Table Of Contents
InfiniBand Subnet Management Tasks
Viewing and Managing Subnet Manager Properties
Viewing Subnet Manager Properties
Configuring Subnet Manager Properties
Configuring Subnet Manager Priority
Configuring the Sweep Interval
Configuring the Master Poll Interval
Configuring the Number of Master Poll Retries
Configuring the Maximum Supported Number of Active Standby Subnet Managers
Configuring Switch Link HoQ Life
Configuring Wait Report Response
Configuring Subnet Administrator MAD Queue Depth
Viewing and Managing Database Synchronization
Viewing Database Synchronization
Viewing Standby Subnet Managers that Synchronize with the Master Subnet Manager
Configuring Database Synchronization
Enabling Subnet Manager Database Synchronization
Configuring the Maximum Number of Backup Subnet Managers to Synchronize
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Timeout Value
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Value
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Period
Configuring the New Session Delay
Configuring the Resynchronization Interval
Viewing the Database Synchronization State
Viewing Database Synchronization Active Subnet Manager
Viewing and Managing Nodes and Ports
Routing Around Nodes and Ports
Viewing and Managing Partitions
Enabling or Disabling IPoIB for a Partition
Adding Full Members to a Partition
Adding Available Members to a Partition
Adding Unavailable Members to a Partition
Adding Limited Members to a Partition
Adding Available Limited Members
Viewing and Managing Multicast Groups
Viewing Multicast Group Details
Viewing Multicast Group Members
Adding IPoIB Broadcast Multicast Groups
Viewing and Managing InfiniBand Routes
Routing Around Components in an InfiniBand Network
Viewing Route-Around Information
Adding Routes to the Route-Around Table
Removing Routes from the Route-Around Table
Viewing and Managing Port Spans
Viewing Other Subnet Managers Information
Viewing Multicast Forwarding Information
Viewing Linear Forwarding Information
Viewing and Managing Arbitration Profiles
Viewing SLtoVLMapping Table of Switches
Viewing SLtoVLMapping Table of CAs
Viewing SLtoVL Mapping Profiles
Viewing VL Arbitration Profiles
Configuring VL Arbitration Config Group
InfiniBand Subnet Management Tasks
These topics describe the InfiniBand menu subnet management tasks for Element Manager:
•
Viewing and Managing Subnet Manager Properties
•
Viewing and Managing Database Synchronization
•
Viewing and Managing Nodes and Ports
•
Viewing and Managing Partitions
•
Viewing and Managing Multicast Groups
•
Viewing and Managing InfiniBand Routes
•
Viewing Other Subnet Managers Information
•
Viewing and Managing InfiniBand Routes
•
Viewing Other Subnet Managers Information
Note
See "InfiniBand Concepts" to familiarize yourself with the InfiniBand technology. For hardware-specific information, consult the relevant hardware documentation.
Using the InfiniBand Menu
The InfiniBand menu has two choices for performing InfiniBand subnet management tasks:
•
Subnet Management
•
Subnet Management (tabular format)
These topics describe how to use the Subnet Management menu option. Most of the tasks can also be performed by selecting the Subnet Management (tabular format) menu option, which presents information and configurable options in tables, but is a less user friendly way to perform your InfiniBand subnet management tasks.
Viewing and Managing Subnet Manager Properties
These topics describe procedures for performing the following tasks:
•
Viewing Subnet Manager Properties
•
Configuring Subnet Manager Properties
Viewing Subnet Manager Properties
To view Subnet Manager properties, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Select a subnet.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab. Table 8-1 describes the fields.
See the "Configuring Subnet Manager Properties" procedure for details on how to configure these properties.
Adding a Subnet Manager
To add a Subnet Manager to your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
In the navigation pane, click Subnet Managers.
The Subnet Managers display appears in the right pane of the window.
Step 3
Click Add.
The Add Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 4
In the Subnet Prefix field, enter a subnet prefix.
Step 5
In the Priority field, enter a subnet priority level.
Step 6
(Optional) In the smKey field, enter a subnet management key.
Step 7
(Optional) In the LID Mask Control field, enter a value to increase the number of LIDs assigned to each port to increase the number of potential paths to reach each port.
Step 8
Click Add.
The new Subnet Manager appears in the Summary table in the Subnet Managers display.
Removing a Subnet Manager
To remove a Subnet Manager from your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
In the navigation pane, click Subnet Managers.
The Subnet Managers display appears in the right pane of the window.
Step 3
In the Summary table in the Subnet Managers display, click the Subnet Manager that you want to remove.
Step 4
Click Remove.
The entry disappears from the display and the server switch configuration.
Configuring Subnet Manager Properties
The Subnet Managers navigation menu provides tuning for a number of system-wide attributes. These topics explain each attribute and describe how to configure it:
•
Configuring Subnet Manager Priority
•
Configuring the Sweep Interval
•
Configuring the Master Poll Interval
•
Configuring the Number of Master Poll Retries
•
Configuring the Maximum Supported Number of Active Standby Subnet Managers
•
Configuring Switch Link HoQ Life
•
Configuring Maximum Hop Count
•
Configuring Wait Report Response
•
Configuring Subnet Administrator MAD Queue Depth
Configuring Subnet Manager Priority
Every Subnet Manager in the InfiniBand network carries a priority value, and at any given time the Subnet Manager with the highest integer value priority becomes the master Subnet Manager. To configure the Subnet Manager priority on your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Priority field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
The integer value 15 has the highest priority.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Sweep Interval
The sweep interval specifies how frequently the Subnet Manager queries the InfiniBand fabric for network changes. To configure the sweep interval on your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Sweep Interval field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
This interval represents the number of seconds between sweeps.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Response Timeout
The response timeout of a Subnet Manager specifies the maximum amount of time that the Subnet Manager waits for a response after it sends a packet to a port. If the Subnet Manager does not receive a response in the response-time interval, the Subnet Manager identifies the port as unresponsive. To configure the response timeout, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Response Timeout field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
The Subnet Manager measures the response timeout in milliseconds.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Master Poll Interval
The master poll interval determines the interval at which the slave Subnet Manager polls the master to see if the master still runs. To configure the master poll interval, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Master Poll Interval field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
The value represents the interval, in seconds.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Number of Master Poll Retries
Master poll retries specifies the number of unanswered polls that cause a slave to identify a master as dead. To specify this value, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Master Poll Retries field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring the Maximum Supported Number of Active Standby Subnet Managers
Note
To configure an unlimited number of active standby (slave) Subnet Managers, enter a value of 0. However, the limit set here is not enforced in this release.
To configure the maximum number of active standby Subnet Managers that the master Subnet Manager supports, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Max active SMs field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring LID Mask Control
Local ID mask control assigns the number of path bits present in the base LID to each channel adapter port. Increasing the LMC value increases the number of LIDs assigned to each port to increase the number of potential paths to reach each port. To configure LID mask control, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the LID Mask Control field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Switch Lifetime
Switch lifetime is one parameter that governs the transmitter packet discard policy of switches in the subnet. It determines the lifetime of packets in a switch from the point of ingress to egress. If this parameter is set to 20 or greater, then switch lifetimes are infinite (default). See InfiniBand Architecture Release 1.2, Volume 1 for more information. To configure the switch lifetime, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Switch Life Time field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Switch Link HoQ Life
Switch link head of queue (HoQ) life determines how long an InfiniBand packet lives at the head of a switch port Virtual Lane (VL) queue before it is discarded. If this parameter is set to 20 or greater, then HoQ lifetimes are infinite (default). See InfiniBand Architecture Release 1.2, Volume 1 for more information.
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Switch Link HoQ Life field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Maximum Hop Count
We recommend that InfiniBand switch elements be connected so that all paths between any pair of switch elements are the same distance (same number of hops), if possible.
The range of values is from 0 to 64. Default is 64. A value of 0 causes the Subnet Manager to calculate and use the lowest possible value that will still ensure connectivity between all endpoints.
Note
Selecting any nondefault value restricts the length of paths used by the Subnet Manager. The Subnet Manager might therefore select paths that are optimal for distance, but not for other factors, such as link capacity.
To configure the maximum number of hops for an InfiniBand Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Maximum Hop Count field, select the value, and replace it with the value you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring MAD Retries
Management Diagram (MAD) retries specifies the number of times that a Subnet Manager resends a management datagram after not receiving a response. The default value is 5.
To configure MAD retries, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of subnet manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the MAD Retries field, select the value, and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Node Timeout
Node Timeout is the minimum amount of time in seconds that a HCA is unresponsive before the Subnet Manager removes it from the InfiniBand fabric. The default value is 10 seconds.
To configure the node timeout, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Node Timeout field, select the value, and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Wait Report Response
Wait Report Response configures whether or not a Subnet Manager waits to receive Report Response MADs in response to the Report MAD that it forwards. If you set this Boolean value to false, the Subnet Manager only sends the Report MADs once; if you set it to true, the Subnet Manager will continue to send the Report MADs until either the Report Response MAD is received or the maximum number of Report MADs have been sent. The default value is false.
To configure the wait report response, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of Subnet Manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the Wait Report Response field, check the Enable box.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Configuring Subnet Administrator MAD Queue Depth
This procedure configures the size of a Subnet Administrator internal queue for receiving MADs. The default value is 256.
To configure the Subnet Administrator MAD queue depth, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
A table of subnet manager properties appears under the General tab.
Step 3
In the SA MAD Queue Depth field, select the value, and replace it with the value that you want to apply.
Step 4
Click Apply.
Viewing and Managing Database Synchronization
Element Manager provides multiple screens that you can use to view and configure database synchronization. This section describes the following tasks:
•
Viewing Database Synchronization.
•
Viewing Standby Subnet Managers that Synchronize with the Master Subnet Manager
•
Configuring Database Synchronization
•
Viewing Database Synchronization Active Subnet Manager
Viewing Database Synchronization
To view database synchronization details, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Select a subnet
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab.
Details appear in the table below the tab. Table 8-2 describes the fields.
Note
Database synchronization is enabled by default.
Viewing Standby Subnet Managers that Synchronize with the Master Subnet Manager
To view the database synchronization attributes for standby Subnet Managers that are synchronizing with the master Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Select a subnet.
Step 3
Click the Subnet Managers Info.
Step 4
In the right pane, click Database Sync.
The summary and details appear in the right pane. Table 8-3 describes the summary fields.
Table 8-4 describes the Details fields.
Configuring Database Synchronization
The database synchronization feature propagates information from the database of the master Subnet Manager to the standby Subnet Managers. These topics describe how to configure this feature:
•
Enabling Subnet Manager Database Synchronization
•
Configuring the Maximum Number of Backup Subnet Managers to Synchronize
•
Configuring a Session Timeout
•
Configuring the Poll Interval
•
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Timeout Value
•
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Value
•
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Period
•
Configuring the New Session Delay
•
Configuring the Resynchronization Interval
•
Viewing the Database Synchronization State
Enabling Subnet Manager Database Synchronization
If you are configuring more than one InfiniBand chassis in your fabric, you probably will want to enable database synchronization of the Subnet Managers.
Note
This feature is enabled by default.
To enable Subnet Manager database synchronization to update standby Subnet Managers with information from the master Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
Click the Database Sync tab in the right pane.
Step 4
In the SM Database Synchronization field, check the Enable check box.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Maximum Number of Backup Subnet Managers to Synchronize
To configure the maximum number of backup Subnet Managers that will synchronize with the master Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
In the right pane, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 4
In the Max Backup SMs field, enter an integer value.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring a Session Timeout
To configure the session timeout interval, in seconds, during which a synchronization session status MAD packet must arrive at the master Subnet Manager to maintain synchronization, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
In the right pane of the display, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 4
In the Session Timeout field, enter an integer value.
This value determines the timeout duration, in seconds.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Poll Interval
To configure the interval, in seconds, at which the master Subnet Manager polls an active slave Subnet Manager to verify synchronization, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
Step 2
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 3
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 4
In the right pane of the display, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 5
Enter an integer value in the Poll Interval field.
This value sets the poll interval, in seconds.
Step 6
Click Apply.
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Timeout Value
To configure the amount of time, in seconds, that a cold synchronization tries to initiate before it times out, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
In the right pane of the display, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 4
In the Cold Sync Timeout field, enter an integer value.
This value sets the timeout interval, in seconds.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Value
To configure the maximum number of cold synchronizations to perform during a given cold synchronization period, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
In the right pane of the display, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 4
In the Cold Sync Limit field, enter an integer value.
This value sets the maximum number of synchronizations that can occur during the synchronization period. (See "Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Period" section.)
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Cold Synchronization Limit Period
To specify the length of the interval during which cold synchronizations may occur, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
In the right pane of the display, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 4
In the Cold Sync Limit Period field, enter an integer value.
This value sets the length of the interval during which cold synchronizations may occur.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the New Session Delay
To configure the amount of time that the master Subnet Manager waits before it attempts to initiate a synchronization session with a new Subnet Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
In the right pane of the display, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 4
In the New Session Delay field, enter an integer value.
This value determines the amount of time, in seconds, that the master Subnet Manager waits before it attempts to initiate a synchronization session with a new Subnet Manager.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Configuring the Resynchronization Interval
To specify the interval at which the master Subnet Manager sends a resynchronization request to all active synchronization sessions, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Click the Subnet Manager that you want to configure.
Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 3
In the right pane of the display, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 4
In the Resync Interval field, enter an integer value.
This value specifies the interval, in seconds, at which the master Subnet Manager sends a resynchronization request to all active synchronization sessions.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Viewing the Database Synchronization State
To view the database synchronization state and verify that the master Subnet Manager and slave Subnet Manager(s) are synchronized, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Select the Subnet Manager with the state you wan to view.
Step 3
In the right pane of the display, click the Database Sync tab.
Step 4
Look at the State field.
Viewing Database Synchronization Active Subnet Manager
To view the list of standby databases that are synchronizing with the master subnet manager and their synchronization status follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Click DB Sync Active SM tab.
Table 8-5 describes the fields in this tab.
Viewing and Managing Nodes and Ports
This section provides procedures for performing the following tasks:
•
Routing Around Nodes and Ports
Viewing Node Information
To view Subnet Manager node information, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager that you want to view.
Step 3
Select Nodes.
The Nodes in Subnet tab displays the Node GUID, Type, Description, Number of Ports, System Image GUID, and the Vendor ID information. See Table 8-6 for details.
Step 4
Click Show Advanced to display the additional information about each of the nodes in the subnet. This information includes Base Version, Class Version, Port GUID, Partition Cap, Device ID, Revision, and Local Port Number. Table 8-6 describes these fields.
Viewing Port Information
To view information about specific ports, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with ports you want to view.
Step 3
Select Nodes.
Step 4
Expand Nodes.
Step 5
Expand the computer icon for the node with ports you want to view
Step 6
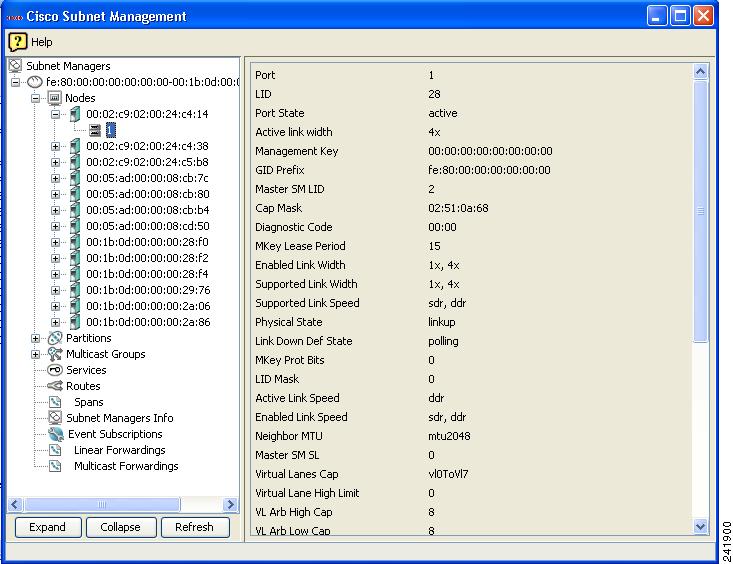
Select a specific port to see the information described in Table 8-7. Figure 8-1 shows a sample display.
Figure 8-1 Individual Port Information
Routing Around Nodes and Ports
These topics describe how to route around nodes and ports using the Nodes displays:
For a complete discussion of routing around components, including routing around chassis, see the "Routing Around Components in an InfiniBand Network" section.
Routing Around Nodes
To route around a node or to re-include a node that had previously been excluded, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager that manages the node you want to work on.
Step 3
Expand Nodes.
A list of nodes managed by the Subnet Manager appears in the left pane.
Step 4
Select the node you want to exclude from routing calculations or include in routing calculations.
Step 5
Right-click the highlighted node.
Step 6
Select Start Routing Around or Stop Routing Around.
Routing Around Ports
To route around a port, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens. Each Subnet Manager appears in the navigation pane with a Subnet Manager icon (
).
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager that you want to view.
Step 3
Expand Nodes.
A list of nodes managed by the Subnet Manager appears in the left pane.
Step 4
Expand the node containing the port you want to work on.
Step 5
Select the port you want to exclude from routing calculations or to include in routing calculations.
Step 6
Right-click the highlighted port.
Step 7
Select Start Routing Around or Stop Routing Around.
Viewing and Managing Partitions
This section provides procedures for performing the following tasks:
•
Enabling or Disabling IPoIB for a Partition
•
Adding Full Members to a Partition
•
Adding Limited Members to a Partition
Viewing Partitions
To view the partitions on your InfiniBand network, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Click the Partitions (
) branch.
The partitions summary appears in the right pane. Table 8-8 describes the fields in this pane.
Creating a Partition
To create an InfiniBand partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager under which you want to create a partition.
Step 3
Select the Partitions (
) branch.
Step 4
Click Add.
The Add Partition window opens.
Step 5
In the PKey field, enter a partition key for the new partition.
Step 6
Check the IPoIB check box to enable or uncheck to disable IPoIB for the partition.
Step 7
Click OK.
Removing a Partition
To delete a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partition that you want to delete.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch.
Step 4
Click the partition in the Summary display that you want to remove, and then click Remove.
Enabling or Disabling IPoIB for a Partition
Disabling IPoIB removes all current multicast group members and prevents further multicast joins. To enable or disable IPoIB on a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with the partitions for which you want to enable or disable IPoIB.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Click the Partitions (
) branch.
The partitions summary appears in the right pane.
Step 4
Click on the summary line of the partition for which you want to enable or disable IPoIB.
Step 5
Click Edit.
The Add Partition window opens.
Step 6
Check the IPoIB check box to check (enable) or uncheck (disable) IPoIB for the partition.
Step 7
Click OK.
Viewing Partition Details
To view partition details, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions.
Step 4
Click the partition key of the partition with details that you want to view.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Note
To view the GUIDs of the Server Switch management ports in the display, click Show Switch Mgmt Ports. Click Hide Switch Mgmt Ports to remove these GUIDs from the display.
Adding Full Members to a Partition
Full members of a partition can communicate to other full members and to limited members.
These topics describe how to add full members to a partition:
•
Adding Available Members to a Partition
•
Adding Unavailable Members to a Partition
Adding Available Members to a Partition
To add available members to a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with the partition to which you want to add a member.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Select the partition key of the partition to which you want to add members.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Step 5
In the Available Members field, click the port that you want to add to the partition, and then click the right arrow next to the Full Members field.
Adding Unavailable Members to a Partition
To add unavailable members (members that do not appear in the Available Members pool) to a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with the partitions to which you want to add a member.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Click the partition key of the partition to which you want to add members.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Step 5
Click Add Other.
The Add Other Partition Member window opens.
Step 6
In the Node GUID field, enter the GUID of the host that includes the port(s) that you want to add to the partition.
Step 7
In the Port field, specify the port(s) that you want to add to the partition.
Step 8
Click the Full radio button, and then click Add.
Adding Limited Members to a Partition
Limited members of a partition can communicate with full members of the partition but not with other limited members.
These topics describe how to add limited members to a partition:
•
Adding Available Limited Members
Adding Available Limited Members
To add available limited members to a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with the partition to which you want to add a member.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Click the partition key of the partition to which you want to add members.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Step 5
In the Available Members field, click the port that you want to add to the partition, and then click the right arrow next to the Limited Members field.
Adding Unavailable Members
To add an unavailable member (member does not appear in the Available Members pool) to a partition, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with the partition to which you want to add a member.
Step 3
Expand the Partitions (
) branch to display all partitions in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Select the partition key of the partition to which you want to add members.
The members (full and limited) of the partition appear in the display.
Step 5
Click Add Other.
The Add Other Partition Member window opens.
Step 6
In the Node GUID field, enter the GUID of the node that includes the port(s) that you want to add to the partition.
Step 7
In the Port field, specify the port(s) that you want to add to the partition.
Step 8
Click the Limited radio button, and then click Add.
Viewing and Managing Multicast Groups
This section provides procedures for performing the following tasks:
•
Viewing Multicast Group Details
•
Viewing Multicast Group Members
•
Adding IPoIB Broadcast Multicast Groups
Viewing Multicast Groups
To view the multicast groups on your InfiniBand network, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with partitions that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Select the Multicast Groups (
) branch.
The multicast groups summary appears in the right pane. Table 8-9 describes the fields in this pane.
Viewing Multicast Group Details
To view multicast group details, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with multicast groups that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Expand the Multicast Groups (
) branch to display all groups in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Click the MGID of the multicast group with details that you want to view, and then click the General tab.
Multicast group details appear in the display. Table 8-10 describes the fields in this display.
Viewing Multicast Group Members
To view multicast group members, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with multicast groups that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Expand the Multicast Groups (
) branch to display all groups in the navigation menu.
Step 4
Click the MGID of the multicast group with details that you want to view.
Multicast group members appear in a table at the bottom of the display. Table 8-11 describes the fields in this display.
Adding Multicast Groups
To configure multicast groups, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Expand a subnet.
Step 3
Select Multicast Groups.
Step 4
Click Add.
Step 5
From the drop-down list, select MGID.
Step 6
In the Multicast Group ID field, enter an MGID.
Step 7
(Optional) In the QKey field, enter a queue key.
Step 8
In the MTU field, select a value to configure the maximum transmission unit of the group.
Step 9
In the PKey field, enter a partition key.
Step 10
In the Rate field, select a rate.
Step 11
In the Service Level field, enter an integer value (between 0 and 15).
Step 12
Click Add.
Note
The TClass, Packet Lifetime, Flow Label, and Hop Limit attributes are not supported in this release.
Adding IPoIB Broadcast Multicast Groups
To configure IPoIB broadcast multicast groups, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Manager window opens.
Step 2
Expand a subnet.
Step 3
Select Multicast Groups.
Step 4
Click Add.
Step 5
From the drop-down list, choose IPoIB.
Step 6
(Optional) In the QKey field, enter a queue key.
Step 7
From the drop-down list, select an MTU value.
Step 8
Enter a partition key in the PKey field.
Step 9
From the Rate field, select a data rate.
Step 10
In the Service Level field, enter an integer value (between 0 and 15).
Step 11
In the Scope field, choose a scope value.
Step 12
Click Add.
Note
The TClass, Packet Lifetime, Flow Label, and Hop Limit attributes are not included in this release.
Viewing and Managing InfiniBand Routes
This section provides procedures for performing the following tasks:
•
Routing Around Components in an InfiniBand Network
•
Removing Routes from the Route-Around Table
Viewing InfiniBand Routes
To view the route between a pair of LIDs in the InfiniBand fabric, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Managers with services that you want to view.
Step 3
Select the Routes (
) branch.
Step 4
Click the Route Filter tab.
InfiniBand routes fields appear in the right pane.
Step 5
In the Source LID field, enter the source LID of the route.
Step 6
In the Destination LID field, enter the destination LID of the route.
Step 7
Click Show Route.
Step 8
Click the Switch Route tab.
Table 8-12 describes the fields under the Switch Route tab.
Table 8-12 Switch Route Field Descriptions
Node GUID
Global unique ID of the node.
In Port
Port of ingress.
Out Port
Port of egress.
Step 9
Click the Switch Element Route tab.
Table 8-13 describes the fields under the Switch Element Route tab.
Table 8-13 Switch Element Route Field Descriptions
Chassis GUID
Global unique ID of the node.
In Port
Port of ingress.
Out Port
Port of egress.
Routing Around Components in an InfiniBand Network
To route around a chassis, nodes, or ports that are accumulating errors or to route around a component that you want to remove, follow the steps outlines in the subsections that follow.
Uses of this feature include the following:
•
Isolating ports that have accumulated errors to avoid a potential job failure. The route-around feature enables you to stop traffic from passing over a link while a job is still running, without disrupting the job.
•
Isolating a specific component, such as an InfiniBand switch card, allowing that component to be removed without the potential for job failure. You might do this, for example, before component upgrade or other replacement.
CautionThe route-around feature has the potential to exclude any chassis, node, or port from routing calculations to the extent that it is possible to disable entirely a connection between a pair of endpoints. Use care to avoid segmenting the InfiniBand fabric when using this feature.
Note
You can also route around nodes or ports (but not chassis) from the Nodes table as described in the "Routing Around Nodes and Ports" section.
These topics describe how to route around components in an InfiniBand network:
•
Viewing Route-Around Information
•
Adding Routes to the Route-Around Table
•
Removing Routes from the Route-Around Table
Viewing Route-Around Information
To view active route-around operations, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
Step 3
Select the Routes (
) branch.
Step 4
Click the Route Around tab.
Excluded routes appear in the right pane. Table 8-14 describes the fields in the pane.
Adding Routes to the Route-Around Table
To add a component to the route-around table, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with the routing information that you want to change.
Step 3
Select the Routes (
) branch.
Step 4
Click the Route Around tab.
Step 5
Click Add..
A Route Around dialog box appears.
Step 6
In the Add Route Around dialogue box, define the route you want to exclude from routing calculations:
a.
In the Type drop-down menu, select the Port, Node, or Chassis to be excluded.
b.
In the GUID field, enter the GUID of the node or chassis.
c.
In the Port Number field, specify the port number if you selected Port from the Type drop-down menu.
Step 7
Click Add.
Removing Routes from the Route-Around Table
To remove a route-around from the table, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with the routing information that you want to change.
Step 3
Select the Routes (
) branch.
Step 4
Click the Route-Around tab.
Step 5
Select the route-around that you want to remove from the table.
Step 6
Click Remove.
Viewing InfiniBand Services
To view the InfiniBand services that run on your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
Step 3
Click the Services (
) branch.
Details of InfiniBand services appear in the right pane. Table 8-15 describes the fields in the Summary section of the pane.
Viewing and Managing Port Spans
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) feature enables users to mirror the packets ingressing from one switch port to one or more specified ports (destination). With this feature you can mirror traffic only to ports on the same switch.
Note
The SPAN feature is not supported by SFS 3001 and SFS 3012 server switches.
These topics describe procedures for performing the following tasks:
Viewing Port SPAN
To view the SPAN on your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
Step 3
Click the Spans branch.
Details of InfiniBand SPANs appear in the right pane. Table 8-16 describes the fields in the Summary section of the display.
Adding a Port SPAN
To add a port SPAN to your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
Step 3
Click the Spans branch.
Details of SPANs appear in the right pane.
Step 4
To add a new Port SPAN, click Add.
The Add Port Span window opens.
Step 5
In the Source Node GUID field, enter source GUID.
Step 6
In the Source Port Number enter a valid port number.
Step 7
In the Destination Node GUID, enter the destination GUID.
Step 8
In the Destination Port Number, enter a valid port number.
Step 9
Click Add.
Removing a Port SPAN
To remove a port SPAN from your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with services that you want to view.
Step 3
Click the Spans branch.
Details of SPANs appear in the right pane.
Step 4
In the right pane, click the port SPAN that you want to delete.
Step 5
Click Remove.
Viewing Port Span Route
To view the port SPAN route information on your server switch, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
The Subnet Management (tabular format) window opens.
Step 2
Click the Port Span Route tab.
Table 8-17 describes the fields under the Port Span Route tab.
Viewing Other Subnet Managers Information
To view information on other Subnet Managers in the network, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with neighbor Subnet Managers that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Expand Subnet Managers Info.
The Port GUID, Priority, and Subnet Manager state information appears in the right pane.
Table 8-18 describes the fields in the Details pane.
Note
This menu provides information on subnet managers that are not local to the chassis to which an Element Manager is connected.
Viewing Event Subscriptions
To view the Subnet Management event subscriptions information, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
The Subnet Management window opens.
Step 2
Expand the Subnet Manager with event subscriptions that you want to view.
The navigation menu expands.
Step 3
Choose Event Subscriptions.
The LID, Node GUID, and Port Number information appears in the right pane.
Table 8-19 describes the fields under Subnet Management Event Subscriptions Details.
Viewing Forwarding Tables
This section provides procedures for performing the following tasks:
•
Viewing Multicast Forwarding Information
•
Viewing Linear Forwarding Information
Viewing Multicast Forwarding Information
To view the multicast forwarding configuration, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
Step 2
Click the MulticastForwardings tab.
Table 8-20 describes the information that appears.
Viewing Linear Forwarding Information
To view the linear forwarding configuration, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management.
Step 2
Click the LinearForwardings tab.
Table 8-21 describes the displayed fields.
Table 8-21
Linear Forwarding Entries
Viewing and Managing Arbitration Profiles
These topics describe procedures for performing the following tasks:
•
Viewing SLtoVLMapping Table of Switches
•
Viewing SLtoVLMapping Table of CAs
•
Viewing SLtoVL Mapping Profiles
•
Viewing VL Arbitration Profiles
•
Viewing VL Arbitration Tables
•
Configuring VL Arbitration Config Group
Viewing SLtoVLMapping Table of Switches
To view the SLtoVLMapping table of switches, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
Subnet Management window (tabular format) opens.
Step 2
Click the SLtoVLMappingTables of Switches tab.
Table 8-22 describes the fields.
Viewing SLtoVLMapping Table of CAs
To view SLtoVL mapping table of CAs, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
Subnet Management window (tabular format) window opens.
Step 2
Click the SLtoVL Mapping Table of CAs tab.
Table 8-23 describes the fields
Viewing SLtoVL Mapping Profiles
To view SLtoVL mapping profiles, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
Subnet Management window (tabular format) window opens.
Step 2
Click the SLtoVL Mapping Profiles tab.
Table 8-24 describes the fields
Viewing VL Arbitration Profiles
To view VL arbitration profiles, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
Subnet Management window (tabular format) opens.
Step 2
Click the VL Arbitration Profile tab.
Table 8-25 describes the fields.
Viewing VL Arbitration Tables
To view VL arbitration tables, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
Subnet Management window (tabular format) opens.
Step 2
Click the VL Arbitration Tables tab.
Table 8-26 describes the fields
Configuring VL Arbitration Config Group
Config group is for provisioning the VLArbitrationTables profile for the ports in a fabric switch. Data provisioned through this group can be retrieved using the Subnet Management VL ArbitrationProfiles Table.
To configure the card type for one interface card, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the InfiniBand menu, choose Subnet Management (tabular format).
Subnet Management (tabular format) opens.
Step 2
Click the VLArbitrationConfigGroup tab.
Step 3
In the SubnetPrefix column, enter the 64 bit subnet prefix.
Step 4
In the Action field, click the radio button of the action that you want to perform for this group.
Step 5
In the NodeGUID field, enter the 64 bit node GUID.
Step 6
In the PortNum field, enter the port number.
Step 7
In the HighLimit field, enter the value that limits the high-priority component of the VL arbitration table described by the profile.
Step 8
In the Priority field, click the radio button of the priority you want to set for the VL arbitration table.
Step 9
In the Index field, enter the value for index (valid values are 1 to 31).
Step 10
In the VL field, enter the value of the virtual lane (valid values are 1 to14).
Step 11
In the Weight field, enter the value (valid values are 0 to 255).
Step 12
Click Apply.

 Feedback
Feedback