-
CT5760 Controller Deployment Guide
-
Preface
-
Product Overview
-
Supported Features
-
CT5760 Centralized Configuration Example
-
Mobility Architecture
-
Mobility Design and Configuration
-
Bring Your Own Device Security Configuration
-
Secure WLAN Configuration
-
802.11ac Support on WLC5760 and Catalyst 3850
-
Radio Resource Management Configuration
-
CleanAir
-
High Availability
-
Interface Group
-
Multicast Configuration
-
Installing and Upgrading Software Image on a CT5760
-
Adding WLC to Prime
-
Application Visibility and Flexible Netflow
-
Service Discovery Gateway (mDNS Gateway)
-
QoS Configuration
-
Table Of Contents
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) and Security Configuration
Single Authentication of SSID BYOD for Apple Device Use Case
Dual Authentication of SSID BYOD for Apple Device Use Case
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) and Security Configuration
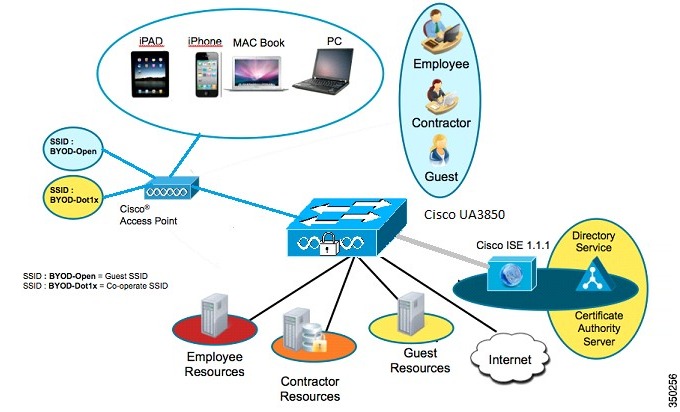
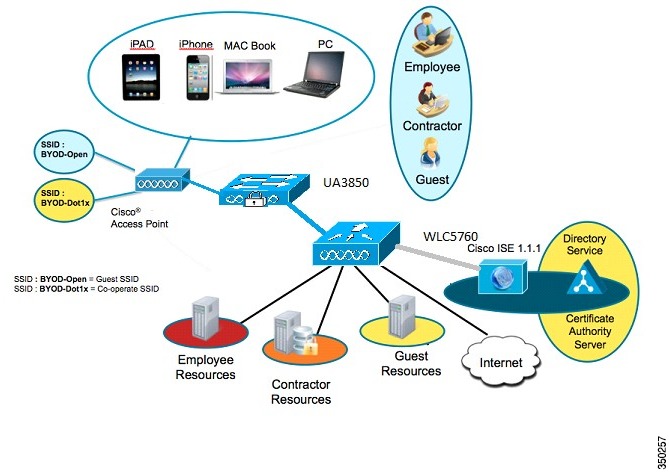
This section discusses the self-service additions of personal devices securely. An employee registers a new device, and a certificate is automatically provisioned for that user and device. The certificate is installed along with a supplicant profile that is pre-configured to use that certificate and on- board the device into the corporate network. Two BYOD use cases supported for wireless supplicant included are:
•
Single authentication of SSID BYOD for Apple device
•
Dual authentication of SSID BYOD for Apple device.
Single Authentication of SSID BYOD for Apple Device Use Case
In this use case, there is a single SSID (BYOD-Dot1x) for corporate access that is authenticated and authorized with both Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) and Extensible Authentication Protocol Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS).
1.
User associates to BYOD-Dot1x.
2.
User enters employee username and password for PEAP authentication.
3.
Authenticator authenticates user and performs URL-Redirect based on authorization policy.
4.
User opens a browser and is redirected to self-registration portal for device registration.
5.
Mac address gets pre-populated in the device registration page for DeviceID, and user enters a description and registers their device.
6.
User's supplicant is provisioned, and certificates are installed.
7.
After certificate installation, Change of Authorization (CoA) occurs; supplicant is authenticated and authorized using EAP-TLS.
8.
Dynamic VLAN assignment occurs, and supplicant is placed in corporate VLAN
Dual Authentication of SSID BYOD for Apple Device Use Case
In a dual SSID use case, there are two SSIDs - one that is BYOD-Open for guest and one that authenticates for corporate access.
1.
User associates to guest BYOD-Open SSID.
2.
User opens a browser and is redirected to the Identity Services Engine (ISE) Central Web Authentication (CWA) guest portal.
3.
Authenticator authenticates the associate user as an employee and directs the user to the employee device registration guest portal.
4.
Mac address is pre-populated in the device registration page, and user enters a description and registers their device.
5.
User's supplicant is provisioned and certificate is installed.
6.
User disconnects from guest SSID.
7.
User connects to corporate SSID and is authenticated/authorized to use the new profile.
Topology
Figure 6-1 BYOD Topology with Catalyst 3850 as the Authenticator
Figure 6-2 BYOD Topology with WLC5760 as the Authenticator
Components

 Feedback
Feedback