Table Of Contents
Class of Service Restrictions and
Outgoing Call BarringNational Call Restrictions (Toll Restrictions)
Casual Call (101XXXX) White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
National White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
International White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
Originating Line Information White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
Nature of Dial White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
Account Codes and Authorization Codes
Authorization Codes (Verified Account Codes)
Use of Prompt-Delay Timers for PBX System Connected via IAD
ANI Screening on Incoming Calls
High-Level Flowchart of COS Screening Process
OCB Subscription and Provisioning
OCB Activation and User Options
Class of Service Screening via Black and White List
Interaction with Call Forwarding
Interaction with COS Restriction
Class of Service Restrictions and
Outgoing Call Barring
Revised: March 19, 2007, OL-5906-14The Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch supports class of service restrictions and call barring options on outgoing calls. There are two suites of call restrictions:
•
Class of Service Restrictions
Note
For information on network features, see "Network Features."
For information on subscriber features, see "Subscriber Features."
Class of Service Restrictions
The Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch supports class of service (COS) restrictions on certain call types. COS restrictions prevent certain types of calls from being completed from a particular line or station. The service provider can provision COS restrictions for individual subscribers, groups of subscribers, trunk groups (TGs), automatic number identification (ANI), and authorization codes. When a call is blocked, the calling party receives a blocking treatment such as reorder tone or announcement. Number blocking is activated/deactivated and administered by the service provider on a per-line or per-group-of-lines basis. The service provider can prohibit calls based on dialing plans and call types.
Certain types of calls are exempt from COS and OCB restrictions:
•
Emergency calls
•
Call types on the NOD exception list (NOD restrict list)—The service provider can provision an exception list to override COS and OCB screening on certain types of calls. The types of calls on this list can include, for example, emergency calls, toll-free calls, and so forth. The applicable types of calls are listed in the NATURE-OF-DIAL (NOD) table, and the specific exceptions are provisioned in the NOD-RESTRICT-LIST table. These exceptions are applicable at the switch level (all office codes) and cannot be specified for individual subscribers.
Note
A complete list of NOD values is provided in the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Command Line Interface Reference Guide.
This section covers the following topics:
•
National Call Restrictions (Toll Restrictions)
•
Casual Call (101XXXX) White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
•
National White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
•
International White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
•
Originating Line Information White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
•
Nature of Dial White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
•
Account Codes and Authorization Codes
•
ANI Screening on Incoming Calls
•
High-Level Flowchart of COS Screening Process
National Call Restrictions (Toll Restrictions)
The national call restrictions are used to allow or restrict calls to destinations based on a predefined grouping of local lines, LATA, state, country, or group of countries. Customers can subscribe to one of the following:
•
All North American Numbering Plan (NANP) calls—All calls within NANP are allowed (can be applied only to calls originated in NANP).
•
National only—Only calls terminating within the country are allowed.
•
Intrastate only—Only calls within the state are allowed.
•
IntraLATA only—Only calls within the LATA are allowed, including intraLATA toll calls (can be applied only to calls originated in NANP).
•
Local only—Only local calls are allowed.
For NANP operator calls (0+NPA-NXX-XXXX), NANP call restriction screening is not performed, even if the NANP call restriction is provisioned in the cos-restrict table for the calling party.
Casual Call (101XXXX) White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
The casual call white and black lists are used to allow or restrict calls dialed with a casual code prefix (101XXXX). The COS can be set up to perform either white list screening or black list screening, but not both. The following restrictions can be provisioned:
•
No casual calls allowed—User cannot make 101XXXX calls.
•
All casual calls allowed—User can make 101XXXX calls.
•
101XXXX white list—Only a predefined set of XXXX codes can be dialed.
•
101XXXX black list—All XXXX codes can be dialed except for a predefined set.
For NANP operator calls (0+NPA-NXX-XXXX) and international operator calls (01+CC+NN), casual-call screening is not performed, even if the casual-call restriction is provisioned in the cos-restrict table for the calling party.
National White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
The national white and black lists are used to allow or block national calls based on a predefined list. The COS can be set up to perform either white list screening or black list screening, but not both. The following restrictions can be applied:
•
No restrictions.
•
National white list—Only calls on a predefined prefix list can be called. The list could consist of full or partial DNs (for example, NDC or NDC-EC codes, or NPA or NPA-NXX codes for North America).
•
National black list—All calls on a predefined prefix list are blocked. The list could consist of full or partial DNs (for example, NDC or NDC-EC codes, or NPA or NPA-NXX codes for North America).
For NANP operator calls (0+NPA-NXX-XXXX), NANP call restriction screening is not performed, even if the NANP call restriction is provisioned in the cos-restrict table for the calling party.
International calls within NANP will be screened against the national white and black lists, and not against the international white and black lists.
International White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
The international white and black lists are used to allow or block calls made outside the country. The COS can be set up to perform either white list screening or black list screening, but not both. The following restrictions can be applied:
•
No international calls allowed—Does not allow any international calls.
•
International white list—Allows only those calls that have a country code (CC) noted in the white list.
•
International black list—Does not allow any calls that have a CC noted in the black list.
•
All international calls allowed—No restrictions are applied on international calls.
For international operator calls (01+CC+NN), international call restriction screening is not performed, even if the international call restriction is provisioned in the cos-restrict table for the calling party.
International calls within NANP will be screened against the national white and black lists, and not against the international white and black lists.
Originating Line Information White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
The originating line information (OLI) white and black lists (also referred to as II white and black lists) are used to allow or block calls made from certain types of lines, such as hotels, prisons, and so forth. This is a Tandem call screening function. The COS can be set up to perform either white list screening or black list screening, but not both. The following restrictions can be applied:
•
No OLI screening performed.
•
Use the II white/black screening list as a white list—Allows the specified OLI types to place calls.
•
Use the II white/black screening list as a black list—Blocks calls from the specified OLI types.
Note
II digits 24 and 25 are exempt from COS screening (these are translated toll-free 8XX calls from POTS lines).
Nature of Dial White and Black Lists (Number Blocking)
The nature of dial (NOD) white and black lists are used to allow or block certain categories of calls, such as casual dialing (dialing around), time/weather, international operator assistance, premium calls, and so forth. The following restrictions can be applied:
•
No NOD screening performed.
•
Use the NOD white/black screening list as white list—Allow the specified NOD types to be called.
•
Use the NOD white/black screening list as black list—Block calls to the specified NOD types.
Note
For calls that originate from locations inside NANP, to block calls terminating outside the country but inside NANP (for example, calls from the United States to Canada), use the INTL-WZ1 token in the NOD White Black List.
Tip
All call types can be placed on the NOD White Black List.
Note
Refer to the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Command Line Interface Reference Guide for a complete list of NOD types.
Blocking Flags
The service provider can provision the blocking flags listed below. These have the same effect as provisioning the NOD black list for the same feature.
Tip
All call types that can be blocked using blocking flags can also be blocked by placing that call type on the NOD black list. Cisco recommends using the NOD black list.
•
Block 900 (premium) calls—Blocks all calls of the form 1-900-XXX-XXXX.
•
Block 976 (local information) calls—Blocks all calls of the form 976-XXXX or NPA-976-XXXX.
•
Block info calls—Blocks all calls to information services.
•
Block time/weather calls—Blocks all calls to time and weather services.
•
Block directory assistance (DA) calls—Blocks all directory assistance calls of the form 411, 1+411 or NPA-555-XXXX.
•
Block NANP operator assistance calls—Blocks all calls to an operator within NANP, specifically, 0 calls and 0+ calls (0+NPA-NXX-XXXX).
•
Block international calls—The behavior of this flag depends upon the location of the originating station:
–
For call that originate from locations outside NANP, this flag blocks all calls terminating outside the country.
–
For calls that originate from locations inside NANP, this flag blocks all calls terminating outside NANP.
Note
For calls that originate from locations inside NANP, to block calls terminating outside the country but inside NANP (for example, calls from the United States to Canada), use the INTL-WZ1 token in the NOD White Black List.
•
Block international operator assistance calls—Blocks all calls to an operator outside the country, including 01+ calls (01+CC+NN).
Account Codes and Authorization Codes
The Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch supports account code and authorization code features as described in this section.
Note
The system does not support account and authorization codes for ISDN trunks in this release.
Account Codes (Nonverified)
Account codes provide collection of 2 to 12 digits to allow call charging to user projects, departments or special accounts. The user activates account codes by dialing a number (usually a long-distance call) that requires an account code for call completion. A prompt tone is issued after the digits are dialed. The user then enters an account code of a specified length. These account codes are not verified. (See the next section for verified account codes.) The account code is provided in the call detail records (CDRs) associated with the call. Account codes are not collected for any of the following call types:
•
National operator calls
•
International operator calls
•
Local calls
The system has a provisionable token that can be used to introduce delay (up to one second) before playing the account-code prompt.
Authorization Codes (Verified Account Codes)
Authorization codes, also referred to as verified account codes, can be used by an intended user or group to override certain COS calling restrictions. For example, long-distance calls could be restricted on certain phones, such as phones in a lobby or conference room, unless the user knows a valid authorization code. When an authorization code is required, the user is prompted via a tone. The user can override the restriction by dialing an authorization code that has enough privileges to make long-distance calls. Authorization codes can be from 3 to 23 digits in length.
The user takes the following action when an authorization code is required:
•
The user goes off hook and receives a dial tone.
•
The user dials a DN. The system determines that an authorization code is required and returns a confirmation tone (2 beeps) to the user.
•
The user enters the digits for the authorization code.
–
If the user enters the correct authorization code, the call is screened based on COS assigned to that authorization code. If this authorization code has appropriate privileges, the call is allowed.
–
If the user enters a code that is incorrect, does not have appropriate privileges for the call being attempted, or if the associated account is invalid, the call is diverted to a preselected announcement.
Note
Authorization codes can be used to override call category restrictions, but cannot be used to override black/white lists. For example, an authorization code can be used to override "no international calls allowed", but cannot be used to override any type of black/white list.
The system has a provisionable token that can be used to introduce delay (up to one second) before playing the authorization-code prompt.
Use of Prompt-Delay Timers for PBX System Connected via IAD
When an account code or authorization code is required, a caller connected to an IAD or MGW is provided with a prompting tone. However, if a caller is connected to a PBX that is connected to an IAD, the PBX might not be capable of cutting through the prompting audio quickly enough for the caller to actually receive the prompt. To help resolve this problem, the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch has provisionable tokens that can be used to introduce delay before playing the account-code or authorization-code prompt. When this prompt delay is provisioned appropriately, PBX users are able to hear the confirmation tone when they make calls requiring an access code. The option to delay the MGCP RQNT message applies only to CAS trunk groups without main-subscriber, or CAS trunk groups with main-subscriber whose category is PBX. The delay is provisionable via CLI using the following tokens in the CA-CONFIG table:
•
ACCT-CODE-PROMPT-DELAY, for introducing delay prior to playing the account code prompt.
•
AUTH-CODE-PROMPT-DELAY, for introducing delay prior to playing the authorization code prompt.
Note
The prompt-delay feature is not supported for SS7, H.323, ISDN, or SIP endpoints, or for analog subscriber lines.
ANI Screening on Incoming Calls
Automatic number identification (ANI) screening is a service commonly found in Tandem switches, and is used for long-distance access service. The ANI is the number of the calling party (NDC + EC + DN). Full or partial ANIs can be specified for screening. The ANI screening feature validates the ANI on incoming trunk group (TG) calls from the public switched telephone network (PSTN) before routing. All ANIs to be screened are stored in the Feature Server database. If an ANI is not available, or does not appear in the Feature Server ANI table, the call is considered as a casual call. The TG restrictions are checked to see if casual calls are allowed. If casual calls are not allowed, the call is denied and routed to an announcement. If the ANI exists in the table, the ANI status is checked next. The ANI status can either be allowed or blocked. If the status is blocked, the call is blocked and routed to an announcement. COS can also be applied on an ANI basis.
COS Restriction Priorities
For any call, it is possible that a combination of call categories are applicable. Under these conditions, the system performs Black White List screening first. If the call passes (is allowed from) Black White List screening, then the system applies COS restriction screening.
COS restrictions can be assigned to any ANI, authorization code, trunk group, or POTS subscriber. When multiple COS restrictions apply to a trunk call, the system uses the order of precedence as follows:
1.
Use the COS assigned to ANI if found in the ANI screening table.
2.
If not found in ANI screening table, use the COS assigned to the TG.
3.
If an authorization code is required, then use the COS assigned to authorization code.
When a call is blocked due to COS screening, the call event shows which type of screening blocked the call. The service provider can provision the treatment of blocked calls, and can include, for example, playing an announcement or sending a cause code to the originator.
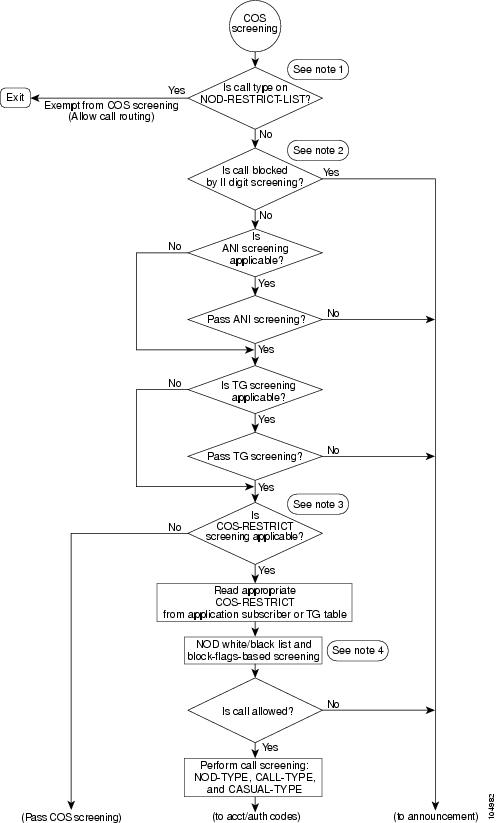
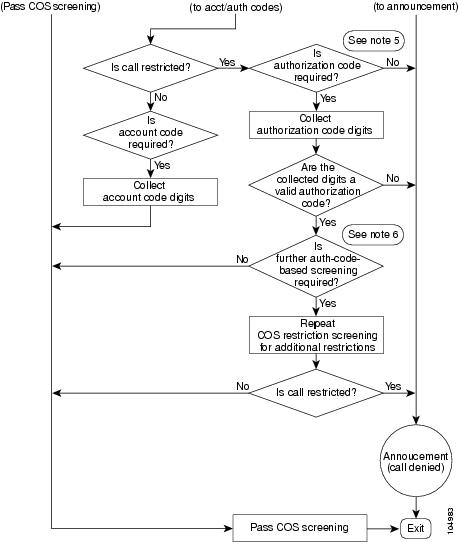
High-Level Flowchart of COS Screening Process
Figure 5-1 and Figure 5-2 show a high-level flowchart of the COS screening process. The flowchart is split into two parts (two drawings) for easier viewing.
Figure 5-1 COS Screening Process (Part 1)
Figure 5-2 COS Screening Process (Part 2)
Notes for Figure 5-1 and Figure 5-2:1.
Call types on the NOD-RESTRICT-LIST are exempt from COS screening.
2.
II = 24 and 25 are reserved for translated toll-free calls and are exempt from II screening.
3.
COS-RESTRICT screening is applicable if either the subscriber or the TG has an associated COS-RESTRICT-ID.
4.
Block flags are as follows:
–
BLOCK-900
–
BLOCK-976
–
BLOCK-DA
–
BLOCK-INFO
–
BLOCK-TW
–
BLOCK-INTL
–
BLOCK-NANP-OPER-ASSIST
–
BLOCK-INTL-OPER-ASSIST
Note
NOD-WB-LIST has a higher precedence that the block flags during screening.
5.
The initial check of the authorization code is based on the provisioned value for AUTH-CODE-ALLOW in the applicable COS-RESTRICT table.
6.
The additional check of authorization code is based on the COS-RESTRICT-ID provisioned in the applicable AUTH-CODE table.
Outgoing Call Barring (OCB)
The outgoing call barring (OCB) feature allows an individual subscriber or business group administrator to restrict certain types of outgoing calls. Once the OCB feature is provisioned and activated on a calling line, the OCB restrictions are transparently invoked on all outgoing calls.
This section covers the following topics:
•
OCB Subscription and Provisioning
•
OCB Activation and User Options
•
Class of Service Screening via Black and White List
Note
For Release 4.4.1, the OCB feature has been enhanced with additional provisionable options. If your system is running Release 4.4.1, and you would like to use those additional options, see the Enhanced Outgoing Call Barring feature module in the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch documentation set.
Note
The class of service (COS) feature is an optional functionality (subset) of OCB. The service provider can provision the COS feature by itself, without the OCB feature. The details are discussed later in this section.
OCB Subscription and Provisioning
The service provider sets up OCB service at the request of the subscriber. There are a number of service provider provisionable parameters that affect the behavior of the feature on the subscriber line:
•
Vertical service code (VSC)—ASCII strings that the user must enter to access OCB activation, deactivation, and interrogation options (for example, *54*, #54* and *#54#).
Note
The VSCs used throughout this document are typical values. The service provider can provision these values with any unique ASCII string up to five characters long. For a complete list of preprovisioned VSCs, see the Vertical Service Code appendix in the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Command Line Interface Reference Guide.
•
Personal identification number (PIN)—A digit string that the user must enter for authorization to set OCB activation and deactivation options from his or her local phone.
•
PIN length (PIN-LEN)—The number of digits required for a valid PIN (can be provisioned as 1 to 8 digits).
Note
The PIN and PIN-LEN are provisioned by the service provider. They cannot be provisioned by the user via the handset, and cannot be changed by the user.
•
Allowed activation/deactivation attempts and lockout parameters—Parameters can be provisioned to limit the number of times that a user can enter incorrect data or PIN within a specified time. If the limit is exceeded, the system ignores further activation and deactivation attempts for a provisionable length of time (lockout period).
Detailed provisioning steps for these options are provided in the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Provisioning Guide. Additional reference information on the provisionable parameters is available in the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Command Line Interface Reference Guide.
OCB Activation and User Options
OCB activation (OCBA) allows a user to activate OCB and select various call barring options on the handset (local phone). A user does this by dialing *54*K-VALUE<PIN># (the trailing # is optional to signify the end of entry). The parameters are defined as follows:
•
*54* is the VSC the user enters on the handset to access the OCBA feature.
•
K-VALUE is the parameter that determines the type of outgoing calls to be barred:
–
K-VALUE=1: all outgoing calls barred
–
K-VALUE=2: domestic long-distance and international outgoing calls barred
–
K-VALUE=3: international outgoing calls barred
•
<PIN> is the assigned private digit string that the user must enter. A success announcement is given on a successful activation, and an error announcement, indicating the type of error, is given if activation is unsuccessful.
Note
The K-VALUE can be changed only when the OCB feature is in the deactivated state.
If a user enters incorrect data or PIN repeatedly in a specified time period, the system can lock out further activation or deactivation attempts, as described in the "OCB Subscription and Provisioning" section.
The following user actions are invalid, and the system provides an appropriate error announcement:
•
The user enters a value for K-VALUE that is not 1, 2, or 3.
•
The user enters an incorrect PIN.
•
The user is not provisioned for the OCB feature.
OCB Deactivation
OCB deactivation (OCBD) allows a user to deactivate all OCB on the handset. The user does this by dialing #54*K-VALUE<PIN>#. The parameters are defined as follows:
•
#54* is the VSC the user enters on the handset to access the OCBD feature
•
K-VALUE must be entered as 1, 2, or 3. However, the actual value is ignored by the system, because OCBD deactivates all call barring.
•
<PIN> is the same as for OCBA.
A success announcement is given on a successful deactivation, and an error announcement, indicating the type of error, is given if deactivation is unsuccessful.
Note
Refer to the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Command Line Interface Reference Guide for provisioning details.
If a user enters incorrect data or PIN repeatedly in a specified time period, the system can lock out further activation or deactivation attempts, as described in the "OCB Subscription and Provisioning" section.
OCB Interrogation
OCB interrogation allows a user to check the level of outgoing call restrictions on the handset. The default dial string for OCB interrogation is *#54#. No PIN is required to use this feature. The system provides an appropriate announcement to the user.
OCB Invocation and Screening
For a calling party that is subscribed to OCB, and has activated the feature, OCB is invoked for every call made after the called party digits are dialed.
OCB Lockout Behavior
The LOCK-OUT, TO (timeout), and FAIL-CNT (fail count) tokens in the feature table are intended to prevent unauthorized changes or bypassing of OCB screening. If a user repeatedly enters the password or other OCBA/OCBD data incorrectly on the handset, the system can lock the line against both OCBA and OCBD. These tokens control the lockout behavior as described in Table 5-1.
Tip
Note that there is no service lockout when either the TO or FAIL-CNT token is set to zero.
Class of Service Screening via Black and White List
The Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch supports class of service (COS) screening, which is provisioned and assigned by the service provider, and cannot be controlled or deactivated by individual subscribers. The service provider can provision a list of directory numbers (DNs) to appear on a black list or a white list as follows:
•
Black-listed calls do not undergo further screening, and all calls on this list are rejected.
•
White-listed calls are subject to additional normal OCB restrictions based on call type.
Note
The service provider provisions the desired COS restrictions for all subscribers that have the OCB feature. This ensures that the black and white list restrictions are in effect, even if the user deactivates OCB.
Note
Separate black and white lists are maintained for local/national calls and international calls.
•
National White Black Lists are used to allow or restrict calls to specified destinations within a region or within a local area.
Note
A region is a country or numbering plan area. The national White Black List identifies a set of national destination codes (NDCs) and/or exchange codes (ECs) to be allowed or blocked.
Outgoing calls are restricted as follows:
–
No restrictions (default), except that all calls are subject to the additional OCB restrictions.
–
National white list—Allows calls within a predefined list, except that all calls are subject to the additional OCB restrictions.
–
National black list—Blocks all calls within a predefined list.
Note
National call restrictions do not apply to operator calls. This is true even if national call restriction is provisioned in the cos-restrict table for the calling party.
•
International black/white lists are used to allow or restrict calls made to specific country codes. Outgoing calls are restricted as follows:
–
No international calls allowed—Does not allow any international calls
–
International white list—Allows those calls that have a prefix noted in the white list, except that all calls are subject to the additional OCB restrictions
–
International black list—Does not allow any calls that have a prefix noted in the black list
–
All international calls allowed—No restrictions are applied on any international calls, except that all calls are subject to the additional OCB restrictions
Note
International call restrictions do not apply to operator calls. This is true even if international call restriction is provisioned in the cos-restrict table for the calling party.
The service provider can provision an exception list to override COS and OCB screening on certain types of calls. The types of calls on this list can include, for example, emergency calls, toll-free calls, and so forth. The applicable types of calls are listed in the NATURE-OF-DIAL (NOD) table, and the specific exceptions are provisioned in the NOD-RESTRICT-LIST table. These exceptions are applicable at the switch level (all office codes) and cannot be specified for individual subscribers.
Note
A complete list of NOD values is provided in the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Command Line Interface Reference Guide.
OCB Feature Interactions
The section describes the interactions of OCB with other features.
Interaction with Call Forwarding
The interaction of OCB and call forwarding features depends upon the sequence in which they are activated.
Note
In this section, "CFx" refers to any of the call forwarding features, CFU, CFB, or CFNA.
•
If OCB is activated prior to CFx activation—OCB screening is performed on each DN the user enters when attempting to activate CFx. Successful CFx activation depends on the existing OCB K-VALUE and the forward-to DN:
–
If the existing OCB K-VALUE is set to block calls to the forward-to DN, then the system does not allow CFx activation. The user receives an error announcement.
–
If the OCB K-VALUE allows calls to this DN, then the CFx activation process continues. Once the CFx activation attempt to a specific DN is accepted by the system, it is applicable permanently regardless of any future OCB K-VALUE changes. That is, future changes to the OCB K-VALUE have no effect on CFx invocation. CFx to this DN can be deactivated by the user in the normal manner (#XX#).
•
If CFx is activated prior to OCB activation—The user can activate the OCB feature, or change the OCB K-VALUE, regardless of the existing CFx feature. However, invocation of OCB depends upon the type of call:
–
User-dialed calls—User-dialed calls can be blocked by OCB (depending on the K-VALUE).
–
Forwarded calls—CFx remains active as originally set up by the user, therefore, calls forwarded by the CFx feature are not blocked using OCB screening.
Interaction with COS Restriction
The COS feature is an optional functionality (subset) of OCB. To use the COS functionality, the service provider must provision individual COS restriction settings for the subscriber line. Table 5-2 lists additional details about the interaction of COS and OCB.
Table 5-2 Interactions between COS and OCB Features
Billing DataUser-controlled screening only
OCB
Do not provision individual COS restrictions. Leave all COS table tokens set to their default values.
OCB
User-controlled screening
and network (office) screeningOCB 2
Provision individual COS restriction tables.
OCB
Network (office) screening only
COS
Provision individual COS restriction tables.
COS
1 The COS restriction tables include the following: COS-RESTRICT, NATIONAL-WB-LIST, INTL-WB-LIST, NOD-RESTRICT-LIST, and NOD-WB-LIST.
2 The COS feature is contained in the OCB feature.

 Feedback
Feedback