-
Cisco Content Security and Control SSM Administrator Guide Version 6.6
-
Preface
-
Introducing the CSC SSM
-
Verifying Initial Setup
-
Configuring SMTP and POP3 Mail Traffic
-
Configuring Web (HTTP) and File Transfer (FTP) Traffic
-
Managing Updates and Log Queries
-
Administering Trend Micro InterScan
-
Monitoring Content Security
-
Troubleshooting Trend Micro InterScan
-
CSC SSM Syslog Messages
-
Reimaging and Configuring the CSC SSM Using the CLI
-
Using CSC SSM with Trend Micro Control Manager
-
Using CSC SSM with Trend Micro Damage Cleanup Services
-
Open Source License Acknowledgments
-
Glosary
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Managing Online Help Updates and Log Queries
Configuring Syslog Message Settings
Logging of Scanning Parameter Exceptions
Managing Online Help Updates and Log Queries
This chapter describes how to manage component updates, proxy and syslog message settings, and log queries, and includes the following sections:
•
Configuring Syslog Message Settings
Updating Components
New viruses and other security risks are released on the global computing community via the Internet or other distribution means at various times. TrendLabsSM immediately analyzes a new threat, and takes appropriate steps to update the components required to detect the new threat, such as the virus pattern file. This quick response enables Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM to detect, for example, a new worm that was launched from the computer of a malicious hacker in Amsterdam at 3:00 A.M. in the morning.
It is critical that you keep your components up-to-date to ensure that new threats do not penetrate your network. To accomplish this, you can do the following:
•
Perform a manual update of the components at any time, on demand.
•
Set up an update schedule that automatically updates the components on a periodic basis.
The managed components, either manually or via a schedule, are the following:
•
Virus pattern file
•
Virus scan engine
•
Spyware pattern file (also includes patterns for other types of grayware)
•
Anti-spam rules
•
Anti-spam engine
•
IntelliTrap pattern
•
IntelliTrap exception pattern
The anti-spam rules and anti-spam engine are active and updated only if you have purchased the Plus License.
To determine if you have the most current components installed, go to the Manual Update window and check the component status.
Note
The CSC SSM software does not support rollback of these updates for neither the scan engine nor the pattern file.
Manual Update
To view component status or update components manually, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Choose Update > Manual.
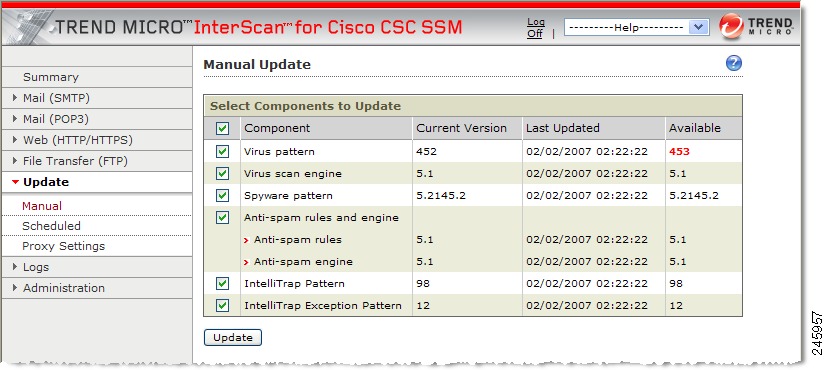
The Manual Update window appears (shown in Figure 5-1).
Figure 5-1 Manual Update Window
To view the component status, check the Available column on the right side of the window. If a more current component is available, the component version appears in red.
Step 2
Click Update to download the latest pattern file version.
A progress message displays while the new pattern is downloading. When the update is complete, the Manual Update window refreshes, showing that the latest update has been applied.
See the online help for more information about this feature.
Scheduled Update
You can configure component updates to occur as frequently as every 15 minutes.
To schedule component updates, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Choose Update > Scheduled to view the Scheduled Update window.
Step 2
Check the Enable Scheduled Update check box.
Step 3
Choose the components to be updated according to the update schedule.
Step 4
Make the desired schedule changes.
Step 5
Click Save to update the configuration.
See the online help for more information about this feature.
Configuring Proxy Settings
If you are using a proxy server to communicate with the Trend Micro ActiveUpdate server, you must specify a proxy server name or IP address and port during installation.
If you use a proxy server to access the Internet, you must enter the proxy server information into the CSC SSM before attempting to update components and web reputation queries. Any proxy information that you enter is used for both updating components from Trend Micro's update servers and for product registration and licensing.
To configure proxy settings, perform the following steps:
Step 1
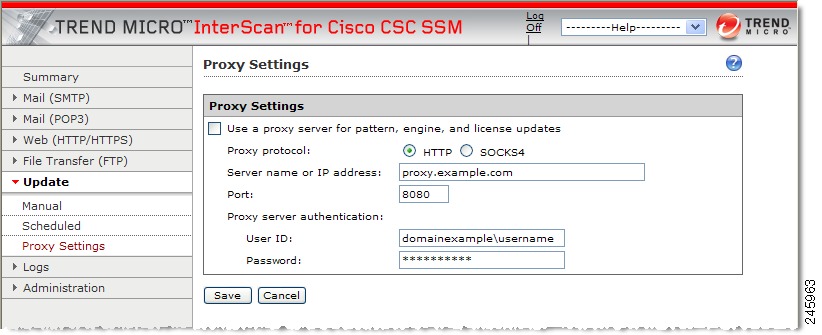
To view current proxy server settings on the Proxy Settings window (shown in Figure 5-2), choose Update > Proxy Settings.
The Proxy Settings window appears.
Figure 5-2 Proxy Settings Window
Step 2
If you set up a proxy server during installation, the HTTP proxy protocol is configured by default. To change the proxy protocol to SOCKS4, click the SOCKS4 radio button.
Step 3
If needed, add an optional proxy authentication username and password in the User ID and Password fields.
Step 4
Click Save to update the configuration when you finish.
See the online help for more information about this feature.
Configuring Syslog Message Settings
After installation, log data such as virus and spyware or grayware detection are saved temporarily. To store log data, you must configure at least one syslog server. You may configure up to three syslog servers. For more information on specific syslog messages, see Appendix A, "CSC SSM Syslog Messages."
Configuring Syslog Servers
To configure syslog messages, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Choose Logs > Settings to display the Log Settings window.
Step 2
Configure at least one syslog server. Check the Enable check box, and then enter the syslog server IP address, port, and preferred protocol (either UDP or TCP).
Step 3
Click Save.
See the online help for more information about this feature.
For information about choosing and viewing log data, see the "Viewing Log Data" section. Syslog messages are also viewable from ASDM. For more information, see the ASDM online help.
Configuring Syslog Settings
Syslog settings may be configured by the syslog facility, syslog priority, and by selecting the logs that should be saved.
By default, detected security risks are logged. You can turn off logging for features you are not using. For example, if you purchased a Plus License, but do not want to log data for URL Filtering/ Anti-Phishing and URL Blocking, uncheck these settings.
To configure the syslog settings, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Choose Logs > Settings, and go to the Syslog Settings section.
Step 2
Choose a facility from the drop-down list to associate an identifier (local0 to local7) with the device you are configuring to the syslog server.
Step 3
Check the check boxes of the logs that should be saved. The options are shown in Table 5-1.
Step 4
Click Save.
Viewing Log Data
After you have installed and configured Trend Micro InterScan for Cisco CSC SSM, security risks are being detected and acted upon according to the settings you chose for each type of risk. These events are recorded in the logs. To conserve system resources, you need to purge these logs periodically.
Note
Ad hoc queries are available through the Trend Micro Control Manager. For more information, see the "Ad Hoc Queries" section on page C-8. Ad hoc queries allow users to search, sort and save CSC SSM data in a user-friendly format.
To view log data, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Choose Logs > Query to display the Log Query window.
Step 2
Specify the inquiry parameters and click Display Log to view the log.
See the online help for more information about this feature and exporting logs.
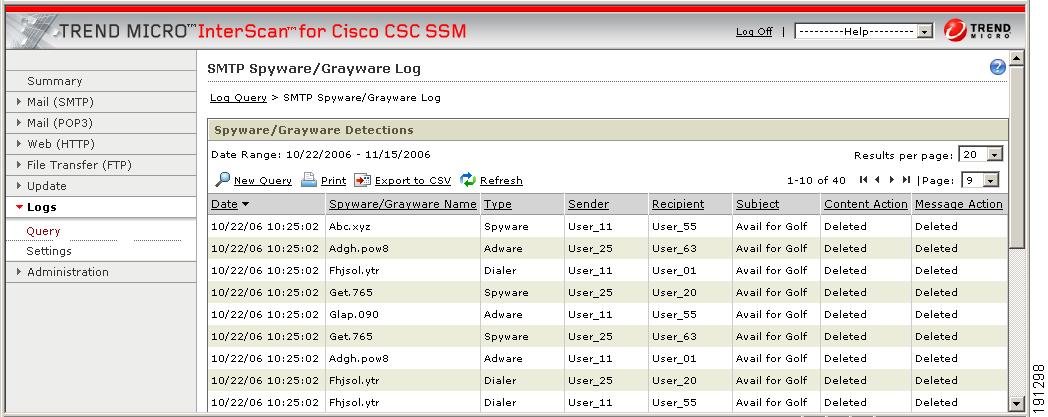
Figure 5-3 shows an example of the SMTP spyware and grayware log.
Figure 5-3 SMTP Spyware/Grayware Log
Logging of Scanning Parameter Exceptions
Exceptions to the scanning parameters are specified in the following locations:
•
Mail (SMTP)> Scanning > Incoming/Target tab
•
Mail (SMTP)> Scanning > Outgoing/Target tab
•
Mail (POP3) > Scanning/Target tab
•
Web (HTTP/HTTPS) > Scanning/Target tab
•
File Transfer (FTP) > Scanning/Target tab
Exceptions to the following scanning parameters display in the Virus/Malware log. For SMTP, POP3, HTTP/HTTPS, and FTP, the exceptions are as follows:
•
Compressed files that when decompressed, exceed the specified file count limit.
•
Compressed files that when decompressed, exceed the specified file size limit.
•
Compressed files that exceed the number of layers of compression limit.
•
Compressed files that exceed the compression ratio limit (the size of the decompressed files is "x" times the size of the compressed files).
•
Password-protected files (if configured for deletion).
Note
For HTTP/HTTPS and FTP only, additional exceptions are files or downloads that are too large for scanning. Instead of the virus or malware name, these files are identified by messages similar to the following:
Decompressed_File_Size_Exceeded
Large_File_Scanning_Limit_Exceeded

 Feedback
Feedback