PB503086
Last Updated: July, 2009
1. Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(33)SXI Introduction
2. Release 12.2(33)SXI Packaging, Migration, Service Module Support, and Software Modularity Considerations
3. Release 12.2(33)SXI Highlights
4. Release 12.2SX Additional Information
1. Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(33)SXI Introduction
2. Release 12.2(33)SXI IP Version 6 (IPV6) Repackaging
• IPbase image-IPv6 Host features like:
– IPv6 addressing
– ICMPv6 and redirect
– IPv6 Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) path discovery
– IPv6 Neighbor discovery
– Syslog over IPv6
– Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) over IPv6
– Telnet over IPv6
– SSH over IPv6
• IPservices image-Same IPv6 features as supported in advipservicesk9 images in prior releases, including EIGRPv6, IPv6 multicast, IPv6 tunneling, DHCPv6 and 6VPE
Benefits
Product Management Contact
• Niraj Gopal (niraj@cisco.com)
• Amit Datar (datar@cisco.com)
2.1. Release 12.2(33)SXI Migration
• Supervisor-720 IOS Software images:
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS IP Services
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS IP Services (MODULAR)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS IP Services (SSH) LAN ONLY
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS IP Services (SSH) LAN ONLY (MODULAR)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS IP Services (SSH)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS IP Services (SSH) (MODULAR)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS Advanced IP Services (SSH)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS Advanced IP Services (SSH) (MODULAR)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS Advanced Enterprise services (SSH)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 720 IOS Advanced Enterprise services (SSH) (MODULAR)
Figure 1. Supervisor-720 Software Image Upgrade to 12.2(33)SXI
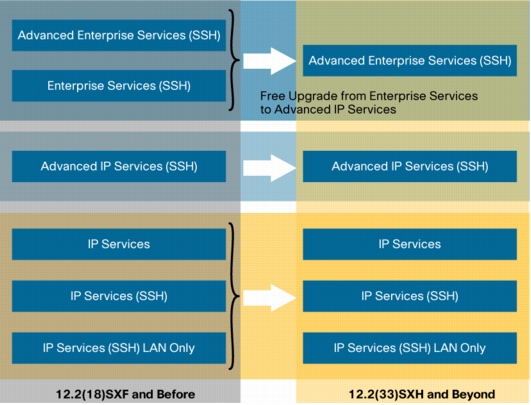
• Supervisor-32 IOS Software images:
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS IP Base LAN ONLY
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS IP Base LAN ONLY (MODULAR)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS IP Base (SSH) LAN ONLY
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS IP Base (SSH) LAN ONLY (MODULAR)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS IP Services SSH
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS IP Services SSH (MODULAR)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS Advanced IP Services (SSH)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS Advanced IP Services (SSH) (MODULAR)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS Advanced Enterprise Services (SSH)
– Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 32 IOS Advanced Enterprise Services (SSH) (MODULAR)
Figure 2. Supervisor-32 Software Image Upgrade to 12.2(33)SXI
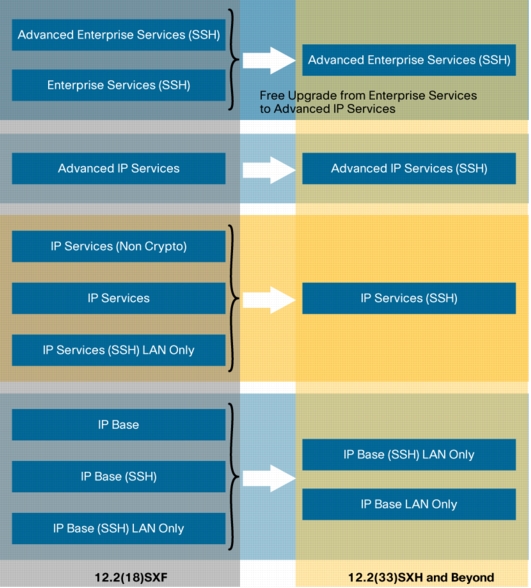
• ME6524 Software Feature sets:
– Cisco ME 6524 IOS IP Base (SSH) LAN ONLY
– Cisco ME 6524 IOS IP Base (SSH) LAN ONLY (MODULAR)
– Cisco ME 6524 IOS IP Base LAN ONLY
– Cisco ME 6524 IOS IP Base LAN ONLY (MODULAR)
– Cisco ME 6524 IOS Advanced IP Services (SSH) LAN ONLY
– Cisco ME 6524 IOS Advanced IP Services (SSH) LAN ONLY (MODULAR)
Figure 3. Catalyst 6500 ME-6524 Software Image Upgrade to 12.2(33)SXI
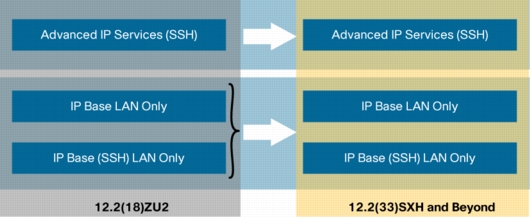
2.2. Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Service Module Support in Release 12.2(33)SXH and Release 12.2(33)SXI
Table 1.
Table 2.
|
Service Module |
Description |
Migration Path |
Description |
|
WS-SVC-AGM-1-K9 |
Catalyst 6500 Cisco Anomaly Guard Module |
AGXT-5650-MMF-B-K9 For more information, please visit http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns615/networking_solutions_sub_solution.html |
Cisco Guard XT 5650, 1000Base-SX MMF, Dual AC, RAID |
|
WS-SVC-ADM-1- K9 |
Catalyst 6500 Cisco Anomaly Detector Module |
ADXT-5600-MMF-B-K9 For more information, please visit http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns615/networking_solutions_sub_solution.html |
Cisco Traffic Anomaly Detector XT 5600,1000Base MMF |
|
WS-SVC-CSG-1 |
Content Services Gateway |
||
|
WS-SVC-IPSEC-1 |
IPSec VPN Services Module for Cisco Catalyst 6500 and Cisco 7600 Series Routers |
SPA-IPSEC-2G and 7600-SSC-400 For more information, please visit: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/modules/ps8768/ps4221/prod_end-of-life_notice0900aecd80349e2c_ps8768_Products_End-of-Life_Notice.html |
Cisco 7600/Catalyst 6500 IPSec VPN SPA with DES/3DES/AES; Cisco 7600/Catalyst 6500 Services SPA Carrier Card |
|
WS-SVC-WLAN-1-K9 |
Wireless LAN Services Module, CEF256 |
WS-SVC-WISM-1-K9 For more information, please visit http://cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/modules/ps2706/prod_eol_notice0900aecd80550b4c.html |
Cisco Wireless Services Module (WiSM) |
2.3. Release 12.2(33)SXH (and Later 12.2SX Releases) Software Modularity Deployment Considerations
• Complete hardware and software feature parity between Cisco IOS Software Modular and Cisco IOS Native images
• Cisco IOS Software Modularity as a feature set of Cisco IOS Native images
Table 3.
3. Release 12.2(33)SXI Feature Highlights
Table 4. Release 12.2(33)SXI Highlights
Hardware
Cisco® Dense Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (DWDM) X2 Pluggable Module
• The Cisco DWDM X2 supports 10GBASE Ethernet
• The hot-swappable input/output device plugs into an Ethernet X2 port of a Cisco switch or router to link the port with the network
• The Cisco DWDM X2 supports the Cisco Quality Identification (ID) feature, which enables a Cisco switch or router to identify whether or not the module is an X2 module certified and tested by Cisco
• The module supports 32 non-tunable ITU 100-GHz wavelengths compatible with the Cisco ONS DWDM channel plan
• The Cisco DWDM X2 supports digital optical monitoring capability
For Additional Information
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/modules/ps5455/ps6576/data_sheet_c78_489725.html
Cisco X2-10GB-ZR Module
For Additional Information
Catalyst 6500 Series Shared Port Adapter (SPA) and SPA Interface Processor (SIP) Support Enhancements
• Previously supported on SIP-200, new support on SIP-400:
– SPA-8XCHT1/E1
– SPA-2XT3/E3
– SPA-4XT3/E3
– SPA-2XCT3/DS0
– SPA-4XCT3/DS0
• The ATM SPAs were previously supported in Release 12.2(33)SXH, and is also available in Release 12.2(33)SXI:
– SPA-2XOC3-ATM
– SPA-4XOC3-ATM
– SPA-1XOC12-ATM
– SPA-1XOC48-ATM
• SIP-600 support is now available with support for the following SPAs:
– SPA-2XOC48POS/RPR
– SPX-4XOC48POS/RPR
– SPA-OC192POS-VSR
– SPA-OC192POS-LR
– SPA-OC192POS-XFP
– SPA-5X1GE
– SPA-10X1GE
– SPA-1XTENGE-XFP
– SPA-10X1GE-V2
– SPA-1X10GE-L-V2
Cisco Catalyst® 6500 Series VPN Services Port Adapter (VSPA)
Figure 4. Cisco VSPA

Benefits
• High performance: The Cisco VSPA can deliver up to 8 Gbps of Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) traffic at large packet sizes and 7 Gbps Internet mix (IMIX) traffic
• Modular design and scalability: Terminate up to 16,000 site-to-site or remote-access IPSec tunnels on each VSPA; Up to 10 VSPAs can be combined in a single chassis
• Enhanced Quality of Service (QoS): The VSPA is designed to handle pre-encryption QoS configured on IPsec tunnel interfaces and provides priority, bandwidth, and traffic shaping services
• Scalable IPv6 encryption: Support for multi-gigabit IPv6 networks based on Static Virtual Tunnel Interfaces (sVTIs)
• Support for industry-leading encryption technology: In addition to Data Encryption Standard (DES) and Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES), the Cisco VSPA also supports AES 192 and 256, the latest standard in encryption technology demanded by most government agencies and the leading financial institutions in the most secure network environments
For Additional Information
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9893/index.html
Product Management Contact
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Services SPA Carrier-600 (WS-SSC-600)
Figure 5. Cisco Services SPA Carrier-600 with Two Cisco VPN Services Port Adapters
Benefits
• Modularity-Creates investment protection and offers flexibility for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches
• Scalability-Up to 10 Cisco Services SPA Carrier-600 modules and 10 Cisco VSPAs in a Cisco Catalyst 6500 chassis
For Additional Information
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9893/index.html
Product Management Contact
MPLS
Layer 3 MPLS VPN Feature Enhancements
• MPLS VPN-VPN Routing/Forwarding Instance (VRF) Command-Line Interface (CLI) for IPv4 and IPv6 VPNs
• MPLS VPN-IPv6 VPN over MPLS (6VPE) Support over IP tunnels
Benefits
• MPLS VPN-VRF CLI for IPv4 and IPv6 VPNs: Provides a CLI improvement and integration for VRF IPv4 and IPv6 commands
• MPLS VPN 6VPE support over IP tunnels: This new option of the L3VPN solutions suite enables network providers to run IPv6 VPNs over classical IPv4 transport networks without the requirement to run MPLS and LDP/MPLS-TE within the core network
For Additional Information
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6604/products_ios_protocol_group_home.html
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6017/products_feature_guides_list.html
Product Management Contact
• Bertrand Duvivier (bduvivie@cisco.com)
Ethernet OAM Enhancements
IEEE 802.1ag Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (CFM)
1. Continuity check messages-these are "heartbeat" messages issued periodically by maintenance endpoints. They allow maintenance endpoints to detect loss of service connectivity among themselves. They also allow maintenance endpoints to discover other maintenance endpoints within a domain, and allow maintenance intermediate points to discover maintenance endpoints.
2. Link trace messages-these are transmitted by a maintenance endpoint on the request of the administrator to track the path (hop-by-hop) to a destination maintenance endpoint. They allow the transmitting node to discover vital connectivity data about the path. Link trace is similar in concept to UDP Traceroute.
3. Loopback messages-these are transmitted by a maintenance endpoint on the request of the administrator to verify connectivity to a particular maintenance point. Loopback indicates whether the destination is reachable or not; it does not allow hop-by-hop discovery of the path. It is similar in concept to ICMP Echo (Ping).
Maintenance End Points (MEPs) on Switchports (Inward)
Maintenance Intermediate Points (MIPs)
CFM MIP/MEP over EtherChannel
CFM-Outward Facing MEPs on Routed Ports
• Continuity Check (CC) 3
• Traceroute
• Loopback
• Crosscheck
• SNMP Traps
Product Management Contact
• Eric Matkovich (ematkovi@cisco.com)
Link Layer OAM-IEEE 802.3ah Ethernet Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM)
Figure 6. OAM Protocol Data Units
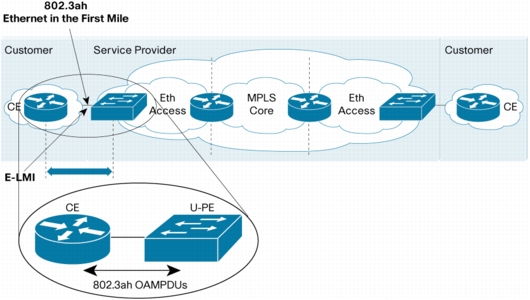
• OAM Discovery
Discovery is the first phase of Link Layer OAM. It identifies the devices at each end of the link along with their OAM capabilities.
• Link Monitoring
Link monitoring OAM serves for detecting and indicating link faults under a variety of conditions. Faults in link connectivity that are caused by slowly deteriorating quality are difficult to detect. Link OAM provides a mechanism for an OAM entity to convey these types of failure conditions to its peer via specific flags in the OAMPDUs. It provides statistics on the number of frame errors (or percent of frames that have errors) as well as the number of coding symbol errors.
• Remote Loopback
An OAM entity can put its remote peer into loopback mode using the loopback control OAMPDU. In loopback mode, every frame received is transmitted back on the same port (except for OAMPDUs needed to maintain the OAM session). This helps the administrator ensure the quality of links during installation or when troubleshooting, and can also be used to test SLA requirements such as delay, jitter, and throughput. This feature is asymmetric, the provider device can put the customer device into loopback mode, but not conversely.
• Remote Fault Indication (RFI)-Dying Gasp
The failure conditions that can be communicated are a loss of signal in one direction on the link, an unrecoverable error (such as a power failure), or some critical event. Currently, Cisco supports the Dying Gasp generation and can receive the Critical Event and Link Fault.
– Administratively Down
– Error Disabled
– Reload
Product Management Contact
• Eric Matkovich (ematkovi@cisco.com)
Ethernet Local Management Interface (E-LMI)
Figure 7. Ethernet Local Management Interface
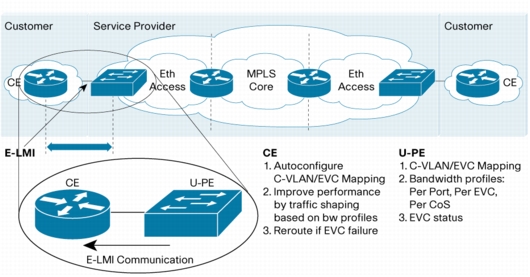
• Notification to the Customer Edge (CE) device of the addition of an EVC
An example use case of this is if a new branch office is connected to headquarters. The CE device at headquarters will be notified via the U-PE of the EVC and the associated VLAN to be configured. Future releases of E-LMI will also support auto-configuration, which provides notable benefits in that the branch office CE device can be deployed at the convenience of the customer and it will begin operation as soon as the Service Provider turns up the service.
• Notification to the CE device of the deletion of an EVC
This is very similar to the previous examples, except the EVC is being removed.
• CE EVC State notification (active) or (inactive)
The primary benefit is that the CE device can take some corrective action, such as re-routing traffic to a different EVC or other WAN service, when informed that an EVC has become inactive.
• EVC and Remote User Network Interface (UNI) Status
Remote UNI status is a Cisco proprietary extension which is supported by the OAM Interworking component.
• Traffic Shutdown on CE based on EVC Status
Product Management Contact
• Eric Matkovich (ematkovi@cisco.com)
Cisco Performance Management and Monitoring Through IP SLAs for Ethernet
• A reduction in OPEX by employing:
– Point-to-Point and Multipoint support
– Auto-discovery of endpoints (Moves/Adds/Changes)
– No IP overlay required to manage native Ethernet service
• Hierarchical Performance Management
– Monitor Customer, Operator and Service Provider networks
– Monitoring is transparent to lower layers
• In-Band Performance Management using Ethernet Frames
• Policy threshold alerts via SNMP Traps
Product Management Contact
• Eric Matkovich (ematkovi@cisco.com)
Cisco Ethernet OAM Interworking
• 802.3ah to Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) Interworking
Many of the OAM technologies today only deal with specific points of failure. Either the Link, the Service, or EVC status can be achieved independently. Cisco advanced OAM Interworking capabilities bridges the gap by providing the glue to complete a truly end-to-end OAM for your transport network, and the services that utilize it. Connectivity Fault Management has the capabilities to provide service level fault notification and fault isolation. 802.3ah provides link level monitoring information. 802.3ah to CFM interworking allows us to interpret errors happening at the link level and communicate it across the network to affected peers. This dramatically reduces the effects of potential black holing of services. This also reduces the time associated with fault isolation and repair.
• CFM to E-LMI
The power of Cisco advanced Ethernet OAM can be fully realized through our OAM manager. The OAM manager is a component that allows for the seamless interworking of various OAM protocols providing the basis for true end-to-end OAM. In this case, the OAM manager handles the interaction between CFM and E-LMI. The E-LMI interaction with the OAM manager is unidirectional, running only from the OAM manager to E-LMI on the User Provider-Edge (UPE) side of the switch. Information is exchanged either as a result of a request from E-LMI or triggered by OAM when it receives notification of a change from the OAM protocol. The following type of information is relayed:
– EVC name and availability status
– Remote UNI name and status
– Remote UNI counts
You can configure Ethernet Virtual Connections (EVCs), service VLANs, UNI ids (for each CE-to-PE link), and UNI count and attributes. You need to configure CFM to notify the OAM manager of any change to the number of active UNIs, and or the remote UNI ID for a given S-VLAN domain.
On the UPE side, the OAM manager defines an abstraction layer that relays data collected from OAM protocols (in this case CFM) running within the metro network to the E-LMI switch. CFM can thus be leveraged to notify E-LMI of any remote defects that may affect the active UNI counts in a point-to-point or multipoint service. This will allow E-LMI on the CE side to take the associative action and bring down the affected EVC's interface.
The information flow is unidirectional (from the OAM manager to the E-LMI) but is triggered in one of two ways:
– Synchronous data flow triggered by a request from the E-LMI
– Asynchronous data flow triggered by OAM manager when it receives notification from CFM that the number of remote UNIs has changed
This data includes:
– EVC name and availability status (active, not active, partially active, or not defined)
– Remote UNI name and status (up, disconnected, administratively down, excessive FCS failures, or not reachable)
– Remote UNI counts (the total number of expected UNIs and the actual number of active UNIs)
– The asynchronous update is triggered only when the number of active UNIs has changed
Product Management Contact
• Eric Matkovich (ematkovi@cisco.com)
High Availability
In-Service Software Upgrade Support for Catalyst 6500 Series Switches-Phase I
Benefits
• Provides the ability to upgrade/downgrade a complete Cisco IOS Software image with minimal system downtime
• Provides streamlined process for software upgrade/downgrade covering maintenance-fixes as well as new features
• Reduces planned downtime and operational expenses
Hardware Support
• All Catalyst 6500 Series chassis are supported
• Catalyst 6500 Supervisor Engines: Sup32-GE, Sup32-10GE, Sup720-GE and Sup720-10GE
• Line Cards with Warm Reload Support: 67xx series cards, SIP200, and SIP400 with 512MB minimum memory
Note: Line cards not capable of warm reload will reload normally
For Additional Information
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps7149/products_ios_protocol_group_home.html
• Feature Guide: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12.2SX/configuration/guide/issu_efsu.html
Product Management Contact
• Tom Cramer, (tcramer@cisco.com)
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) Enhancements
• Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) VRF support
BFD VRF support extends BFD failure detection capability within a VRF context. It is now possible to run BFD from a VRF based interface, so that any failure in the forwarding path between PE and CE devices can be detected even though the physical link might still be up. The combination of BFD VRF support along with the different embedded OAM MPLS tools such as MPLS Ping and Traceroute give network operators a comprehensive end-to-end solution to address overall network reliability and enhance their L3VPN service availability.
Benefits
• BFD-VRF aware support: Offers the capability to improve convergence on the PE-CE link and ultimately improves overall layer 3 VPN network reliability and availability
For Additional Information
• Bidirectional Forwarding Detection Feature Guide: http://cco.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_0s/feature/guide/fs_bfd.html
Product Management Contact
• Hari Rakotoranto, (hrakotor@cisco.com)
IP Services
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Relay Enhancements
Figure 8. DHCPv6 Option Handling at the Relay Agent

Benefits
• DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation is now fully deployable when a Relay is involved with route maintenance and Relay options to enable Prefix selection at the Server side (Remote Id) and proper message forwarding at the Relay side (Interface Id).
For Additional Information
• DHCPv6 Configuration Guide: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-dhcp.html
Product Management Contact
• Benoit Lourdelet, (blourdel@cisco.com)
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) for IPv6
Figure 9. HSRP for IPv6 Topology
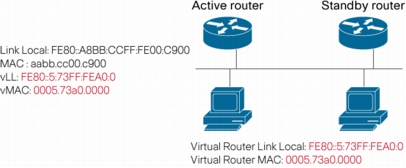
Benefits
• Increases network availability by providing protection against router failures
• Decreases outages and their duration
For Additional Information
• Cisco IOS Software Release Specifics for IPv6 Features: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-fhrp.html
Product Management Contact
• Benoit Lourdelet, (blourdel@cisco.com)
Cisco Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) for IPv6
Figure 10. GLBP for IPv6 Topology
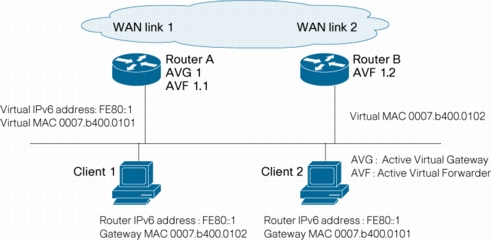
Benefits
• Increases network availability by providing protection against router failures
• Provides network redundancy and load sharing for IPv6 networks, ensuring that user traffic immediately and transparently recovers from first hop failures in network edge devices or access circuits
For Additional Information
• GLBP for IPv6 Product Literature: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-fhrp.html
Product Management Contact
• Benoit Lourdelet, (blourdel@cisco.com)
GLBP Client Cache
• How well GLBP clients have been distributed among forwarders
• Which forwarder a particular client is assigned to
• How many clients are assigned to each forwarder
• Which clients are assigned to each forwarder
• Percentage of all clients currently assigned to each forwarder
• Forwarder assigned to a specified client MAC address
• Number of client assigned to each forwarder
• Information about each client assigned to each forwarder
Benefits
• Manageability and network troubleshooting of GLBP is greatly improved.
For Additional Information
• GLBP Feature Information: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipapp/configuration/guide/ipapp_glbp.html
Product Management Contact
• Benoit Lourdelet, (blourdel@cisco.com)
VRRP Stateful Switch Over (SSO)
Benefits
• GLBP SSO can detect when a router is failing over to the secondary RP and continue in its current group state, creating an unparallel gateway high availability scheme.
For Additional Information
• VRRP Feature Information: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipapp/configuration/guide/ipapp_vrrp.html
Product Management Contact
• Benoit Lourdelet, (blourdel@cisco.com)
Enhanced Object Tracking Integration with Embedded Event Manager
Benefits
• Access to the richness of Embedded Event Manager events in Enhanced Object Tracking
• Access to Enhanced Object Tracking from Embedded Event Manager
• Enhanced Object Tracking Product Literature: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/netmgmt/configuration/guide/nm_eem_overview_ps6441_TSD_Products_Configuration_Guide_Chapter.html
Product Management Contact
• Benoit Lourdelet, (blourdel@cisco.com)
IPv6 Support on VPN Services Port Adapter
Benefits
• Dual Stack on egress interface
• Extended Address Space
• Header Simplification
• Auto Config
• No fragmentation done by routers, only by end hosts
For Additional Information
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9893/index.html
Product Management Contact
Security and Identity
IEEE 802.1x Feature Enhancements
• Flexible Authentication Sequencing
Flexible authentication sequencing provides a flexible fallback mechanism among IEEE 802.1x, MAC authentication Bypass and Web authentication methods. It also allows switch administrators to control the sequence of the authentication methods. This simplifies the identity configuration by providing a single-set of configuration commands to handle different types of end points connecting to the switch ports. In addition, it allows users to configure any authentication method on a standalone basis ie: MAB can be configured without requiring IEEE 802.1X configuration.
• IEEE 802.1x with Open Access
This feature allows users to have limited network access, such as the Intel Preboot Execution Environment (PXE) boot server, prior to IEEE 802.1x authentication. The limited access is controlled by an ACL that is defined by the switch administrator and applied on the switch port.
• IEEE 802.1x, MAB and Web Authentication with downloadable ACL
This feature allows per-user ACLs to be downloaded from the Cisco ACS server as policy enforcement after authentication using IEEE 802.1x, MAC authentication Bypass or Web authentication.
• IEEE 802.1x, MAB with QoS Policy
This feature allows per-user per-port QoS policy to be applied on the switch port after authentication using IEEE 802.1x or MAC Authentication Bypass.
• Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) enhancement for second port disconnect
CDP protocol is enhanced to add a new TLV for the IP phone to indicate the switch in the event of the PC disconnecting from the IP phone. Upon receiving this notification, the switch can clear the security record for the PC.
• Inactivity timer for IEEE 802.1x and MAC Authentication Bypass
This feature provides a local inactivity timer for IEEE 802.1x and MAC Authentication Bypass. If the authenticated devices stay idle for longer than defined period, the switch resets the security record of the devices.
• Multi-Domain Authentication
Multi-Domain Authentication allows an IP Phone (Cisco or non-Cisco) and a PC to authenticate on the same switch port while it places them on appropriate Voice and Data VLANs.
• IEEE 802.1x with multi-auth
Multiple authentication allows more than one host to authenticate on a IEEE 802.1x enabled switch port. With mulit-auth, each host must authenticate individually before it can gain access to the network resources.
• Centralized Web Authentication
This feature allows the switch to redirect users via HTTP URL redirection to a central web authentication server or a guest access server for authentication before accessing the network resources.
• Identity to port description mapping
This feature allows a user-identity based switch interface description to be displayed on the interface to which the user connects.
• Web authentication enhancement-Inaccessible authentication bypass
Web authentication is enhanced to support inaccessible authentication bypass. In the event that the Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) servers are unreachable or nonresponsive, user authentication typically fails with the port closed, and the user is denied access. Web Authentication inaccessible authentication bypass provides a configurable alternative on the switch to grant a critical port network access in a locally specified VLAN. After the AAA servers become reachable again, those ports will either remain critically authorized or be reinitialized. Inaccessible authentication bypass can be enabled on a per-port basis for access ports, private VLAN host ports, or routed ports. It is typically enabled on ports connected to critical devices, minimizing business impact for the duration of the AAA server outage.
• Common Session ID
IEEE 802.1X and MAB will use a session ID identifier for all 802.1X and MAB authenticated sessions. This session ID will be used for all reporting purposes such as show commands, MIBs, Syslog and RADIUS messages and allow users to distinguish messages for one session from others.
• Conditional Logging
IEEE 802.1X and MAB will provide a capability to filter debug messages for a range of interfaces, MAC Addresses, IP Addresses or Session IDs to simplify troubleshooting.
Product Management Contact
• Niraj Gopal, (niraj@cisco.com)
Pre-Encryption QoS on VPN Services Port Adapter
Benefits
• Egress congestion will rely on system level QoS policies
• Pre-encryption solves the problem of trying to apply a QoS policy on the egress interface after the traffic has been encrypted
• Solves problem of Anti-Replay drops caused by post-encryption
For Additional Information
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9893/index.html
Product Management Contact
Embedded Management
Embedded Event Manager Version 2.4
• Two new Event Detectors:
– Remote Procedure Call Event Detector-allows for programs outside of the device to invoke specific device-resident, embedded policies by sending a Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) request over an SSHv2 connection. The device-resident policy runs on the device and may reply with information in a subsequent SOAP response.
– SNMP Proxy Event Detector-creates events when a specified SNMP trap or inform is received at the device. This allows for policies to be triggered by events from other devices.
• Multiple Event Correlation-EEM Version 2.4 now allows for multiple events to be considered for policy invocation. Previously a single event specification triggered a policy. Now up to 8 events may be correlated together using logical operators allowing for more granular and very powerful policy triggers.
• Script Policy Refresh-This feature allows for easy management, distribution, and update of device resident polices using a pull model.
• Additional ease of use enhancements and extensions:
– Interface Counter ED-rate based trigger; Bytecode support; Support for parameters on the event manager run command; Clear command to kill a policy; Registration substitution enhancement; SNMP ED enhancement-delta value; TCL package support
Table 5. EEM 2.4 Features and Benefits
|
Feature |
Benefit |
|
Extensible and Powerful Subsystem Architecture |
|
|
Architecture |
The EEM subsystem is designed with modularity in mind. It consists of Event Detectors, an Event Manager Server, and action routines called Policies |
|
CLI interface |
An interface to the Cisco IOS CLI to allow automated commands and access to any information that can be displayed |
|
Policy Scheduler |
EEM policies are scheduled one at a time or concurrently according to the number of threads configured |
|
Built-In Actions |
Policies can invoke a number of built-in actions for easy automation |
|
Extensive Set of Event Detectors (ED) |
|
|
Application |
Custom application events, action script interaction |
|
CLI |
CLI command match and run |
|
Counter |
Custom counter events |
|
GOLD |
Generic Online Diagnostics (GOLD) event detection |
|
Interface |
Interface counters and events |
|
Memory Threshold (Deprecated) |
Detect memory resource related events |
|
None (by Run Command) |
Allows execution of an EEM policy by direct command, event manager run |
|
Object Tracking |
Integration with Enhanced Object Tracking (EOT) |
|
OIR |
Card Online Insertion and Removal detection |
|
Remote Procedure Call |
Allows for authorized programs outside of the device to invoke specific device-resident, embedded policies by sending a SOAP request over an SSHv2 connection. |
|
Resource Threshold |
Integration with Embedded Resource Manager, supersedes Memory Threshold ED. |
|
RF |
Cisco IOS infrastructure Redundancy Facility (RF) events |
|
SNMP |
Detect MIB Variable match and thresholds |
|
SNMP Proxy |
Creates events when a specified SNMP trap or inform is received at the device. This allows for policies to be triggered by events from other devices. |
|
Syslog |
Regular expression pattern match on emitted Syslog messages |
|
Timer |
Custom timed events |
|
IOS Watchdog Monitor |
Cisco IOS scheduler, watchdog events |
|
WDSysMon |
Cisco IOS Software Modularity: System monitor event |
|
Secure System Operation |
|
|
EEM Scripts Run within System Constraints |
Protects system from harm.ie: A looping script will not stop Cisco IOS. |
|
User Scripts Run in Safe-Tcl mode |
Certain programmable options are disabled for protection |
|
Controlled Environment |
Only a network administrator with privileged access can define and set up EEM scripts. No one else can install software to compromise the system. |
|
Support for TACACS+/RADIUS |
EEM scripts can be associated with a configured User ID and be checked for permission. |
|
EEM is Optional |
If you don't want to use this powerful capability, you don't have to enable it. |
|
Online Scripting Community |
|
|
Cisco Beyond-Product Extension Community |
A place for customers to share and download scripts. Don't reinvent the wheel. Build and extend the work of others. Learn by example. Go to: http://www.cisco.com/go/ciscobeyond . |
For Additional Information
• For more information about Cisco IOS EEM go to http://cisco.com/go/eem or contact your local Cisco account representative.
Product Management Contact
• Rick Williams, (rwill@cisco.com)
Catalyst OS Software (CatOS) Parity MIBs in Release 12.2(33)SXI
1. CISCO-MODULE-AUTO-SHUTDOWN-MIB
2. CISCO-IGMP-SNOOPING-MIB
3. CISCO-PACKET-CAPTURE-MIB
1. CISCO-VTP-MIB
2. CISCO-L2-TUNNEL-CONFIG-MIB
3. MAU-MIB
4. CISCO-MAU-EXT-MIB
For additional information:
• http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
Product Management Contact:
• Sairaj Pakkam (spakkam@cisco.com)
IP Routing and Multicast
EIGRP for IPv6
• IPv4 Address Space Depletion: Due to the 32 bit limit of IPv4, the availability of Class A, B and C Internet addresses, and the ever growing size of networks, the IPv4 address space available for use is rapidly being consumed and limited in its ability to scale to the requirements of next generation infrastructure requirements.
• Mobile Wireless: With the ongoing convergence of video/voice and data on Mobile Wireless devices, there is a rapidly growing demand for IP address space from these mobile devices that exceeds the capabilities of current IPv4 networks.
• Mobile Networks: New applications such as mobile networks using mobile platforms such as automobiles, ships, trains, and planes add to the pressure on IPv4 address space availability.
• Public Sector: Many parts of the US Government have created memos (DoD memo June 2003, OMB Memo M-05-22), task forces (Commerce Department task force on IPv6), and recommendations (GAO-05-471) to transition from IPv4 to IPv6 based networking solutions by 2008.
• Higher Education/Research Networks: These networks are pushing the limits of networking technology and applications. As such, they require networking equipment and protocols that can extend beyond the boundaries of existing IPv4 based solutions.
• Supportability of IPv4 and IPv6: The migration to IPv6 will be a gradual one and administrators will require the flexibility to keep both their IPv4 users and IPv6 users on the same network infrastructure at the same time. Hence, the network needs to be able to support both IPv4 and IPv6.
• EIGRP for IPv4: EIGRP is an area of continual innovation by Cisco with support for such functionality as:
– Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) with Stateful Switchover (SSO)
– Stub Routing; MPLS VPN PE-CE with Site of Origin (SoO)
– Route Redistribution Limiting and Max-Prefix Limits
– SNMP MIBs
– Enhanced Route Map support
• Ease of Use: EIGRP is simple to learn, configure, and deploy compared to other major Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs). This a major source of time saving for EIGRP customers.
• Scalability: EIGRP contains functionality that allows it be suitable and scalable for deployment in multiple scenarios including hub and spoke, broadcast domains, and meshed architectures.
• Sub-Second Convergence: Backup routes are pre-computed and instantaneously used in case of failure.
• High Availability: Provides comprehensive support for High Availability improves the reliability of network and minimizes downtime.
• Investment Protection: Since EIGRP is widely available across Cisco platforms suitable for both Enterprises and Service Providers, it provides a significant degree of capital investment protection for customers needing different routers to meet their networking needs.
Figure 11. Routing Domain Based Upon EIGRP for IPv4
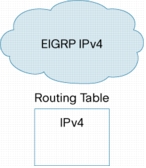
Figure 12. Routing Domain Integrating EIGRP Based IPv4 and IPv6
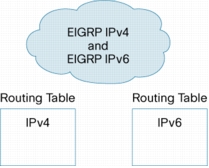
Benefits
• Extends key EIGRP benefits, including ease of use, fast convergence times, minimal routing traffic overhead, and scalability, to IPv6 environments.
• Fast, seamless IPv6 Integration: Allows existing EIGRP IPv4 customers to integrate IPv6 based upon EIGRP into their network. This is important for applications in Enterprises, public sector (government/defense), and wireless networks.
• Delivery of IPv6 Services: Enables the creation of next-generation IPv6 infrastructure to deliver services such as Mobile Wireless or Mobile Networks.
Product Management Contact
• Kevin Delgadillo, (delgadil@cisco.com)
Per Interface Multicast Route (Mroute) State Limit
Figure 13. Example Use of Per Interface Mroute State Limit for Admission Control
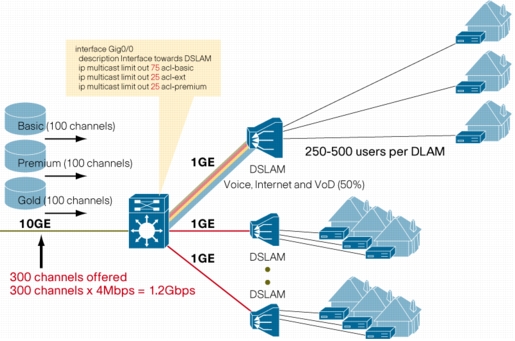
Benefits
• Extends the benefits of Ethernet as a last-mile technology
• Offers more granular DoS attack prevention
• Provides a multicast Call Admission Control (CAC) mechanism
Product Management Contact
• Ritesh Mukherjee, (ritmukhe@cisco.com)
Bandwidth based Call Admission Control (CAC) for IP Multicast
Figure 14. Example Use of Per Interface Mroute State Limit for Admission Control
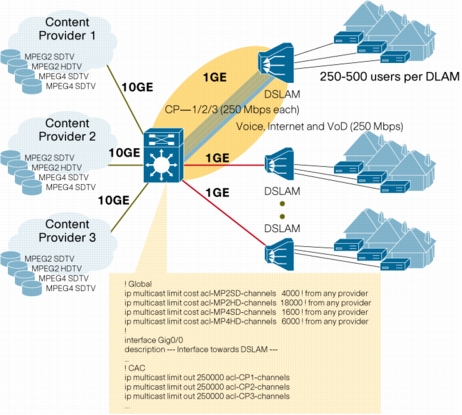
Benefits
• Provides a bandwidth based multicast Call Admission Control (CAC) mechanism
• Operates when multicast flows utilize different amounts of bandwidth
Product Management Contact
• Ritesh Mukherjee, (ritmukhe@cisco.com)
Multicast Address Group Range Support
Benefits
• Provides ability to disable PIM, IGMP and MSDP control plane actions
• No IGMP (cache), PIM, MRIB/MFIB state created for denied groups
• Drops all data packets for denied groups
Product Management Contact
• Ritesh Mukherjee, (ritmukhe@cisco.com)
IPv6: Multicast Address Group Range Support
Benefits
• Provides ability to disable PIMv6, MLD and MSDP control plane actions
• No MLD (cache), PIMv6, Multicast Routing Information Base (MRIB)/Multicast Forwarding Information Base (MFIB) state created for denied groups
• Drops all data packets for denied groups
Product Management Contact
• Ritesh Mukherjee, (ritmukhe@cisco.com)
IPv4 Multicast High Availability (HA) Support for Group to Rendezvous Points (RP) Mappings
Figure 15. Syncing of group-to-RP mapping cache
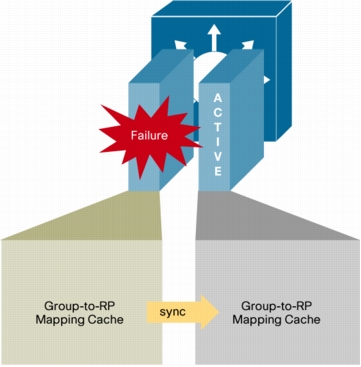
Benefits
• Reduces multicast data stream interruption times following a switchover to levels that will be transparent to most applications
Product Management Contact
• Ritesh Mukherjee, (ritmukhe@cisco.com)
4. Release 12.2SX Additional Information
Cisco IOS Software Information
Release 12.2SX Information
• http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6017/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
• http://www/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/prod_bulletin0900aecd804f0694.html
Cisco IOS Software Product Lifecycle Dates and Milestones
Cisco IOS Software Center
• Download Cisco IOS Software releases and access software upgrade planners. http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/
Cisco Software Advisor (Requires Cisco.com Account)
• Determine the minimum supported software for platforms. http://tools.cisco.com/Support/Fusion/FusionHome.do
Cisco Feature Navigator (Requires Cisco.com Account)
• A Web-based application that allows you to quickly match Cisco IOS Software releases, features, and hardware. http://tools.cisco.com/ITDIT/CFN/jsp/index.jsp
Cisco IOS Planner (Requires Cisco.com Account)
• View all major releases, all platforms, and all software features from a single interface. http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/Software/Iosplanner/Planner-tool/iosplanner.cgi
Cisco MIB Locator
• MIB Locator finds MIBs in Cisco IOS Software releases. http://tools.cisco.com/ITDIT/MIBS/servlet/index
Cisco Bug Toolkit (Requires Cisco.com Account)
• Search for known bugs based on software version, feature set and keywords. http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/Support/Bugtool/launch_bugtool.pl