-
Cisco Unified CallManager Release 5.1(1) New and Changed Information Guide
-
Index
-
Preface
- About This Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager System Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager Features and Services Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager Serviceability Administration Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager Serviceability System Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager CDR Analysis and Reporting Administration Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager Call Detail Record Definitions
- Cisco Unified CallManager Security Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager Bulk Administration Guide
- Cisco Unified CallManager Developers Guide
- Cisco Unified IP Phones Information
-
Table Of Contents
Cisco WebDialer Security Support
SIP Phone Support in Cisco WebDialer
Desktop-based Client Application Call Flow
Browser-Based Application Call Flow
WebDialer API Programming
This chapter describes the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) and HTML over secure HTTP (HTTPS) interfaces that are used to develop customized directory search applications for Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer Version 1.2 and contains the following sections:
Definitions
Overview
Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer, which is installed on a Cisco Unified CallManager server and used in conjunction with Cisco Unified CallManager, allows Cisco Unified IP Phone users to make calls from web and desktop applications. For example, Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer uses hyperlinked telephone numbers in a company directory to allow users to make calls from a web page by clicking the telephone number of the person that they are trying to call.
The two main components of Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer comprise the WebDialer Servlet and the Redirector Servlet.
WebDialer Servlet
The WebDialer servlet, a Java servlet, allows Cisco Unified CallManager users in a specific cluster to make and end calls, as well as to access their phone and line configuration.
Cisco WebDialer applications interact with the WebDialer servlet through two interfaces:
•
SOAP over HTTPS —This interface that is based on the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) gets used to develop desktop applications such as Microsoft Outlook Add-in and SameTime Client Plug-in. Developers can use the isClusterUserSoap interface to design multicluster applications that require functionality similar to a Redirector servlet.
•
HTML over HTTPS—This interface that is based on the HTTPS protocol gets used to develop web-based applications such as the Cisco Unified CallManager directory search page (directory.asp). Developers who use this interface can use the Redirector servlet for designing multicluster applications.
Redirector Servlet
The Redirector servlet, a Java-based servlet, finds the Cisco Unified CallManager cluster for a request that a Cisco WebDialer user makes. It redirects that request to the specific Cisco WebDialer server that is located in that user's Cisco Unified CallManager cluster. Availability of the Redirector servlet occurs only for multicluster applications and only for applications that are developed by using HTML over HTTPS interfaces.
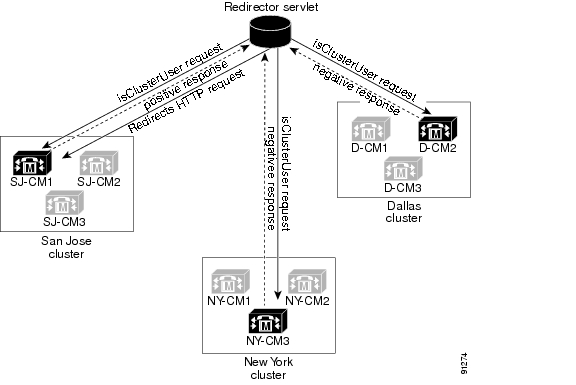
Figure 37-1 illustrates how a Redirector servlet redirects a call in a multicluster environment.
Figure 37-1 Multiple Clusters
Example of Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer Using the Redirector Servlet
For example, consider three clusters, each one in a single city such as San Jose, Dallas, and New York. Each cluster contains three Cisco Unified CallManager servers with WebDialer servlets that have been configured for Cisco Unified CallManager servers SJ-CM1, D-CM2, and NY-CM3.
The system administrator configures the WebDialer servlets on any Cisco Unified CallManager server by entering the IP address of that specific Cisco Unified CallManager server in the wdservers service parameter.
For information on configuring WebDialer and Redirector servlets, refer to the "Cisco WebDialer" chapter in the Cisco Unified CallManager Features and Services Guide, Release 5.0.
When a user who is located in San Jose clicks a telephone number in the corporate directory search page that is enabled by Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer, the following actions happen:
1.
The Cisco Unified CallManager server sends an initial makeCall HTTPS request to the Redirector servlet.
2.
If this request is received for the first time, the Redirector servlet reads the Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer server cookie and finds it empty.
For a repeat request, the Redirector servlet reads the IP address of the Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer server that previously serviced the client and sends a isClusterUser HTTPS request only to that server.
3.
The Redirector servlet sends back a response that asks for information, which results in the authentication dialog box opening for the user.
4.
The user enters the Cisco Unified CallManager user ID and password and clicks the Submit button.
5.
The Redirector servlet reads only the user identification from this information and sends a isClusterUser HTTPS request to each Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer server that the system administrator configured.
Figure 37-1 illustrates how this request is sent to the WebDialer servlets that have been configured for SJ-CM1, D-CM2, and NY-CM3. Depending on the geographical location of the calling party, the WebDialer servlet from the cluster that represents that location responds positively to the Redirector servlet. The remaining WebDialer servlets that were contacted return a negative response. The WebDialer servlet SJ-CM1 responds positively to the request because the calling party is located in San Jose (SJ-CM).
The Redirector servlet redirects the original request from the user to SJ-CM1 and sets a cookie on the user browser for future use.
Changes in Release 5.1
Cisco Unified CallManager Release 5.1 includes the following change to Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer:
•
WebDialer and Redirector now require HTTPS.
Developers should format Redirector and WebDialer requests to use HTTPS. Cisco Unified CallManager requires the secured protocol to prevent unauthorized applications from reading user data.
Refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager Developers Guide for Release 5.0 for important changes to WebDialer API programming in the 5.0 release.
Cisco WebDialer Security Support
Cisco WebDialer supports secure connections to CTI (TLS connection). For this feature, Cisco WebDialer uses the security API that JTAPI provides. Refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager JTAPI Developers Guide for the JTAPI API. WebDialer uses the Application User, "WDSysUser", for obtaining the CTI connection.
You must complete the following configuration before WebDialer can be configured to open a CTI connection in secure mode.
Step 1
Activate the Cisco CTL Provider service in Cisco Unified CallManager Service Administration.
Step 2
Activate the Cisco Certificate Authority Proxy Function Service.
Step 3
Download the Cisco CTL Client from the Application plug-in and install it on any machine.
Step 4
Run the CTL Client, choose the option to "enable Cluster Security," and follow the instructions that display. This requires USB E-tokens.
Step 5
To verify that cluster security is enabled, go to Cisco Unified CallManager Administration and look at [System-> Enterprise Parameter configuration]. Look at the Security Parameters; the cluster security should be set to 1.
Step 6
In Cisco Unified CallManager Administration page, from the User Management drop-down menu, select the Application User CAPF Profile option.
Step 7
Click Add new InstanceID.
Step 8
In the CAPF Profile configuration window, set up an InstanceID and CAPF profile for the InstanceID for the Application User WDSysUser.
a.
InstanceID: Enter the value of instance ID, for example, 001.
b.
Certificate Operation: Select Install/Upgrade from the drop-down menu.
c.
Authentication Mode: Select By Authorization String from the drop-down menu.
d.
Authorization String: Enter the value of authorization string, for example, 12345.
e.
Key Size: Select key size from drop-down menu, for example, 1024.
f.
Operation Completes By: Enter the date and time in following format yyyy:mm:dd:hh:mn where yyyy=year, mm=month, dd=date, hh=hour, mn=minutes, such as 2006:07:30:12:30.
Note
If this date and time is past, the certificate update operation will fail.
g.
Ignore the Packet Capture Mode, Packet Capture Duration, and Certificate fields.
h.
Certificate Status: Select Operation pending from the drop-down menu.
If anything else is selected, the certificate update will fail.
Security Service Parameters
Cisco WebDialer includes two mode-specific service parameters for CTI connection security.
•
CTI Manager Connection Security Flag—This required service parameter indicates whether security for the Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer service CTI Manager connection is enabled or disabled.
If enabled (true), Cisco WebDialer will open a secure connection to CTI Manager by using the Application CAPF profile that is configured for the instance ID (as configured in CTI Manager Connection Instance ID service parameter) for Application user WDSysUser. The default value specifies false.
•
Application CAPF Profile Instance ID: This service parameter specifies the Instance ID of the Application CAPF Profile for Application User WDSysUser that this Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer server will use to open a secure connection to CTI Manager. You must configure this parameter if the CTI Manager Connection Security Flag parameter is enabled (true).
•
Algorithm:
1.
Read the service parameters.
2.
Get the node IP/name of the nodes where TFTP and CAPF are activated.
3.
For the instanceID (input in service parameters), if the Certificate Operation is `Install/Upgrade' or `Delete', delete the current certificates, if any.
4.
If the Certificate Operation is not `Install/Upgrade' or `Delete', and a current certificate exists, use this certificate.
5.
If no certificate is present, request one by using JTAPI API setSecurityPropertyForInstance; this will need username, instanceID, authCode, tftpServerName, tftpPort, capfServerName, capfPort, certPath, and securityFlag. This call will contact the TFTP server, download the certificate, contact the CAPF server, verify the CTL file, and request the client and server certificates.
6.
If Step 5 is successful, set the following items on the ICCNProvider and call open().provider.setInstanceID(instanceID);provider.setTFTPServer(tftpServerName);provider.setCAPFServer(capfServerName);provider.setCertificatePath(certPath);provider.setSecurityOptions(securityFlag);
7.
If Step 5 fails, throw initFailedException. You can see this in the WebDialer traces.
Install Changes
Cisco WebDialer rpm creates a new directory "/usr/local/cm/wd/wd-certificates/" and sets permissions for users on this directory, which is used to store the certificates.
Files Changed: /vob/ccm/Projects/CMAppServices/rpm/cm-webdialer.specSIP Phone Support in Cisco WebDialer
Cisco WebDialer supports SIP phones in this release. CTI only supports the new SIP phones and not the existing SIP phones, so the same support is extended by Cisco WebDialer. JTAPI provides the APIs that are used to distinguish between these two kinds of phones and to hide the unsupported phones from the user in the Cisco WebDialer preferences window.
Call Flows
The call flows in this section describe the flow of events for client and browser-based applications that use Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer, which should help you design customized applications for Cisco WebDialer.
Desktop-based Client Application Call Flow
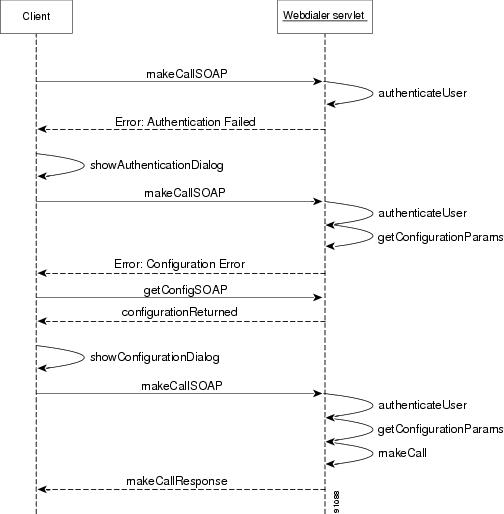
Figure 37-2 shows the call flow for an outgoing call from a client application such as Microsoft Outlook Plug-in to a WebDialer servlet. The user clicks the Dial or Make Call button in the address book of the client application. If the user is making a call for the first time, the application does not have authentication or configuration information on the user.
If the user makes a call for the first time,
1.
The client sends a makeCallSoap request to the configured WebDialer servlet.
2.
The WebDialer servlet attempts to authenticate the user. Figure 37-2 shows an authentication failure that occurred because the authentication information is incomplete or does not exist.
3.
The WebDialer servlet sends an authentication failure response to the client application.
4.
The client application displays a dialog box on the computer screen of the user that asks for the user ID and password. The user enters this information and clicks the submit button. The user ID and password now gets stored for future invocations of the application.
5.
The application sends a repeat SOAP request to the WebDialer servlet. The request contains credential information on the user.
6.
The WebDialer servlet authenticates the user.
7.
The WebDialer servlet reads any missing configuration information in the request.
8.
The WebDialer servlet returns a configuration error message to the client application.
9.
The client application sends a getConfigSoap request to the WebDialer servlet.
10.
The WebDialer servlet responds with the user configuration information that is stored in the directory.
11.
The client application displays a configuration dialog box on the user computer screen that asks the user to select or update the configuration. The user enters the information and clicks the submit button. The user configuration information now gets stored for future invocations of the application.
12.
The client resends the makeCallSoap request to the WebDialer servlet. This request contains the user configuration information.
13.
The WebDialer servlet authenticates the user and dials the telephone number by using the information that the makeCallSoap request contains. It responds to the client with a success or failure message.
Note
The call flow goes directly to step 12:
•
If the credential and configuration information is already stored when the application is installed.
•
For all subsequent requests that the user makes.
Figure 37-2 Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer Call Flow for a Client-Based Application
Browser-Based Application Call Flow
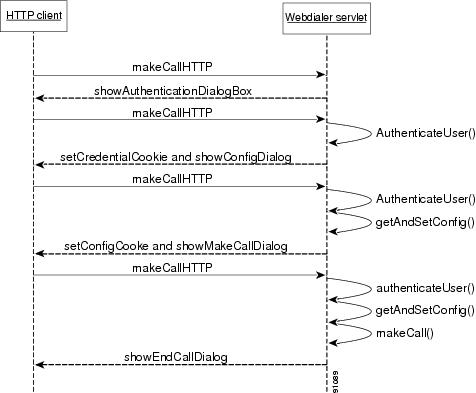
Figure 37-3 shows the call flow for an HTTP-based browser application such as a directory search page, personal address book, or the Cisco Unified CallManager directory search page (directory.asp).
The user clicks the Dial or Make Call button in the address book of the client application. If the user is making a call for the first time, the application does not have authentication or configuration information on the user.
Figure 37-3 Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer Call Flow for a Browser-Based Application
If the user makes a call for the first time:
1.
The client sends a makeCall HTTPS request to the configured WebDialer servlet. The query string contains the number to be called.
2.
The WebDialer servlet authenticates the user. Authentication fails because the authentication information is incomplete or does not exist.
Note
Authentication succeeds if the user credentials are sent with the request, and the call flow goes directly to number seven.
3.
The WebDialer servlet sends an authentication dialog to the client browser for user authentication.
4.
The user enters the user ID and password and clicks the Submit button.
5.
The client sends a makeCallHTTPS request that contains the user credentials to the WebDialer servlet.
6.
The WebDialer servlet authenticates the user.
7.
The WebDialer servlet reads the configuration information in the cookie that is sent with the request.
8.
Assuming that the request is made for the first time, the servlet sends a response that contains a cookie to the client browser. The cookie that contains the client credentials gets stored on the client browser. The client credentials comprise user ID, IP address, and the time of the request.
9.
The user enters the updates in the configuration dialog box and clicks the Submit button.
10.
The client browser sends a makeCall HTTPS request to the WebDialer servlet. The request contains a cookie with the credential and configuration information in parameter form.
11.
The WebDialer servlet uses the credentials to authenticate the user and saves the configuration information in its memory.
12.
The WebDialer servlet sends a makeCall confirmation dialog to the client browser with the configuration information that is stored in a cookie. The cookie gets stored on the client browser for future invocations.
13.
The Make Call dialog box appears on the user computer screen. The user clicks the Dial button, which sends another makeCall HTTPS request to the WebDialer servlet.
14.
The WebDialer servlet authenticates the user by using the credentials in the cookie, retrieves the configuration information from the cookie, and makes the call.
15.
The servlet responds by sending an endCall confirmation dialog to the user to end the call. The End Call dialog box appears on the user computer screen and stays there for the time interval that is configured in the service parameters.
For all subsequent requests, the call flow starts at number 12 and ends at number 15.
Interfaces
Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer applications interact with the WebDialer servlet through two interfaces:
•
SOAP over HTTPS — This interface, which is based on the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP), gets used to develop desktop applications such as Microsoft Outlook Add-in and SameTime Client Plug-in. Developers can use the isClusterUserSoap interface to design multicluster applications that require functionality similar to a Redirector servlet.
•
HTML over HTTPS — This interface, which is based on the HTTPS protocol, gets used to develop web-based applications such as the Cisco Unified CallManager directory search page (directory.asp). Developers who are using this interface can use the Redirector servlet for designing multicluster applications.
Note
The following files must be run to properly set the ENV variable and Java classes:
installWDService.bat
installWDSOAP.bat
SOAP over HTTPS Interface
To access the SOAP interfaces for Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer, use the Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer Web Service Definition Language (WSDL) in the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section.
makeCallSoap
You access the makeCallSoap interface by initiating a SOAP request to the URL https://CCM-IP:8080/webdialer/services/WebdialerSoapService where CCM-IP specifies the IP address of the Cisco Unified CallManager server where Cisco WebDialer is configured.
Destination
Mandatory
Standard canonical form. For example, +1 408 5551212 or extensions such as 2222.
String
None
None
Credential
Mandatory
The user ID or password of the user or proxy user. For more information on creating a proxy user, see the Cisco WebDialer chapter in the Cisco Unified CallManager Features and Services Guide, Release 5.0.
Refer to the credential data type in the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section.
None
None
Profile
Mandatory
The profile that is used to make a call. A typical profile is a calling device such as an IP phone or line.
Refer to the profile data type in the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section.
None
None
Results
Refer to the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section for return values and their data type.
endCallSoap
You access the endCallSoap interface by initiating a SOAP request to the URL https://CCM-IP:8080/webdialer/services/WebdialerSoapService where CCM_IP specifies the IP address of the Cisco Unified CallManager server where Cisco WebDialer is configured.
ValueCredential
Mandatory
The user ID or password of the user or proxy user. For information on creating a proxy user, see the Cisco WebDialer chapter in the Cisco Unified CallManager Features and Services Guide, Release 5.0.
Refer to the credential data type in "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section.
None
None
Profile
Mandatory
The profile that is used to make a call. A typical profile is a calling device such as an IP phone or line.
Refer to the profile data type in the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section.
None
None
Refer to the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section for return values and their data type.
getProfileSoap
You access the getProfileSoap interface, which is used by plug-in based clients, by initiating a SOAP request to the URL https://CCM-IP:8080/webdialer/services/WebdialerSoapService where CCM-IP specifies the IP address of the Cisco Unified CallManager server where Cisco WebDialer is configured.
Credential
Mandatory
User ID or password of the user or proxy user. For information on creating a proxy user, see the Cisco WebDialer chapter in Cisco Unified CallManager Features and Services Guide, Release 5.0.
Refer to the credential data type in the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section.
None
None
UserID
Mandatory
The user ID for which the configuration is requested.
String
None
None
Refer to the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section for return values and their data type.
isClusterUserSoap
You access the isClusterUserSoap interface by initiating a SOAP request to the URL https://CCM-IP:8080/webdialer/services/WebdialerSoapService where CCM-IP specifies the IP address of the Cisco Unified CallManager server where WebDialer is configured.
Use this SOAP interface for multicluster applications that require functionality, similar to a Redirector servlet, for redirecting calls to the various locations where Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer is installed on a network. The application uses this interface to locate and verify the Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer that is servicing the user, followed by makeCall, endCall, or getProfile requests to that Cisco WebDialer.
UserID
Mandatory
The user ID for which the the request is made.
String
None
None
Refer to the "Cisco WebDialer WSDL" section for return values and their data type.
result
Boolean
The result specifies true if the user is present in the directory of the cluster. The result specifies false if the user is not present in the directory.
HTML over HTTPS Interfaces
This section describes the HTML over HTTPS interfaces.
makeCall
You use the makeCall interface in customized directory search applications. The Cisco Unified CallManager directory search page (directory.asp) also uses this interface. Access the makeCall interface by initiating an HTTPS request to the URL https://<ipaddress>/webdialer/Webdialer. In this URL, ipaddress specifies the IP address of the Cisco Unified CallManager server where Cisco WebDialer is configured.
Browser-based applications in which the browser accepts cookies use this interface. The user profile exists only for the length of the session if the cookies are disabled in a browser. For a sample script that is used to enable directory search pages, go to the "Sample JavaScript" section.
makeCallProxy
You access the makeCallProxy interface by initiating an HTTPS request to the URL https://ipaddress/webdialer/Webdialer?cmd=doMakeCallProxy. Browser-based applications in which the browser accepts cookies use this interface. If the cookies are disabled in a browser, the user profile exists only for the length of the session.
Applications such as a personal address book, defined in the Unified CMUser pages at https://cmserver/CMUser, can use the makeCallProxy interface. The credential of the application gets used, as a proxy, to make calls on behalf of users. Because these users have authenticated themselves before accessing the Unified CMUser window, they do not get prompted again for their user ID and password. The application sends the user ID and password of the proxy user in the form of a query string in the request or as a parameter in the body of the POST message.
For a sample script that is used to enable directory search pages, go to the "Sample JavaScript" section.
result
Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer displays the appropriate dialog and its applicable success or error message.
Cisco WebDialer WSDL
The WSDL specification provides the basis for the Web Service Definition Language (WSDL) for Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer. You can access the WSDL for Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer on the Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer server installation at:
https://CCM-IP:8080/webdialer/services/WebdialerSoapService?wsdl
Use this specific WSDL and the interfaces that are mentioned in this document to develop customized applications for Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer. For a list of references on Cisco Unified CallManager, SOAP, and WSDL, refer to the "Related Documentation" section in the Preface to the Cisco Unified CallManager Developers Guide for Release 5.0.
<wsdl:definitions xmlns:tns="urn:WebdialerSoap" xmlns:soap="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:http="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/http/" xmlns:mime="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/mime/" xmlns:xsd="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soapenc="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" xmlns:wsdl="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" xmlns="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" targetNamespace="urn:WebdialerSoap" name="urn:WebdialerSoap"><wsdl:types><xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:tns="urn:WebdialerSoap" targetNamespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"><xsd:import namespace="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/"/><xsd:complexType name="CallResponse"><xsd:sequence><xsd:element name="responseCode" type="xsd:int"/><xsd:element name="description" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/></xsd:sequence></xsd:complexType><xsd:complexType name="Credential"><xsd:sequence><xsd:element name="userID" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/><xsd:element name="password" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/></xsd:sequence></xsd:complexType><xsd:complexType name="UserProfile"><xsd:sequence><xsd:element name="user" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/><xsd:element name="deviceName" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/><xsd:element name="lineNumber" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/><xsd:element name="supportEM" type="xsd:boolean"/><xsd:element name="locale" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/></xsd:sequence></xsd:complexType><xsd:complexType name="GetConfigResponse"><xsd:sequence><xsd:element name="responseCode" type="xsd:int"/><xsd:element name="description" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/><xsd:element name="deviceInfoList" nillable="true" type="tns:ArrayOfWDDeviceInfo"/></xsd:sequence></xsd:complexType><xsd:complexType name="WDDeviceInfo"><xsd:sequence><xsd:element name="deviceName" nillable="true" type="xsd:string"/><xsd:element name="lines" nillable="true" type="tns:ArrayOfstring"/></xsd:sequence></xsd:complexType><xsd:complexType name="ArrayOfWDDeviceInfo"><xsd:complexContent><xsd:restriction base="soapenc:Array"><xsd:attribute ref="soapenc:arrayType" wsdl:arrayType="tns:WDDeviceInfo[]"/></xsd:restriction></xsd:complexContent></xsd:complexType><xsd:complexType name="ArrayOfstring"><xsd:complexContent><xsd:restriction base="soapenc:Array"><xsd:attribute ref="soapenc:arrayType" wsdl:arrayType="xsd:string[]"/></xsd:restriction></xsd:complexContent></xsd:complexType></xsd:schema></wsdl:types><wsdl:message name="makeCallSoap0In"><wsdl:part name="cred" type="tns:Credential"/><wsdl:part name="dest" type="xsd:string"/><wsdl:part name="prof" type="tns:UserProfile"/></wsdl:message><wsdl:message name="makeCallSoap0Out"><wsdl:part name="Result" type="tns:CallResponse"/></wsdl:message><wsdl:message name="endCallSoap1In"><wsdl:part name="cred" type="tns:Credential"/><wsdl:part name="prof" type="tns:UserProfile"/></wsdl:message><wsdl:message name="endCallSoap1Out"><wsdl:part name="Result" type="tns:CallResponse"/></wsdl:message><wsdl:message name="getProfileSoap2In"><wsdl:part name="cred" type="tns:Credential"/><wsdl:part name="userid" type="xsd:string"/></wsdl:message><wsdl:message name="getProfileSoap2Out"><wsdl:part name="Result" type="tns:GetConfigResponse"/></wsdl:message><wsdl:message name="isClusterUser3In"><wsdl:part name="userid" type="xsd:string"/></wsdl:message><wsdl:message name="isClusterUser2Out"><wsdl:part name="Result" type="xsd:boolean"/></wsdl:message><portType name="WebdialerSoapService"><wsdl:operation name="makeCallSoap"><wsdl:input message="tns:makeCallSoap0In"/><wsdl:output message="tns:makeCallSoap0Out"/></wsdl:operation><wsdl:operation name="endCallSoap"><wsdl:input message="tns:endCallSoap1In"/><wsdl:output message="tns:endCallSoap1Out"/></wsdl:operation><wsdl:operation name="getProfileSoap"><wsdl:input message="tns:getProfileSoap2In"/><wsdl:output message="tns:getProfileSoap2Out"/></wsdl:operation><wsdl:operation name="isClusterUserSoap"><wsdl:input message="tns:isClusterUser3In"/><wsdl:output message="tns:isClusterUser2Out"/></wsdl:operation></portType><binding name="WebdialerSoapService" type="tns:WebdialerSoapService"><soap:binding style="rpc" transport="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"/><wsdl:operation name="makeCallSoap"><soap:operation soapAction="urn:makeCallSoap"/><input><soap:body use="encoded" encodingStyle= "https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" namespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"/></input><output><soap:body use="encoded" encodingStyle= "https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" namespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"/></output></wsdl:operation><wsdl:operation name="endCallSoap"><soap:operation soapAction="urn:endCallSoap"/><input><soap:body use="encoded" encodingStyle= "https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" namespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"/></input><output><soap:body use="encoded" encodingStyle= "https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" namespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"/></output></wsdl:operation><wsdl:operation name="getProfileSoap"><soap:operation soapAction="urn:getProfileSoap"/><input><soap:body use="encoded" encodingStyle= "https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" namespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"/></input><output><soap:body use="encoded" encodingStyle= "https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" namespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"/></output></wsdl:operation><wsdl:operation name="isClusterUserSoap"><soap:operation soapAction="urn:isClusterUserSoap"/><input><soap:body use="encoded" encodingStyle= "https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" namespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"/></input><output><soap:body use="encoded" encodingStyle="https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" namespace="urn:WebdialerSoap"/></output></wsdl:operation></binding><service name="WebdialerSoap"><port name="WebdialerSoapService" binding="tns:WebdialerSoapService"><soap:address location= "https://WebDialer_ip_address:8080/webdialer/services/WebdialerSoapService"/></port></service></wsdl:definitions>Sample JavaScript
This sample JavaScript script enables Cisco Unified CallManager WebDialer from a directory search page.
Single Cluster Applications
Use this script for single cluster applications if all users are in only one cluster.
function launchWebDialerWindow( url ) {webdialer=window.open( url, "webdialer", "status=no, width=420, height=300, scrollbars=no, resizable=yes, toolbar=no" );}function launchWebDialerServlet( destination ) {url = 'https://<%=server_name%>/webdialer/Webdialer?destination=' + escape(destination);launchWebDialerWindow( url );}!These functions can be called from the HTML page which has a hyperlink to the phone number to be called. An example of it is:<TD><A href="javascript:launchWebDialerServlet( <%= userInfo.TelephoneNumber %> )"><%= userInfo.TelephoneNumber %></A> </TD>Multiple Cluster Applications
Use this script if all users are spread across different clusters.
function launchWebDialerWindow( url ) {webdialer=window.open( url, "webdialer", "status=no, width=420, height=300, scrollbars=no, resizable=yes, toolbar=no" );}function launchWebDialerServlet( destination ) {url= 'https://<%=server_name%>/webdialer/Redirector?destination='+escape(destination);launchWebDialerWindow( url );}!These functions can be called from the HTML page which has a hyperlink to the phone number to be called. An example of it is:<TD><A href="javascript:launchWebDialerServlet( <%= userInfo.TelephoneNumber %> )"><%= userInfo.TelephoneNumber %></A> </TD>

 Feedback
Feedback