Table Of Contents
Sequence Association vs. Root-Cause Correlation
Introducing EventVision
Cisco ANA EventVision is the intuitive interface used by administrators for viewing system events and tickets that are generated within the Cisco ANA system.
About EventVision
EventVision is a GUI application that serves as a browser for viewing and retrieving detailed information about the different types of system events and tickets that are generated within the Cisco ANA system. Monitoring EventVision helps predict and identify the sources of system problems, which in turn assists in preventing future problems.
You can configure EventVision to display the following information:
•
Number of events per page (default 50 events).
•
Amount of events to be exported to a file.
•
Display previous dated events (in weeks).
•
Filter options.
•
What information appears in EventVision tabs, such as the Audit tab.
System managers or administrators periodically review and manage the events list using EventVision. In addition, when an event occurs in the Cisco ANA system the details are available in EventVision.
All administrator activities in Cisco ANA Manage are logged and available in EventVision. For more information on Cisco ANA Manage, refer to the Cisco Active Network Abstraction ANA Administrator's Guide.
EventVision Overview
Every event that occurs in the Cisco ANA system and the Cisco ANA Gateway is logged. This includes all events that are performed as part of the normal operation of the Cisco ANA system, as well as events that may need further attention. Events are categorized and any of these log entries can be viewed in EventVision events list tabs as follows:
•
Audit
•
Provisioning
•
Security
•
Service
•
Syslog
•
System
•
Ticket
•
V1 Trap
•
V2 Trap
Basic Concepts and Terms
Alarm
An alarm represents a fault scenario that occurs in the network or management system. Alarms represent the complete fault lifecycle, from the time that the alarm is opened (when the fault is first detected) until it is closed and acknowledged. Examples of alarms include:
•
Link down
•
Device unreachable
•
Card out
•
An alarm is composed of a sequence of events, each representing a specific point in the alarm's lifecycle.
Event
An event is an indication of a distinct "activity" that occurred at a specific point in time. Events are derived from incoming traps or notifications and from detected status changes. Examples of events include:
•
Port status change
•
Route entry drop
•
Device reset
•
Device becoming reachable
•
User acknowledgement of an alarm
Events are written to the Cisco ANA database once and never change.
Event Sequence
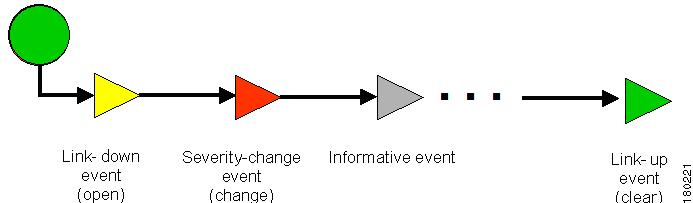
An event sequence is the set of related events, which composes a single alarm. For example, Link down - Ack - Link up.
Figure 1-1 Link Down Example
Typically, a complete event sequence includes three mandatory events:
•
Alarm Open (in this example, a Link Down event).
•
Alarm Clear (in this example, a Link Up event).
•
Alarm Acknowledge (not shown in this example).
Optionally, there can be any number of alarm change events, which can be triggered by new severity events, affected services update events, and so on.
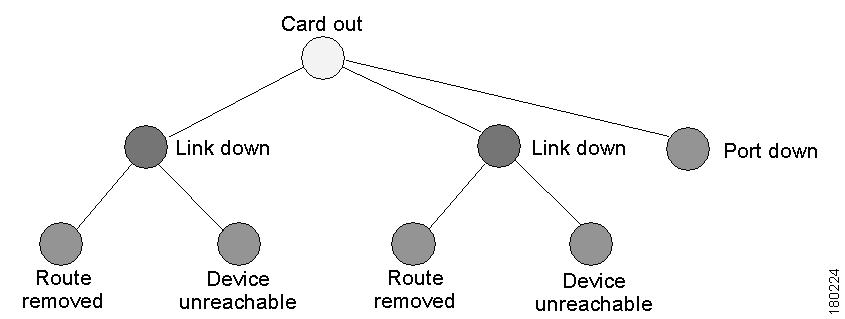
Correlation by Root Cause
Root-cause correlation is determined between alarms (namely, between event sequences). It represents a causal relationship between an alarm and the consequent alarms that originate from it.
For example, a card-out alarm can be the root cause of several link-down alarms, which in turn can be the root cause of multiple route lost and device unreachable alarms, and so on (a consequent alarm can serve as the root cause of other consequent alarms).
Figure 1-2 Card-Out Example
Ticket
A ticket represents the complete alarm correlation tree of a specific fault scenario. It can be also identified by the topmost ("root of all roots") alarm. EventVision's Ticket Properties dialog box displays only tickets, but allows drilling down to view the consequent alarm hierarchy.
From an operator's point of view, the managed entity is always a complete ticket. Operations such as Acknowledge, Force-Clear or Remove are always applied to the whole ticket. The ticket also assumes an overall, propagated severity.
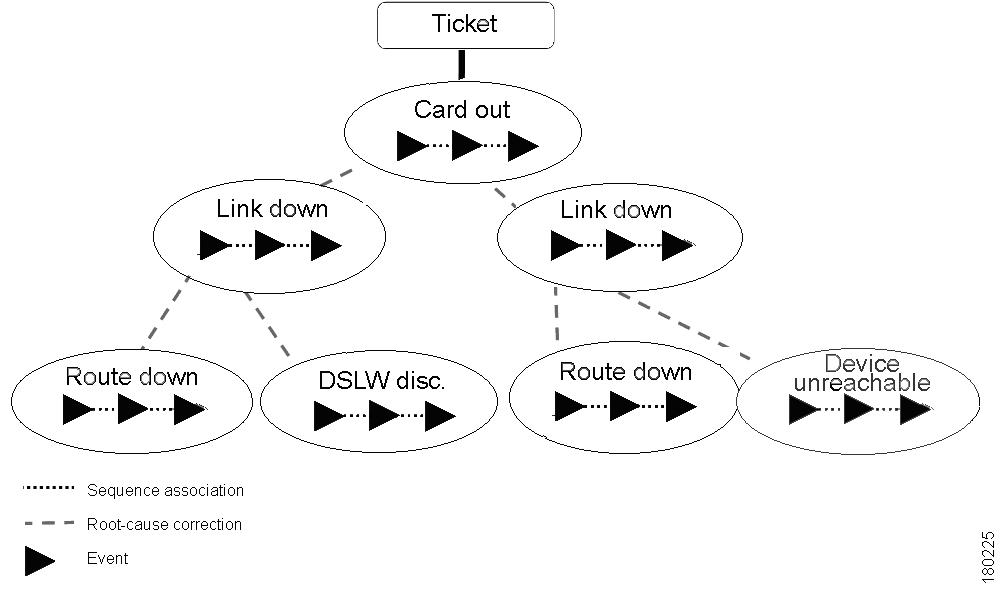
Sequence Association vs. Root-Cause Correlation
It is important not to confuse between the two types of relationships in Cisco ANA alarm management:
•
Sequence Association—The association between events, which creates the event sequences (namely, alarms). It implements either built-in or user-defined relations (namely, specification of the event types composing each sequence).
•
Root-Cause Correlation—The association between alarms (event sequences), which represents the root cause relationship.
The following figure shows how both types of relations are implemented in the ticket hierarchy. The alarms are correlated into a hierarchy according to root cause. Within each alarm is its respective event sequence, representing the lifecycle of the alarm.
Figure 1-3 Sequence Association and Root-Cause Correlation
EventVision Categories
EventVision recognizes the following categories of events:
•
Audit—Related to the running of commands in the Cisco ANA Gateway.
•
Provisioning—Related to configuration and provisioning activities.
•
Security—Related to client login and user activity when managing the system and the environment.
•
Service—Related to the alarms that are generated by the Cisco ANA system.
•
Syslog—Related to the predefined set of syslogs received from the devices by the VNEs, which are used to generate the syslog events.
•
System—Related to the everyday working of the internal system and its components. These events may be related to Cisco ANA and Cisco ANA Gateway resources, representing the system log.
•
Ticket—Related to all the tickets that were opened in Cisco ANA.
•
V1 Trap—Related to SNMPv1 traps from the devices by the VNEs, which are used to generate the trap events.
•
V2 Trap—Related to SNMPv2 traps from the devices by the VNEs, which are used to generate the trap events.
You can also view all the events in the All tab, if required. For more information about the All tab, see All Tab.

 Feedback
Feedback