-
Cisco 1800 Series Software Configuration
-
Cisco Integrated Services Routers: Preface
-
Cisco 1800 Series Integrated Services Routers (Modular): Overview
-
Configuration: Basic Software Configuration Using the Setup Facility
-
Configuration: Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface
-
Configuration Example: Secured Branch Router
-
Configuration Example: IP Communication Solution for Group Applications
-
Configuration Example: Easy VPN
-
Configuration Example: Hoot and Holler over V3PN
-
Finding Feature Documentation
-
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Changing the Configuration Register Settings
-
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Using the ROM Monitor
-
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Using CompactFlash Memory Cards
-
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Upgrading the System Image
-
Troubleshooting Links
-
Table Of Contents
Easy VPN Configuration Example
Headquarters Office Configuration (Cisco 3845 Router)
Branch 1 Router Configuration (Cisco 1841 Router)
Branch 2 Router Configuration (Cisco 2811 Router)
Easy VPN Configuration Example
This document provides a Easy VPN (EzVPN) sample configuration, using Cisco 1800 series, Cisco 2800 series, and Cisco 3800 series routers.
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample Easy VPN (or EzVPN) configuration with the following characteristics:
•
All traffic between two client branch sites and headquarters passes through a Virtual Private Network (VPN) of IP Security (IPSec) encrypted tunnels.
•
Techniques used include Internet Key Exchange (IKE) dead peer detection (DPD), split tunneling, and group policy on the server with Domain Name Server (DNS) information, Windows Information Name Service (WINS) information, domain name, and an IP address pool for clients.
•
Headquarters uses an EzVPN concentrator, a Cisco 3800 series router, with an ATM interface.
•
One branch uses a Cisco 2800 series router and employs a network-mode EzVPN client with a serial interface, while another branch uses a Cisco 1800 series router and uses client mode EzVPN with an SHDSL interface.
•
The various show commands demonstrate configurations for the Internet Security Association Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) and IPSec Security Associations (SAs) on the EzVPN concentrator, as well as IPSec client EzVPN status on the clients.
List of Terms
ATM—Asynchronous Transfer Mode. A connection switching protocol that organizes data into 53-byte cell units, transmitting them via digital signals. Each cell is processed asynchronously (hence the name) relative to the transmission or arrival of other cells within a single message. Cells are also queued before being transmitted in a multiplexing fashion. ATM can be used for many different services, including voice, video, or data.
DNS—Domain Name Server. Maps names to Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and addresses to names. Domain Name Servers maintain lists of domain name and IP address mappings.
DPD—Dead peer detection. An implementation of a client keepalive functionality, to check the availability of the VPN device on the other end of an IPSec tunnel.
IKE—Internet Key Exchange. IKE establishes a shared security policy and authenticates keys for services (such as IPSec) that require keys. Before any IPSec traffic can be passed, each router/firewall/host must verify the identity of its peer. This can be done by manually entering preshared keys into both hosts or can be done by a certification authority (CA) service.
IPSec—IP Security. A framework of open standards that provides data confidentiality, data integrity, and data authentication between participating peers. IPSec provides these security services at the IP layer. IPSec uses IKE to handle the negotiation of protocols and algorithms based on local policy and to generate the encryption and authentication keys to be used by IPSec. IPSec can protect one or more data flows between a pair of hosts, between a pair of security gateways, or between a security gateway and a host.
ISAKMP—Internet Security Association Key Management Protocol. A protocol for key exchange encryption and authentication. ISAKMP requires at least one pair of messages to be exchanged between two VPN-connected peers before a secure link can be established.
NETBEUI—NetBIOS extended user interface. A transport protocol associated with Microsoft-based networks. Unlike TCP/IP, NETBEUI is not a routable network protocol.
NetBIOS—Network Basic Input/Output System. A peer-to-peer low-level networking protocol dating back to the 1980s, NetBIOS links network operating systems with network hardware. NetBIOS is not routable and must be encapsulated with TCP/IP to pass through routers.
SA—Security association. This is a unidirectional channel negotiated by IPSec, with a pair of SAs required for two-way communication. SAs are used to index session keys and initialization vectors.
SHDSL—Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line. An implementation of DSL that operates at equal speeds in both transmission directions, at rates from 192 kbps to 2.3 Mbps.
WINS—Windows Internet Naming Service. A service in Microsoft-based networks that translates hostnames into IP addresses. Using NETBEUI protocol, it is also compatible with NetBIOS.
Before You Begin
The following are the requirements for using this configuration example.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
•
At Headquarters, a Cisco 3845 router with a Cisco CallManager cluster, and with ATM access to the Internet
•
At Branch 1, a Cisco 1841 router with a WIC-1SHDSL interface card installed, and with DSL access to the Internet
•
At Branch 2, a Cisco 2811 router with a serial interface connection to the Internet
•
For Cisco 1800 series routers and Cisco 2800 series routers: Cisco IOS Release 12.3(8)T4
•
For Cisco 3800 series routers: Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T
•
Advanced Enterprise Services feature set
The information presented in this document resulted from the use of devices in a specific lab setup and environment. All the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If you are working in a live network, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command before you use it.
Note
When configuring stateful failover for IPSec on the Cisco 2811 router, you may get the following message if there is no AIM-VPN module installed:
%crypto_ha_ipsec-4-crypto_ha_not_supported_by_hw 2811
Once an AIM-VPN module is installed in the Cisco 2811 router, this error message will no longer appear.
Related Products
This configuration can also be used with the following hardware:
•
Cisco 1800 series routers
•
Cisco 2800 series routers
•
Cisco 3800 series routers
Configure
This section presents the information for configuring the features described in this document.
Note
For additional information on the commands used in this document, use the Cisco IOS Command Lookup tool. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Configuration Tips
•
Make sure that the tunnels work before you apply the crypto maps.
•
Apply IPSec crypto maps to both the tunnel interface and the physical interface
Network Diagram
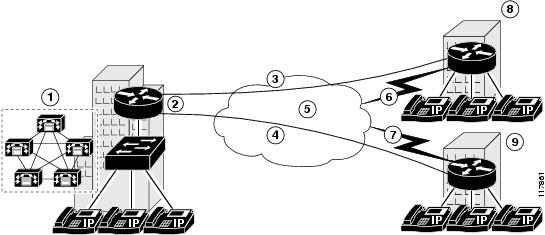
This document uses the network setup shown in the following illustration:
Following are the callout terms and definitions for the diagram, identified by number:
The Headquarters location (callout 1) uses a Cisco 3845 router with these characteristics:
•
EzVPN server
•
ATM access to the Internet
•
Operating in a Cisco CallManager cluster
•
Public IP address: 10.32.152.26
•
Private IP address pool: 192.168.1.0/24
The Branch 1 location (callout 8) uses a Cisco 1841 router with these characteristics:
•
EzVPN client using client mode
•
DSL access to the Internet
•
WIC-1SHDSL interface card installed
•
Public IP address: 10.32.152.46
•
Private IP address pool: 192.168.3.0/24
The Branch 2 location (callout 9) uses a Cisco 2811 router with these characteristics:
•
EzVPN client using network mode
•
Serial access to the Internet
•
Public IP address: 10.32.150.46
•
Private IP address pool: 192.168.3.1/24
Configurations
This example uses these configurations:
•
Headquarters Office Configuration (Cisco 3845 Router)
•
Branch 1 Router Configuration (Cisco 1841 Router)
•
Branch 2 Router Configuration (Cisco 2811 Router)
Headquarters Office Configuration (Cisco 3845 Router)
EzVPN-Hub# show running-configBuilding configuration...Current configuration : 6824 bytes!version 12.3no service padservice timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecservice password-encryption!hostname EzVPN-Hub!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!enable secret 5 $1$t8oN$hXnGodPh8ZM/ka6k/9aO51!username admin secret 5 $1$cfjP$kKpB7e3pfKXfpK0RIqX/E.username ezvpn-spoke2 secret 5 $1$vrSS$AhSPxEUnPOsSpJkGdzjXg/username ezvpn-spoke1 secret 5 $1$VK0p$4D0YXNOtC6K7MR4/vinUL.mmi polling-interval 60no mmi auto-configureno mmi pvcmmi snmp-timeout 180aaa new-model!!aaa authentication login USER_AAA localaaa authentication login USERLIST localaaa authorization network GROUP_AAA localaaa session-id commonip subnet-zero!ip cefno ip domain lookupip domain name cisco.comip audit notify logip audit po max-events 100no ftp-server write-enablevoice-card 0no dspfarm!!--- IKE configuration!crypto isakmp policy 10encr 3deshash md5authentication pre-sharegroup 2crypto isakmp keepalive 90 12!crypto isakmp client configuration group VPN1acl SPLIT_Tip access-list extended SPLIT_Tpermit ip 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 anykey cisco123dns 192.168.168.183 192.168.226.120wins 192.168.179.89 192.168.2.87domain cisco.compool VPN-POOLsave-password!!--- IPSec configuration!crypto ipsec transform-set TRANSFORM-1 esp-3des esp-md5-hmac!crypto dynamic-map INT_MAP 1set security-association lifetime kilobytes 530000000set security-association lifetime seconds 14400set transform-set TRANSFORM-1!!crypto map INT_MAP client authentication list USER_AAAcrypto map INT_MAP isakmp authorization list GROUP_AAAcrypto map INT_MAP client configuration address respondcrypto map INT_MAP 30000 ipsec-isakmp dynamic INT_MAP!!!interface GigabitEthernet0/0no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed automedia-type rj45no negotiation auto!interface GigabitEthernet0/1no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed automedia-type rj45no negotiation auto!interface ATM0/0/0description === public interface ===ip address 10.32.152.26 255.255.255.252ip pim sparse-dense-modeip ospf network point-to-pointno atm ilmi-keepalivepvc 10/100protocol ip 10.32.152.25 broadcast!crypto map INT_MAP!interface FastEthernet4/0no ip addressshutdown!interface FastEthernet4/1switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/2switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/3switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/4switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/5switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/6switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/7switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/8switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/9switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/10switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/11switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/12switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/13switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/14switchport access vlan 10no ip address!interface FastEthernet4/15switchport access vlan 10no ip address!!-- Entries for FastEthernet 4/16 through 4/35 omitted for redundancy!interface GigabitEthernet4/0no ip addressshutdown!interface GigabitEthernet4/1no ip addressshutdown!interface Vlan1no ip address!interface Vlan10ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0!!ip local pool VPN-POOL 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.10ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.32.152.25!ip http serverno ip http secure-server!!control-plane!!line con 0line aux 0line vty 0 4login authentication USERLIST!!end!Branch 1 Router Configuration (Cisco 1841 Router)
EzVPN-Spoke-1# show running-configBuilding configuration.....Current configuration : 4252 bytes!version 12.3no service padservice timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecservice password-encryption!hostname EzVPN-Spoke-1!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!logging buffered 4096 informationalenable secret 5 $1$b7.Q$Y2x1UXyRifSStbkH/YyrP.!username admin password 7 0519030B234D5C0617memory-size iomem 20mmi polling-interval 60no mmi auto-configureno mmi pvcmmi snmp-timeout 180aaa new-model!!aaa authentication login USERLIST localaaa session-id commonip subnet-zeroip cef!!ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.2.1!ip dhcp pool PRIVATE_DHCPimport allnetwork 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0default-router 192.168.2.1!!no ip domain lookupip domain name cisco.comip sap cache-timeout 30ip ssh time-out 30ip ids po max-events 100no ftp-server write-enable!!--- IPSec configuration!crypto ipsec client ezvpn VPN1connect autogroup VPN1 key cisco123mode clientpeer 10.32.152.26username ezvpn-spoke1 password cisco1!interface FastEthernet0/0description === private interface ===ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed autocrypto ipsec client ezvpn VPN1 inside!interface FastEthernet0/1no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed auto!interface ATM0/1/0no ip addressno atm ilmi-keepalivedsl equipment-type CPEdsl operating-mode GSHDSL symmetric annex Adsl linerate AUTOpvc 0/35encapsulation aal5snap!pvc 8/35encapsulation aal5mux ppp dialerdialer pool-member 1!!interface Dialer0description === public interface ===ip address 10.32.152.46 255.255.255.252ip pim sparse-dense-modeencapsulation pppdialer pool 1dialer-group 1crypto ipsec client ezvpn VPN1!ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.32.152.45!ip http serverno ip http secure-server!control-plane!line con 0line aux 0line vty 0 4login authentication USERLIST!!endBranch 2 Router Configuration (Cisco 2811 Router)
EzVPN-Spoke-2# show running-configBuilding configuration....Current configuration : 4068 bytes!version 12.3no service padservice timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecservice password-encryption!hostname EzVPN-Spoke-2!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!enable secret 5 $1$9BB/$KP4mHUWzUxzpuEPg5s7ow/!username admin password 7 10481A110C07memory-size iomem 25aaa new-model!!aaa authentication login USERLIST localaaa session-id commonip subnet-zero!!ip cefip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.3.1!ip dhcp pool PRIVATE_DHCPimport allnetwork 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0default-router 192.168.3.1!!no ip domain lookupip multicast-routingip ids po max-events 100!no ftp-server write-enablevoice-card 0no dspfarm!!--- IPSec configuration!crypto ipsec client ezvpn VPN1connect autogroup VPN1 key cisco123mode network-extensionpeer 10.32.152.26username ezvpn-spoke2 password cisco2!interface FastEthernet0/0description === private interface ===ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed autocrypto ipsec client ezvpn VPN1 inside!interface FastEthernet0/1no ip addressduplex autospeed autoshutdown!interface Serial0/0/0description === public interface ===ip address 10.32.150.46 255.255.255.252crypto ipsec client ezvpn VPN1!ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.32.150.45!ip http serverno ip http secure-server!control-plane!dial-peer cor custom!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0line aux 0line vty 0 4login authentication USERLIST!endVerify
This section provides instructions for verifying that your configuration works properly.
Certain show commands are supported by the Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only), which allows you to view an analysis of show command output. In summary:
•
show crypto engine connections active—Shows the encrypted and decrypted packets.
•
show crypto ipsec sa—Shows the phase 2 IPSec security associations for the hub.
•
show crypto ipsec client ezvpn—Shows the phase 2 IPSec security associations for the EzVPN client.
•
show crypto isakmp sa—Shows the phase 1 ISAKMP security associations.
One of the first indications of successful IPSec negotiation is a message displayed on the Virtual Private Network (VPN) concentrator console. Upon successful IPSec negotiation by the EzVPN clients, a message similar to the following is displayed on the VPN concentrator console, indicating the establishment of crypto connections to the remote EzVPN clients.
EzVPN-Hub#*Feb 23 10:33:10.663: %CRYPTO-5-SESSION_STATUS: Crypto tunnel is UP . Peer 10.32.150.46:500 Id: VPN1*Feb 23 10:33:37.439: %CRYPTO-5-SESSION_STATUS: Crypto tunnel is UP . Peer 10.32.152.46:500 Id: VPN1The following examples show sample output for the show crypto ipsec sa and show crypto ipsec client ezvpn commands.
The following is sample output from the show crypto ipsec sa command, performed using the configuration on the EzVPN Hub location:
EzVPN-Hub# show crypto ipsec sainterface: ATM0/0/0Crypto map tag: INT_MAP, local addr. 10.32.152.26protected vrf:local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0/0)remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (10.1.1.3/255.255.255.255/0/0)current_peer: 10.32.152.46:500PERMIT, flags={}#pkts encaps: 0, #pkts encrypt: 0, #pkts digest: 0#pkts decaps: 0, #pkts decrypt: 0, #pkts verify: 0#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed: 0#pkts not decompressed: 0, #pkts decompress failed: 0#send errors 0, #recv errors 0local crypto endpt.: 10.32.152.26, remote crypto endpt.: 10.32.152.46path mtu 4470, media mtu 4470current outbound spi: EBA2AC93inbound esp sas:spi: 0xDBEB20(14412576)transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac ,in use settings ={Tunnel, }slot: 0, conn id: 5131, flow_id: 11, crypto map: INT_MAPcrypto engine type: Hardware, engine_id: 2sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4570368/14331)ike_cookies: 787F69F1 41C7488D 92A37C71 AE8FEC38IV size: 8 bytesreplay detection support: Yinbound ah sas:inbound pcp sas:outbound esp sas:spi: 0xEBA2AC93(3953306771)transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac ,in use settings ={Tunnel, }slot: 0, conn id: 5132, flow_id: 12, crypto map: INT_MAPcrypto engine type: Hardware, engine_id: 2sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4570368/14331)ike_cookies: 787F69F1 41C7488D 92A37C71 AE8FEC38IV size: 8 bytesreplay detection support: Youtbound ah sas:outbound pcp sas:protected vrf:local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0/0)remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (192.168.3.0/255.255.255.0/0/0)current_peer: 10.32.150.46:500PERMIT, flags={}#pkts encaps: 0, #pkts encrypt: 0, #pkts digest: 0#pkts decaps: 0, #pkts decrypt: 0, #pkts verify: 0#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed: 0#pkts not decompressed: 0, #pkts decompress failed: 0#send errors 0, #recv errors 0local crypto endpt.: 10.32.152.26, remote crypto endpt.: 10.32.150.46path mtu 4470, media mtu 4470current outbound spi: 59C46762inbound esp sas:spi: 0xA9344358(2838774616)transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac ,in use settings ={Tunnel, }slot: 0, conn id: 5129, flow_id: 9, crypto map: INT_MAPcrypto engine type: Hardware, engine_id: 2sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4574224/14292)ike_cookies: A479BC19 B6199FB9 E043AE83 9DECB0E8IV size: 8 bytesreplay detection support: Yinbound ah sas:inbound pcp sas:outbound esp sas:spi: 0x59C46762(1506043746)transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac ,in use settings ={Tunnel, }slot: 0, conn id: 5130, flow_id: 10, crypto map: INT_MAPcrypto engine type: Hardware, engine_id: 2sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4574224/14292)ike_cookies: A479BC19 B6199FB9 E043AE83 9DECB0E8IV size: 8 bytesreplay detection support: Youtbound ah sas:outbound pcp sas:The following is sample output from the show crypto ipsec client ezvpn command, performed using the configuration on the EzVPN Spoke 1 location:
EzVPN-Spoke-1#show crypto ipsec client ezvpnEasy VPN Remote Phase: 2Tunnel name : VPN1Inside interface list: FastEthernet0/0,Outside interface: Dialer0Current State: IPSEC_ACTIVELast Event: SOCKET_UPAddress: 10.1.1.3Mask: 255.255.255.255DNS Primary: 192.168.168.183DNS Secondary: 192.168.226.120NBMS/WINS Primary: 192.168.179.89NBMS/WINS Secondary: 192.168.2.87Default Domain: cisco.comThe following is sample output from the show crypto ipsec client ezvpn command, performed using the configuration on the EzVPN Spoke 2 location:
EzVPN-Spoke-2#show crypto ipsec client ezvpnEasy VPN Remote Phase: 2Tunnel name : VPN1Inside interface list: FastEthernet0/0,Outside interface: Serial0/0/0Current State: IPSEC_ACTIVELast Event: SOCKET_UPDNS Primary: 192.168.168.183DNS Secondary: 192.168.226.120NBMS/WINS Primary: 192.168.179.89NBMS/WINS Secondary: 192.168.2.87Default Domain: cisco.comTroubleshoot
This section provides information for troubleshooting your configuration.
See the following tech note:
•
IP Security Troubleshooting - Understanding and Using debug Commands
Troubleshooting Commands
Note
Before issuing debug commands, please see Important Information on Debug Commands.
The following debug commands must be running on both IPSec routers (peers). Security associations must be cleared on both peers.
•
debug crypto engine—Displays information pertaining to the crypto engine, such as when Cisco IOS software is performing encryption or decryption operations.
•
debug crypto ipsec—Displays the IPSec negotiations of phase 2.
•
debug crypto ipsec client ezvpn—Displays the negotiation of the EzVPN client to the VPN concentrator.
•
debug crypto isakmp—Displays the ISAKMP negotiations of phase 1.
•
clear crypto ipsec client ezvpn—Clears an existing EzVPN connection.
•
clear crypto isakmp—Clears the security associations for phase 1.
•
clear crypto sa—Clears the security associations for phase 2.
The following is an example of output for the debug crypto ipsec client ezvpn command:
EzVPN-Spoke-1# debug crypto ipsec client ezvpn*May 24 03:04:51.923: EZVPN(VPN1): New State: CONNECT_REQUIRED!!--- The following line shows the connection going down, not part of the debug output.!*May 24 03:04:51.923: %CRYPTO-5-SESSION_STATUS: Crypto tunnel is DOWN. Peer 10.32.152.26:500 Id: 10.32.152.26!!---Debug output resumes!*May 24 03:04:51.927: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: CONNECT_REQUIRED*May 24 03:04:51.927: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: CONNECT*May 24 03:04:51.927: EZVPN(VPN1): ezvpn_connect_request*May 24 03:04:51.927: EZVPN(VPN1): New State: READY*May 24 03:04:51.999: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: READY*May 24 03:04:51.999: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: CONN_UP*May 24 03:04:51.999: EZVPN(VPN1): ezvpn_conn_up 7F890E16 DB923EE3 67C9C0D2 7EE723AC*May 24 03:04:51.999: EZVPN(VPN1): No state change*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: READY*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: XAUTH_REQUEST*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): ezvpn_xauth_request*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): ezvpn_parse_xauth_msg*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN: Attributes sent in xauth request message:*May 24 03:04:52.007: XAUTH_USER_NAME_V2(VPN1):*May 24 03:04:52.007: XAUTH_USER_PASSWORD_V2(VPN1):*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): send saved username ezvpn-spoke1 and password <omitted>*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): New State: XAUTH_REQ*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: XAUTH_REQ*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: XAUTH_REQ_INFO_READY*May 24 03:04:52.007: EZVPN(VPN1): ezvpn_xauth_reply*May 24 03:04:52.007: XAUTH_USER_NAME_V2(VPN1): ezvpn-spoke1*May 24 03:04:52.011: XAUTH_USER_PASSWORD_V2(VPN1): <omitted>*May 24 03:04:52.011: EZVPN(VPN1): New State: XAUTH_REPLIED*May 24 03:04:52.023: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: XAUTH_REPLIED*May 24 03:04:52.023: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: XAUTH_STATUS*May 24 03:04:52.023: EZVPN(VPN1): New State: READY*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: READY*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: MODE_CONFIG_REPLY*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN(VPN1): ezvpn_mode_config*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN(VPN1): ezvpn_parse_mode_config_msg*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN: Attributes sent in message:*May 24 03:04:52.039: Address: 10.1.1.4*May 24 03:04:52.039: DNS Primary: 192.168.168.183*May 24 03:04:52.039: DNS Secondary: 192.168.226.120*May 24 03:04:52.039: NBMS/WINS Primary: 192.168.179.89*May 24 03:04:52.039: NBMS/WINS Secondary: 192.168.2.87*May 24 03:04:52.039: Split Tunnel List: 1*May 24 03:04:52.039: Address : 192.168.0.0*May 24 03:04:52.039: Mask : 255.255.0.0*May 24 03:04:52.039: Protocol : 0x0*May 24 03:04:52.039: Source Port: 0*May 24 03:04:52.039: Dest Port : 0*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN: Unknown/Unsupported Attr: SPLIT_DNS (0x7003)*May 24 03:04:52.039: Default Domain: cisco.com*May 24 03:04:52.039: Savepwd on*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN: Unknown/Unsupported Attr: BACKUP_SERVER (0x7009)*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN: Unknown/Unsupported Attr: APPLICATION_VERSION (0x7)*May 24 03:04:52.039: EZVPN(VPN1): ezvpn_nat_config*May 24 03:04:52.043: EZVPN(VPN1): New State: SS_OPEN*May 24 03:04:52.047: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: SS_OPEN*May 24 03:04:52.047: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: SOCKET_READY*May 24 03:04:52.047: EZVPN(VPN1): No state change!!--- The following line shows the connection coming up, not part of the debug output.!*May 24 03:04:52.075: %CRYPTO-5-SESSION_STATUS: Crypto tunnel is UP . Peer 10.32.152.26:500 Id: 10.32.152.26!!---Debug output resumes!*May 24 03:04:52.079: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: SS_OPEN*May 24 03:04:52.079: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: MTU_CHANGED*May 24 03:04:52.079: EZVPN(VPN1): No state change*May 24 03:04:52.079: EZVPN(VPN1): Current State: SS_OPEN*May 24 03:04:52.079: EZVPN(VPN1): Event: SOCKET_UP*May 24 03:04:52.079: ezvpn_socket_up*May 24 03:04:52.079: EZVPN(VPN1): New State: IPSEC_ACTIVERelated Information
•
Cisco IOS Wide-Area Networking Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IOS Interface and Hardware Component Configuration Guide
•
Cisco Technical Assistance Center
Copyright © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.

 Feedback
Feedback