PB687565
Cisco IOS® Software Release 15.0(1)SY supports Cisco Catalyst® 6500 Series Supervisor Engine 2T only. Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY inherits features from Release 12.2(50)SY and adds several new software and hardware features specifically developed for Catalyst 6500 Series platforms with the new Supervisor Engine 2T. The release also reflects the evolution of Cisco's software development model, which accelerates the consistency of features and applications across platforms and enables Cisco® Services for Borderless Networks.
• Support for the Cisco Wireless Services Module 2 (WiSM2) with Supervisor Engine 2T
• Support for the Cisco ACE Application Control Engine Module with Supervisor Engine 2T
• More than 70 new software and hardware features
Release Packaging
New Features
New Hardware
Table 1. Supported Service Modules
|
Service Module Description |
Part Number |
|
Cisco ACE30 hardware |
ACE30-MOD-K9 |
|
Cisco WiSM2 |
WS-SVC-WiSM-2-K9 |
Cisco Wireless Services Module 2
Cisco Application Control Engine Module
• Increase application availability
• Accelerate application performance
• Secure the data center and critical business applications
• Facilitate data center consolidation through the use of fewer servers and load balancers
Transceivers Supported
• SFP-10GB-LRM (10GBASE-LRM)
• SFP-10GB-LR (10GBASE-LR)
• SFP-10GB-ER (10GBASE-ER)
Software Innovations
High Availability
• Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) graceful restart: The graceful restart feature in OSPFv3 prevents routing protocol reconvergence during a processor switchover by allowing nonstop data forwarding along routes that are already known while the OSPFv3 routing protocol information is being restored. To perform the graceful restart function, a router must be in high-availability stateful switchover (SSO) mode. For more information, please visit http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-ospf.html.
• BFD for IPv6 (BFDv6) protocol: BFD is a detection protocol designed to provide fast forwarding path failure detection times for all media types, encapsulations, topologies, and routing protocols. In addition to fast forwarding path failure detection, BFD provides a consistent failure detection method for network administrators. BFDv6 provides IPv6 support by accommodating IPv6 addresses, and it provides the capability to create BFDv6 sessions. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-bfd.html.
• BFD support for OSPFv3: With Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY, OSPFv3 is now a registered protocol with BFD and receives forwarding path detection failure messages from BFD. For more information, please visit http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-bfd.html.
• Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for IPv6 address family NSF and graceful restart: The graceful restart capability is supported for the IPv6 BGP unicast, multicast, and VPNv6 address families, enabling the Cisco NSF function for BGP IPv6. The BGP graceful restart capability allows the BGP routing table to be recovered from peers without keeping the TCP state. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-mptcl_bgp.html.
• Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN 6VPE and 6PE SSO support: The SSO feature maintains stateful protocol and application information. User session information is maintained during a switchover, and line cards continue to forward network traffic with no loss of sessions, providing improved network availability. SSO initializes and configures the standby rendezvous point and synchronizes state information, which can reduce the time required for routing protocols to converge. Network stability may be improved with the reduction in the number of route flaps created when routers in the network fail and lose their routing tables. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mpls/configuration/guide/mp_6vpe_6pe_issu_sso.html.
IPv6
• Link-state advertisement (LSA) and shortest-path-first (SPF) throttling OSPFv3 fast convergence enhancements: The LSA and SPF throttling OSPFv3 fast convergence enhancements provide dynamic mechanisms to slow down link-state advertisement updates in OSPFv3 during times of network instability. These enhancements also allow faster OSPFv3 convergence by providing LSA rate limiting in milliseconds. Previously, OSPFv3 used static timers for rate-limiting SPF calculations and LSA generation. Although these timers are configurable, the values used are specified in seconds, which poses a limitation for OSPFv3 convergence. LSA and SPF throttling achieves subsecond convergence by providing a more sophisticated SPF and LSA rate-limiting mechanism that can respond quickly to changes and also provides stability and protection during prolonged periods of instability. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-ospf.html/.
• Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) IPv6 global address support: The HSRP global IPv6 address feature allows users to configure multiple nonlink local addresses as virtual addresses, and it allows the storage and management of multiple global IPv6 virtual addresses in addition to the existing primary link-local address. If an IPv6 address is used, it must include an IPv6 prefix length. If a link-local address is used, it must not have a prefix. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-fhrp.html#wp1070413.
Routing
• MPLS VPN Inter-Autonomous System (Inter-AS) Option AB: The MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB feature combines the best functions of Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B networks to allow an MPLS VPN service provider to interconnect different autonomous systems to provide VPN services. These networks are defined in RFC 4364 section 10 multi-AS backbones, option A and option B, respectively. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mpls/configuration/guide/mp_vpn_ias_optab.html.
• MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB+: Option AB+ is an enhancement to allow the next hop to be in the global table. It allows MPLS forwarding between provider-edge autonomous system border routers (ASBRs) on the same link as the one with Multiprotocol Exterior BGP (MP-eBGP) VPNv4 peering. Option AB requires the next hop to be in the Virtual Route Forwarding (VRF) instance (configured as hybrid VRF) and thus allows only IP forwarding between provider-edge ASBRs. Option AB+ is an enhancement to allow the next hop to be in the global table, and it allows MPLS forwarding between provider-edge ASBRs (on the same link as the one with MP-eBGP VPNv4 peering). This feature allows the Inter-AS hybrid next hop to be in the global table (instead of the VRF table) and uses the MPLS forwarding path (instead of the IP path).
• OSPF demand circuit disable: This feature prevents potential problems with point-to-multipoint (P2MP) links and adjacency drop problems. It disables demand circuit negotiation for hub-and-spoke environments.
• BGP event-based VPN import: This feature introduces a modification to the existing BGP path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is directed by events: when a BGP path changes, all its imported copies are updated as soon as processing is available. Convergence times are significantly reduced because the propagation of routes is no longer delayed by the software's waiting for a periodic scanner time interval before processing the updates. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/iproute_bgp/configuration/guide/irg_event_vpn_import_ps10591_TSD_Products_Configuration_Guide_Chapter.html.
• Round-trip changes without affecting provider-edge and customer-edge neighbors: this feature enables alteration of the round-trip values without resetting the affected provider-edge and customer-edge neighbors. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/iproute_bgp/configuration/guide/irg_event_vpn_import.html.
• Support for an Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) instance per VRF instance for IP: This feature provides multiple VPN VRF-aware IS-IS instances. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_0s/feature/guide/vrf_isis.html.
• OSPF graceful shutdown: The OSPF graceful shutdown feature allows network administrators to remove a router from the network gracefully without affecting data traffic. When a user runs an OSPF shutdown command, the router informs all its neighbors that it is going offline by sending OSPF messages indicating that all links originating from the router are not useful for data forwarding. In addition, it sends an empty hello message to bring down any OSPF adjacency relationships with its neighbors. Note that the router can be reached after the graceful shutdown for troubleshooting or upgrading of router software or hardware. This feature enables software and hardware upgrades in a single route processor device because users can gracefully shut down the router from the network and then upgrade software or hardware in the router as needed. It also allows troubleshooting without affecting data traffic because users can log in to the router for debugging after shutting it down.
• OSPFv2 local routing information base (RIB): With the OSPFv2 local RIB feature, each OSPF protocol instance has its own local RIB. The OSPF local RIB serves as the primary state for OSPF SPF route computation. The global RIB is not updated with intermediate results during the SPF. Instead, the global RIB is updated only when routes are added, deleted, or changed, thereby reducing global RIB computations. This reduced update activity may result in fewer dropped packets. This feature is enabled by default and does not need to be configured. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_4t/12_4t15/ht_osrib.html.
• OSPF support for Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA) RFC 3101: This feature adds an OSPF knob to prefer Type 7 over equal-cost Type 5. This feature is provided to comply with updates in RFC 3101.
Multicast
• Multicast VPN (MVPN) data multicast distribution tree (MDT) enhancements: This feature provides the capability to map the groups in a VRF instance to particular MDT groups in a deterministic fashion. Traditionally, the MDT groups are selected at random when the traffic passes the threshold. A 1:1 mapping of VRF groups to MDT groups would ease troubleshooting and traffic engineering. Previously, there was a limit of 255 MDTs before they were reused. Customers want to map many of their services to specific MDTs and deliver them only to provider edges that have interested receivers. With this new function,1024 data MDTs are supported.
• Internet Group Management Protocol Version 3 (IGMPv3) host stack: The IGMPv3 host stack feature enables routers and switches to function as multicast network endpoints or hosts. The feature adds Include mode capability to the IGMPv3 host stack for Source-Specific Multicast (SSM) groups. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_3t/12_3t14/feature/guide/gtigmpv3.html.
• IP Multicast load splitting - ECMP using S, G, and next hop: This feature introduces more flexible support for ECMP multicast load splitting by adding support for load splitting based on source and group addresses and on source, group, and next-hop addresses. This feature enables multicast traffic from devices that send many streams to groups or that broadcast many channels, such as IPTV servers or MPEG video servers, to be more effectively load-split across equal-cost paths. Prior to the introduction of this feature, the Cisco IOS Software supported only ECMP multicast load splitting based on the source address, which prevented multicast traffic sent by a single source to multiple groups from being load-split across equal-cost paths. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2sr/12_2srb/feature/guide/srbmpath.html.
• VRF and Multicast VRF (MVRF) syslog: Syslog information for MVRF messages contains VRF information, allowing users to see VRF-aware multicast syslogs for troubleshooting.
Virtual Private LAN Service
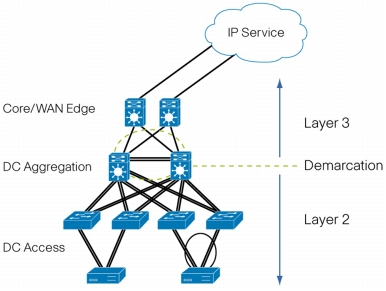
Medianet
• Mediatrace: Mediatrace is a network diagnostic tool that monitors the state of an audio, video or data flow across a network path. Mediatrace discovers layer 2 and layer 3 devices along the flow path and can provide different levels of information ranging to the device specific (CPU, memory), interface specific (input interface speed, output interface drops), to the flow specific (DSCP values, network jitter and packet loss).
For more information, please visit http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/media_monitoring/configuration/guide/mm_mediatrace.html.
• RSVP based CAC (Call Admission Control): RSVP based CAC provided a robust CAC mechanism for deployments across WAN resulting in superior QoS and reliability for calls amid meshed and multitier networks.
• Medianet 2.2 Support in GOLD: Microburst Detection is added to GOLD diagnostic tool which helps troubleshoot packet microbursts in the port-asic and log the event.
• RIP for IPv6 (RIPng) NSF
• Service advertisement framework (SAF)
• BGP show ip bgp neighbor policy
• BGP neighbor site-of-origin (SoO) command neighbor soo
• IP-RIP delayed startup
• OSPFv2 enablement on an interface using the ip ospf area command
• OSPF time-to-live (TTL) security check
• NSF and SSO support in IPv6 multicast
Certifications
Manageability
Table 2. Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY MIB Enhancements
Support
Ordering Information
Table 3. Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY Ordering Information
For More Information
• Cisco IOS Software product lifecycle dates and milestones
– http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/switches/ps5718/ps708/prod_bulletin0900aecd804f0694.pdf
• Cisco IOS Software information
– http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/products_ios_cisco_ios_software_category_home.html
• Cisco IOS Software Center
– Download Cisco IOS Software releases and access software upgrade planners: http://www.cisco.com/cisco/software/navigator.html?a=a&i=rpm
• Cisco Software Advisor (requires Cisco.com account)
– Determine the minimum supported software for platforms: http://tools.cisco.com/Support/Fusion/FusionHome.do
• Cisco Feature Navigator (requires Cisco.com account)
– Use a web-based application to quickly match Cisco IOS Software releases, features, and hardware: http://tools.cisco.com/ITDIT/CFN/jsp/index.jsp
• Cisco IOS Software Planner (requires Cisco.com account)
– View all major releases, all platforms, and all software features from a single interface: http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/Software/Iosplanner/Planner-tool/iosplanner.cgi
• Cisco Catalyst switching portfolio
– View the full Cisco Catalyst switching portfolio in one document: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/switches/ps5718/ps6406/CatalystPoster_Final.pdf
• Product management contact
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series marketing team (cco-6500-external@cisco.com)