Figure 1. Cisco Prime Fulfillment
Cisco Prime Fulfillment
Why Is It Important?
The Service Provider Revolution
Figure 2. The Complex Service Ecosystem
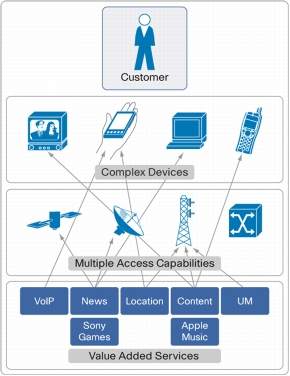
Changing Expectations
Changing OSS
Business Benefits
• Accelerated time-to-revenue of new services
• Compatibility with existing systems for delivery of new, value-added services
• Efficient re-use of resources and intelligence
• Secure alignment of order processing, inventory management, and network activation prior to new service launch
• Automated provisioning of next-generation services across multiple architectures
• Capability to enable customer self-service and service configuration
• Consistent service delivery
• Reduced costs for customer care and problem resolution
• Continuous business process improvement through trend analysis
• Extensive support for Cisco and multi-vendor devices and platforms
Solution
The Complete Design, Creation, Delivery, and Analysis Cycle
Design Components
Create Services
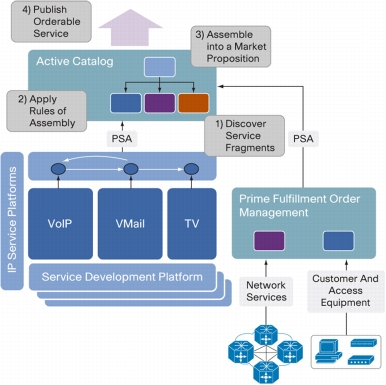
Figure 3. Cisco Prime Fulfillment Active Catalog
Deliver Services
Analyze Services
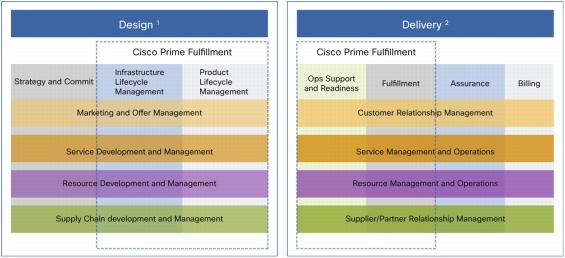
Moving in Line with Standards
Figure 4. Cisco Prime Fulfillment in the eTOM Model
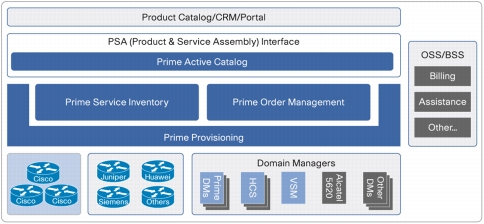
Cisco Prime Fulfillment - Key Components
• Cisco Prime Active Catalog is a service creation and process orchestration platform designed to be fully interoperable with both Cisco Prime Fulfillment and other third party platforms. It addresses the challenge of creating and managing substantial numbers of services without needing to build an OSS stack for each service. Active Catalog allows network, service, and other resource capabilities to be modeled as reusable service components and then aggregated into publishable services and products. It then uses those service and product specifications as orchestration templates for specific product fulfillment. Active Catalog allows technical capability within the operator's own domain and from partner organizations to be combined into a single usable catalog.
• Cisco Prime Order Management monitors and controls all the detailed order processes involved in the customer service fulfillment cycle. It manages complex task interdependencies and exception processes and facilitates rapid creation and introduction of new service order types.
• Cisco Prime Service Inventory manages all the resources required for successful service delivery and network operations, from customer handsets and devices to access and core network equipment. It provides the unique capability not only to model all required physical and logical resources but also to apply comprehensive business processes to the usage of those resources.
• Cisco Prime Provisioning performs all the communications required to activate services, from the configuration of individual network elements to the activation of entire technological domains in a multi-vendor environment Preconfigured communications interface components undertake activation functions for common network device types.
• Cisco Prime Service Dashboard gives an immediate, up-to-date view of the service delivery function, including a complete, real-time analysis of order status, resource usage, and trends.
Figure 5. Cisco Prime Fulfillment - Architecture
Cisco Prime Order Management
Improved Service Order Design
• Use the Cisco Prime Order Management Designer Client to create customized order components to suit specific business needs. (Figures 6 through 9)
Figure 6. Order Management: Order Design
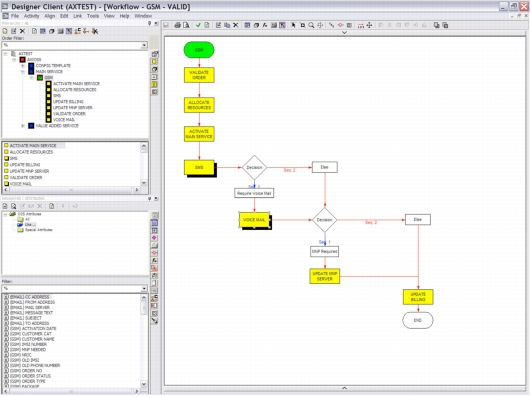
• Utilize preconfigured order components to help ensure best practices and a consistent process for service delivery.
• Include details such as task precedence, dependency, elapsed time, milestones, task attributes, and exception handling and rollback processes.
• Use simple drag-and-drop techniques to add attributes to any of the tasks in the resulting order component.
• Add new work-request processes to order components in a structured fashion, lining up the right people (internal and external) to carry out the right tasks at the right time.
• Use the sophisticated work-allocation and work-notification mechanisms to help ensure that profitable services are consistently delivered according to stated service-level agreements. (SLAs)
Figure 7. Order Management: Order Entry
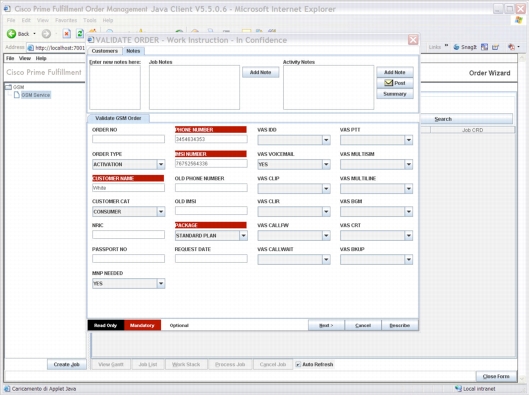
Broader Order Entry
• Improve self-service by enabling customers to enter and view service orders through specially designed web portals.
• Enable bulk order entry through formatted files.
• Utilize the Cisco Prime Fulfillment Java-based architecture to accommodate a broad choice of order entry from other sources including CRM packages.
Figure 8. Order Management: Process Dependencies
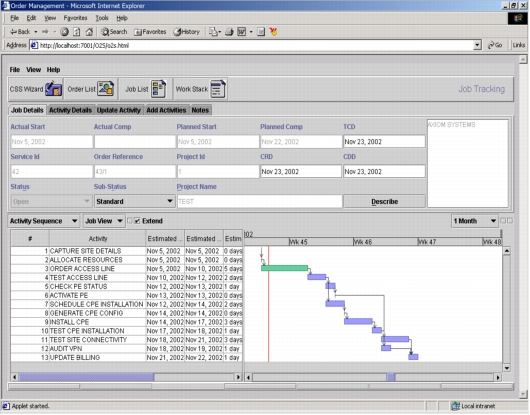
Increased Automation
• Use order components to deliver services more rapidly and consistently by triggering tasks automatically based on the results of other tasks.
• Pass work requests quickly and efficiently between the users and user groups that must action them.
• Make detailed work instructions for each task web accessible.
• Send standard or customized letters, faxes, emails, or data transfers to anyone involved in the service delivery chain.
• Monitor users' work stacks and issue alerts concerning any activity under their control that is jeopardizing committed delivery times.
Improved Job Control
• Create fully configurable dependencies between tasks within order components, so that the effect of change on any one task is clearly shown on all others.
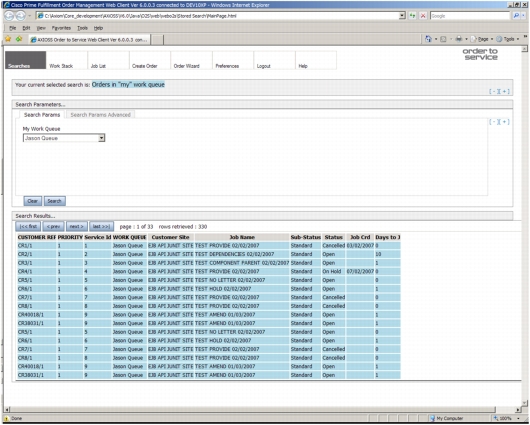
Figure 9. Order Management: Stored Search Capability
• Create dynamic dependencies based on the prevailing business rules embedded within the workflow component.
• Provide visibility of order status to all involved in the delivery process.
• Show any issues that may impact delivery times clearly including any bottlenecks and delays.
• Define automatic remedial action as required.
• Provide comprehensive search facilities (Figure 9) for support staff to retrieve critical service, order, and customer information. You can configure searches and then store them as "favorites" for reuse. Order search facilities can go to the job or activity level and replace browsing of rigid work stacks.
Cisco Prime Service Inventory
Faster Resource Definition
• Use preconfigured modules within Cisco Prime Fulfillment Service Inventory to maintain best practices for resource management.
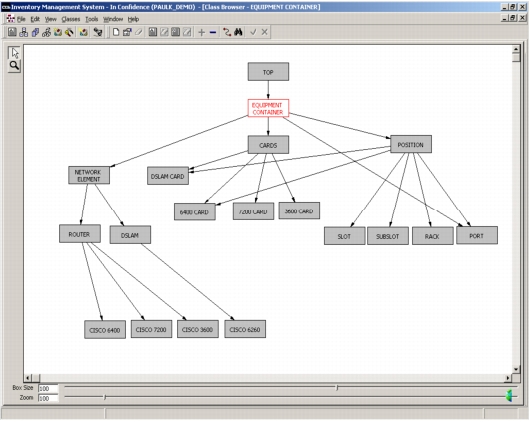
Figure 10. Service Inventory: Object Modeling
• Resource Designer to create customized resource components to undertake resource management tasks more quickly and reliably.
• Represent any object, from a physical piece of equipment to a logical entity or action to be taken (Figure 11).
• Create associations between those objects, including relationships among equipment, services, and customers.
• Define tasks within resource components, including (for example) how resources are to be retrieved from stores and what extra tasks are to be carried out when they are.
• Apply business rules to objects so that all the knowledge associated with them is made available to all service delivery business processes.
• Run resource components automatically from Cisco Prime Fulfillment or from any other OSS or other business support system (BSS).
Improved Visibility
Figure 11. Service Inventory: Resource Visualization
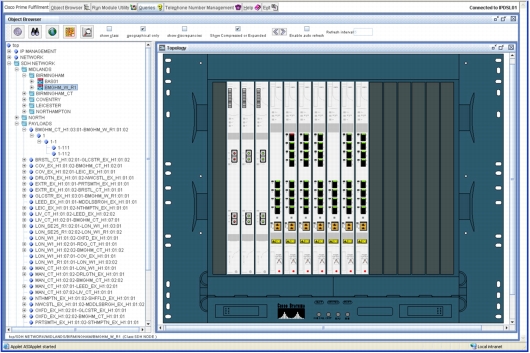
• Display logical circuits such as VPN and transmission network routes.
• Create and distribute reports containing any resource information, including that relating to customers, services, networks, capacity plans, and so on.
• Manage the allocation and modeling of bulk items such as IP addresses and telephone numbers.
Better Resource Utilization
• Check the utilization levels of all network inventory objects required to complete the end-to-end service delivery process.
• Automatically allocate unused resources, keeping utilization of existing equipment at optimal levels.
• Facilitate organic growth of the network by triggering "just-in-time" ordering sequences such as:
– Send a request to the financial controller asking for approval to purchase new equipment.
– Automatically place an order with the appropriate supplier and track through to delivery.
– Automatically place a task in a field engineer's work stack to install the equipment.
• Manage allocation of IP addresses using standards bodies such as Réseaux IP Européens (RIPE).
• Dramatically improve the whole network planning, operation, and upgrade function.
Synchronized Resources
Figure 12. Service Inventory: Network Inventory Synchronization
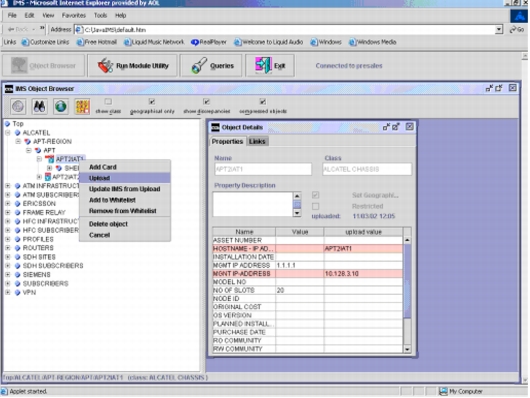
• Recover "stranded" assets that appear to be in use based on inventory records but are not actually linked to any customer or service.
• Provide a statement on resource availability and capacity usage in the network.
• Synchronize configurations held on the network equipment with those held in the "master" inventory systems.
Apply to Core Network Management
• Map and monitor the core network. (Figure 13)
• Document equipment, location information, and capacity information.
• Help ensure through autodiscovery that the inventory record is aligned with the installed physical network.
Figure 13. Service Inventory: Core Network Management
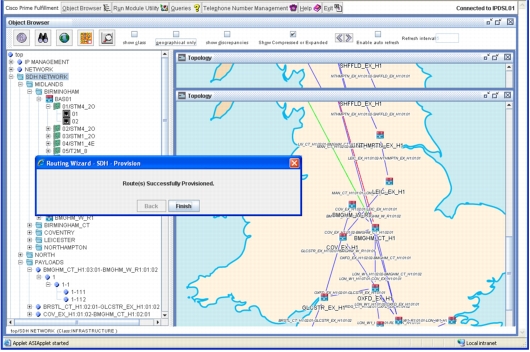
• Manage the rollout and upgrade of network elements through sophisticated workflow and inventory capability.
• Apply routing algorithms and policy through dedicated routing wizards.
Cisco Prime Provisioning
Greater Support for Multitechnology Environments
• Utilize preconfigured activation components (snap-ins) to interface directly with network elements, with network element management systems, and with other OSS/BSS applications used in the service delivery process.
• Use the Cisco Prime Fulfillment Integration and Software Development Kit to create interfaces to suit specific network element communication needs.
• Guarantee the timely delivery of end-to-end services using a comprehensive library of communications protocols, technologies, and network equipment.
Improved Activation
• Group together activations on one or many network elements as a single batch job.
• Process activation orders either immediately or on a scheduled basis to improve automated flow-through activation.
• Automatically pass information back to the originating order management system to further accelerate the order management process.
• Handle changes to services through the same process, quickly and efficiently.
• Reduce provisioning time from days or hours down to minutes or seconds.
• Reduce accumulated backlog.
• Reduce the need for complex reengineering of OSS/BSS applications.
• Exploit the advanced architecture of the Cisco Prime Fulfillment to provide the glue between such systems without the need for expensive code or database schema changes.
• Integrate all communications processes from start to completion.
Enhanced Service Rollback
• Detect exception conditions using the business process engine within the Cisco Prime Fulfillment Order Management module.
• Act promptly and efficiently according to the business rules stated in the preconfigured activation components.
• Notify all appropriate customer support and problem resolution systems where necessary.
• Indicate that such a rollback has occurred in the service delivery process chart.
• Schedule retries automatically after the problem is rectified.
• Indicate the effect of rollback on the overall delivery process.
• Improve communication of the latest order status to all involved - most importantly, to the customer.
Cisco Prime Service Dashboard
Improved View of Orders
• Immediate, up-to-date view of the service delivery functions, including a complete, real-time analysis of order status, resource usage, and trends. (Refer to Figure 14.)
• Real-time analysis of orders entering the business, orders in progress, orders in jeopardy, orders cancelled, and orders completed.
Figure 14. Service Dashboard: Order Visibility
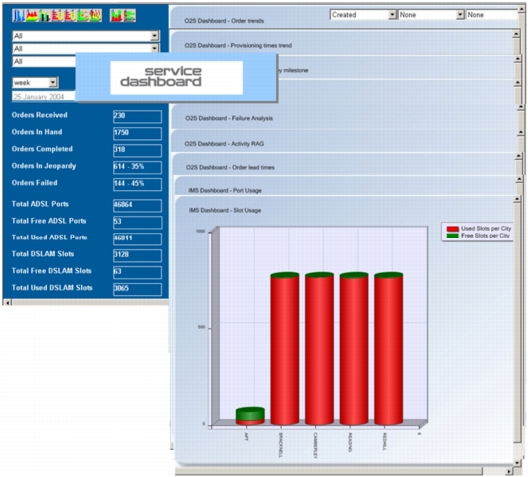
• Monitor activation performance, including minimum and maximum days to provision orders, average days to provision orders, and a comparison with target times per product or product group and by operation or operational department.
• Get an indication of future order trends and the changes needed to help ensure continued profitability.
Improved View of Resources
• View in real time the usage of all resources throughout the organization, including unused, reserved, planned, allocated, and in-use resources.
• Assess how resource usage could be optimized by service, by product, and by organizational group.
• Monitor and control the usage of company assets, services, and customers - everything that drives profitable service delivery.
Cisco Prime Active Catalog
Service Design and Process Orchestration in a Complex Service Ecosystem
Figure 15. Cisco Prime Active Catalog: Capability Mapping
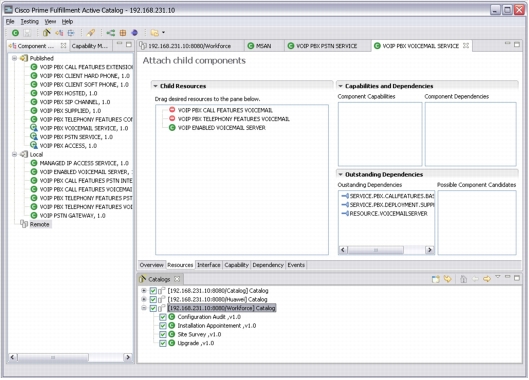
• Reduced development effort in building new products and services
• More efficient use of specialist expertise in customer-facing functions
• Reduced integration costs
• Reduced customization costs
• Fewer points of failure in the delivery chain
• Faster time to market and quicker revenue
• Increased customer satisfaction
• Reduced customer churn
Further Information
About Cisco Prime
Service and Support