Cisco® Content Networking delivers the network agility required by the enterprise to deploy new Internet business applications critical to securing competitive advantage by increasing revenue while reducing operating costs. By creating end-to-end intelligent network services required for Internet business applications such as e-commerce, supply chain management, and workforce optimization, Cisco Content Networking integrates the enterprise with customers, suppliers, and business partners.
Content Networking
• Intelligent network classification and network services delivered through Cisco IOS® Software
• Intelligent network devices that integrate Internet business applications with network services
• An intelligent policy management framework for configuration, monitoring, and accounting
Network-Based Application Recognition Overview
Figure 1. NBAR Provides Intelligent Network Classification
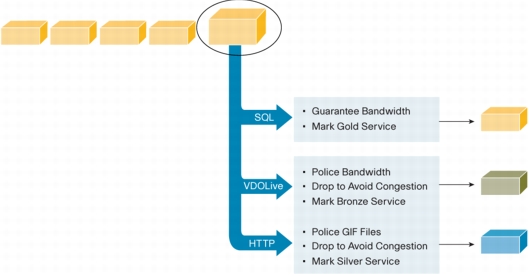
Features at a Glance
• NBAR supports a wide range of network protocols, including some of these stateful protocols that were difficult to classify before NBAR:
– HTTP classification by URL, host, and Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) type
– Oracle SQL*Net
– Sun RPC
– Microsoft Exchange
– UNIX r commands
– VDOLive
– RealAudio
– Microsoft Netshow
– FTP
– StreamWorks
– Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
• NBAR also classifies traditional static port protocols for supporting a wide range of solutions. The complete list is given at the end of this document.
• Support for new protocols can be easily and quickly added using packet description language modules (PDLMs) from Cisco Systems®. PDLMs contain the rules used by NBAR to recognize an application and in most cases can be loaded without the need for a new Cisco IOS Software image or even a reboot.
• Protocol discovery shows you the mix of applications currently running on the network. This helps you define QoS classes and polices, such as how much bandwidth to provide to mission-critical applications and how to determine which protocols should be policed. The following per-protocol, bidirectional statistics are available:
– Packet and byte counts
– Bit rates
• After applications are intelligently classified, the network can apply the following QoS features:
– Guaranteed bandwidth with Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing (CBWFQ)
– Enforce bandwidth limits using policing
– Marking for differentiated service downstream or from the service provider using type of service (ToS) bits or Diff Serv code points (DSCPs) in the IP header
– Drop policy to avoid congestion (Weighted Random Early Detection [WRED])
Benefits and Applications
Help Ensure Performance for Mission-Critical Applications
Reduce WAN Expenses
Improve Web Response
• Customers accessing the sales ordering page would be given priority. This prevents the customer from getting frustrated at the point of sale.
• Sales tools can be given absolute priority and guaranteed bandwidth, helping ensure that your sales force is never forced to wait for a price quote because another employee is browsing the latest version of the firm's new television commercial on streaming video.
• Web-based applications often load slowly. With NBAR, applications can be identified by MIME type and be given priority in the network.
• Some classes of content, such as JPEG pictures, consume large amounts of bandwidth, but may not be considered critical Web-based information. In such cases, you can control the amount of bandwidth consumed by such types of content.
Improve VPN Performance
Improve Multiservice Performance
Availability and Orderability
Table 1. NBAR Features and Benefits Summary
Protocols Supported by NBAR
Table 2. Non-UDP and Non-TCP Protocols
Table 3. TCP and UDP Static Port Protocols
|
Protocol |
Type |
Well-Known Port Number |
Description |
Syntax |
Cisco IOS Software Release1 |
|
BGP |
TCP/UDP |
179 |
Border Gateway Protocol |
bgp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
CU-SeeMe |
TCP/UDP |
7648, 7649 |
Desktop videoconferencing |
cuseeme |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
CU-SeeMe |
UDP |
24032 |
Desktop videoconferencing |
cuseeme |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
DHCP/BOOTP |
UDP |
67, 68 |
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol/Bootstrap Protocol |
dhcp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
DNS |
TCP/UDP |
53 |
Domain Name System |
dns |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Finger |
TCP |
79 |
Finger user information protocol |
finger |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Gopher |
TCP/UDP |
70 |
Internet Gopher Protocol |
gopher |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
HTTP |
TCP |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
http |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
|
HTTPS |
TCP |
443 |
Secured HTTP |
secure-http |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
IMAP |
TCP/UDP |
143, 220 |
Internet Message Access Protocol |
imap |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
IRC |
TCP/UDP |
194 |
Internet Relay Chat |
irc |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Kerberos |
TCP/UDP |
88, 749 |
Kerberos Network Authentication Service |
kerberos |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
L2TP |
UDP |
1701 |
L2F/L2TP tunnel |
l2tp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
LDAP |
TCP/UDP |
389 |
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol |
ldap |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
MS-PPTP |
TCP |
1723 |
Microsoft Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol for VPN |
pptp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
MS-SQLServer |
TCP |
1433 |
Microsoft SQL Server Desktop Videoconferencing |
sqlserver |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
NetBIOS |
TCP |
137, 139 |
NetBIOS over IP (MS Windows) |
netbios |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
NetBIOS |
UDP |
137, 138 |
NetBIOS over IP (MS Windows) |
netbios |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
NFS |
TCP/UDP |
2049 |
Network File System |
nfs |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
NNTP |
TCP/UDP |
119 |
Network News Transfer Protocol |
nntp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Notes |
TCP/UDP |
1352 |
Lotus Notes |
notes |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Novadigm |
TCP/UDP |
3460-3465 |
Novadigm Enterprise Desktop Manager (EDM) |
novadigm |
Release 12.1(2)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
NTP |
TCP/UDP |
123 |
Network Time Protocol |
ntp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
PCAnywhere |
TCP |
5631, 65301 |
Symantec PCAnywhere |
pcanywhere |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
PCAnywhere |
UDP |
22, 5632 |
Symantec PCAnywhere |
pcanywhere |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
POP3 |
TCP/UDP |
110 |
Post Office Protocol |
pop3 |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Printer |
TCP/UDP |
515 |
Printer |
printer |
Release 12.1(2)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
RIP |
UDP |
520 |
Routing Information Protocol |
rip |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
RSVP |
UDP |
1698, 1699 |
Resource Reservation Protocol |
rsvp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SFTP |
TCP |
990 |
Secure FTP |
secure-ftp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SHTTP |
TCP |
443 |
Secure HTTP |
secure-http |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SIMAP |
TCP/UDP |
585, 993 |
Secure IMAP |
secure-imap |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SIRC |
TCP/UDP |
994 |
Secure IRC |
secure-irc |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SLDAP |
TCP/UDP |
636 |
Secure LDAP |
secure-ldap |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SMTP |
TCP |
25 |
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol |
smtp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SNMP |
TCP/UDP |
161, 162 |
Simple Network Management Protocol |
snmp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SNNTP |
TCP/UDP |
563 |
Secure NNTP |
secure-nntp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SOCKS |
TCP |
1080 |
Firewall security protocol |
socks |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SPOP3 |
TCP/UDP |
995 |
Secure POP3 |
secure-pop3 |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SSH |
TCP |
22 |
Secured Shell |
ssh |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
STELNET |
TCP |
992 |
Secure Telnet |
secure-telnet |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Syslog |
UDP |
514 |
System Logging Utility |
syslog |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Telnet |
TCP |
23 |
Telnet Protocol |
telnet |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
X Windows |
TCP |
6000-6003 |
X11, X Windows |
xwindows |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
Table 4. TCP and UDP Stateful Protocols
|
Protocol |
Type |
Description |
Syntax |
Cisco IOS Software Release |
|
Citrix ICA |
TCP/UDP |
Citrix ICA traffic by application name |
citrix app |
Release 12.1(2)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
FTP |
TCP |
File Transfer Protocol |
ftp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
Exchange |
TCP |
MS-RPC for Exchange |
exchange |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
FastTrack |
|
FastTrack For a list of common FastTrack applications, go to: Classification of Peer-to-Peer File-Sharing Applications |
fasttrack |
Release 12.1(12c)E |
|
Gnutella |
TCP |
Gnutella For a list of common Gnutella applications, go to: Classification of Peer-to-Peer File-Sharing Applications |
gnutella |
Release 12.1(12c)E |
|
HTTP |
TCP |
HTTP with URL, MIME, or host classification |
http |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T (HTTP host classification is not available on the 12.0 XE release train) |
|
Napster |
TCP |
Napster traffic |
napster |
Release 12.1(5)T |
|
Netshow |
TCP/UDP |
Microsoft Netshow |
netshow |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
R-Commands |
TCP |
rsh, rlogin, rexec |
Rcmd |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
RealAudio |
TCP/UDP |
RealAudio Streaming Protocol |
realaudio |
Release 12.0(5)XE2,12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
RTP |
TCP/UDP |
Real-Time Transport Protocol Payload Classification |
rtp |
Release 12.2(8)T |
|
SQL*NET |
TCP/UDP |
SQL*NET for Oracle |
sqlnet |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
StreamWorks |
UDP |
Xing Technology Stream Works audio and video |
streamwork |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
SunRPC |
TCP/UDP |
Sun Remote Procedure Call |
sunrpc |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
TFTP |
UDP |
Trivial File Transfer Protocol |
tftp |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
|
VDOLive |
TCP/UDP |
VDOLive Streaming Video |
vdolive |
Release 12.0(5)XE2, 12.1(1)E and 12.1(5)T |
References
• Configuring Network-Based Application Recognition: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/qos/configuration/guide/qcfnbar.pdf
• NBAR Packet Description Language Modules: http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/pdlm
• Feature Navigator: http://www.cisco.com/go/fn