-
Cisco CMTS Feature Guide, Release 12.3BC
-
Title Pages
-
Preface
-
Admission Control for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
-
Cable Duplicate MAC Address Reject for the Cisco CMTS
-
Cable Interface Bundling and Virtual Interface Bundling for the Cisco CMTS
-
Cable Monitor and Intercept Features on the Cisco CMTS
-
COPS Engine Operation on the Cisco CMTS
-
DHCP, ToD, and TFTP Services for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
-
DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco CMTS
-
DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Services on the Cisco CMTS
-
EtherChannel on the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
-
Flap List Troubleshooting for the Cisco CMTS
-
Maximum CPE or Host Parameters for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
-
N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
-
PacketCable and PacketCable Multimedia for the Cisco CMTS
-
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet Support on the Cisco CMTS
-
Service Flow Admission Control for the Cisco CMTS
-
Service Flow Mapping to MPLS-VPN on the Cisco CMTS
-
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management for the Cisco CMTS
-
Telco Return for the Cisco CMTS
-
Time-of-Day Server for the Cisco CMTS
-
Unique Device Identifier Retrieval for the Cisco CMTS
-
Upstream Scheduler Mode for the Cisco CMTS
-
Glossary
-
Table Of Contents
Telco Return for the Cisco CMTS
Prerequisites for Telco Return
Information about Telco Return
How to Configure the Telco Return Feature
Configuring the Service Provider Descriptor Attributes
Configuring the Registration IP Address (optional)
Monitoring Telco Return Operations
Telco Return for the Cisco CMTS
Revised: February 5, 2007, 0L-1467-08
The Telco Return feature allows service providers to offer Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) 1.0 internet access over a one-way cable network. Downstream data is sent to the telco return cable modems over the cable network, while upstream data is sent from the cable modem to the headend over a separate dial-up connection.
Feature Specifications for Telco Return
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Telco Return
•
Restrictions for Telco Return
•
Information about Telco Return
•
How to Configure the Telco Return Feature
•
Monitoring Telco Return Operations
Prerequisites for Telco Return
The Telco Return feature has the following prerequisites and requirements:
•
The Cisco CMTS router must be running a Cisco IOS Release 12.1 EC software image that contains a "t" in the filename.
•
The Cisco CMTS must be using a DOCSIS-compliant cable interface line card. The Cisco uBR-MC11C cable interface line card (which has only one upstream port) is sufficient for cable plants that will never be upgraded from one-way-only operation. If, however, you plan to upgrade your plant to two-way operation, consider installing other cable interface cards, such as the Cisco uBR-MC16C or Cisco uBR-MC28C card, so as to simplify the conversion process when two-way operation is implemented.
•
The downstream cable plant must meet DOCSIS specifications.
•
The headend is wired for narrowcast downstream data transmission.
•
You have assigned downstream frequencies.
•
All equipment needed to support upstream traffic over the PSTN, as well as to monitor telco return service features, is installed. Key components include:
–
Dial-up access server (for example, the Cisco AS5300 or Cisco AS5800)
–
RADIUS dial security server
•
Upstream data from a PC through the CM to the Internet is carried over a dial-up connection. This dial-up connection can include a log or security server.
•
All third-party, telco return cable modems are DOCSIS-compliant and configured for telco return.
•
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and DOCSIS configuration files have been created and pushed to appropriate servers so that each cable modem, when initialized, can transmit a DHCP request, receive an IP address, obtain TCP/IP and Time-of-Day (ToD) server addresses, and download a DOCSIS configuration file.
•
The DOCSIS configuration files being used for telco return cable modems should include the relevant telco return Type/Length/Value (TLV) fields.
•
The customer premises equipment (CPE) (telco return cable modem or PCs) should meet the requirements for your network and server offerings.
Restrictions for Telco Return
•
DOCSIS Baseline Privacy Interface (BPI) encryption is not supported over the telco return path.
•
EuroDOCSIS cable interfaces (Cisco uBR-MC16E cable interface line card and Cisco uBR7111E/Cisco uBR7114E routers) do not support Telco Return operations.
•
Cisco IOS Release 12.2 BC does not support Telco Return operations.
•
Some vendors' telco return cable modems cannot receive traffic over the same downstream channel as cable modems operating on a two-way data system. In these instances, segment your cable plant to allow more than one downstream channel.
•
A DOCSIS ping (which is sent using the ping docsis command) cannot be used with telco return modems. An IP ping, however, can still be used.
•
The show cable flap-list command does not display telco return cable modems.
•
The clear cable modem reset command has no affect on telco return cable modems.
Information about Telco Return
This section contains the following information that describes the Telco Return feature:
Feature Overview
The DOCSIS specifications included optional support for Telco Return operations, which allows service providers to offer Internet data connectivity to cable customers who are still on cable plants that do not yet support two-way operations. Service providers can immediately provide data connectivity to their customers as they incrementally upgrade their cable plants to support two-way connections.
In a Telco Return configuration, the subscriber uses a telco return cable modem that receives downstream traffic over the cable network, but transmits the upstream traffic over a dial-up connection that is made using the local Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). The telco return cable modem makes the dial-up connection using a standard telephone modem, which can be either internal or external, depending on the type and model of the cable modem being used.
Telco Return operations is made possible by the fact that most Internet sessions are asymmetrical, with approximately 80 to 90% of the total traffic being transmitted in the downstream direction from the headend to the cable modem. The upstream transmits a much smaller volume of traffic, so Telco Return customers can still have broadband-quality Internet access.
Note
To support telco return operations, the subscriber must be using a DOCSIS-compliant telco return cable modem
DOCSIS Cable Plants
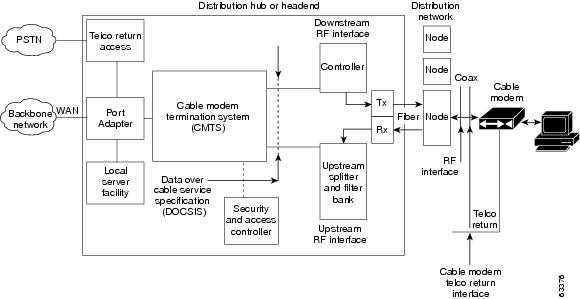
DOCSIS-compliant cable plants can support both two-way and telco return connections over the same cable network. Figure 18-1 illustrates a typical DOCSIS cable network that supports both two-way and telco return cable modems.
Figure 18-1 DOCSIS Two-Way and Telco Return Architecture
Typically, the headend uses high-speed WAN links, such as a fiber backbone, to connect to the Internet backbone network. The Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) at the headend is responsible for routing traffic between the backbone network and cable network.
Two-way and telco return operations on the downstream use the same facilities and servers at the headend. In both cases, the CMTS routes traffic over the cable interface to the appropriate cable modems.
For upstream traffic, the two-way cable modems transmit over the same coaxial cable network that is used for the downstream (although using different frequencies). Telco Return cable modems, however, use a dial-up modem connection to connect to the PSTN, which routes the upstream traffic to a Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) server at the headend. This server in turn forwards the traffic to the appropriate destination, either on the Internet or cable network.
Note
Some brands of telco return cable modems cannot receive traffic over the same downstream channel as cable modems operating on a two-way data system. To accommodate both two-way and telco return operation, segment your cable plant so that it uses multiple downstream channels, with at least one downstream channel dedicated for telco return cable modems.
Telco Return Operation
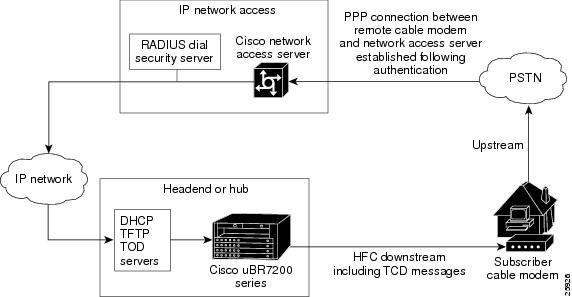
To support Telco Return operations, the Cisco CMTS must interoperate with both the cable network, and a RADIUS authentication system that is connected to the local PSTN. Figure 18-2 illustrates a typical telco return configuration.
Figure 18-2 Typical Telco Return Network
To coordinate the telco return traffic between the cable and PSTN/RADIUS networks, the Cisco CMTS transmits Telephony Channel Descriptor (TCD) messages along with the other downstream traffic. The TCD messages contain the routing and other information that the telco return cable modem needs to access the headend through the PSTN.
In particular, the TCD messages contain at least one (and up to five) Service Provider Descriptors (SPD). Each SPD contains dialing and authentication information that the telco return cable modem should use when it creates a dial-up Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) connection with the network access server (NAS) that provides the upstream access to the Internet and headend networks.
At minimum, the SPD contains the following three elements that are critical in creating the dial-up upstream connection:
•
At least one, and up to three, dial-up telephone numbers for the telco return cable modem to use when using the PSTN to connect to the headend's network access server.
•
Username to be used for the PPP authentication procedure.
•
Password to be used for the PPP authentication procedure.
When the telco return cable modem establishes the dial-up connection, it sends the username and password to the RADIUS server for network authentication. If access is granted, the network server creates the PPP session that will be used for upstream traffic.
The telco return cable modem maintains the dial-up connection as long as necessary. If the connection times out because of inactivity or because of noise problems on the PSTN, the telco return cable modem uses the information from the SPD to automatically redial the appropriate number and reestablish the dial-up connection.
Note
Some telco return cable modems require that the user manually dial the telephone number to establish the dial-up connection.
Benefits
•
Allows cable companies to offer Internet access services to their subscribers without first upgrading their plant to support two-way operations.
•
Allows service providers to support their cable subscribers without replacing existing hardware.
•
Service providers can begin providing cable access using low-density cable interface cards because upstream ports are not required. As the cable plant is upgraded to two-way operations, the cable interface line cards can be upgraded as needed.
How to Configure the Telco Return Feature
To enable and configure Telco Return operations on a cable interface, use the following procedures:
•
Configuring the Service Provider Descriptor Attributes
•
Configuring the Registration IP Address (optional)
Enabling Telco Return
To enable telco return on the Cisco CMTS, perform the following steps beginning in EXEC mode:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface cable x/y
4.
cable telco-return enable
5.
cable telco-return interval seconds
6.
exit
7.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Service Provider Descriptor Attributes
To configure the telephony attributes for a Service Provider Descriptor (SPD), perform the following steps, beginning in EXEC mode. Up to five SPDs can be defined on each cable interface (but only one SPD per cable interface is active at any one time).
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface cable x/y
4.
cable telco-return spd spd-number phonenum dial-string
5.
cable telco-return spd spd-number username login-string
6.
cable telco-return spd spd-number password password-string
7.
cable telco-return spd spd-number radius realm string
8.
cable telco-return spd spd-number ppp-authenticate [both | chap | pap]
9.
cable telco-return spd spd-number dhcp-authenticate
10.
cable telco-return spd spd-number dhcp-server ip-address
11.
cable telco-return spd spd-number dial-timer seconds
12.
cable telco-return spd spd-number threshold threshold
13.
cable telco-return spd spd-number service-provider string
14.
cable telco-return spd spd-number factory-default
15.
cable telco-return spd spd-number manual-dial
16.
exit
17.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
enable
Example:Router> enable
Router#
Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted.
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:Router# configure terminal
Router(config)#
Enters global configuration mode.
Step 3
interface cable x/y
Example:Router(config)# interface cable 4/0
Router(config-if)#
Enters cable interface configuration mode for the specified cable interface.
Step 4
cable telco-return spd spd-number phonenum dial-string
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 phonenum 15105551212
Router(config-if)#
Specifies the telephone number that the telco return CM uses when connecting to the headend's network access server.
•
spd-number = ID for this SPD. The valid range is 1 to 5, with no default.
•
dial-string = Actual telephone number to be dialed. Enter only digits, without any spaces, hyphens, or other special characters.
Note
Optionally repeat this command to specify a maximum of three phone numbers.
Note
Use the same spd-number value for all of the following commands in this procedure.
Step 5
cable telco-return spd spd-number username login-string
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 username joeuser123
Router(config-if)#
Specifies the user name that the cable modem uses during initialization to establish the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) connection.
Step 6
cable telco-return spd spd-number password password-string
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 password 9JwoKd7
Router(config-if)#
Specifies the password that the cable modem uses during initialization to establish the PPP connection.
Step 7
cable telco-return spd spd-number ppp-authenticate [chap | pap | both]
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 ppp-authenticate chap
Router(config-if)#
(Optional) Selects the authentication procedure that the cable modem should use to establish the PPP connection:
•
chap = Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
•
pap = Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
•
both = (default) Both CHAP and PAP
Step 8
cable telco-return spd spd-number radius realm string
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 radius-realm cisco
Router(config-if)#
Specifies the RADIUS Realm string that the cable modem should use to construct a domain name to be used with the login name during the PPP authentication procedure.
Step 9
cable telco-return spd spd-number dhcp-authenticate
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 dhcp-authenticate
Router(config-if)#
(Optional) Requires that the cable modem use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server that is specified with the cable telco-return spd dhcp-server command. The default is for the cable modem to use any available DHCP server.
Step 10
cable telco-return spd spd-number dhcp-server ip-address
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 dhcp-server 192.168.100.213
Router(config-if)#
(Optional) Specifies the IP address of the DHCP server that the cable modem should use during its authentication and initialization process. The default is for the cable modem to use any available DHCP server.
Step 11
cable telco-return spd spd-number dial-timer seconds
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 dial-timer 86400
Router(config-if)#
(Optional) Sets the number of seconds that the telephone connection is idle before the cable modem disconnects the call. The valid range is 0 through 4,294,967,295 seconds. The default is 0, which indicates that the dial-timer is not used and that inactive calls are not disconnected.
Step 12
cable telco-return spd spd-number threshold threshold
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 threshold 3
Router(config-if)#
(Optional) Specifies the number of times that the cable modem attempts to dial the numbers specified by the cable telco-return spd phonenum command before declaring a connection failure. (The cable modem allows the remote end of the connection to ring 10 times before handing up.) The valid range is 1 through 255, with a default of 1.
Step 13
cable telco-return spd spd-number service-provider string
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 service-provider CableProviderName
Router(config-if)#
(Optional) Specifies that the cable modem should include the specified string in the Telephony Channel Descriptor (TCD) messages as the service provider's name.
Step 14
cable telco-return spd spd-number factory-default
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 factory-default
Router(config-if)#
(Optional) Indicates that the cable modem should use this SPD during the initialization process. The default is for the SPD not to be used during initialization.
Note
At least one and only one SPD must be defined as the factory-default on each cable interface.
Step 15
cable telco-return spd spd-number manual-dial
Example:Router(config-if)# cable telco-return spd 2 manual-dial
Router(config-if)#
(Optional) Allows the cable modem to operate in manual dial mode.
Note
Repeat Step 4 through Step 15 for each SPD to be configured (up to a maximum of 5 per cable interface).
Step 16
exit
Example:Router(config-if)# exit
Router(config)#
Exits interface configuration mode.
Step 17
exit
Example:Router(config)# exit
Router#
Exits global configuration mode.
Configuring the Registration IP Address (optional)
To specify an alternate registration IP address to be sent in Termination System Information (TSI) message, use the following procedure, beginning in EXEC mode. By default, the Cisco CMTS uses the IP address for the downstream cable interface as the registration address. Use this procedure to specify a different registration address.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface cable x/y
4.
cable telco-return registration-ip ip-address
5.
exit
6.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Monitoring Telco Return Operations
To display the telco return cable modems that are currently online, use the show cable modem command. For example:
Router# show cable modemInterface Prim Online Timing Rec QoS CPE IP address MAC addressSid State Offset PowerCable4/0/U0 2 online 2848 -0.50 5 1 10.2.0.3 0010.7b6b.53d5Cable4/0/T 3 online 2853 0.25 2 1 10.2.0.101 0020.4001.4af6Cable4/0/U0 4 online 2852 -0.75 5 1 10.2.0.6 0010.7b6b.7255Cable4/0/U0 5 online 2850 0.25 5 1 10.2.0.7 0010.7b6b.5669Cable4/0/U0 6 online 2851 0.00 2 1 10.2.0.4 0010.7b6b.53c9Cable4/0/T 7 online 2849 0.50 2 0 10.2.0.102 0020.4001.4b32Router#The show cable modem command identifies telco return cable modems by displaying a "T" instead of an upstream port.
Configuration Examples
Typical Telco Return Example
The following excerpt from a configuration file shows a typical sample configuration that enables Telco Return operations on a cable interface:
!interface cable 6/0ip address 172.16.1.1 secondaryip address 10.1.1.1no ip directed-broadcastip helper-address 192.168.1.1no keepalivecable insertion-interval 500cable downstream annex Bcable downstream modulation 64qamcable downstream interleave-depth 32cable downstream frequency 687000000cable upstream 0 frequency 13008000no cable upstream 0 shutdowncable telco-return enablecable telco-return spd 1 factory-defaultcable telco-return spd 1 phonenum 8005551212cable telco-return spd 1 phonenum 4085551212cable telco-return spd 1 phonenum 6505551212cable telco-return spd 1 service-provider norcalcable telco-return spd 1 dhcp-server 172.31.172.172cable telco-return spd 1 username joecable telco-return spd 1 password testingcable telco-return spd 1 dhcp-authenticatecable telco-return spd 1 threshold 5cable telco-return spd 1 ppp-authenticate bothcable telco-return spd 1 manual-dialcable telco-return spd 1 dial-timer 7200cable telco-return registration-ip 172.16.1.1Minimal Telco Return Example
The following excerpt from a configuration file shows the minimal configuration that is needed to enable Telco Return operations on a cable interface:
cable telco-return enablecable telco-return spd 1 factory-defaultcable telco-return spd 1 dhcp-authenticatecable telco-return spd 1 dhcp-server 24.1.1.84cable telco-return spd 1 ppp-authenticate chapcable telco-return spd 1 phonenum 918005555555cable telco-return spd 1 phonenum 18005555555cable telco-return spd 1 username testcable telco-return spd 1 password testMinimal RADIUS Configuration
The following excerpt from a configuration file shows the minimal configuration that is needed to enable RADIUS support on the Cisco CMTS to allow the required authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) support:
aaa new-modelaaa authentication login default radius enableaaa authentication login vty lineaaa accounting update newinfoaaa accounting exec default start-stop radiusaaa accounting commands 15 default start-stop radiusaaa accounting network default start-stop radiusaaa accounting system default start-stop radiusAdditional References
For additional information related to the Telco Return feature, refer to the following references:
Related Documents
CMTS Command Reference
Cisco Broadband Cable Command Reference Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.htmlCisco IOS Release 12.2 Command Reference
Cisco IOS Release 12.2 Configuration Guides and Command References, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps1835/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.htmlhttp://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps1835/prod_command_reference_list.html
Cisco IOS Release 12.1 Multiservice Applications Information
Cisco IOS Multiservice Applications Configuration Guide, Release 12.1, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/121cgcr/multi_c/index.htmlCisco IOS Multiservice Applications Command Reference, Release 12.1
Note
This document has reached End of Life. For more information, see the following End-of-Life Announcement at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/redirect/eol.html
AAA and RADIUS Configuration
For information on configuring the AAA and RADIUS servers, see the Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) chapter in the Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/security/configuration/guide/fsecur_c.htmlCisco uBR7100 Series Universal Broadband Router Documentation
Cisco uBR7100 Series Universal Broadband Router Hardware Installation Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/ubr7100/hig7100/index.htmCisco uBR7100 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/ubr7100/scg7100/index.htmCisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Documentation
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Hardware Installation Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/ubr7200/installation/guide/ub72khig.htmlCisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/cable/cab_rout/cr72scg/index.htm
Standards
ANSI/SCTE 22-1 2002 (formerly SP-RFI-C01-011119)
Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specification DOCSIS 1.0 Radio Frequency Interface (RFI) (http://www.cablelabs.com/cablemodem)
Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specification Cable Modem Telephony Return Interface Specification, version 1.0 (http://www.cablelabs.com/cablemodem)
1 Not all supported standards are listed.
MIBs
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature.
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL:
1 Not all supported MIBs are listed.
RFCs
Technical Assistance

 Feedback
Feedback