What You Will Learn
Challenge
Cisco WAAS Solution for the WAN
• Enhance productivity by mitigating the effects of WAN latency. Applications perform better, and data is transferred faster.
• Offer a superior end-user application experience by enabling rich-media applications and live and on-demand video streaming with high performance without affecting the performance of other applications across the WAN.
• Allow migration of business applications to the cloud and deliver high-performance cloud services and software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications without affecting application performance for end users at remote branch offices, campuses, and data centers.
• Reduce bandwidth consumption, delaying or eliminating increased recurring bandwidth costs. Cisco WAAS enables IT consolidation, reducing both CapEx and recurring expenses for branch-office IT infrastructure.
• Lower operating costs by providing on-demand WAN optimization with integration into Cisco Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 (ISR G2) routers through Cisco IOS® Software-based Cisco WAAS Express and Cisco WAAS on Services-Ready Engine (SRE) Modules.
Figure 1. Cisco WAAS Deployment Architecture
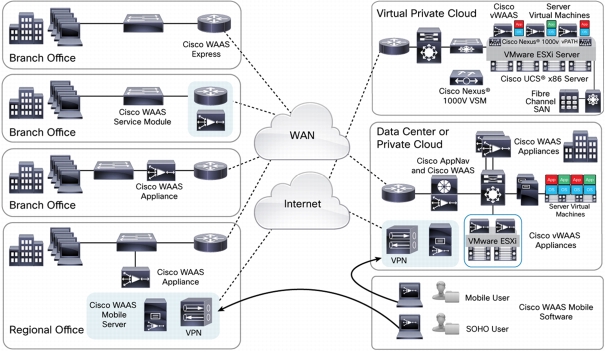
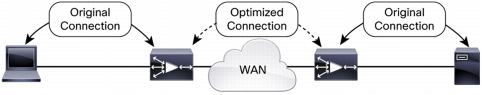
Figure 2. Cisco WAAS Optimizes Connections over the WAN
• Consolidate and virtualize data centers
• Deliver desktop virtualization
• Deploy new, rich-media applications
• Deliver high-performance cloud services and software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications
• Optimize organization branch-office sites with reduced network and IT infrastructure
• Optimize bandwidth for rich media and telepresence
• Manage bandwidth expenses
• Protect remote data and help ensure business continuity for regulatory compliance
• Application-vendor-validated protocol-specific acceleration: Cisco WAAS provides application-specific acceleration features that are validated by application vendors themselves for both encrypted and unencrypted applications. These techniques for improving application performance over the WAN reduce the effects of latency and bandwidth use through protocol acceleration, read-ahead, operation batching, multiplexing, and safe caching. The result is full correctness with the protocol specification, full coherency of data, and a dramatically improved user experience when compared with native WAN access. Applications include Microsoft file services (Common Internet File System [CIFS]) and Microsoft Exchange Messaging API Remote Procedure Call [MAPI-RPC]), plus numerous other application protocols.
• Advanced protocol-agnostic WAN optimization: Cisco WAAS provides powerful WAN optimization capabilities that overcome limitations associated with the movement of data over the WAN. Cisco WAAS can compress data in flight using long-lived compression techniques including standards-based compression and Context-Aware Data Redundancy Elimination (DRE). Coupled with TCP optimizations that enable more intelligent and high-performance use of the network, the result is a significant reduction in network bandwidth consumption, more efficient network use, improved application throughput, and LAN-like performance for remote-office users and inter-data center applications.
• Branch-office consolidation through virtual blades: Cisco WAAS uniquely provides customers with the capability to consolidate application infrastructure on scalable, high-performance Cisco WAAS Appliances for applications that must remain in the branch office. Cisco WAAS provides virtual blade support for Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 with its entire suite of applications. Furthermore, Cisco WAAS support for Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 adheres to the Microsoft Server Virtualization Validation Program (SVVP).
Figure 3. Cisco WAAS WAVE Appliances and Connectivity Options

WAN Optimization with Cisco WAAS
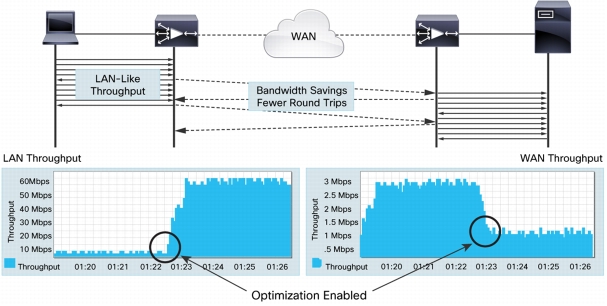
Figure 4. Effects of Cisco WAAS WAN Optimization Features
Transport Flow Optimization
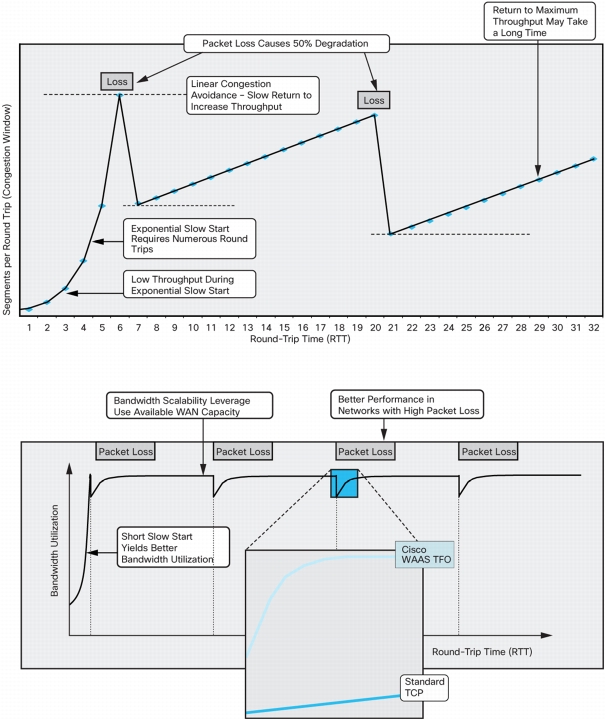
Figure 5. Cisco WAAS TFO
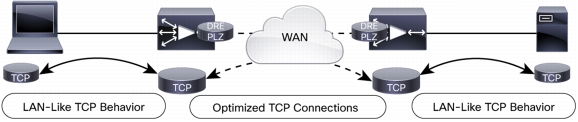
Figure 6. Cisco WAAS TFO Enables Efficient Usage and Improves Application Performance
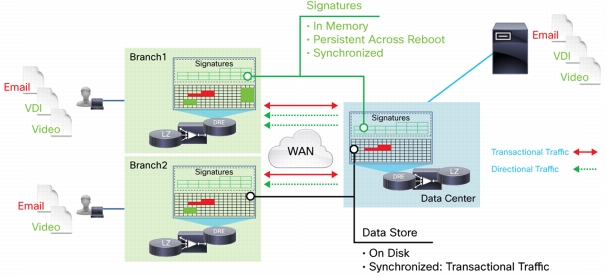
Data Redundancy Elimination
• Transactional: Transactional traffic moves between the client and the server on the same TCP connection and includes email send and receive traffic and file uploads and downloads. Typically, all traditional client and server application traffic is in this category.
• Directional: Directional traffic tends to travel in only one direction on the same TCP connection. Examples are traffic from VDI screen scrapping, video streams, and cloud-based applications such as backup. This type of traffic flow represents a new trend in applications.
• Bidirectional DRE: Data chunks and signatures are written to the disk on both the sender- and receiver-side Cisco Wide Area Application Engines (WAEs) to provide optimal compression.
• Unidirectional DRE: Only signatures are written on the sender-side Cisco WAE, and both signatures and data chunks are written on the disk on the receiver-side Cisco WAE. In addition to providing optimal compression, this mode effectively uses the DRE cache for higher scalability.
• Adaptive DRE: Context-Aware DRE intelligently chooses between the bidirectional and unidirectional DRE caching mechanism, depending on the type of application traffic.
Context-Aware DRE also stores signatures in the data center (headend) Cisco WAE on a per-branch-office basis, and the actual data chunks are shared across branch offices. The tight synchronization of branch-office signatures combined with shared chunks of data across branch offices helps provide consistent, reliable, and fair DRE performance for all branch offices. Figure 7 shows the architecture of Cisco WAAS Context-Aware adaptive DRE.
Figure 7. Cisco WAAS Context-Aware Adaptive DRE
PLZ Compression
SSL Optimization
Figure 8. Cisco WAAS SSL Optimization
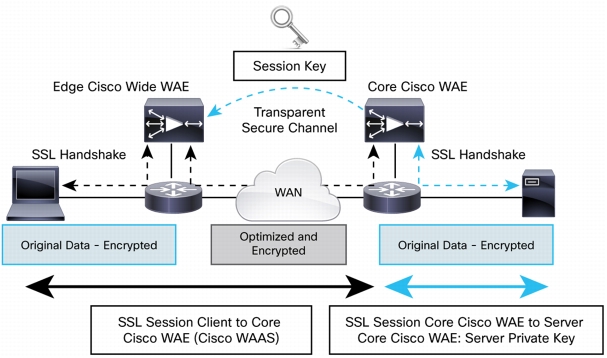
• Preservation of trust boundary: Cisco WAAS does not distribute private keys beyond the data center Cisco WAAS devices.
• Secure storage of keys: All certificates and private keys are stored securely on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
• Interoperability with existing proxy infrastructure: Cisco WAAS provides full support for automatic identification, interception, optimization, and acceleration of SSL traffic, even in environments in which web proxies have already been deployed or clients are configured to use explicit proxies.
• Client authentication support: Cisco WAAS provides full support for client certificate-based authentication during initial session establishment.
• Online certificate status protocol support: By providing support for the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OSCP), Cisco WAAS can provide a real-time security check of certificates to improve security.
• SSL services on the SaaS provider cloud: Cisco WAAS can simplify the configuration needed to handle the large numbers of IP addresses and IP address changes required by SSL services hosted through a third-party SaaS provider cloud.
• HTTP optimization techniques: Cisco WAAS SSL optimization uses HTTP optimization techniques such as local HTTP responses through the metadata cache, DRE hints, and server compression offload. Refer to the section "HTTP Acceleration" later in this document for more information.
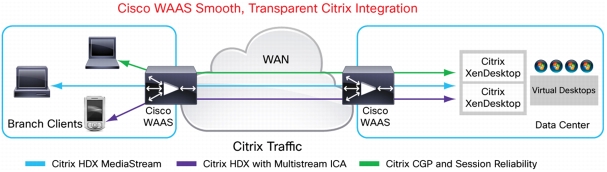
Citrix XenDesktop and XenApp Optimization
• Citrix XenDesktop delivers desktops and applications hosted on virtualized infrastructure in the data center.
• Cisco WAAS, deployed on both sides of the WAN, optimizes Citrix HDX traffic between the end users and the data center using a sophisticated combination of TCP optimizations that reduce the effects of the WAN, persistent session-based compression, and sophisticated algorithms to reduce data redundancy in Citrix HDX traffic.
• Cisco WAAS Central Manager is used to manage the Cisco WAAS solution from a central point, reducing operation burdens and costs.
Figure 9. Cisco Optimization for Citrix XenDesktop and XenApp Solution Components
• Full support for Citrix XenDesktop and XenApp: Cisco WAAS optimization techniques are applicable to Citrix XenDesktop and XenApp deployments.
• Transparent to Citrix encryption: You can transparently insert Cisco WAAS into encrypted communications (Basic and RC5) without requiring changes to the Citrix configuration or infrastructure.
• Full compatibility with Citrix MultiStream ICA (MSI) and the ability to apply differentiated-services-code-point (DSCP) tagging of both MSI and non-MSI ICA and Citrix Common Gateway Protocol (CGP) traffic.
• Full compatibility with Citrix Session Reliability (CGP) including enhanced optimization for CGP.
• Full compatibility with Citrix HDX MediaStream: Citrix HDX MediaStream exposes media stream, which enables Cisco WAAS optimization of the streaming media protocol.
• Context-Aware DRE: Directional understanding of data enables best performance as well as increased bandwidth savings as a result of improved compression.
Application Acceleration with Cisco WAAS
Figure 10. Cisco WAAS Application Acceleration
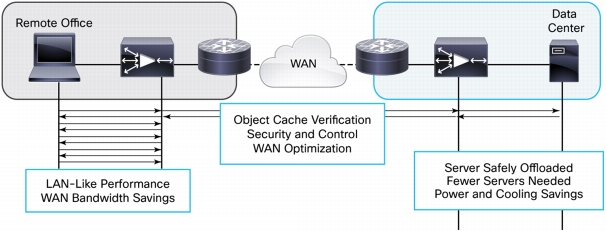
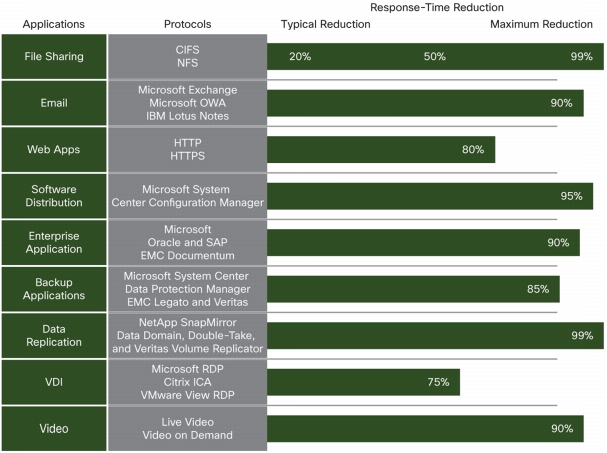
Figure 11. Typical and Peak Performance Improvements Provided by Cisco WAAS
CIFS, Microsoft Windows Print, and Server Message Block Acceleration
• Safe data and metadata caching: By caching copies of objects and metadata, Cisco WAAS can reduce the transmission of CIFS data over the WAN, thereby providing tremendous levels of optimization for branch-office users accessing file servers in the data center. All data is validated against the server for coherency to help ensure that a user never receives out-of-date (stale) data.
• Read-ahead: For situations in which objects are not cached or cannot be cached, Cisco WAAS employs read-ahead to bring the data to the user more quickly. Read-ahead reduces the negative effects of latency on CIFS by requesting the data on behalf of the user. This data can then be used, when safe, to respond to the user on behalf of the server.
• Message pipelining: CIFS messages can be pipelined over the WAN to mitigate the effects of send-and-wait behavior of CIFS. This feature allows operations to occur in parallel rather than serially, thus improving performance for the user.
• Prepositioning: File server data and metadata can be copied in a scheduled manner to improve performance for first-user access. This feature is helpful in environments in which large objects must traverse the WAN, including software distribution, video, and desktop-management applications.
• Microsoft Windows printing acceleration: Cisco WAAS can intelligently accelerate CIFS printing traffic over the WAN to allow centralization of print services in the data center. This feature helps reduce the branch-office infrastructure without compromising printing performance and is transparent to the existing printer and queue-management architectures.
• Intelligent file server offloading: Cisco WAAS CIFS acceleration reduces the burden placed on the origin file server through advanced caching techniques that can serve data locally to the requesting user when the user is authenticated and authorized and the cached contents are validated as coherent with the origin file server. Thus, file servers see fewer requests and are required to transfer less data, thereby enabling file server scalability and better economics.
• Invalid File ID: Cisco WAAS can deny requests to access files with invalid file handle values locally instead of sending the requests to the server, thus improving performance for the user.
• Batch close optimization: Cisco WAAS can perform asynchronous file close optimization for file-sharing traffic.
• Signed SMBv2: SMBv2 message signing is supported.
HTTP Acceleration
• Fast connection reuse: Connection reuse decreases the load time for complex pages or pages with numerous embedded objects when the client or server cannot use persistent connections. Optimized connections on the WAN remain active for a short time period so that they can be reused if additional data between the client-server pair needs to be exchanged.
• Connection multiplexing: Rather than requiring that multiple connections be established between client-server pairs, connections established between clients and servers are reused. This feature eliminates the latency caused by the process of establishing multiple connections between clients and servers.
• Local response: Use of cached metadata allows Cisco WAAS branch-office devices to respond locally to certain HTTP requests. These local responses are based on cached metadata from previously seen server responses and are continuously updated. This powerful HTTP optimization feature greatly reduces protocol chattiness and helps improve application response times through faster page downloads.
• Enhanced SharePoint: Cisco WAAS SharePoint Optimization provides specific optimization benefits for Microsoft Office documents hosted on a 2010 Microsoft SharePoint Server. The SharePoint feature provides optimization by prefetching objects for Word or Excel and storing them in the Cisco WAAS metadata cache. This optimization saves Round-Trip Time (RTT) for each successful fetch to reduce latency from the client's point of view and improve overall user experience.
• Content-aware optimization: The Cisco WAAS advanced HTTP parser provides intelligent recommendations that make DRE more effective and enable offloading of compression from the server resources.
MAPI Acceleration
• Full application support: Cisco WAAS acceleration for Microsoft Exchange is developed in conjunction with Microsoft to help ensure full compatibility with all major versions, including Microsoft Outlook 2000, 2003, and 2007, and the same versions of Microsoft Exchange.
• Advanced email compression: Cisco WAAS can automatically defer native compression provided by the Microsoft Exchange Server and Microsoft Outlook in favor of Cisco WAAS DRE and PLZ compression. Additionally, Cisco WAAS can natively decode messages encoded by Microsoft Exchange or Outlook to provide additional levels of compression, and full data coherency is preserved end to end.
• Object read-ahead: Objects being fetched from the server, such as email, calendar items, and address books, are fetched at an accelerated rate because Cisco WAAS prefetches objects on behalf of the user. This feature helps mitigate the effects of the send-and-wait behavior of Microsoft Exchange and Outlook.
• Object delivery acceleration: Objects being sent to the server, such as email, folder updates, and calendar entries, are sent at an accelerated rate because of the pipelining and batching capabilities provided by Cisco WAAS.
• Payload aggregation: Cisco WAAS recognizes many Microsoft Exchange messages that are small and can either batch them for optimized delivery or dynamically adjust DRE and PLZ compression to improve compression ratios for these messages.
• Transparent integration: Cisco WAAS acceleration for Microsoft Exchange does not keep user sessions open as in other solutions, a situation that can lead to security vulnerabilities and limit the overall scalability of the Microsoft Exchange Server itself.
Encrypted MAPI Optimization
Figure 12. Cisco WAAS E-MAPI Optimization
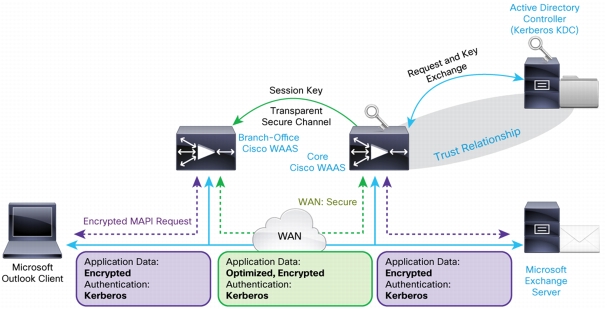
• It maintains trust boundaries and does not distribute the private keys of the data center.
• Keys are dynamically retrieved from Active Directory on demand and are never permanently stored on any Cisco WAAS device.
• E-MAPI acceleration interoperates transparently for all network interception methods and does not require special handling.
• Application transparency allows E-MAPI acceleration without the need to make changes to application clients or application servers.
• Outlook 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010 are supported (supporting a mix of encrypted and unencrypted traffic).
NFS Acceleration
• Metadata optimization: Cisco WAAS pipelines interactive operations such as directory traversal to reduce the amount of time required to traverse directories and view file and directory metadata. Additionally, Cisco WAAS caches metadata when safe to do so, to reduce the number of performance-limiting operations that traverse the WAN.
• Read-ahead optimization: Cisco WAAS performs read-ahead operations on behalf of the requesting node to prefetch data from the file being accessed. This feature makes the data readily available at the edge device for faster read throughput.
• File write optimization: Asynchronous write operations are used to batch write messages and eliminate the send-and-wait behavior of NFS file write operations while working in conjunction with existing NFS protocol semantics to help ensure file data integrity.
Video Delivery Services
Figure 13. Cisco WAAS Video-Delivery Services
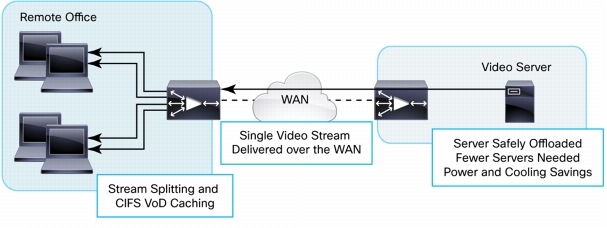
• Microsoft Windows Media stream splitting: Cisco WAAS interoperates with Microsoft Windows Media Technologies (WMT) over the Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) to enable one video stream over the WAN to be served to numerous users in the remote branch office, thereby reducing bandwidth consumption of video traffic.
• Data reduction and optimization for non-WMT and non-RTSP video: Cisco WAAS provides WAN optimization and bandwidth reduction for other video formats, including video over HTTP, Adobe Flash, Apple QuickTime, RealVideo, and any other video protocol that uses TCP as a transport.
• VoD caching: You can use Cisco WAAS CIFS acceleration in conjunction with prepositioning to provide a powerful VoD delivery architecture for enterprise e-learning, training, and video message archiving and playback.
• Intelligent video server offloading: Cisco WAAS video-delivery services reduce the burden on the origin video server by intelligently multiplexing remote-user requests over a single connection per location. Thus, video servers see fewer connections and are required to serve less data, thereby enabling video server scalability.
Cisco Virtual WAAS: The First Cloud-Ready WAN Optimization Solution
Cisco IOS Software WAN Optimization Solution on Cisco ISR G2 Routers with Cisco WAAS Express
Branch-Office Consolidation with Cisco WAAS
• Lower TCO: Fewer infrastructure devices are required at the branch office, thereby reducing power, cooling, and rack-space requirements, along with ongoing operating expenses (OpEx) and capital expenditures (CapEx).
• Transparent integration: Integration into existing Microsoft management technologies, including Microsoft Management Console (MMC) and network services such as Active Directory, is transparent, and Cisco WAAS can fully optimize and accelerate access to the virtual blade.
• Platform and service isolation: Dedicated resources (CPU, memory, and disk) are allocated to the virtual blade, thereby isolating resources from interference from other virtual blades or from the underlying WAN optimization and application acceleration services.
• IT agility: You can deploy infrastructure services and applications throughout the network in a way that provides outstanding flexibility.
Simple, Scalable, Secure Network Integration with Cisco WAAS
Transparency
Figure 14. Cisco WAAS Transparency Preserves Packet Header Information
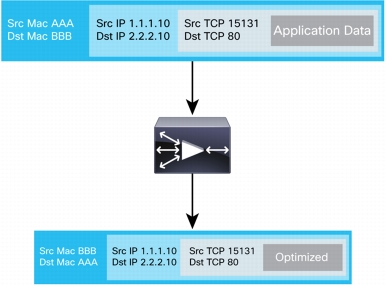
• Network QoS: Cisco WAAS preserves DSCP markings, or alternatively can apply DSCP markings through application QoS, working together with classification, policing, and shaping in the network. Network classification is preserved because the header information is not manipulated, thereby enabling Cisco WAAS to interoperate with network-based classification techniques for QoS.
Figure 15. Cisco WAAS Complements Network QoS
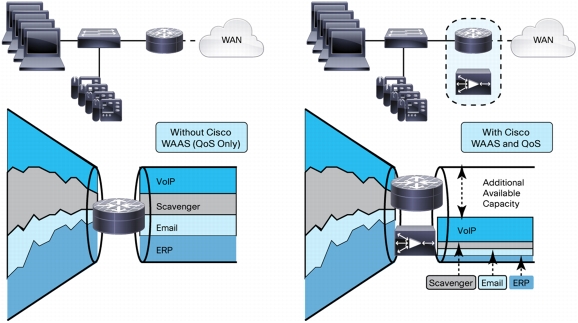
• Dynamic routing: Cisco WAAS interoperates transparently with dynamic routing technologies such as Performance Routing (PfR), Optimized Edge Routing (OER), and Policy-Based Routing (PBR).
• Access control: Cisco WAAS interoperates transparently with access control lists (ACLs) and Cisco firewall policies to block certain types of traffic from traversing network devices.
• NetFlow and performance monitoring tools: Cisco WAAS interoperates transparently with NetFlow and other performance tools to help ensure full visibility into the traffic encountered on the network.
Security
Figure 16. Cisco WAAS and Secure WAN Optimization
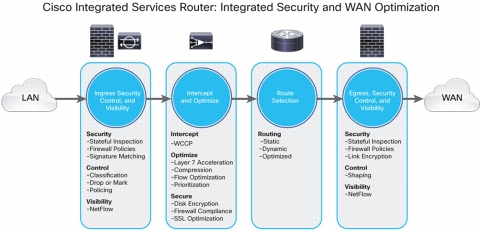
• Full integration with Cisco firewalls: Cisco firewall devices and software, including Cisco IOS Firewall, the Cisco Catalyst® 6500 Series Firewall Services Module (FWSM), Cisco PIX® Firewall Software, and Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances Enterprise Firewall Edition, are all Cisco WAAS aware and can identify flows that are optimized by Cisco WAAS. This behavior helps ensure that new service ports do not need to be open and that stateful inspection is not compromised.
• Full integration with Cisco Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): Cisco IDS and IPS devices recognize flows optimized by Cisco WAAS and eliminate the false positives that plague competitive WAN optimization and application acceleration solutions deployed in networks with signature- or anomaly-based IDS and IPS.
• Full integration with VPN infrastructure: Cisco WAAS automatically adjusts parameters on optimized connections to help ensure transparent transport through the VPN infrastructure.
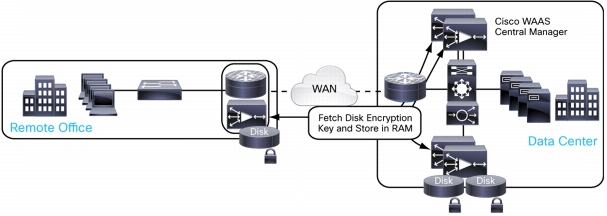
• Disk encryption: You can enable disk encryption selectively or globally, with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager managing disk encryption keys, to help ensure that data written to the Cisco WAAS device disks is completely unusable if a system is compromised. This behavior helps ensure compliance with Payment Card Industry (PCI) regulations along with other federal and industry-related compliance initiatives, as shown in Figure 17.
Figure 17. Cisco WAAS Disk Encryption
Cisco AppNav WAN Optimization Virtualization
• Efficient and cost-effective expansion of WAN optimization services within a company: The Cisco AppNav solution provides an on-demand pool of Cisco WAAS devices (appliances or virtual appliances or a mixture of both) that can be used in all data center deployment models.
• Flexibility in WAN optimization deployment to address various business needs: The Cisco AppNav solution allows flexible policy definitions that dynamically bind business logical constructs to a set of Cisco WAAS pools, and it makes intelligent load-distribution decisions based on the state of the nodes currently providing services.
• Improved business continuity with highly available Cisco WAAS services: The Cisco AppNav clustering mechanism enables redundancy in the pool of Cisco WAAS devices and Cisco AppNav services.
• The Cisco AppNav elastic provisioning and deployment of WAN optimization services along with the upcoming integration of Cisco AppNav technology into the Cisco Cloud Services Router (CSR) provides a transparent, optimized connection from the branch office to the cloud.
• Capability to address challenges posed by today's data center infrastructure: Cisco AppNav native solutions address directional asymmetry in the multipath environment of the data center while preserving the user-intended network path (network path affinity).
Network Interception
• Physical inline deployment: Using the Cisco inline interception card, you can easily deploy Cisco WAAS Appliances by simply inserting the Cisco WAAS Appliance in line between the router (or firewall) and the adjacent switch. With the use of fail-to-wire capabilities, if the Cisco WAAS Appliance experiences a hardware or software failure, within seconds the appliance will transparently become a bridge and remove itself from operation. When deploying them in line, you can deploy Cisco WAAS Appliances in a serial cluster if you want high availability of optimization services. You can deploy serial inline clusters in the data center as well as in the branch office.
• WCCP Version 2 (WCCPv2): Cisco WAAS provides full support for WCCPv2, allowing deployment of up to 32 Cisco WAAS devices in a single device group with load balancing, failover, and nondisruptive Cisco WAAS device insertion and removal. Unlike solutions that implement only a portion of the WCCPv2 specification, Cisco WAAS provides full WCCPv2 compatibility for efficient integration into both the branch office and data center without compromising performance, scalability, or existing infrastructure.
• PBR: You can deploy Cisco WAAS in the network using PBR, which defines the Cisco WAAS device as a next-hop router. PBR allows you to configure multiple Cisco WAAS devices as next-hop routers; you also can use PBR in conjunction with IP service-level agreements (SLAs) for high-availability failover configurations.
• The Cisco ACE Application Control Engine Module or Cisco Content Switching Module (CSM): You can deploy Cisco WAAS Appliances in the data center using the Cisco ACE Module or Cisco CSM for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series for tremendous scalability. You can manage up to 4 million connections per Cisco ACE Module, with redirection to a farm of Cisco WAAS Appliances and supporting data rates of up to 16 Gbps. You can deploy up to four Cisco ACE Modules in a Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series chassis, enabling scalability to up to 64 Gbps and 16 million TCP connections.
• Cisco Nexus vPath Interception: The Cisco Nexus 1000V provides virtualization-aware network services to all application server virtual machines. Central to this capability are port profiles, which are a collection of interface configuration commands that you can dynamically apply at either physical or virtual interfaces. Any changes to a given port profile are propagated immediately to all ports that have been associated with it. Port profiles are visible as VMware port groups in the VMware vCenter management console. The Cisco Nexus 1000V provides a mechanism for attaching Cisco vWAAS to the port profiles of servers that need to be optimized. vPath will intercept all traffic to and from these servers and forward it to the Cisco vWAAS virtual machine for optimization. vPath interception uses Cisco Nexus 1000V port-profile attributes (vn-service) to redirect traffic to Cisco vWAAS. Administrators need to identify the port profiles of servers to be optimized by Cisco vWAAS. After the port profile is identified, Cisco vWAAS needs to attach to one or multiple port profiles to optimize the traffic. Cisco WAAS autodiscovery helps ensure that a particular TCP connection will be optimized only by the endpoint devices (Cisco WAE or Cisco vWAAS).
• Integrated router (Cisco ISR G2) forwarding: With Cisco WAAS Express on Cisco ISR G2 routers, the default optimization policy will apply to traffic entering and leaving the interface as soon as the feature is enabled for those specific interfaces. In this case, there is no need to configure inline or WCCP interception mechanisms.
Automatic Discovery
• No manual topology definition: No tunnel or overlay network definition is required, because Cisco WAAS devices do not use tunnels, and they automatically determine what devices are in the path, negotiating optimization levels automatically without the need for administrative configuration.
• Automatic bypass of intermediary Cisco WAAS devices: Optimization is applied only between the outermost Cisco WAAS devices to help ensure efficient use of resources and optimal optimization of connections.
Secure, Scalable Centralized Management with Cisco WAAS
Figure 18. Cisco WAAS Central Manager Dashboard
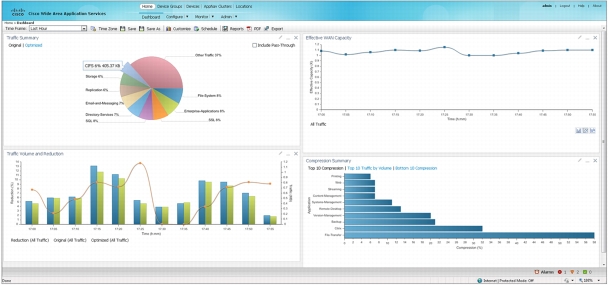
• Highly available, secure platform: All communications among Cisco WAAS devices and the Cisco WAAS Central Manager are encrypted, and you can deploy the central manager itself in a high-availability configuration with automatic failover.
• Scalability: You can deploy multiple Cisco WAAS Central Managers to scale to any number of deployed Cisco WAAS devices.
• Configuration simplicity through device groups: Multiple Cisco WAAS devices can belong to a single device group, and you can apply configuration changes to the device group and then automatically apply them to the group's members. The use of device groups reduces the number of clicks necessary to make broad-reaching changes to the Cisco WAAS deployment.
• Customizable, schedulable reports: You can view powerful reporting statistics covering device and system health, WAN optimization performance, application acceleration performance, and traffic by device, by device group, and systemwide. You can schedule all reports for automatic delivery using email, and real-time connection statistics are available. Additionally, a monitoring API that uses XML is available to enable integration into existing monitoring and reporting architectures. Figure 19 shows some of the many powerful reports that the Cisco WAAS Central Manager provides.
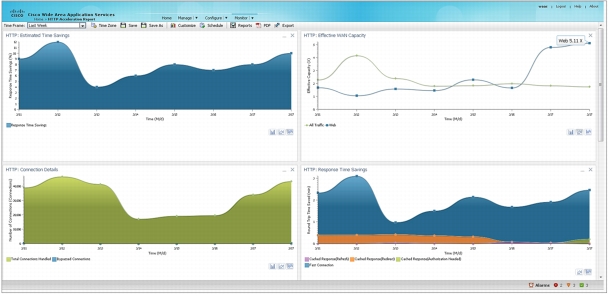
Figure 19. Sample HTTP Acceleration and Optimization Reports Provided by Cisco WAAS Central Manager
• Centralized policy management: You can centrally manage the optimization and acceleration capabilities of Cisco WAAS devices through the Application Traffic Policy (ATP) Manager on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, providing an intuitive policy builder you can use to define the applications to be optimized and the levels of optimization to be applied. More than 150 policies are configured by default, supporting today's most commonly used applications and protocols.
• Full role-based access control (RBAC): The Cisco WAAS Central Manager provides full RBAC capabilities to define the users who can interact with the management and monitoring components on specific devices and whether read or write permissions are allowed. Additionally, you can integrate identity with Microsoft Active Directory, TACACS, or RADIUS to allow a centralized provider to manage authentication based on user or group definition.
• Encryption services: The Cisco WAAS Central Manager provides management of encryption services for all Cisco WAAS devices in the network, including the secure vault for encryption key pairs and the keys necessary for Cisco WAAS device disk encryption. All sensitive data used or generated by a Cisco WAAS deployment is stored and transmitted securely.
• Integrated application performance monitoring (APM): The Cisco WAAS Central Manager includes integrated performance monitoring capabilities that integrate the Cisco NAM reports that are most relevant to Cisco WAAS deployment. This feature simplifies the configuration and monitoring processes, expands reporting capabilities beyond Cisco WAAS visibility to the entire network, and provides end-to-end application performance analytics and optimization statistics. Figure 20 shows some of the ways in which the Cisco WAAS Central Manager provides application performance visibility.
Figure 20. Cisco WAAS Central Manager Network and Application Performance Analyses

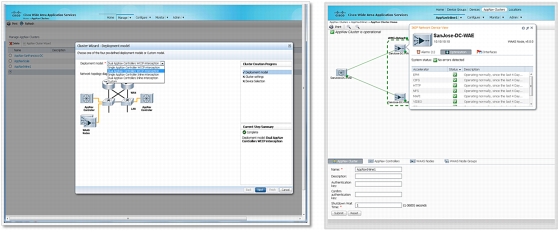
• Integrated Cisco AppNav configuration and monitoring: The Cisco WAAS Central manager includes an integrated Cisco AppNav configuration and monitoring capability. This feature provides a comprehensive, cohesive, and simple interface for configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting the entire Cisco AppNav cluster. Figure 21 provides examples of the wizard-guided configuration and comprehensive cluster and device views that the Cisco WAAS Central Manager AppNav interface provides.
Figure 21. Cisco WAAS Central Manager AppNav Cluster Configuration Wizard and Health Statistics Through 360o Network View
Conclusion
For More Information