-
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide, Release 12.2
-
About Cisco IOS Software Documentation
-
Using Cisco IOS Software
-
IP Overview
- Part 1: IP Addressing Services
- Part 2: IP Routing Protocols
-
Part 3: IP Multicast
-
Configuring IP Multicast Routing
-
Configuring Source Specific Multicast
-
Configuring Bidirectional PIM
-
Configuring Multicast Source Discovery Protocol
-
Configuring PGM Host and Router Assist
-
Configuring Unidirectional Link Routing
-
Using IP Multicast Tools
-
Configuring Router-Port Group Management Protocol
-
Configuring DVMRP Interoperability
-
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring PGM Host and Router Assist
PGM Host Configuration Task List
Enabling PGM Host with a Virtual Host Interface
Enabling PGM Host with a Physical Interface
Verifying PGM Host Configuration
PGM Router Assist Configuration Task List
Enabling PGM Router Assist with a Virtual Host Interface
Enabling PGM Router Assist with a Physical Interface
Monitoring and Maintaining PGM Host and Router Assist
Monitoring and Maintaining PGM Host
Monitoring and Maintaining PGM Router Assist
PGM Host and Router Assist Configuration Examples
PGM Host with a Virtual Interface Example
PGM Host with a Physical Interface Example
PGM Router Assist with a Virtual Interface Example
PGM Router Assist with a Physical Interface Example
Configuring PGM Host and Router Assist
Note
Support for the PGM Host feature has been removed. Use of this feature is not recommended.
This chapter describes the PGM Host and Router Assist feature. PGM Host and Router Assist enables Cisco routers to support multicast applications that operate at the PGM transport layer and the PGM network layer, respectively.
The PGM Reliable Transport Protocol itself is implemented on the hosts of the customer. For information on PGM Reliable Transport Protocol, refer to the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) protocol specification draft named PGM Reliable Transport Protocol Specification.
For a complete description of the PGM Host and Router Assist commands in this chapter, refer to the "PGM Host and Router Assist Commands" chapter of the Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 3 of 3: Multicast. To locate documentation of other commands that appear in this chapter, use the command reference master index, or search online.
To identify the hardware platform or software image information associated with a feature, use the Feature Navigator on Cisco.com to search for information about the feature or refer to the software release notes for a specific release. For more information, see the "Identifying Supported Platforms" section in the "Using Cisco IOS Software" chapter.
PGM Overview
Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) is a reliable multicast transport protocol for multicast applications that require reliable, ordered, duplicate-free multicast data delivery from multiple sources to multiple receivers. PGM guarantees that a receiver in a multicast group either receives all data packets from transmissions and retransmissions, or can detect unrecoverable data packet loss. PGM is intended as a solution for multicast applications with basic reliability requirements. PGM has two main parts: a host element (also referred to as the transport layer of the PGM protocol) and a network element (also referred to as the network layer of the PGM protocol).
The transport layer of the PGM protocol has two main parts: a source part and a receiver part. The transport layer defines how multicast applications send and receive reliable, ordered, duplicate-free multicast data from multiple sources to multiple receivers. PGM Host is the Cisco implementation of the transport layer of the PGM protocol.
The network layer of the PGM protocol defines how intermediate network devices (such as routers and switches) handle PGM transport data as the data flows through a network. PGM Router Assist is the Cisco implementation of the network layer of the PGM protocol.
Note
PGM contains an element that assists routers and switches in handling PGM transport data as it flows through a network. Unlike the Router Assist element, the Host element does not have a current practical application.
PGM is network-layer independent; PGM Host and Router Assist in the Cisco IOS software support PGM over IP. Both PGM Host and Router Assist use a unique transport session identifier (TSI) that identifies each individual PGM session.
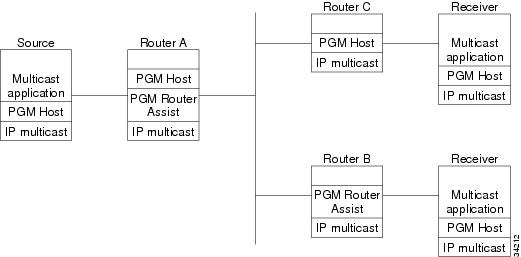
Figure 81 shows a simple network topology using the PGM Host and Router Assist feature.
Figure 81 Network Topology Using PGM Host and Router Assist
When the router is functioning as a network element (PGM Router Assist is configured) and PGM Host is configured (Router A in Figure 81), the router can process received PGM packets as a virtual PGM Host, originate PGM packets and serve as its own first hop PGM network element, and forward received PGM packets.
When the router is functioning as a network element and PGM Host is not configured (Router B in Figure 81), the router forwards received PGM packets as specified by PGM Router Assist parameters.
When the router is not functioning as a network element and PGM Host is configured (Router C in Figure 81), the router can receive and forward PGM packets on any router interface simultaneously as specified by PGM Host feature parameters. Although this configuration is supported, it is not recommended in a PGM network because PGM Host works optimally on routers that have PGM Router Assist configured.
PGM Host Configuration Task List
Note
Support for the PGM Host feature has been removed. Use of this feature is not recommended.
To configure PGM Host, perform the tasks described in the following sections. The tasks in the first section are required; the tasks in the remaining section are optional.
•
Enabling PGM Host (Required)
•
Verifying PGM Host Configuration (Optional)
See the end of this chapter for the section "PGM Host and Router Assist Configuration Examples."
Prerequisites
Before you configure PGM Host, ensure that the following tasks are performed:
•
PGM Reliable Transport Protocol is configured on hosts connected to your network.
•
PGM Router Assist is configured on intermediate routers and switches connected to your network.
•
IP multicast routing is configured on all devices connected to your network that will be processing IP multicast traffic, including the router on which you are configuring PGM Host.
•
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) or another IP multicast routing protocol is configured on each PGM interface in your network that will send and receive IP multicast packets.
•
A PGM multicast virtual host interface (vif) is configured on the router (if you do not plan to source PGM packets through a physical interface installed on the router). The vif enables the router to send and receive IP multicast packets on several different interfaces at once, as dictated by the multicast routing tables on the router.
Enabling PGM Host
Note
Support for the PGM Host feature has been removed. Use of this feature is not recommended.
When enabling PGM Host on your router, you must source PGM packets through a vif or out a physical interface installed in the router.
Sourcing PGM packets through a vif enables the router to send and receive PGM packets through any router interface. The vif also serves as the interface to the multicast applications that reside at the PGM network layer.
Sourcing IP multicast traffic out a specific physical or logical interface type (for example, an Ethernet, serial, or loopback interface) configures the router to send PGM packets out that interface only and to receive packets on any router interface.
Enabling PGM Host with a Virtual Host Interface
To enable PGM Host globally on the router and to configure the router to source PGM packets through a vif, use the following command in global configuration mode:
See the "PGM Host with a Virtual Interface Example" section later in this chapter for an example of enabling PGM Host with a virtual interface.
Enabling PGM Host with a Physical Interface
To enable PGM Host globally on the router and to configure the router to source PGM packets through a physical interface, use the following commands in global configuration mode:
See the "PGM Host with a Physical Interface Example" section later in this chapter for an example of enabling PGM Host with a physical interface.
Verifying PGM Host Configuration
Note
Support for the PGM Host feature has been removed. Use of this feature is not recommended.
To verify that PGM Host is configured correctly on your router, use the following show commands in EXEC mode:
•
Use the show ip pgm host sessions command to display information about current open PGM transport sessions:
Router> show ip pgm host sessionsIdx GSI Source Port Type State Dest Port Mcast Address1 000000000000 0 receiver listen 48059 224.3.3.32 9CD72EF099FA 1025 source conn 48059 224.1.1.1Specifying a traffic session number or a multicast IP address with the show ip pgm host sessions command displays information specific to that PGM transport session:
Router> show ip pgm host sessions 2Idx GSI Source Port Type State Dest Port Mcast Address2 9CD72EF099FA 1025 source conn 48059 224.1.1.1stream-type (apdu), ttl (255)spm-ambient-ivl (6000), txw-adv-secs (6000)txw-adv-timeout-max (3600000), txw-rte (16384), txw-secs (30000)ncf-max (infinite), spm-rpt-ivl (3000), ihb-min (1000)ihb-max (10000), join (0), tpdu-size (16384)txw-adv-method (time), tx-buffer-mgmt (return)ODATA packets sent 0bytes sent 0RDATA packets sent 0bytes sent 0Total bytes sent 0ADPUs sent 0APDU transmit memory errors 0SPM packets sent 6NCF packets sent 0NAK packets received 0packets received in error 0General bad packets 0TX window lead 0TX window trail 0•
Use the show ip pgm host traffic command to display traffic statistics at the PGM transport layer:
Router> show ip pgm host trafficGeneral Statistics :Sessions in 0out 0Bytes in 0out 0Source Statistics :ODATA packets sent 0bytes sent 0RDATA packets sent 0bytes sent 0Total bytes sent 0ADPUs sent 0APDU transmit memory errors 0SPM packets sent 0NCF packets sent 0NAK packets received 0packets received in error 0Receiver Statistics :ODATA packets received 0packets received in error 0valid bytes received 0RDATA packets received 0packets received in error 0valid bytes received 0Total valid bytes received 0Total bytes received in error 0ADPUs received 0SPM packets received 0packets received in error 0NCF packets received 0packets received in error 0NAK packets received 0packets received in error 0packets sent 0Undeliverable packets 0General bad packets 0Bad checksum packets 0PGM Router Assist Configuration Task List
To configure PGM Router Assist, perform the required task described in the following section:
•
Enabling PGM Router Assist (Required)
Prerequisites
Before you enable PGM Router Assist, ensure that the following tasks are completed:
•
PGM Reliable Transport Protocol is configured on hosts connected to your network.
•
IP multicast is configured on the router upon which you will enable PGM Router Assist.
•
PIM is configured on each PGM interface.
Enabling PGM Router Assist
When enabling PGM Router Assist on your router, you must set up your router to forward PGM packets through a vif or out a physical interface installed in the router.
Setting up your router to forward PGM packets through a vif enables the router to forward PGM packets through any router interface. The vif also serves as the interface to the multicast applications that reside at the PGM network layer.
Setting up your router to forward PGM packets out a specific physical or logical interface type (for example, an Ethernet, serial, or loopback interface) configures the router to forward PGM packets out that interface only.
Enabling PGM Router Assist with a Virtual Host Interface
To enable PGM Router Assist on a vif, use the following command in interface configuration mode:
See the "PGM Router Assist with a Virtual Interface Example" section later in this chapter for an example of enabling PGM Router Assist with a virtual interface.
Enabling PGM Router Assist with a Physical Interface
To enable PGM Router Assist on the router and to configure the router to forward PGM packets through a physical interface, use the following commands in interface configuration mode:
Router(config-if)# ip pgm router
Enables the router to assist PGM on this interface.
See the "PGM Router Assist with a Physical Interface Example" section later in this chapter for an example of enabling PGM Router Assist with a physical interface.
Monitoring and Maintaining PGM Host and Router Assist
This section provides information on monitoring and maintaining the PGM Host and Router Assist feature.
Monitoring and Maintaining PGM Host
Note
Support for the PGM Host feature has been removed. Use of this feature is not recommended.
To reset PGM Host connections, use the following command in privileged EXEC mode:
Router# clear ip pgm host {defaults | traffic}Resets PGM Host connections to their default values and clears traffic statistics.
To enable PGM Host debugging, use the following command in privileged EXEC mode:
To display PGM Host information, use the following commands in user EXEC mode, as needed:
Monitoring and Maintaining PGM Router Assist
To clear PGM traffic statistics, use the following command in privileged EXEC mode:
Router# clear ip pgm router [[traffic [type number]] | [rtx-state [group-address]]]
Clears the PGM traffic statistics. Use the rtx-state keyword to clear PGM retransmit state.
To display PGM information, use the following command in privileged EXEC mode:
PGM Host and Router Assist Configuration Examples
Note
Support for the PGM Host feature has been removed. Use of this feature is not recommended.
This section provides the following configuration examples:
•
PGM Host with a Virtual Interface Example
•
PGM Host with a Physical Interface Example
•
PGM Router Assist with a Virtual Interface Example
•
PGM Router Assist with a Physical Interface Example
Note
For clarity, extraneous information has been omitted from the examples in the following sections.
PGM Host with a Virtual Interface Example
Note
Support for the PGM Host feature has been removed. Use of this feature is not recommended.
The following example shows PGM Host (both the source and receiver part of the PGM network layer) enabled globally on the router and PGM packets sourced through virtual host interface 1 (vif1). PGM packets can be sent and received on the vif and on the two physical interfaces (ethernet1 and ethernet2) simultaneously.
ip multicast-routingip routingip pgm hostinterface vif1ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheinterface ethernet1ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachemedia-type 10BaseTinterface ethernet2ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachemedia-type 10BaseTPGM Host with a Physical Interface Example
Note
Support for the PGM Host feature has been removed. Use of this feature is not recommended.
The following example shows PGM Host (both the source and receiver part of the PGM network layer) enabled globally on the router and PGM packets sourced out of physical Ethernet interface 1. PGM packets can be received on physical Ethernet interfaces 1 and 2 simultaneously.
ip multicast-routingip routingip pgm hostip pgm host source-interface ethernet1ip pgm host source-interface ethernet2interface ethernet1ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachemedia-type 10BaseTinterface ethernet2ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachemedia-type 10BaseTPGM Router Assist with a Virtual Interface Example
The following example shows PGM Router Assist (the PGM network layer) enabled on the router and the router set up to forward PGM packets on virtual host interface 1 (vif1). PGM packets can be received on interfaces vif1, ethernet1, and ethernet2 simultaneously.
ip multicast-routingip routinginterface vif1ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeip pgm routerno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cacheinterface ethernet1ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeip pgm routerno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachemedia-type 10BaseTinterface ethernet2ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeip pgm routerno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachemedia-type 10BaseT
PGM Router Assist with a Physical Interface Example
The following example shows PGM Router Assist (the PGM network layer) enabled on the router and the router set up to forward PGM packets out of physical Ethernet interfaces 1 and 2. PGM packets can be received on physical Ethernet interfaces 1 and 2 simultaneously.
ip multicast-routingip routinginterface ethernet1ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeip pgm routerno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachemedia-type 10BaseTinterface ethernet2ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.0ip pim dense-modeip pgm routerno ip directed-broadcastno ip mroute-cachemedia-type 10BaseT

 Feedback
Feedback