Figure 1. Substation Migration in Process
Substation Automation Business Factors and Benefits
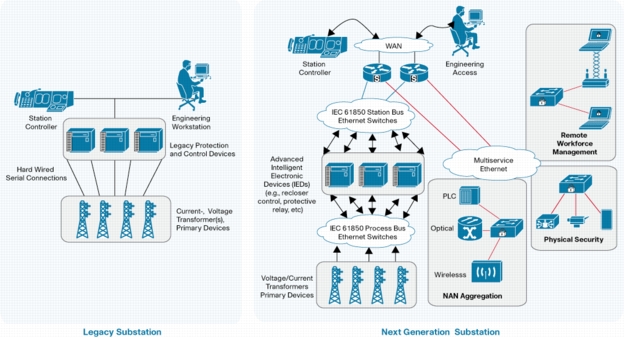
• Reduce operations expense: The future substation reduces operational expenses by converging multiple control and monitoring systems onto a single IP network while helping ensure higher priority for grid operational and management traffic. This network convergence enables utility companies to reduce power outages and service interruptions as well as decrease response times by quickly identifying, isolating, diagnosing, and repairing faults. These improvements are achieved through automation and flexible access to operational control systems and, in the future, through better data correlation across multiple monitoring systems.
In addition, many utilities are facing an aging workforce, which will be retiring in the next 5 to 10 years. Utilities need to fill their pipeline of talent with a younger workforce that is capable of operating today's electric grid, but who can also help build the smart grid of the future. Utilities can benefit from substation automation by more efficiently using their existing workforce and reducing the amount of service calls through programs such as condition-based maintenance.
Further, substation automation allows utilities to extract further value from their corporate networks by providing a remote workforce secure access to applications and data that are located in the operations center.
• Reduce capital expense: As demand for energy continues to grow, utilities must find ways to generate power to meet peak loads. As a regulated industry, utilities must provide power regardless of the amount of power consumed. The cost of providing spinning reserves for peak load hours of the year is extremely high for society. Utilities are challenged to find new ways to shave peak load to help reduce costs and manage supply and demand of energy more efficiently.
Substation automation can be the enabling technology for mass-scale peak load shaving and demand response, which will reduce the need to build as many power plants to meet peak demand.
Additionally, substation automation can reduce the expense and complexity of dedicated control wiring between devices found in many transmission and distribution substations today by converging to an Ethernet-based network. Logical network segmentation and reconfiguration of IED connectivity are much simpler to achieve. Point-to-point wiring not only is expensive, but also increases the difficulty of fault isolation detection.
• Enable distributed intelligence: As network intelligence expands beyond the control center out into the substations, new applications can be developed that enable distributed protection, control, and automation functions. A distributed intelligent network also introduces opportunities for new service creation, such as business and home energy management.
• Meet regulatory compliance: For many governments, utilities are considered critical infrastructure and have economic and national security concerns. Because of this, various regulatory mandates exist or are emerging that require utilities to secure, monitor, and manage their critical data networks in accordance with regulatory requirements, such as NERC-CIP.
• Improve grid security: Grid security is not just about securing the electronic security perimeter (ESP) in the substation; it is also about creating a secure end-to-end architecture that maximizes visibility into the entire network environment, devices, and events.
Substation automation enables an important part of the end-to-end security architecture and allows network operators to control network users, device, and traffic. Physical security can be layered on top of this network security to create security zones of access control, IP cameras for surveillance monitoring, and video analytics to protect and alert network administrators of intruders.
A secure IP network for transmission of grid communications, physical security, and remote workforce management applications can be achieved through substation automation.
Cisco's Substation Automation Vision
• Use cost-effective, well-known protocols (Ethernet/IP) that are easily integrated into other parts of the network and the associated operations environment.
• Take a solutions based approach instead of simply providing single point products to provide a secure, end-to-end architecture.
Open Standards
Solutions Approach
• Next-generation substation automation with and without GOOSE (Generic Object Oriented Substation Events) messaging
• Substation automation with phasor measurement units (PMUs)
• Substation physical security
• Substation remote workforce management
• Substation remote engineering access
• Substation precise timing distribution
• Network and security management
• Condition-based maintenance
• Distributed analytics
• IP telephony
• Networking solutions: Building on Cisco's tradition of networking excellence, Cisco offers advanced rugged networking equipment and scalable architectures to enable reliable and secure two-way communication between substation SCADA equipment and the Energy Management System (EMS). These products are designed with substation in utilities environments in mind and offer zero-touch configuration methods.
• Security solutions: Defense in depth, as opposed to point solutions, is crucial for securing substation communications. Cisco offers security solutions on the host, on the routers, and on the switching platforms and specialized security solutions such as firewall, VPN, authentication, and IPS solutions. Cisco security solutions on the host, routers, switches, and appliances provide an end-to-end infrastructure that enables and protects critical communication networks.
• Network management solutions: Simple and common management software for managing thousands of substation devices provides easy policy enforcement across substations. Cisco also offers management and alarm reporting system software that can collect alarms from all the networking devices (including switches and routers), security devices (ASA and IPS modules on the ASA), and integration with third-party devices.
• Advanced technology solutions: Cisco offers the following advanced technology solutions for substations:
– Physical security access solutions, which assist in NERC-CIP physical security compliance requirements
– Video surveillance solutions, including cameras, video storage solutions, and analytical solutions
– Voice solutions, which include ruggedized IP phones and Cisco CallManager solutions
Conclusion
