Summary
Table 1. Support for Cisco Unified Communications Manager by Version
|
Cisco Prime Collaboration Version 10.0 Offering |
Supported Cisco Unified Communications Manager Versions |
|
Standard |
10.0 and later |
|
Advanced |
8.0 and later |
Cisco Prime Collaboration
What Is Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance?
Table 2. Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance: Standard and Advanced Features
|
Standard and Advanced Features |
Standard |
Advanced |
|
Web-enabled single interface for fault and performance monitoring of core Cisco Unified Communications Manager Version 10.0 and Cisco TelePresence systems. |
Yes |
Yes |
|
"At-a-glance" predefined and customizable performance dashboards to monitor short-term performance metric trends. |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Real-time alarm browser to display faults and allow administrators to take action to troubleshoot or escalate the problem. |
Yes |
Yes |
|
UC cluster components search and status capability: Quick search for UC cluster-associated inventory (phones, trunks, and more) and real-time status dashboard. |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Customizable alerts based on performance thresholds allows administrator to add new threshold-based alerts for selective and focused monitoring. |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Email notification enables on-demand and automated escalations for alerts. |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Support for single cluster of Cisco Unified Communications Manager and core Cisco TelePresence components such as Video Communication Service (VCS), MCU, Cisco TelePresence Server, and Conductor. |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Advanced-Only Features |
||
|
Scale: Multicluster support for Cisco Unified Communications and Cisco TelePresence deployments. |
No |
Yes |
|
Autodiscovery of the entire Cisco Unified Communications and Cisco TelePresence environment, including endpoints, unified communication applications, Cisco Unified Border Elements, gateways, switches, and more. The solution automatically models the Cisco collaboration network and presents it using topology views for visualizing deployment and status. |
No |
Yes |
|
At-a-glance health dashboards with built in root-cause identification best practices, including diagnostic views and troubleshooting drill down for issue isolation and troubleshooting. |
No |
Yes |
|
Audio and video session trace, session quality monitoring, and reports: Monitors quality of each and every audio and video call and traces video and audio calls. Provides intuitive reports for call traffic categorization and analysis. |
No |
Yes |
|
Audio call quality monitoring and reports: Analyzes each and every audio call and its quality to determine service degradation. Provides location-by-location service impact report. |
No |
Yes |
|
Video session monitoring and troubleshooting: Autodetection of video sessions and session topology. Provides deep session service monitoring and troubleshooting powered by Medianet capabilities. On Cisco Medianet routers, jitter and packet loss statistics help pinpoint hotspots that affect session quality. |
No |
Yes |
|
Infrastructure synthetic tests: Scheduled pretesting of key components and circuits using end-to-end site connectivity tests, unified communications application feature tests, and WAN link performance tests. |
No |
Yes |
|
Video precall synthetic test: Helps enable administrators to make a video test call to ensure the quality of the session before the actual end user makes the call and to detect any issues before important executive sessions begin. |
No |
Yes |
|
Event correlation streamlines dependent events into fewer alarms. |
No |
Yes |
|
User 360 and Device 360 views provide complete information about an end user or an infrastructure device. |
No |
Yes |
|
Group customization allows administrators to create new endpoints or device groups for focused monitoring needs. |
No |
Yes |
|
OSS integration: Northbound alarms in Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap and syslog format allow easy integration with existing operational support systems. |
No |
Yes |
|
Breadth of UC and Cisco TelePresence endpoints and applications support: Support for all key services in Cisco collaboration networks, including Cisco Unified Communications, Contact Center Enterprise and Cisco Unified Contact Center Express, Cisco video infrastructure components, as well as third-party devices. Refer to the compatibility Information at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps12363/products_device_support_tables_list.html. |
No |
Yes |
|
Collaboration network infrastructure support: Helps enable monitoring of underlying network devices that can affect collaboration services such as Cisco Unified Border Elements, Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISRs), voice gateways, gatekeepers, routers, and switches. Refer to the supported devices list at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps12363/products_device_support_tables_list.html. |
No |
Yes |
Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance Standard
Key Features of Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance Standard
• "At-a-glance" predefined and customizable performance dashboards:
More than 17 predefined dashboards provide relevant performance metrics and insight into corresponding short-term trends. Users can also select metrics to create custom dashboards to meet their unique business needs. Figure 1 shows a sample predefined performance dashboard.
Figure 1. A Sample Predefined Performance Dashboard
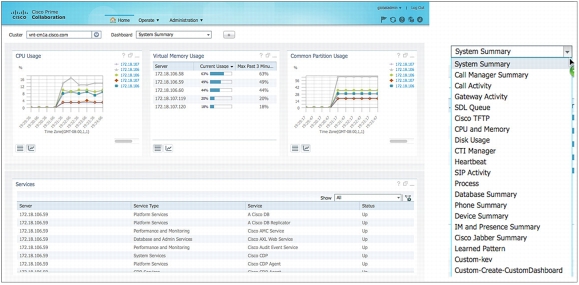
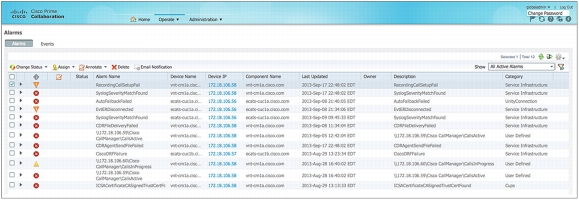
• Alarm browser: An easy to use alarm browser displays predefined as well as user-customized alerts and events in real time.
The faults shown in the alarm browser are sourced from the Cisco Unified Real-Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT) backend service for Cisco Unified Communications Manager, IM and Presence services, and Cisco Unity Connection deployments. Cisco TelePresence Management Suite, Cisco TelePresence VCS, and video endpoints for video deployment faults are reported from VCS endpoint tickets.
Figure 2. Alarm Browser
• Customizable alerts based on performance thresholds:
– Users can easily set up custom alerts based on selected metrics and corresponding thresholds. Once a threshold is violated, an alert will be seen in the alarm browser.
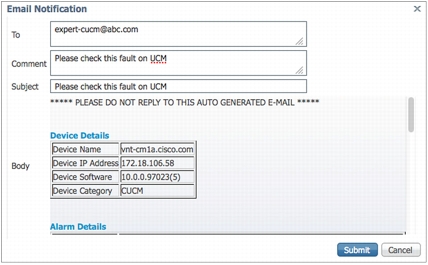
• Email notification: Users can easily forward alerts to experts (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Email Notification
• UC cluster components search and status capability:
The search and status feature offers focused and granular monitoring capabilities for key components of a unified communications cluster.
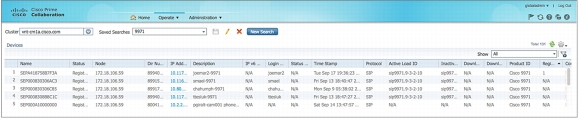
As with the RTMT's device search and status feature, the user will be able to define search criteria to select specific cluster components, such as phones, H.323 gateways, Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) devices, voice mail devices, media resources, SIP trunks, or hunt lists that are associated with a Cisco Unified Communications Manager cluster. The user can filter the criteria further, for example, to show all Cisco Unified IP Phone 9971 model phones registered with UCM-1 that have "failed firmware downloads." Once the search is defined and "named," the user can save it for future use and can display the results on screen to monitor status updates (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Cisco Prime Collaboration Search Results
What Is Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance Advanced?
Key Features of Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance Advanced
• Scale: A single instance or installation of Cisco Prime Collaboration Advanced Assurance scales to support multiple Cisco Unified Communications Manager and VCS clusters.
• Autodiscovery: The Advanced offer simplifies the administrator's task of inventory collection using automatic discovery. Based on publisher and device credential profile information input by an administrator, it discovers the entire Cisco Unified Communications environment, including endpoints, unified communication applications, and gateways. The autodiscovery mechanism also can discover video deployment components such as VCS and its associated endpoints. The Advanced offer also provides Cisco Discovery Protocol and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)-based discovery mechanisms to discover network infrastructure that includes gateways, Cisco Unified Border Elements, and switches.
The Advanced offer not only autodiscovers collaboration network inventory, but also automatically models the collaboration network. An operator can visualize the collaboration deployment and status of the components using the Topology View Dashboard.
• At-a-glance health dashboards with built in root-cause identification best practices. The Advanced offer provides at-a-glance dashboards under the Home menu item. The at-a-glance dashboards offer key metrics that users need to know to keep tabs on the entire collaboration network. For example the End User Impact dashboard provides information that helps the administrator identify top-N locations where endpoints in the network are experiencing the most outages, call failures, or service quality issues. Based on the information provided, the operator can focus troubleshooting on the most affected areas. Based on integrated best practices for troubleshooting, the system also allows intuitive drill down that helps the operator understand the frequency of the problem as well as identify the associated node (gateway or switch) that may be causing the problem.
• Audio and video session trace: The ability to trace calls and sessions in progress end to end to determine all the midpoints on a call path helps users to quickly identify the components that are affecting service degradation. The session troubleshooting feature offers call trace capabilities for both audio and video calls. Cisco Prime Collaboration uses Medianet capabilities to trace the call and present the identified midpoints (routers and switches). Cisco Medianet-enabled routers and switches provide detailed jitter and packet loss statistics that help pinpoint hotspots affecting session quality.
• Audio call quality monitoring and reports: The Advanced offer uses call detail record (CDR) and call management record (CMR) information from Cisco Unified Communications Manager to analyze the quality of each and every call. The system dashboards provide the most affected locations where quality degradation is observed. The solution categorizes affected calls into simple categories such as Poor, Acceptable, and Good. The solution also provides detailed reports that show information about every call and its detailed quality information.
• Video session monitoring and troubleshooting: Using video session diagnostics, an administrator can effectively identify sessions with degraded services and then troubleshoot those sessions to detect the root cause.
Cisco Prime Collaboration Advanced autodetects all the point-to-point or multipoint video sessions initiated by the monitored endpoints. The solution lists all the active and past sessions on the Session Diagnostics page and also presents the topology of the session where it shows all participating endpoints and conferencing devices such as MCUs. Users can obtain all the key information about the session such as session component faults, session service quality, endpoint faults, and more, using the session diagnostics feature. Deep session service monitoring and troubleshooting capabilities are powered by Medianet capabilities.
• Infrastructure synthetic tests: The Advanced offer provides synthetic tests to help detect key issues before they affect end users. Using synthetic tests, network users can test key features of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager and voicemail system. Endpoint reachability and end-to-end connectivity tests help determine phone availability and operational status. WAN performance tests IP SLA) capabilities on routers to test the performance parameters for WAN connections.
The infrastructure tests can be scheduled around business needs. Any failed test will generate alerts on the dashboard, and the administrator will be able to take action to troubleshoot and fix the problem before end users experience service issues.
• Video precall synthetic test: This feature is useful in situations where users need visibility into any potential issues before the video calls happen, for example, a session for corporate executives. The video precall function helps enable users to make a video test call to ensure the quality of the session before an actual end user makes the call. The solution monitors the test call just like an actual call and provides deep session information in session diagnostics. The session information or fault information can help users detect any issues on the call path - in time to troubleshoot and address any problems before key end users experience issues in an actual call.
• Event correlation: The event correlation engine helps reduce the clutter of events and alerts on dashboards. Users can easily see key alerts and events on the alarm browser and can take action to fix them, improving mean time to repair (MTTR). Event correlation offers built-in rules to correlate data and generate aggregated alerts.
Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance offers three kinds of correlation rules - time-based correlation, threshold-based correlation, and root-cause correlation.
Time-based correlation helps users to treat an event as a problem that needs troubleshooting, if and only if it occurs frequently within a particular time window. For example, an administrator may not want an alert on an occasional call admission control (CAC) location out of bandwidth. However, if a CAC location goes out of bandwidth three times within 20 minutes, the administrator may expect a critical alert, as this clearly indicates a bandwidth shortage for that location. Other examples of time-based correlation supported by Cisco Prime Collaboration include "Too many high CPU conditions within a user configurable time window," "Prolonged low memory condition," "Interface flapping," and more.
Threshold-based correlation rules help users to focus on an issue only when it violates a particular threshold level. For example, an administrator may not want an alert on per phone connectivity or a service quality issue. However, if a location/device pool is experiencing a bulk of phone connectivity or service quality issues, the administrator does expect a critical alert (as it would likely indicate broken infrastructure such as where the Cisco Unified Communications Manager or phones connect to switches.
Root-cause correlation rules help users to focus on addressing components or devices causing the issue as opposed to symptoms of events. For example, "UCM CodeYellow" is a symptom of the real CPU pegging alarm that is causing the call drop. Similarly, a large number of "device Unresponsive" events from devices at a remote location would likely be related to outage of a WAN link connecting to that remote location.
• User 360 and Device 360 views: Cisco Prime Collaboration Advanced offers a User 360 feature that displays user information (from Active Directory integration) and shows all the endpoints assigned to an end user. In the same view, User 360 shows service quality and call statistics for every endpoint owned by the end user. This helps the administrator get complete information about the end user and his or her experience with the collaboration services. Users also can cross-launch tools to troubleshoot service degradation issues. The Device 360 view provides complete information about a device or application along with device faults and performance metrics information for all components on the device or application. Users can cross-launch contextual troubleshooting tools from the Device 360 view.
• Group customization: Administrators can create custom groups for endpoints and devices. For example, an administrator can create a group called "New York Ex60 units" or "Dallas Data Center Devices." These custom groups show up in various dashboards; for example, using the alarm browser, the administrator can select the specific custom group to see a set of alerts corresponding to the group. This feature allows administrators to organize monitoring to obtain information or alerts for a specific set of devices or endpoints.
• OSS integration: Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance can be integrated with external OSS system or email system using the northbound notifications feature. Northbound alarms in SNMP trap and syslog format allow easy integration with existing operational support systems.
Cisco Prime Collaboration Assurance: How to Upgrade from Standard to Advanced
• Select the "upgrade" button at the top right corner of the screen.
or
• Select the "View and Evaluate Advanced Features" link in the "Getting Started" menu and follow the instructions to upgrade to the Evaluation (Advanced) mode.
Figure 5. Click the Add Licenses Button to Install an Advanced License

What Is Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning?
Table 3. Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning: Standard and Advanced Features
What Is Prime Collaboration Provisioning Standard?
Key Features of Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning Standard
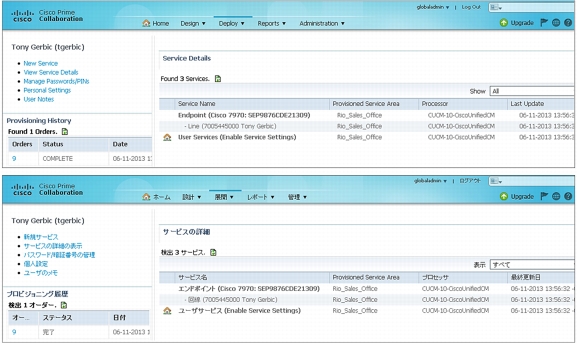
• Single interface for provisioning services: Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning provides a single interface for provisioning end-user services for voice, video, and Cisco TelePresence endpoints, Presence, voicemail, and mobility. With Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning, service activation is easy. An administrator simply orders a service (like voicemail) for an end user rather than manually setting attributes and applying templates on individual UC servers - processes that are time-consuming and error prone.
Figure 6. Localized Product Interfaces
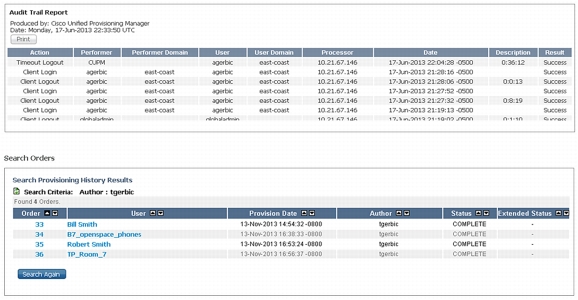
• Administrator audit log and order tracking: Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning uses an order paradigm to create and manage services for users. When an administrator orders a new service, like a phone and line service, information about the order, including who ordered it, when, what was ordered, and individual settings are put into the database for tracking purposes. Orders can also be searched and exported based on a number of different criteria such as date range, to whom, by whom, order success, and order state. The system also has an audit trail report that shows admin activity such as admin userID, login time, logout time, logged in duration, and reason for logout. The audit trail also shows security-related information such as changes in passwords and security lockouts (Figure 7).
Figure 7. Audit Trail Report
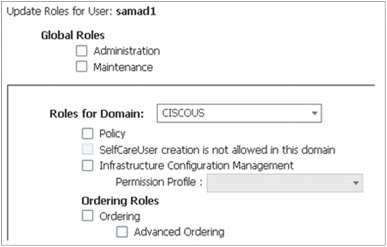
• Three levels of RBAC: System management level, advanced ordering level, and basic ordering level. The administration levels are global in scope, so an ordering administrator can order services for all users in the provisioning application (Figure 8).
Figure 8. Role-Based Access Control
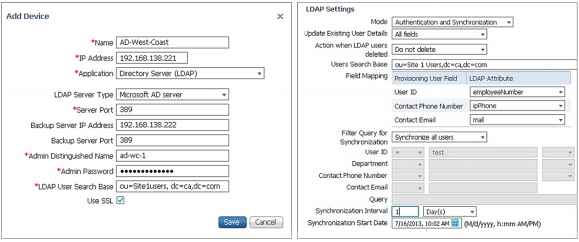
• LDAP integration: Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning can both sync new users from LDAP and provide user/admin authentication. Additionally, multiple LDAP servers can be added and each assigned to one or more provisioning domains. This can provide support for multiple companies or nonfederated Active Directory environments to be managed in one instance of Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning. Federated LDAP servers, using Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM) or Lightweight Directory Services (LDS), can be supported along with nonfederated servers (Figure 9).
Figure 9. LDAP Setup for Provisioning
• Single-cluster batch provisioning for Cisco Unified Communications Manager and end-user services
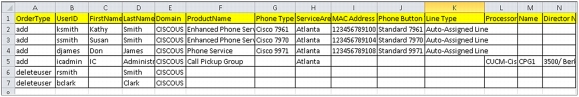
Batches used with Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning differ in scope from BAT files. A BAT file only acts on the UC application it is built for. Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning batch files provision settings for Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco Unity Connection, and IM and Presence servers in one file (Figure 10).
Figure 10. Sample Batch File
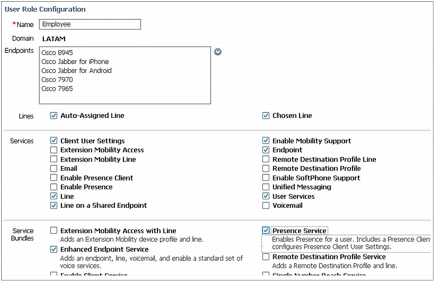
• Policy enforcement for user services: Companies typically have policies around what endpoints and services different job roles can get. Additionally open space phones and conference/Cisco TelePresence rooms typically have a restricted set of phone types and services. The concept of user roles in Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning provides a way for the provisioning system engineers to define and restrict which endpoints and services a person or conference room can get. This set of restrictions also filters out the choices an ordering admin would see during the ordering process, reducing the time needed to make a selection and increasing the accuracy of orders (Figure 11).
Figure 11. Endpoint and Service Association to User Role
What Is Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning Advanced?
Key Features of Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning Advanced
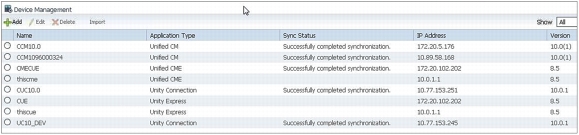
• Multicluster and multi-version support: The solution can concurrently support multiple clusters and mixed versions of UC applications. When services are ordered for a user, the solution knows which cluster or combinations of clusters must be provisioned. It also knows, for example, which Cisco Unity Connection clusters are integrated with a given Cisco Unified Communications Manager cluster. The solution is also aware of different versions of the UC applications and will adjust the options seen by the administrator or used during provisioning depending on what features are supported on the target UC applications (Figure 12).
Figure 12. Device Management Screen
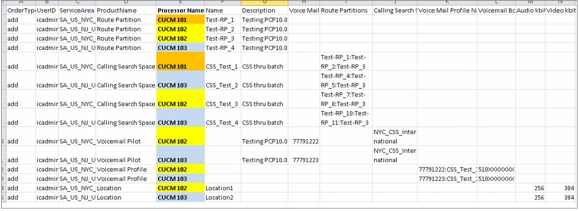
• Single-cluster batch provisioning for Cisco Unified Communications Manager and end-user services
Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning Advanced is multicluster. Batches differ in scope from the Standard offer. A single batch can act on multiple clusters and multiple UC applications (Figure 13).
Figure 13. Sample Batch File for Multicluster Configuration
• Advanced RBAC: In addition to the three levels of RBAC available in the Standard offer, the Advanced offer allows delegation of administrator access. The delegation feature allows an administrator with an ordering role to be assigned to manage one or more specific groups of users (domain groups). Other groups of users not assigned will not be visible to this admin. Other assignable roles for managing infrastructure provisioning and workflow steps are available in the Advanced offer (Figure 14).
Figure 14. Role-Based Access Control Screen
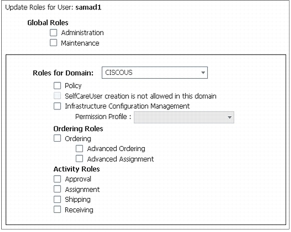
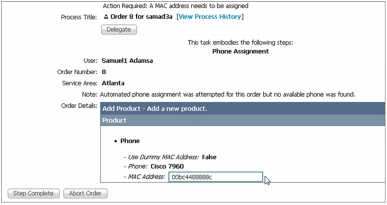
• Optional ordering workflow steps: In some applications additional ordering workflow is required. There are four steps that can be individually enabled: Approver stage, Assigner stage, Shipper stage, and Receiver stage. Once a service order is created for a user, one or more of these stages can be added to the process workflow before the actual provisioning takes place. The ordering workflow feature works in conjunction with the group-based email notification system to alert administrators of outstanding ordering tasks. See the administration guide for details for each workflow step (Figure 15).
Figure 15. MAC Address Assignment Screen
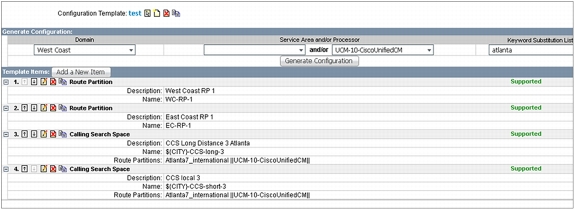
• Infrastructure templates: These are schedulable, keyword-based templates used by admins for repetitive Cisco Unified Communications Manager infrastructure provisioning tasks. The infrastructure templates function also allows prebuilt Cisco IOS Software templates to be imported for provisioning devices that use Cisco IOS commands. These Cisco IOS templates can be scheduled and use keywords for repetitive tasks (Figure 16).
Figure 16. Configuration Template
• Northbound API: This interface allows Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning to be integrated with a third-party application or OSS. The interface allows access to Cisco Unified Communications Manager infrastructure settings and user-related settings. The interface can use the provisioning automation found in the administration interface, so a service bundle, for example, a phone, line, and voicemail, can be ordered in one step (Figure 17). An SDK is available at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps12363/tsd_products_support_configure.html.
Figure 17. Northbound API

Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning: How to Upgrade from Standard to Advanced
• Select the "upgrade" button at the top right corner of the screen
• Select the "View and Evaluate Advanced Features" link in the "Getting Started" menu and follow the instructions to upgrade to the Evaluation (Advanced) mode