As applications are being centralized and users become increasingly distributed, the performance limitations of WAN such as limited bandwidth, significantly longer latency, and packet loss are seriously slowing down application delivery. Cisco® Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) and Cisco Performance Routing (PfR) can work together to intelligently optimize application delivery across the WAN-at both the application level and network level. Although Cisco WAAS provides WAN optimization and application-level acceleration to improve application performance over the WAN, Cisco PfR routes data packets through the best IP path between disparate network locations. Specifically, PfR provides best-path decision-making based on network latency, packet loss, monetary WAN usage cost, jitter, link capacity, and more. Cisco PfR complements Cisco WAAS to improve application delivery and help enable infrastructure consolidation while providing optimized path selection.
Accelerating Appliations Using Cisco WAAS and Cisco PfR
Cisco Wide Area Application Services
• Deliver centralized applications with LAN-like speed to remote users, while preserving visibility and branch security
• Consolidate costly branch office servers, storage, and backup infrastructure into data centers, while optimizing WAN bandwidth usage
• Maximize regulatory compliance and data protection through consolidation of branch storage, as well as acceleration of branch backup applications
• Increase visibility of application data flows within the network
• Application acceleration-latency and bandwidth reduction: Advanced protocol optimizations such as read ahead, prediction, and suppression are coupled with sophisticated caching techniques to minimize latency and unnecessary data crossing the WAN.
• WAN optimization-bandwidth and throughput improvement:
– Data Redundancy Elimination (DRE) coupled with compression improves efficiency and mitigates unnecessary bandwidth consumption.
– TCP flow optimization (TFO) optimizes TCP to enable better performance and efficiency in WAN environments.
• Transparent network integration:
– Dynamic auto discovery of endpoints helps ensure efficient deployment without the need to create and manage overlay networks.
– Cisco WAAS offers end-to-end visibility and compatibility with existing network functions such as quality of service (QoS), firewall security, Cisco NetFlow monitoring, and high availability.
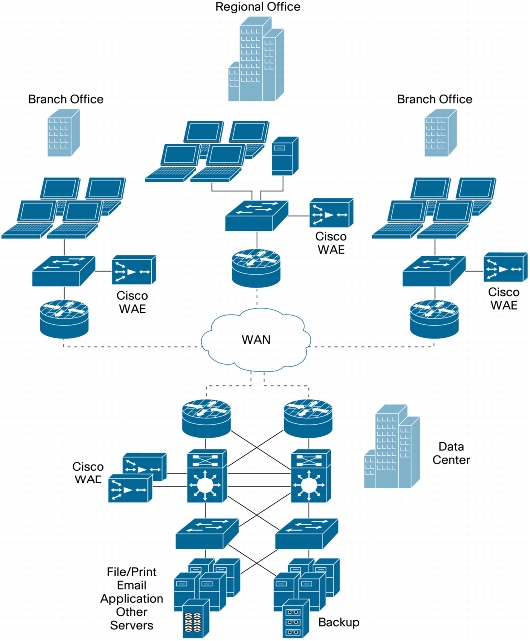
• One Cisco Wide Area Application Engine (WAE) at each end of the WAN connection to be optimized: The WAE at the central data center can service multiple branch WAEs.
• One central manager, deployed at the data center for centralized administration, management, and monitoring of the services provided by the WAE devices
Figure 1. Cisco WAE Appliances and Router-Integrated Network Module

Figure 2. Typical Cisco WAAS Deployment Scenario
Cisco Performance Routing
Increased Uptime
• Users can experience improved response time because the automated route optimization in Cisco PfR can detect and route around poorly performing paths by finding an optimal Internet Service Provider (ISP) exit.
• Performance optimization can minimize the effects of network degradation because it can monitor for them. For example, when high latency or packet loss occurs, for example, the network traffic can be automatically rerouted around the affected path to an alternative, better-performing path.
Reduced Costs
• Bandwidth cost minimization allows companies to minimize traffic sent over expensive links or consolidate multiple flat-rate connections to fewer and lower-cost tiered services.
• Modeling and cost minimization for tier-based pricing models allows real-time cost estimation and intelligent cost-based WAN path selection.
• Automatic performance optimization reduces engineering operating expenses associated with manual network performance analysis and tuning of IP routing.
• Reports for traffic distribution and usage before and after route optimization help customers manage ISP service-level agreements (SLAs) more effectively because they now have more specific and detailed SLA reporting than the ISPs.
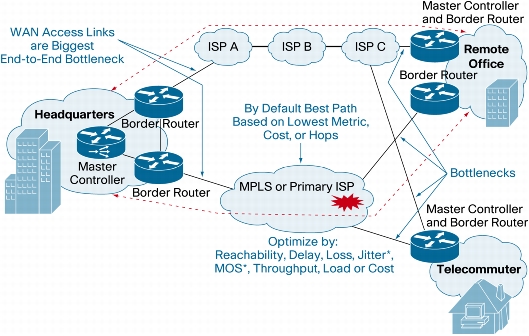
• Master controller
• One or more border routers
• Two or more network egress interfaces
Figure 3. Cisco PfR Topological Overview
• Performance
– Latency
– Packet loss
– Reachability
– Throughput
– Jitter or Mean Opinion Score (MOS)
• Load sharing and link usage
• Cost minimization
Combining Cisco PfR and Cisco WAAS Technologies
Cisco PfR and Cisco WAAS: Deployment Considerations
Figure 4. Logical Design for Integrating Cisco WAAS and Cisco PfR
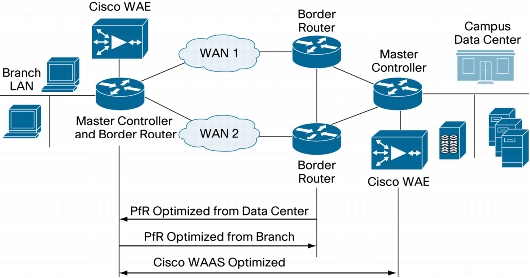
Figure 5. Topology Design for Cisco PfR and Cisco WAAS Deployment
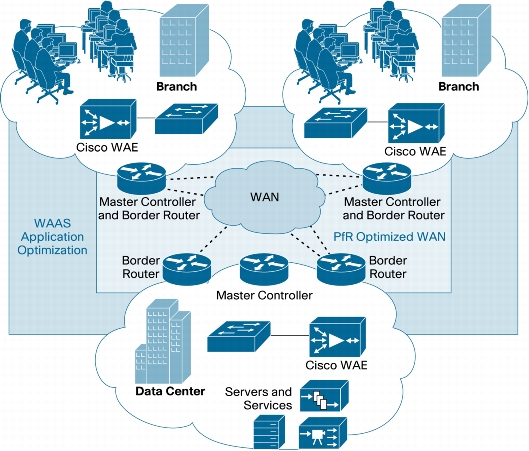
Summary of Cisco PfR and Cisco WAAS Combination
• Cisco WAAS reduces bandwidth usage by DRE and LZ caching.
• Cisco WAAS improves throughput by reducing effects of network latency.
• Cisco WAAS offers application-specific acceleration.
• Cisco PfR allows for effective WAN usage by better load management on WAN links.
• Specific application traffic is directed to the measured best WAN path for each application.
• SLAs are measured on a per-application basis, and mitigation occurs during threshold-crossing events.
References
• Cisco online PfR technology page: http://www.cisco.com/go/pfr
• Cisco PfR reference guide for Cisco IOS Software Release 12.4:
– http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios124/124cg/hoer_c/index.htm
– http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6441/products_configuration_guide_book09186a008049e22f.html
• Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS): http://www.cisco.com/go/waas