-
Cisco Self-Service Phone Administration
-
Preface
-
Overview of Cisco SPA
-
Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Provisioning Prerequisites for Cisco SPA
-
Installing Cisco SPA
-
Operating and Configuring Cisco SPA
-
Troubleshooting Cisco SPA
- Release Notes for Cisco Self-Service Phone Administration Release 1.0
-
Cisco Self-Service Phone Administration Online Help Customization and Localization Procedures
-
Table Of Contents
About the Cisco SPA Operation and Configuration Tool
About the Cisco SPA Web Server Application
About Cisco SPA in the Network Architecture
About Cisco SPA and Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Communications
About Cisco SPA Service Provider Administrators
About Cisco SPA Account Administrators
About Cisco SPA Group Administrators (Optional)
About Supported Phone Features in Cisco SPA
Overview of Cisco SPA
Cisco SPA enables the end user to manipulate existing phone features and query account information without service provider intervention.
This chapter contains the following topics:
•
About Cisco SPA in the Network Architecture
•
About Cisco SPA and Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Communications
•
About Supported Phone Features in Cisco SPA
About the Cisco SPA Workflow
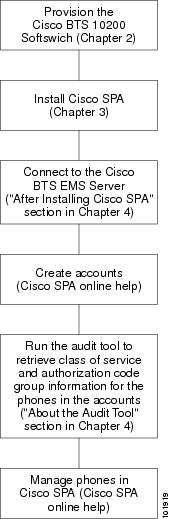
This section shows two workflows for Cisco SPA. Figure 1-1 shows the workflow for a new Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch and Cisco SPA customer, whereas Figure 1-2 shows the workflow for an existing Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch customer who has installed Cisco SPA for the first time.
Figure 1-1 Workflow for New Cisco BTS 10200 Customers
Figure 1-2 Workflow for Existing Cisco BTS 10200 Customers
About Cisco SPA
Cisco SPA is an add-on product to the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch and allows phones to be organized into accounts and managed by non service personnel. This reduces service provider costs while enhancing the user's product experience. When the service provider has installed Cisco SPA and configured it by using the Cisco SPA operation and configuration tool, all that remains is creating accounts for users to manage their own phones. The Cisco SPA GUI interface is designed to be self-explanatory, and specific user tasks are accomplished by navigating the windows and consulting the help files that are included. The Cisco SPA application and the Cisco SPA operation and configuration tool are described in the "About Cisco SPA Applications" section.
Cisco SPA is based on accounts and their management. An account has the following characteristics:
•
An account identifies (and is assigned to) a customer of the service provider. The customer can be an enterprise or residential user.
•
An account consists of a logical grouping of phones, their assigned features, and related data.
Cisco SPA users have the following characteristics:
•
A user exists within an account.
•
Phones are assigned to users.
•
The four types of Cisco SPA users are as follows:
–
Service provider administrator (see the "About Cisco SPA Service Provider Administrators" section)
–
Account administrator (see the "About Cisco SPA Account Administrators" section)
–
Group administrator (see the "About Cisco SPA Group Administrators (Optional)" section)
–
End user (see the "About Cisco SPA End Users" section)
About Cisco SPA Applications
Cisco SPA consists of two applications:
•
Cisco SPA operation and configuration tool (see the "About the Cisco SPA Operation and Configuration Tool" section)
•
Cisco SPA web server application (see the "About the Cisco SPA Web Server Application" section)
About the Cisco SPA Operation and Configuration Tool
The Cisco SPA operation and configuration tool is used by service providers to set up, configure, and operate the Cisco SPA web server application. This is a standalone (not web-based) GUI application that runs directly on the hardware platform on which Cisco SPA is installed. With this tool, you can configure initial settings as well as perform maintenance in the following areas:
•
Customize Cisco SPA with your product brand
•
Manage databases
•
Configure Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch connections
•
Configure web servers
•
Log levels of data
•
Backup and restore database and configuration information
•
Start and stop operations
The Cisco SPA operation and configuration tool is described in the "About Cisco SPA Operation and Configuration Tool Features" section.
About the Cisco SPA Web Server Application
The Cisco SPA web server application supports a number of capabilities that allow service providers to alter characteristics of the application and the content offered to end users.
•
Account management—By using Cisco SPA windows, service providers can view and modify current accounts. For information on Cisco SPA windows, see the online help.
•
Store traps—Service providers can check traps issued by Cisco SPA over a span of time extending up to the last 48 hours and check alarms generated by the Cisco SPA application or the underlying monitoring application. For more information, see the "Using the Configuration Tab" section.
Note
Cisco SPA does not manage the hardware computing platform that the application is running on. The operating system (Solaris) performs this function.
•
Security—Cisco SPA provides intrusion detection, restricts multiple logins, and implements security checks for each Cisco SPA user level. For additional information, see the "About Cisco SPA Security" section.
•
Multiple user levels—Cisco SPA enables you to establish from one to four user levels. The account administrator, group administrator, and end user are optionally created by the service provider administrator. The account administrator can also create group administrators and end users. For additional information, see the "About Cisco SPA User Levels" section.
•
Audit tool—Cisco SPA contains a standalone application that compares the data in the Cisco SPA database with the data in the Cisco BTS EMS server database. For additional information, see the "Using the Audit Tab" section and the "About the Audit Tool" section.
•
Bulk loading (XML interface)—Use this interface to create, edit, and delete Cisco SPA accounts without using the GUI. For additional information, see the "About the Bulk Load Function" section.
•
Scalability—Cisco SPA can handle up to 100,000 managed phones and up to 1000 simultaneous users. For additional information, see the "Using the Configuration Tab" section.
•
Localization—Cisco SPA provides a platform that can be localized.
•
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) support—Generates trap information that can be stored on a specified server. For additional information, see the "Using the Configuration Tab" section.
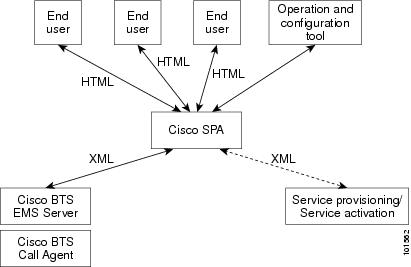
About Cisco SPA in the Network Architecture
Figure 1-3 shows how Cisco SPA is positioned in a service provider network.
Figure 1-3 Cisco SPA Network Architecture
About Cisco SPA and Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Communications
The connection between Cisco SPA and the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch is described in the "Using the Configuration Tab" section.
Cisco SPA communicates with the Cisco BTS 10200 through the Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) interface. Multiple sessions including complex queries can be conducted simultaneously between the two servers.
The data on the Cisco BTS EMS server is not replicated in the Cisco SPA database. In order to avoid data synchronization issues, any references to Cisco BTS EMS server data are performed by querying the Cisco BTS EMS server.
The Cisco SPA audit tool compares information in the Cisco SPA database with that in the Cisco BTS EMS server database. If a discrepancy is detected, the audit tool displays error messages.
The audit tool is described in the "About the Audit Tool" section.
About Cisco SPA User Levels
Cisco SPA supports four levels of users who occupy a hierarchy with decreasing capabilities. From the highest to the lowest level, these users are described in the following sections:
•
About Cisco SPA Service Provider Administrators
•
About Cisco SPA Account Administrators
•
About Cisco SPA Group Administrators (Optional)
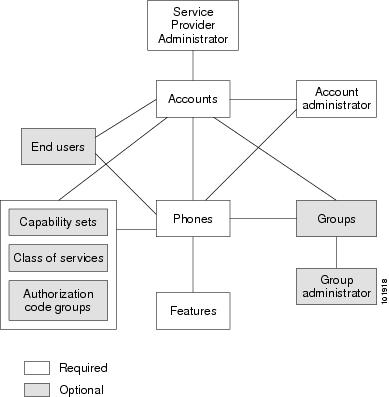
Figure 1-4 shows the required and optional entities in Cisco SPA.
Figure 1-4 Cisco SPA Required and Optional Entities
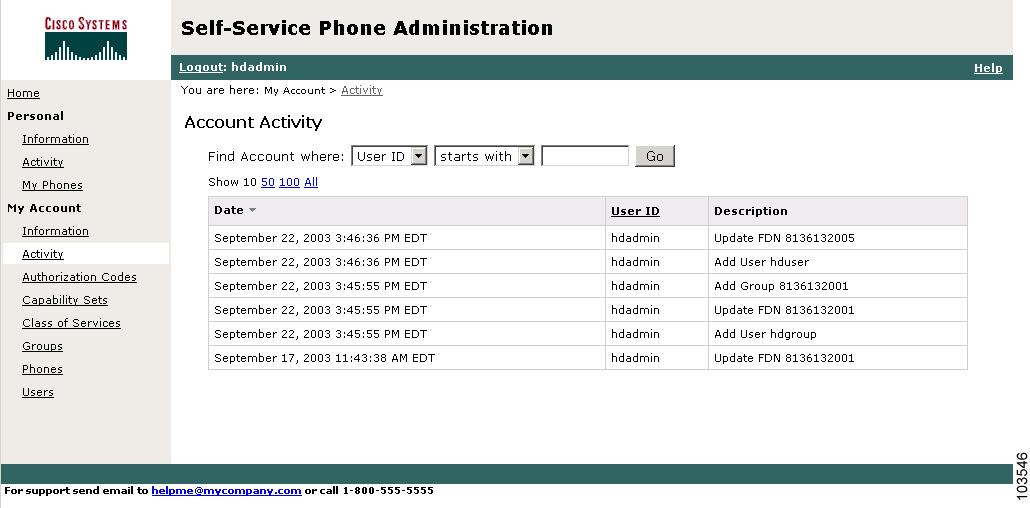
About Cisco SPA Service Provider Administrators
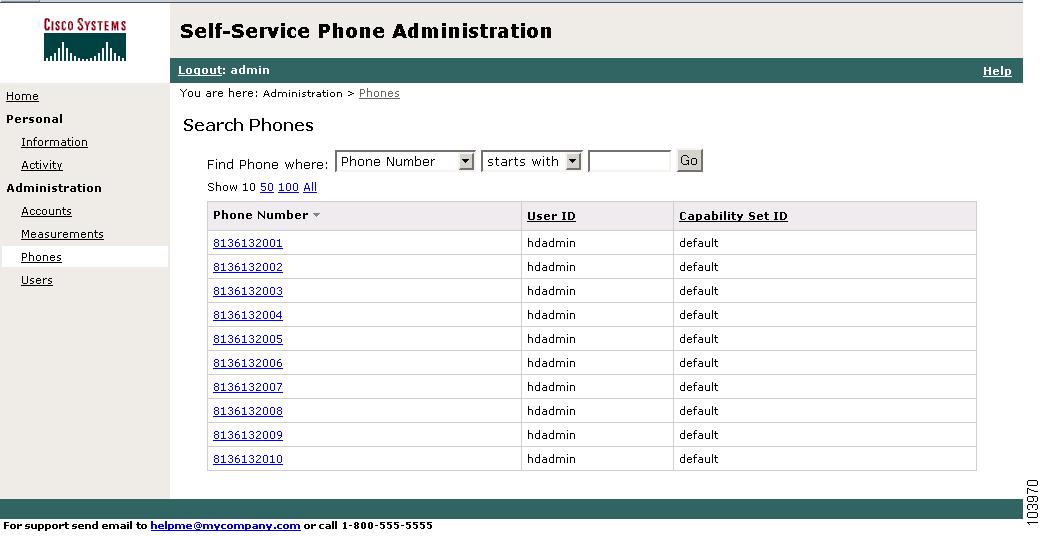
Figure 1-5 Sample Service Provider Administrator Window
Service provider administrators have the highest level of access to Cisco SPA and can perform the following functions:
•
Display and edit personal and account activity
•
Create, modify, search, display, and delete user accounts
•
Create, modify, search, and delete authorization codes
•
Create, modify, search, and delete capability sets
•
Create, modify, search, and delete class of services (CoS)
•
Display and modify Centrex and multiline hunt groups
•
Display system events and activities
•
Display and modify phones
•
Create, search, modify, and delete users
•
Modify phone features
Note
The main users of Cisco SPA are customers of service providers (consisting of account administrators, group administrators, and end users).
About Cisco SPA Account Administrators
Figure 1-6 Sample Account Administrator Window
Account administrators have the second highest level of access to Cisco SPA. They can perform the following functions for phones and users in the account:
•
Display personal and account activity
•
Display user accounts
•
Create, modify, search, and delete authorization codes
•
Create, modify, search, and delete capability sets
•
Create, search, edit, or delete class of services
•
Display and modify Centrex and multiline hunt groups
•
Search and modify phones
•
Create, search, modify, and delete users
•
Display and modify assigned phone features
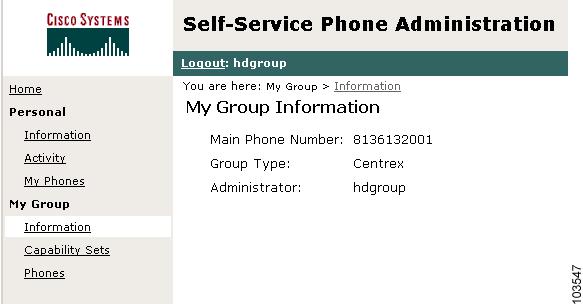
About Cisco SPA Group Administrators (Optional)
Figure 1-7 Sample Group Administrator Window
Group administrators have the third highest level of access to Cisco SPA and can perform the following functions for the phones and users in the multiline hunt (MLH) or Centrex group within an account:
•
Display group information
•
Display and edit personal activity
•
Search and display capability sets
•
Modify groups
•
Search and modify phones in the group
•
Display and modify assigned phone features
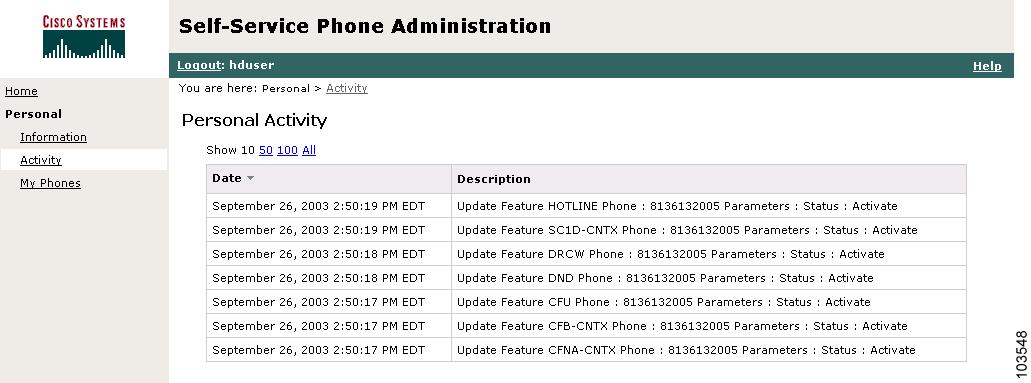
About Cisco SPA End Users
Figure 1-8 Sample End User Window
End users have the lowest level of access to Cisco SPA and can perform the following functions for their assigned phones:
•
Display and edit personal activity
•
Display and modify assigned phone features
About Cisco SPA Security
Cisco SPA supports an HTTP-based interface for a web-based end user self-management GUI. This interface uses a combination of hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) and secure sockets layer (SSL) for security purposes. Access to this interface is through a known URL provided by the service provider. The HTTP connection is described in the "Using the Configuration Tab" section.
Cisco SPA security features consist of the following:
•
Detecting intrusion—Cisco SPA logs and maintains a counter for the number of invalid login attempts for a user ID. The allowed number of consecutive failed passwords is configurable. When this number is exceeded, the user ID is locked and an alarm occurs. For additional information, see the "Using the Configuration Tab" section.
When you log in successfully, the failed login counter is reset.
Service provider and account administrators can unlock a locked user ID. For additional information, see the "Using the Configuration Tab" section.
•
Restricting multiple logins—If you are already logged in to Cisco SPA and attempt to access the login page again from the same browser window, you are redirected to the Cisco SPA home page.
If you are already logged in to Cisco SPA and attempt to access the login page again from a second browser window, your second login is successful, but the earlier session is terminated.
•
Checking access for user levels—Cisco SPA implements up to four levels of security checks before data access is granted:
–
Service provider administrator—Has access to all pages and resources.
–
Account administrator—Has access to all pages except the add and edit account pages. The content displayed is limited to the administrator's account only.
–
Group administrator—Has access to pages pertaining to the group. This level of access allows the administrator to update hunt group types, update phones assigned to the group, and view capability sets in the account.
–
End user—Has access to features on the end user's phones, personal information, and activity logs.
As each level of user is created by the administrators, Cisco SPA automatically sets up these levels of access.
About Supported Phone Features in Cisco SPA
You can view your phone features by using the Cisco SPA GUI windows. The features are also described in the online help which is accessed by clicking Help located at the upper right corner of each window (see the "About Cisco SPA User Levels" section).
Cisco SPA supports the following phone features:
Call Forwarding Features
•
Call Forward Unconditional—Forwards all incoming calls to another telephone number until you explicitly deactivate it.
•
Call Forward Busy—Forwards incoming calls to another telephone number when you are already on a call.
•
Call Forward No Answer—Instructs the network to forward calls when there is no answer from the subscriber phone. A typical forwarding address is to voice mail.
Call Management Features
•
Selective Call Acceptance—Allows you to select which calls to accept.
•
Selective Call Forwarding—Allows you to forward specific calls to another phone number.
•
Selective Call Reject—Allows you to block calls from a selected list of numbers.
•
Distinctive Ring Call Waiting—Allows you to set up different ringing sequences or call waiting indicators for calls received from numbers on a specified list.
Enterprise Features
•
Do Not Disturb—Routes incoming calls either to an announcement or to a special tone.
•
Hotline—Allows you to connect to a predefined phone number when you lift the handset.
•
Warmline—Allows you a predetermined time to dial a number when you lift the handset. If you do not dial a number in that time, you are automatically connected to a predefined telephone number.
Miscellaneous Features
•
Automatic Callback—Calls the last party whom you called without you redialing the telephone number. If the called party is busy, you can hang up and activate this feature; the call is automatically connected when the called party becomes idle.
•
Anonymous Call Rejection—Rejects calls from parties that have set their privacy features to prevent their calling number to be displayed. The called party receives no alert for incoming calls that are rejected. The incoming call is rerouted to a denial announcement, indicating that private numbers are not accepted by the called party.
•
Busy Line Verification—Connects to the operator in order to determine if a called line is in use.
•
Customer Originated Trace—Generates a record of an incoming unwanted call. The data that is recorded is as follows:
–
Date and time of the trace
–
Calling directory number (DN)
–
Unique or nonunique nature of the calling DN
–
Customer's DN
–
Customer's termination ID
–
Answer indication
–
Call-waiting indication
–
Date and time of the call
Speed-Dialing Features
•
One Digit Speed-Calling Features—Assigns a one digit code to frequently called numbers.
•
Two Digit Speed-Calling Features—Assigns a two digit code to frequently called numbers.

 Feedback
Feedback