Overview
• Secure the network from traffic interception, spoofing, and DoS attacks
• Control access to resources in your network with access control lists (ACLs), including ACLs based on user/device type
• Secure network access based on user identity and user role
• Provision device-based policies through device profiling
• Protect confidentiality and Integrity of network traffic through encryption* (hardware capability)
• Securely boot digitally signed Cisco IOS® Software images
• IPv4 First Hop Security (FHS): Cisco Catalyst switches offer Cisco Integrated Security Features(CISF), an industry-leading solution that provides superior Layer 2 threat defense capabilities for mitigating man-in-the-middle attacks (such as MAC, IP, and Address Resolution Protocol [ARP] spoofing). Delivering powerful, easy-to-use tools to effectively prevent the most common and potentially damaging Layer 2 security threats, CISF provides robust security throughout the network.
• IPv6 First Hop Security: IPv6 raises a number of FHS concerns that were not present in IPv4. Those concerns stem from the protocol's unique manner in which it performs router and neighbor discovery, address assignment, and address resolution using Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). These mechanisms could allow an attacker to deploy attacks such as traffic interception, DoS, or man-in-the-middle.
• Device profiling: Trends such as BYOD require customers to have visibility into the various types of devices accessing the network and being able to administer access control, segmentation policies, and QoS policies based on the type of device connected. Cisco Catalyst switches have built-in device profiling capabilities to identify the type of device connected and apply policies based on device type.
• Identity-based networking: Cisco supports a wide range of authentication options, including 802.1x for managed devices and users, web authentication for guests or non-802.1x users, and MAC authentication bypass for unmanaged or non-802.1x devices. The order and priority of authentication methods can be configured, along with behavior after 802.1x or AAA server failures.
• Cisco TrustSec: Cisco TrustSec® enables role-based policy definitions in a centralized policy engine (ISE) and the distributed enforcement of those policies in the network infrastructure independent of network architecture. This provides for ability to define granular policies based on user role, device, location, posture, and so on while making policy definition and change management operationally efficient.
• Hardware capability to encrypt traffic using 802.1AE-based MACsec* (hardware capable at FCS, software support on roadmap).
IPv4 First Hop Security
• Port Security: Prevents MAC address-flooding attacks by limiting the MAC addresses of stations allowed access to the same physical port. Port Security limits the number of learned MAC addresses to deny MAC address flooding.
• DHCP Snooping: Prevents DHCP server spoofing and "man-in-the-middle" attacks with the access switch acting much like a small security firewall between users and the legitimate DHCP server. Network attackers can no longer assign themselves as the default gateway or reroute and monitor traffic flow between the two endpoints.
• Dynamic ARP Inspection: Prevents ARP spoofing by helping ensure that the access switch relays only "valid" ARP requests and responses. This capability prevents malicious hosts from invisibly eavesdropping on the conversation between the two endpoints to glean passwords or data or to listen to IP phone conversations.
• IP Source Guard: Prevents IP host spoofing from attackers and Internet worms assuming a valid user's IP address. IP Source Guard permits forwarding of only packets with valid source addresses.
IPv6 First Hop Security
• RA Guard: Blocks unauthorized Router Advertisements.
• DHCP Guard: Blocks unauthorized DHCP servers.
• IPv6 Snooping: Analyzes control/data switch traffic, detects IP address, and stores/updates them in a binding table.
Device Profiling
Identity-Based Networking
• Flexible authentication that supports multiple authentication mechanisms, including 802.1X, MAC authentication bypass, and web authentication, using a single, consistent configuration
• Guest Access capabilities integrated with Cisco ISE
• Open mode that enables a user-friendly environment for 802.1X operations
• Integration of device-profiling technology and guest access handling with Cisco switching to significantly improve security while reducing deployment and operational challenges
• Comprehensive policy management capabilities such as RADIUS Change of Authorization and downloadable access control lists (ACLs)
• End-to-end system troubleshooting, monitoring, and reporting capabilities
Cisco TrustSec
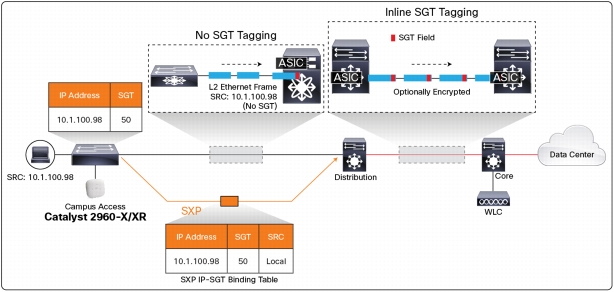
Figure 1. SXP Protocol to Propagate SGT Information
For More Information
http://www.cisco.com/web/strategy/docs/gov/turniton_cisf.pdf
http://www.cisco.com/web/about/security/intelligence/ipv6_first_hop.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/iosswrel/ps6537/ps6553/whitepaper_c11-602135.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-first_hop_security.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios-xml/ios/sec_usr_aaa/configuration/15-1sg/sec-dev-sensor.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/auto_smartports/15.0_1_se/configuration/guide/asp_cg.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6638/products_ios_protocol_group_home.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios-xml/ios/san/configuration/xe-3se/3850/san-overview.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/trustsec/configuration/guide/arch_over.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/solutions/ns340/ns414/ns742/ns744/landing_DesignZone_TrustSec.html