|
Feature
|
Benefit
|
|
Access Technology Support
|
|
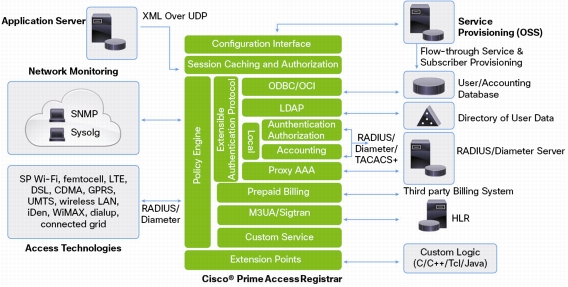
Support for a broad range of wireless and wireline access technologies, including Service Provider Wi-Fi (SP Wi-Fi), femtocell, LTE, DSL, Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service (UMTS), wireless LAN (WLAN), iDen, WiMAX, dialup, Connected Grid, and others.
|
By helping enable standardization on a common AAA server platform complying to appropriate 3GPP AAA standards, the solution delivers operational and capital expense savings while providing flexibility to the service provider regarding choice in AAA.
|
|
Support for femtocell network rollouts in conjunction with Cisco Prime Cable Provisioning and Cisco Prime Network Registrar. Cisco Prime Access Registrar acts as the RADIUS headend to authenticate and authorize a 3G femtocell.
|
Extends AAA resources where they may already be deployed. For a mobile operator, femtocells provide improvements to both coverage and capacity, especially indoors where access would otherwise be limited or unavailable. Consumers benefit from improved coverage and potentially better voice quality and battery life.
|
|
Identity and access management for Cisco® Connected Grid solutions on IPv6 networks. This is achieved using the Elliptic Curve Cryptographic (ECC)-based certificate validation and also supports TACACS+ authentication, command authorization, and accounting.
For EAP services, in addition to RSA certificates, the solution supports verification of ECC certificates. ECC uses elliptic curves to encrypt data when creating keys, which enables creation of shorter and stronger keys for better efficiency. This is achieved using the Cisco SSL library APIs.
|
Provides high performance AAA support for authenticating smart meters on a Connected Grid network.
Allows granular control of device/user administration of pole top routers through TACACS+ authentication.
|
|
Authentication and Authorization
|
|
High-speed internal embedded user database
|
• Provides a rapid start point for small-scale deployments
• Allows easy, logical grouping of users
• Offers easy configuration to return attributes in responses and check attributes ("check items") in requests
• Provides operator ability to enable and disable user access
|
|
Ability to authenticate/authorize user information stored in an external data store: LDAP directory (like Microsoft AD, OpenLDAP), Oracle or MySQL database, combined with the ability to:
• Store return and check-items attributes
• Add custom logic based on information in user's record
|
Integration support is data-store schema independent, simplifying deployment and day-to-day operations, providing OpEx savings by using existing infrastructure, and helping to support networks with tens of millions of subscribers.
|
|
Advanced RADIUS/Diameter proxy support for service provider environments
• Includes ability to add/modify/delete attributes while proxying attributes
|
Facilitates roaming arrangements with other service providers and load balancing.
|
|
Rich set of authentication protocols including support for EAP-proxy and certificate revocation list (CRL)
• PAP, CHAP, MSCHAPv2, LEAP, PEAPv0, PEAPv1
• EAP-MD5, GTC, EAP-FAST, EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS
• EAP-SIM/AKA/AKA' to authenticate with HLR over M3UA/SIGTRAN or HSS over SWx (Diameter)
• EAP Negotiate (run-time selection of EAP service)
• EAP proxy
• Diameter NASREQ
• HTTP Digest Authentication
• LDAP remote server bind-based authentication
• CRL support for EAP services
|
Broad user support with the ability to extend to others such as POP3 through custom services for meeting unique requirements.
|
|
EAP-SIM authentication from an EAP-AKA or EAP-AKA' source (quintets to triplets conversion)
|
Provides backward compatibility.
|
|
IETF RADIUS tunnel support
|
Provides support for VPN authentication.
|
|
Automatic and customizable reply-message generation
|
Helps provide detailed information in case of authentication rejects.
|
|
Accounting
|
|
Local file
• Ability to store accounting records in a single file or multiple files
• Automatic file rollover based on file age, size, or specific time
|
Speeds up processing through the ability to store accounting information on the same server on which the AAA services are running.
|
|
Proxy
• Option to ignore acknowledgements and continue processing
|
Accelerates decision-making logic when responses (or lack of) from certain remote systems can be ignored.
|
|
Database/LDAP
• Ability to write accounting records directly to an Oracle or MySQL database or an LDAPv3 directory
• Buffering option for relational database management systems (RDBMSs) for higher throughput and fault tolerance
|
Integration support is schema independent, simplifying deployment and day-to-day operations, providing OpEx savings by using existing infrastructure, and helping to support networks with tens of millions of subscribers.
|
|
Option to have a mix of multiple types of accounting (local file, proxy, database) and destinations within each type.
|
Provides flexibility and customer choice.
|
|
Platform Support
|
|
Supported operating systems:
• Oracle Solaris 10*
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 6.0, 6.1, and 6.2
|
Broad operating system support for customer choice.
|
|
Support for virtualization technologies: Oracle VM Server for SPARC and VMware ESXi 5.0
|
Lowers total cost of ownership (TCO), eases deployment, and provides greater flexibility in migration and backup.
|
|
Various Technology Support
|
|
IPv6 support:
• Performs processing of RADIUS/Diameter requests from IPv6 RADIUS/Diameter clients/servers
• Proxies requests to and receives responses from a remote IPv6 RADIUS/Diameter server
• Interacts with external database servers using IPv6, including LDAP, Oracle, and MySQL
• Allows HTTP and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to be queried over IPv6
|
Provides support for IPv6 networks and dual-stack IPv4/IPv6 networks.
|
|
Diameter support
|
Provides the following facilities:
• Supports authentication and authorization of Diameter packets with the help of a local database or an external database with interfaces such as LDAP and ODBC
• Performs session management and resource management
• Supports writing a Diameter accounting packet in a local file or proxying to another AAA server
• Supports adding, modifying, or deleting the attribute-value pairs (AVPs) in Diameter packets through extension point scripting
• Supports open-ended Diameter applications
• Supports translation of incoming RADIUS requests and responses to Diameter and vice versa
|
|
Compliance with the WiMAX Network Working Group (NWG) stage 3 document version 1.3.1.
|
Meets the various WiMAX NWG requirements for WiMAX networks.
|
|
Support for SP Wi-Fi/hotspot markets and wireless data offload including:
• Wx interface support for HSS lookup: Cisco Prime Access Registrar supports SIM and Universal SIM (USIM) authentication for data access against the newer generation subscriber database HSS through the Diameter interface Wx
• Cisco Prime Access Registrar also provides authentication support against the Home Location Register and external databases including Oracle, MySQL, OpenLDAP, and AD
• M3UA/SIGTRAN interface to HLR server on Linux operating systems for providing seamless Wi-Fi data offload services using SIM and USIM authentication
|
Helps enable service providers to effectively provide SP Wi-Fi and wireless data offload functionality.
|
|
Proxy, Database, and LDAP Configuration
|
|
Remote server support:
• Operator is able to define a list of remote systems to be used in failover or round-robin modes
• Operator is able to define the individual characteristics of each remote system, for example, ports, timeouts, retries, or reactivate timers
• Sophisticated algorithms detect status of remote systems
|
Provides option to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting against a wide variety of remote systems with adequate options for load balancing and handling failure scenarios.
|
|
Outage policies: When no remote systems are available, Accept All, Reject All, and Drop Packet outage policies are available.
|
Helps enable AAA processing to occur based on preconfigured policies even when remote systems are not available.
|
|
Rule and Policy Engine for Decision Making
|
|
• Ability to process requests using different types of data stores; for example, use LDAP for some access requests, the internal database for others
• Ability to process requests using a variety of options; for example, store an accounting request to a local file and proxy it to a number of remote RADIUS/Diameter servers, in series or in parallel, waiting for acknowledgement from some and not from others
• Ability to split authentication and authorization by selecting one method for authentication and another for authorization (One-Time Password [OTP] server and Oracle database, for example)
• Ability to decide how to process a packet based on attributes in the request packet such as source or destination IP address or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port or based on Cisco Prime Access Registrar's environment variables settings such as reauthentication service, reauthorization service, and reaccounting service
• Easy request processing options based on a variety of attributes/values like DNS domain, username prefix, dialed number, calling number, NAS, and others, using the predefined policies in Cisco Prime Access Registrar policy engine
|
Provides a variety of predefined rules and policies for meeting most usual requirements in service provider environments. Provides the ability to extend default logic with custom policies written using C/C++/Tool Command Language [Tcl]/Java.
|
|
Flexible AAA processing through use of logical operators
|
Logical operators AND, OR, PARALLEL-AND, PARALLEL-OR provide extreme flexibility in evaluating AAA processing choices in serial or parallel. Parallel is used when a response from any one subsystem is sufficient to trigger a decision process and also helps reducing processing time. Serial is used when a sequential response from subsystems is required.
|
|
Simplified GUI/CLI mechanism to easily choose the right authentication, authorization, and accounting service(s) required for processing a packet.
|
• Provides maximum flexibility and ease in matching information in the incoming packets for choosing the appropriate service to apply
• Provides a very simple method to add, modify, or delete AVPs in packets
• Reduces the need for scripting or requirement of familiarity with programming languages such as TCL, C, C++, or Java
• Provides easy and efficient alternative to rule/policy engine and scripting points for most common use cases
|
|
Session Management and Resource Allocation
|
|
Built-in feature to track user sessions
|
|
|
Dynamic resource allocation including:
• Session limits
• IP addresses
|
Supports:
• Enforcement of session limits per user and per group
• Allocation of critical resources such as IP-addresses and home-agents
|
|
Options to store active session information to an external database like Oracle
|
Helps enables scaling up to tens of millions of sessions per server.
|
|
In an environment with multiple Cisco Prime Access Registrar servers, the operator may designate one Cisco Prime Access Registrar to manage all sessions
|
Helps avoid bypass of session limits and to allocate IP addresses and other resources centrally.
|
|
Session query capabilities:
• Real-time query of the session table using the command-line interface (CLI), XML over UDP, RADIUS, or Diameter
• Able to query cached attributes through the query session
• Able to query and release sessions based on session age, username, NAS, and other criteria
|
Allows external/business applications to query Access Registrar for information on users who are logged in and the resources (like IP-address) that they are allocated. This can then be used for making other business decisions such as providing personalized services, reduced sign-on, and enhanced video delivery.
|
|
Session release capabilities:
• Manual release of sessions and resources
• Automatic session release when accounting stop is lost (inactivity timeout)
• Able to release sessions and generate Packet of Disconnect (PoD)
• Automatic session release when accounting on/off is detected (system accounting)
|
Helps manage session state information across the network automatically or through administration intervention.
|
|
Session information not lost even if Cisco Prime Access Registrar or the system is restarted
|
Avoids information loss during server restarts that can otherwise wreck user/group session limit enforcement or allocation of IP addresses.
|
|
Session tracking for accounting-only servers: Able to count the number of user sessions
|
Session management can be done for servers through which only accounting messages pass through. This can be used in cases such as username to IP address resolution or International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) to IP address resolution where only accounting traffic is forwarded through Cisco Prime Access Registrar.
|
|
Ability to send Change of Authorization (CoA) request
|
Helps in changing service levels of users who are logged in, on the fly. For example, a user on a 1 MB plan could be bumped up to 2 MB without having to log off.
|
|
Scalability
|
|
An external session manager allows tens of millions of simultaneous active sessions by storing the active session records on an external database server (Oracle10g and 11i) instead of storing them in the internal memory of Cisco Access Registrar
|
Supports large service deployments with a single instance of Cisco Prime Access Registrar.
|
|
Multithreaded architecture provides performance that scales with additional CPUs
|
Supports large service deployments with a single instance of Cisco Prime Access Registrar and allows the solution to grow with the business.
|
|
Customization/Extensibility
|
|
Ability to add custom logic to the request processing flow using Tcl, C or C++, or Java through extension point scripting:
• Access request and response packets
• Modify processing decisions in real time
• Target specific requests with multiple callout points
• Add, delete, or modify the AVPs
EPS allows users to interact with request processing and communicate with Cisco Prime Access Registrar at numerous API points
|
Helps enable meeting unique business, regulatory, and technical requirements.
|
|
Able to create custom processing methods
|
Helps to meet new/unique business requirements. For example, custom code can be written and integrated to support authentication mechanisms, such as POP3, which are not built into Cisco Prime Access Registrar.
|
|
Extensible attribute dictionary
• Populated with latest attribute definitions, including third-party, vendor-specific attributes
• Easy addition of new attributes (add/modify/delete)
• Variable-length vendor type in vendor-specific attributes
|
Easy interoperability with third-party devices.
|
|
Resilience
|
|
• Automatic configuration replication to other Cisco Prime Access Registrar servers
• Specify lists of alternate remote systems for each processing method
• Specify multiple methods to process a request
• Automatic server restart
|
Provides multiple levels of redundancy including server redundancy, remote-system redundancy, and processing-method redundancy.
|
|
Veritas, Sun, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) clustering for high availability
|
Minimizes application downtime.
|
|
Troubleshooting and Monitoring
|
|
Multilevel debugging output
|
Helps troubleshoot and isolate incidents faster. Allows controlling error, debug output.
|
|
Statistics:
• Real-time query of statistics
• Reset statistics without restarting Cisco Prime Access Registrar
|
Statistics are provided for a variety of events occurring within the server, such as number of packets processed, number of packets dropped, number of packets proxied to remote server, received response, and so on. These help in analyzing usage patterns, troubleshoot issues, and more.
|
|
Able to query status of all Cisco Prime Access Registrar processes and utilities
|
Offers simple utilities that show status of all Cisco Prime Access Registrar-related processes to help in troubleshooting.
|
|
Logging:
• Log files for each Cisco Prime Access Registrar process
• Audit log of all configuration changes
• Able to direct logs to a syslog server
|
Provides multiple logs for various components and logging levels that help manage and isolate incidents quicker.
Provides audit trails that can be maintained through configuration change logs.
|
|
SNMP:
• RADIUS SNMP support
• SNMP traps generated for critical events
|
Allows for easy monitoring from network management systems.
|
|
Utility to generate RADIUS AAA requests: Radclient
|
Helps to simulate network deployment scenarios in a lab through:
• Creation of individual packets of various types - access-requests, accounting requests, and more.
• Simulating stress/performance testing scenarios to exhibit server behavior and for tuning the system
|
|
Configuration
|
|
• Powerful command-line configuration utility with interactive/noninteractive full and view-only modes
• Dynamic configuration feature allows configuration changes to take effect without a server restart
• Command and value recall, inline editing, autocommand completion, and a context-sensitive list of options
• Revamped web-based interface for configuring most of the objects in Cisco Prime Access Registrar
• Wildcard definitions for grouping RADIUS clients
|
Noninteractive modes allow for configuration automation and OSS integration. Powerful CLI allows easy interactive operations saving operators time and helping avoiding errors.
|
|
Broad Systems Integration Capabilities
|
|
Support for integration with provisioning, billing, and other service-management components
|
Reduces operational costs and speeds service rollout.
|
|
Prepaid billing interface allows billing vendors to integrate their systems into Cisco Prime Access Registrar for prepaid functionality
|
Service providers may offer prepaid data or usage-based premium services while reusing their existing billing system and protecting their investments.
|
|
Management
|
|
• Replication of the internal databases allows multiple servers to be similarly configured
• Supports SNMP and syslog for network management
|
Centralized management and ease of use.
|