Table Of Contents
Understanding the Subnet Manager
Understanding Subnet Manager Routing Terms
Minimum Contention, Shortest Path, and Load Balancing Algorithm
Deterministic Source-Based Routing Algorithm
Configuring Your Network For Optimal Routing
Viewing Subnet Manager Properties
Configuring Subnet Manager Priority
Configuring a Subnet Manager Sweep Interval
Configuring a Subnet Manager Response Timeout
Configuring a Subnet Manager Master Poll Interval
Configuring Subnet Manager Master Poll Retries
Configuring the Maximum Number of Active Subnet Managers
Configuring the LID Mask Control
Configuring Switch Link HoQ Life
Configuring Wait Report Response
Configuring Subnet Agent MAD Queue Depth
Viewing Database Synchronization Details
Hexadecimal to Binary Conversions
Examples of Valid P_Key Values
Understanding how P_Keys are Saved
Configuring IPoIB Broadcast Multicast Groups
Viewing Multicast Group Details
Viewing Multicast Member Details
Viewing Switch Route Element Details
Configuring Subnet Manager Properties
Configuring Subnet Manager Priority
Configuring the Sweep Interval
Configuring the Master Poll Interval
Configuring the Number of Master Poll Retries
Configuring Switch Link HoQ Life
Configuring Wait Report Response
Configuring Subnet Agent MAD Queue Depth
Configuring Database Synchronization
Enabling Subnet Manager Database Synchronization
Configuring the Maximum Number of Backup Subnet Managers to Synchronize
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Timeout Value
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Value
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Period
Configuring the New Session Delay
Configuring the Resynchronization Interval
Viewing the Database Synchronization State
Adding Full Members to a Partition
Adding Available Members to a Partition
Adding Unavailable Members to a Partition
Adding Limited Members to a Partition
Adding Available Limited Members
Viewing Multicast Group Details
Viewing Multicast Group Members
Viewing Subnet Managers Information
Enabling InfiniBand Port Performance Management
Disabling Performance Management
Creating a Connection to Monitor
Viewing Connection Monitor Counters
Viewing Port Counters of Connections
Viewing Cumulative Port Counters
Configuring Port Monitoring Thresholds
Resetting Counters on All Ports on a Node
Resetting Counters on All Ports in a Connection
Resetting All Counters in a Subnet
Viewing Internal Server Switch Components and TCAs
Viewing Subnet Management Agents
Viewing Subnet Manager Node Details
Viewing Subnet Manager Switch Details
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Switch Cap Details
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Ports(1) Details
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Ports(2) Details
Viewing Subnet Manager Multicast Details
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Linear Forwarding Table Details
Viewing the Subnet Manager Agent Partition Details
InfiniBand Menu Tasks
This chapter describes the InfiniBand menu tasks for Element Manager and contains these sections:
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Properties
•
Viewing Database Synchronization Details
•
Configuring IPoIB Broadcast Multicast Groups
•
Viewing Multicast Group Details
•
Viewing Multicast Member Details
•
Viewing Switch Route Element Details
•
Configuring Subnet Manager Properties
•
Configuring Database Synchronization
•
Viewing the Database Synchronization State
•
Viewing Subnet Managers Information
•
Enabling InfiniBand Port Performance Management
•
Viewing Subnet Management Agents
Note
This section provides information to familiarize you with the InfiniBand technology. For hardware-specific information, consult the relevant hardware documentation.
Understanding InfiniBand
InfiniBand is a high speed, high density serial interconnect that increases CPU utilization, decreases latency, and eases the management problems of data centers. The term "InfiniBand" refers to the entire hardware, communication, and management infrastructure. Use of this technology increases the communication speed between the following:
•
CPUs
•
Devices within servers
•
Subsystems located throughout a network.
InfiniBand combines high-speed hardware, specialized protocols, and Remote Data Memory Access (RDMA) techniques to increase CPU utilization and decrease latency. Operations of the InfiniBand Architecture are managed by the Subnet Manager.
InfiniBand Components
One or more of the following hardware components may be used to maximize your server network:
•
InfiniBand switch—Passes traffic between InfiniBand-capable devices over the InfiniBand network
•
Host channel adapters (installed in host)—Serves as an InfiniBand version of a network interface card (NIC) to connect the host to the InfiniBand network
•
Ethernet gateway—Provides Ethernet connectivity to an InfiniBand network
•
Fibre Channel gateway—Provides Fibre Channel connectivity to an InfiniBand network
Protocols
InfiniBand requires a new set of protocols. All of the necessary protocol drivers are included with the Server Switch.
IPoIB
The IP over InfiniBand (IPoIB) link driver provides standardized IP encapsulation over InfiniBand fabrics. IPoIB can transparently use IP over InfiniBand technology, which is similar to the way that IP runs over Ethernet.
You can use the IPoIB driver to perform an address resolution and manage the multicast membership.
SDP
The Sockets Direct Protocol (SDP) is a transparent protocol used on InfiniBand networks to allow sockets-based applications to take advantage of the RDMA performance over an InfiniBand network. SDP reduces the amount of software running inside a process context. The zero-copy SDP support enables databases, application servers, and CPUs to operate more efficiently because the databases spend less time waiting for work, the application servers spend less time waiting for responses, and the CPUs have more cycles free for other work.
SRP
The SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP) is an upper-layer storage protocol for InfiniBand that runs SCSI commands across RDMA-capable networks for InfiniBand hosts to communicate with Fibre Channel storage devices. This protocol allows InfiniBand hosts to natively send SCSI commands as if the storage was directly attached.
The SRP protocol uses an RDMA communication service that provides communication between pairs of consumers; it uses messages for control information and RDMA operations for data transfers.
The SRP protocol is used only if you have a Fibre Channel Gateway installed in your InfiniBand system.
uDAPL
The user Direct Access Programming Library (uDAPL) is a standardized user mode API that natively supports InfiniBand fabrics. uDAPL performs name-to-address translations, establishes connections, and transfers data reliably. The primary responsibilities of uDAPL are: connection management and low latency data transfer and completion
Architectural Elements
The following structures serve as foundational elements of InfiniBand architecture:
•
RDMA
•
Services
RDMA
InfiniBand uses RDMA technology. RDMA allows one computer to place information directly into the memory of another computer. RDMA allows user space applications to directly access hardware and zero-copy data movement.
A combination of hardware and software allows user space applications to read and write the memory of a remote system without kernel intervention or unnecessary data copies. This feature results in lower CPU utilization per I/O operation and more efficient use of machine resources because applications place most of the messaging burden upon InfiniBand's high-speed network hardware.
Queue Pairs
The queue pair (QP) is one of the primary architectural elements of InfiniBand. In InfiniBand, communication occurs between queue pairs, instead of between ports.
A queue pair is an addressable entity that consists of two work queues: a Send work queue and a Receive work queue. The Channel Adapter hardware arbitrates communication by multiplexing access to the send queue or demultiplexing messages on the receive queue.
Note
A verb is used to define the functionality of the Host Channel Adapter (HCA). A verb consumer refers to the direct user of the verb.
A work queue provides a consumer with the ability to queue up a set of instructions that are executed by the Channel Adapter. There are two types of work queues: Send work queues (outbound) and a receive work queues (inbound). Together these work queues create a queue pair.
A connection is made by linking a local queue pair to a remote queue pair. Applications do not share queue pairs; once you set them up, you can manage them at the application level without incurring the overhead of system calls.
Send and receive work queues have these characteristics:
•
Always created as a pair
•
Always remain a pair
•
Known as QPs
•
Identified by a queue pair number, which is within the Channel Adapter.
Queue pairs have:
•
A region of memory to be used as buffers (numbers of queue pairs are only limited by memory).
•
A key that must match on each incoming packet (the Q_Key) to verify the validity of the packet,
•
(Potentially) a partition key, which specifies the portion of the fabric that this queue pair may access.
The queue pair is the mechanism by which you define quality of service, system protection, error detection and response, and allowable services.
Each queue pair is independently configured for a particular type of service. These service types provide different levels of service and different error-recovery characteristics as follows:
•
Reliable connection
•
Unreliable connection
•
Reliable datagram
•
Unreliable datagram
Once the fabric connections are discovered, queue pairs and protection domains are established, the type and quality of service are defined for each queue pair, and the fabric operates reliably and securely at full QoS without impacting system hardware or software resources.
Understanding the Subnet Manager
The Subnet Manager configures and maintains fabric operations. There can be multiple Subnet Managers, but only one master. The Subnet Manager is the central repository of all information that is required to set up and bring up the InfiniBand fabric.
The master Subnet Manager does the following:
•
Discovers the fabric topology.
•
Discovers end nodes.
•
Configures switches and end nodes with their parameters, such as the following:
–
Local Identifiers (LIDs)
–
Global Unique Identifier (GIDs)
–
Partition Key (P_Keys)
•
Configures switch forwarding tables.
•
Receives traps from Subnet Management Agents (SMAs).
•
Sweeps the subnet, discovering topology changes and managing changes as nodes are added and deleted.
Subnet Management Agents
Subnet Manager Agents are part of the Subnet Manager. A Subnet Manager Agent is provided with each node and process packets from the Subnet Manager.
If a Subnet Manager is elected master, all of its components, including Subnet Agent, are implicitly elected master. If a Subnet Manager ceases to be the master, all of its components cease responding to messages from clients.
Subnet Manager Hot Standby
The master and slave Subnet Managers can be synchronized so that the information in the master is carried over to the slave if a fail-over occurs. See the "Enabling Subnet Manager Database Synchronization" section to configure the hot-standby Subnet Manager.
The hot standby/database synchronization feature is used to synchronize the databases between Subnet Managers running on separate chassis.
The Subnet Manager maintains a database in the volatile memory of the master Subnet Manager. Database synchronization is accomplished in two stages:
•
Cold Synchronization—This stage is initiated by the master Subnet Manager when it is ready to start a synchronization session with a standby Subnet Manager. In this stage, tables that are not synchronized are copied from the master Subnet Manager to the standby Subnet Manager.
•
Transactional Synchronization—This stage is entered following the successful completion of the cold synchronization stage. In this stage, all database update transaction requests that are processed by the master, are replicated to the standby Subnet Manager.
A standby Subnet Manager can become the master in any of these situations:
•
The node that is running the current master Subnet Manager crashes.
•
Partitioning of the subnet (such as due to a link failure) takes place.
•
Graceful shutdown of the master (such as for maintenance purposes) takes place.
The following occurs in the event of a failure:
•
The standby Subnet Manager becomes the new master.
•
The new master rebuilds the database from information retrieved during the subnet discovery phase.
•
Existing LID assignments are retained, where possible.
•
All ports are reset to force them to rejoin multicast groups, advertise the services again, request event forwarding again, and reestablish connections.
•
A SlaveToMaster event trap is generated to trigger any necessary processing by external management applications.
Subnet Manager Routing
There are two different concepts associated with InfiniBand routing:
•
Routing internally within a switch (hops between switch chips)
•
Routing between whole switches (hops between nodes)
Note
This process is also referred to as routing between switch elements.
Internal switch routing can be configured to provide the highest performance in passing traffic and to minimize the threat of congestion within the switch.
The routing process is as follows:
Step 1
The Subnet Manager discovers all the InfiniBand switch chips in the network.
Step 2
The Subnet Manager groups the internal switch chips within each chassis into a switch element.
Step 3
The Subnet Manager process continues until all the InfiniBand switches are grouped into switch elements.
Step 4
After all the switch chips are grouped, the Subnet Manager routes the switch elements according to the routing algorithm discussed in the "Minimum Contention, Shortest Path, and Load Balancing Algorithm" section.
Step 5
The internal network of each InfiniBand switch is then routed based on the best algorithm for each switch element.
Multiple Paths
The Subnet Manager allows you to define the Local Identifier Mask Control (LMC) value per subnet. The default value of the LMC is 0. By default, only one Local Identifier (LID) is assigned to each host port.
Once the LMC value has been assigned, the Subnet Manager will route different paths for each LID associated with the same host port. The result of these paths is based on the applied routing algorithm.
Understanding Subnet Manager Routing Terms
The following terms are important to understand before distinguishing the various types of algorithms that the Subnet Manager uses for routing:
•
Tolerance is used when deciding if a particular path is better in distance than the already selected path. You can choose the tolerance to be used for the shortest path calculation as follows:
–
If the tolerance is set to 0, a pair of distinct paths to an endport are said to be of equal distance if the number of hops in the paths is the same.
–
If the tolerance is set to 1,a pair of distinct paths to an endport are said to be of equal distance if the difference in their hop count is less than or equal to one.
•
Contention is declared for every switch port on the path that is already used for routing another LID associated with the same host port.
Minimum Contention, Shortest Path, and Load Balancing Algorithm
The Minimum Contention, Shortest Path and Load Balancing algorithm is used by default to route between the switch elements and between the internal InfiniBand switch chips within each switch element.
The following process shows how the algorithm makes the calculation:
Step 1
The shortest path for each of the host ports is calculated.
Step 2
Contention is calculated for all the available paths that are within the (shortest path + tolerance) distance.
a.
The path with the least contention is selected.
b.
If two paths have the same contention, the path with less distance is selected.
c.
If two paths have the same contention and the same distance, the port usage count is used to provide load balancing over the two paths. The usage count is a measure of how many LIDs have been configured to use that particular port.
Deterministic Source-Based Routing Algorithm
The Deterministic Source Based Routing algorithm is used in some high-performance computing environments where the requirements may need to be more stringently defined. An administrator can identify the exact route that a given port and LID takes for traversing through the network.
Currently, only the internal routing for the Cisco SFS 7008 (a 96-port switch) supports this routing scheme. See the Cisco SFS 7008 Hardware Guide, or contact technical support for more information.
Configuring Your Network For Optimal Routing
For optimal routing, we recommend that you follow these steps:
•
Create equal paths between switch elements
•
Determine the first path that will be discovered
We recommend that InfiniBand switch elements be connected so that all paths between any pair of switch elements are the same distance (same number of hops), if possible. This process enables you to obtain the optimal paths using the default tolerance of 0. If the paths have different lengths, then the tolerance value will need to be determined.
The Subnet Manager Routing Algorithm selects the first best path that it finds. If multiple paths with the same properties are available, then the first of these paths found is the one that is selected. It is possible to set up the cabling between switch elements to force the algorithm to prioritize certain paths. Depending on the network requirements, the prioritized paths can either be concentrated on a particular switch element or spread across multiple switch elements to improve fault tolerance.
Viewing Subnet Manager Properties
To view Subnet Manager properties, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Select a subnet.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab. Table 8-1 describes the fields.
Configuring Subnet Manager Priority
To configure Subnet Manager priority, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Select the value in the Priority column and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring a Subnet Manager Sweep Interval
To configure a Subnet Manager sweep interval, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Select the value in the Sweep Interval column and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring a Subnet Manager Response Timeout
To configure Subnet Manager response timeout, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Response Timeout column and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring a Subnet Manager Master Poll Interval
To configure the interval at which the switch polls the master switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Master Poll Interval column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Subnet Manager Master Poll Retries
To configure the number of Subnet Manager master poll retries, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Master Poll Retries column and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Maximum Number of Active Subnet Managers
To configure the maximum number of active Subnet Managers on the InfiniBand network, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Max Active SMs column and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the LID Mask Control
To configure the local ID mask control, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the LID Mask Control column and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Switch Lifetime
To configure the switch lifetime, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Switch Life Time column and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Switch Link HoQ Life
To configure the switch link head of queue (HoQ) life, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Switch Link HoQ Life column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring CA Link HoQ Life
To configure the collision allowance (CA) link for head of queue (HoQ) life, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the CA Link HoQ Life column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Maximum Hop Count
We recommend that InfiniBand switch elements be connected so that all paths between any pair of switch elements are the same distance (same number of hops), if possible. To configure the maximum hop count, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Maximum Hop Count column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring MAD Retries
To configure MAD retries, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the MAD retries column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Node Timeout
To configure the node timeout, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Node Timeout column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Wait Report Response
To configure the wait report response, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Wait Report Response column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Subnet Agent MAD Queue Depth
To configure Subnet Agent MAD queue depth, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the SA MAD Queue Depth column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Viewing Database Synchronization Details
Element Manager provides multiple screens that you can use to configure database synchronization. Configuration details and field descriptions are in the "Configuring Database Synchronization" section.
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Database Sync tab.
Details appear in the table below the tab.
Note
Database synchronization is enabled by default.
Understanding Partitions
A partition defines a set of InfiniBand nodes that are permitted to communicate with one another. Partitions do the following:
•
Increase security.
•
Divide a large cluster into small isolated subclusters.
•
Map InfiniBand nodes to selected VLANs.
Note
If db-sync is enabled, changes to partition configuration are only allowed on the chassis running the master subnet manager. For more information, see the "Configuring Database Synchronization" section.
How Partitions Work
A partition defines a set of InfiniBand nodes that are permitted to communicate with one another. Each node may be part of multiple partitions so that a system administrator can define overlapping partitions as the situation requires. Normal data packets carry a 16-bit P_Key, or partition key, that defines a unique partition. The Subnet Manager configures each node's channel adapter with its set of P_Keys. When a packet arrives at a node, the channel adapter checks that the packet's P_Key is valid based on the Subnet Manager's configuration. Packets with invalid P_Keys are discarded. P_Key validation prevents a server from communicating with another server outside of its partition.
InfiniBand partitions are comparable to hardware-enforced security features of conventional I/O networking technologies, such as Ethernet VLANs and Fibre-Channel zones.
Partition Members
Without members, a partition does not have meaning to the system. Ports are added to the partition, and become members of that partition. Each port may be part of multiple partitions so that you can define overlapping partitions as the situation requires.
At the time a port member is added to the partition, you must decide whether that particular port will have full or limited membership.
Membership Types
A partition contains a group of members, but different types of members can exist within a single partition. Partition memberships allows even further control because it defines communication within the members of that group, not just outside of it.
There are two types of partition memberships: full membership and limited membership. A full-membership partition member can communicate with all other partition members including other full members and limited members. A limited-membership partition member cannot communicate with other limited-membership partition members. However, a limited partition member can communicate with a full member.
About the Default Partition
The Subnet Manager automatically configures a default partition, which is always p_key ff:ff.
The default partition controls all connected ports, and by default, everything is a full member of the default partition. The default p_key cannot be altered or deleted as it is the controlling mechanism that manages the configuration of all the partitions.
Selecting a P_Key Value
For a list of acceptable P_Key values, see Table 8-3.
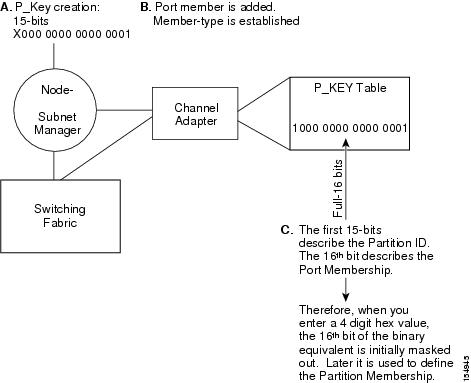
Upon creation, the p_key value (see Figure 8-1) is technically a 15-bit number. However, after the p_key is created and the port(s) membership type has been established, the entire value becomes 16 bits. The most significant bit (MSB) displays the type of membership (0 = Limited member, 1 = Full member).
When assigning a p_key value, you need to choose four hexadecimal numbers. However, because of the way that the 16th bit is used, only certain numbers can be used for the left-most variable (the MSB). For example, do not create two p_keys:
Do not create two p_keys because they will be viewed as the same number by the system. For example, if you created 0 #:# # and 8#:# #, the system would view them as the same number.
Figure 8-1 Partition Keys
Hexadecimal to Binary Conversions
Table 8-2 is provided to assist in the creation of P_keys. When creating the partition p_key, enter a hexadecimal value that is the equivalent of 16 bits in binary. For example, enter 80:00 (hex) to be 10000000000000000 (binary). The default partition (which cannot be altered) is 7f:ff.
Table 8-2 Binary Conversions
0
0000
1
0001
2
0010
3
0011
4
0100
5
0101
6
0110
7
0111
8
1000
9
1001
A
1010
B
1011
C
1100
D
1101
E
1110
F
1111
Examples of Valid P_Key Values
You can choose your own p_key values, or you can choose your values from the list in Table 8-3.
Table 8-3 Valid P_Key Numbers
00:01
00:11
00:02
00:12
00:03
00:13
00:04
00:14
00:05
00:15
00:06
00:16
00:07
00:17
00:08
00:18
00:09
00:19
00:10
00:20
Understanding how P_Keys are Saved
Partition information is saved by the master Subnet Manager. If db-sync is enabled, the master Subnet Manager synchronizes P_key information to standby Subnet Managers (currently, only one standby manager is allowed). A synchronized standby retains the information from the master.
If you configure only one InfiniBand switch, it is automatically the master, and the partition configuration is saved persistently on the switch. See the "Enabling Subnet Manager Database Synchronization" section for details.
Viewing Partition Details
To view the attributes of the partitions on your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Partitions tab.
Details appear in the table below the tab. Table 8-4 describes the fields in the table.
Note
A more user friendly view of the information appears if you select Subnet Management in step 1.
Configuring Multicast Groups
To configure multicast groups, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Expand a subnet.
Step 3
Select Multicast Groups.
Step 4
Click Add.
Step 5
Select MGID from the drop-down list.
Step 6
Enter an MGID in the Multicast Group ID field.
Step 7
(Optional) Enter a queue key in the QKey field.
Step 8
Select a value in the MTU field to configure the maximum transmission unit of the group.
Step 9
Enter a partition key in the PKey field.
Step 10
Select a rate in the Rate field.
Step 11
Enter an integer value (between 0 and 15) in the Service Level field.
Step 12
Select a scope value in the Scope field.
Step 13
Click Add.
Note
The TClass, Packet Lifetime, Flow Label, and Hop Limit attributes are not supported in this release.
Configuring IPoIB Broadcast Multicast Groups
To configure IPoIB broadcast multicast groups, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Expand a subnet.
Step 2
Select Multicast Groups.
Step 3
Click Add.
Step 4
Choose IPoIB from the drop-down list.
Step 5
Enter an MGID in the Multicast Group ID field.
Step 6
(Optional) Enter a queue key in the QKey field.
Step 7
Select an MTU value from the drop-down list.
Step 8
Enter a partition key in the PKey field.
Step 9
Select a data rate from the Rate field.
Step 10
Enter an integer value (between 0 and 15) in the Service Level field.
Step 11
Choose a scope value in the Scope field.
Step 12
Click Add.
Note
The TClass, Packet Lifetime, Flow Label, and Hop Limit attributes are not included in this release.
Viewing Multicast Group Details
To view the attributes of the multicast groups on your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Expand a subnet.
Step 2
Expand Multicast Groups.
You see the multicast information in the right pane. Table 8-5 describes the fields.
Note
A more user friendly view of the information appears if you choose Subnet Management in step 1.
Viewing Multicast Member Details
To view the details of the multicast members on your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Multicast Member tab.
Details appear in the table below the tab. Table 8-5 describes the fields in the table.
Note
A more user friendly view of the information appears if you choose Subnet Management in step 1.
Viewing InfiniBand Services
Subnet services provide your InfiniBand fabric with various features, such as the ability to run particular protocols. To view the subnet services on your InfiniBand fabric, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Services tab.
Details appear in the table below the tab. Table 8-7 describes the fields in the Subnet Managers table.
Viewing Switch Route Details
Switch routes represent the complete path that traffic takes through the InfiniBand fabric from the source LID to the destination LID. To view the details of the switch routes on your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the SwitchRoute tab.
Details appear in the table below the tab. Table 8-8 describes the fields in the table.
Note
A more user friendly view of the information appears if you choose Subnet Management in step 1.
Viewing Switch Route Element Details
To view the details of the switch element routes on your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the SwitchElementRoute tab.
Details appear in the table below the tab. Table 8-9 describes the fields in the table.
Note
A more user friendly view of the information appears if you choose Subnet Management in step 1.
Adding a Subnet Manager
To add a Subnet Manager to your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
In the navigation pane, click Subnet Managers.
The Subnet Managers display appears in the right pane of the window.
Step 3
Click Add.
The Add Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 4
Enter a subnet prefix in the Subnet Prefix field.
Step 5
Enter a subnet priority level in the Priority field.
Step 6
(Optional) Enter a subnet management key in the smKey field.
Step 7
(Optional) Enter a value in the LID Mask Control field to increase the number of LIDs assigned to each port to increase the number of potential paths to reach each port.
Step 8
Click Add.
The new Subnet Manager appears in the Summary table in the Subnet Managers display.
Removing a Subnet Manager
To remove a Subnet Manager from your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
In the navigation pane, click Subnet Managers.
The Subnet Managers display appears in the right pane of the window.
Step 3
In the Summary table in the Subnet Managers display, click the Subnet Manager that you want to remove.
Step 4
Click Remove.
The entry disappears from the display and the Server Switch configuration.
Configuring Subnet Manager Properties
The Subnet Managers navigation menu provides tuning for a number of system-wide attributes. The sections that follow explain each attribute and describe how to configure it.
Configuring Subnet Manager Priority
Every Subnet Manager in the InfiniBand network carries a priority value, and at any given time the Subnet Manager with the highest integer value priority becomes the master Subnet Manager. To configure the Subnet Manager priority on your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Priority field.
The integer value 1 has the highest the priority.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Sweep Interval
The sweep interval specifies how frequently the Subnet Manager queries the InfiniBand fabric for network changes. To configure the sweep interval on your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Sweep Interval field.
This interval represents the number of seconds between sweeps.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Response Timeout
The response timeout of a Subnet Manager specifies the maximum amount of time that the Subnet Manager waits for a response after it sends a packet to a port. If the Subnet Manager does not receive a response in the response-time interval, the Subnet Manager identifies the port as unresponsive. To configure the response timeout, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Response Timeout field.
The Subnet Manager measures the response timeout in milliseconds.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Master Poll Interval
The master poll interval determines the interval at which the slave Subnet Manager polls the master to see if the master still runs. To configure the master poll interval, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Master Poll Interval field.
The value represents the interval, in seconds.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Number of Master Poll Retries
Master poll retries specifies the number of unanswered polls that cause a slave to identify a master as dead. To specify this value, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Master Poll Retries field.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Maximum Number of Active Standby Subnet Managers that the Master Subnet Manager Supports
Note
To configure an unlimited number of active standby (slave) Subnet Managers, enter a value of 0. However, the limit set here is not enforced in this release.
To configure the maximum number of active standby Subnet Managers that the master Subnet Manager supports, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Max active SMs field.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring LID Mask Control
Local ID mask control assigns the number of path bits present in the base LID to each channel adapter port. Increasing the LMC value increases the number of LIDs assigned to each port to increase the number of potential paths to reach each port. To configure LID mask control, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the LID Mask Control field.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Switch Lifetime
Switch lifetime is one parameter that governs the transmitter packet discard policy of switches in the subnet. It determines the lifetime of packets in a switch from the point of ingress to egress. If this parameter is set to 20 or greater, then switch lifetimes are infinite (default). See InfiniBand Architecture Release 1.2, Volume 1 for more information.
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Switch Life Time field.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Switch Link HoQ Life
Switch link head of queue life determines how long an InfiniBand packet lives at the head of a switch port VL queue before it is discarded. If this parameter is set to 20 or greater, then HoQ lifetimes are infinite (default). See InfiniBand Architecture Release 1.2, Volume 1 for more information.
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Select the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Switch Link HoQ Life field.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Maximum Hop Count
To configure the maximum number of hops for an InfiniBand Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Enter an integer value in the Maximum Hop Count field.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring MAD Retries
To configure MAD retries, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the MAD retries column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Node Timeout
To configure the node timeout, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Node Timeout column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Wait Report Response
To configure the wait report response, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the Wait Report Response column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Subnet Agent MAD Queue Depth
To configure the Subnet Agent MAD queue depth, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager tab.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears.
Step 3
Highlight the value in the SA MAD Queue Depth column and replace the value.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Database Synchronization
The database synchronization feature propagates information from the database of the master Subnet Manager to the standby Subnet Managers. The sections that follow describe how to configure this feature.
Enabling Subnet Manager Database Synchronization
If you are configuring more than one InfiniBand chassis in your fabric, it is likely that you will want to enable database synchronization of the Subnet Managers.
Note
This features is enabled by default.
To enable Subnet Manager database synchronization to update standby Subnet Managers with information from the master Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Check the Enable check box in the SM Database Synchronization field.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Maximum Number of Backup Subnet Managers to Synchronize
To configure the maximum number of backup Subnet Managers that will synchronize with the master Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Enter an integer value in the Max Backup SMs field.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring a Session Timeout
To configure the session timeout interval, in seconds, during which a synchronization session status MAD packet must arrive at the master Subnet Manager to maintain synchronization, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Enter an integer value in the Session Timeout field.
This value determines the timeout duration, in seconds.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Poll Interval
To configure the interval, in seconds, at which the master Subnet Manager polls an active slave Subnet Manager to verify synchronization, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
Step 2
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 3
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 4
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 5
Enter an integer value in the Poll Interval field.
This value sets the poll interval, in seconds.
Step 6
Click Apply.
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Timeout Value
To configure the amount of time, in seconds, that a cold synchronization tries to initiate before it times out, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Enter an integer value in the Cold Sync Timeout field.
This value sets the timeout interval, in seconds.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Value
To configure the maximum number of cold synchronizations to perform during a given cold synchronization period, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Enter an integer value in the Cold Sync Limit field.
This value sets the maximum number of synchronizations that can occur during the synchronization period ("Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Period" section).
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Period
To specify the length of the interval during which cold synchronizations may occur, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Enter an integer value in the Cold Sync Limit Period field.
This value sets the length of the interval during which cold synchronizations may occur.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the New Session Delay
To configure the amount of time that the master Subnet Manager waits before it attempts to initiate a synchronization session with a new Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Enter an integer value in the New Session Delay field.
This value determines the amount of time, in seconds, that the master Subnet Manager waits before it attempts to initiate a synchronization session with a new Subnet Manager.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Resynchronization Interval
To specify the interval at which the master Subnet Manager sends a resynchronization request to all active synchronization sessions, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Enter an integer value in the Resync Interval field.
This value specifies the interval, in seconds, at which the master Subnet Manager sends a resynchronization request to all active synchronization sessions.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Viewing the Database Synchronization State
To view the database synchronization state and verify that the master Subnet Manager and slave Subnet Manager(s) are synchronized, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Select the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane of the display.
Step 4
Look at the State field.
Viewing Nodes
To view Subnet Manager node information, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager that you want to view.
Step 3
Expand Nodes.
The Nodes in Subnet tab displays the Node GUID, Type, Description, Number of Ports, System Image GUID, and the Vendor ID information.
Step 4
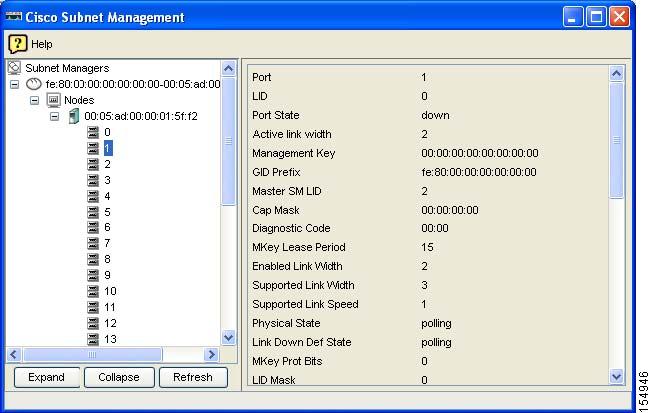
Expand a computer icon and select an individual node to see the information shown in Figure 8-2.
Figure 8-2 Individual Node Information
Viewing Partitions
To view the partitions on your InfiniBand network, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Click the Partitions (
) branch.
The partitions summary appears in the right pane. Table 8-10 describes the fields in this display.
Creating a Partition
To create an InfiniBand partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
Step 3
Select the Partitions (
) branch.
Step 4
Click Add.
The Add Partition window opens.
Step 5
Enter a partition key for the new partition in the PKey field, and then click Add.
Removing a Partition
To delete a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch.
Step 4
Click the partition in the Summary display that you want to remove, and then click Remove.
Viewing Partition Details
To view partition details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions.
Step 4
Click the partition key of the partition with details that you want to view.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Note
To view the GUIDs of the Server Switch management ports in the display, click Show Switch Mgmt Ports. Click Hide Switch Mgmt Ports to remove these GUIDs from the display.
Adding Full Members to a Partition
Full members of a partition can communicate to other full members and to limited members.
Adding Available Members to a Partition
To add available members to a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Select the partition key of the partition to which you want to add members.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Step 5
Click the port in the Available Members field, that you want to add to the partition, and then click the right arrow next to the Full Members field.
Adding Unavailable Members to a Partition
To add unavailable members ( members that do not appear in the Available Members pool) to a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Click the partition key of the partition to which you want to add members.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Step 5
Click Add Other.
The Add Other Partition Member window opens.
Step 6
Enter the GUID of the host that includes the port(s) that you want to add to the partition in the Node GUID field.
Step 7
Specify the port(s) that you want to add to the partition in the Port field.
Step 8
Choose the Full radio button, and then click Add.
Adding Limited Members to a Partition
Limited members of a partition can communicate with full members of the partition but not with other limited members.
Adding Available Limited Members
To add available limited members to a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Click the partition key of the partition to which you want to add members.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Step 5
Click the port in the Available Members field, that you want to add to the partition and then click the right arrow next to the Limited Members field.
Adding Unavailable Members
To add an unavailable member (member does not appear in the Available Members pool) to a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Select the partition key of the partition to which you want to add members.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Step 5
Click Add Other.
The Add Other Partition Member window opens.
Step 6
Enter the GUID of the node that includes the port(s) that you want to add to the partition in the Node GUID field.
Step 7
Specify the port(s) that you want to add to the partition in the Port field.
Step 8
Choose the Limited radio button, and then click Add.
Viewing Multicast Groups
To view the multicast groups on your InfiniBand network, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Select the Multicast Groups (
) branch.
The multicast groups summary appears in the right pane. Table 8-11 describes the fields in this display.
Viewing Multicast Group Details
To view multicast group details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with multicast groups that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Expand the Multicast Groups (
) branch to display all groups in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Click the MGID of the multicast group with details that you want to view, and then click the General tab.
Multicast group details appear in the display. Table 8-12 describes the fields in this display.
Viewing Multicast Group Members
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with multicast groups that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Expand the Multicast Groups (
) branch to display all groups in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Click the MGID of the multicast group with details that you want to view, and then click the Members tab.
Multicast group members appear in the display. Table 8-13 describes the fields in this display.
Viewing InfiniBand Services
To view the InfiniBand services that run on your Server Switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
Step 3
Click the Services (
) branch.
Details of InfiniBand services appear in the right pane.
Table 8-14 describes the fields in the Summary section of the display.
Table 8-15 describes the fields in the Services Details section of the display.
Viewing InfiniBand Routes
To view the route between a pair of LIDs in the InfiniBand fabric. follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
Step 3
Select the Routes (
) branch.
InfiniBand routes fields appear in the right pane.
Step 4
Enter the source LID of the route in the Source LID field.
Step 5
Enter the destination lid of the route in the Destination LID field.
Step 6
Click Show Route.
Step 7
Click the Switch Route tab.
Table 8-16 lists the fields under the Switch Route tab.
Table 8-16 Switch Route Field Descriptions
Node GUID
Global unique ID of the node.
In Port
Port of ingress.
Out Port
Port of egress.
Step 8
Click the Switch Element Route tab.
Table 8-17 displays the fields under the Switch Element Route tab.
Table 8-17 Switch Element Route Field Descriptions
Chassis GUID
Global unique ID of the node.
In Port
Port of ingress.
Out Port
Port of egress.
Viewing Subnet Managers Information
To view information on other Subnet Managers in the network, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Expand Subnet Managers Info.
The Port GUID, Priority, and Subnet Manager state information appears in the right pane.
Table 8-18 describes the fields in the Details pane.
Table 8-18 Subnet Managers Information Details Pane
Note
This menu provides information on subnet managers that are not local to the chassis to which an Element Manager is connected.
Viewing Event Subscriptions
To view the Subnet Management event subscriptions information, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Choose Event Subscriptions.
The LID, Node GUID, and Port Number information appears in the right pane.
Table 8-19 describes the fields under Subnet Management Event Subscriptions Details.
Enabling InfiniBand Port Performance Management
Use performance management to view InfiniBand port counters, test connectivity between InfiniBand ports, and monitor InfiniBand ports for errors. To enable InfiniBand-port performance management, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the subnet of the ports that you want to manage (for instance, fe:80:00:00:00:00:00:00).
The Port Counter Configuration display appears in the right pane of the window.
Step 3
Choose the Enable radio button.
Disabling Performance Management
To disable performance management, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the subnet of the ports that you want to manage (for instance, fe:80:00:00:00:00:00:00).
The Port Counter Configuration display appears in the right pane of the window.
Step 3
Choose the Disable radio button.
Monitoring Connections
To monitor connections, you complete tasks such as:
•
Creating a Connection to Monitor
•
Viewing Monitored Connections
•
Viewing Connection Monitor Counters
•
Viewing Port Counters of Connections
Creating a Connection to Monitor
To create a connection to monitor, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Choose Connection Counters.
The Monitored Connection tab appears in the right pane of the window.
Step 4
Click Add.
The Add Connection window opens.
Step 5
Enter a source LID in the Source LID field.
Note
To view available source and destination LIDs, return to the main Element Manager display, click the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management, and then click the SwitchRoute tab. For more information, see the "Viewing Switch Route Details" section.
Step 6
Enter a destination LID in the Destination LID field.
Step 7
Check the Enable Connection Monitoring check box.
Note
If this check box is not selected, you an view only counter information and cannot view monitoring information.
Step 8
Click Add.
The connection entry appears under the Monitored Connections tab.
Viewing Monitored Connections
These instructions assume that you have already defined connections to monitor. To view monitored connections, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
The navigation tree expands.
Step 3
Select the Connection Counters branch.
The Monitored Connection tab appears in the right pane of the window. Table 8-20 describes the fields in this display.
Table 8-20 Monitored Connections Field Descriptions
Subnet Prefix
Subnet prefix of the monitored connection.
Source LID
16-bit source Local ID of the connection.
Destination LID
16-bit destination Local ID of the connection.
Error Status
Displays unknown, exceeded, or notExceeded to indicate if the error value has exceeded the threshold that you configured. To configure thresholds, see the "Configuring Port Monitoring Thresholds" section.
Util Status
Displays unknown, exceeded, or notExceeded to indicate if the utilization value has exceeded the threshold that you configured. To configure thresholds, see the "Configuring Port Monitoring Thresholds" section.
Viewing Connection Counters
Each hop in the display is a port on a node. When connections move through nodes, they enter the node in one hop (GUID A, port a), and exit in another hop (GUID A, port b). Though the GUIDs of subsequent hops may match, the ports do not match. To view connection counters, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Connection Counters branch.
Step 4
Select the connection with counters that you want to view.
Step 5
Click the Connection Counters tab.
Table 8-21 describes the fields in the display.
Viewing Connection Monitor Counters
To view connection monitor counters, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Connection Counters branch.
Step 4
Select the connection with counters that you want to view.
Step 5
Click the Connection Monitor Counters tab.
Table 8-22 describes the fields in the display.
Testing Connections
To test connections, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Connection Counters branch.
Step 4
Select the connection with counters that you want to view.
Step 5
Click the Test Connection tab.
Step 6
Click Test.
Viewing Port Counters of Connections
To view port counters, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Connection Counters branch.
Step 4
Expand the connection with port counters that you want to view.
Step 5
Select the port (in GUID - port-number format) with counters that you want to view.
Table 8-23 describes the fields in this display.
Viewing Port Counters
To view port counters, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Port Counters branch.
Step 4
View port counters using one of the following methods:
•
Click the GUID with port counters that you want to view; all available port counters appear.
•
Expand the GUID of the node with port counters that you want to view, and then select the port with counters that you want to view.
Counters appear for that individual port. Table 8-24 describes the fields in the port counters display.
Viewing Cumulative Port Counters
To view cumulative port counters, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Port Counters branch.
Step 4
Expand the node of the port with cumulative counters that you want to view.
Step 5
Click the port with navigation counters that you want to view.
Step 6
Click the Port Cumulative Counters tab.
Table 8-25 describes the fields in the display.
Enabling Port Monitoring
To enable port monitoring, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Select the Port Monitor branch.
Step 4
Click the General tab.
Step 5
Choose Enable from the State drop-down menu.
Note
Enable enables port monitoring only for the ports that are configured in the Monitor Port Config table; enableAll enables port monitoring for all ports regardless of whether the port is configured in the Monitor Port Config table or not.
Step 6
Click Apply.
Configuring Port Monitoring
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
The navigation tree expands.
Step 3
Select the Port Monitor branch.
Step 4
Click the General tab.
Step 5
Enter an integer value between 1 and 600 in the Polling Period field to configure the number of seconds between polls.
Step 6
Enter an integer value between 1 and 600 in the Start Delay field to configure the delay between startup and polling.
Configuring Port Monitoring Thresholds
To configure port monitoring thresholds, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
The navigation tree expands.
Step 3
Select the Port Monitor branch.
Step 4
Click the Threshold tab.
Step 5
Enter an integer value in the fields where you want to apply a threshold. Enter none in the fields to which you do not want to apply a threshold.
Step 6
Click Apply.
Resetting Counters
You can reset counters for the following:
•
Resetting Counters on All Ports on a Node
•
Resetting Counters on All Ports in a Connection
•
Resetting All Counters in a Subnet
Resetting Counters on a Hop
To reset counters on a hop, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Connection Counters branch.
Step 4
Expand the connection that includes the hop that you want to clear.
Step 5
Right-click the hop with counters you want to clear and choose Clear counters on this Hop.
Resetting Counters on All Ports on a Node
To reset counters on all ports of a node, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Connection Counters branch.
Step 4
Expand the connection that includes the node that you want to clear.
Step 5
Right-click the node with counters you want to clear and choose Clear counters on this Node.
Resetting Counters on All Ports in a Connection
To reset counters on all ports in a connection, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Expand the Connection Counters branch.
Step 4
Right-click the connection with counters you want to clear and choose Clear counters on this Connection.
Resetting All Counters in a Subnet
To reset all counters in a subnet, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Performance Management.
The Performance Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the subnet of the connections that you want to monitor.
Step 3
Right-click the Connection Counters branch and choose Clear Counters for All Connections.
Launching the Topology View
To launch the topology view, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column of any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology appears.
Note
Navigation icons appear at the top of the InfiniBand Topology window. Table 8-26 describes these icons.
Table 8-26 InfiniBand Topology Navigation Icons

The Refresh icon refreshes the topology display.

The Layout icon evenly arranges the switch and HCA icons.

The Zoom In icon enlarges the display.

The Zoom Out icon condenses the display.

The Fit to Screen icon zooms in or out to fit the topology in the window.

The Specify Topspin Devices icon opens the Specify Cisco Devices dialog box to add Server Switches to the display.

The Legend icon displays the different colors that represent different types of links.

The Subnet Details icon displays subnet details. For more information, see the "Viewing Subnet Details" section.

The Help icon launches the online help.
Viewing Internal Server Switch Components and TCAs
To view the internal server switch components and target channel adapters (TCAs) inside a server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column of any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Note
Navigation icons appear at the top of the InfiniBand Topology window. Table 8-27 describes these icons.
Table 8-27 Internal InfiniBand Topology Navigation Icons

The Layout icon evenly arranges the switch and HCA icons.

The Zoom In icon enlarges the display.

The Zoom Out icon condenses the display.

The Fit to Screen icon zooms in or out to fit the topology in the window.

The Layout icon evenly arranges the switch and HCA icons.
The Subnet Management Agents icon displays Subnet Manager agent details. For information, see the "Viewing Subnet Management Agents" section.

The Help icon launches the online help.
Viewing Subnet Details
You can view any of the following subnet details:
Viewing Nodes
To view the nodes in the topology view, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column of any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Click Details.
The InfiniBand Subnet Details window opens.
Step 5
Click the Nodes tab.
Table 8-28 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Ports
To view the ports in the topology view, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column of any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Click Details.
The InfiniBand Subnet Details window opens.
Step 5
Click the Ports tab.
Table 8-29 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Switches
To view the switches in the topology view, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and chooseTopology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column of additional InfiniBand devices to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Click Details.
The InfiniBand Subnet Details window opens.
Step 5
Click the Switches tab.
Table 8-30 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Neighboring Ports
To view neighboring ports in the topology view, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and chooseTopology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check bo, in the Enabled column of any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Click Details.
The InfiniBand Subnet Details window opens.
Step 5
Click the Neighbors tab.
Table 8-31 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Subnet Management Agents
You can view any of the following Subnet Manager Agent details:
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Node Details
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Switch Details
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Switch Cap Details
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Ports(1) Details
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Ports(2) Details
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Multicast Details
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Linear Forwarding Table Details
•
Viewing the Subnet Manager Agent Partition Details
Viewing Subnet Manager Node Details
To view Subnet Manager Agent node details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column for any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
Step 5
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 6
Click SMAs.
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 7
Click the Nodes tab.
Table 8-32 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Subnet Manager Switch Details
To view Subnet Manager Agent switch details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column for any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 5
Click SMAs.
Step 6
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 7
Click the Switches tab.
Table 8-33 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Switch Cap Details
To view Subnet Manager Agent switch cap details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column for any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 5
Click SMAs.
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 6
Click the Switch Cap tab.
Table 8-34 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Ports(1) Details
To view Subnet Manager Agent port details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column of any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 5
Click SMAs.
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 6
Click the Ports (1) tab.
Table 8-35 describes the fields under this tab.
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Ports(2) Details
To view extended Subnet Manager Agent port details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column for any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 5
Click SMAs.
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 6
Click the Ports (2) tab.
Table 8-36 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Subnet Manager Multicast Details
To view Subnet Manager Agent multicast details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column for any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 5
Click SMAs.
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 6
Click the Mcast tab.
Table 8-37 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing Subnet Manager Agent Linear Forwarding Table Details
To view Subnet Manager Agent linear forwarding table details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column for any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 5
Click SMAs.
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 6
Click the Linear Forwarding tab.
Table 8-38 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing the Subnet Manager Agent Partition Details
To view Subnet Manager Agent partition details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column for any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 5
Click SMAs.
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 6
Click the PKey tab.
Table 8-39 describes the fields in this tab.
SLVL Map
To view Subnet Manager Agent SLVL details, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose Topology View.
The Specify Topspin Devices dialog box opens.
Step 2
(Optional) Click the check box in the Enabled column for any additional InfiniBand devices that you want to add to the Topology View display.
Step 3
Click OK.
The InfiniBand Topology window appears.
Step 4
Double-click a server switch icon.
The Internal InfiniBand Topology window opens.
Step 5
Click SMAs.
The Subnet Manager Agents window opens.
Step 6
Click the SLVL Map tab.
Table 8-40 describes the fields in this tab.
Table 8-40 SLVL Map Tab Field Descriptions
NodeGuid
Global unique ID of the node.
InIbPort
Ingress port number.
OutIbPort
Egress port number.
Sl#toVI
SL# to VL mapping.
Viewing Device Management
Device Management (DM) features only are available on I/O chassis (Cisco SFS 3001 and Cisco SFS 3012). With Device Management, you can do the following:
Viewing IOUs
To view the I/O Units (IOUs) on your device, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose DM.
The Device Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the IOU tab.
IOU details appear in the right pane. Table 8-41 describes the fields in this display.
Viewing IOCs
To view the I/O controllers (IOCs) on your device, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose DM.
The Device Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click the IOC tab.
A table of IOC details appears. Table 8-42 describes the fields in this display.
Viewing IOC Services
To view the IOC services on your device, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose DM.
Step 2
The Device Manager window opens.
Step 3
Click the IOC Services tab.
A table of IOC Services details appears. Table 8-43 describes the fields in this table.
Viewing Forwarding Tables
Viewing Multicast Forwarding
To view the multicast forwarding configuration, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose either Subnet Management or Subnet Management(Tabular format).
Step 2
Click the MulticastForwardings tab.
You see the information shown in Table 8-44.
Table 8-44 Multicast Forwarding Entries
Node GUID
Guid of the switch node in the subnet with the FDB that you want to access.
MLID
Local ID of the subnet.
Port Mask
Port mask.
Viewing Linear Forwarding
To view the linear forwarding configuration, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the InfiniBand menu and choose either Subnet Management or Subnet Management(Tabular format).
Step 2
Click the LinearForwardings tab.
You see the information shown in Table 8-45.
Table 8-45
Node GUID
Guid of the switch node in the subnet with the FDB that you want to access.
LID
Local ID of the subnet.
Port Number
Port number.
Linear Forwarding Entries

 Feedback
Feedback