>show destinationDEST_ID=local-subCALL_TYPE=LOCALROUTE_TYPE=SUBZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NDestination Carrier
The Destination Carrier CLI example is used in the Basic Dial Plan Routing routing example.
Destination Carrier Example:
CLI>show destination dest-id=800;Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=800CALL_TYPE=TOLL_FREEROUTE_TYPE=CARRIERCARRIER_ID=7777ZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NDestination Interlata
The Destination Interlata CLI example is used in the 1+ Interlata Call routing example.
Destination Interlata Example:
CLI>show destination dest-id=interlataReply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=interlataCALL_TYPE=INTERLATAROUTE_TYPE=ROUTEROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NDestination RID
The Destination RID CLI example is used in the Basic Dial Plan Routing routing example.
Destination RID Example:
CLI>show destination dest-id=65019Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=65019CALL_TYPE=LOCALROUTE_TYPE=RIDZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YROUTE_ID=65019GAP_ROUTING=NDestination ROUTE
The Destination ROUTE CLI example is used in the Basic Dial Plan Routing routing example.
Destination ROUTE Example:
CLI>show destination dest-id=65019Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=65019CALL_TYPE=LOCALROUTE_TYPE=ROUTEROUTE_GUIDE_ID=local6561200ZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NDestination SUB
The Destination SUB CLI example is used in the Basic Dial Plan Routing routing example.
Destination SUB Example:
CLI>show destination dest-id=65019Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=65019CALL_TYPE=LOCALROUTE_TYPE=SUBZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NDial-Plan
The Dial-Plan CLI example is used in the Basic Trunk Routing routing example.
Dial-Plan Example:
CLI>show dial-plan id=dp50;digit-string=312-454;Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=312454REQD_DIGITS=10DEST_ID=local-subSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALDial-Plan Ca-Config
The Dial-Plan Ca-Config CLI example is used in the Basic Dial Plan Routing routing example.
Dial-Plan Ca-Config Example:
CLI>show dial-plan-profile id=dp51Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=dp51INTL_DIAL_PLAN_ID=dp50NANP_DIAL_PLAN=YCLI>show dial-plan-profile id=dp50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=dp50DESCRIPTION=dialing plan 1NANP_DIAL_PLAN=YCLI>show ca-config TYPE=DEFAULT-INTL-DIAL-PLAN-ID;Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.TYPE=DEFAULT-INTL-DIAL-PLAN-IDDATATYPE=STRINGVALUE=DEFAULTDial-Plan "dp50"
The Dial-Plan "dp50" CLI example is used in the Basic Subscriber Routingthe following routing example.
Dial-Plan "dp50" Example:
CLI>show dial-plan id=dp50Reply : Success: Entries 1-3 of 3 returned.ID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=212454REQD_DIGITS=10DEST_ID=local-subSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=312454REQD_DIGITS=10DEST_ID=local-subSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=412454REQD_DIGITS=10DEST_ID=local-subSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALDN2sub
The DN2sub CLI example is used in the Basic Subscriber Routingthe following and Ported-In Call Processing routing examples.
DN2sub Example:
CLI>show ndc digit-string=312Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DIGIT_STRING=312CLI>show exchange-code ndc=312Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.NDC=312EC=454OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=1188MIN_DN_LENGTH=10MAX_DN_LENGTH=10CLI>show office-code ndc=312; ec=454Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DIGIT_STRING=312454OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=1188DID=NCALL_AGENT_ID=CA552DIALABLE=YNDC=312EC=454DN_GROUP=xxxxCLI>show dn2subscriber office-code-index=1188Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=1188DN=0001STATUS=ASSIGNEDRING_TYPE=1LNP_TRIGGER=NNP_RESERVED=NSUB_ID=test2Dp50 Digit-String = 202
The Dp50 Digit-String = 202 CLI example is used in the 1+ Interlata Call routing example.
Dp50 Digit-String = 202 Example:
CLI>show dial-plan id=dp50; digit-string=202;Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=202REQD_DIGITS=10DEST_ID=interlataSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALCLI>show destination dest-id=interlataReply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=interlataCALL_TYPE=INTERLATAROUTE_TYPE=ROUTEROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NEa-Use = Y
The Ea-Use = Y CLI example is used in the 0+ Interlata Call routing example.
Ea-Use = Y Example:
CLI>show sub-profile id=sp50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=sp50DIAL_PLAN_ID=dp50LOCAL_PFX1_OPT=NRTOLL_PFX1_OPT=RQPOP_ID=50OLI=0EA_USE_PIC1=YIn DN2Sub
The In DN2Sub CLI example is used in the Ported-In Call Processing routing examples.
In DN2Sub Example:
CLI>show office-code digit-string=214-387Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DIGIT_STRING=214387OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=657DID=NCALL_AGENT_ID=CA552DIALABLE=YNDC=214EC=387DN_GROUP=xxxxCLI>show dn2subscriber OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=657;dn=1000Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=657DN=1000STATUS=ASSIGNEDRING_TYPE=1LNP_TRIGGER=NNP_RESERVED=NSUB_ID=test1LNP Local Sub
The LNP Local Sub CLI example is used in the Ported-In Call Processing routing examples.
LNP Local Sub Example:
CLI>show dial-plan id=dp50;digit-string=214-387Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=214387DEST_ID=local-subSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALCLI>show destination dest-id=local-subReply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=local-subCALL_TYPE=LOCALROUTE_TYPE=SUBZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NLNP Route
The LNP Route CLI example is used in the Ported-In Call Processing routing examples.
LNP Route Example:
CLI>show dial-plan id=dp50;digit-string=214-387Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=214387DEST_ID=outSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALCLI>show destination dest-id=local-subReply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=outCALL_TYPE=LOCALROUTE_TYPE=ROUTEROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NLNP Trigger = Y
The LNP Trigger = Y CLI example is used in the Ported-In Call Processing routing examples.
LNP Trigger = Y Example:
CLI>show dn2subscriber OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=657;dn=1000Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=657DN=1000STATUS=ASSIGNEDRING_TYPE=1LNP_TRIGGER=YNP_RESERVED=NSUB_ID=test1Not in DN2Sub
The Not in DN2Sub CLI example is used in the Ported-In Call Processing routing examples.
Not in DN2Sub Example:
CLI>show office-code digit-string=214-387Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DIGIT_STRING=214387OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=657DID=NCALL_AGENT_ID=CA552DIALABLE=YNDC=214EC=387DN_GROUP=xxxxCLI>show dn2subscriber OFFICE_CODE_INDEX=657;dn=1000Reply : Success: Database is void of entries.POP 50 Block
The POP 50 Block CLI example is used in the 1+ Interlata Call routing example.
POP 50 Block Example:
CLI>show pop id=50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=50STATE=txCOUNTRY=usaTIMEZONE=CSTLOCAL_7D_DIALING=YITP=NZERO_MINUS=LECBLOCK_EAWOPIC=YCNAM_OPTION=NONEPIC2_REQD=NTREAT_IMS_ANONYMOUS=NPOP 50 No Block
The POP 50 No Block CLI example is used in the 1+ Interlata Call routing example.
POP 50 No Block Example:
CLI>show pop id=50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=50STATE=txCOUNTRY=usaTIMEZONE=CSTLOCAL_7D_DIALING=YITP=NZERO_MINUS=LECBLOCK_EAWOPIC=NCNAM_OPTION=NONEPIC2_REQD=NTREAT_IMS_ANONYMOUS=NPOP Block-ea = N
The POP Block-ea = N CLI example is used in the 0+ Interlata Call routing example.
POP Block-ea = N Example:
CLI>show pop id=50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=50STATE=txCOUNTRY=usaTIMEZONE=CSTLOCAL_7D_DIALING=YITP=YZERO_MINUS=LECBLOCK_EAWOPIC=NCNAM_OPTION=NONEPIC2_REQD=NLECOSS_ROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testTREAT_IMS_ANONYMOUS=NPOP Block-ea = Y
The POP Block-ea = Y CLI example is used in the 0+ Interlata Call routing example.
POP Block-ea = Y Example:
CLI>show pop id=50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=50STATE=txCOUNTRY=usaTIMEZONE=CSTLOCAL_7D_DIALING=YITP=YZERO_MINUS=LECBLOCK_EAWOPIC=YCNAM_OPTION=NONEPIC2_REQD=NLECOSS_ROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testTREAT_IMS_ANONYMOUS=NPOP Ea-use = N
The POP Ea-use = N CLI example is used in the 0+ Interlata Call routing example.
POP Ea-use = N Example:
CLI>show sub-profile id=sp50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=sp50DIAL_PLAN_ID=dp50LOCAL_PFX1_OPT=NRTOLL_PFX1_OPT=RQPOP_ID=50OLI=0EA_USE_PIC1=NPOP ITP = Y
The POP ITP = Y CLI example is used in the 1+ Intralata Call and 0+ Intralata Call routing examples.
POP ITP = Y Example:
CLI>show pop id=50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=50STATE=txCOUNTRY=usaTIMEZONE=CSTLOCAL_7D_DIALING=YITP=YZERO_MINUS=LECBLOCK_EAWOPIC=YCNAM_OPTION=NONEPIC2_REQD=NLECOSS_ROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testTREAT_IMS_ANONYMOUS=NPOP LEC-OSS
The POP LEC-OSS CLI example is used in the 1+ Interlata Call, 1+ Intralata Call, 0+ Interlata Call, and 0+ Intralata Call routing examples.
POP LEC-OSS Example:
CLI>show pop id=50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=50STATE=txCOUNTRY=usaTIMEZONE=CSTLOCAL_7D_DIALING=YITP=NZERO_MINUS=LECBLOCK_EAWOPIC=YCNAM_OPTION=NONEPIC2_REQD=NLECOSS_ROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testTREAT_IMS_ANONYMOUS=NPorted-Office-Code in CA
The Ported-Office-Code in CA CLI example is used in the Ported-In Call Processing routing examples.
Ported-Office-Code in CA Example:
CLI>show ported-office-code digit-string=214-387Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DIGIT_STRING=214387IN_CALL_AGENT=YPorted-Office-Code in CA = N
The Ported-Office-Code in CA = N CLI example is used in the Ported-In Call Processing routing examples.
Ported-Office-Code CA = N Example:
CLI>show ported-office-code digit-string=214-387Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DIGIT_STRING=214387IN_CALL_AGENT=NService Provider
The Service Provider CLI example is used in the Carrier Based Routing routing example.
Service Provider Example:
CLI>show service-provider id=testReply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=testSP_BASED_ROUTING=NUSE_DIAL_PLAN=YANI_WB_LIST=NONESub DP Dest Interlata
The Sub DP Dest Interlata CLI example is used in the 0+ Interlata Call routing example.
Sub DP Dest Interlata Example:
CLI>show sub-profile id=sp50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=sp50DIAL_PLAN_ID=dp50LOCAL_PFX1_OPT=NRTOLL_PFX1_OPT=RQPOP_ID=50OLI=0EA_USE_PIC1=YCLI>show dial-plan id=dp50;digit-string=202Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=202REQD_DIGITS=10DEST_ID=interlataSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALCLI>show destination dest-id=interlataReply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=interlataCALL_TYPE=INTERLATAROUTE_TYPE=ROUTEROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testZERO_PLUS=YINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NSub DP Dest Intralata
The Sub DP Dest Intralata CLI example is used in the 1+ Intralata Call and 0+ Intralata Call routing examples.
Sub DP Dest Intralata Example:
CLI>show sub-profile id=sp50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=sp50DIAL_PLAN_ID=dp50LOCAL_PFX1_OPT=NRTOLL_PFX1_OPT=RQPOP_ID=50OLI=0EA_USE_PIC1=YCLI>show dial-plan id=dp50;digit-string=817Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=dp50DIGIT_STRING=817DEST_ID=tollSPLIT_NPA=NONEMIN_DIGITS=10MAX_DIGITS=10NOA=NATIONALCLI>show destination dest-id=tollReply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.DEST_ID=tollCALL_TYPE=TOLLROUTE_TYPE=ROUTEROUTE_GUIDE_ID=testZERO_PLUS=NINTRA_STATE=YGAP_ROUTING=NSubscriber Test1
The Subscriber Test1 CLI example is used in the Basic Subscriber Routingthe following, 1+ Interlata Call, 1+ Intralata Call, 0+ Interlata Call, and 0+ Intralata Call routing examples.
Subscriber Test1 Example:
CLI>show subscriber id=test1Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=test1CATEGORY=INDIVIDUALNAME=c2421-227-2-1STATUS=ACTIVEBILLING_DN=2124540001DN1=2124540001PRIVACY=NONERING_TYPE_DN1=1TERM_ID=aaln/S1/1MGW_ID=c2421-227-2PIC1=NONEPIC2=NONEPIC3=NONEGRP=NUSAGE_SENS=YSUB_PROFILE_ID=sp50TERM_TYPE=TERMIMMEDIATE_RELEASE=NTERMINATING_IMMEDIATE_REL=NSEND_BILLING_DN=NSubscriber Test2
The Subscriber Test2 CLI example is used in the Basic Subscriber Routingthe following and Basic Trunk Routing routing examples.
Subscriber Test2 Example:
CLI>show sub id=test2Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=test2CATEGORY=INDIVIDUALNAME=c2421-227-125-1STATUS=ACTIVEBILLING_DN=3124540001DN1=3124540001PRIVACY=NONERING_TYPE_DN1=1TERM_ID=aaln/S1/1MGW_ID=c2421-227-125PIC1=NONEPIC2=NONEPIC3=NONEGRP=NUSAGE_SENS=YSUB_PROFILE_ID=sp50TERM_TYPE=TERMIMMEDIATE_RELEASE=NTERMINATING_IMMEDIATE_REL=NSEND_BILLING_DN=NSubsciber and Sub-Profile
The Subsciber and Sub-Profile CLI example is used in the Basic Subscriber Routingthe following and 1+ Interlata Call routing examples.
Subsciber and Sub-Profile Example:
CLI>show subscriber id=test1Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=test1CATEGORY=INDIVIDUALNAME=c2421-227-2-1STATUS=ACTIVEBILLING_DN=2124540001DN1=2124540001PRIVACY=NONERING_TYPE_DN1=1TERM_ID=aaln/S1/1MGW_ID=c2421-227-2PIC1=NONEPIC2=NONEPIC3=NONEGRP=NUSAGE_SENS=YSUB_PROFILE_ID=sp50TERM_TYPE=TERMIMMEDIATE_RELEASE=NTERMINATING_IMMEDIATE_REL=NSEND_BILLING_DN=NCLI>show sub-profile id=sp50Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=sp50DIAL_PLAN_ID=dp50LOCAL_PFX1_OPT=NRTOLL_PFX1_OPT=RQPOP_ID=50OLI=0EA_USE_PIC1=YTrunk-grp 6969
The Trunk-grp 6969 CLI example is used in the Basic Trunk Routing routing example.
Trunk-grp 6969 Example:
CLI>show trunk-grp id=6969Reply : Success: Entry 1 of 1 returned.ID=6969CALL_AGENT_ID=CA552TG_TYPE=SS7NUM_OF_TRUNKS=96DPC=19-1-1TG_PROFILE_ID=3STATUS=OOSDIRECTION=BOTHSEL_POLICY=ASCGLARE=SLAVEALT_ROUTE_ON_CONG=NSIGNAL_PORTED_NUMBER=NDIAL_PLAN_ID=dp50DEL_DIGITS=0OPER_STATUS=NFTRAFFIC_TYPE=LOCALANI_BASED_ROUTING=NNO_ANSWER_TMR=185

 Feedback
Feedback