Table Of Contents
Service Alarms
Service Alarms
Adaptive Polling
All IP Interfaces Down
ATM IMA Service
BFD Connectivity Down
BFD Neighbor Loss
BGP Link Down
BGP Neighbor Loss
BGP Process Down
Broken LSP Discovered
Card Down
Card Out
CFM Domain Fault
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
Chassis Disconnected
Cloud Problem
Component Unreachable
CPU Utilization
Device Unsupported
Discard Packets
Dropped Packets
DS0 Bundle Service Alarm
DS1 Path Link Down
DS1 Path Port Down
DS3 Path Link Down
DS3 Path Port Down
Dual Stack IP Changed
DWDM Controller Down
DWDM G709 Status Down
EFP Down
ESMC Process Down
Fan-Tray Down
Fan-Tray Out
GRE Keepalive
GRE Tunnel Down
HSRP Group Status Changed
Interface Status
Investigation State
L2TP Peer Not Established
L2TP Sessions Threshold
Lag Down
Lag Link Down
Layer 2 Tunnel Down
LDP Neighbor Loss
Link Down
Link Utilization
Log Archive is Disabled on the Device
Local Switching Down
Logical Port Down
LSP Down
Members Changed
Memory Utilization
MLPPP Bundle
MPLS Black Hole Found
MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
MPLS Interface Removed
MPLS TE FRR State Changed
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
MPLS TP Tunnel Down
Network-Clock Synchronization
OSPF Neighbor State Change
Port Down
Power Supply Down
Power Supply Out
Pluggable Transceiver Out
REP Port Role Change
Rx Dormant
Rx Utilization
Shelf Out
SONET Path Link Down
SONET Path Port Down
Subinterface Down
Tx Dormant
Tx Utilization
VSI Down
Registry Parameters
Adaptive Polling
All IP Interfaces Down
ATM IMA Down
BFD Connectivity Down
BFD Neighbor Loss
BGP Link Down
BGP Neighbor Loss
BGP Process Down
Broken LSP Discovered
Card Down
Card Out
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
CFM Domain Fault
Chassis Disconnected
Cloud Problem
Component Unreachable
CPU Utilization
Device Unsupported
Discard Packets
Dropped Packets
DS0 Bundle
DS1 Path Link Down
DS1 Path Port Down
DS3 Path Link Down
DS3 Path Port Down
Dual Stack IP Changed
DWDM Controller
DWDM G709 Status
EFP Down
ESMC Process Down
Fan-Tray Down
Fan-Tray Out
GRE Keepalive
GRE Tunnel Down
HSRP Group Status Changed
Interface Status
Investigation State
L2TP Peer Not Established
L2TP Sessions Threshold
Lag Down
Lag Link Down
Layer 2 Tunnel Down
LDP Neighbor Loss
Link Down
Link Utilization
Local Switching Down
Logical Port Down
LSP Down
Members Changed
Memory Utilization
MLPPP Bundle
MPLS Black Hole Found
MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
MPLS Interface Removed
MPLS TE FRR State Changed
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
MPLS TP Tunnel Down
Network-Clock Synchronization
OSPF Neighbor State Change
Port Down
Power Supply Down
Power Supply Out
Pluggable Transceiver Out
REP Port Role Change
Rx Dormant
Rx Utilization
Shelf Out
SONET Path Link Down
SONET Path Port Down
Subinterface Down
Tx Dormant
Tx Utilization
VSI Down
Alarm Source OIDs
BFD Connectivity Down OID
BFD Neighbor Loss OID
BGP Neighbor Entry OID (IBgpNeighborEntryOid)
Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid)
Chassis Oid (ChassisId)
DS0 Bundle OID (IDS0BundleOid)
DS1 Path OID (IDS1PathOid)
DS3 Path OID (IDS3PathOid)
DWDM Controller OID (IDWDMOid)
EFP OID (IEFPOID)
Fan Tray OID
IMA Service (IIMAGroupOid)
IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid)
Lag Down OID
Lag Link Down OID
L2TP Peer OID (IL2tpPeerOid)
Local Switching Entry Down OID
Logical Port OID (ILogicalPortOid)
LSP Endpoint OID (LSP EndPoint OID)
LSE Entry OID (IMplsEntryOid)
LSE OID (ILseOid)
Alarm Differentiators
Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid)
Members Changed OID (IDataLinkAggregationOid)
MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid)
Module OID (IModuleOid)
MPBGP OID (IMpBgpOid)
MPLS TE Tunnel OID (IMplsTETunnelOid)
TP Tunnel Endpoint OID (TP Tunnel EndPoint OID)
ISyncEOID
OSPF Neighbor State Change OID
Port OID
Power Supply OID
Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid)
Shelf OID (IShelfOid)
SONET Path Port Down OID
SONET Path Link Down OID
Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid)
Supported Alarms with Topological Link OID Source
Link Down Endpoint OID Structure
GRE Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure
Layer 2 MPLS Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure
BGP Link Down Endpoint OID Structure
VLAN Tagged Interface OID (IVlanTaggedInterfaceOID)
VSI OID (IVSIOID)
Service Alarms
This section describes the Prime Network service alarms (events). Service alarms appear in the Prime Network Events Service tab. For information about Prime Network Events, see the Cisco Prime Network 3.9 User Guide. These topics describe the Prime Network service alarms, registry parameters, and source OIDs:
• Service Alarms
Service Alarms
• Registry Parameters
Registry Parameters
• Alarm Source OIDs
Alarm Source OIDs
Each alarm is described in a section containing:
• A short description, including background about the network state or system (Prime Network) state that caused the alarm. The short description of the service alarm is what appears in the ticket, in the Service tab of Cisco Prime Network Events. The short description for each type and subtype can be viewed in Registry Parameters.
A short description, including background about the network state or system (Prime Network) state that caused the alarm. The short description of the service alarm is what appears in the ticket, in the Service tab of Cisco Prime Network Events. The short description for each type and subtype can be viewed in Registry Parameters.
When a flapping event occurs, the short description is changed.
Note  The name of the service alarm is the same as the short description.
The name of the service alarm is the same as the short description.
• A table of all the subtype events that represent one of the states the alarm can be in, and a description of when they are issued. For example, the Link Down alarm can have multiple subtype events (states) which include Link Down Due to Admin Down, Link Down Due to Oper Down, and Link Up. The description also shows if the event is a clearing event.
A table of all the subtype events that represent one of the states the alarm can be in, and a description of when they are issued. For example, the Link Down alarm can have multiple subtype events (states) which include Link Down Due to Admin Down, Link Down Due to Oper Down, and Link Up. The description also shows if the event is a clearing event.
• Information related to the correlation of the alarm, mainly:
Information related to the correlation of the alarm, mainly:
– The alarm issue correlation process and location (local or network).
The alarm issue correlation process and location (local or network).
– If other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
If other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
– The keys that are used in the correlation process.
The keys that are used in the correlation process.
– The specific correlation filters in use for the alarm, if any. The filter indicates if a specific event cannot be selected as the root cause event in the correlation process.
The specific correlation filters in use for the alarm, if any. The filter indicates if a specific event cannot be selected as the root cause event in the correlation process.
• By default, any new event filters the following events: Cloud Problem, BGP Process Down, LDP Neighbor Down, MPLS Interface Removed, the event itself, and events with lower or equal correlation weight.
By default, any new event filters the following events: Cloud Problem, BGP Process Down, LDP Neighbor Down, MPLS Interface Removed, the event itself, and events with lower or equal correlation weight.
Each section describes a group of alarms sharing the same event type.
Service Alarms
The following service alarms are supported in Prime Network:
• Adaptive Polling
Adaptive Polling
• All IP Interfaces Down
All IP Interfaces Down
• ATM IMA Service
ATM IMA Service
• BFD Connectivity Down
BFD Connectivity Down
• BFD Neighbor Loss
BFD Neighbor Loss
• BGP Link Down
BGP Link Down
• BGP Neighbor Loss
BGP Neighbor Loss
• BGP Process Down
BGP Process Down
• Broken LSP Discovered
Broken LSP Discovered
• Card Down
Card Down
• Card Out
Card Out
• CFM Domain Fault
CFM Domain Fault
• Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
• Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
• Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
• Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
• Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
• Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
• Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
• Chassis Disconnected
Chassis Disconnected
• Cloud Problem
Cloud Problem
• Component Unreachable
Component Unreachable
• CPU Utilization
CPU Utilization
• Device Unsupported
Device Unsupported
• Discard Packets
Discard Packets
• Dropped Packets
Dropped Packets
• DS0 Bundle Service Alarm
DS0 Bundle Service Alarm
• DS1 Path Link Down
DS1 Path Link Down
• DS1 Path Port Down
DS1 Path Port Down
• DS3 Path Link Down
DS3 Path Link Down
• DS3 Path Port Down
DS3 Path Port Down
• Dual Stack IP Changed
Dual Stack IP Changed
• DWDM Controller Down
DWDM Controller Down
• DWDM G709 Status Down
DWDM G709 Status Down
• EFP Down
EFP Down
• ESMC Process Down
ESMC Process Down
• Fan-Tray Down
Fan-Tray Down
• Fan-Tray Out
Fan-Tray Out
• GRE Keepalive
GRE Keepalive
• GRE Tunnel Down
GRE Tunnel Down
• HSRP Group Status Changed
HSRP Group Status Changed
• Interface Status
Interface Status
• Investigation State
Investigation State
• L2TP Peer Not Established
L2TP Peer Not Established
• L2TP Sessions Threshold
L2TP Sessions Threshold
• Lag Down
Lag Down
• Lag Link Down
Lag Link Down
• Layer 2 Tunnel Down
Layer 2 Tunnel Down
• LDP Neighbor Loss
LDP Neighbor Loss
• Link Down
Link Down
• Link Utilization
Link Utilization
• Log Archive is Disabled on the Device
Log Archive is Disabled on the Device
• Local Switching Down
Local Switching Down
• Logical Port Down
Logical Port Down
• LSP Down
LSP Down
• Members Changed
Members Changed
• Memory Utilization
Memory Utilization
• MLPPP Bundle
MLPPP Bundle
• MPLS Black Hole Found
MPLS Black Hole Found
• MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
• MPLS Interface Removed
MPLS Interface Removed
• MPLS TE FRR State Changed
MPLS TE FRR State Changed
• MPLS TE Tunnel Down
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
• MPLS TP Tunnel Down
MPLS TP Tunnel Down
• Network-Clock Synchronization
Network-Clock Synchronization
• OSPF Neighbor State Change
OSPF Neighbor State Change
• Port Down
Port Down
• Power Supply Down
Power Supply Down
• Power Supply Out
Power Supply Out
• Pluggable Transceiver Out
Pluggable Transceiver Out
• REP Port Role Change
REP Port Role Change
• Rx Dormant
Rx Dormant
• Rx Utilization
Rx Utilization
• Shelf Out
Shelf Out
• SONET Path Link Down
SONET Path Link Down
• SONET Path Port Down
SONET Path Port Down
• Subinterface Down
Subinterface Down
• Tx Dormant
Tx Dormant
• Tx Utilization
Tx Utilization
• VSI Down
VSI Down
Adaptive Polling
Adaptive polling is a mechanism that handles situations in which the device CPU is crossing a predefined, configurable threshold. It reduces the polling when the CPU reaches high threshold values for a configurable sample, and returns the polling to a normal rate when the CPU reaches the lower threshold. Where the CPU stays high for several samplings, the VNE is automatically moved to the maintenance state to avoid continuous polling of the device.
In all cases, alarms are issued when the device or the VNE state changes.
Table 15-1 Adaptive Polling—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
VNE Switched to Low Polling Rate Due to CPU High Usage
|
Issued when the CPU level has been above the high threshold (configurable, default=90%) for several samplings (configurable, default=5). The polling rate of the device is lowered by adding a delay between requests (default delay is 500 msec).
|
VNE Switched Back to Regular Polling Rate
|
Clearing event. Issued when the CPU level has been below the lower threshold (configurable, default=70%) for several samplings (configurable, default=2). The polling rate of the device is changed back to normal (no delay between requests).
|
VNE Switched to a Limited Investigation Mode Due to High CPU Usage
|
Issued when the CPU level raises above a threshold and the VNE stops polling the device. The VNE starts polling the device automatically once the CPU usage decreases.
|
Correlation
The alarm correlates to other alarms using the local correlation mechanism with the ManagedElement key. No other alarms can correlate to it.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid).
All IP Interfaces Down
The All IP Interfaces Down alarm is used when all IP interfaces configured on the same port are down, and implies that another fault has occurred in lower layers (such as the physical layer). In this case, one alarm is issued, and all IP interface status alarms are correlated to it.
Table 15-2 All IP Interfaces Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
All IP Interfaces Down
|
Issued when all the IP interfaces configured above a physical interface change their state to down.
|
Active IP Interfaces Found
|
Clearing event. Issued when at least one of the IP interfaces changes its state to up.
|
Correlation
The alarm correlates to other alarms using the local correlation mechanism with the PortLayer1 key representing the physical layer. The PortLayer1 key is the port that all the IP interfaces were configured on.
Other alarms might correlate to this alarm using the physical port key, in particular the Interface Status Down alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
ATM IMA Service
The ATM IMA Service alarm is generated by the IMA group. IMA Group Down events are generated when the number of IMA group members is reduced by a user-defined percentage configured in the registry. The severity depends on the percentage of member removed. To avoid false correlations, the events are combined with the IMA group status. An IMA group down generates the highest severity. Other severities are user-defined.
Table 15-3 ATM IMA Service Alarm
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
IMA Admin Down
|
Generated when the IMA group is administratively shut down. All the members are correlated to this event.
|
IMA Oper Down
|
Generated when the IMA group is operationally down.
|
Correlation
The IMA Admin Down alarm can be the root cause of other events, but other ATM IMA events cannot be root cause of other events. No events are correlated.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See IMA Service (IIMAGroupOid).
BFD Connectivity Down
The BFD Connectivity Down Alarm is generated when the connectivity is lost between two BFD neighbors.
Table 15-4 BFD Connectivity Down
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
BFD Connectivity Down
|
Generated when BFD connection is lost.
|
BFD Connectivity Up
|
Clearing Event. Generated when BFD connection is found.
|
Correlation
BFD Connectivity Down alarm uses flow based correlation.
The VNE with flow based correlation mechanisim uses an active correlation flow that traverses among three layers of the network (Layer 1,Layer 2, and Layer 3) and tries to correlate along a specified network path to an alarm. Based on the alarm that could occur in any one of the layers, it will try to find the root cause alarm. BFD Connectivity Down alarm can corrleate to alarms that are found upto Layer 3.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See BFD Connectivity Down OID.
BFD Neighbor Loss
A BFD Neighbor Loss alarm is triggered when the status of BFD changes. When the status of a BFD is changed, an alarm will be issued by each neighbor as a separate event. These alarms will remain displayed until the parent ticket is cleared, that is until the status of the BFD neighbor changes to its previous state.
A BFD Neighbor Found alarm is a clearing event for the BFD Neighbor Loss alarm. It is triggered when the alarm state changes from down to up.
Table 15-5 BFD Neighbor Loss
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
BFD Neighbor Loss
|
Generated when the connection to BFD neighbor is lost.
|
BFD Neighbor Found
|
Clearing Event.Generated when the BFD Neighbor is found.
|
Correlation
BFD Neighbor Loss alarm uses flow based correlation.
The VNE with flow based correlation mechanisim uses an active correlation flow that traverses among three layers of the network (Layer 1,Layer 2, and Layer 3) and tries to correlate along a specified network path to an alarm. Based on the alarm that could occur in any one of the layers, it will try to find the root cause alarm. BFD Neighbor loss alarm can corrleate upto Layer 3.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See BFD Neighbor Loss OID.
BGP Link Down
When a connection between two BGP peers is lost, no route information is exchanged between the two peers. This situation affects the network connectivity because route entries which are not refreshed start to be dropped from the routing table, causing packets to be dropped.
In this scenario, when a BGP neighbor has an adjacent peer (meaning that it is connected to another BGP neighbor with a discovered link), a BGP Link Down alarm is issued. When the adjacent peer is not managed, a BGP Neighbor Loss alarm is issued. A VNE identifies this situation based on changes in the BGP neighbor table of the device.
Due to the nature of this fault, it is possible that one of the devices may be unreachable. In this case, the respective VNE does not identify the changes in the BGP neighbor table of the unreachable device, but a BGP Link Down is still issued.
A negotiation process between the two link edges is issued when the BGP neighbor entry state changes from Established, indicating that a BGP Link Down should be invoked.
Table 15-6 BGP Link Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
BGP Link Down Due to Admin Down
|
Issued when a BGP neighbor entry has changed its state from Established to another state, or a BGP neighbor entry that had an Established state has been removed from the BGP neighbors table and the entry has an adjacent peer.
BGP neighbor state complies with the definitions in BGP4-MIBBFDbgpPeerState (1.3.6.1.2.1.15.3.1.2). In the case of a state change, any state other than Established implies that the connection between the BGP peers is not fully functioning, which means the route information is not exchanged.
This alarm is issued when a BGP link is administratively down.
|
BGP Link Down Due to Oper
|
Issued when a BGP neighbor entry has changed its state from Established to another state, or a BGP neighbor entry that had an Established state has been removed from the BGP neighbors table and the entry has an adjacent peer.
BGP neighbor state complies with the definitions in BGP4-MIB::bgpPeerState (1.3.6.1.2.1.15.3.1.2). In the case of a state change, any state other than Established implies that the connection between the BGP peers is not fully functioning, which means the route information is not exchanged.
This alarm is issued when a BGP link is operatively down.
|
BGP Link Down VRF Due to Admin
|
Issued in the same conditions as the BGP Link Down alarm except that the neighbor is defined in the context of a VRF (BGP connection between PE router and CE router).
This alarm is issued when a BGP link is administratively down.
|
BGP Link Down VRF Due to Oper
|
Issued in the same conditions as the BGP Link Down alarm except that the neighbor is defined in the context of a VRF (BGP connection between PE router and CE router).
This alarm is issued when a BGP link is operatively down.
|
BGP Link Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when one of the edge BGP neighbor entries has changed its state from any state other than Established to Established. This is the clearing alarm for both the BGP Link Down alarms previously described.
|
Correlation
The alarm correlates to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward IP flow to the BGP neighbor peer IP. This flow runs a forward flow from each of the BGP neighbors to its peer IP, and might collect the following alarms: Interface Status Down, Port Down, Link Down, Device Unreachable, and so on.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the MPBgp key or the MPBgp key concatenated with the neighbor peer IP. Furthermore, the relevant BGP Neighbor Down syslogs are correlated to the service alarm.
Note  The BGP Link Down and BGP Link Down VRF alarms do not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
The BGP Link Down and BGP Link Down VRF alarms do not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See MPBGP OID (IMpBgpOid).
BGP Neighbor Loss
If BGP connectivity to a specific device in an MPLS VPN network is lost, VPN sites lose connectivity. The VNE models the BGP connection between routers and actively monitors its state. A BGP Neighbor Loss alarm is generated from both sides of the connection when a connectivity loss occurs. Alarms and tickets are issued and impact analysis information displayed.
The correlation engine identifies various faults that affect the BGP connection and reports them as the root cause for the BGP Neighbor Loss alarm, for example, Link Down, CPU Overutilized, and Link Data Loss.
Note  BGP Neighbor Loss alarms are not correlated to each other. They are correlated to the root cause of the connectivity loss.
BGP Neighbor Loss alarms are not correlated to each other. They are correlated to the root cause of the connectivity loss.
The BGP Neighbor Loss alarm is detected actively by the system, and service alarms are generated. The system also supports BGP neighbor down syslogs.
When the VNE BGP component polls the BGP neighbor status (expedite or normal polling) and finds that an entry for a neighbor no longer exists or its state changed from Established to another state, the BGP component issues a BGP Neighbor Loss alarm. This alarm causes the BGP component to issue a Root Cause Analysis (RCA) correlation flow to find the root cause. If RCA does not find an alarm to correlate, the VNE sends the alarm to the gateway as a ticket.
If a BGP neighbor loss occurs and the BGP component has no other BGP PE links, all VRFs with route entries to the PE as BGP next hops are true-affected. This information is sent as an update to the previous BGP Neighbor Loss alarm.
Table 15-7 BGP Neighbor Loss—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
BGP Neighbor Loss Due to Admin
|
Issued when a BGP neighbor entry has changed its state from Established to another state due to admin, or when a BGP neighbor entry with the Established state has been removed from the BGP neighbors table.
BGP neighbor state complies with the definitions in BGP4-MIB::bgpPeerState (1.3.6.1.2.1.15.3.1.2). In the case of a state change, any state other than Established implies that the connection between the BGP peers is not fully functioning, meaning that the route information is not exchanged.
|
BGP Neighbor Loss Due to Oper
|
Issued when a BGP neighbor entry has changed its state from Established to another state due to oper, or when a BGP neighbor entry with the Established state has been removed from the BGP neighbors table.
|
BGP Neighbor Loss VRF Due to Admin
|
Issued in the same conditions as the BGP Neighbor Loss Due to Admin alarm, except that the neighbor is defined in the context of a VRF (BGP connection between PE router and CE router).
|
BGP Neighbor Loss VRF Due to Oper
|
Issued in the same conditions as the BGP Neighbor Loss Due to Oper alarm, except that the neighbor is defined in the context of a VRF (BGP connection between PE router and CE router).
|
BGP Neighbor Found
|
Clearing event. Issued when a BGP neighbor entry has changed its state from any state other than Established to the Established state, or a new BGP neighbor entry that has an Established state has been discovered in the BGP neighbors table. This is the clearing alarm of both neighbor loss alarms previously described.
|
Correlation
The alarm correlates to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward IP flow to the BGP neighbor peer IP. This flow runs a forward flow from each of the BGP neighbors to its peer IP, and might collect the following alarms: Interface Status Down, Port Down, Link Down, Device Unreachable, and so on.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the MPBgp key or the MPBgp key concatenated with the neighbor peer IP. Furthermore, the relevant BGP Neighbor Down syslogs are correlated to the service alarm.
Note  The BGP Neighbor Loss and BGP Neighbor Loss VRF alarms do not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
The BGP Neighbor Loss and BGP Neighbor Loss VRF alarms do not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
Impact Analysis
The alarm issues an impact analysis process that calculates the affected services of this fault. In this case, the affected service is represented as a pair of VRFs that cannot communicate due to this BGP Neighbor Loss fault.
The affected pair (service) can be marked as potentially affected or real affected. In this case, because the BGP reports on a neighbor loss only after a hold-time interval (default 180 sec), in which it did not get the hello message from its neighbor, it assumes that the connection was lost and cannot be recovered. The identified affected pairs are marked as real affected.
Source OID
See MPBGP OID (IMpBgpOid).
BGP Process Down
A Prime Network query checks the status of the BGP process when the VNE BGP component polls for the status and configuration of its BGP neighbors (expedite or normal polling). If the BGP process is not running, the VNE BGP component issues a BGP Process Down alarm. This alarm is always a ticket and does not try to correlate to other alarms. All BGP Neighbors Down alarms issued in response to the BGP Process Down alarm are correlated to the BGP Process Down ticket.
Table 15-8 BGP Process Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
BGP Process Down
|
Issued when the BGP process/service is down after it was up. The BGP component in the VNE identifies this change, updates its state, and issues the alarm.
|
BGP Process Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the BGP process/service changes its state back to up. The BGP component in the VNE identifies this change, updates its state, and issues the clearing alarm.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of this alarm, it cannot be correlated to other alarms, thus this alarm does not try to run any correlation process.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the MPBgp key, in particular BGP Neighbor Loss alarms caused by this failure correlate to it.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See MPBGP OID (IMpBgpOid).
Broken LSP Discovered
A Broken LSP Discovered alarm is issued as a companion to the MPLS Black Hole Found alarm (see MPLS Black Hole Found.)
A Broken LSP Discovered event means that an LSP, at some point, went through an MPLS black hole. Because of this, the MPLS labels were removed from the packet, and one of the following scenarios occurs:
• If the packet contains more than one MPLS label (data contained in the packet is VPN traffic), the packet is dropped or is forwarded to an incorrect destination. This happens because the IP header in the packet belongs to a different routing domain.
If the packet contains more than one MPLS label (data contained in the packet is VPN traffic), the packet is dropped or is forwarded to an incorrect destination. This happens because the IP header in the packet belongs to a different routing domain.
• If the packet contains only one MPLS label (data contained in the packet belongs to the same routing domain), the packet continues to be forwarded based on the IP header information instead of the MPLS labels. This is not a problem.
If the packet contains only one MPLS label (data contained in the packet belongs to the same routing domain), the packet continues to be forwarded based on the IP header information instead of the MPLS labels. This is not a problem.
The following information applies to the Broken LSP Discovered alarm:
• This alarm does not have a clearing alarm, which means that after it is issued, its severity cannot be changed.
This alarm does not have a clearing alarm, which means that after it is issued, its severity cannot be changed.
• To overcome the previous limitation, the alarm auto-clear flag is set to true. This means that this alarm severity does not have an impact on the severity of other alarms that it correlates to.
To overcome the previous limitation, the alarm auto-clear flag is set to true. This means that this alarm severity does not have an impact on the severity of other alarms that it correlates to.
• Though the Broken LSP Discovered alarm is issued as a companion to the MPLS Black Hole Found, it does not imply that it is issued from the same device that issued the MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
Though the Broken LSP Discovered alarm is issued as a companion to the MPLS Black Hole Found, it does not imply that it is issued from the same device that issued the MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
After an MPLS Black Hole Found alarm is issued, a process starts and looks for broken LSPs that go through this MPLS black hole. The process of discovering the broken LSPs is as follows:
1.  At the VNE on which the MPLS Black Hole Found was issued, all label switching entries that were destined for the black hole have an untagged out label. All MPLS labels are removed from packets traversing using this label switching entry.
At the VNE on which the MPLS Black Hole Found was issued, all label switching entries that were destined for the black hole have an untagged out label. All MPLS labels are removed from packets traversing using this label switching entry.
2.  Each untagged label switching entry starts traversing the LSP using a backward flow.
Each untagged label switching entry starts traversing the LSP using a backward flow.
Note  The direction of a backward flow traversing the VNE model is opposite that of a standard packet flow traversing the network.
The direction of a backward flow traversing the VNE model is opposite that of a standard packet flow traversing the network.
3.  On each device traversed in the backward flow, Prime Network checks for configured MPLS-based services on the device. The following identification services are supported:
On each device traversed in the backward flow, Prime Network checks for configured MPLS-based services on the device. The following identification services are supported:
– Existence of VRFs (BGP/MPLS VPN services based on RFC2547).
Existence of VRFs (BGP/MPLS VPN services based on RFC2547).
– Existence of MPLS Layer2 tunnels (PWE3 services based on RFC4448).
Existence of MPLS Layer2 tunnels (PWE3 services based on RFC4448).
4.  If the device contains such services, a Broken LSP Discovered alarm is issued for each LSP traversed backward to that point.
If the device contains such services, a Broken LSP Discovered alarm is issued for each LSP traversed backward to that point.
This means that only PE routers issue such alarms. It is possible that the same LSP has entry points in multiple devices, and thus multiple alarms are issued for it.
5.  Information that is important for each broken LSP alarm issued is the entry point (label switching entry) and the exit point (the IP subnet destination).
Information that is important for each broken LSP alarm issued is the entry point (label switching entry) and the exit point (the IP subnet destination).
This information is used in the impact analysis process to identify the relevant affected pairs (services).
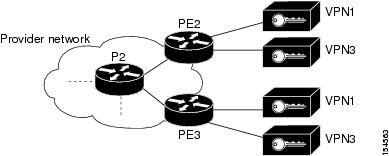
In the network described in Figure 15-1, the shortest path from PE2 to PE3 is PE2< >P2< >PE3. The link between P2 and PE3 is an MPLS link, meaning interfaces on both sides of the link are configured as MPLS interfaces. Also assume that for some reason, the MPLS configuration is incomplete or incorrect; for example:
• Only one interface is configured as an MPLS interface.
Only one interface is configured as an MPLS interface.
• The label distribution protocol is configured differently on both interfaces (protocol mismatch).
The label distribution protocol is configured differently on both interfaces (protocol mismatch).
In this case, the label switching table on P2 and PE3 will have untagged entries for the LSPs between PE2 and PE3. If PE2 and PE3 have VPN services (for example VRFs and pseudowires), the outcome will be that the data flow between PE2 and PE3 will be affected.
Figure 15-1 Example of an MPLS Black Hole Scenario
In this case, Prime Network does the following:
• Identifies untagged label switching entries on P2 and PE3.
Identifies untagged label switching entries on P2 and PE3.
• Issues MPLS Black Hole Found alarms on the interfaces on both sides of the link (since the LSP is unidirectional).
Issues MPLS Black Hole Found alarms on the interfaces on both sides of the link (since the LSP is unidirectional).
• Initiates a backward flow starting from the link on the specific untagged entries and identifies the two LSPs traversing the link:
Initiates a backward flow starting from the link on the specific untagged entries and identifies the two LSPs traversing the link:
– LSP from PE2 to PE3
LSP from PE2 to PE3
– LSP from PE3 to PE2
LSP from PE3 to PE2
• Issues Broken LSP Discovered alarms on both LSPs in PE2 and PE3, which are correlated to the corresponding MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
Issues Broken LSP Discovered alarms on both LSPs in PE2 and PE3, which are correlated to the corresponding MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
Note  The clearing alarm does not activate flows to locate the LSPs that were passing through it in order to issue a clearing alarm for Broken LSPs, but rather uses the auto-clear functionality. The gateway periodically reviews the tickets and checks if all the alarms under each ticket are cleared or configured as auto-cleared alarms and whether the gateway correlation timeout has passed, in which case the gateway closes the ticket.
The clearing alarm does not activate flows to locate the LSPs that were passing through it in order to issue a clearing alarm for Broken LSPs, but rather uses the auto-clear functionality. The gateway periodically reviews the tickets and checks if all the alarms under each ticket are cleared or configured as auto-cleared alarms and whether the gateway correlation timeout has passed, in which case the gateway closes the ticket.
After the MPLS Black Hole alarm clears, and the configured gateway correlation timeout period is reached, the gateway can close the ticket because all the alarms correlated to MPLS Black Hole and Broken LSP are auto-cleared.

Note  If an MPLS Network Link Down event causes an IP reroute and an LDP redistribution, new LSPs might be redirected through nonMPLS segments, which will create a black hole. In this case, Broken LSP Discovered alarms are issued. However, the discovered broken LSPs are correlated to the Link Down alarm and not to the MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
If an MPLS Network Link Down event causes an IP reroute and an LDP redistribution, new LSPs might be redirected through nonMPLS segments, which will create a black hole. In this case, Broken LSP Discovered alarms are issued. However, the discovered broken LSPs are correlated to the Link Down alarm and not to the MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
Table 15-9 Broken LSP Discovered—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Broken LSP Discovered
|
Issued as a companion to the MPLS Black Hole Found alarm as described previously. For every LSP traversing the black hole, a Broken LSP Discovered alarm is issued.
There is no clearing event.
|
Correlation
This alarm is correlated by definition to one of the following:
• The MPLS Black Hole Found that triggered the discovery of this broken LSP.
The MPLS Black Hole Found that triggered the discovery of this broken LSP.
• Link Down alarm, if the link down caused the MPLS traffic to change its course and pass through the black hole.
Link Down alarm, if the link down caused the MPLS traffic to change its course and pass through the black hole.
No other alarms can correlate to it.
Impact Analysis
The alarm issues an impact analysis process that identifies the local affected services of this fault. In this case, affected services can be of two types:
• A pair of VRFs that cannot communicate due to this broken LSP (for BGP/MPLS VPN services).
A pair of VRFs that cannot communicate due to this broken LSP (for BGP/MPLS VPN services).
• A pair of MPLS Layer 2 tunnel edges representing a PWE3 service endpoint.
A pair of MPLS Layer 2 tunnel edges representing a PWE3 service endpoint.
The affected pairs in this alarm are marked as potentially affected.
Note  The system can be configured to present the affected pairs for BGP/MPLS VPN services as pairs of VRF IP interfaces instead of just the VRFs. This creates, in most cases, additional pairs that might cause a load on the system. Configuring them as IP interfaces is disabled by default.
The system can be configured to present the affected pairs for BGP/MPLS VPN services as pairs of VRF IP interfaces instead of just the VRFs. This creates, in most cases, additional pairs that might cause a load on the system. Configuring them as IP interfaces is disabled by default.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid) (the LSE entry that is the entry point to the broken LSP).
Card Down
The Card Down alarm represents a state in which a card is not operational. This can be caused by a hardware failure, or by changing the administrative state of the card.
Table 15-10 Card Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Card Down
|
Issued when the operational state of a card is changed to down. This can be caused by a hardware failure, or by changing the administrative state of the card
|
Card Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the operational state of the card changes back to up.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of this alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the Card key.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Module OID (IModuleOid).
Card Out
The Card Out alarm represents a state where a card is removed from the device. The Card Out alarm is also issued when a device stops reporting on the existence of a card due to another failure, even if the card is actually still in the device. It is assumed that any functionality that was implemented by the card is not working anymore if the card had no redundancy configuration.
Note  When a Card Out alarm occurs, Prime Network Vision displays an alarm icon next to the affected card in the inventory display. Even though the card has been physically removed, it is still displayed in Prime Network Vision so that you can identify which network element is generating the alarm.
When a Card Out alarm occurs, Prime Network Vision displays an alarm icon next to the affected card in the inventory display. Even though the card has been physically removed, it is still displayed in Prime Network Vision so that you can identify which network element is generating the alarm.
Table 15-11 Card Out—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Card Out
|
Issued when a card is removed from the device. It is possible that some card failures are identified as Card Out because the device does not report on the card's existence after a failure.
|
Subcard Out
|
Issued when a card that is contained in another card is removed from the device. When a card that contains other cards is removed, in addition to the Card Out alarm issued on the main card, a Subcard Out alarm is issued for each of its subcards. It is possible that some failures of cards that contain subcards are identified as Card Down on the parent card and Subcard Out for the subcards, because the device stops reporting on the existence of the subcards.
|
Card Out due to Chassis Disconnected
|
Issued when a chassis is removed from the network element corresponding to which the cards in the chassis are unavailable in the network element. It is possible that some card failures are identified as Card Out because the device does not report on the card's existence after a failure.
|
Card In
|
Clearing event. Issued when the card is inserted back into the device.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Card Out alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket. The Subcard Out alarm correlates to other alarms using the local correlation mechanism with Subcard key and its parent Card key.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the Card and Subcard keys.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Module OID (IModuleOid).
CFM Domain Fault
The CFM Domain Fault service alarm is created for every CFM domain having at least one event attached to an entity belonging to that domain (Maintenance Association, Maintenance Endpoint, and Remote Maintenance Endpoint). The CFM Domain Fault service alarm is cleared after all the correlated events are cleared.
Events can be aggregated as long as they have a common source OID.
The CFM application is used to aggregate the different CFM syslogs and traps by domain.
The domain OID is contained in the MEP OID.
Table 15-12 CFM Domain Fault
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
CFM Domain Aggregation Down
|
Created for every domain that has at least one event attached to an entity belonging to the domain: Maintenance Association, Maintenance Endpoint (MEP), or Remote MEP.
|
CFM Domain Aggregation Up
|
Issued after all correlated events are cleared.
|
Correlation
Because Prime Network does not discover CFM topologies, CFM event correlation is not available.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
IMaintenanceDomainOID
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
When data packets traverse from the private to public network, the Cisco CRS-1 routers (configured with Carrier Grade NAT) translate many private IPv4 addresses into fewer public IPv4 addresses. Similarly, when data packets traverse from the public to private network, many public IPv4 addresses are translated into fewer private IPv4 addresses.
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate represents the number of translation entries that are created in the last one second. Alarms are issued when the number of translations exceeds or drops below the threshold value. The threshold values can be changed by the user.
Correlation
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate service alarm does not try to correlate with any other alarm.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid).
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
When data packets traverse from the private to public network, the Cisco CRS-1 routers (configured with Carrier Grade NAT) translate many private IPv4 addresses into fewer public IPv4 addresses. Similarly, when data packets traverse from the public to private network, many public IPv4 addresses are translated into fewer private IPv4 addresses.
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate represents the number of translation entries that are deleted in the last one second. Alarms are issued when the number of translations exceeds or drops below the threshold value. The threshold values can be changed by the user.
Correlation
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate service alarm does not try to correlate with any other alarm.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid).
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
Data packets enter the Cisco CRS-1 routers (configured with Carrier Grade NAT) from the private network. The destination address of the packet is changed to a global address and is forwarded to the public network.
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate represents the number of packets that have been forwarded from the private to the public network in the last one second. Alarms are issued when the number of forwarded packets, exceeds or drops below the threshold value. The threshold values can be changed by the user.
Correlation
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate service alarm does not try to correlate with any other alarm.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid).
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
Data packets enter the Cisco CRS-1 routers (configured with Carrier Grade NAT) from the public network. The destination address of the packet is changed to a private address and the packet is forwarded to the private network.
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate represents the number of packets that have been forwarded from the private to the public network in the last one second. Alarms are issued when the number of forwarded packets, exceeds or drops below the threshold value. The threshold values can be changed by the user.
Correlation
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate service alarm does not try to correlate with any other alarm.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid).
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
When data packets traverse from the private network to public network, Cisco CRS-1 routers (configured with Carrier Grade NAT) translates the private addresses into global addresses. Data packets can get dropped during the inside-to-outside translations, when the port limit is exceeded.
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded alarm is issued when the number of dropped packets, exceeds or drops below the threshold value. The threshold values can be changed by the user.
.
Correlation
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded service alarm does not try to correlate with any other alarm.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid).
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
When data packets traverse from the private network to public network, Cisco CRS-1 routers (configured with Carrier Grade NAT) translates the private addresses into global addresses. Data packets can get dropped during the inside-to-outside translations, when the system limit is reached.
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached alarm is issued when the number of dropped packets, exceeds or drops below the threshold value. The threshold values can be changed by the user.
.
Correlation
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached service alarm does not try to correlate with any other alarm.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid).
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
When data packets traverse from the private network to public network, Cisco CRS-1 routers (configured with Carrier Grade NAT) translates the private addresses into global addresses. Data packets can get dropped during the inside-to-outside translations, when no ports are available.
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion alarm is issued when the number of dropped packets, exceeds or drops below the threshold value. The threshold values can be changed by the user.
Correlation
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion service alarm does not try to correlate with any other alarm.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid).
Chassis Disconnected
The Chassis Disconnected represents a state where a chassis is removed from a network element. The Chassis Disconnected alarm is also issued when a port connecting the chassis is removed from the network element, even if the chassis is actually still in the network element. As the port is removed, the corresponding cards in the chassis are also disconnected from the network element. The system administrator would need to manually connect the chassis or the port to the network element.
Note  When a Chassis Disconnected alarm occurs, Prime Network Vision displays an alarm icon next to all the affected cards of the chassis in the inventory display. This enables you to identify which network element is generating the alarm.
When a Chassis Disconnected alarm occurs, Prime Network Vision displays an alarm icon next to all the affected cards of the chassis in the inventory display. This enables you to identify which network element is generating the alarm.
Table 15-20 Chassis Disconnected—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Chassis Disconnected
|
Issued when a chassis is removed from a network element.
|
Chassis Connected
|
Clearing event. Issued when the chassis is inserted back into the network element.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Chassis Disconnected alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket. A clearance event is generated when the chassis is connected back into the network element.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Chassis Oid (ChassisId)
Cloud Problem
Cloud VNEs represent unmanaged network segments, so that operations such PathTracer and Root Cause Analysis (RCA) can be viewed or processed end-to-end. A Cloud VNE represents the unmanaged segment of a network as a single device to which two or more managed segments of the network can be connected.
In a network in which a segment of the network is unmanaged, Prime Network runs a correlation flow to find the root cause. If no root cause is found within the managed segment, a Cloud Problem service alarm is created, to which events are correlated.
Table 15-21 Cloud Problem—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Cloud Problem
|
An alarm might use network correlation using IP-based forward flow to a destination. During the flow, the alarm collects possible alarms with which to correlate. If it can find no such alarms, and the flow has traversed a Cloud VNE (a network segment unmanaged by Prime Network), at the end of the flow a Cloud Problem alarm is issued. The original alarm is correlated to it.
This alarm does not have a clearing alarm, thus the severity of the Cloud Problem alarm is informational.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Cloud Problem alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, but creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
Note  When required, a correlation filter filters the Cloud Problem alarm. This enables or disables the ability of an alarm to create a Cloud Problem alarm and to correlate to it. The default value is false for all alarms in the system, meaning that an alarm does not correlate to the Cloud Problem alarm by default. However, there are several events that override the default configuration (these events are specific to Cisco devices) and are set to true, as follows:
When required, a correlation filter filters the Cloud Problem alarm. This enables or disables the ability of an alarm to create a Cloud Problem alarm and to correlate to it. The default value is false for all alarms in the system, meaning that an alarm does not correlate to the Cloud Problem alarm by default. However, there are several events that override the default configuration (these events are specific to Cisco devices) and are set to true, as follows:
• BGP Neighbor Down syslog
BGP Neighbor Down syslog
• OSPF Neighbor Loss syslog
OSPF Neighbor Loss syslog
• EIGRP Router Query to Neighbors Timeouted syslog
EIGRP Router Query to Neighbors Timeouted syslog
As described previously, other alarms might be correlated to it using the logic in the Cloud Problem subalarm. See Cloud Problem.
Note  The Cloud Problem alarm does not filter the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
The Cloud Problem alarm does not filter the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid).
Component Unreachable
A VNE might be configured to poll its respective device in multiple network protocols (for example both SNMP and Telnet). In addition, each protocol can be configured for reachability testing. This means that when the VNE stops responding using a protocol, the device is considered unreachable.
Table 15-22 Component Unreachable—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Component Unreachable
|
Issued when the device is not responding to at least one of the network protocols that are configured for reachability.
The VNE uses a retry mechanism to make sure the problem persists for a certain configurable duration before issuing an alarm. This means that it is resilient during short periods of network packet loss.
Note  Prime Network will generate Device Unreachable events, with corresponding SNMP Timeout messages in the AVM log file, for devices with nonunique SNMP engine identifiers. These identifiers are normally derived from the unique MAC address of the device and assigned automatically. You can also customized them. But then you must try to avoid custom SNMP engine identifiers. However if you do use them, ensure that they are unique. Prime Network will generate Device Unreachable events, with corresponding SNMP Timeout messages in the AVM log file, for devices with nonunique SNMP engine identifiers. These identifiers are normally derived from the unique MAC address of the device and assigned automatically. You can also customized them. But then you must try to avoid custom SNMP engine identifiers. However if you do use them, ensure that they are unique.
|
Component Reachable
|
Clearing event issued when the device responds to all the network protocols that are configured for reachability.
|
Device Partially Managed
|
Warning event issued when the device is partially managed.
|
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid) (the managed element of the Cloud VNE).
Checking Reachability
Reachability used by the VNEs (to check the reachability between the VNEs and network elements) depends on the configuration of the VNE, and involves multiple connectivity tests using SNMP, Telnet/SSH, and ICMP, as appropriate.
The following table describes the various situations where an NE fails to respond to the protocols:
Table 15-23 Unreachable Network Elements
VNE Type
|
Protocol Used to Check Reachability
|
Action Taken When NE Fails to Respond
|
Action Taken When NE is Reachable
|
ICMP VNE
|
ICMP only. During the ICMP test, the unit pings the NE every configured interval.
|
ICMP ping is suspended, and a VNE Unreachable event is sent to the Prime Network Gateway. Thereafter, only the reachability tests are run to detect when the device is reachable again.
|
ICMP ping is restarted, and the alarm is cleared.
|
Generic VNE
|
• SNMP only (default). Polls the sysoid of the NE using an SNMP get command during the SNMP reachability test, and expects to receive a response; or SNMP only (default). Polls the sysoid of the NE using an SNMP get command during the SNMP reachability test, and expects to receive a response; or
• SNMP only (default), and adding an ICMP test. SNMP only (default), and adding an ICMP test.
|
General polling is suspended, and a VNE Unreachable event is sent to the Prime Network Gateway. Thereafter, only the reachability tests are run to detect when the device is reachable again.
If more than one protocol is used, it is enough for one of them to become unreachable to generate the event. The event is generic to all the protocols.
|
• General polling is restarted, and all commands are sent to the device, smoothed across the polling interval. General polling is restarted, and all commands are sent to the device, smoothed across the polling interval.
• The alarm is cleared. The alarm is cleared.
|
Full VNE
|
• SNMP only (default). Polls the sysoid of the NE using an SNMP get command during the SNMP reachability test, and expects to receive a response; or SNMP only (default). Polls the sysoid of the NE using an SNMP get command during the SNMP reachability test, and expects to receive a response; or
• SNMP only (default), and adding ICMP and Telnet. During the Telnet test, the unit sends SNMP only (default), and adding ICMP and Telnet. During the Telnet test, the unit sends Enter via the open session and expects to get a prompt back.
|
General polling is suspended, and a VNE Unreachable event is sent to the Prime Network Gateway. Thereafter, only the reachability tests are run to detect when the device is reachable again.
If more than one protocol is used, it is enough for one of them to become unreachable to generate the event. The event is generic to all the protocols.
|
• General polling is restarted, and all commands are sent to the device, smoothed across the polling interval. General polling is restarted, and all commands are sent to the device, smoothed across the polling interval.
• The alarm is cleared. The alarm is cleared.
|
Each of these scenarios has two possible settings in the registry:
• Track reachability (true/false). The default is true.
Track reachability (true/false). The default is true.
When this parameter is true, reachability is tracked according to the specific protocol (ICMP, SNMP, Telnet, and so forth).
When this parameter is false, the test is not performed.
• Lazy reachability (true/false). The default is false. This parameter determines whether there is a dedicated reachability command in charge of tracking reachability or whether reachability is determined by the regular polled commands.
Lazy reachability (true/false). The default is false. This parameter determines whether there is a dedicated reachability command in charge of tracking reachability or whether reachability is determined by the regular polled commands.
When this parameter is true, reachability is based on polling, and a dedicated command is not activated.
When this parameter is false, a dedicated SNMP command is activated, and this test verifies the response from a specific SNMP OID (sysoid is the default that can be changed).
After the first failure of a command and all its retries, the device is considered unreachable. At this point, Prime Network starts to poll the device using the dedicated reachability command (see Table 15-23). In normal track reachability mode (lazy=false), the reachability commands run all the time. When the reachability test succeeds for the first time, it stops running and the device is considered reachable again.
Note  Changes to the registry should be performed only with the support of Cisco. For details, contact your Cisco account representative.
Changes to the registry should be performed only with the support of Cisco. For details, contact your Cisco account representative.
Correlation
The alarm correlates to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism, which runs a forward IP flow from the global routing entity to the management IP address (that is, to the IP address of the unit on which the VNE resides). This flow might collect the following alarms: Device Unreachable, Link Down, Port Down, Interface Status Down, BGP Neighbor Loss, and so forth.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the ManagedElement key.
Note  The Device Unreachable alarm filters out the Link Down on Unreachable alarm in the correlation process. Events with the same weight are not filtered out.
The Device Unreachable alarm filters out the Link Down on Unreachable alarm in the correlation process. Events with the same weight are not filtered out.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid).
CPU Utilization
VNEs are configured to trace their device CPU utilization. An alarm is issued when device CPU utilization crosses a configured threshold. The thresholds, as defined in the registry under the managed element, are:
• Upper threshold—80%
Upper threshold—80%
• Lower threshold—40%
Lower threshold—40%
Table 15-24 CPU Utilization—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
CPU Overutilized
|
Issued when the device CPU usage is above the configured upper threshold.
|
CPU Normal Utilization
|
Clearing event. Issued when the device CPU usage returns to below the lower threshold.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of CPU utilization alarms, the event does not try to correlate to another event; it creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
No other alarm tries to correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid).
Device Unsupported
A VNE identifies various loading situations that prevent regular operation of the VNE. When such a situation occurs, the VNE issues a Device Unsupported alarm.
Table 15-25 Device Unsupported—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Device Unsupported
|
Issued for the following scenarios:
• The device type identified by its sysOid is not identified by the system. The device type identified by its sysOid is not identified by the system.
• The device software version is not supported, and the VNE is configured to react when a device is unsupported. Other possible actions are: use the default version, load generic VNE, or load ICMP VNE. The device software version is not supported, and the VNE is configured to react when a device is unsupported. Other possible actions are: use the default version, load generic VNE, or load ICMP VNE.
• Registry problems occur when trying to load generic or ICMP VNEs. Registry problems occur when trying to load generic or ICMP VNEs.
• The VNE failed to retrieve the device sysOid or software version. The VNE failed to retrieve the device sysOid or software version.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Device Unsupported alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid).
Discard Packets
VNEs are configured to trace the discarded packet counters on their device ports. An alarm is issued when the discarded counter for a port crosses the configured thresholds. The thresholds, as defined in the registry under PortLayer1, are:
• Upper threshold—500 packets per second.
Upper threshold—500 packets per second.
• Lower threshold—50 packets per second.
Lower threshold—50 packets per second.
Table 15-26 Discard Packets—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Discard Packets
|
Issued when the number of discarded packets on a device port is higher than the configured threshold.
|
Normal Discard Packets
|
Clearing alarm. Issued when the number of discarded packets on a devices port is lower than the configured threshold.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Discard Packets alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
By default, impact analysis is not supported for this alarm, but it can be enabled. If enabled, a flow starts to collect all the affected services passing this port. The endpoint of such services can be any termination point, such as an IP interface, VC, Port, VRF, and so on.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
Dropped Packets
VNEs are configured to trace the dropped packet counters on their device ports. An alarm is issued when a dropped packet counter from a port crosses the configured thresholds. The thresholds, as defined in the registry under PortLayer1, are:
• Upper threshold—500 packets per second.
Upper threshold—500 packets per second.
• Lower threshold—50 packets per second.
Lower threshold—50 packets per second.
Table 15-27 Dropped Packets—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Dropped Packets on Port
|
Issued when the number of dropped packets on a device port is higher than the configured threshold.
|
Stopped Dropping Packets on Port
|
Clearing event. Issued when the number of dropped packets on a device port is lower than the configured threshold.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Dropped Packets on Port alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event. It creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
By default, impact analysis is not supported for this alarm, but it can be enabled. If enabled, a flow starts to collect all the affected services passing this port. The endpoint of such services can be any termination point, such as an IP interface, VC, port, VRF, and so on.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
DS0 Bundle Service Alarm
DS0 Bundle is a logical interface with an administration and operational status. The DS0Bundle Service alarm is generated when the administration or operational status changes.
Table 15-28 DS0 Bundle Service—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
DS0 Bundle Admin Down
|
Generated when the DS0 Bundle status changes from OK to Admin Down.
|
DS0 Bundle Oper Down
|
Generated when the DS0 Bundle status changes from OK to Oper Down.
|
DS0 Bundle Up
|
Generated when the DS0 Bundle status changes from Not OK to OK.
|
Correlation
This alarm will be correlated to lower layer events, such as Port Down. Upper layer events can be correlated to this event.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See DS0 Bundle OID (IDS0BundleOid).
DS1 Path Link Down
DS1 Path Link Down is generated when an administrative or operational path shutdown occurs.
Correlation
DS1 Path Link Down can be correlated to lower level alarms, such as Port Down. It can be the root cause for higher level alarms.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid), where each endpoint is a DS1 Path OID (IDS1PathOid).
DS1 Path Port Down
DS1 Path Port Down is generated when an administrative or operational path shutdown occurs.
Correlation
DS1 Path Port Down can be correlated to lower level alarms, such as Port Down. It can be the root cause for higher level alarms.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See DS1 Path OID (IDS1PathOid).
DS3 Path Link Down
DS3 Path Link Down is generated due to administrative or operational shutdown of the path.
Correlation
DS3 Path Link Down can be correlated to lower level alarms, such as Port Down. It can be the root cause for higher level alarms.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid), where each endpoint is a DS3 Path OID (IDS3PathOid).
DS3 Path Port Down
DS3 Path Port Down is generated when an administrative or operational path shutdown occurs.
Correlation
DS3 Path Port Down can be correlated to lower level alarms, such as Port Down. It can be the root cause for higher level alarms.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See DS3 Path OID (IDS3PathOid).
Dual Stack IP Changed
The dual stack IP interface alarm generates events when an interface goes from a dual IP address (IPv4 and IPv6) to a single stack, and when it goes from a single stack to a dual. That is, the event is generated when an IPv6 (global unicast address) or IPv4 address is removed from an interface. The event does not do any correlation but can be a root cause.
Table 15-33 Dual Stack IP Changed
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Dual Stack IP Removed
|
Generated when all IPv6 (global unicast address) or all IPv4 addresses are removed from a dual-stack (two IP addresses) interface.
|
Dual Stack IP Added
|
Generated when an IPv6 (global unicast address) or IPv4 address is configured on a single-stack (one IP address) interface that was previously configured as a dual stack.
|
Correlation
No correlation is performed for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid).
DWDM Controller Down
The DWDM controller has an Up and Admin-Down status. The DWDM Controller Down alarm is generated when the DWDM controller state changes. A DWDM Controller Down ticket is generated. The DWDM Controller Down alarm is based on polling results.
Correlation
No correlation is performed for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See DWDM Controller OID (IDWDMOid).
DWDM G709 Status Down
The DWDM G709 wrapper has a status of up and down, The DWDM G709 Status Down alarm is generated when the G709 wrapper state changes, and the DWDM G709 Status Down ticket is generated. The alarm is based on the polling result; if the DWDM G709 wrapper status changes, the service alarm is triggered.
Correlation
No correlation is performed for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See DWDM Controller OID (IDWDMOid).
EFP Down
The EFP Down alarm represents a state in which an Ethernet flow point (EFP) administrative or operational status changes from up to down. The alarm is cleared after the status value is set to up.
The polling of the status property can happen at every standard polling interval, or can be expedited following syslog handling.
The severity of the service alarms is Major, with the exception of EFP Up, which has the severity Cleared.
Table 15-36 EFP Down — Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
EFP Admin Down
|
EFP is in administrative status down.
|
EFP Down Due to Error Disabled
|
EFT is in operational status down and the error disabled property value is true.
|
EFP Oper Down
|
EFP is in operational status down.
|
EFP Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the EFP status returns to up.
|
Correlation
The generated service alarm searches for its root cause through the correlation mechanism. In addition, the EFP Down alarm is the root cause for every relevant network event caused by the EFP Down event.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See EFP OID (IEFPOID).
ESMC Process Down
The ESMC Process Down alarm is generated when an ESMC process is enabled or disabled. The alarm is cleared after the status value is set to up.
The polling of the status property can happen at every standard polling interval, or can be expedited following syslog handling.
Table 15-37 ESMC Process Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
ESMC Process Down
|
The alarm triggering event when ESMC process is down.
|
ESMC Process Up
|
The alarm triggering event when ESMC process is up.
|
Correlation
No correlation is performed for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See ISyncEOID.
Fan-Tray Down
The Fan-Tray Down alarm is generated when the fan tray of the network element is powered down in the network elelment.
Table 15-38 Fan-Tray Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Fan-Tray Down
|
The alarm triggering event when fan tray is powered down.
|
Fan-Tray Up
|
The alarm triggering event when fan tray is powered up.
|
Correlation
No correlation is performed for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Fan Tray OID.
Fan-Tray Out
The Fan-Tray Out alarm is generated when the fan tray of the network element is removed.
Table 15-39 Fan-Tray Out—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Fan-Tray Out
|
The alarm triggering event when fan tray is removed.
|
Fan-Tray In
|
The alarm triggering event when fan tray is available.
|
Correlation
No correlation is performed for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Fan Tray OID.
GRE Keepalive
The GRE Keepalive alarm is generated when the GRE keepalive attribute is not configured or has been removed from a discovered GRE tunnel.
Table 15-40 GRE Keepalive—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Keepalive Not Set
|
The alarm triggering event when GRE Keepalive is not configured. The event is ticketable with a minor severity.
|
Keepalive Set
|
The clearing event.
|
Correlation
No correlation is performed for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See GRE Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure.
GRE Tunnel Down
Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunnels are basically stateless, meaning that when the tunnel is down, the tunnel edges might not identify this situation and continue reporting the tunnel as up. To overcome this, the GRE tunnel edge can be configured to send keepalive messages. If at some point a GRE tunnel edge does not receive keepalive messages, it can change its state to down.
The GRE Tunnel Down alarm is supported only on GRE tunnels that are configured with keepalive messages. When keepalive is configured on the GRE tunnel edge, if a failure occurs in the GRE tunnel at any point, both IP interfaces of the GRE tunnel edges change their state to down. This ensures that the alarm is identified. If keepalive is not configured on the GRE tunnel edge, because the alarm creation is triggered by the state change of the IP interface of the GRE tunnel, the GRE Tunnel Down alarm might not be generated.
Table 15-41 GRE Tunnel Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
GRE Tunnel Down
|
Issued when a GRE link exists between the two tunnel edges and the state of the IP interface of one of the GRE tunnel edges changes to down. A simple negotiation procedure is done to avoid sending the event from both edges of the GRE tunnel, and a GRE Tunnel Down event is issued.
|
GRE Tunnel Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the IP interface state changes back to up. The clearing event is issued even if the GRE link does not exist (for example, if you have chosen to clear and remove the event).
|
Correlation
The GRE Tunnel Down alarm tries to correlate to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward IP flow from the local GRE tunnel edge to the tunnel destination IP. This flow might collect the following alarms: Link Down, Port Down, Interface Status Down, and more.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the TunnelGre key.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid) (each endpoint is Layer 2 GRE Tunnel OID (ITunnelGreOid).
HSRP Group Status Changed
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is used in IP networks and allows one router to automatically assume the function of the second router if the second router fails. The current support relates to the instance where only one backup router is configured in the HSRP group, though it is possible to configure more than one.
Table 15-42 HSRP Group Status Changed—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Primary HSRP Interface Is Not Active
|
Issued when the primary interface within an HSRP group has changed its state to down. This means that one of the other interfaces in the group becomes the active interface in the group.
This alarm tries to correlate to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward IP flow from the local global routing entity to the HSRP group backup interface IP.
Alarms can correlate to this alarm using the local IPInterface key.
|
Primary HSRP Interface Is Active
|
Clearing event for the Primary HSRP Interface Is Not Active alarm. Issued when the primary interface within a HSRP group has changed its state back to up after it was down. This means that if one of the other interfaces in the group was currently active it becomes secondary. This alarm is the clearing alarm for the Primary HSRP Interface Is Not Active alarm.
|
Secondary HSRP Interface Is Active
|
Issued when a secondary interface within an HSRP group has changed its state to up. This happens when the original active interface changes its state to down and the backup interface takes over.
This alarm tries to correlate to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward IP flow from the local global routing entity to the HSRP group virtual IP.
Alarms can correlate to this alarm using the local IPInterface key.
|
Secondary HSRP Interface Is Not Active
|
Clearing event for the Secondary HSRP Interface Is Active alarm. Issued when a secondary interface within a HSRP group has changed its state back to down after it was up. This means that the original active interface in that group has changed its state to up.
|
Correlation
For correlation to work, there must be a correlation path between the routers. Correlation details are described in the relevant subtype events in Table 15-42.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid) (IP interface of the active or secondary interface).
Interface Status
VNEs are configured to trace the operational state of their IP interfaces. When the status of an IP interface changes, the VNE issues the relevant alarm. There are multiple subtype events for Interface Status Down, and the subtype that is issued depends on the scenario. Each has a different behavior; these are described in Table 15-43.
Table 15-43 Interface Status—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Interface Status Down GRE Tunnel
(GRE tunnel)
|
Issued when the IP interface on a GRE tunnel changes its state to down.
Correlation—This alarm issues a local correlation process and tries to correlate to the GRE Tunnel Down alarm. If the GRE tunnel down does not exist (for example, in the case where no GRE link exists), the alarm is issued as the root cause. When the GRE tunnel is issued from the other edge of the tunnel, it uses the local alarm to correlate to it.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the IPInterface key. This includes alarms such as Device Unreachable or any other alarms that perform network correlation and where the correlation flow traverses the IP interface.
|
Interface Status Down Connection
(connection that is a point-to-point connection)
|
Issued when a point-to-point IP interface changes its state to down. The identification of this type of interface is done using the following:
1.  The subnet mask is /30 or /31. The subnet mask is /30 or /31.
2.  The IP interface is on one VC encapsulation. The IP interface is on one VC encapsulation.
Correlation—The alarm correlates to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward down IP flow from the IP interface to other IP addresses in the IP interface's IP address subnet. This flow might collect the following alarms: Link Down, Port Down, and so on.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the IPInterface or the physical port (PortLayer1) keys.
|
Interface Status Down Nonconnection
(nonconnection that is a multipoint connection)
|
Issued when a point-to-point IP interface changes its state to down. The identification of this type of interface is done using the following:
1.  The number of encapsulations under the IP interface/MPLS is greater than one. The number of encapsulations under the IP interface/MPLS is greater than one.
2.  Any other case not covered in the previously-described scenarios. Any other case not covered in the previously-described scenarios.
Correlation—The alarm correlates to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward down flow from the IP interface to the physical port (PortLayer1) under this interface.
|
Interface Status Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when an IP interface changes its operational state from down to up.
|
Correlation
Correlation details are described in the relevant subtype events in Table 15-43.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid).
Investigation State
Situations might occur where one or more physical components (specifically modules) are not identified by the physical investigation component in a VNE. This is not an unusual scenario because many devices have large sets of supported modules, and not all of the modules may be supported by the VNE. The Investigation State alarm is issued in this scenario.
Table 15-44 Investigation State—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Investigation State
|
Issued when one or more modules are not identified by the physical investigation component of the VNE.
There is no clearing event.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Investigation State alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid).
L2TP Peer Not Established
This alarm is specific to the Redback Networks implementation of Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP), and is based on the state of an L2TP peer that is basically a logical entity from which L2TP tunnels are created. The L2TP peer is also used as a container for these L2TP tunnels. The alarm is issued when the L2TP peer has an incorrect tunnel configuration and the tunnels between the L2TP access concentrator (LAC) and the L2TP network server (LNS) cannot be created.
Table 15-45 L2TP Peer Not Established—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
L2TP Peer Not Established
|
Issued when the L2TP peer has an incorrect configuration, and L2TP tunnels cannot be created between the LAC and the LNS. This is identified by querying the state of the L2TP peer tunnels that do not change to Established.
|
L2TP Peer Is Removed
|
Issued when the L2TP peer is removed from the L2TP peer list, or when the first tunnel in the peer changes its state from Established to another state.
|
L2TP Peer Established
|
Clearing event. Issued when at least one tunnel of the L2TP peer is in an Established state.
|
Correlation
The alarm correlates to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward down flow from the L2TP peer to the remote IP.
Other alarms can correlate to this alarm using the local L2TPpeer key.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See L2TP Peer OID (IL2tpPeerOid).
L2TP Sessions Threshold
This alarm is specific to the Redback Networks implementation of L2TP and is implemented as a TCA of the number of sessions in a L2TP peer. The alarm is issued when the number of L2TP sessions related to the L2TP peer crosses a configurable threshold.
Table 15-46 L2TP Sessions Threshold—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
L2TP Sessions Count Exceeds Maximum Threshold
|
Issued when the number of active sessions associated with the L2TP peer crosses a configurable threshold (the default is 80%). The calculation is done as follows:
active-sessions/(max-session-per-tunnel * max-tunnels-per-peer) * 100.
|
L2TP Sessions Count Has Returned to Normal
|
Clearing event. Issued when the number of active sessions associated with the L2TP peer drops below the lower threshold (the default is 70%).
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the L2TP Sessions Count Exceeds Maximum Threshold alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See L2TP Peer OID (IL2tpPeerOid).
Note  This alarm is implemented as TCA, which means that no information about this alarm is found in the standard event-related registry.
This alarm is implemented as TCA, which means that no information about this alarm is found in the standard event-related registry.
Lag Down
The Lag Down alarm is generated when the status of the Link Aggregation changes.
Table 15-47 Lag Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Lag Admin Down
|
Issued when the status changes due to administrative status change.
|
Lag Oper Down
|
Issued when the status changes due to oper status change.
|
Lag Up
|
Clearing Event. Issued when the status is up again.
|
Correlation
Lag Down alarm does not correlate to any alarm. No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Lag Down OID.
Lag Link Down
The Lag Link Down alarm is generated when the status of the Lag Link changes in the logical inventory.
Correlation
Lag Link Down alarm does not correlate to any alarm. No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Lag Link Down OID.
Layer 2 Tunnel Down
A Layer 2 tunnel represents a point-to-point pseudowire in the network, also known as an AToM. This alarm is issued when the operational state of a Layer 2 tunnel changes.
Table 15-49 Layer 2 Tunnel Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Layer 2 Tunnel Down
|
Issued when the operational state of the Layer 2 tunnel changes its state to down. This can happen due to a problem between the two edges of the tunnel or on the local tunnel interface.
When the state changes on both edges, a simple negotiation procedure is done to avoid sending the alarm from both edges of the Layer 2 tunnel.
|
Layer 2 Tunnel Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the Layer 2 tunnel changes its state back to up.
|
Correlation
Because this alarm can be caused by multiple conditions, it issues multiple network correlation flows, which run as follows:
• A network flow from the Layer 2 tunnel to the remote IP to identify problems that occur between the tunnel edges.
A network flow from the Layer 2 tunnel to the remote IP to identify problems that occur between the tunnel edges.
This flow might collect the following alarms: Link Down, Port Down, MPLS alarms, and so on.
• A network flow from the local Layer 2 tunnel edge to the physical port on which it is configured, to identify problems that occur on the local physical interface.
A network flow from the local Layer 2 tunnel edge to the physical port on which it is configured, to identify problems that occur on the local physical interface.
This flow might collect the following alarms: Link Down, Port Down, and so on.
• A network flow from the remote Layer 2 tunnel edge to the physical port on which it is configured, to identify problems that occur on the remote physical interface.
A network flow from the remote Layer 2 tunnel edge to the physical port on which it is configured, to identify problems that occur on the remote physical interface.
This flow might collect the following alarms: Link Down, Port Down, and so on.
Any alarm can correlate to this alarm using the PTP Layer2 MPLS Tunnel (which represents the Layer 2 tunnel edge) key.
Note  The Layer 2 Tunnel Down alarm does not filter out the LDP Neighbor Down alarm in the correlation process.
The Layer 2 Tunnel Down alarm does not filter out the LDP Neighbor Down alarm in the correlation process.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid) (each endpoint is Layer 2 MPLS Tunnel OID (IPTPMplsLayer2TunnelOid).
LDP Neighbor Loss
LDP enables neighboring P or PE routers acting as LSRs to discover peers in an MPLS network to which they can establish LDP sessions. The sessions allow the routers to negotiate and exchange labels used for forwarding packets.
If a session to an LDP neighbor goes down, an LDP Neighbor Down alarm is issued. This can happen as the result of a failure in the TCP connection used by the LDP session, or if the interface is no longer running MPLS. The LDP neighbor down alarm is cleared by a corresponding LDP Neighbor Up alarm.
The alarm is issued when a peer is removed from the table in the LDP Neighbors tab. The alarm runs a correlation flow to detect the network core triggering event. A root cause analysis is performed to find the root cause. The alarm initiates an IP-based flow toward the peer transport address destination. If an alarm is found during the flow, that alarm is correlated to the LDP Neighbor Down alarm.
Note  The LDP Neighbor Down alarm can correlate to the MPLS Interface Removed alarm.
The LDP Neighbor Down alarm can correlate to the MPLS Interface Removed alarm.
VNEs are configured to trace the state of the current LDP neighbor of their devices. The VNE issues the relevant alarm when it identifies that an existing LDP neighbor has been removed, or that an LDP neighbor that was removed has been restored.
The identification of this alarm is expedited by notifications such as syslogs or traps.
Table 15-50 LDP Neighbor Loss—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
LDP Neighbor Down
|
Issued when an LDP neighbor of the device that was previously discovered is removed.
|
LDP Neighbor Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the LDP neighbor that was previously removed is restored and is currently active.
|
Correlation
This alarm issues a network correlation flow that runs a forward down flow from the global routing entity to the LDP peer IP address.
This flow might collect the following alarms: MPLS Interface Removed, Link Down, Port Down, and so on.
Any alarm can correlate to this alarm using the LDPPeer or LDPpeerDiscoverySources keys.
Note  The LDP Neighbor Down alarm does not filter out the MPLS Interface Removed alarm in the correlation process.
The LDP Neighbor Down alarm does not filter out the MPLS Interface Removed alarm in the correlation process.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See LSE OID (ILseOid) (Label Switching Entity with the differentiator object of the LDP peer).
Link Down
This is one of the basic service alarms supported in the system. When a port has an adjacent peer (that is, it is connected to another port and has a discovered link), and its operational state changes from up to down or from down to up, the alarm is issued. When the port is not adjacent, a Port Down alarm is issued instead of a Link Down alarm. See Port Down.
The negotiation process between the two link edges occurs when the port's operational state changes to down to identify the exact event that should be issued.
Table 15-51 Link Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Link Down Due to Admin Down
|
Issued when the admin state of at least one of the link ports changes to down.
Correlation—Due to the nature of this alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway that is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
|
Link Down Due to Oper Down
|
Issued when the admin state is up on both ports and none of the scenarios described below occur.
Correlation—This alarm issues a local correlation process and tries to correlate to other alarms using the physical port (PortLayer1) key.
|
Link Down Due to Card Event
|
Issued when at least one of the ports is on a card that was removed from the device, or is currently in an operational down state.
Correlation—This alarm issues a local correlation process and tries to correlate to other alarms (specifically Card Out or Card Down) using the Module key.
|
Link Down on Unreachable
|
Issued when at least one of the ports is on a device that is currently unreachable by its VNE.
Correlation—This alarm issues a local correlation process in order to correlate to the Device Unreachable alarm (using the ManagedElement key).
|
Link Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the port operational state changes back to up.
|
Link Down supports flapping with the following subevents:
• Link Down Flapping
Link Down Flapping
• Link Down Flapping Update
Link Down Flapping Update
• Link Down Stopped Flapping Cleared
Link Down Stopped Flapping Cleared
• Link Down Stopped Flapping Noncleared
Link Down Stopped Flapping Noncleared
Note  In Prime Network Events, these flapping subevent names are displayed in the event's short description field.
In Prime Network Events, these flapping subevent names are displayed in the event's short description field.
Correlation
Other alarms can try to correlate to any link down alarm using the physical port (PortLayer1) key.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid) where each endpoint is Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
Link Utilization
VNEs are configured to trace the Rx and Tx counters on their device ports, where a port has an adjacent peer (that is, it is connected to another port), and it already issued a Rx Overutilized or Tx Overutilized alarm. (For more information on these alarms, see Rx Utilization and Tx Utilization.) This alarm has complementary functionality so that all the utilization alarms from both ports of the link correlate to it, instead of issuing multiple root cause alarms.
Table 15-52 Link Utilization—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Link Overutilized
|
Issued after Tx Overutilized or Rx Overutilized alarms are issued on a physical port, if the port has an adjacent peer to enable correlation of all port level utilizations alarms from the ports on both sides of the link to one link utilization alarm.
|
Link Utilization Normal
|
Clearing event. Issued if both sides of the link send clearing alarms on the Tx utilization and Rx utilization alarms.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of this alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
Other alarms can correlate to this alarm using the physical port (PortLayer1) key.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid) where each endpoint is Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
Log Archive is Disabled on the Device
A VNE that is modeled in the reduced polling mode uses the device log archive feature to identify the changed configuration applied on the device to update the VNE in Prime Network. If the archive is disabled on device, Prime Network generates the service alarm. The Prime Network administrator must enable the archive on the selected device as a corrective action.
For more information on device specific settings required, see Device Configuration Tasks for VNE Creation in the Cisco Prime Network 3.9 Administrator Guide.
Correlation
No correlation.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid).
Local Switching Down
The Local Switching Entry Down Alarm is issued when the status of the local switching entry changes.
Correlation
Local Switching Entry Down alarm uses flow based correlation.
The VNE with flow based correlation mechanisim uses an active correlation flow that traverses among three layers of the network (Layer 1,Layer 2, and Layer 3) and tries to correlate along a specified network path to an alarm. Based on the alarm that could occur in any one of the layers, it will try to find the root cause alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Local Switching Entry Down OID.
Logical Port Down
Logical ports are logical interfaces that are defined on physical ports. Logical ports are used to logically separate the traffic of the physical port, and to control the separated traffic in a different manner. Logical ports are currently implemented in Prime Network for specific VNE types (for example, Lucent WAN Switches) and specific technologies (such as ATM and Frame Relay). Each logical port has an independent administrative and operational state. When the operational state of a logical port changes, the VNE issues an alarm.
Table 15-54 Logical Port Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Logical Port Down
|
Issued when the operational state of a logical port changes to down.
|
Logical Port Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the operational state of a logical port changes back to up.
|
Correlation
This alarm issues a local correlation process and tries to correlate to alarms on the physical port using the physical port (PortLayer1) key. Possible alarms that this alarm can correlate to are Link Down, Port Down, or any alarm on the physical port.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the logical port key, including alarms that perform network correlation, and the correlation flow traverses the logical port.
Note  The Logical Port Down alarm does not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
The Logical Port Down alarm does not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Logical Port OID (ILogicalPortOid).
LSP Down
LSP down is generated from both the endpoints of the MPLS-TP tunnel if the endpoint status goes down. The alarm is cleared after the status value changes from down to up.
Table 15-55 LSP Down
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
LSP Down
|
Issued when LSP Endpoint goes down.
|
LSP Down Due to Label Mismatch
|
Issued when LSP Endpoint status goes down, it will start the flow to find out whether it is down due to label mismatch in the flow (out going label / in going label does not match). It can be generated for the first time when LSP endpoint discovers. It is not necessary to have LSP Status Transition from Up to Down.
|
LSP Down Due to Lock Out
|
Issued when user configures a lock out. It will be also generated without a state transition. It means that this service alarm will be generated first time, if LSP Endpoint status is locked out.
|
LSP Up
|
Issued when LSP Endpoint goes up.
|
Correlation
This alarm issues a local correlation process and tries to correlate to alarms on the physical port using the physical port (PortLayer1) key.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See LSP Endpoint OID (LSP EndPoint OID).
Members Changed
Members Changed alarm is generated if there is a status change for any member of the aggregation entity such as Ethernet LAG, MLPPP or IMA Group. For example, if an Ethernet LAG group has 4 Ethernet links (members) configured as part of the group and if one link goes down, a low priority Members Changed is generated indicating that 1 out of 4 links (25% of links) are down. If three or all links go down (75% of links or all links), a high priority service alarm is generated. Based on the configuration of thresholds in the registry the aggregation service alarm is a low priority, medium priority or high priority service alarm.
Table 15-56 Members Changed
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
High Priority Member Down
|
Issued when the percentage of active links is greater than zero and less than or equal to the high priority threshold defined in the registry.
|
Medium Priority Member Down
|
Issued when the percentage of active links is less than or equal to the medium priority threshold and greater than the high priority threshold defined in the registry.
|
Low Priority Member Down
|
Issued when the percentage of active links is less than or equal to the low priority threshold and greater than the medium priority threshold defined in the registry.
|
All Members Operationally Up
|
Issued when all the member links are up.
|
Correlation
Members Changed service alarm does not try to correlate with any other alarm.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
Members Changed Alarms will have any one of the following OIDs based on the members that have changed.
• IMA Service (IIMAGroupOid)
IMA Service (IIMAGroupOid)
• MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid)
MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid)
• Lag Down OID
Lag Down OID
• Members Changed OID (IDataLinkAggregationOid)
Members Changed OID (IDataLinkAggregationOid)
If the status of the IMA group members is changed, Source OID will be IIMAGroupOid.
If the status of the MLPPP members is changed, it will be IMLPPPOid.
If the status of the EthernetChannel or LAG members is changed, Source OID will be IDataLinkAggregationOid.
Memory Utilization
VNEs are configured to trace their device memory utilization. A memory utilization alarm is issued when the device memory utilization crosses a configured threshold. The thresholds, as defined in the registry under ManagedElement, are:
• Upper threshold—80%
Upper threshold—80%
• Lower threshold—40%
Lower threshold—40%
Table 15-57 Memory Utilization—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Memory Overutilized
|
Issued when the device memory usage is above the configured upper threshold.
|
Memory OK
|
Clearing event. Issued when the device memory usage is back below the lower threshold.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Memory Utilization alarm, the event does not try to correlate to another event, and creates a new ticket in the gateway where the event is the root cause alarm of the ticket.
No other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid).
MLPPP Bundle
MLPPP Bundle does not generate a Service alarm for each endpoint; it generate the alarm for links. If a link is not available, the service alarm is generated for individual endpoints. MLPPP Bundle can be a root cause. However, it cannot be correlated to other service alarms; that is, another event cannot be the root cause of MLPPP Down. MLPPP Bundle is ticketable.
Correlation
MLPPP Down cannot be correlated to other events. However, other events can correlate to MLPPP Down.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid) or Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid), where each endpoint is a MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid).
MPLS Black Hole Found
An MPLS black hole is an abnormal termination of an MPLS path (an LSP) inside an MPLS network. An MPLS black hole exists when there are untagged entries destined for a known PE router on a specific interface. Note that the untagged interfaces might exist in the network in normal situations. For example, where the boundary of the MPLS cloud has untagged interfaces, this is still considered normal.
MPLS black hole cause the loss of all the MPLS labels on a packet, including the VPN information that lies in the inner MPLS label. Therefore, if a packet goes through an untagged interface, the VPN information is lost. The VPN information loss translates directly to VPN sites losing connectivity.
Black hole alarms are detected in either of the following situations:
• When the system is loaded for the first time and performs the initial discovery of the network.
When the system is loaded for the first time and performs the initial discovery of the network.
• Changes in the network are identified through the ongoing discovery process.
Changes in the network are identified through the ongoing discovery process.
Note  MPLS black hole discovery is supported only when the PEs are managed by Prime Network.
MPLS black hole discovery is supported only when the PEs are managed by Prime Network.
Table 15-59 MPLS Black Hole Found—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
MPLS Black Hole Found
|
Issued when an MPLS interface has at least one untagged LSP leading to a known PE router; in other words, an LSE entry changed to an Untagged action with a PE as a next hop. After an MPLS Black Hole Found alarm is issued, a process begins looking for broken LSPs that go through the MPLS black hole. See Broken LSP Discovered.
|
MPLS Black Hole Cleared
|
Clearing event. Issued when the MPLS interface that had untagged LSPs to a known PE router has no more untagged entries to any known PE neighbor.
|
Correlation
The MPLS Black Hole Found alarm can correlate to MPLS Interface Removed and LDP Neighbor Loss alarms. Broken LSP Discovered alarms can correlate to MPLS Black Hole Found alarms.
Note  The MPLS Black Hole Found alarm does not filter out the MPLS Interface Removed and LDP Neighbor Down alarms in the correlation process.
The MPLS Black Hole Found alarm does not filter out the MPLS Interface Removed and LDP Neighbor Down alarms in the correlation process.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See LSE OID (ILseOid) (appended with a differentiator of the next hop interface name).
MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
The MPLS TP bandwidth mismatch alarm is generated when there is a bandwidth mismatch in the two directions of the MPLS-TP tunnel.
Table 15-60 MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
|
Issued when there is a bandwidth mismatch in the two directions of the MPLS-TP tunnel.
|
Correlation
There is no correlation for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See LSP Endpoint OID (LSP EndPoint OID)
MPLS Interface Removed
The MPLS interface is basically a representation of the MPLS sublayer in an interface configuration. The interface can be configured with or without MPLS capabilities. If this type of configuration change takes place while the VNE is loaded, it issues MPLS interface removed or added alarms.
Table 15-61 MPLS Interface Removed—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
MPLS Interface Removed
|
Issued when an MPLS interface has at least one untagged LSP leading to a known PE router (that is, an LSE entry changed to an Untagged action with a PE as a next hop). After an MPLS Black Hole Found alarm is issued, a process that looks for broken LSPs that go through this MPLS black hole is started. See Broken LSP Discovered.
|
MPLS Interface Added
|
Clearing event. Issued when the MPLS capabilities of an interface are enabled after they were disabled.
|
Correlation
The alarm correlates to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism which runs a forward flow to the underlying physical port. This flow might collect the Card Out and Card Down alarms, because the only other cases in which it happens are due to other faults that are hardware related.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the MPLS key, including MPLS black hole alarms, MPLS TE Tunnel Down alarm, and so on.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See LSE OID (ILseOid) (Label Switching Entity with differentiator object of the MPLS interface description).
MPLS TE FRR State Changed
The MPLS TE FRR State Changed service alarm is triggered when the backup MPLS TE FRR tunnel changes from Ready to Active, and from Active to Ready.
Table 15-62 MPLS TE FRR State Changed
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
MPLS TE FRR State Changed to Active
|
Generated when the status of the protecting MPLS TE FRR tunnel changes from Ready to Active because of a network failure in the primary tunnel segment.
|
MPLS TE FRR State Changed to Ready
|
Generated when the status of the protecting MPLS TE FRR tunnel changes back to Ready.
|
Correlation
Correlation is performed.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See MPLS TE Tunnel OID (IMplsTETunnelOid).
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
MPLS TE tunnel alarms include:
• MPLS TE Tunnel Down
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
• MPLS TE Tunnel Flapping
MPLS TE Tunnel Flapping
• Tunnel Reoptimized
Tunnel Reoptimized
If a TE tunnel operational status changes to down, an MPLS TE Tunnel Down alarm is generated. The Prime Network correlation engine supports the MPLS TE Tunnel link between the head and tail ends of the network element. The engine also identifies the faults that affect the TE tunnel status and identifies the root cause for the MPLS TE Tunnel Down alarm. For example, a Link Down will cause a TE tunnel to go down. Multiple up and down alarms that are generated during a short time interval are suppressed and displayed as an MPLS TE Tunnel Flapping alarm (according to the specific flapping configuration).
MPLS TE Tunnel Down and MPLS TE Tunnel Flapping alarms are actively detected and service alarms are generated. The system also supports MPLS TE Tunnel Down syslogs, which are correlated to the service alarm.
For Cisco CRS-1 routers running Cisco IOS XR 3.6 software and using PBTS in MPLS or MPLS VPN networks, Prime Network supports the following subalarms for the MPLE TE Tunnel Down alarm:
• High Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
High Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
• Medium Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Medium Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
• Low Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Low Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
The specific subalarm that is generated depends on the EXP bit specified for the traffic. Prime Network maps the specified EXP bit to tunnel priority and uses that mapping to generate the resultant subalarm. The alarm description includes information about the EXP bit.
VNEs are configured to trace the operational state of their MPLS TE tunnel interfaces. When the state of the tunnel changes, the VNE issues the relevant alarm.
Table 15-63 MPLS TE Tunnel Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
MPLS TE Tunnel Rerouted
|
Issued when the tunnel changes it state to down.
MPLS TE Tunnel Down alarm supports flapping with the following subevents:
• MPLS TE Tunnel Flapping MPLS TE Tunnel Flapping
• MPLS TE Tunnel Update MPLS TE Tunnel Update
• MPLS TE Tunnel Stopped Flapping Cleared MPLS TE Tunnel Stopped Flapping Cleared
• MPLS TE Tunnel Stopped Flapping Noncleared MPLS TE Tunnel Stopped Flapping Noncleared
Note  In Prime Network Events, these flapping subevent names are displayed in the event's short description field. In Prime Network Events, these flapping subevent names are displayed in the event's short description field.
|
High Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
|
This alarm is issued if the EXP bit is set to denote high priority. Prime Network maps the bit to a high priority alarm.
|
Medium Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
|
This alarm is issued if the EXP bit is set to denote medium priority. Prime Network maps the bit to a medium priority alarm.
|
Low Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
|
This alarm is issued if the EXP bit is set to denote low priority. Prime Network maps the bit to low priority alarm.
|
MPLS TE Tunnel Rerouted
|
This alarm is issued when the MPLS TE Tunnel is Rerouted.
|
MPLS TE Tunnel Reoptimized
|
Tunnel reoptimization occurs when a tunnel is up and its route changes but the tunnel continues to remain up. When a TE tunnel is reoptimized to take a different path, the system parses the tunnel reoptimized syslog, if such a syslog is available, and displays it as a ticket.
The Tunnel Reoptimized alarm is generated from a syslog message sent by the router.
|
MPLS TE Tunnel Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when an MPLS TE tunnel changes its operational state from down to up.
|
Correlation
For all the down alarms, any other alarm can try to correlate to this alarm using the MPLS TE tunnel OID (IMplsTETunnelOid) key. The alarm correlates to other alarms using the network correlation mechanism that runs a forward down IP flow from the MPLS TE tunnel to its tunnel destination IP address. This flow might collect the following alarms: Link Down, Port Down, and so on.
The MPLS TE Tunnel Down alarm does not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
When MPLS TE Tunnel Down alarm is generated, the corresponding MPLS TE Tunnel link will have the same severity of MPLS TE Tunnel Down Ticket.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See MPLS TE Tunnel OID (IMplsTETunnelOid).
MPLS TP Tunnel Down
An MPLS TP Tunnel Down alarm is triggered when one side of the tunnel is down or when both sides of the tunnel are down. This alarm is generated based on a negotiation.
The polling of the status property can happen at every standard polling interval, or can be expedited following syslog handling.
Correlation
This alarm by itself can be the root cause of the alarm; and also can find the root cause of the alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See TP Tunnel Endpoint OID (TP Tunnel EndPoint OID).
Network-Clock Synchronization
A network-clock synchronization alarm is triggered when network synchronization is enabled/disabled in the port. The alarm is cleared after the status value is changed from disabled to enabled.
The polling of the status property can happen at every standard polling interval, or can be expedited following syslog handling.
Correlation
No correlation for these alarms.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See ISyncEOID
OSPF Neighbor State Change
An OSPF Neighbor Down alarm is triggered when the status of an OSPF changes. When the status of an OSPF is changed, an alarm will be issued by each neighbor as a separate event. These alarms will remain displayed until the parent ticket is cleared, that is until the status of the OSPF neighbor changes to its previous state.
An OSPF Neighbor Up alarm is a clearing event for the OSPF Neighbor Down alarm. It is triggered when the alarm state changes from down to up.
Table 15-66 OSPF Neighbor State Changed
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
OSPF Neighbor Up
|
Issued by the neighboring VNEs after the OSPF device status has changed to up.
|
OSPF Neighbor Down
|
Issued by the neighboring VNEs after the OSPF device status has changed to down.
|
Correlation
The root cause for an OSPF Neighbor Down can be correlated by the correlation flow towards the neighbor's interface IP address. OSPF neighbor down key is the OID of the neighbor, and is used for correlating OSPF Neighbor Down syslogs and traps to OSPF Neighbor Down alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See OSPF Neighbor State Change OID
Port Down
When a physical port does not have an adjacent peer (that is, it is connected to another port) and its operational state changes from up to down, or from down to up, port down alarms are issued. When the port does have an adjacent peer, instead of a Port Down alarm, a similar Link Down alarm is issued.
Port Down supports flapping with the following subevents:
• Port Down Flapping
Port Down Flapping
• Port Down Flapping Update
Port Down Flapping Update
• Port Down Stopped Flapping Cleared
Port Down Stopped Flapping Cleared
• Port Down Stopped Flapping Noncleared.
Port Down Stopped Flapping Noncleared.
See Link Down.
Table 15-67 Port Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Port Down Due to Admin
|
Issued when the admin state of a physical port changes to down.
|
Port Down Due to Oper
|
Issued when the operational state of a physical port changes to down.
|
Port Down Due to Card Event
|
Issued when the port is on a card that was removed from the device or is currently in an operational down state.
Correlation—This alarm issues a local correlation process and tries to correlate to other alarms (specifically Card Out or Card Down) using the Module key.
|
Port Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the operational state of a logical port changes back to up.
|
Correlation
For all the down alarms, any other alarm can try to correlate to this alarm using the physical port (PortLayer1) key.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
Power Supply Down
The power supply down alarm is generated when the power supply unit is powered down.
Table 15-68 Power Supply Down
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Power Supply Down
|
Issued when the power supply unit is powered down.
|
Power Supply Up
|
Issued when the power supply unit is powered up.
|
Correlation
There is no correlation for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Power Supply OID.
Power Supply Out
The power supply down out alarm is generated when the power supply unit is removed.
Table 15-69 Pluggable Transceiver Out
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Power Supply Out
|
Issued when power supply unit is removed.
|
Power Supply In
|
Issued when power supply unit is inserted.
|
Correlation
There is no correlation for this alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Power Supply OID.
Pluggable Transceiver Out
A pluggable transceiver out alarm is generated when a pluggable transceiver is removed from the physical port of the network element.
Table 15-70 Pluggable Transceiver Out
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Pluggable Transceiver In
|
Issued when pluggable transceiver is inserted back in the interface of the network element.
|
Pluggable Transceiver Out
|
Issued when pluggable transceiver is removed from the interface of the network element.
|
Correlation
This alarm will correlate to port\link down due to oper\admin.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Port OID.
REP Port Role Change
A REP Port Role Change alarm is generated when there is a port role change from failed to okay. The alarm is cleared after the status value is set to okay.
The polling of the status property can happen at every standard polling interval, or can be expedited following syslog handling.
Correlation
For all the alarms, any other alarm can try to correlate to this alarm using the physical port (PortLayer1) key.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
Rx Dormant
VNEs are configured to trace the Rx packet counters on their device ports. An alarm is issued when the Rx counter on a port drops below the configured threshold.
Note  This alarm is disabled by default.
This alarm is disabled by default.
Table 15-72 Rx Dormant—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Rx Dormant
|
Issued when the number of Rx packets on a device port is lower than the configured threshold.
|
Rx Dormant Normal
|
Clearing event. Issued when the number of Rx packets on a device port returns to a number lower than the configured threshold.
|
Correlation
The port Rx Dormant alarm does not start a correlation process and is always issued as a root cause alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
Rx Utilization
VNEs are configured to trace the Rx packet counters on their device ports. An alarm is issued when a the Rx counter for a port crosses the configured thresholds. The thresholds, as defined in the registry under PortLayer1, are:
• Upper threshold—75%
Upper threshold—75%
• Lower threshold—50%
Lower threshold—50%
When a port has an adjacent peer (that is, it is connected to another port) a Link Utilization alarm is also issued. For more information on these alarms, see Link Utilization.
Table 15-73 Rx Utilization—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Rx Overutilized
|
Issued when the number of Rx packets on a device port is higher than the configured threshold.
|
Rx Utilization Normal
|
Clearing event. Issued when the number of Rx packets on a device port returns to a number lower than the configured threshold.
|
Correlation
The Rx utilization alarms do not start a correlation process. No other alarms can correlate to this alarm, because there are no supported alarms that can be affected by the Rx utilization alarm.
Impact Analysis
By default, impact analysis is not supported for this alarm, but can be enabled. If it is enabled, a flow starts to collect all the affected services passing this port. The endpoint of such services can be any termination point, such as an IP interface, VC, port, VRF, and so on.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
Shelf Out
The Shelf Out alarm represents a state in which the shelf is removed from the device. The Shelf Out alarm is also issued when the device stops reporting on the existence of a shelf due to another failure, even if the shelf is actually still in the device. It is assumed that any functionality that was implemented by the shelf is not working anymore if the shelf had no redundancy configuration.
Table 15-74 Shelf Out—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Shelf Out
|
Issued when a shelf is removed from the device. It is possible that some shelf failures are identified as Shelf Out, because the device does not report on the shelf's existence after the failure.
|
Shelf In
|
Clearing event. Issued when the shelf is inserted back into the device.
|
Correlation
Due to the nature of the Shelf Out alarm, it does not start a correlation process and is always issued as a root cause alarm.
Other alarms might correlate to it using the Shelf key, such as the Card Out alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Shelf OID (IShelfOid).
SONET Path Link Down
The SONET Path Link Down Alarm is issued when the status of the SONET path link changes.
Correlation
This alarm correlates to port down and link down alarms.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See SONET Path Link Down OID.
SONET Path Port Down
The SONET Path Port Down is issued when the status of the SONET path port changes.
Correlation
This alarm correlates to port down and link down alarms.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See SONET Path Port Down OID.
Subinterface Down
QinQ technology refers to the nesting of a VLAN header in an Ethernet frame in an already existing VLAN header. Both VLAN headers must be of the type 802.1Q. When one VLAN header is nested within another VLAN header, they are often referred to as stacked VLANs. QinQ technology allows service provider networks to carry traffic with double-tagged, stacked VLAN (802.1Q-in-Q) headers of multiple customers while maintaining the VLAN and Layer 2 protocol configurations of each customer without impacting the traffic of other customers.
A subinterface is a logical division of traffic on an interface, such as multiple subnets across one physical interface. A subinterface name is represented as an extension to an interface name using dot notation, such as Interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/1/2/3.10. In this example, the main interface name is Gigabit Ethernet 0/1/2/3 and the subinterface is 10.
A Subinterface Down alarm is issued when the administrative or operational state of an Ethernet subinterface of a stacked VLAN changes. This state can be polled at standard polling intervals or can be expedited following syslog handling.
Table 15-77 Subinterface Down—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Subinterface Down
|
Issued when the operational status of the subinterface changes from up to down.
|
Subinterface Admin Down
|
Issued when the administrative status of the subinterface changes from up to down.
|
Subinterface Up
|
Clearing event. Issued when the operational or administrative status of the subinterface changes from down to up.
|
Correlation
The Subinterface Down event searches for the root cause through the correlation mechanism. The Subinterface Admin Down event does not search for the root cause through the correlation mechanism.
Subinterface Down is the root cause for every relevant network event caused by the Subinterface Down event.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See VLAN Tagged Interface OID (IVlanTaggedInterfaceOID).
Tx Dormant
VNEs are configured to trace the Tx packet counters on their device ports. An alarm is issued when an Rx counter on a port drops below the configured thresholds. The upper and lower thresholds are defined in the registry under PortLayer1.
Note  This alarm is disabled by default.
This alarm is disabled by default.
Table 15-78 Tx Dormant—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Tx Dormant
|
Issued when the number of Tx packets on a device port is lower than the configured threshold.
|
Tx Dormant Normal
|
Clearing event. Issued when the number of Tx packets on a device port returns to a number higher than the configured threshold.
|
Correlation
The port Tx Dormant alarm does not start a correlation process and is always issued as a root cause alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
Tx Utilization
VNEs are configured to trace the Tx packets counters on their device ports. An alarm is issued when a Rx counter on a port crosses the configured thresholds. The thresholds, as defined in the registry under PortLayer1, are:
• Upper threshold—75%
Upper threshold—75%
• Lower threshold—50%
Lower threshold—50%
When a port has an adjacent peer (that is, it is connected to another port), a Link Utilization alarm is also issued. For more information on these alarms, see Link Utilization.
Table 15-79 Tx Utilization—Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
Tx Overutilized
|
Issued when the number of Tx packets on a device port is higher than the configured threshold.
|
Tx Utilization Normal
|
Clearing event. Issued when the number of Tx packets on a device port returns to a number lower than the configured threshold.
|
Correlation
The port Tx Utilization alarm does not start a correlation process. No other alarm tries to correlate to this alarm, because there are no supported alarms that can be affected by the Tx Utilization on Port alarm.
Impact Analysis
By default, impact analysis is not supported for this alarm, but can be enabled. If impact analysis is enabled, a flow starts to collect all the affected services passing this port. The endpoint of such services can be any termination point, such as an IP interface, VC, port, VRF, and so on.
Source OID
See Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid).
VSI Down
The VSI Down alarm represents a state in which a virtual switch instance (VSI) administrative or operational status changes from up to down. The alarm is cleared after the status value is set to up.
The polling of the status property can happen at every standard polling interval, but it can be expedited following the trap handling of one of the following:
• VLAN interface status change of a VLAN that is connected to a VSI.
VLAN interface status change of a VLAN that is connected to a VSI.
• Pseudowire status change of a pseudowire configured on the VSI.
Pseudowire status change of a pseudowire configured on the VSI.
The severity of the service alarms is Major, except for VSI Admin Down alarm.
Table 15-80 VSI Down —Subtype Events
Subtype Event Name
|
Description
|
VSI Down
|
VSI is in operational status down.
|
VSI Admin Down
|
VSI is in administrative status down.
|
VSI Up
|
VSI status is up.
|
Correlation
The VSI Down alarm does not start a correlation process and is always issued as a root cause alarm.
Impact Analysis
No impact analysis is performed for this alarm.
Source OID
See VSI OID (IVSIOID).
Registry Parameters
The following registry parameters are included in this section:
• Adaptive Polling
Adaptive Polling
• All IP Interfaces Down
All IP Interfaces Down
• ATM IMA Down
ATM IMA Down
• BGP Link Down
BGP Link Down
• BGP Neighbor Loss
BGP Neighbor Loss
• BGP Process Down
BGP Process Down
• BFD Connectivity Down
BFD Connectivity Down
• BFD Neighbor Loss
BFD Neighbor Loss
• Broken LSP Discovered
Broken LSP Discovered
• Card Down
Card Down
• Card Out
Card Out
• Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
• Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
• Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
• Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
• Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
• Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
• Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
• CFM Domain Fault
CFM Domain Fault
• Chassis Disconnected
Chassis Disconnected
• Cloud Problem
Cloud Problem
• Component Unreachable
Component Unreachable
• CPU Utilization
CPU Utilization
• Device Unsupported
Device Unsupported
• Discard Packets
Discard Packets
• Dropped Packets
Dropped Packets
• DS0 Bundle
DS0 Bundle
• DS1 Path Link Down
DS1 Path Link Down
• DS1 Path Port Down
DS1 Path Port Down
• DS3 Path Link Down
DS3 Path Link Down
• DS3 Path Port Down
DS3 Path Port Down
• Dual Stack IP Changed
Dual Stack IP Changed
• DWDM Controller
DWDM Controller
• DWDM G709 Status
DWDM G709 Status
• EFP Down
EFP Down
• GRE Keepalive
GRE Keepalive
• GRE Keepalive
GRE Keepalive
• GRE Tunnel Down
GRE Tunnel Down
• HSRP Group Status Changed
HSRP Group Status Changed
• Interface Status
Interface Status
• Investigation State
Investigation State
• L2TP Peer Not Established
L2TP Peer Not Established
• L2TP Sessions Threshold
L2TP Sessions Threshold
• Lag Down
Lag Down
• Lag Link Down
Lag Link Down
• Layer 2 Tunnel Down
Layer 2 Tunnel Down
• LDP Neighbor Loss
LDP Neighbor Loss
• Link Down
Link Down
• Link Utilization
Link Utilization
• Local Switching Down
Local Switching Down
• Logical Port Down
Logical Port Down
• LSP Down
LSP Down
• Members Changed
Members Changed
• Memory Utilization
Memory Utilization
• MLPPP Bundle
MLPPP Bundle
• MPLS Black Hole Found
MPLS Black Hole Found
• MPLS Interface Removed
MPLS Interface Removed
• MPLS TE FRR State Changed
MPLS TE FRR State Changed
• MPLS TE Tunnel Down
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
• MPLS TP Tunnel Down
MPLS TP Tunnel Down
• Network-Clock Synchronization
Network-Clock Synchronization
• OSPF Neighbor State Change
OSPF Neighbor State Change
• Port Down
Port Down
• Power Supply Down
Power Supply Down
• Pluggable Transceiver Out
Pluggable Transceiver Out
• REP Port Role Change
REP Port Role Change
• Rx Dormant
Rx Dormant
• Rx Utilization
Rx Utilization
• Shelf Out
Shelf Out
• SONET Path Link Down
SONET Path Link Down
• SONET Path Port Down
SONET Path Port Down
• Subinterface Down
Subinterface Down
• Tx Dormant
Tx Dormant
• Tx Utilization
Tx Utilization
• VSI Down
VSI Down
Adaptive Polling
Table 15-81 VNE Switched to Low Polling Rate Due to CPU High Usage
Service Alarm Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Adaptive Polling
|
Subtype
|
high polling interval
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=124
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
|
is-ticketable=true
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VNE switched to low polling rate due to CPU high usage
|
Table 15-82 VNE Switched to a Limited Investigation Mode Due to High CPU Usage
Service Alarm Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Adaptive polling
|
Subtype
|
maintenance
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=124
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VNE switched to a limited investigation mode due to high CPU usage
|
Table 15-83 VNE Switched Back to Regular Polling Rate
Service Alarm Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Adaptive polling
|
Subtype
|
regular polling interval
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=124
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VNE switched back to regular polling rate
|
All IP Interfaces Down
Table 15-84 Active IP Interfaces Found
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
all ip interfaces down
|
Subtype
|
active ip interfaces found
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=837
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Active ip interfaces found
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-85 All IP Interfaces Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
all ip interfaces down
|
Subtype
|
all ip interfaces down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=750
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=837
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=All ip interfaces down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
ATM IMA Down
Table 15-86 IMA Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ima down
|
Subtype
|
ima admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=110000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=681
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=ima administratively down
|
Table 15-87 IMA Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ima down
|
Subtype
|
ima oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=680
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=ima operationally down
|
Table 15-88 High Priority IMA Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ima down
|
Subtype
|
high priority ima down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=680
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=high priority ima down
|
Table 15-89 Medium Priority IMA Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ima down
|
Subtype
|
medium priority ima down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=680
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=medium priority ima down
|
Table 15-90 Low Priority IMA Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ima down
|
Subtype
|
low priority ima down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=680
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MINOR
|
short-description=low priority ima down
|
BFD Connectivity Down
Table 15-91 BFD Connectivity Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BFD connectivity down
|
Subtype
|
BFD connectivity down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=840
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1222
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BFD connectivity down
|
Table 15-92 BFD Connectivity Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BFD connectivity down
|
Subtype
|
BFD connectivity up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1222
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BFD connectivity up
|
BFD Neighbor Loss
Table 15-93 BFD Neighbor Loss
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BFD neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
BFD neighbor loss
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=840
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1234
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BFD neighbor loss
|
Table 15-94 BFD Neighbor Found
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BFD neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
BFD neighbor found
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1234
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BFD neighbor found
|
BGP Link Down
Table 15-95 BGP Link Down Due to Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP link down
|
Subtype
|
BGP link down due to admin
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1221
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP link down due to admin
|
Table 15-96 BGP Link Down Due to Oper
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP link down
|
Subtype
|
BGP link down due to oper
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=599
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1221
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP link down due to oper
|
Table 15-97 BGP Link Down VRF Due to Admin
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP link down
|
Subtype
|
BGP link down vrf due to admin
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1221
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP link down vrf due to admin
|
Table 15-98 BGP Link Down VRF Due to Oper
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP link down
|
Subtype
|
BGP link down vrf due to oper
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=400
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1221
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP link down vrf due to oper
|
Table 15-99 BGP Link Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP link down
|
Subtype
|
BGP link up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1221
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP link up
|
BGP Neighbor Loss
Table 15-100 BGP Neighbor Found
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
BGP neighbor found
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=127
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP neighbor found
|
Table 15-101 BGP Neighbor Loss Due to Admin
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
BGP neighbor loss due to admin
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=127
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP neighbor loss due to admin
|
Table 15-102 BGP Neighbor Loss Due to Oper
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
BGP neighbor loss due to oper
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=601
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=127
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP neighbor loss due to oper
|
Table 15-103 BGP Neighbor Loss VRF Due to Admin
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
bgp-neighbor-loss-vrf due to admin
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=flase
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=127
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP neighbor loss vrf due to admin
|
Table 15-104 BGP Neighbor Loss VRF Due to Oper
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
BGP neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
bgp-neighbor-loss-vrf
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=400
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=127
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP neighbor loss vrf due to oper
|
BGP Process Down
Table 15-105 BGP Process Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
bgp-process-down
|
Subtype
|
bgp-process-down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=850
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1501
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP process down
|
Table 15-106 BGP Process Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
bgp-process-down
|
Subtype
|
bgp-process-up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1501
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=BGP process up
|
Broken LSP Discovered
Table 15-107 Broken LSP Discovered
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Broken LSP discovered
|
Subtype
|
Broken LSP discovered
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=129
|
auto-cleared=true
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Broken LSP discovered
|
Card Down
Table 15-108 Card Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
card down
|
Subtype
|
card down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=100000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=11
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Card down
|
Table 15-109 Card Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
card down
|
Subtype
|
card up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=11
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Card up
|
Card Out
Table 15-110 Card In
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
card out
|
Subtype
|
card in
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=3
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Card in
|
Table 15-111 Card Out
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
card out
|
Subtype
|
card out
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=100000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=3
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Card out
|
Table 15-112 Subcard Out
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
card out
|
Subtype
|
subcard out
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=1000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=3
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Card out
|
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
Table 15-113 Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate Higher Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics translationsCreate
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics translationsCreate higher threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5001
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
gw-correlation-timeout=1200000
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics translationsCreate higher threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-114 Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate Lower Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics translationsCreate
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics translationsCreate lower threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5001
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics translationsCreate lower threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-115 Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate Threshold Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics translationsCreate
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics translationsCreate threshold normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5001
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics translationsCreate threshold normal
|
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
Table 15-116 Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate Higher Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics translationsDelete
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics translationsDelete higher threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5002
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics translationsDelete higher threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-117 Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate Lower Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics translationsDelete
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics translationsDelete lower threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5002
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics translationsDelete lower threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-118 Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate Threshold Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics translationsDelete
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics translationsDelete threshold normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5002
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics translationsDelete threshold normal
|
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
Table 15-119 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate Higher Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics fwdIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics fwdIn2Out higher threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5003
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics fwdIn2Out higher threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-120 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate Lower Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics fwdIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics fwdIn2Out lower threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5003
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics fwdIn2Out lower threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-121 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate Threshold Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics fwdIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics fwdIn2Out threshold normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5003
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics fwdIn2Out threshold normal
|
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
Table 15-122 Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate Higher Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics fwdOut2In
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics fwdOut2In higher threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5004
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics fwdOut2In higher threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-123 Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate Lower Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics fwdOut2In
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics fwdOut2In lower threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5004
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics fwdOut2In lower threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-124 Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate Threshold Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics fwdOut2In
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics fwdOut2In threshold normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5004
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics fwdOut2In threshold normal
|
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
Table 15-125 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Higher Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out Limit higher threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5005
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out Limit higher threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-126 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Lower Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out lower threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5005
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out lower threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-127 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Threshold Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out threshold normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5005
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsPortLimitIn2Out threshold normal
|
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
Table 15-128 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached Higher Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out higher threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5006
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out higher threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-129 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached Lower Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out lower threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5006
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out lower threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-130 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached Threshold Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out threshold normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5006
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsSystemLimitIn2Out threshold normal
|
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
Table 15-131 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion Higher Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out higher threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5007
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out higher threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-132 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion Lower Threshold Exceeded
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out lower threshold exceeded
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5007
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out lower threshold exceeded
|
Table 15-133 Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion Threshold Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out
|
Subtype
|
cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out threshold normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5007
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cgn statistics dropsResourceDepletionIn2Out threshold normal
|
CFM Domain Fault
Table 15-134 CFM Domain Aggregation Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
CFM Domain Fault
|
Subtype
|
CFM Domain Aggregation Down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=2
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=3016
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=INFO
|
short-description=CFM Domain fault
|
Table 15-135 CFM Domain Aggregation Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
CFM Domain Fault
|
Subtype
|
CFM Domain Aggregation Up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=3016
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=CFM Domain fault cleared
|
Chassis Disconnected
Table 15-136 Chassis Disconnected
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Chassis Disconnected
|
Subtype
|
Chassis Disconnected
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=100000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=3
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Chassis disconnected
|
Table 15-137 Card Out due to Chassis Disconnected
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Chassis Disconnected
|
Subtype
|
Card Out due to Chassis Disconnected
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=100000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=3
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Card out due to chassis disconnected
|
Table 15-138 Chassis Connected
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Chassis Disconnected
|
Subtype
|
Chassis Connected
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=3
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Chassis connected
|
Cloud Problem
Table 15-139 Cloud Problem
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cloud problem
|
Subtype
|
cloud problem
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=2000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=122
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=INFO
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cloud problem
|
Table 15-140 Cloud Problem Fixed
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cloud problem
|
Subtype
|
cloud up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=122
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=cloud problem fixed
|
Component Unreachable
Table 15-141 Component Reachable
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
component unreachable
|
Subtype
|
component reachable
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Device Reachable
|
Table 15-142 Component Unreachable
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
component unreachable
|
Subtype
|
component unreachable
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=600
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Device Unreachable
|
Table 15-143 Device Partially Managed
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
component unreachable
|
Subtype
|
device partially managed
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=5
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=WARNING
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Device reachable
|
CPU Utilization
Table 15-144 CPU Normal Utilization
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cpu utilization
|
Subtype
|
cpu normal use
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=17
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=CPU utilization less than lower threshold
|
Table 15-145 CPU Overutilized
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
cpu utilization
|
Subtype
|
cpu over utilized
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=17
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=CPU utilization exceeded lower threshold
|
Device Unsupported
Table 15-146 Device Initializing
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
device unsupported
|
Subtype
|
device initializing
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=16
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
gw-correlation-timeout=1200000
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Device initializing
|
Table 15-147 Device Unsupported
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
device unsupported
|
Subtype
|
device unsupported
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=16
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Device unsupported
|
Discard Packets
Table 15-148 Discard Packets
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
discard packets
|
Subtype
|
discard packets
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=9
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Discarded packet rate exceeded upper threshold
|
Table 15-149 Normal Discard Packets
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
discard packets
|
Subtype
|
normal discard packets
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=9
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Discarded packet rate is below lower threshold
|
Dropped Packets
Table 15-150 Dropped Packets on Port
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
dropped packets
|
Subtype
|
dropped packets
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=10
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Dropped packet rate exceeded upper threshold
|
Table 15-151 Stopped Dropping Packets on Port
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
dropped packets
|
Subtype
|
normal dropped packets
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=10
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Dropped packet rate is below lower threshold
|
DS0 Bundle
Table 15-152 DS0 Bundle Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds0 bundle down
|
Subtype
|
ds0 bundle admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=750
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=660
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=ds0 bundle admin down
|
Table 15-153 DS0 Bundle Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds0 bundle down
|
Subtype
|
ds0 bundle oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=725
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=660
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=ds0 bundle oper down
|
Table 15-154 DS0 Bundle Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds0 bundle down
|
Subtype
|
ds0 bundle up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=660
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=ds0 bundle up
|
DS1 Path Link Down
Table 15-155 DS1 Path Link Down Due to Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path link down due to admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=815
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1344
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=DS1 Path Link down due to admin down
|
Table 15-156 DS1 Path Link Down Due to Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path link down due to oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=810
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1344
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=DS1 Path Link down due to oper down
|
Table 15-157 DS1 Path Link Down Due to Card
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path link down due to card
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=815
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1344
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=DS1 Path Link down due to card event
|
Table 15-158 DS1 Path Link Down on Unreachable
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path link down on unreachable
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=810
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1344
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=DS1 Path Link down on unreachable
|
Table 15-159 DS1 Path Link Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path link up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1344
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=DS1 Path Link up
|
DS1 Path Port Down
Table 15-160 DS1 Path Port Down Due to Admin
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path port down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path port down due to admin
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=810
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1381
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=DS1 Path down due to Admin
|
Table 15-161 DS1 Path Port Down Due to Oper
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path port down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path port down due to oper
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=810
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1381
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=DS1 Path down due to Oper
|
Table 15-162 DS1 Path Port Down Due to Card
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path port down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path port down due to card
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=815
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1381
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=DS1 Path down due to Card
|
Table 15-163 DS1 Path Port Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds1path port down
|
Subtype
|
ds1path port up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1381
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=DS1 Path up
|
DS3 Path Link Down
Table 15-164 DS3 Path Link Down Due to Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path link admin due to admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=825
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1356
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=DS3 Path Link down due to admin down
|
Table 15-165 DS3 Path Link Down Due to Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path link down due to oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=820
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1356
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=DS3 Path Link down due to oper down
|
Table 15-166 DS3 Path Link Down Due to Card
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path link down due to card
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=825
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1356
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=DS3 Path Link down due to Card event
|
Table 15-167 DS3 Path Link Down on Unreachable
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path link down on unreachable
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=820
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1356
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=DS3 Path Link down on unreachable
|
Table 15-168 DS3 Path Link Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path link down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path link up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1356
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=DS3 Path Link up
|
DS3 Path Port Down
Table 15-169 DS3 Path Port Down Due to Admin
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path port down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path port down due to admin
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=820
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1357
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=DS3 path port down due to Admin
|
Table 15-170 DS3 Path Port Down Due to Oper
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path port down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path port down due to oper
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=820
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1357
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=DS3 Path Down due to Oper
|
Table 15-171 DS3 Path Port Down Due to Card
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path port down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path port down due to card
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=825
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1357
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=DS3 Path Down due to Card
|
Table 15-172 DS3 Path Port Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ds3path port down
|
Subtype
|
ds3path port up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1357
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=DS3 Path up
|
Dual Stack IP Changed
Table 15-173 Dual Stack IP Removed
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Dual stack IP Changed
|
Subtype
|
Dual stack IP removed
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=820
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1170
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MINOR
|
short-description=Dual stack IP removed
|
Table 15-174 Dual Stack IP Added
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Dual stack IP Changed
|
Subtype
|
Dual stack IP added
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1170
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=Dual stack IP added
|
DWDM Controller
Table 15-175 DWDM Controller Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
dwdm controller down
|
Subtype
|
dwdm controller down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1888
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=dwdm controller down
|
Table 15-176 DWDM Controller Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
dwdm controller down
|
Subtype
|
dwdm controller up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1888
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=dwdm controller up
|
DWDM G709 Status
Table 15-177 DWDM G709 Status Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
dwdm g709 status down
|
Subtype
|
dwdm g709 status down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1889
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MINOR
|
short-description=dwdm g709 status down
|
Table 15-178 DWDM G709 Status Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
dwdm g709 status down
|
Subtype
|
dwdm g709 status up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1889
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=dwdm g709 status up
|
EFP Down
Table 15-179 EFP Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
efp down
|
Subtype
|
efp admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=849
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=918
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=EFP admin down
|
Table 15-180 EFP Down Due to Error Disabled
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
efp down
|
Subtype
|
efp down due to error disabled
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=849
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=918
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=EFP down due to error disabled
|
Table 15-181 EFP Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
efp down
|
Subtype
|
efp oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=849
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=918
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=EFP oper down
|
Table 15-182 EFP Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
efp down
|
Subtype
|
efp up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=918
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=EFP up
|
ESMC Process Down
Table 15-183 ESMC Process Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
esmc process down
|
Subtype
|
esmc process down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=750
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=690
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=esmc process down
|
Table 15-184 ESMC Process Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
esmc process up
|
Subtype
|
esmc process up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=690
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=esmc process up
|
Fan-Tray Down
Table 15-185 Fan-Tray Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
fan-tray down
|
Subtype
|
fan-tray down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13003
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=fan-tray down
|
Table 15-186 Fan-Tray Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
fan-tray down
|
Subtype
|
fan-tray up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13003
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=fan-tray up
|
Fan-Tray Out
Table 15-187 Fan-Tray Out
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
fan-tray out
|
Subtype
|
fan-tray out
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13002
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=fan-tray out
|
Table 15-188 Fan-Tray In
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
fan-tray out
|
Subtype
|
fan-tray in
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13002
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=fan-tray in
|
GRE Keepalive
Table 15-189 Keepalive Not Set
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
keepalive set
|
Subtype
|
Keepalive not set
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=915
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MINOR
|
short-description=keepalive not configured
|
Table 15-190 Keepalive Set
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
keepalive set
|
Subtype
|
keepalive set
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=915
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=keepalive configured
|
GRE Tunnel Down
Table 15-191 GRE Tunnel Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
GRE tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
GRE tunnel down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=830
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=358
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=GRE tunnel down
|
Table 15-192 GRE Tunnel Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
GRE tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
GRE tunnel up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=358
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=GRE tunnel up
|
HSRP Group Status Changed
Table 15-193 Primary HSRP Interface Is Active
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
hsrp group status changed
|
Subtype
|
Primary HSRP interface is active
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=22
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Primary HSRP interface is active
|
Table 15-194 Primary HSRP Interface Is Not Active
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
hsrp group status changed
|
Subtype
|
Primary HSRP interface is not active
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=720
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=22
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Primary HSRP interface is not active
|
Table 15-195 Secondary HSRP Interface Is Active
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
hsrp group status changed
|
Subtype
|
Secondary HSRP interface is active
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=720
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=22
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Secondary HSRP interface is active
|
Table 15-196 Secondary HSRP Interface Is Not Active
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
hsrp group status changed
|
Subtype
|
Secondary HSRP interface is not active
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=22
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Secondary HSRP interface is not active
|
Interface Status
Table 15-197 Interface Status Down GRE Tunnel
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
interface status
|
Subtype
|
interface status down GRE tunnel
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=825
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=700
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Interface status down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-198 Interface Status Down Connection
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
interface status
|
Subtype
|
interface status down connection
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=500
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=700
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Interface status down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-199 Interface Status Down Nonconnection
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
interface status
|
Subtype
|
interface status down non connection
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=700
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=700
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Interface status down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-200 Interface Status Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
interface status
|
Subtype
|
interface status up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=700
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Interface status up
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Investigation State
Table 15-201 Investigation State
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
investigation state
|
Subtype
|
investigation state module unsupported
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=262
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Module unsupported
|
L2TP Peer Not Established
Table 15-202 L2TP Peer Established
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
l2tp peer not established
|
Subtype
|
l2tp peer established
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=185
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=l2tp peer established
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-203 L2TP Peer Is Removed
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
l2tp peer not established
|
Subtype
|
l2tp peer is removed
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=185
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=l2tp peer is removed
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-204 L2TP Peer Not Established
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
l2tp peer not established
|
Subtype
|
l2tp peer not established
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=185
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=l2tp peer not established
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
L2TP Sessions Threshold
Table 15-205 L2TP Sessions Count Exceeds Maximum Threshold
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
l2tp sessions threshold
|
Subtype
|
l2tp sessions count exceeds max threshold
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=N/A (TCA alarm)
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=l2tp sessions count exceeds max threshold
|
Table 15-206 L2TP Sessions Count Has Returned to Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
l2tp sessions threshold
|
Subtype
|
l2tp sessions count has returned to normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=N/A (TCA alarm)
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=l2tp sessions count has returned to normal
|
Lag Down
Table 15-207 Lag Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Lag down
|
Subtype
|
Lag admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=718
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=LAG down due to admin down
|
Table 15-208 Lag Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
lag down
|
Subtype
|
lag oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=718
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Lag down due to oper down
|
Table 15-209 Lag Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
lag down
|
Subtype
|
lag up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=718
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Lag up
|
Lag Link Down
Table 15-210 Lag Link Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
lag link down
|
Subtype
|
lag link admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=719
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Lag Link down due to admin down
|
Table 15-211 Lag Link Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
lag link down
|
Subtype
|
lag link oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=719
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Lag Link down due to oper down
|
Table 15-212 Lag Link Down on Unreachable
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
lag link down
|
Subtype
|
lag link down on unreachable
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=719
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Lag Link down on unreachable
|
Table 15-213 Lag Link Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
lag link down
|
Subtype
|
lag link up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=719
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Lag link up
|
Layer 2 Tunnel Down
Table 15-214 Layer 2 Tunnel Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
layer 2 tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
layer 2 tunnel down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=179
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Layer 2 tunnel down
|
Table 15-215 Layer 2 Tunnel Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
layer 2 tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
layer 2 tunnel up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=179
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Layer 2 tunnel up
|
LDP Neighbor Loss
Table 15-216 LDP Neighbor Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
LDP neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
LDP neighbor down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=670
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=557
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=LDP neighbor down
|
Table 15-217 LDP Neighbor Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
LDP neighbor loss
|
Subtype
|
LDP neighbor up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=557
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=LDP neighbor up
|
Link Down
Table 15-218 Link Down Due to Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
link down
|
Subtype
|
link down due to admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=850
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Link down due to admin down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-219 Link Down Due to Card Event
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
link down
|
Subtype
|
link down due to card
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=850
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Link down due to Card event
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-220 Link Down Due to Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
link down
|
Subtype
|
link down due to oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=850
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Link down due to oper down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-221 Link Down on Unreachable
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
link down
|
Subtype
|
link down on unreachable
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=850
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Link down on unreachable
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-222 Link Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
link down
|
Subtype
|
link up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Link up
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Link Utilization
Table 15-223 Link Overutilized
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
link utilization
|
Subtype
|
link over Utilized
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=642
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Link over utilized
|
Table 15-224 Link Utilization Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
link utilization
|
Subtype
|
link utilization normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=642
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Link utilization normal
|
Local Switching Down
Table 15-225 Local Switching Entry Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
local switching down
|
Subtype
|
local switching down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1299
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Local switching entry down
|
Table 15-226 Local Switching Entry Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
local switching down
|
Subtype
|
local switching up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1299
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Local switching entry up
|
Logical Port Down
Table 15-227 Logical Port Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
logical port down
|
Subtype
|
logical port down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=198
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Logical port down
|
Table 15-228 Logical Port Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
logical port down
|
Subtype
|
logical port up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=198
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Logical port up
|
LSP Down
Table 15-229 LSP Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
LSP Down
|
Subtype
|
LSP Down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=110
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=189
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=LSP down
|
Table 15-230 LSP Down Due to Label Mismatch
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
LSP Down
|
Subtype
|
LSP Down Due to Label Mismatch
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=115
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=189
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=LSP down due to label mismatch
|
Table 15-231 LSP Down Due to Lock Out
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
LSP Down
|
Subtype
|
LSP Down Due to Lock Out
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=120
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=189
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=LSP locked out
|
Table 15-232 LSP Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
LSP Down
|
Subtype
|
LSP Up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=189
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=LSP up
|
Members Changed
Table 15-233 High Priority Member Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Members Changed
|
Subtype
|
high priority member down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=682
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=High priority member down
|
Table 15-234 Medium Priority Member Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Members Changed
|
Subtype
|
medium priority member down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=682
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Medium priority member down
|
Table 15-235 Low Priority Member Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
members changed
|
Subtype
|
low priority member down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=682
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Low priority member down
|
Table 15-236 All Members Operationally Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
members changed
|
Subtype
|
members up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=682
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=All members operationally up
|
Memory Utilization
Table 15-237 Memory OK
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
memory utilization
|
Subtype
|
memory normal use
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=18
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Memory utilization less than normal threshold
|
Table 15-238 Memory Overutilized
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
memory utilization
|
Subtype
|
memory over utilized
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=-
|
correlate=-
|
is-correlation-allowed=-
|
weight=-
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=18
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Memory utilization exceeded upper threshold
|
MLPPP Bundle
Table 15-239 MLPPP Down Due To Flapping
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mlppp down
|
Subtype
|
flapping
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=1000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=914
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=mlppp down flapping
|
Table 15-240 MLPPP Down Flapping Update
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mlppp down
|
Subtype
|
flapping update
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=1000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=914
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=mlppp down flapping update
|
Table 15-241 MLPPP Down Due To Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mlppp down
|
Subtype
|
mlppp admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=1000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=914
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
short-description=mlppp administratively down
|
Table 15-242 MLPPP Down Flapping Proxy
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mlppp down
|
Subtype
|
local flapping proxy
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=1000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=914
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=false
|
severity=INFO
|
short-description=mlppp down flapping proxy
|
Table 15-243 MLPPP Down Due To Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mlppp down
|
Subtype
|
mlppp oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=1000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=914
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=mlppp operationally down
|
Table 15-244 MLPPP Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mlppp down
|
Subtype
|
mlppp up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=1000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=914
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=mlppp up
|
MPLS Black Hole Found
Table 15-245 MPLS Black Hole Cleared
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
MPLS Black hole found
|
Subtype
|
MPLS Black hole cleared
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=128
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS Black hole cleared
|
Table 15-246 MPLS Black Hole Found
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
MPLS Black hole found
|
Subtype
|
MPLS Black hole found
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=650
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=128
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=WARNING
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS Black hole found
|
MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
Table 15-247 MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
|
Subtype
|
MPLS TP Bandwidth Mismatch
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=—
|
correlate=—
|
is-correlation-allowed=—
|
weight=—
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=972
|
auto-cleared=true
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=WARNING
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=TPTunnel bandwidth mismatch
|
MPLS Interface Removed
Table 15-248 MPLS Interface Added
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
MPLS interface removed
|
Subtype
|
MPLS interface added
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=972
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS interface added
|
Table 15-249 MPLS Interface Removed
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
MPLS interface removed
|
Subtype
|
MPLS interface removed
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=700
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=972
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS interface removed
|
MPLS TE FRR State Changed
Table 15-250 MPLS TE FRR State Changed to Active
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
MPLS TE FRR State Changed
|
Subtype
|
MPLS TE FRR State Changed to Active
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=700
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1322
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=MAJOR
|
short-description=MPLS TE FRR State Changed to Active
|
Table 15-251 MPLS TE FRR State Changed to Ready
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
MPLS TE FRR State Changed
|
Subtype
|
MPLS TE FRR State Changed to Ready
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
root-cause-timeout=420000
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1322
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
auto-removed-timeout=5000000
|
duplication-counter=1
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
priority=0
|
reduction-counter=1
|
send-to-gw=true
|
severity=CLEARED
|
short-description=MPLS TE FRR State Changed to Ready
|
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Table 15-252 MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mpls te tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
mpls te tunnel down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=555
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS TE tunnel down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-253 High Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mpls te tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
High Priority mpls te tunnel down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=555
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=High Priority MPLS-TE tunnel down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-254 Medium Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mpls te tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
Medium Priority mpls te tunnel down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=555
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Medium Priority MPLS-TE tunnel down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-255 Low Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mpls te tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
Low Priority mpls te tunnel down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=555
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Low Priority MPLS-TE tunnel down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-256 MPLS TE Tunnel Reoptimized
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mpls te tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
mpls te tunnel down reoptimized
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=555
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=INFO
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS TE-tunnel reoptimized
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-257 MPLS TE Tunnel Rerouted
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mpls te tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
mpls te tunnel rerouted
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=800
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=555
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=INFO
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS-TE tunnel rerouted
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-258 MPLS TE Tunnel Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
mpls te tunnel down
|
Subtype
|
mpls te tunnel up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=555
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS-TE tunnel up
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=240000
|
flapping-interval=60000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-259 TP Tunnel Down Due to Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
TP Tunnel Down
|
Subtype
|
TP Tunnel Down Due to Admin Down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=150
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=180
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=MPLS-TP tunnel admin down
|
MPLS TP Tunnel Down
Table 15-260 TP Tunnel Down Due to Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
TP Tunnel Down
|
Subtype
|
TP Tunnel Down Due to Oper Down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=100
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=180
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description= MPLS-TP tunnel oper down.
|
Network-Clock Synchronization
Table 15-261 Network-Clock Synchronization Enabled
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
network-clock synchronization
|
Subtype
|
network-clock synchronization enabled
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=685
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description= network-clock synchronization enabled
|
Table 15-262 Network-Clock Synchronization Disabled
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
network-clock synchronization
|
Subtype
|
network-clock synchronization disabled
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=750
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=685
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=network-clock synchronization disabled
|
OSPF Neighbor State Change
Table 15-263 OSPF Neighbor Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ospf neighbor state change
|
Subtype
|
ospf neighbor down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=200
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1350
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=OSPF Neighbor Down
|
Table 15-264 OSPF Neighbor Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
ospf neighbor state change
|
Subtype
|
ospf neighbor up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1350
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=OSPF Neighbor Up
|
Port Down
Table 15-265 Port Down Due to Admin
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
port down
|
Subtype
|
port down due to admin
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=100000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=2
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Port down due to admin
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-266 Port Down Due to Oper
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
port down
|
Subtype
|
port down due to oper
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=100000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=2
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Port down due to oper
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-267 Port Down Due to Card Event
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
port down
|
Subtype
|
port down due to card
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=900
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=2
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Port down due to Card event
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-268 Port Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
port down
|
Subtype
|
port up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=2
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Port up
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Power Supply Down
Table 15-269 Power Supply Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Power Supply Down
|
Subtype
|
Power Supply Down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13001
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Power supply down
|
Table 15-270 Power Supply Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Power Supply Down
|
Subtype
|
Power Supply Up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13001
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Power supply up
|
Power Supply Out
Table 15-271 Power Supply Out
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Power supply out
|
Subtype
|
Power supply out
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13000
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Power supply out
|
Table 15-272 Power Supply In
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Power supply out
|
Subtype
|
Power supply in
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13000
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Power supply in
|
Pluggable Transceiver Out
Table 15-273 Pluggable Transceiver In
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
pluggable transceiver out
|
Subtype
|
pluggable transceiver in
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13004
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Pluggable transceiver in
|
Table 15-274 Pluggable Transceiver Out
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
pluggable transceiver out
|
Subtype
|
pluggable transceiver out
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=750
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=13004
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Pluggable transceiver out
|
REP Port Role Change
Table 15-275 REP Port Role Failed
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
REP Port Role Change
|
Subtype
|
REP Port Role Failed
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=101
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=4000000
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=REP Port Role Failed
|
Table 15-276 REP Port Role Ok
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
REP Port Role Change
|
Subtype
|
REP Port Role Ok
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=4000000
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=REP Port Role Ok
|
Rx Dormant
Table 15-277 Rx Dormant
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
rx dormant
|
Subtype
|
rx dormant
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=378
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=rx dormant
|
Table 15-278 Rx Dormant Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
rx dormant
|
Subtype
|
rx dormant normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=378
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=rx dormant normal
|
Rx Utilization
Table 15-279 Rx Overutilized
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
rx utilization
|
Subtype
|
rx over Utilized
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=8
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Rx utilization exceeded upper threshold
|
Table 15-280 Rx Utilization Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
rx utilization
|
Subtype
|
rx utilization normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=8
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Rx utilization is below lower threshold
|
Shelf Out
Table 15-281 Shelf In
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
shelf out
|
Subtype
|
shelf in
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=33
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Shelf in
|
Table 15-282 Shelf Out
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
shelf out
|
Subtype
|
shelf out
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=110000
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=33
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Shelf out
|
SONET Path Link Down
Table 15-283 SONET Path Link Down Due to Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath link down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath link down due to admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=845
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1345
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path link down due to admin down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-284 SONET Path Link Down Due to Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath link down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath link down due to oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=840
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1345
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path link down due to oper down
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-285 SONET Path Link Down Due to Card
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath link down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath link down due to card
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=845
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1345
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path link down due to Card event
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-286 SONET Path Link Down on Unreachable
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath link down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath link down due on unreachable
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=840
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1345
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CRITICAL
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path Link down on unreachable
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-287 SONET Path Link Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath link down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath link up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1345
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path Link up
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
SONET Path Port Down
Table 15-288 SONET Path Port Down Due to Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath port down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath port down due to admin
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=840
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1333
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path down due to Admin
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-289 SONET Path Port Down Due to Oper Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath port down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath port down due to oper
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=840
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1333
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path down due to Oper
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-290 SONET Path Port Down Due to Card
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath port down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath port down due to card
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=845
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1333
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path down due to Card
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Table 15-291 SONET Path Port Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sonetpath port down
|
Subtype
|
sonetpath port up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=845
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=1333
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=SONET Path up
|
Flapping information
|
clear-interval=360000
|
flapping-interval=150000
|
flapping-threshold=5
|
update-interval=200000
|
update-threshold=20
|
Subinterface Down
Table 15-292 Subinterface Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sub-interface down
|
Subtype
|
sub-interface oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=849
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=917
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VLAN SubInterface oper down
|
Table 15-293 Subinterface Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sub-interface down
|
Subtype
|
sub-interface admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=849
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=917
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VLAN Sub Interface admin down
|
Table 15-294 Subinterface Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
sub-interface down
|
Subtype
|
sub-interface up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=917
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VLAN Sub Interface up
|
Tx Dormant
Table 15-295 Tx Dormant
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
tx dormant
|
Subtype
|
tx dormant
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=377
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=tx dormant
|
Table 15-296 Tx Dormant Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
tx dormant
|
Subtype
|
tx dormant normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=377
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=tx dormant normal
|
Tx Utilization
Table 15-297 Tx Overutilized
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
tx utilization
|
Subtype
|
tx over Utilized
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=7
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MINOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Tx utilization exceeded upper threshold
|
Table 15-298 Tx Utilization Normal
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
tx utilization
|
Subtype
|
tx utilization normal
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=7
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=Tx utilization is below lower threshold
|
VSI Down
Table 15-299 VSI Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
vsi down
|
Subtype
|
vsi oper down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=true
|
correlate=true
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=845
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=916
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VSI oper down
|
Table 15-300 VSI Admin Down
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
vsi down
|
Subtype
|
vsi admin down
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=true
|
weight=101
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=916
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=MAJOR
|
is-ticketable=true
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VSI admin down
|
Table 15-301 VSI Up
Event Setting
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
vsi down
|
Subtype
|
vsi up
|
Correlation information
|
activate-flow=false
|
correlate=false
|
is-correlation-allowed=false
|
weight=0
|
Northbound metadata
|
alarm-type=916
|
auto-cleared=false
|
auto-removed=true
|
functionality-type=SERVICE
|
severity=CLEARED
|
is-ticketable=false
|
|
send-to-gw=true
|
short-description=VSI up
|
Alarm Source OIDs
These topics describe the possible source object identifiers (OIDs) of alarms generated by Prime Network. A description of each source OID and OID structure is given, with examples of OIDs and service alarms that use those OIDs as their source.
Note  The source OID must be unique in the alarm type context. For example, it is not possible to generate multiple different alarms with the same type from the same component using the component OID as the source. An additional differentiator should be added to the base component OID. See LSE OID (ILseOid), for an example.
The source OID must be unique in the alarm type context. For example, it is not possible to generate multiple different alarms with the same type from the same component using the component OID as the source. An additional differentiator should be added to the base component OID. See LSE OID (ILseOid), for an example.
The following source OIDs are described:
• BFD Connectivity Down OID
BFD Connectivity Down OID
• BFD Neighbor Loss OID
BFD Neighbor Loss OID
• BGP Neighbor Entry OID (IBgpNeighborEntryOid)
BGP Neighbor Entry OID (IBgpNeighborEntryOid)
• Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid)
Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid)
• Chassis Oid (ChassisId)
Chassis Oid (ChassisId)
• DS0 Bundle OID (IDS0BundleOid)
DS0 Bundle OID (IDS0BundleOid)
• DS1 Path OID (IDS1PathOid)
DS1 Path OID (IDS1PathOid)
• DS3 Path OID (IDS3PathOid)
DS3 Path OID (IDS3PathOid)
• DWDM Controller OID (IDWDMOid)
DWDM Controller OID (IDWDMOid)
• EFP OID (IEFPOID)
EFP OID (IEFPOID)
• Fan Tray OID
Fan Tray OID
• IMA Service (IIMAGroupOid)
IMA Service (IIMAGroupOid)
• IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid)
IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid)
• L2TP Peer OID (IL2tpPeerOid)
L2TP Peer OID (IL2tpPeerOid)
• Lag Down OID
Lag Down OID
• Lag Link Down OID
Lag Link Down OID
• Local Switching Entry Down OID
Local Switching Entry Down OID
• Logical Port OID (ILogicalPortOid)
Logical Port OID (ILogicalPortOid)
• LSE OID (ILseOid)
LSE OID (ILseOid)
• Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid)
Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid)
• Members Changed OID (IDataLinkAggregationOid)
Members Changed OID (IDataLinkAggregationOid)
• MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid)
MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid)
• Module OID (IModuleOid)
Module OID (IModuleOid)
• MPBGP OID (IMpBgpOid)
MPBGP OID (IMpBgpOid)
• MPLS TE Tunnel OID (IMplsTETunnelOid)
MPLS TE Tunnel OID (IMplsTETunnelOid)
• TP Tunnel Endpoint OID (TP Tunnel EndPoint OID)
TP Tunnel Endpoint OID (TP Tunnel EndPoint OID)
• ISyncEOID
ISyncEOID
• OSPF Neighbor State Change OID
OSPF Neighbor State Change OID
• Power Supply OID
Power Supply OID
• Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid)
Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid)
• Shelf OID (IShelfOid)
Shelf OID (IShelfOid)
• SONET Path Port Down OID
SONET Path Port Down OID
• SONET Path Link Down OID
SONET Path Link Down OID
• Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid)
Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid)
• VLAN Tagged Interface OID (IVlanTaggedInterfaceOID)
VLAN Tagged Interface OID (IVlanTaggedInterfaceOID)
• VSI OID (IVSIOID)
VSI OID (IVSIOID)
BFD Connectivity Down OID
The BFD Connectivity Down OID supports the BFD Connectivity Down Alarm.
Example
{[TopologicalLink(AEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=p1)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Def
ault
context)][BfdService]})(LinkType=14)(TunnelID=-1)(ZEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=c3-npe1-7
6)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][BfdService][ServiceEvent(DiffObject=2.0.0.29 <-> 2.0.0.30)]})]}
BFD Neighbor Loss OID
The BFD Neighbor Loss OID supports the BFD Neighbor Loss Alarm.
Example
ManagedElement(Key=p1)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default context)][BfdService]})
BGP Neighbor Entry OID (IBgpNeighborEntryOid)
The BGP Neighbor Entry OID is the source OID for any alarms related to BGP neighbors.
The BGP Neighbor Entry source OID supports the BGP Neighbor Loss alarm.
The structure of the BGP Neighbor Entry OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=7)][MpBgp][BgpNeighborEntry(PeerIdentifier=peerIP)(VrfName=vrfName)]}
The VrfName identifier in the BGP entry part exists if the entry is under VRF.
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=PE3-NY-7300)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=7)][MpBgp][BgpNe
ighbourEntry(PeerIdentifier=10.0.7.4)(VrfName=Red)]}
Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid)
The Carrier Grade NAT OID is the source OID for Carrier Grade NAT alarms.
The structure of the Carrier Grade NAT OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceIP)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=10)][CgnService(CgnName=CgnInstanceName)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=169.254.192.135)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=10)]
[CgnService(CgnName=demo)]}
Chassis Oid (ChassisId)
The Chassis OID is the source OID for any alarms related to a chassis in a network element.
The structure of the Chassis OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=VNE_NAME)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis(ChassisId="0")]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=UCS)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis(ChassisId="sys/switch-A")]}
DS0 Bundle OID (IDS0BundleOid)
The DS0 Bundle OID is the source OID for any alarms related to DS0 Bundle.
The alarm supported by Prime Network with DS0 Bundle OID source OID is:
• DS0 Bundle Down
DS0 Bundle Down
The structure of the DS0 Bundle OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=mlppp-mlppp number)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=slot number)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=shot number)][Module][Port(PortNumber=port number)][PhysicalLayer][Lop(Id=identifier)][DS0Bundle(BundleLocation=Bundle: location)(Id=identifier)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=mlppp-2)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=4)][Module][Slot(SlotNu
m=3)][Module][Port(PortNumber=T3
4/3/0)][PhysicalLayer][Lop(Id=14)][DS0Bundle(BundleLocation=Bundle:
Serial4/3/0/14:0)(Id=0)]}
DS1 Path OID (IDS1PathOid)
The DS1 Path OID is the source OID for any alarms related to DS1 port and link down.
Alarms supported by DS1 Path OID include:
• DS1 Path Port Down
DS1 Path Port Down
• DS1 Path Link Down
DS1 Path Link Down
The structure of the DS1 Path OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=element key)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=slotnumber)][Module \][Slot(SlotNum=slotnumber)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portnumber][PhysicalLayer][Sonet_SdhHop(Id=hop identifier)][Lop(Id=LOP ID)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=ana-dev-7609-1)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=8)][Module \
][Slot(SlotNum=1)][Module][Port(PortNumber=SONET \
8/1/0)][PhysicalLayer][Sonet_SdhHop(Id=3)][Lop(Id=3/5/3)]}
DS3 Path OID (IDS3PathOid)
The DS3 Path OID is the source OID for any alarms related to DS3 port down.
Alarms supported by DS3 Path OID include:
• DS3 Path Port Down
DS3 Path Port Down
• DS3 Path Link Down
DS3 Path Link Down
The structure of the DS3 Path OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=element key)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=slotnumber)][Module \][Slot(SlotNum=slotnumber)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portnumber][PhysicalLayer][Sonet_SdhHop(Id=hop identifier)][Lop(Id=LOP ID)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=ana-dev-7609-1)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=8)][Module \
][Slot(SlotNum=1)][Module][Port(PortNumber=SONET \
8/1/0)][PhysicalLayer][Sonet_SdhHop(Id=3)][Lop(Id=3/5/3)]}
DWDM Controller OID (IDWDMOid)
The DWDM Controller OID is the IMO class of the DWDM controller. Alarms supported with the DWDM Controller OID include:
• DWDM Controller Down
DWDM Controller Down
• DWDM G709 Status Down
DWDM G709 Status Down
The structure of the DWDM Controller OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=devicename)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=shelfnumber)][Slot(SlotNum=slotnumber)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portnumber)][PhysicalLayer]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=CRS1-simu-41)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=0)][Slot(SlotNum
=5)][Module][Port(PortNumber=POS0/5/0/0)][PhysicalLayer]}
EFP OID (IEFPOID)
The structure of the EFP OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=7)][MpBgp][BgpNeighbourEntry(PeerIdentifier=peerIP)(VrfName=vrfName)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=PE3-NY-7300)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=7)][MpBgp][BgpNe
ighbourEntry(PeerIdentifier=10.0.7.4)(VrfName=Red)]}
Fan Tray OID
The Fan Tray OID supports the Fan Tray service alarm. The structure of the Fan Tray OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=ASR1K)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=Fan)][Module][Slot(SlotNum= Slot Fan 0)][FanTray]}
IMA Service (IIMAGroupOid)
The IMA Service OID supports the ATM IMA Service alarm. The structure of the IMA Service OID is:
IIMAGroupOid: {[ManagedElement(Key=ManagedElementkey)][LogicalRoot][PhysicalLayerAggregationContainer(Type=type)][IMAGroup(Id=IMAGroupID)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=vne-146)][LogicalRoot][PhysicalLayerAggregationContainer(Type=1)][IMA
Group(Id=ATM8/1/ima10)]}
IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid)
The IP Interface OID is the source OID for any alarms related to the IP interface.
Alarms supported by Prime Network with IP Interface source OID are:
• Interface Status
Interface Status
• HSRP Group Status Changed
HSRP Group Status Changed
• Dual Stack IP Changed
Dual Stack IP Changed
The structure of the IP Interface OID can be one of the following:
• IP interface under the global routing (RoutingEntity):
IP interface under the global routing (RoutingEntity):
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=1)][RoutingEntity][IpInterface(IpInterfaceName=ifName)]}
• IP interface under a VRF:
IP interface under a VRF:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=3)][Vrf(VrfName=vrfName)][IpInterface(IpInterfaceName=ifName)]}
Examples
IP Interface OID under the RoutingEntity:
{[ManagedElement(Key=PE2-TX-GSR)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=1)][RoutingEntity
][IpInterface(IpInterfaceName=POS0/0)]}
IP Interface OID under a VRF:
{[ManagedElement(Key=PE-South)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=3)][Vrf(VrfName=vrf
A)][IpInterface(IpInterfaceName=Serial2/0.400)]}
Lag Down OID
The Lag Down OID is the source OID for Lag Down Alarm.
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=169.254.77.108)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][DataLinkAggregationContainer(Type=1)][DataLinkAggregation(Index=11)]} .
Lag Link Down OID
The Lag Link Down OID is the source OID for the Lag Link alarm. The OID is a topological link with A and Z side endpoints similiar to Lag Down OID.
L2TP Peer OID (IL2tpPeerOid)
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) modeling in Prime Network is available only for Redback SMS devices. L2TP Peer is a component that is used to model the administrative aspect of L2TP tunnels. It is basically an entity responsible for creating L2TP tunnels based on its configuration.
The L2TP Peer OID is the source OID for any alarms related to L2TP Peer components.
Alarms supported by Prime Network with L2TP Peer source OID are:
• L2TP Peer Not Established
L2TP Peer Not Established
• L2TP Session Threshold
L2TP Session Threshold
The structure of the L2TP Peer OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=contextName)][FWComponentContainer(Type=6)][L2tpPeer(PeerName=peerName)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=redback)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=l2tpCtx)][FWComponentConta
iner(Type=6)][L2TPPeer(PeerName=peer5)]}
Local Switching Entry Down OID
Local Switching Entry Down OID is the source OID for Local Switching Entry Down alarm.
Example
Oid: {[ManagedElement(Key=169.254.77.108)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][FWComponentContainer(Type=8)][LocalSwitchingEntity]}
with DiffObject as the LocalSwitchingEntryKey
Logical Port OID (ILogicalPortOid)
A logical port represents a logical ATM/FrameRelay interface which is configured on top of a physical port. One physical port might have multiple logical ports. In ATM, logical ports are differentiated by VP muxing, that is, each logical port is configured with a range of VPIs. This type of configuration exists in Lucent GX/CBX, which are supported by Prime Network.
The Logical Port OID is the source OID for any alarms related to logical ports.
The alarm supported by Prime Network with the Logical Port source OID is:
• Logical Port Down
Logical Port Down
The structure of the Logical Port OID can be one of the following:
• Logical port on a module's physical port:
Logical port on a module's physical port:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=slotNum)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portNum)][PhysicalLayer][VpMux][LogicalPort(LogicalPortNumber=logicalPortNum)]}
• Logical port on a submodule's physical port:
Logical port on a submodule's physical port:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=slotNum)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=subSlotNum)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portNum)][PhysicalLayer][VpMux][LogicalPort(LogicalPortNumber=logicalPortNum)]}
• Logical port of a subport:
Logical port of a subport:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=slotNum)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portNum)][PhysicalLayer][SubPort(SubPortNumber=subPortNumber)][VpMux][LogicalPort(LogicalPortNumber=logicalPortNum)]}
LSP Endpoint OID (LSP EndPoint OID)
The LSP Endpoint OID is used as the source OID for any alarms related to LSP entries.
The alarms supported by Prime Network with the LSP Endpoint OID is:
• LSP Down
LSP Down
• LSP down due to label mismatch
LSP down due to label mismatch
• LSP down due to lock out
LSP down due to lock out
• LSP up
LSP up
The structure of the LSP EndPoint OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=device IP)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default context)][FWComponentContainer(Type=14)][MPLSTPGlobal][LSPEPEntry(Identifier)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=172.23.222.233)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][FWComponentContainer(Type=14)][MPLSTPGlobal][LSPEPEntry(InternalId=111::10.1.99.
1::1019::111::10.3.99.1::1019::1)]}
LSE Entry OID (IMplsEntryOid)
The LSE Entry OID is used as the source OID for any alarms related to LSE entries.
The alarm supported by Prime Network with the LSE Entry source OID is:
• Broken LSP Discovered
Broken LSP Discovered
The structure of the LSE Entry OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse][LSEEntries(InLabel=inLabel)][MplsEntry(OutInterface=outIfOid)]}
The OutInterface is the IP interface OID of the outgoing interface.
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=PE1-NY-GSR)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse][LSEEntri
es(InLabel=74)][MplsEntry(OutInterface={[ManagedElement(Key=PE1-NY-GSR)][LogicalRoot][FWCo
mponentContainer(Type=1)][RoutingEntity][IpInterface(IpInterfaceName=POS0/0)]})]}
Note  The structure of the OutInterface is a separate OID.
The structure of the OutInterface is a separate OID.
LSE OID (ILseOid)
The Label Switching Entity (LSE) OID is used as the source for various alarms related to MPLS.
Alarms supported by Prime Network with LSE OID are:
• MPLS Black Hole Found
MPLS Black Hole Found
• MPLS Interface Removed
MPLS Interface Removed
• LDP Neighbor Loss
LDP Neighbor Loss
The structure of the LSE OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse]}
Alarm Differentiators
Multiple alarms of the same type cannot have the same source. When this occurs, then the LSE OID is used as a base OID and is augmented with a differentiator. A specific alarm differentiator is used for each type of alarm.
The following examples show how specific alarm differentiators are used in the different types of alarms:
Example 1
MPLS Black Hole Found—[ServiceEvent(DiffObject=ifName nextHop)]
Source OIDs of MPLS Black Hole Found:
{[ManagedElement(Key=RR1-IOU)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse][ServiceEven
t(DiffObject=Ethernet0/0 192.168.1.210)]}
{[ManagedElement(Key=RR1-IOU)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse][ServiceEven
t(DiffObject=Ethernet0/0 192.168.1.310)]}
Example 2
MPLS Interface Removed—[ServiceEvent(DiffObject=mplsIfDescr)]
Source OIDs of MPLS Interface Removed:
{[ManagedElement(Key=PE4-NY-7200)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse][Service
Event(DiffObject=MPLS on interface FastEthernet0/1)]}
{[ManagedElement(Key=PE4-NY-7200)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse][Service
Event(DiffObject=MPLS on interface FastEthernet0/2)]}
Example 3
LDP Neighbor Loss—[ServiceEvent(DiffObject=peerLdpId)]
Source OIDs of LDP Neighbor Loss:
{[ManagedElement(Key=CORE2-NY-GSR)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse][Servic
eEvent(DiffObject=172.255.0.1:0)]}
{[ManagedElement(Key=CORE2-NY-GSR)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=4)][Lse][Servic
eEvent(DiffObject=172.255.0.1:5)]}
Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid)
Managed Element represents the root component of the VNE. Any alarm related to the top-level component of the VNE will have the Managed Element OID as the source.
Alarms which have Managed Element OID as their source are:
• Device Unreachable
Device Unreachable
• Device Unsupported
Device Unsupported
• CPU Overutilized
CPU Overutilized
• Module Unsupported (Investigation State)
Module Unsupported (Investigation State)
• Adaptive Polling
Adaptive Polling
• Cloud Problem (for cloud VNEs)
Cloud Problem (for cloud VNEs)
The structure of the Managed Element OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=PE4-NY-7200)]}
Members Changed OID (IDataLinkAggregationOid)
The Members Changed OID is used as a source OID for service aggregation alarms.
The structure of the Members Changes OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=contextName)][DataLinkAggregationContainer(Type=1)][DataLinkAggregation(Index=snmpIndex)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=vne-146)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][DataLinkAggregationContainer(Type=1)][DataLinkAggregation(Index=50)]}
MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid)
The MLPPP OID is the source OID for any alarms related to MLPPP. The structure of the MLPPP OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=mlppp-key)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default context)] [EncapsulationAggregationContainer(Type=type)][EncapsulationAggregation(Group=group)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=mlppp-2)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][EncapsulationAggregationContainer(Type=1)][EncapsulationAggregation(Group=200)]}
Module OID (IModuleOid)
The Module OID is the source OID for any alarms related to a card or module.
Alarms which have Module OID as their source are:
• Card Out
Card Out
• Card Down
Card Down
Possible structures of the Module OIDs are:
• Module under chassis:
Module under chassis:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=shelfNum)][Slot(SlotNum=slotNum)][Module]}
• Module under other module (submodule):
Module under other module (submodule):
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=shelfNum)][Slot(SlotNum=slotNum)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=subSlotNum)][Module]}
Shelf is an optional part of the OID.
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=CRS-1)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=0)][Slot(SlotNum=4
-Back)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=10)][Module]}
MPBGP OID (IMpBgpOid)
The MPBGP OID will be the source OID for any alarms related to BGP service.
The alarm supported by Prime Network with MPBGP source OID is:
• BGP Process Down
BGP Process Down
The structure of the MPBGP OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=7)][MpBgp]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=Juniper M5)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=7)][MpBgp]}
MPLS TE Tunnel OID (IMplsTETunnelOid)
The MPLS TE Tunnel OID is the source OID for any alarms related to MPLS TE tunnels.
The alarm supported by Prime Network with MPLS TE Tunnel source OID is:
• MPLS TE Tunnel Down
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
The structure of the MPLS TE Tunnel OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=1)][RoutingEntity][IpInterface(IpInterfaceName=ifName)][MplsTETunnel]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=CRS1-PE)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=1)][RoutingEntity][I
pInterface(IpInterfaceName=tunnel-te0)][MplsTETunnel]}
Note  The structure of the OID is different when the IP interface is under a VRF (see IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid)).
The structure of the OID is different when the IP interface is under a VRF (see IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid)).
TP Tunnel Endpoint OID (TP Tunnel EndPoint OID)
The TP Tunnel Endpoint OID is the source OID for any alarms related to MPLS TP tunnels:
The alarm supported by Prime Network with MPLS TP Tunnel source OID is:
• TP Tunnel Down Due to Admin Down
TP Tunnel Down Due to Admin Down
• TP Tunnel Down to Oper Down
TP Tunnel Down to Oper Down
The structure of the TP Tunnel End Point OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=device-IP)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default context)][FWComponentContainer(Type=Value)][MPLSTPGlobal][MPLSTPTunnelEP(TunnelId=Value]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=172.23.222.233)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][FWComponentContainer(Type=14)][MPLSTPGlobal][MPLSTPTunnelEP(TunnelId=1014)]}
ISyncEOID
The ISyncEOID is the source OID for any alarms related to network synchronization.
The alarms supported by Prime Network with ISyncEOID is:
• Network-Clock Synchronization Disabled
Network-Clock Synchronization Disabled
• Network-Clock Synchronization Enabled
Network-Clock Synchronization Enabled
• Esmc Process Up
Esmc Process Up
• Esmc Process Down
Esmc Process Down
The structure of the ISyncEOID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=Device IP)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default context)][ClockService][SyncE]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=172.25.106.53)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][ClockService][SyncE]}
OSPF Neighbor State Change OID
The OSPF Neighbor State Change OID is the source OID for the OSPF Neighbor Up and the OSPF Neighbor Down alarms. The OID of the Members Changed alarm is the OID of the affected Neighbor.
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=172.25.87.145)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=11)][OspfProce
ss(OspfVersion=v2)(ProcessId=1)][OspfNeighbor(AreaId=0)(IfName=TenGigabitEthernet2/4)(Ospf
NeighborId=10.10.20.3)]}
Port OID
The Port OID is the source OID for Pluggable transceiver alarms.
The structure of the Port OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=c4-npe1-76)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=4)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=0)][Module][Port(PortNumber=GigabitEthernet4/0/6)]}
Power Supply OID
The Power Supply OID is the source OID for Power supply alarms.
The structure of the Power Supply OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=ASR1K)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=Power)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=0)][PowerSupply]}
Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid)
The Physical Layer OID is the source OID for any alarm related to the physical layer of a port.
Alarms which have Physical Layer OID as their source are:
• Port Down
Port Down
• Tx/Rx Utilization (no adjacent)
Tx/Rx Utilization (no adjacent)
• Tx/Rx Dormant
Tx/Rx Dormant
• Dropped/Discarded Packets
Dropped/Discarded Packets
• All IP Interfaces Down
All IP Interfaces Down
The structure of the Physical Layer OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=shelfNum)][Slot(SlotNum=slotNum)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=subSlotNum)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portNum)][PhysicalLayer]}
Optional parts of the OID are:
• Shelf
Shelf
• Second-level slot
Second-level slot
• Module representing submodule
Module representing submodule
PortNum can also be the port name (see the following examples).
Examples
Source of port down where the port is on a submodule:
{[ManagedElement(Key=CRS-1)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=0)][Slot(SlotNum=4
-Back)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=4)][Module][Port(PortNumber=GigabitEthernet0/4/4/1)][Physical
Layer]}
Shelf OID (IShelfOid)
The Shelf OID is the source OID for any alarms related to shelf.
The alarm which has Shelf OID as its source is:
• Shelf Out
Shelf Out
The structure of the Shelf OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=shelfNum)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=CRS-1)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=0)]}
SONET Path Port Down OID
The Sonet Path Port Down OID is the source OID for SONET Path Port Down alarm.
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=172.25.87.146)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=8)][Module][Slot(
SlotNum=1)][Module][Port(PortNumber=SONET 8/1/0)][PhysicalLayer][Sonet_SdhHop(Id=2)]}
SONET Path Link Down OID
The SONET Path Link Down OID is the source OID for the SONET Path Link alarm. The OID is a topological link with A and Z side endpoints similiar to SONET Path port Down OID.
Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid)
The Topological Link OID is the source OID for any Link Down alarm. It has the following structure:
{[TopologicalLink(AEndPoint=AEndOid)(TunnelID=tunnelId)(ZEndPoint=ZEndOid)]}
• AEndOid, ZEndOid—The OIDs of the link endpoint components.
AEndOid, ZEndOid—The OIDs of the link endpoint components.
• TunnelID—Where multiple links can exist between two components, the TunnelID value is used to distinguish between the links.
TunnelID—Where multiple links can exist between two components, the TunnelID value is used to distinguish between the links.
Supported Alarms with Topological Link OID Source
The alarms supported in Prime Network which have Topological Link OID source are:
• Link Down—Link down between physical ports, the endpoint OIDs of the physical layer. In this case, the TunnelId is not used and is set to -1. See Link Down Endpoint OID Structure.
Link Down—Link down between physical ports, the endpoint OIDs of the physical layer. In this case, the TunnelId is not used and is set to -1. See Link Down Endpoint OID Structure.
Note  There are various alarm subtypes of link down (for example, Link Down to Admin Down, and Link Down on Unreachable). They all have the same source OID.
There are various alarm subtypes of link down (for example, Link Down to Admin Down, and Link Down on Unreachable). They all have the same source OID.
• Link Utilization—The source OID is the same as for link down.
Link Utilization—The source OID is the same as for link down.
• Tx/Rx Utilization—The source OID is the same as for link down where the physical layer component is adjacent.
Tx/Rx Utilization—The source OID is the same as for link down where the physical layer component is adjacent.
• GRE Tunnel Down—The endpoint OIDs are the GRE tunnel endpoints. In this case, the TunnelID is not used and is set to -1. See GRE Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure.
GRE Tunnel Down—The endpoint OIDs are the GRE tunnel endpoints. In this case, the TunnelID is not used and is set to -1. See GRE Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure.
• Layer 2 Tunnel Down—The endpoint OIDs are the Layer 2 MPLS tunnel endpoints. In this case, the TunnelID is not used, nor is it initialized. See Layer 2 MPLS Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure.
Layer 2 Tunnel Down—The endpoint OIDs are the Layer 2 MPLS tunnel endpoints. In this case, the TunnelID is not used, nor is it initialized. See Layer 2 MPLS Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure.
• BGP Link Down—The endpoint OIDs are the MpBGP. In this case, the TunnelID is not used, nor is it initialized. See BGP Link Down Endpoint OID Structure.
BGP Link Down—The endpoint OIDs are the MpBGP. In this case, the TunnelID is not used, nor is it initialized. See BGP Link Down Endpoint OID Structure.
• DS1 Path Link Down—See DS1 Path Link Down.
DS1 Path Link Down—See DS1 Path Link Down.
• DS3 Path Link Down—See DS3 Path Link Down.
DS3 Path Link Down—See DS3 Path Link Down.
• MLPPP Down Due to Admin Down—See MLPPP Bundle.
MLPPP Down Due to Admin Down—See MLPPP Bundle.
• MLPPP Down Due to Oper Down—See MLPPP Bundle.
MLPPP Down Due to Oper Down—See MLPPP Bundle.
Link Down Endpoint OID Structure
The structure of the Link Down Endpoint OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Shelf(ShelfNum=shelfNum)][Slot(SlotNum=slotNum)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=subSlotNum)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portNum)][PhysicalLayer]}
Optional parts of the Link Down Endpoint OID are:
• Shelf
Shelf
• Second-level slot
Second-level slot
• Module representing a submodule
Module representing a submodule
PortNum can also be the port name (see the following examples).
Examples
Source of link down where the physical ports are on a module:
{[TopologicalLink(AEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=PE3-NY-7300)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot
(SlotNum=1)][Module][Port(PortNumber=FastEthernet1/1)][PhysicalLayer]})(TunnelID=-1)(ZEndP
oint={[ManagedElement(Key=PE1-NY-GSR)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=1)][Module][Slo
t(SlotNum=1)][Module][Port(PortNumber=GigabitEthernet1/1/2)][PhysicalLayer]})]}
Source of link down where the physical port of AendPoint is on a submodule:
{[TopologicalLink(AEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=PE1-NY-GSR)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(
SlotNum=1)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=1)][Module][Port(PortNumber=GigabitEthernet1/1/1)][Physic
alLayer]})(TunnelID=-1)(ZEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=NPE1-NY-7600)][PhysicalRoot][Chassi
s][Slot(SlotNum=4)][Module][Port(PortNumber=FastEthernet4/48)][PhysicalLayer]})]}
See also, DS3 Path OID (IDS3PathOid), DS3 Path OID (IDS3PathOid), MLPPP OID (IMLPPPOid).
GRE Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure
The structure of the GRE Tunnel Endpoint OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=contextName)][TunnelContainer(TunnelType=4)][TunnelGre(TunnelName=tunnelName)]}
Examples
Source of GRE Tunnel Down alarm:
{[TopologicalLink(AEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=PE-East-IOU-158)][LogicalRoot][Context(Co
ntextName=Default
context)][TunnelContainer(TunnelType=4)][TunnelGre(TunnelName=Tunnel1)]})(TunnelID=-1)(ZEn
dPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=PE-South-IOU-158)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][TunnelContainer(TunnelType=4)][TunnelGre(TunnelName=Tunnel1)]})]}
Layer 2 Tunnel Down—The endpoint OIDs are the Layer 2 MPLS tunnel endpoints. In this case, the TunnelID is not used and is not initialized.
Layer 2 MPLS Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure
The structure of the Layer 2 MPLS Tunnel Endpoint OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=contextName)][TunnelContainer(TunnelType=1)][PTPLayer2MplsTunnel(PeerRouterIp=peerRouterIP)(TunnelId=tunnelId)]}
Example
Source of Layer 2 Tunnel Down:
{[TopologicalLink(AEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=NPE1-NY-7600)][LogicalRoot][Context(Conte
xtName=Default
context)][TunnelContainer(TunnelType=1)][PTPLayer2MplsTunnel(PeerRouterIp=172.255.1.5)(Tun
nelId=100)]})(TunnelID=)(ZEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=PE4-NY-7200)][LogicalRoot][Context
(ContextName=Default
context)][TunnelContainer(TunnelType=1)][PTPLayer2MplsTunnel(PeerRouterIp=172.255.1.3)(Tun
nelId=100)]})]}
BGP Link Down Endpoint OID Structure
The structure of the MpBGP Link Down Endpoint OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][LogicalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=7)] [TunnelId=tunnelId)]}
Example
Source of BGP Link Down:
{[TopologicalLink(AEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=PE-East-IOU-159)][LogicalRoot][FWComponen
tContainer(Type=7)][MpBgp]})(TunnelID=-1)(ZEndPoint={[ManagedElement(Key=RR2-IOU-159)][Log
icalRoot][FWComponentContainer(Type=7)][MpBgp]})]}
VLAN Tagged Interface OID (IVlanTaggedInterfaceOID)
The VLAN Tagged Interface OID is used as the source OID for alarms related to QinQ or stacked VLANs, such as Subinterface Down.
A subinterface is a logical division of traffic on an interface, such as multiple subnets across one physical interface. A subinterface name is represented as an extension to an interface name using dot notation, such as Interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/1/2/3.10. In this example, the main interface name is Gigabit Ethernet 0/1/2/3 and the subinterface is 10.
The structure of the VLAN Tagged Interface OID is:
{[ManagedElement(Key=deviceName)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=slotNum)][Module][Slot(SlotNum=subSlotNum)][Module][Port(PortNumber=portNum)][PhysicalLayer][DataLinkLayer][VlanEncapMux][VLANTaggedInterface(InterfaceName=subInterfaceName)]}
Example
{[ManagedElement(Key=10.56.101.133)][PhysicalRoot][Chassis][Slot(SlotNum=4)][Module][Slot(
SlotNum=0)][Module][Port(PortNumber=GigabitEthernet4/0/2)][PhysicalLayer][DataLinkLayer][V
lanEncapMux][VLANTaggedInterface(InterfaceName=Gi4/0/2.1)]}
VSI OID (IVSIOID)
The VSI OID is used as a source for VSI IMOs and VSI alarms including VSI Admin Down, VSI Down, and VSI Up.
The VSI OID is structured so that the VPLS name and VPN ID are identifiers for the VSI entity concatenated to the logical context OID.
Example
[ManagedElement(Key=7606S-PE1)][LogicalRoot][Context(ContextName=Default
context)][FWComponentContainer(Type=10)] [VSI(VplsInstanceName=eli_VFI)(VpnId=101)]}


A short description, including background about the network state or system (Prime Network) state that caused the alarm. The short description of the service alarm is what appears in the ticket, in the Service tab of Cisco Prime Network Events. The short description for each type and subtype can be viewed in Registry Parameters.
The name of the service alarm is the same as the short description.
A table of all the subtype events that represent one of the states the alarm can be in, and a description of when they are issued. For example, the Link Down alarm can have multiple subtype events (states) which include Link Down Due to Admin Down, Link Down Due to Oper Down, and Link Up. The description also shows if the event is a clearing event.
Information related to the correlation of the alarm, mainly:
The alarm issue correlation process and location (local or network).
If other alarms can correlate to this alarm.
The keys that are used in the correlation process.
The specific correlation filters in use for the alarm, if any. The filter indicates if a specific event cannot be selected as the root cause event in the correlation process.
By default, any new event filters the following events: Cloud Problem, BGP Process Down, LDP Neighbor Down, MPLS Interface Removed, the event itself, and events with lower or equal correlation weight.
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
Log Archive is Disabled on the Device
Network-Clock Synchronization
The BGP Link Down and BGP Link Down VRF alarms do not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
BGP Neighbor Loss alarms are not correlated to each other. They are correlated to the root cause of the connectivity loss.
The BGP Neighbor Loss and BGP Neighbor Loss VRF alarms do not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
If the packet contains more than one MPLS label (data contained in the packet is VPN traffic), the packet is dropped or is forwarded to an incorrect destination. This happens because the IP header in the packet belongs to a different routing domain.
If the packet contains only one MPLS label (data contained in the packet belongs to the same routing domain), the packet continues to be forwarded based on the IP header information instead of the MPLS labels. This is not a problem.
This alarm does not have a clearing alarm, which means that after it is issued, its severity cannot be changed.
To overcome the previous limitation, the alarm auto-clear flag is set to true. This means that this alarm severity does not have an impact on the severity of other alarms that it correlates to.
Though the Broken LSP Discovered alarm is issued as a companion to the MPLS Black Hole Found, it does not imply that it is issued from the same device that issued the MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
At the VNE on which the MPLS Black Hole Found was issued, all label switching entries that were destined for the black hole have an untagged out label. All MPLS labels are removed from packets traversing using this label switching entry.
Each untagged label switching entry starts traversing the LSP using a backward flow.
The direction of a backward flow traversing the VNE model is opposite that of a standard packet flow traversing the network.
On each device traversed in the backward flow, Prime Network checks for configured MPLS-based services on the device. The following identification services are supported:
Existence of VRFs (BGP/MPLS VPN services based on RFC2547).
Existence of MPLS Layer2 tunnels (PWE3 services based on RFC4448).
If the device contains such services, a Broken LSP Discovered alarm is issued for each LSP traversed backward to that point.
Information that is important for each broken LSP alarm issued is the entry point (label switching entry) and the exit point (the IP subnet destination).
Only one interface is configured as an MPLS interface.
The label distribution protocol is configured differently on both interfaces (protocol mismatch).
Identifies untagged label switching entries on P2 and PE3.
Issues MPLS Black Hole Found alarms on the interfaces on both sides of the link (since the LSP is unidirectional).
Initiates a backward flow starting from the link on the specific untagged entries and identifies the two LSPs traversing the link:
LSP from PE2 to PE3
LSP from PE3 to PE2
Issues Broken LSP Discovered alarms on both LSPs in PE2 and PE3, which are correlated to the corresponding MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
The clearing alarm does not activate flows to locate the LSPs that were passing through it in order to issue a clearing alarm for Broken LSPs, but rather uses the auto-clear functionality. The gateway periodically reviews the tickets and checks if all the alarms under each ticket are cleared or configured as auto-cleared alarms and whether the gateway correlation timeout has passed, in which case the gateway closes the ticket.
If an MPLS Network Link Down event causes an IP reroute and an LDP redistribution, new LSPs might be redirected through nonMPLS segments, which will create a black hole. In this case, Broken LSP Discovered alarms are issued. However, the discovered broken LSPs are correlated to the Link Down alarm and not to the MPLS Black Hole Found alarm.
The MPLS Black Hole Found that triggered the discovery of this broken LSP.
Link Down alarm, if the link down caused the MPLS traffic to change its course and pass through the black hole.
A pair of VRFs that cannot communicate due to this broken LSP (for BGP/MPLS VPN services).
A pair of MPLS Layer 2 tunnel edges representing a PWE3 service endpoint.
The system can be configured to present the affected pairs for BGP/MPLS VPN services as pairs of VRF IP interfaces instead of just the VRFs. This creates, in most cases, additional pairs that might cause a load on the system. Configuring them as IP interfaces is disabled by default.
When a Card Out alarm occurs, Prime Network Vision displays an alarm icon next to the affected card in the inventory display. Even though the card has been physically removed, it is still displayed in Prime Network Vision so that you can identify which network element is generating the alarm.
When a Chassis Disconnected alarm occurs, Prime Network Vision displays an alarm icon next to all the affected cards of the chassis in the inventory display. This enables you to identify which network element is generating the alarm.
When required, a correlation filter filters the Cloud Problem alarm. This enables or disables the ability of an alarm to create a Cloud Problem alarm and to correlate to it. The default value is false for all alarms in the system, meaning that an alarm does not correlate to the Cloud Problem alarm by default. However, there are several events that override the default configuration (these events are specific to Cisco devices) and are set to true, as follows:
BGP Neighbor Down syslog
OSPF Neighbor Loss syslog
EIGRP Router Query to Neighbors Timeouted syslog
The Cloud Problem alarm does not filter the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
Track reachability (true/false). The default is true.
Lazy reachability (true/false). The default is false. This parameter determines whether there is a dedicated reachability command in charge of tracking reachability or whether reachability is determined by the regular polled commands.
Changes to the registry should be performed only with the support of Cisco. For details, contact your Cisco account representative.
The Device Unreachable alarm filters out the Link Down on Unreachable alarm in the correlation process. Events with the same weight are not filtered out.
Upper threshold—80%
Lower threshold—40%
Upper threshold—500 packets per second.
Lower threshold—50 packets per second.
Upper threshold—500 packets per second.
Lower threshold—50 packets per second.
The subnet mask is /30 or /31.
The IP interface is on one VC encapsulation.
The number of encapsulations under the IP interface/MPLS is greater than one.
Any other case not covered in the previously-described scenarios.
This alarm is implemented as TCA, which means that no information about this alarm is found in the standard event-related registry.
A network flow from the Layer 2 tunnel to the remote IP to identify problems that occur between the tunnel edges.
A network flow from the local Layer 2 tunnel edge to the physical port on which it is configured, to identify problems that occur on the local physical interface.
A network flow from the remote Layer 2 tunnel edge to the physical port on which it is configured, to identify problems that occur on the remote physical interface.
The Layer 2 Tunnel Down alarm does not filter out the LDP Neighbor Down alarm in the correlation process.
The LDP Neighbor Down alarm can correlate to the MPLS Interface Removed alarm.
The LDP Neighbor Down alarm does not filter out the MPLS Interface Removed alarm in the correlation process.
Link Down Flapping
Link Down Flapping Update
Link Down Stopped Flapping Cleared
Link Down Stopped Flapping Noncleared
In Prime Network Events, these flapping subevent names are displayed in the event's short description field.
The Logical Port Down alarm does not filter out the BGP Process Down alarm in the correlation process.
Members Changed OID (IDataLinkAggregationOid)
Upper threshold—80%
Lower threshold—40%
When the system is loaded for the first time and performs the initial discovery of the network.
Changes in the network are identified through the ongoing discovery process.
MPLS black hole discovery is supported only when the PEs are managed by Prime Network.
The MPLS Black Hole Found alarm does not filter out the MPLS Interface Removed and LDP Neighbor Down alarms in the correlation process.
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
MPLS TE Tunnel Flapping
Tunnel Reoptimized
High Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Medium Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Low Priority MPLS TE Tunnel Down
Port Down Flapping
Port Down Flapping Update
Port Down Stopped Flapping Cleared
Port Down Stopped Flapping Noncleared.
This alarm is disabled by default.
Upper threshold—75%
Lower threshold—50%
This alarm is disabled by default.
Upper threshold—75%
Lower threshold—50%
VLAN interface status change of a VLAN that is connected to a VSI.
Pseudowire status change of a pseudowire configured on the VSI.
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Create Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Translations Delete Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Outside-to-Inside Forward Rate
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Port Limit Exceeded
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops System Limit Reached
Carrier Grade NAT Inside-to-Outside Drops Resource Depletion
Network-Clock Synchronization
The source OID must be unique in the alarm type context. For example, it is not possible to generate multiple different alarms with the same type from the same component using the component OID as the source. An additional differentiator should be added to the base component OID. See LSE OID (ILseOid), for an example.
BGP Neighbor Entry OID (IBgpNeighborEntryOid)
Carrier Grade NAT OID (ICgnServiceOid)
DS0 Bundle OID (IDS0BundleOid)
DWDM Controller OID (IDWDMOid)
IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid)
Local Switching Entry Down OID
Logical Port OID (ILogicalPortOid)
Managed Element OID (IManagedElementOid)
Members Changed OID (IDataLinkAggregationOid)
MPLS TE Tunnel OID (IMplsTETunnelOid)
TP Tunnel Endpoint OID (TP Tunnel EndPoint OID)
OSPF Neighbor State Change OID
Physical Layer OID (IPhysicalLayerOid)
Topological Link OID (ITopologicalLinkOid)
VLAN Tagged Interface OID (IVlanTaggedInterfaceOID)
DS0 Bundle Down
Interface Status
HSRP Group Status Changed
Dual Stack IP Changed
IP interface under the global routing (RoutingEntity):
IP interface under a VRF:
L2TP Peer Not Established
L2TP Session Threshold
Logical Port Down
Logical port on a module's physical port:
Logical port on a submodule's physical port:
Logical port of a subport:
LSP Down
LSP down due to label mismatch
LSP down due to lock out
LSP up
Broken LSP Discovered
The structure of the OutInterface is a separate OID.
MPLS Black Hole Found
MPLS Interface Removed
LDP Neighbor Loss
Device Unreachable
Device Unsupported
CPU Overutilized
Module Unsupported (Investigation State)
Adaptive Polling
Cloud Problem (for cloud VNEs)
Card Out
Card Down
Module under chassis:
Module under other module (submodule):
BGP Process Down
MPLS TE Tunnel Down
The structure of the OID is different when the IP interface is under a VRF (see IP Interface OID (IPInterfaceOid)).
TP Tunnel Down Due to Admin Down
TP Tunnel Down to Oper Down
Network-Clock Synchronization Disabled
Network-Clock Synchronization Enabled
Esmc Process Up
Esmc Process Down
Port Down
Tx/Rx Utilization (no adjacent)
Tx/Rx Dormant
Dropped/Discarded Packets
All IP Interfaces Down
Shelf
Second-level slot
Module representing submodule
Shelf Out
AEndOid, ZEndOid—The OIDs of the link endpoint components.
TunnelID—Where multiple links can exist between two components, the TunnelID value is used to distinguish between the links.
Link Down—Link down between physical ports, the endpoint OIDs of the physical layer. In this case, the TunnelId is not used and is set to -1. See Link Down Endpoint OID Structure.
There are various alarm subtypes of link down (for example, Link Down to Admin Down, and Link Down on Unreachable). They all have the same source OID.
Link Utilization—The source OID is the same as for link down.
Tx/Rx Utilization—The source OID is the same as for link down where the physical layer component is adjacent.
GRE Tunnel Down—The endpoint OIDs are the GRE tunnel endpoints. In this case, the TunnelID is not used and is set to -1. See GRE Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure.
Layer 2 Tunnel Down—The endpoint OIDs are the Layer 2 MPLS tunnel endpoints. In this case, the TunnelID is not used, nor is it initialized. See Layer 2 MPLS Tunnel Endpoint OID Structure.
BGP Link Down—The endpoint OIDs are the MpBGP. In this case, the TunnelID is not used, nor is it initialized. See BGP Link Down Endpoint OID Structure.
DS1 Path Link Down—See DS1 Path Link Down.
DS3 Path Link Down—See DS3 Path Link Down.
MLPPP Down Due to Admin Down—See MLPPP Bundle.
MLPPP Down Due to Oper Down—See MLPPP Bundle.
Shelf
Second-level slot
Module representing a submodule

 Feedback
Feedback