Table Of Contents
Cisco VAMS in a Wireline Network
Network Elements in the Video Transport Network
Soft Properties and Threshold-Crossing Alerts
Configuration Management and Inventory
Multicast and Video Management
Solution Components and Versions
ANA Hardware and Software Requirements
Cisco Multicast Manager Requirements
Overview
The User Guide for Cisco Video Assurance Management Solution 1.0 is a reference tool that provides a complete overview of the hardware and software products that comprise the Cisco Video Assurance Management Solution (Cisco VAMS). This guide describes key benefits and advantages, key features, and technical specifications for the products that make up the Cisco VAMS. The guide also describes installation, configuration, and troubleshooting tasks.
Network administrators can use the Cisco VAMS to configure, diagnose, and facilitate the tasks of managing the transport section of a multicast video network. You can use these tools to:
•
Simplify and automate configuration tasks
•
Gain visibility into the health and performance of the network
•
Analyze and troubleshoot faults and exceptions
•
Ensure security, accountability and compliance to organizational policies and regulatory requirements
This chapter contains the following:
License Information
See Appendix B, "End User License Agreement Supplement."
Introduction to Cisco VAMS
The successful deployment of video over IP creates new challenges for the service provider. Because video is sensitive to packet loss and jitter, the service provider must carefully monitor bandwidths to ensure that network resources are not overwhelmed. When potential problems are detected, the service provider must quickly determine the source of the problem and take corrective action. Therefore, video service assurance is a primary concern of cable and wireline video service providers.
The Cisco VAMS 1.0 delivers to service providers real-time, centralized monitoring of backbone, regional, and aggregation networks for broadcast video transport. The Cisco VAMS 1.0 provides the framework for a flexible end-to-end assurance platform for video.
The Cisco VAMS 1.0 uses Cisco ANA 3.6 Service Pack 2 (ANA 3.6.2) to build an abstracted network model through a set of virtual network elements (VNEs). Each VNE represents an element in the managed network. The Cisco VAMS 1.0 extends the base functions of Cisco ANA 3.6.2 VNEs for Cisco 7600s Series routers, Cisco Catalyst 4948 switches, and Cisco Carrier Routing System (CRS-1) devices. These VNE extensions address the specific requirements of video delivery across the IP network.
The Cisco VAMS 1.0 uses the Cisco Multicast Manager 2.4 for multicast monitoring and troubleshooting functions. The Cisco Multicast Manager notifies Cisco ANA of any changes in multicast or threshold events on elements in the multicast trees that may affect video performance. The ANA displays device and multicast fault information in the ANA NetworkVision, ANA EventVision, and ANA Manage software tools.
In addition, the Cisco VAMS 1.0 includes dedicated VNEs supporting specific video probes; this release includes VNEs for Ineoquest, Mixed Signals, and Tektronics video probes.
Components of Cisco VAMS
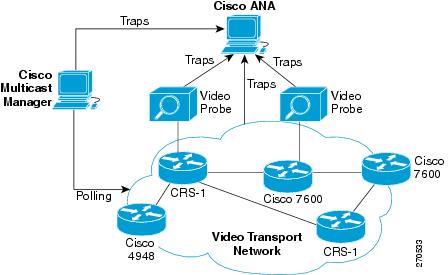
Figure 1-1 shows the components of the Cisco VAMS (the topology is an example).
Figure 1-1 Cisco Video Assurance Management Solution Components
See Solution Components, for descriptions of the Cisco VAMS components shown in Figure 1-1.
Cisco VAMS in a Wireline Network
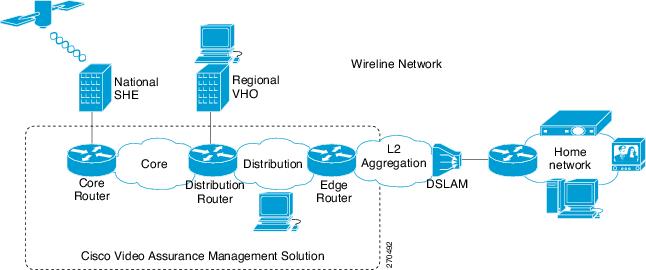
Figure 1-2 shows the Cisco VAMS in a wireline network.
Figure 1-2 Cisco Video Assurance Management Solution in Wireline Network
The Super Head End (SHE) is the network location for live feeds for the broadcast video service. This site contains the real-time encoders used for the broadcast video service, along with the asset distribution systems for on-demand services. This site may also contain back-office systems such as the subscriber database.The Video Hub Office (VHO) is the network location of the video server complex, which includes the video sources for on-demand services and real-time encoders for local television stations.The Cisco VAMS covers the video transport network and focuses on the core and distribution networks shown in Figure 1-2. The Cisco VAMS manages the Cisco devices shown in Figure 1-1.
A Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) connects digital subscriber lines to the network by multiplexing the traffic onto one or more network trunk lines.For detailed information about this supported architecture, see the Cisco Wireline Video/IPTV Solution Design and Implementation Guide, Release 1.1:
More information about Cisco IPTV solutions for wireline carriers is available here:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns610/networking_solutions_solution_category.html
Cisco VAMS in a Cable Network
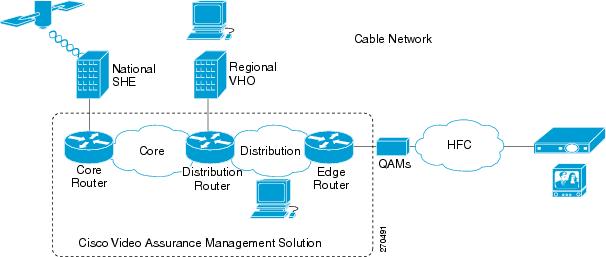
Figure 1-3 shows the Cisco VAMS in a cable network.
Figure 1-3 Cisco Video Assurance Management Solution in Cable Network
Most components of the cable network are the same as those shown in the wireline network (Figure 1-2) except for the home access portion. Hybrid Fiber-Coax technology provides two-way, high-speed data access to the home using a combination of fiber optics and traditional coaxial cable.The Cisco VAMS covers the video transport network and focuses on the core and distribution networks shown in Figure 1-2. The Cisco VAMS manages the Cisco devices shown in Figure 1-1.
For detailed information about this supported architecture, see the Cisco Gigabit-Ethernet Optimized Video Networking Solution for Cable Design and Implementation Guide, Release 3.0:
More information about Cisco cable video solutions is available here:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns457/networking_solutions_solution_category.html
Solution Components
This solution includes several software and hardware components:
•
Network Elements in the Video Transport Network
Network Elements in the Video Transport Network
The Cisco VAMS manages these NEs, which form the core of the video transport network (Figure 1-1):
•
Cisco 7600 Series—A carrier-class edge router that offers integrated, high-density Ethernet switching, carrier-class IP/MPLS routing, and 10-Gb/s interfaces.
•
Cisco Carrier Routing System (CRS-1)—A carrier routing system that service providers use to deliver data, voice, and video services over a highly available and scalable IP network.
•
Cisco Catalyst 4948—A low-latency, Layer 2-4, switch that offers performance and reliability for low-density, multilayer aggregation of high-performance servers and workstations.
Note
You must equip these NEs with IOS software that enables the NEs to monitor multicast video flows in the network. See Solution Components and Versions, for a list of the required IOS software.
Cisco ANA
The Cisco ANA provides mediation and abstraction between NEs and OSS applications, and supports fault collection and root cause analysis for the transport network. The Cisco ANA manages the NEs listed in Network Elements in the Video Transport Network. The Cisco ANA features for the Cisco VAMS include:
•
Soft properties and activation scripts (also called, command-builder scripts) to extend VNEs for monitoring multicast and video flows.
•
Unique VNEs to support the Cisco NEs in the video transport network (Cisco 7600, Catalyst 4948, Cisco CRS-1).
•
Generic VNEs to support Cisco Multicast Manager and video probes.
•
Event-handling and threshold-crossing alerts (TCA) for video-affecting conditions.
•
New trap and syslog support through event configuration and customization.
The ANA automatically detects and manages the network elements in its domain, including their physical and logical inventories. In addition, VNEs provide support for the Cisco Multicast Manager (see Cisco Multicast Manager) and several third-party probes (Third-Party Video Probes) that monitor the video quality of the transport network.
This section of the guide contains these topics:
•
VNEs
•
Soft Properties and Threshold-Crossing Alerts
•
Configuration Management and Inventory
•
Multicast and Video Management
VNEs
The Cisco ANA provides a VNE mediation layer between the managed network elements and the network management applications in the ANA. Generally, a one-to-one correspondence exists between an NE in the managed network and the VNE that depicts it within the Cisco ANA. The VNEs collect information from their corresponding NEs for management purposes.
The Cisco VAMS uses VNEs to represent the solution components in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1 VNEs for the Cisco VAMS
Cisco 7600 Series routers
7600 VNE1
Cisco Catalyst 4948 switches
4948 VNE1
Cisco CRS-1 routers
CRS-1 VNE1
Cisco Multicast Manager
Generic Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) VNE
Tektronix Video Probe
Generic Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) VNE
IneoQuest Video Probe
Generic SNMP VNE
Mixed Signals Video Probe
Generic ICMP VNE
1 Cisco ANA activation scripts and soft properties created for the Cisco VAMS enable this VNE to monitor multicast video flows.
Activation Scripts
The Cisco VAMS introduces activation scripts (created in the ANA Command Builder tool) that configure managed devices to collect, calculate, and analyze multicast and video data and notify the ANA when preconfigured conditions occur. These activation scripts utilize the Event MIB and a rules engine to provide support for multicast alarms in the ANA.
The Cisco VAMS provides an IPTV activation script for the Cisco 7600, CRS-1, and Catalyst 4948 VNEs. The script runs at installation time and whenever managed devices reload. In addition, the operator can run the IPTV activation script on demand. See Run the Setup for IPTV Script, page 3-7.
Soft Properties and Threshold-Crossing Alerts
Soft properties are attributes that appear in the inventory of managed VNEs but are not kept in the database. You can configure these properties to be polled on a regular basis. You can also configure TCAs to raise events based on preset threshold values. You can associate soft properties with a specific VNE, all instances of a VNE type, or all managed elements.
Note
Soft properties and TCAs are already configured in the IPTV activation script (see Activation Scripts) delivered as part of this solution.
Configuration Management and Inventory
The Cisco ANA automatically detects managed network elements (NEs) in the video transport network along with their physical and logical inventories. The Cisco ANA also detects changes in the NEs and automatically synchronizes its archived physical and logical inventories with those changes. Support for traps, syslogs, and polling (SNMP and Telnet) enables this functionality.
The Cisco ANA also supports discovery of the network topology (automatically and manually).
The Cisco ANA monitors and reports interface and operational status for these Cisco NEs in the video transport network:
•
Cisco 7600 Series routers
•
Cisco Carrier Routing System-1 (CRS-1)
•
Cisco Catalyst 4948 switch
This support includes:
•
Logical inventory (for example, subinterfaces, VLANs, and routing tables)
•
Physical inventory (for example, chassis, cards, and serial numbers).
See Network Elements in the Video Transport Network, for details about the Cisco NEs.
Fault Management
The Cisco ANA provides fault management for the video transport network:
See the Cisco ANA Fault Management User Guide for a description of the Cisco ANA fault management system:
Event and Alarm Management
The Cisco ANA also provides the following event-related features:
•
A log of the events.
•
Rules-based event processing (for example, to support changing event severities or customize problem descriptions).
•
Correlation of events and removal of duplicated events.
•
Suppression of events from a particular device or interface.
•
Viewing and sorting events (by time and date, severity, or device), switching between multiple event views, and viewing detailed event data.
•
Viewing syslog events.
•
Changing severity of alarms in the Cisco VAMS.
Polling and CPU Utilization
The Cisco ANA monitors CPU utilization of the supported NEs in the Cisco VAMS. You can define polling groups and designate polling intervals for the ANA-managed NEs. The ANA uses an adaptive polling mechanism to ensure that the NEs are not overpolled.
For more information about ANA polling and its interaction with the CPU utilization of managed NEs, see the Cisco ANA Administrator User Guide:
The Cisco ANA also supports Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to verify that supported NEs are reachable. The ANA VNEs send the ICMP packets to the NEs at a designated rate. You specify the polling rate when you define the VNEs for the Cisco VAMS.
For more information about ICMP polling, see the Cisco ANA Administrator User Guide:
The Cisco ANA also provides dynamic, on-demand polling of specific object identifiers (OIDs) using the ANA Command Builder, a tool which you use to create and run activation scripts.
See the Cisco ANA Command Builder User Guide:
GUIs for Fault Management
The Cisco ANA provides GUIs that show NE:
•
Status information on the components that this solution supports (See Network Elements in the Video Transport Network, for descriptions of the supported NEs.)
•
Events, including severity levels and timestamps
Note
Cisco ANA EventVision, and Cisco ANA NetworkVision are the software tools that provide these GUIs.
Security Management
The Cisco ANA provides user identification and authentication for accessing the ANA to perform configuration and fault management tasks on the supported NEs. For more information about security information in the Cisco ANA, see:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/net_mgmt/active_network_abstraction/3.6/administrator/
mansec.htmlMulticast and Video Management
The Cisco VAMS provides these multicast and video metrics:
PIM Alarms
The Cisco VAMS creates alarms for events related to Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) status changes. The video transport network uses PIM to build a video-specific multicast topology. Therefore, PIM alarms are important for monitoring the status of the solution.
You can view PIM alarms in the ANA EventVision tool. The Cisco VAMS creates alarms for the following multicast-related SNMP traps:
•
pimNeighborLoss—Signifies the loss of an adjacency with a neighbor. This trap is generated when the neighbor timer expires, and the router has no other neighbors on the same interface with a lower IP address than itself.
•
ciscoPimInterfaceUp—Signifies the restoration of a PIM interface.
•
ciscoPimInterfaceDown—Signifies the loss of a PIM interface.
Multicast Routes
The Cisco VAMS uses a VNE soft property to display the number of multicast routes in the device (Cisco 7600, Catalyst 4948, and Cisco CRS-1). ANA NetworkVision displays the number of multicast routes on the selected device.
The Cisco VAMS uses the Event MIB to monitor changes in the number of multicast routes. When the number of multicast routes changes (indicating a possible problem in the video flow), the Event MIB sends an SNMP trap. The ANA receives the trap and creates an event in the ANA EventVision.
The Cisco VAMS creates soft properties on VNEs to support viewing:
•
Whether an NE is enabled for multicast.
•
PIM configurations on an interface (whether PIM is enabled, the PIM mode, and the designated router (DR) address for the PIM interface).
•
IGMP configurations on an interface for a Cisco 7600 router or Catalyst 4948 switch (whether IGMP leave is enabled, the IGMP protocol version, and the number of IGMP interface groups).
Note
The current Cisco VAMS release does not support viewing IGMP status on Cisco CRS-1 NEs.
Non-RPF Drops
The Cisco VAMS monitors non-Reverse Path Forwarding (non-RPF) drops on each multicast stream. Non-RPF packets, also called RPF failure packets, are RPF packets that have been transmitted backwards, against the flow from the source. Multicast streams include video and nonvideo streams. If the number of non-RPF drops on a multicast stream exceeds 5 during a polling period, the device sends an SNMP notification. The ANA receives the notification and generates an alarm. The ANA correlates subsequent alarms and generates subalarms.
Troubleshooting
You perform most fault management tasks through the ANA software tools. You perform advanced troubleshooting of the multicast video network by using the Cisco Multicast Manager 2.4. See Chapter 4, "Troubleshooting with the Cisco Video Assurance Management Solution."
Cisco ANA Software Tools
Cisco ANA includes several application suites that are built on top of the virtual network as the mediation layer. The Cisco ANA applications are:
Cisco ANA Manage
You use the ANA Manage to add, delete, or modify the Cisco NEs in the Layer 2 transport sections of multicast video networks.
Cisco ANA Manage is the GUI tool that you use to perform system administration activities including:
•
Adding and removing Cisco ANA units, Autonomous Virtual Machines (AVMs), and VNEs.
•
Starting and stopping VNEs.
•
Setting polling information per VNE.
•
Customizing polling groups and protection groups.
•
Managing static and persistent topology links.
•
Installing and managing Cisco ANA client licenses.
•
Defining and managing user accounts.
See the Cisco ANA Administrators Guide:
Cisco ANA NetworkVision
Cisco ANA NetworkVision is the main GUI for Cisco ANA. Cisco ANA NetworkVision is a user interface for viewing the network inventory and topology. The ANA NetworkVision also displays events. The mediation layer collects information from the network elements and displays the objects in a topology map. ANA NetworkVision displays status and event information (including severities and timestamps) for supported NEs.
You use Cisco ANA NetworkVision to:
•
View network inventory and multilayer connectivity.
•
Troubleshoot, monitor, and manage NEs.
•
Model and view network maps maintaining up-to-date topological information on device connections, traffic, and routes.
The NetworkVision maps provide a graphical display of active faults and alarms and serves as an easy access point for activation of services. See the Cisco ANA NetworkVision User Guide:
Cisco ANA EventVision
The Cisco ANA EventVision is a GUI for browsing the events in the system. You can use EventVision to view and manage alarms, traps, syslog, provisioning, and system and security events. Monitoring EventVision helps predict and identify the sources of network problems, which may prevent future problems.
You can configure EventVision to display:
•
Number of events per page
•
Number of events to be exported to a file
•
Filter options
•
Information that appears in EventVision tabs
Administrators periodically review and manage the events list by using EventVision. In addition, when an event occurs in the Cisco ANA system, EventVision displays the details.
See the Cisco ANA EventVision User Guide:
Cisco Multicast Manager
The Cisco Multicast Manager (CMM) is a web-based multicast troubleshooting tool that uses SNMP MIB polling to monitor devices and traffic in the network. The Cisco Multicast Manager also provides metrics and alerts, which it then forwards to ANA as SNMP traps. These traps are based on the unique requirements of the network environment and are user-configured.
The Cisco Multicast Manager can monitor multicast-specific data such as:
•
Rendezvous points (RP).
•
Designated routers (DR).
•
Multicast traffic (Layer 2 and Layer 3).
•
Multicast bandwidth (Layer 2 and Layer 3).
•
L3 multicast trees.
The Cisco Multicast Manager also provides detailed diagnostics and health-check capability.
You use the Cisco Multicast Manager to set thresholds, generate notifications, and forward them to the Cisco ANA. See Chapter 3, "Configuring the Components of the Cisco Video Assurance Management Solution."
Third-Party Video Probes
The Cisco VAMS supports the IneoQuest, Mixed Signals, and Tektronix video probes. These video quality monitoring probes are added to key points within the transport network. Their function is to detect impairments and validate the integrity of the Moving Pictures Expert Group (MPEG) transport stream, which carries video.
The ANA discovers physical and logical inventories for the video probes through standard inventory MIBs (depending on the level of support that the probes provide for these MIBS).
Generic VNEs in Cisco ANA support the video-monitoring probes. Generic SNMP VNEs handle the IneoQuest and Tektronix probes. A Generic ICMP VNE (no inventory support) handles the Mixed Signals probe.
The Cisco VAMS receives events from the probes based on thresholds that you configure in the video probes. See Configure Video Probes, page 3-6. The Cisco VAMS associates probe events with a severity level in the ANA.
The video probe VNEs enable the ANA to receive SNMP traps from the video probes. See Appendix A, "Trap Definitions."
Prerequisites
You must have these prerequisites in place before installing the Cisco VAMS:
•
Solution Components and Versions
•
ANA Hardware and Software Requirements
Solution Components and Versions
The Cisco VAMS requires these components and version levels:
Table 1-2 Solution Components and Version Information
Active Network Abstract (ANA)1
3.6 Service Pack 2 (3.6.2)
Cisco VAMS
1.0
Cisco Multicast Manager
2.4
Cisco 7600 (7600-SUP720-3BXL with redundant SUP720-3BXL)
Line cards: WS-X6704-10GE, WS-X6748-SFP, WS-X6748-GE-TX, WS-X6724-SFP, and optional WS-F6700-DFC3BXL
12.2(33)SRB2
Cisco CRS-1
Line cards: CRS-MSC, CRS1-SIP-800 (with SPA-8X1GE), 8-10GE
IOS-XR 3.4.2
Cisco Catalyst 4948 (CAT4948-10GE)
12.2(31)SG
Tektronix video probe
MTM400
Application Firmware Version: 3.1.061.000
FPGA Logic Firmware Version: 4
BIOS Version: 2.0.7
SNMP Interface Version: 2.6.0
Hardware Version: 5
QA Build: Alpha 01
Build Timestamp: Dec 19 2007 22:22:42IneoQuest video probe
Singulus GT-1 Media Analyzer
Firmware Version: TB-2.3a-011707Mixed Signals video probe
Sentry 136 Digital Content Monitor2
Sentry Engine Version: PDM (build 1455.38)
Sentry Database Version: 2.7.0.25
Sentry Configuration: TRANSPORT
1 You must purchase base VNEs before installing the VNE extensions. For example, you must acquire the 7600 group VNE license to use the 7600 VNE extensions.
2 The Cisco VAMS 1.0 does not support carousel-related traps for Mixed Signals Sentry 136.
ANA Hardware and Software Requirements
See these sections for more information:
Note
Cisco ANA requires an Oracle database. Steps for installing the Oracle database are in the Cisco Active Network Abstraction Installation Guide, Version 3.6 Service Pack 2.
ANA Gateway Requirements
Table 1-3 lists the hardware and software requirements for the ANA gateway.
ANA Unit Requirements
Table 1-4 lists the hardware and software requirements for the ANA unit.
ANA Client Requirements
Table 1-5 lists the hardware and software requirements for the ANA client.
Cisco Multicast Manager Requirements
Table 1-6 lists the hardware and software requirements for the Cisco Multicast Manager.
Table 1-6 Cisco Multicast Manager Unit Requirements1
Hardware
Linux
•
Dual AMD Opteron Processor 250 2.4-GHz 64 Bit (more than 500 devices)
•
Dual 2.8-GHz Intel Pentium IV or dual 2.8-GHz Intel Xeon processor (more than 500 devices)
•
2.8-GHz Intel Pentium IV or 2.8-GHz Intel Xeon processor
Solaris
•
Sun Fire v440 up to four 1.593-GHz UltraSPARC IIIi processors (more than 500 devices)
•
Sun Fire v240 One 1.34-GHz or two 1.5-GHz UltraSPARC processors
Memory
•
2 GB
•
4 GB (more than 500 devices)
•
2 GB or more of free space
Operating system
Linux
•
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3
•
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4
Solaris
•
Solaris 8
•
Solaris 9
•
Solaris 10
Note
Solaris x86 is not supported
1 For complete hardware and software requirements, see the Installation Guide for Cisco Multicast Manager 2.4: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6337/products_installation_guide_chapter09186a0080841bec.html#wp1044006.
Software Product Description
Table 1-7 lists the software product information and Cisco part numbers for the Cisco VAMS 1.0 release.
Table 1-7 Software Products with Cisco Part Number1
Cisco Video Assurance Management Solution 1.5 (top level part number)
VAMS-1.0-SOFTWARE
Video Extension to 4948 (G2) VNE—Software (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6VNE4948
Video Extension to 7600 (G3) VNE—Software (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6VNE7600
Video Extension to CRS-1 (G5) VNE—Software (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6VNEG5
Video Extension to CRS-1 (G6) VNE—Software (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6VNEG6
Cisco Multicast Manager (CMM) VNE—Software (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6VNECMM
Ineoquest Video Probe VNE—Software (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6VNEIQ
Mixed Signals Video Probe VNE—Software (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6VNEMS
Tektronics Video Probe—Software (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6VNETK
Ineoquest Video Probe RTU—Right-to-use for one IQ probe (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6IQRTU
Mixed Signals Video Probe RTU—Right-to-use for one IQ probe (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6MSRTU
Tektronix Video Probe RTU—Right-to-use for one IQ probe (optional, qty 0-1)
VAMS-1.0-3.6TKRTU

 Feedback
Feedback