SUMMARY
• Application control: improving the way IT departments deploy, operate, and manage their application infrastructures.
• Application performance: helping ensure better service to end users, including scalability, availability, and failover.
• Application security: helping to protect critical applications, infrastructures, and data from abuse and misuse.
• Infrastructure simplification: reducing the complexity of the infrastructure, shrinking the number of devices and vendors, better integrating the network and the application, and lowering the cost of the infrastructure.
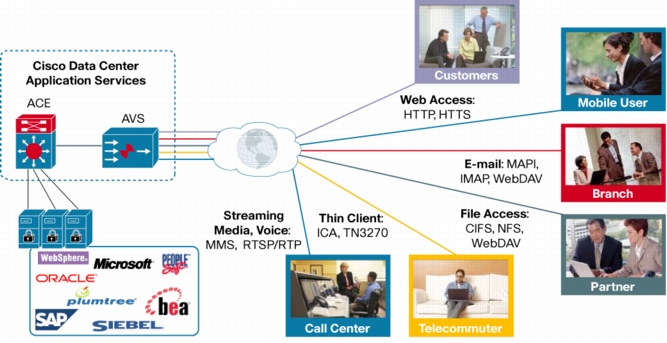
Figure 1. Cisco ACE and Cisco AVS in the Data Center
CHALLENGE
• Deploy and migrate applications without adding to the application infrastructure
• Scale the application infrastructure
• Have multitier data-center and application security
• Provide distributed workflow
• Consolidate functions, devices, and management
• Increase application throughput
SOLUTION
Performance: Latency, Mitigation and Bandwidth Usage Reduction
• FlashForward object acceleration helps the Cisco AVS 3120 Application Velocity System eliminate unnecessary browser cache validation requests. This new technology eliminates the network delays associated with embedded cacheable Web objects such as images, style sheets, and JavaScript files. In a Web deployment, each embedded object must ensure that the user has the proper browser version, and each validation involves a separate HTTP request from the client to the origin server. Pages that embed many objects must wait to be rendered until the client-to-server round trips are completed. Cisco FlashForward technology automates this process at the server. All object validity information is carried in the single download of the parent HTML document. The Cisco AVS 3120 takes responsibility for transparently managing validity and expirations. This automatic aggregation saves traffic by validating object freshness on the server side, rather than on the client. The benefits can be realized in any application.
• Smart Redirect speeds Webpage redirecting by helping the Cisco AVS 3120 convert HTML metatag-based redirects into more efficient HTTP header-based redirects. The result is significantly faster page response time that does not sacrifice the flexibility and productivity of metatag-based redirection.
• Fast Redirect speeds HTTP header-based 301/302 redirects, reducing the round trips required from two to one. The Cisco AVS 3120 processes the 301/302 HTTP status code response and fetches the redirected resource over the LAN in the data center.
• FlashConnect improves browser performance by enabling responses to be processed in parallel rather than serially. By default, Microsoft Internet Explorer fetches objects over only two TCP connections established for each domain name it sees in an HTML container page. This limit means that requests are often queued unnecessarily, and first-visit performance suffers. By multiplexing these connections, the Cisco AVS 3120 accelerates performance.
Reduce Time, Cost and Complexity of Application Deployment
Security
• SSL encryption and decryption
• Directional deep inspection
• Integrated hardware-accelerated protocol control
• Positive and negative (whitelist and blacklist) security
• Protocol compliance
• Anomaly detection
• Transaction logging and reports for application security forensics
• Normalization-The Cisco AVS 3120 first normalizes HTTP and HTTPS traffic by decoding encrypted traffic so that the payload can be examined, not just the TCP header.
• Bidirectional, deep-packet inspection-The Cisco AVS 3120 examines messages in both directions, at the protocol and message payload levels. It identifies malicious traffic by applying policy, such as whitelists and blacklists.
• Blocking-The Cisco AVS 3120 blocks protocol and message payloads that do not comply with policy, using a combination of whitelists (permitted) and blacklists (prohibited). Application behavior is analyzed to ensure that policies appropriately match major application protocol behavior and payload characteristics.
Optimization
• Bandwidth reduction features and minimized application latencies
• Offloading server processing cycles for optimizing applications
• Content switching techniques, which optimize resource usage and help ensure application availability
• Delta encoding-Webpage caching is successful because many pages are static; subsequent requests can be satisfied from the cache instead of the server. However, dynamic resources and content force subsequent server requests for the original page. But when one can encode and deliver to the client just the differences between the cached original page and the updated new page, many cases can be handled by sending just a few bytes. This approach, called delta encoding, is a core technology of the Cisco AVS 3120. It helps the client system dynamically construct new pages from cached pages by applying small deltas. This process is both automatic and transparent-no changes to browser clients, application servers, or content are required.
• Dynamic browser caching-Many enterprise applications for customer relationship management (CRM) and for portals often mark some objects, such as images, JavaScript files, ActiveX control files, or binary files, as noncacheable. This practice can result in slow download performance, especially for remote users with limited bandwidth. Cisco Just-in-Time Object Evaluation technology on the Cisco AVS 3120 automatically tracks the freshness of each of these objects in real time. If a requested object has not changed, the client uses its cached version. The Cisco AVS 3120 delivers the object only when it has changed in that specific context.
• Smart image optimization-The Cisco AVS 3120 device compresses image files intelligently to optimize image quality, resulting in faster image download times, faster page renders, and more efficient bandwidth usage. Other schemes compress images uniformly, a policy that can severely degrade quality of some images while missing opportunities to compress other images further. Some images can be highly compressed, but others need to maintain their detail. For example, a JPG photo for an accident claim can be kept at the highest resolution, whereas a scanned insurance policy document can be highly compressed without compromising readability.
• Compression-Cisco goes beyond standard compression to deliver more advanced optimizations such as adaptive dynamic caching (discussed later in this paper), delta encoding optimization, and FlashForward technologies. Devices and approaches that incorporate simple byte reductions are determined by how much repetitive content a page contains-for typical HTML pages, compression reduces page size by two to five times. In contrast, delta optimization can often reduce page size by 10 to 50 times, depending on how much the page actually changes. The Cisco AVS 3120 uses byte compression to further reduce the size of an already-shrunken delta-optimized page. And unlike existing GZIP and DEFLATE implementations, Cisco's optimized GZIP compression is fully compatible with all browser types, including Mozilla Firefox. Compression is also available in the Cisco Content Services Switch (CSS) as of Version 8.10.
• TCP connection multiplexing for offloading connection management-With the TCP connection feature, the Cisco ACE and Cisco AVS 3120 can take on the overhead of managing network connections by maintaining persistent TCP connections with the Web and application servers. To optimize overall performance as traffic levels change, the Cisco ACE and Cisco AVS 3120 adjust the number of persistent TCP connections to the back-end servers as load conditions dictate, freeing Web and application servers to focus solely on content generation. This feature can double the capacity of the Web server.
• Caching-A high-performance caching architecture enables several innovative optimizations of the Cisco AVS 3120, including delta encoding optimization and FlashForward object acceleration. Static caching also directly offloads servers of requests for frequently requested static objects, such as images and applets. This fully configurable feature adds to the overall application performance and transaction throughput.
• Adaptive and configurable dynamic caching-This feature helps the Cisco AVS 3120 fulfill requests for dynamic content, enabling the offloading of application servers and even core databases. With configurable dynamic caching, the Cisco AVS 3120 can cache multiple responses for a given URL based on specified cache parameters, such as URL query strings, HTTP headers, and cookie values. In effect, it enables dynamic content to be treated as static for accelerated performance. With a simple script, even personalized data can be dynamically cached, leaving more resources for core transactions.
• Load-based dynamic caching-Sophisticated content expiration policies help guarantee the freshness of dynamic content. The Cisco AVS 3120 monitors server load in real time and makes intelligent closed-loop decisions on content expiration to optimize site performance and use hardware resources efficiently during periods of peak traffic. This feature is configurable according to load, timing, and URLs.
• Lazy-request evaluation-Many systems make updates globally and, in effect, block access for some period of time. For example, a user request can initiate a recompile, and during that time any other requests that come in may be queued, possibly causing all users to wait. With lazy-request evaluation, the device can be configured to always serve a cached copy upon request and, when the back-end processing is complete, to automatically refresh the copy from the origin server. With this feature, the device always serves content out of the dynamic cache and, in effect, separates the client request from the origin server response.
• SSL acceleration-The SSL protocol has become the industry standard for providing security, privacy, and confidentiality for enterprise business transactions. To accelerate SSL transactions, the Cisco device handles the SSL handshake with the client, decrypts Web requests from the client, proxies them to the back-end Web or application servers, condenses the server responses (through delta optimization and FlashForward capabilities), encrypts them, and delivers them to the client within the secure SSL connection. This dramatically reduces the number of SSL-based transactions and increases SSL scalability as much as fourfold. SSL processing is available on Cisco ACE, the Cisco Content Switching Module (CSM), Cisco content services switches, and Cisco AVS.
• URL mapping-In another security measure, the Cisco URL mapping capability hides URLs within the HTML source by swapping them with arbitrary URL strings. This helps isolate the back-end infrastructure by preventing end users from seeing the actual URL structure used by the origin server.
• Single sign-on (SSO) optimizations-Many enterprises use SSO mechanisms such as Microsoft's NT LAN Manager to authenticate users as they log into enterprise applications. Authentication is a way of preventing user spoofing. Cisco improves overall application performance in SSO-enabled environments by eliminating redundant authentication traffic associated with object validation requests.
• XML transformation-Applications that output XML offer considerable flexibility in terms of connectivity and reuse. Translating XML on the application server is inefficient and leads to significant back-end performance problems. Instead of the usual standalone XML transformation appliance, Cisco offers integrated XML translation capability through an XML module built into the Cisco AVS 3120. The solution caches XML objects to improve performance and throughput, offloads the transformation of XML from the back end and the client, and then performs all appropriate optimizations to deliver to clients.
• Load-balancing policies-Heavy server loads are distributed using policies based on criteria that identify the requests to be distributed, the eligible devices capable of handling those requests, and the algorithms for distributing the requests. Examples of load-distribution algorithms include round robin, weighted round robin, least connections, weighted least connections, least loaded, and predictive hash.
• Server-failure policies-When a server fails, what happens next is governed by the operator's specific policy. For example, what should be done when a server to which a client has a persistent connection mapped fails during a transaction? Possible options include resetting the connection, issuing an HTTP redirect (perhaps to a server that displays an error message), rebalancing the connection to a new server using the load-balancing policy, or directing it to a special "sorry server" that becomes active if there are no other eligible servers for this policy.
• Content-specific policies-Different treatment can be specified for different types of content. For example, a policy might direct all requests for cacheable content to a set of reverse-proxy caches that offload the processing of static images from application servers. Another might partition a Web server farm into static and dynamic sections.
• Device-specific policies-Different treatment can be specified for different types of devices. For example, clients using a wireless device can be directed to a set of servers that customize content for its format.
SUMMARY
• Unprecedented control for IT over the deployment and management of application service, which can dramatically improve service and reduce management overhead by creating virtual partitions and using role-based access control.
• High application and device performance, including 16-GB throughput and 4-MB bidirectional connections to handle large-scale operations, and unique WAN latency and bandwidth reduction capabilities to improve end-user response times across the network.
• Rich levels of application and network security, including bidirectional support for content inspection, SSL encryption/decryption, and transaction logging for application security forensics.
• Integration of multiple front-end services within a single processing path.
• The new Cisco ACE module
• The new Cisco AVS software update for the Cisco AVS 3120 Application Velocity System
• Application load balancing and acceleration: Cisco CSS 11500 Content Services Switches
• Application load balancing: Cisco Content Switching Module for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
• Application load balancing and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) off-load: Cisco Content Switching Module with SSL for the Cisco Catalyst 6500
• Cisco GSS 4400 Global Site Selector platforms
• HTTP(s) optimization: Cisco AVS 3120 Application Velocity System
• HTTP(s) optimization management device: Cisco AVS 3180 Application Velocity System
• Web and video services: Cisco Application Content Networking System (ACNS) Software
• File and print services software: Cisco Wide Area File Services (WAFS)
• Data-center file services: Cisco Network Attached Storage (NAS)
